Characterization and Functional Analysis of the FBN Gene Family in Cotton: Insights into Fiber Development
Simple Summary
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Identification of Cotton GhFBN Genes
2.2. Multiple Alignment and Phylogenetic Analysis
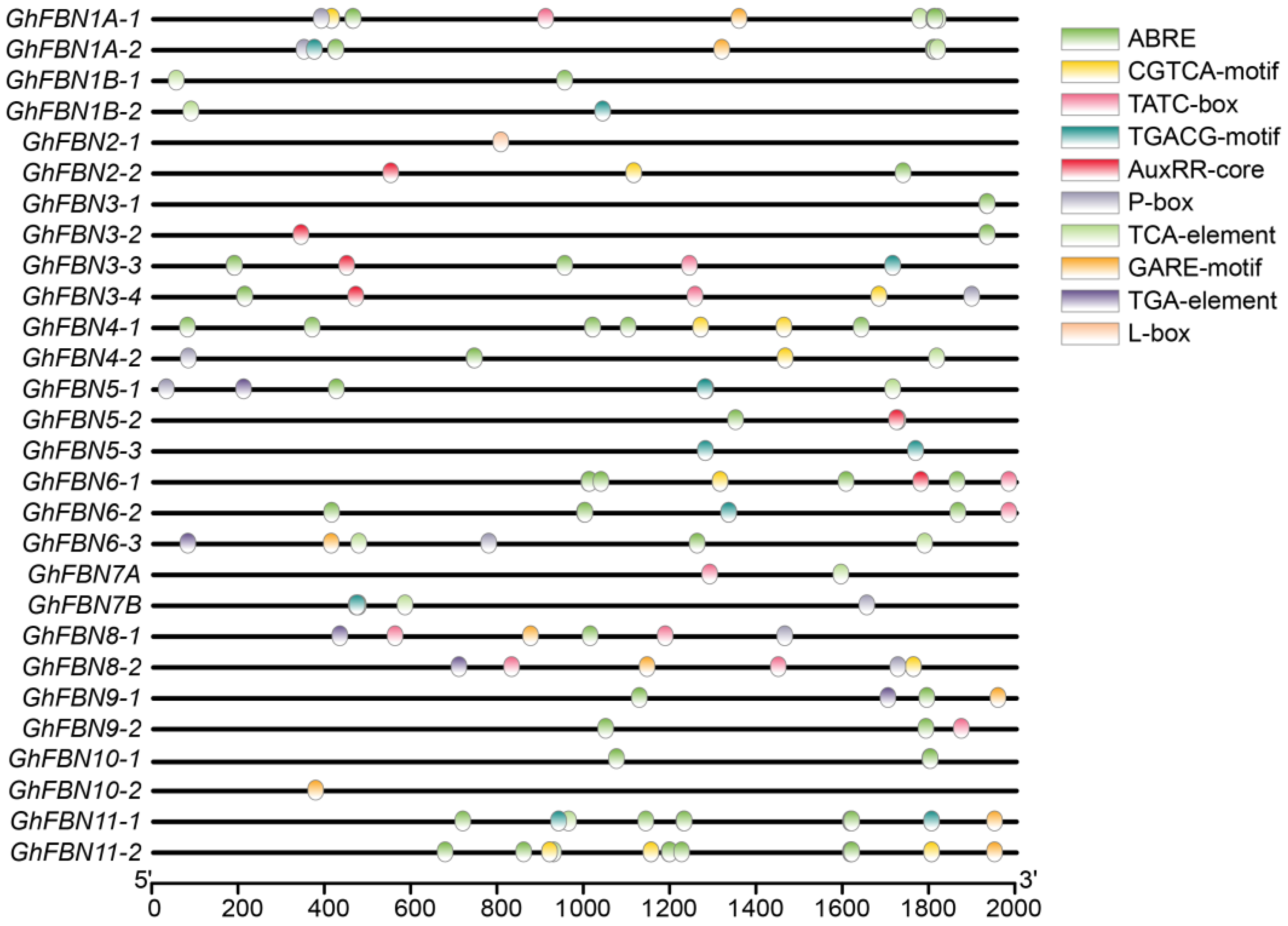
2.3. Structure Analysis and Cis-Element Prediction
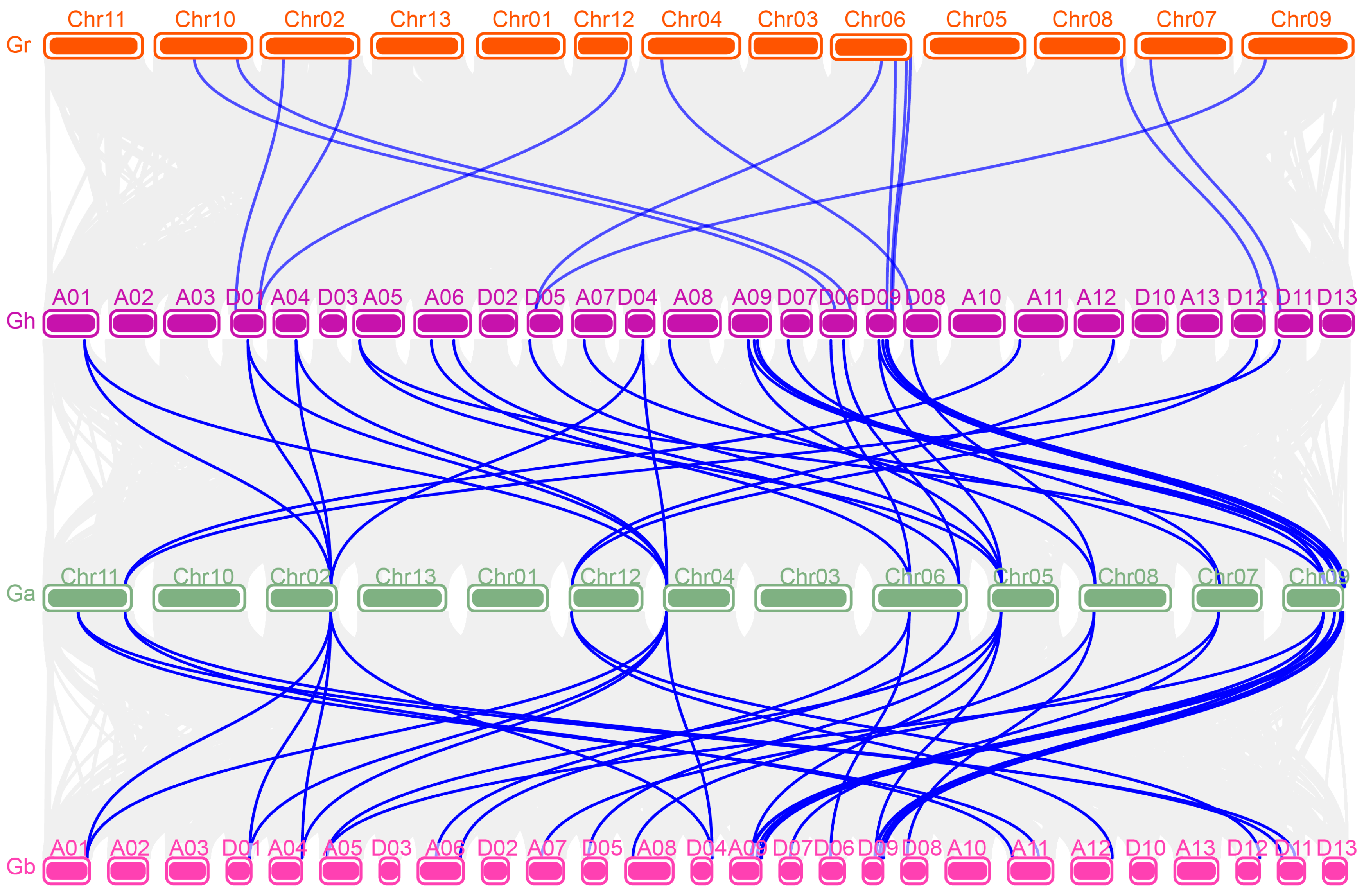
2.4. Chromosomal Location and Collinearity Analysis
2.5. In Vitro Ovule Culture and RNA-Seq
2.6. Evolutionary Selection Pressure Analysis
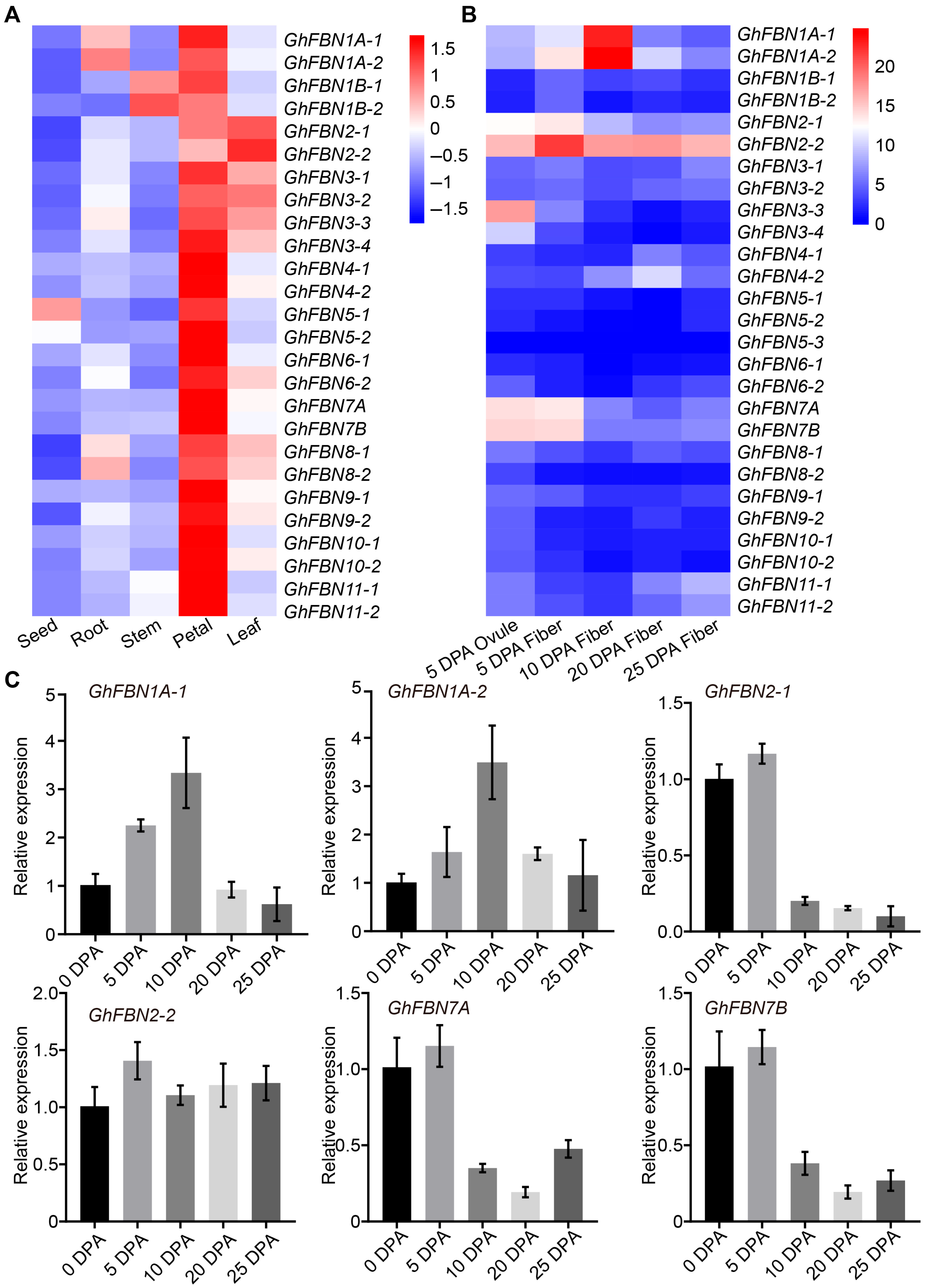
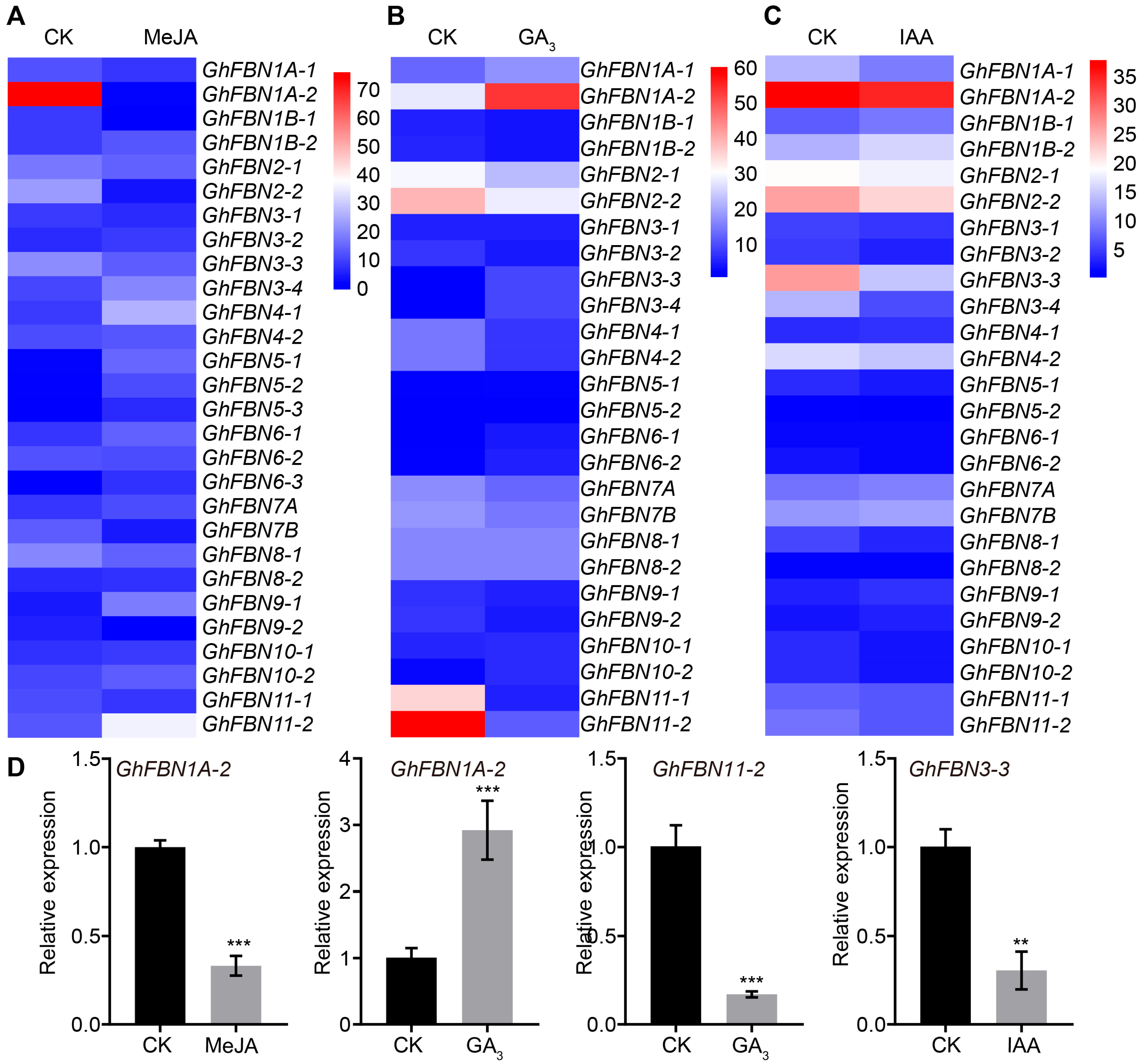
2.7. Expression Pattern Analysis of Cotton FBN Genes
2.8. qRT-PCR Analysis
3. Results
3.1. Identification of FBN Genes in Cotton
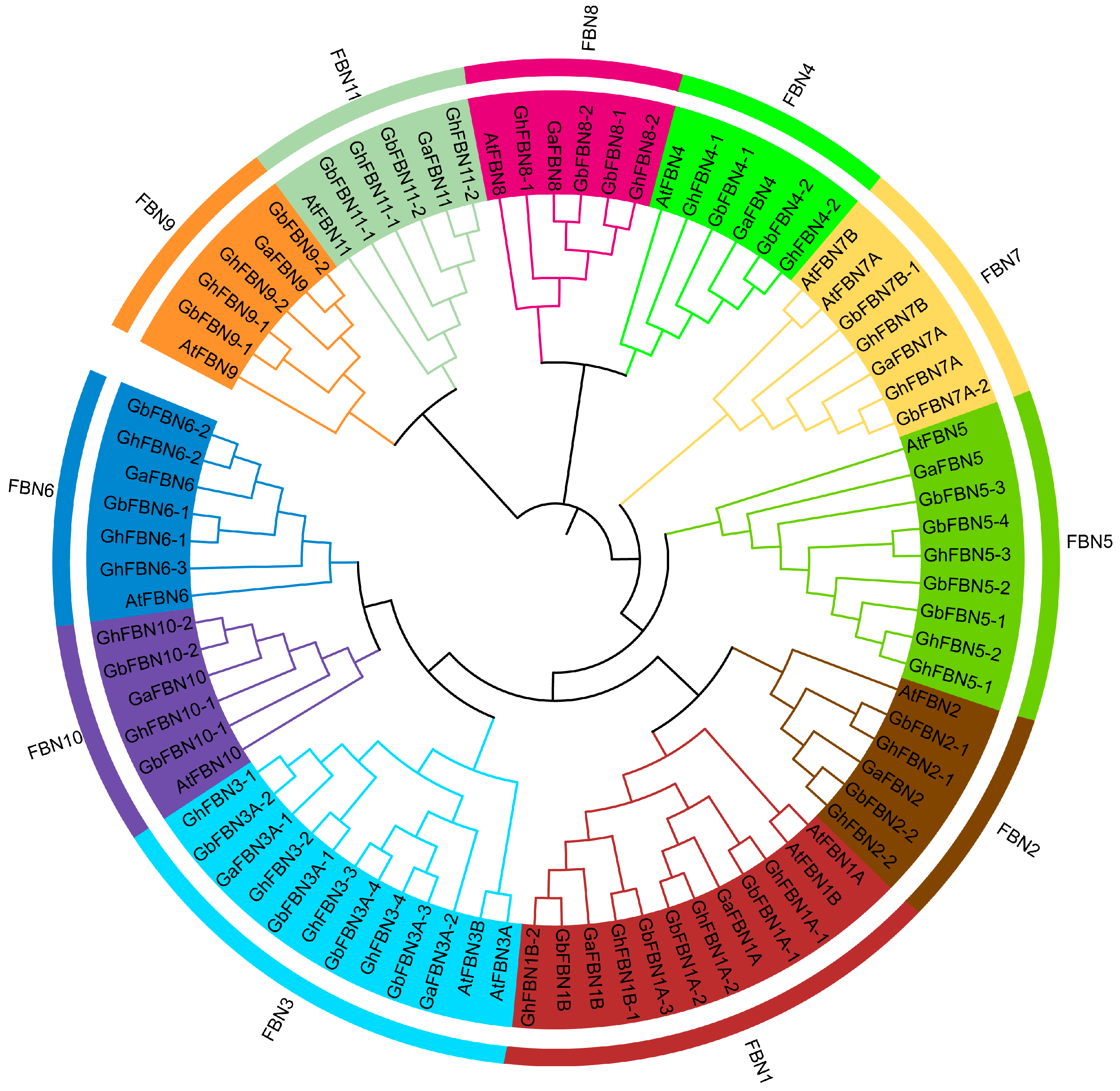
3.2. Phylogenetic Relationships of FBN Genes
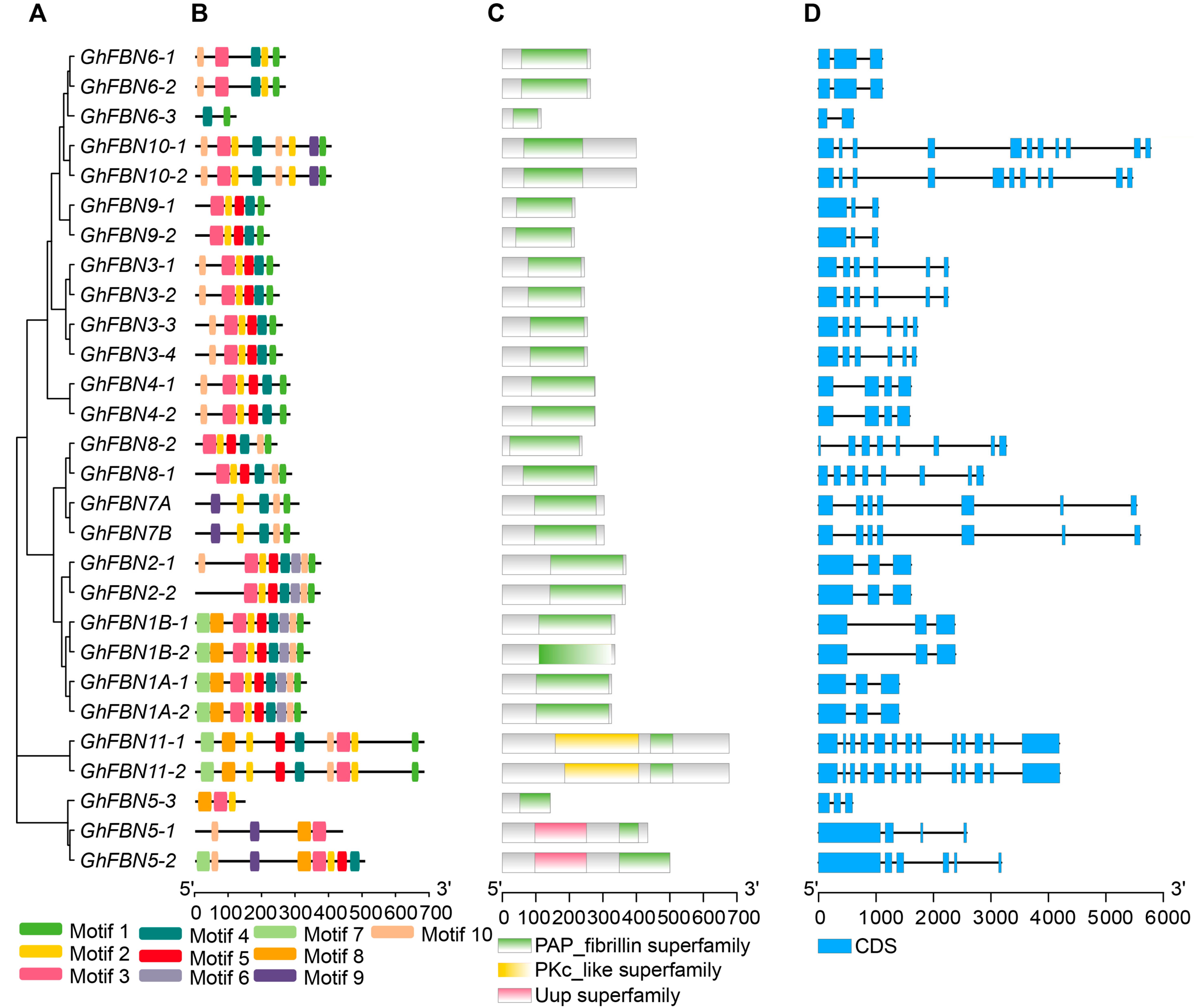
3.3. Structure Analysis of Cotton GhFBN Genes
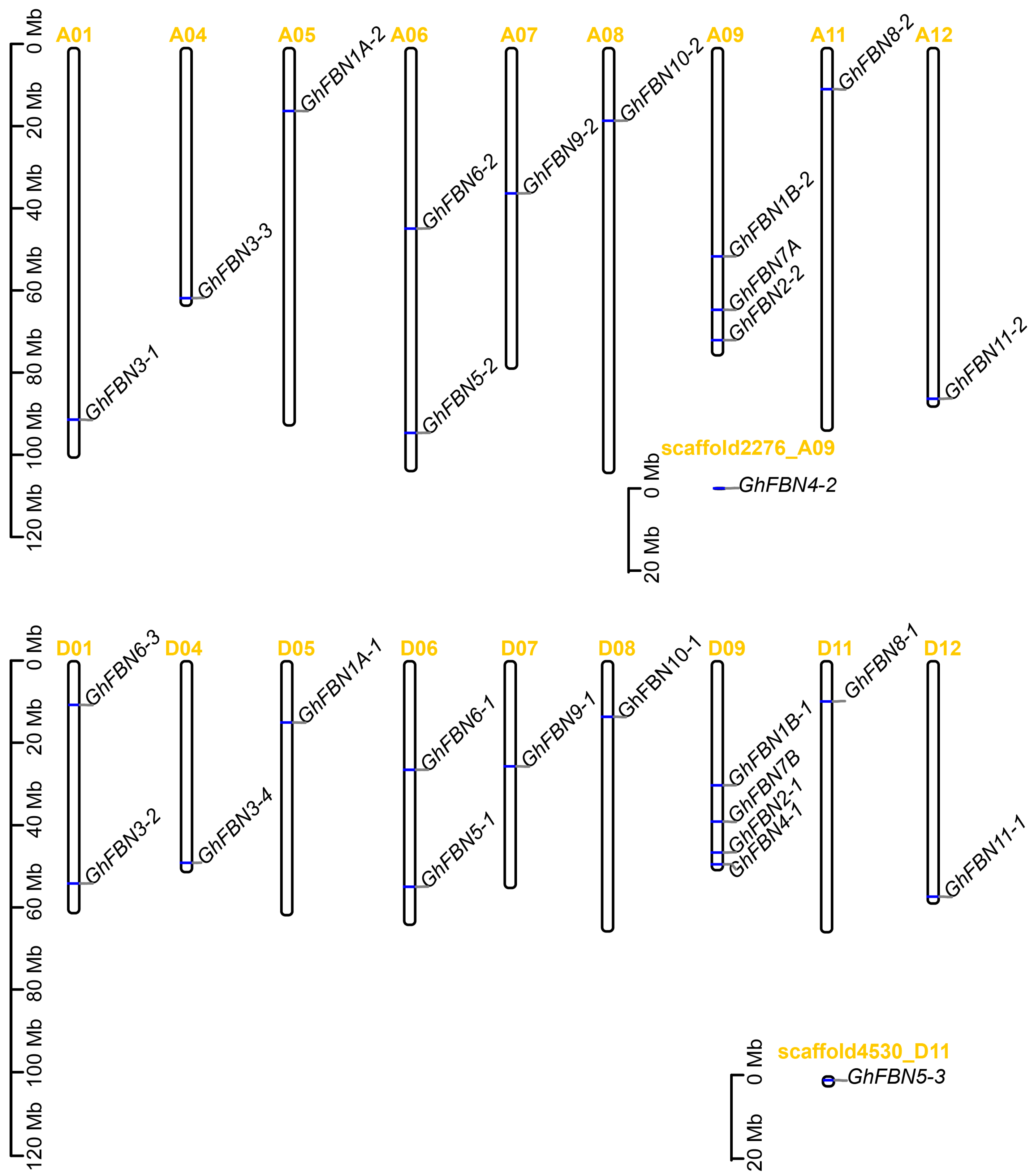
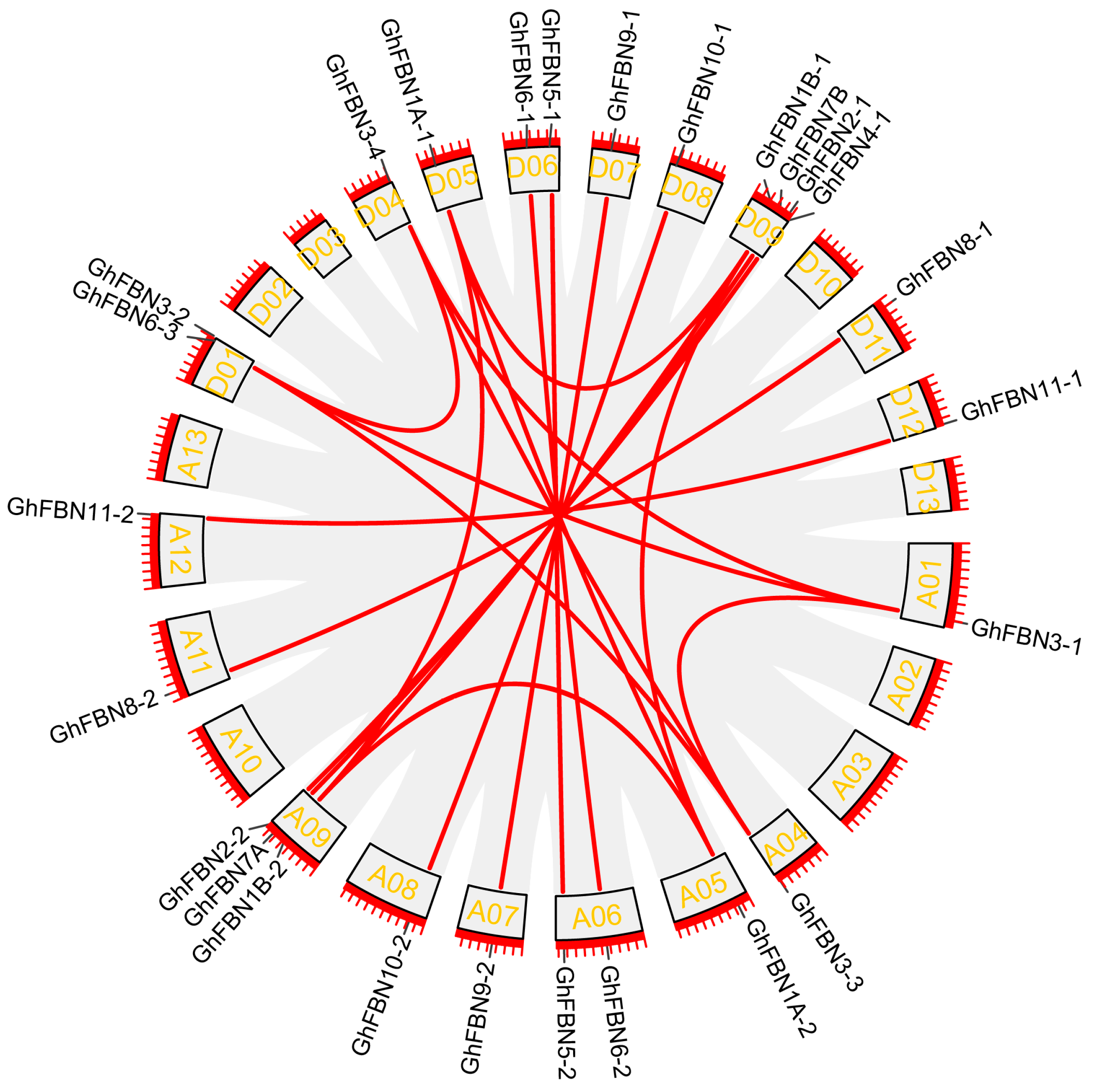
3.4. Chromosomal Location and Gene Duplication of GhFBN Genes
3.5. Selection Pressure Ka/Ks Analysis
3.6. Analysis of Putative Cis-Acting Elements in GhFBN Promoters
3.7. Expression Profiling Based on Transcriptome Data
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Mandel, M.A.; Feldmann, K.A.; Herrera Estrella, L.; Rocha Sosa, M.; León, P. CLA1, a novel gene required for chloroplast development, is highly conserved in evolution. Plant J. 2003, 9, 649–658. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deruère, J.; Römer, S.; Harlingue, A.; Backhaus, R.A.; Kuntz, M.; Camara, B. Fibril assembly and carotenoid overaccumulation in chromoplasts: A model for supramolecular lipoprotein structures. Plant Cell 1994, 6, 119–133. [Google Scholar]
- Lohscheider, J.N.; Río Bártulos, C. Plastoglobules in algae: A comprehensive comparative study of the presence of major structural and functional components in complex plastids. Mar. Genom. 2016, 28, 127–136. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Simkin, A.J.; Gaffé, J.; Alcaraz, J.P.; Carde, J.P.; Bramley, P.M.; Fraser, P.D.; Kuntz, M. Fibrillin influence on plastid ultrastructure and pigment content in tomato fruit. Phytochemistry 2007, 68, 1545–1556. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Newman, L.A.; Hadjeb Nd Price, C.A. Synthesis of two chromoplast-specific proteins during fruit development in Capsicum annuum. Plant Physiol. 1989, 91, 455–458. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kessler, F.; Schnell, D.; Blobel, G. Identification of proteins associated with plastoglobules isolated from pea (Pisum sativum L.) chloroplasts. Planta 1999, 208, 107–113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wuttke, H.G. Chromoplasts in Rosa rugosa: Development and chemical characterization of tubular elements. Z. Naturforsch C Biosci. 1976, 31, 456d–460d. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cunningham, F.X.; Tice, A.B., Jr.; Pham, C.; Gantt, E. Inactivation of genes encoding plastoglobuli-like proteins in Synechocystis sp. PCC 6803 leads to a light-sensitive phenotype. J. Bacteriol. 2010, 192, 1700–1709. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Langenkämper, G.; Manac’h, N.; Broin, M.; Cuiné, S.; Becuwe, N.; Kuntz, M.; Rey, P. Accumulation of plastid lipid-associated proteins (fibrillin/CDSP34) upon oxidative stress, ageing and biotic stress in Solanaceae and in response to drought in other species. J. Exp. Bot. 2001, 52, 1545–1554. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pozueta Romero, J.; Rafia, F.; Houlné, G.; Cheniclet, C.; Carde, J.P.; Schantz, M.L.; Schantz, R. A ubiquitous plant housekeeping gene, PAP, encodes a major protein component of bell pepper chromoplasts. Plant Physiol. 1997, 115, 1185–1194. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ytterberg, A.J.; Peltier, J.B.; van Wijk, K.J. Protein profiling of plastoglobules in chloroplasts and chromoplasts. A surprising site for differential accumulation of metabolic enzymes. Plant Physiol. 2006, 140, 984–997. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lundquist, P.K.; Poliakov, A.; Bhuiyan, N.H.; Zybailov, B.; Sun, Q.; van Wijk, K.J. The functional network of the Arabidopsis plastoglobule proteome based on quantitative proteomics and genome-wide coexpression analysis. Plant Physiol. 2012, 158, 1172–1192. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Suzuki, T.; Tsunekawa, S.; Koizuka, C.; Yamamoto, K.; Imamura, J.; Nakamura, K.; Ishiguro, S. Development and disintegration of tapetum-specific lipid-accumulating organelles, elaioplasts and tapetosomes, in Arabidopsis thaliana and Brassica napus. Plant Sci. 2013, 207, 25–36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, Y.; Hu, H.; Ma, Y.; Zhou, J. Genome-wide identification and characterization of the fibrillin gene family in Triticum aestivum. PeerJ 2020, 8, e9225. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, E.H.; Lee, Y.; Kim, H.U. Fibrillin 5 is essential for plastoquinone-9 biosynthesis by binding to solanesyl diphosphate synthases in Arabidopsis. Plant Cell 2015, 27, 2956–2971. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Singh, D.K.; McNellis, T.W. Fibrillin protein function: The tip of the iceberg? Trends Plant Sci. 2011, 16, 432–441. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rey, P.; Gillet, B.; Römer, S.; Eymery, F.; Massimino, J.; Peltier, G.; Kuntz, M. Over-expression of a pepper plastid lipid-associated protein in tobacco leads to changes in plastid ultrastructure and plant development upon stress. Plant J. 2000, 21, 483–494. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Youssef, A.; Laizet, Y.; Block, M.A.; Maréchal, E.; Alcaraz, J.P.; Larson, T.R.; Pontier, D.; Gaffé, J.; Kuntz, M. Plant lipid-associated fibrillin proteins condition jasmonate production under photosynthetic stress. Plant J. 2010, 61, 436–445. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Monte, E.; Ludevid, D.; Prat, S. Leaf C40.4: A carotenoid-associated protein involved in the modulation of photosynthetic efficiency? Plant J. 1999, 19, 399–410. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, J.; Li, X.; Khatab, A.A.; Xie, G. Phylogeny, structural diversity and genome-wide expression analysis of fibrillin family genes in rice. Phytochemistry 2020, 175, 112377. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, I.; Lee, S.C.; Kim, E.H.; Song, K.; Yang, T.J.; Kim, H.U. Genome-wide identification and expression analyses of the fibrillin family genes suggest their involvement in photoprotection in Cucumber. Plants 2018, 7, 50. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, H.; Ren, M.; Zhang, J. Genome-wide identification and expression analysis of fibrillin (FBN) gene family in tomato (Solanum lycopersicum L.). PeerJ 2022, 10, e13414. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, P.; Wang, S.; Grierson, D.; Xu, C. Transcriptomic changes triggered by carotenoid biosynthesis inhibitors and role of Citrus sinensis phosphate transporter 4;2 (CsPHT4;2) in enhancing carotenoid accumulation. Planta 2019, 249, 257–270. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, R.; Zeng, Q.; Zhang, X.; Jing, J.; Ge, X.; Zhao, L.; Yi, B.; Tu, J.; Fu, T.; Wen, J.; et al. Xanthophyll esterases in association with fibrillins control the stable storage of carotenoids in yellow flowers of rapeseed (Brassica juncea). New Phytol. 2023, 240, 285–301. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, G.; Huang, J.Q.; Chen, X.Y.; Zhu, Y.X. Recent advances and future perspectives in cotton research. Annu. Rev. Plant Biol. 2021, 72, 437–462. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, H.J.; Triplett, B.A. Cotton fiber growth in planta and in vitro. Models for plant cell elongation and cell wall biogenesis. Plant Physiol. 2001, 127, 1361–1366. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Haigler, C.H.; Betancur, L.; Stiff, M.R.; Tuttle, J.R. Cotton fiber: A powerful single-cell model for cell wall and cellulose research. Front. Plant Sci. 2012, 3, 104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, Z.; Qanmber, G.; Wang, Z.; Yang, Z.; Li, F. Gossypium genomics: Trends, scope, and utilization for cotton improvement. Trends Plant Sci. 2020, 25, 488–500. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- El Gebali, S.; Mistry, J.; Bateman, A.; Eddy, S.R.; Luciani, A.; Potter, S.C.; Qureshi, M.; Richardson, L.J.; Salazar, G.A.; Smart, A.; et al. The Pfam protein families database in 2019. Nucleic Acids Res. 2018, 47, D427–D432. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schultz, J.; Milpetz, F.; Bork, P.; Ponting, C.P. SMART, a simple modular architecture research tool: Identification of signaling domains. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 1998, 95, 5857–5864. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mitchell, A.L.; Attwood, T.K.; Babbitt, P.C.; Blum, M.; Bork, P.; Bridge, A.; Brown, S.D.; Chang, H.Y.; El Gebali, S.; Fraser, M.I.; et al. InterPro in 2019: Improving coverage, classification and access to protein sequence annotations. Nucleic Acids Res. 2018, 47, D351–D360. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bailey, T.L.; Boden, M.; Buske, F.A.; Frith, M.; Grant, C.E.; Clementi, L.; Ren, J.; Li, W.W.; Noble, W.S. MEME Suite: Tools for motif discovery and searching. Nucleic Acids Res. 2009, 37, W202–W208. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, C.; Chen, H.; Zhang, Y.; Thomas, H.R.; Frank, M.H.; He, Y.; Xia, R. TBtools: An integrative toolkit developed for interactive analyses of big biological data. Mol. Plant 2020, 13, 1194–1202. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tian, Z.; Zhang, Y.; Zhu, L.; Jiang, B.; Wang, H.; Gao, R.; Friml, J.; Xiao, G. Strigolactones act downstream of gibberellins to regulate fiber cell elongation and cell wall thickness in cotton (Gossypium hirsutum). Plant Cell 2022, 34, 4816–4839. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hurst, L.D. The Ka/Ks ratio: Diagnosing the form of sequence evolution. Trends Genet. 2002, 18, 486–487. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, T.; Hu, Y.; Jiang, W.; Fang, L.; Guan, X.; Chen, J.; Zhang, J.; Saski, C.A.; Scheffler, B.E.; Stelly, D.M.; et al. Sequencing of allotetraploid cotton (Gossypium hirsutum L. acc. TM-1) provides a resource for fiber improvement. Nat. Biotechnol. 2015, 33, 531–537. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Livak, K.J.; Schmittgen, T.D. Analysis of relative gene expression data using real-time quantitative PCR and the 2−ΔΔCT method. Methods 2001, 25, 402–408. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhu, L.; Jiang, B.; Zhu, J.; Xiao, G. Auxin promotes fiber elongation by enhancing gibberellic acid biosynthesis in cotton. Plant Biotechnol. J. 2022, 20, 423–425. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tan, J.; Tu, L.; Deng, F.; Wu, R.; Zhang, X. Exogenous jasmonic acid inhibits cotton fiber elongation. J. Plant Growth Regul. 2012, 31, 599–605. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gillet, B.; Beyly, A.; Peltier, G.; Rey, P. Molecular characterization of CDSP 34, a chloroplastic protein induced by water deficit in Solanum tuberosum L. plants, and regulation of CDSP 34 expression by ABA and high illumination. Plant J. 1998, 16, 257–262. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- El Sappah, A.H.; Li, J.; Yan, K.; Zhu, C.; Huang, Q.; Zhu, Y.; Chen, Y.; El Tarabily, K.A.; AbuQamar, S.F. Fibrillin gene family and its role in plant growth, development, and abiotic stress. Front. Plant Sci. 2024, 15, 1453974. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pandey, A.; Sharma, P.; Mishra, D.; Dey, S.; Malviya, R.; Gayen, D. Genome-wide identification of the fibrillin gene family in chickpea (Cicer arietinum L.) and its response to drought stress. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2023, 234, 123757. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zafer, M.Z.; Tahir, M.H.N.; Khan, Z.; Sajjad, M.; Gao, X.; Bakhtavar, M.A.; Waheed, U.; Siddique, M.; Geng, Z.; Ur Rehman, S. Genome-wide characterization and sequence polymorphism analyses of glycine max Fibrillin (FBN) revealed its role in response to drought condition. Genes 2023, 14, 1188. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eymery, F.; Rey, P. Immunocytolocalization of CDSP 32 and CDSP 34, two chloroplastic drought-induced stress proteins in Solanum tuberosum plants. Plant Physiol. Biochem. 1999, 37, 305–312. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hong, Y.; Wang, Z.; Liu, X.; Yao, J.; Kong, X.; Shi, H.; Zhu, J.K. Two chloroplast proteins negatively regulate plant drought resistance through separate pathways. Plant Physiol. 2020, 182, 1007–1021. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Torres Romero, D.; Gómez Zambrano, Á.; Serrato, A.J.; Sahrawy, M.; Mérida, Á. Arabidopsis fibrillin 1–2 subfamily members exert their functions via specific protein-protein interactions. J. Exp. Bot. 2022, 73, 903–914. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, I.; Kim, H.U. The mysterious role of fibrillin in plastid metabolism: Current advances in understanding. J. Exp. Bot. 2022, 73, 2751–2764. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gámez Arjona, F.M.; de la Concepción, J.C.; Raynaud, S.; Mérida, Á. Arabidopsis thaliana plastoglobule-associated fibrillin 1a interacts with fibrillin 1b in vivo. FEBS Lett. 2014, 588, 2800–2804. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
| Gene Name | Sequence ID | Gene (bp) | CDS (bp) | MWa (kDa) | Theoretical pI | Species |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| GhFBN1A-1 | Gh_D05G1665.1 | 3179 | 978 | 35.42335 | 5.14 | G. hirsutum |
| GhFBN1A-2 | Gh_A05G1494.1 | 1399 | 978 | 35.44943 | 5.14 | G. hirsutum |
| GhFBN1B-1 | Gh_D09G0662.1 | 5532 | 1008 | 36.86466 | 4.93 | G. hirsutum |
| GhFBN1B-2 | Gh_A09G0658.1 | 2380 | 1008 | 36.91571 | 5 | G. hirsutum |
| GhFBN2-1 | Gh_D09G1905.1 | 4196 | 1107 | 39.83073 | 4.49 | G. hirsutum |
| GhFBN2-2 | Gh_A09G1782.1 | 2257 | 1101 | 39.62955 | 4.58 | G. hirsutum |
| GhFBN3-1 | Gh_A01G1493.1 | 3987 | 735 | 27.42963 | 9.65 | G. hirsutum |
| GhFBN3-2 | Gh_D01G1730.1 | 3179 | 735 | 27.49574 | 9.65 | G. hirsutum |
| GhFBN3-3 | Gh_A04G1080.1 | 3987 | 762 | 28.53791 | 9.69 | G. hirsutum |
| GhFBN3-4 | Gh_D04G1687.1 | 3179 | 762 | 28.50085 | 9.54 | G. hirsutum |
| GhFBN4-1 | Gh_D09G2214.1 | 4196 | 831 | 29.92041 | 9.37 | G. hirsutum |
| GhFBN4-2 | Gh_A09G2222.1 | 3179 | 831 | 30.01153 | 9.37 | G. hirsutum |
| GhFBN5-1 | Gh_D06G1644.1 | 5532 | 1302 | 47.95253 | 6 | G. hirsutum |
| GhFBN5-2 | Gh_A06G1315.1 | 1399 | 1500 | 55.18532 | 9 | G. hirsutum |
| GhFBN5-3 | Gh_D11G3441.1 | 4196 | 429 | 15.74633 | 8.67 | G. hirsutum |
| GhFBN6-1 | Gh_D06G1142.1 | 5532 | 789 | 28.93921 | 9.4 | G. hirsutum |
| GhFBN6-2 | Gh_A06G0966.1 | 1399 | 789 | 28.98224 | 9.4 | G. hirsutum |
| GhFBN6-3 | Gh_D01G0744.1 | 3179 | 348 | 12.79046 | 8.06 | G. hirsutum |
| GhFBN7A | Gh_A09G1197.1 | 2380 | 912 | 33.32015 | 6.67 | G. hirsutum |
| GhFBN7B | Gh_D09G1203.1 | 4196 | 912 | 33.29012 | 6.67 | G. hirsutum |
| GhFBN8-1 | Gh_D11G1079.1 | 4196 | 714 | 26.46673 | 8.78 | G. hirsutum |
| GhFBN8-2 | Gh_A11G0937.1 | 3179 | 846 | 31.60553 | 9.22 | G. hirsutum |
| GhFBN9-1 | Gh_D07G1476.1 | 5532 | 651 | 24.49891 | 8.61 | G. hirsutum |
| GhFBN9-2 | Gh_A07G1372.1 | 1399 | 645 | 24.35177 | 8.61 | G. hirsutum |
| GhFBN10-1 | Gh_D08G0826.1 | 5532 | 1200 | 44.77003 | 6.48 | G. hirsutum |
| GhFBN10-2 | Gh_A08G0709.1 | 1399 | 1200 | 44.78029 | 8.64 | G. hirsutum |
| GhFBN11-1 | Gh_D12G2421.1 | 4196 | 2031 | 76.64194 | 9.74 | G. hirsutum |
| GhFBN11-2 | Gh_A12G2271.1 | 3179 | 2031 | 76.67501 | 9.86 | G. hirsutum |
| GaFBN1A | Ga05G1857.1 | 1399 | 978 | 35.43737 | 5.14 | G. arboreum |
| GaFBN1B | Ga09G0772.1 | 2379 | 1008 | 36.92974 | 5 | G. arboreum |
| GaFBN2 | Ga09G2235.1 | 1607 | 1101 | 39.6435 | 4.54 | G. arboreum |
| GaFBN3A-1 | Ga02G1224.1 | 2259 | 735 | 27.44765 | 9.65 | G. arboreum |
| GaFBN3A-2 | Ga04G0211.1 | 1736 | 762 | 28.54992 | 9.69 | G. arboreum |
| GaFBN4 | Ga09G2612.1 | 1590 | 831 | 29.95748 | 9.37 | G. arboreum |
| GaFBN5 | Ga11G1531.1 | 2064 | 867 | 32.03204 | 7.55 | G. arboreum |
| GaFBN6 | Ga06G1253.1 | 1113 | 705 | 25.7124 | 9.08 | G. arboreum |
| GaFBN7A | Ga09G1460.1 | 5543 | 912 | 33.29209 | 6.07 | G. arboreum |
| GaFBN8 | Ga11G2969.1 | 3024 | 846 | 31.58558 | 9.07 | G. arboreum |
| GaFBN9 | Ga07G1647.1 | 1031 | 645 | 24.35177 | 8.61 | G. arboreum |
| GaFBN10 | Ga08G0915.1 | 5511 | 1200 | 44.73919 | 8.65 | G. arboreum |
| GaFBN11 | Ga12G0290.1 | 4018 | 2031 | 76.67501 | 9.86 | G. arboreum |
| GbFBN1A-1 | Gbar_D05G017830.1 | 2891 | 978 | 35.40735 | 5.14 | G. barbadense |
| GbFBN1A-2 | Gbar_A05G017410.1 | 2838 | 978 | 35.44943 | 5.14 | G. barbadense |
| GbFBN1A-3 | Gbar_D09G007520.1 | 2745 | 1008 | 36.87478 | 4.99 | G. barbadense |
| GbFBN1B | Gbar_A09G007800.1 | 2780 | 1008 | 36.90267 | 4.95 | G. barbadense |
| GbFBN2-1 | Gbar_D09G020830.1 | 2524 | 1107 | 39.81765 | 4.49 | G. barbadense |
| GbFBN2-2 | Gbar_A09G021110.1 | 2508 | 1101 | 39.65757 | 4.58 | G. barbadense |
| GbFBN3A-1 | Gbar_D01G018650.1 | 5258 | 747 | 28.08431 | 9.34 | G. barbadense |
| GbFBN3A-2 | Gbar_A01G017480.1 | 2517 | 735 | 27.42963 | 9.65 | G. barbadense |
| GbFBN3A-4 | Gbar_A04G013910.1 | 1706 | 762 | 28.53392 | 9.69 | G. barbadense |
| GbFBN3A-3 | Gbar_D04G018570.1 | 1864 | 762 | 28.49887 | 9.54 | G. barbadense |
| GbFBN4-1 | Gbar_D09G024190.1 | 2000 | 831 | 29.91642 | 9.37 | G. barbadense |
| GbFBN4-2 | Gbar_A09G024530.1 | 1568 | 813 | 29.46222 | 8.77 | G. barbadense |
| GbFBN5-1 | Gbar_D06G016800.1 | 3442 | 1614 | 59.91259 | 7.03 | G. barbadense |
| GbFBN5-2 | Gbar_A06G016120.1 | 2029 | 897 | 33.38748 | 7.64 | G. barbadense |
| GbFBN5-3 | Gbar_D11G024180.1 | 12587 | 894 | 33.03026 | 9.27 | G. barbadense |
| GbFBN5-4 | Gbar_A11G023440.1 | 2514 | 552 | 20.34894 | 9.43 | G. barbadense |
| GbFBN6-1 | Gbar_D06G011790.1 | 1462 | 705 | 25.69841 | 9.19 | G. barbadense |
| GbFBN6-2 | Gbar_A06G011340.1 | 1453 | 717 | 26.18494 | 8.94 | G. barbadense |
| GbFBN7B-1 | Gbar_D09G013520.1 | 6058 | 912 | 33.29012 | 6.67 | G. barbadense |
| GbFBN7A-2 | Gbar_A09G013680.1 | 5971 | 912 | 33.32015 | 6.67 | G. barbadense |
| GbFBN8-1 | Gbar_D11G011270.1 | 3392 | 846 | 31.58953 | 9.25 | G. barbadense |
| GbFBN8-2 | Gbar_A11G010770.1 | 3987 | 1014 | 37.98029 | 9.67 | G. barbadense |
| GbFBN9-1 | Gbar_D07G016160.1 | 3560 | 651 | 24.49891 | 8.61 | G. barbadense |
| GbFBN9-2 | Gbar_A07G015770.1 | 3386 | 645 | 24.35177 | 8.61 | G. barbadense |
| GbFBN10-1 | Gbar_D08G008730.1 | 5745 | 954 | 35.6023 | 6.46 | G. barbadense |
| GbFBN10-2 | Gbar_A08G008420.1 | 5752 | 1119 | 41.6738 | 7.7 | G. barbadense |
| GbFBN11-1 | Gbar_D12G026080.1 | 4751 | 1425 | 54.09186 | 9.87 | G. barbadense |
| GbFBN11-2 | Gbar_A12G026140.1 | 4788 | 2031 | 76.68903 | 9.86 | G. barbadense |
| GrFBN1A-1 | Gorai.009G182500.1 | 2513 | 978 | 35.42335 | 5.14 | G. raimondii |
| GrFBN1A-2 | Gorai.006G082400.1 | 2754 | 1014 | 37.13302 | 5.06 | G. raimondii |
| GrFBN2 | Gorai.006G217700.1 | 2488 | 1125 | 40.3022 | 4.49 | G. raimondii |
| GrFBN3A-1 | Gorai.002G209300.1 | 2559 | 735 | 27.42461 | 9.56 | G. raimondii |
| GrFBN3A-2 | Gorai.012G160700.1 | 1982 | 762 | 28.48682 | 9.54 | G. raimondii |
| GrFBN4 | Gorai.006G252600.1 | 2015 | 831 | 29.97849 | 9.37 | G. raimondii |
| GrFBN5-1 | Gorai.010G181700.1 | 3037 | 1812 | 67.68879 | 8.5 | G. raimondii |
| GrFBN5-2 | Gorai.002G151300.1 | 1994 | 813 | 30.16 | 9.12 | G. raimondii |
| GrFBN6-1 | Gorai.010G123700.1 | 1498 | 705 | 25.68439 | 9.19 | G. raimondii |
| GrFBN6-2 | Gorai.002G101300.1 | 728 | 423 | 15.86637 | 9.16 | G. raimondii |
| GrFBN7B | Gorai.006G142800.1 | 6103 | 912 | 33.29012 | 6.67 | G. raimondii |
| GrFBN8 | Gorai.007G115100.1 | 3493 | 861 | 32.16422 | 9.36 | G. raimondii |
| GrFBN9 | Gorai.001G175700.1 | 3596 | 651 | 24.5059 | 8.61 | G. raimondii |
| GrFBN10 | Gorai.004G092800.1 | 5850 | 1200 | 44.80911 | 6.93 | G. raimondii |
| GrFBN11 | Gorai.008G269500.1 | 4726 | 2031 | 76.79095 | 9.76 | G. raimondii |
| Sequence ID | Ka | Ks | Ka/Ks |
|---|---|---|---|
| GhFBN3-1&GhFBN3-3 | 0.25646808027089535 | 1.8899984771994518 | 0.1356975063021864 |
| GhFBN3-1&GhFBN3-2 | 0.015378195927205629 | 0.031811997515935844 | 0.48340868628265493 |
| GhFBN3-1&GhFBN3-4 | 0.26519839929406197 | 2.0183731848080146 | 0.1313921534878533 |
| GhFBN3-3&GhFBN3-2 | 0.2539649643874308 | 1.9922119769228535 | 0.12747888644847022 |
| GhFBN3-3&GhFBN3-4 | 0.010415327224946307 | 0.022316848711233652 | 0.4667024166231648 |
| GhFBN1A-2&GhFBN1B-2 | 0.11398702336283616 | 0.6464385028816231 | 0.17633080773301285 |
| GhFBN1A-2&GhFBN1A-1 | 0.002682766106657679 | 0.026415055967744308 | 0.10156200728605806 |
| GhFBN1A-2&GhFBN1B-1 | 0.11237961274006769 | 0.6372917984117465 | 0.17633933626658815 |
| GhFBN6-2&GhFBN6-1 | 0.013447621783443438 | 0.03803440541457851 | 0.35356466433123185 |
| GhFBN5-2&GhFBN5-1 | 0.037268406863882296 | 0.05082235814271873 | 0.7333073124868705 |
| GhFBN9-2&GhFBN9-1 | 0.006157038170299509 | 0.0812977842242655 | 0.07573439090682837 |
| GhFBN10-2&GhFBN10-1 | 0.014196438052508897 | 0.025840759627618143 | 0.5493816070846461 |
| GhFBN1B-2&GhFBN1A-1 | 0.11091080011024723 | 0.6246818422013267 | 0.17754766125329788 |
| GhFBN1B-2&GhFBN1B-1 | 0.014403061291802292 | 0.0434431959190317 | 0.33153779290654267 |
| GhFBN7A&GhFBN7B | 0.004380640343959717 | 0.04578080007805861 | 0.0956872823648888 |
| GhFBN2-2&GhFBN2-1 | 0.009753261495566346 | 0.04104225646267837 | 0.23763950465139363 |
| GhFBN8-2&GhFBN8-1 | 0.03976139397807425 | 0.04769566096457199 | 0.8336480336777121 |
| GhFBN11-2&GhFBN11-1 | 0.008441190776946137 | 0.02530551062085989 | 0.3335712487061169 |
| GhFBN3-2&GhFBN3-4 | 0.2626554249946424 | 2.1422101503898068 | 0.12260955114363936 |
| GhFBN1A-1&GhFBN1B-1 | 0.11243405990473135 | 0.6358361961198246 | 0.17682865585642585 |
| ID | Cis-Elements Name | Functions of Cis-Elements |
|---|---|---|
| Gh_A01G1493 | ABRE | cis-acting element involved in abscisic acid responsiveness |
| Gh_A01G1493 | ABRE | cis-acting element involved in abscisic acid responsiveness |
| Gh_A04G1080 | CGTCA-motif | cis-acting regulatory element involved in MeJA responsiveness |
| Gh_A04G1080 | TATC-box | cis-acting element involved in gibberellin responsiveness |
| Gh_A04G1080 | TGACG-motif | cis-acting regulatory element involved in MeJA responsiveness |
| Gh_A04G1080 | ABRE | cis-acting element involved in abscisic acid responsiveness |
| Gh_A04G1080 | ABRE | cis-acting element involved in abscisic acid responsiveness |
| Gh_A04G1080 | ABRE | cis-acting element involved in abscisic acid responsiveness |
| Gh_A04G1080 | AuxRR-core | cis-acting regulatory element involved in auxin responsiveness |
| Gh_A05G1494 | P-box | gibberellin-responsive element |
| Gh_A05G1494 | CGTCA-motif | cis-acting regulatory element involved in MeJA responsiveness |
| Gh_A05G1494 | ABRE | cis-acting element involved in abscisic acid responsiveness |
| Gh_A05G1494 | ABRE | cis-acting element involved in abscisic acid responsiveness |
| Gh_A05G1494 | ABRE | cis-acting element involved in abscisic acid responsiveness |
| Gh_A05G1494 | ABRE | cis-acting element involved in abscisic acid responsiveness |
| Gh_A05G1494 | ABRE | cis-acting element involved in abscisic acid responsiveness |
| Gh_A05G1494 | TGACG-motif | cis-acting regulatory element involved in MeJA responsiveness |
| Gh_A05G1494 | TCA-element | cis-acting element involved in salicylic acid responsiveness |
| Gh_A05G1494 | GARE-motif | gibberellin-responsive element |
| Gh_A06G0966 | CGTCA-motif | cis-acting regulatory element involved in MeJA responsiveness |
| Gh_A06G0966 | TATC-box | cis-acting element involved in gibberellin responsiveness |
| Gh_A06G0966 | ABRE | cis-acting element involved in abscisic acid responsiveness |
| Gh_A06G0966 | ABRE | cis-acting element involved in abscisic acid responsiveness |
| Gh_A06G0966 | ABRE | cis-acting element involved in abscisic acid responsiveness |
| Gh_A06G0966 | ABRE | cis-acting element involved in abscisic acid responsiveness |
| Gh_A06G0966 | TGACG-motif | cis-acting regulatory element involved in MeJA responsiveness |
| Gh_A06G1315 | TCA-element | cis-acting element involved in salicylic acid responsiveness |
| Gh_A06G1315 | AuxRR-core | cis-acting regulatory element involved in auxin responsiveness |
| Gh_A06G1315 | ABRE | cis-acting element involved in abscisic acid responsiveness |
| Gh_A07G1372 | ABRE | cis-acting element involved in abscisic acid responsiveness |
| Gh_A07G1372 | ABRE | cis-acting element involved in abscisic acid responsiveness |
| Gh_A07G1372 | TATC-box | cis-acting element involved in gibberellin responsiveness |
| Gh_A08G0709 | GARE-motif | gibberellin-responsive element |
| Gh_A09G0658 | CGTCA-motif | cis-acting regulatory element involved in MeJA responsiveness |
| Gh_A09G0658 | TGACG-motif | cis-acting regulatory element involved in MeJA responsiveness |
| Gh_A09G0658 | TCA-element | cis-acting element involved in salicylic acid responsiveness |
| Gh_A09G1197 | TATC-box | cis-acting element involved in gibberellin responsiveness |
| Gh_A09G1197 | TCA-element | cis-acting element involved in salicylic acid responsiveness |
| Gh_A09G1782 | ABRE | cis-acting element involved in abscisic acid responsiveness |
| Gh_A09G1782 | AuxRR-core | cis-acting regulatory element involved in auxin responsiveness |
| Gh_A09G1782 | TGACG-motif | cis-acting regulatory element involved in MeJA responsiveness |
| Gh_A09G1782 | CGTCA-motif | cis-acting regulatory element involved in MeJA responsiveness |
| Gh_A09G2222 | ABRE | cis-acting element involved in abscisic acid responsiveness |
| Gh_A09G2222 | ABRE | cis-acting element involved in abscisic acid responsiveness |
| Gh_A09G2222 | TGACG-motif | cis-acting regulatory element involved in MeJA responsiveness |
| Gh_A09G2222 | TCA-element | cis-acting element involved in salicylic acid responsiveness |
| Gh_A09G2222 | P-box | gibberellin-responsive element |
| Gh_A09G2222 | CGTCA-motif | cis-acting regulatory element involved in MeJA responsiveness |
| Gh_A11G0937 | GARE-motif | gibberellin-responsive element |
| Gh_A11G0937 | TGACG-motif | cis-acting regulatory element involved in MeJA responsiveness |
| Gh_A11G0937 | CGTCA-motif | cis-acting regulatory element involved in MeJA responsiveness |
| Gh_A11G0937 | TGA-element | auxin-responsive element |
| Gh_A11G0937 | TATC-box | cis-acting element involved in gibberellin responsiveness |
| Gh_A11G0937 | TATC-box | cis-acting element involved in gibberellin responsiveness |
| Gh_A11G0937 | P-box | gibberellin-responsive element |
| Gh_A12G2271 | TCA-element | cis-acting element involved in salicylic acid responsiveness |
| Gh_A12G2271 | GARE-motif | gibberellin-responsive element |
| Gh_A12G2271 | ABRE | cis-acting element involved in abscisic acid responsiveness |
| Gh_A12G2271 | ABRE | cis-acting element involved in abscisic acid responsiveness |
| Gh_A12G2271 | ABRE | cis-acting element involved in abscisic acid responsiveness |
| Gh_A12G2271 | ABRE | cis-acting element involved in abscisic acid responsiveness |
| Gh_A12G2271 | ABRE | cis-acting element involved in abscisic acid responsiveness |
| Gh_A12G2271 | ABRE | cis-acting element involved in abscisic acid responsiveness |
| Gh_A12G2271 | ABRE | cis-acting element involved in abscisic acid responsiveness |
| Gh_A12G2271 | ABRE | cis-acting element involved in abscisic acid responsiveness |
| Gh_A12G2271 | TGACG-motif | cis-acting regulatory element involved in MeJA responsiveness |
| Gh_A12G2271 | TGACG-motif | cis-acting regulatory element involved in MeJA responsiveness |
| Gh_A12G2271 | TGACG-motif | cis-acting regulatory element involved in MeJA responsiveness |
| Gh_A12G2271 | CGTCA-motif | cis-acting regulatory element involved in MeJA responsiveness |
| Gh_A12G2271 | CGTCA-motif | cis-acting regulatory element involved in MeJA responsiveness |
| Gh_A12G2271 | CGTCA-motif | cis-acting regulatory element involved in MeJA responsiveness |
| Gh_D01G0744 | TGA-element | auxin-responsive element |
| Gh_D01G0744 | P-box | gibberellin-responsive element |
| Gh_D01G0744 | GARE-motif | gibberellin-responsive element |
| Gh_D01G0744 | TCA-element | cis-acting element involved in salicylic acid responsiveness |
| Gh_D01G0744 | TCA-element | cis-acting element involved in salicylic acid responsiveness |
| Gh_D01G0744 | ABRE | cis-acting element involved in abscisic acid responsiveness |
| Gh_D01G1730 | ABRE | cis-acting element involved in abscisic acid responsiveness |
| Gh_D01G1730 | ABRE | cis-acting element involved in abscisic acid responsiveness |
| Gh_D01G1730 | AuxRR-core | cis-acting regulatory element involved in auxin responsiveness |
| Gh_D04G1687 | ABRE | cis-acting element involved in abscisic acid responsiveness |
| Gh_D04G1687 | ABRE | cis-acting element involved in abscisic acid responsiveness |
| Gh_D04G1687 | AuxRR-core | cis-acting regulatory element involved in auxin responsiveness |
| Gh_D04G1687 | TGACG-motif | cis-acting regulatory element involved in MeJA responsiveness |
| Gh_D04G1687 | CGTCA-motif | cis-acting regulatory element involved in MeJA responsiveness |
| Gh_D04G1687 | P-box | gibberellin-responsive element |
| Gh_D04G1687 | TATC-box | cis-acting element involved in gibberellin responsiveness |
| Gh_D05G1665 | TCA-element | cis-acting element involved in salicylic acid responsiveness |
| Gh_D05G1665 | TCA-element | cis-acting element involved in salicylic acid responsiveness |
| Gh_D05G1665 | GARE-motif | gibberellin-responsive element |
| Gh_D05G1665 | ABRE | cis-acting element involved in abscisic acid responsiveness |
| Gh_D05G1665 | ABRE | cis-acting element involved in abscisic acid responsiveness |
| Gh_D05G1665 | ABRE | cis-acting element involved in abscisic acid responsiveness |
| Gh_D05G1665 | ABRE | cis-acting element involved in abscisic acid responsiveness |
| Gh_D05G1665 | ABRE | cis-acting element involved in abscisic acid responsiveness |
| Gh_D05G1665 | TGACG-motif | cis-acting regulatory element involved in MeJA responsiveness |
| Gh_D05G1665 | CGTCA-motif | cis-acting regulatory element involved in MeJA responsiveness |
| Gh_D05G1665 | P-box | gibberellin-responsive element |
| Gh_D05G1665 | TATC-box | cis-acting element involved in gibberellin responsiveness |
| Gh_D06G1142 | TGACG-motif | cis-acting regulatory element involved in MeJA responsiveness |
| Gh_D06G1142 | AuxRR-core | cis-acting regulatory element involved in auxin responsiveness |
| Gh_D06G1142 | ABRE | cis-acting element involved in abscisic acid responsiveness |
| Gh_D06G1142 | ABRE | cis-acting element involved in abscisic acid responsiveness |
| Gh_D06G1142 | ABRE | cis-acting element involved in abscisic acid responsiveness |
| Gh_D06G1142 | ABRE | cis-acting element involved in abscisic acid responsiveness |
| Gh_D06G1142 | ABRE | cis-acting element involved in abscisic acid responsiveness |
| Gh_D06G1142 | TATC-box | cis-acting element involved in gibberellin responsiveness |
| Gh_D06G1142 | CGTCA-motif | cis-acting regulatory element involved in MeJA responsiveness |
| Gh_D06G1644 | P-box | gibberellin-responsive element |
| Gh_D06G1644 | CGTCA-motif | cis-acting regulatory element involved in MeJA responsiveness |
| Gh_D06G1644 | TGA-element | auxin-responsive element |
| Gh_D06G1644 | ABRE | cis-acting element involved in abscisic acid responsiveness |
| Gh_D06G1644 | ABRE | cis-acting element involved in abscisic acid responsiveness |
| Gh_D06G1644 | TGACG-motif | cis-acting regulatory element involved in MeJA responsiveness |
| Gh_D06G1644 | TCA-element | cis-acting element involved in salicylic acid responsiveness |
| Gh_D07G1476 | ABRE | cis-acting element involved in abscisic acid responsiveness |
| Gh_D07G1476 | ABRE | cis-acting element involved in abscisic acid responsiveness |
| Gh_D07G1476 | GARE-motif | gibberellin-responsive element |
| Gh_D07G1476 | TGA-element | auxin-responsive element |
| Gh_D08G0826 | ABRE | cis-acting element involved in abscisic acid responsiveness |
| Gh_D08G0826 | ABRE | cis-acting element involved in abscisic acid responsiveness |
| Gh_D08G0826 | ABRE | cis-acting element involved in abscisic acid responsiveness |
| Gh_D09G0662 | ABRE | cis-acting element involved in abscisic acid responsiveness |
| Gh_D09G0662 | TCA-element | cis-acting element involved in salicylic acid responsiveness |
| Gh_D09G1203 | P-box | gibberellin-responsive element |
| Gh_D09G1203 | CGTCA-motif | cis-acting regulatory element involved in MeJA responsiveness |
| Gh_D09G1203 | ABRE | cis-acting element involved in abscisic acid responsiveness |
| Gh_D09G1203 | ABRE | cis-acting element involved in abscisic acid responsiveness |
| Gh_D09G1203 | TGACG-motif | cis-acting regulatory element involved in MeJA responsiveness |
| Gh_D09G1203 | TCA-element | cis-acting element involved in salicylic acid responsiveness |
| Gh_D09G2214 | ABRE | cis-acting element involved in abscisic acid responsiveness |
| Gh_D09G2214 | ABRE | cis-acting element involved in abscisic acid responsiveness |
| Gh_D09G2214 | ABRE | cis-acting element involved in abscisic acid responsiveness |
| Gh_D09G2214 | ABRE | cis-acting element involved in abscisic acid responsiveness |
| Gh_D09G2214 | ABRE | cis-acting element involved in abscisic acid responsiveness |
| Gh_D09G2214 | ABRE | cis-acting element involved in abscisic acid responsiveness |
| Gh_D09G2214 | TGACG-motif | cis-acting regulatory element involved in MeJA responsiveness |
| Gh_D09G2214 | TGACG-motif | cis-acting regulatory element involved in MeJA responsiveness |
| Gh_D09G2214 | TGACG-motif | cis-acting regulatory element involved in MeJA responsiveness |
| Gh_D09G2214 | CGTCA-motif | cis-acting regulatory element involved in MeJA responsiveness |
| Gh_D09G2214 | CGTCA-motif | cis-acting regulatory element involved in MeJA responsiveness |
| Gh_D09G2214 | CGTCA-motif | cis-acting regulatory element involved in MeJA responsiveness |
| Gh_D11G1079 | P-box | gibberellin-responsive element |
| Gh_D11G1079 | TATC-box | cis-acting element involved in gibberellin responsiveness |
| Gh_D11G1079 | TATC-box | cis-acting element involved in gibberellin responsiveness |
| Gh_D11G1079 | TGA-element | auxin-responsive element |
| Gh_D11G1079 | ABRE | cis-acting element involved in abscisic acid responsiveness |
| Gh_D11G1079 | GARE-motif | gibberellin-responsive element |
| Gh_D11G3441 | CGTCA-motif | cis-acting regulatory element involved in MeJA responsiveness |
| Gh_D11G3441 | CGTCA-motif | cis-acting regulatory element involved in MeJA responsiveness |
| Gh_D11G3441 | TGACG-motif | cis-acting regulatory element involved in MeJA responsiveness |
| Gh_D11G3441 | TGACG-motif | cis-acting regulatory element involved in MeJA responsiveness |
| Gh_D12G2421 | CGTCA-motif | cis-acting regulatory element involved in MeJA responsiveness |
| Gh_D12G2421 | CGTCA-motif | cis-acting regulatory element involved in MeJA responsiveness |
| Gh_D12G2421 | GARE-motif | gibberellin-responsive element |
| Gh_D12G2421 | TCA-element | cis-acting element involved in salicylic acid responsiveness |
| Gh_D12G2421 | TGACG-motif | cis-acting regulatory element involved in MeJA responsiveness |
| Gh_D12G2421 | TGACG-motif | cis-acting regulatory element involved in MeJA responsiveness |
| Gh_D12G2421 | ABRE | cis-acting element involved in abscisic acid responsiveness |
| Gh_D12G2421 | ABRE | cis-acting element involved in abscisic acid responsiveness |
| Gh_D12G2421 | ABRE | cis-acting element involved in abscisic acid responsiveness |
| Gh_D12G2421 | ABRE | cis-acting element involved in abscisic acid responsiveness |
| Gh_D12G2421 | ABRE | cis-acting element involved in abscisic acid responsiveness |
| Gh_D12G2421 | ABRE | cis-acting element involved in abscisic acid responsiveness |
| Gh_D12G2421 | ABRE | cis-acting element involved in abscisic acid responsiveness |
| Gh_D09G1905 | L-box | part of a light-responsive element |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Yan, S.; Hou, L.; Zhu, L.; Feng, Z.; Xiao, G.; Li, L. Characterization and Functional Analysis of the FBN Gene Family in Cotton: Insights into Fiber Development. Biology 2025, 14, 1012. https://doi.org/10.3390/biology14081012
Yan S, Hou L, Zhu L, Feng Z, Xiao G, Li L. Characterization and Functional Analysis of the FBN Gene Family in Cotton: Insights into Fiber Development. Biology. 2025; 14(8):1012. https://doi.org/10.3390/biology14081012
Chicago/Turabian StyleYan, Sunhui, Liyong Hou, Liping Zhu, Zhen Feng, Guanghui Xiao, and Libei Li. 2025. "Characterization and Functional Analysis of the FBN Gene Family in Cotton: Insights into Fiber Development" Biology 14, no. 8: 1012. https://doi.org/10.3390/biology14081012
APA StyleYan, S., Hou, L., Zhu, L., Feng, Z., Xiao, G., & Li, L. (2025). Characterization and Functional Analysis of the FBN Gene Family in Cotton: Insights into Fiber Development. Biology, 14(8), 1012. https://doi.org/10.3390/biology14081012







