Isolation and Identification of Antifungal Polyketones from Bacillus velezensis DJ1 and Their Biocontrol Potential Against Corn Stalk Rot
Abstract
Simple Summary
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Microbiological Material
2.2. Polyketones Production
2.3. Antifungal Activity of the DJ1 Polyketones
2.4. Inhibitory Mechanism of Polyketone of DJ1 on F. graminearum
2.4.1. Effects of Polyketone of DJ1 on Mycelium Morphology of F. graminearum
2.4.2. Effects of Polyketones of DJ1 on Plasma Membrane Damage
2.4.3. Determination of Enzyme Activities of F. graminearum
2.5. Greenhouse Experiment
Total number of emerged seedlings) × 100%
2.6. Soil Metagenomic Sequencing
2.7. Identification of DJ1 Polyketones
2.8. Data Analysis
3. Results
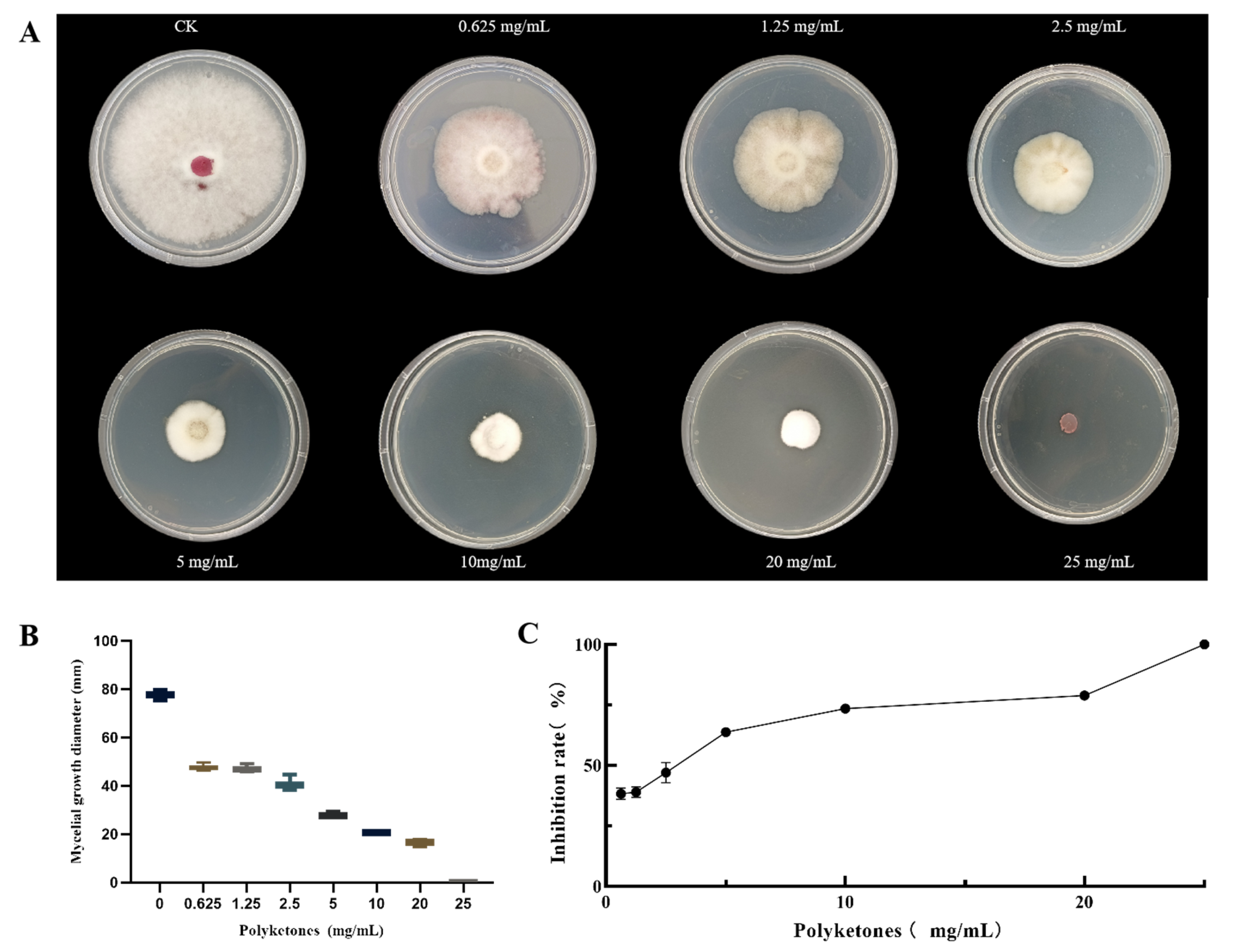
3.1. Antifungal Activity Assay of the Polyketone Produced by DJ1
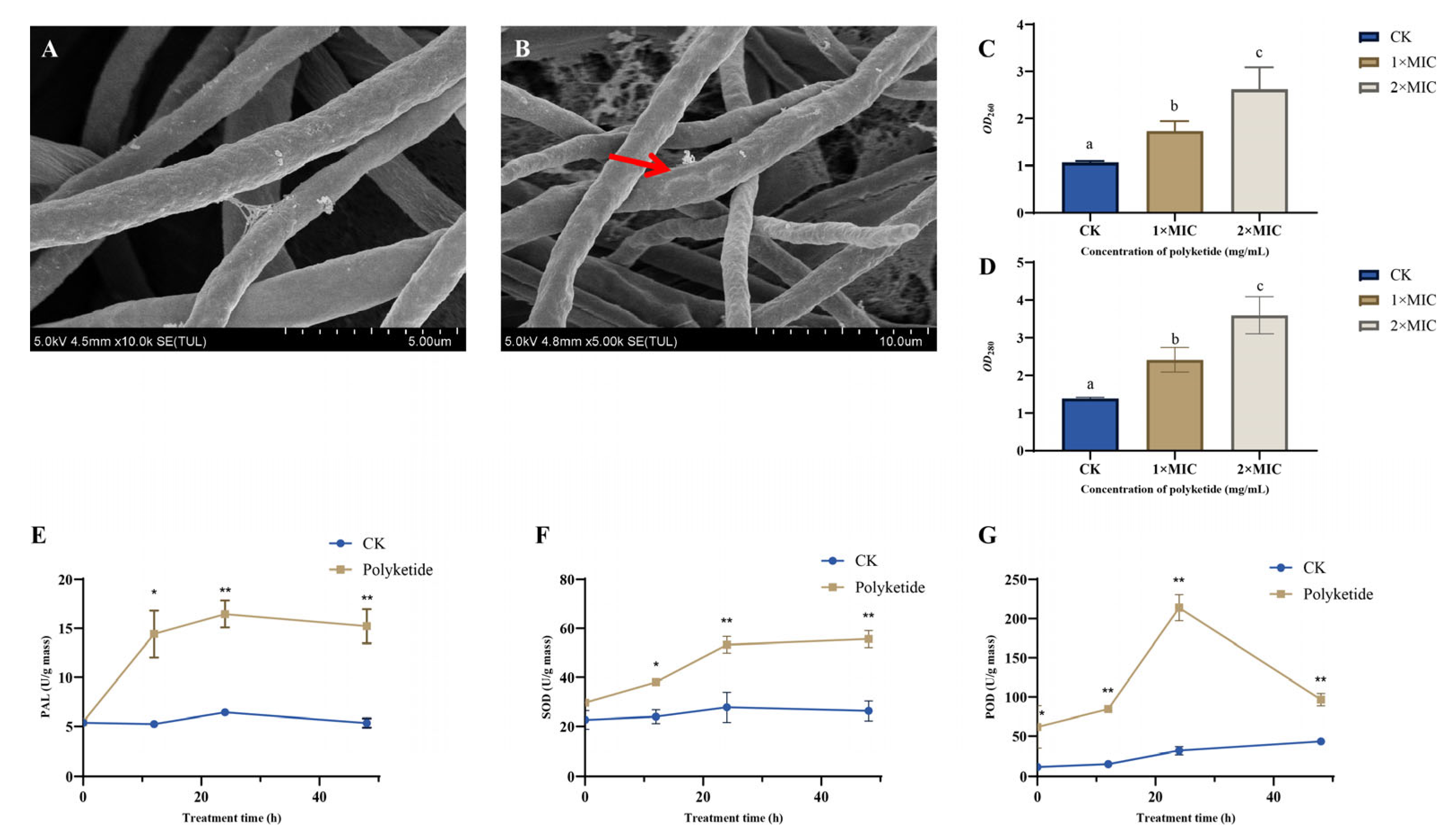
3.2. Inhibitory Mechanism of Polyketone of DJ1 on F. graminearum
3.2.1. Effect of DJ1 Polyketone on F. graminearum Mycelial Morphology
3.2.2. DJ1 Polyketones Disrupts the Cell Membrane Integrity of F. graminearum
3.3. DJ1 Polyketones Inhibit the Occurrence of Maize Stalk Rot in Greenhouse
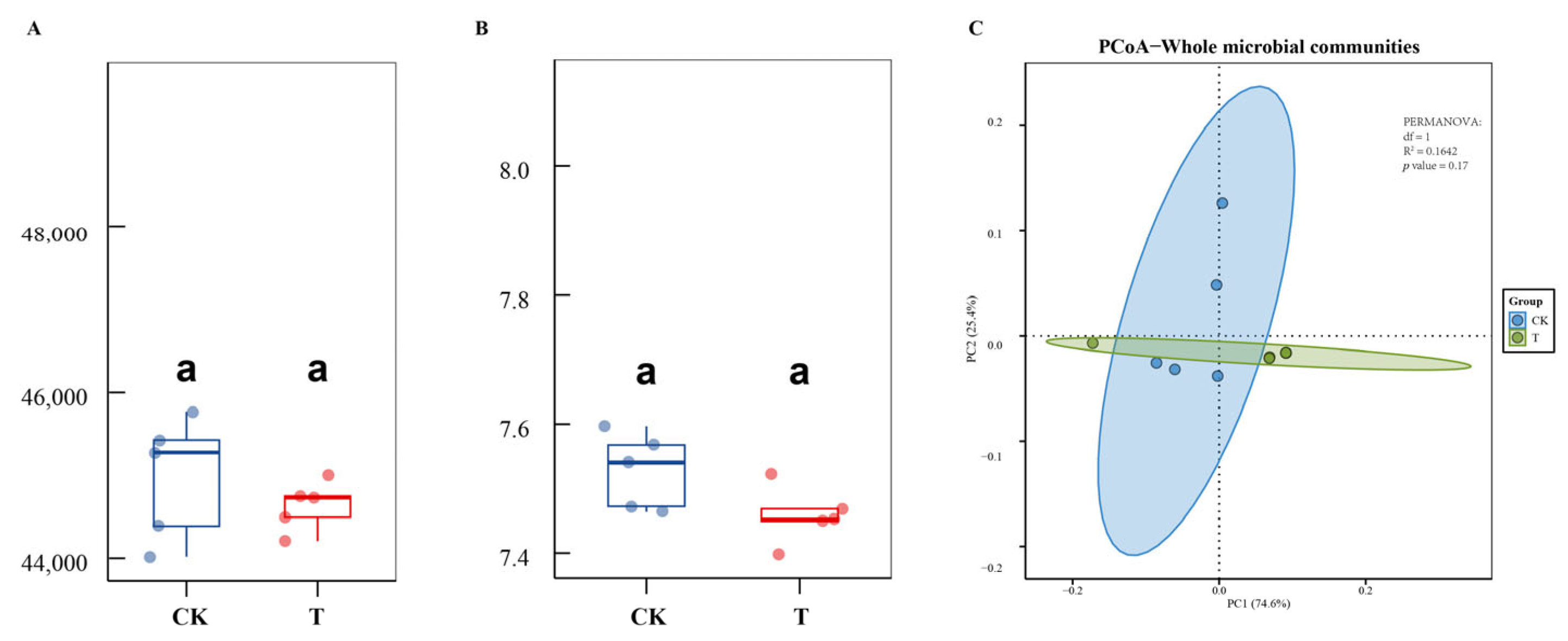
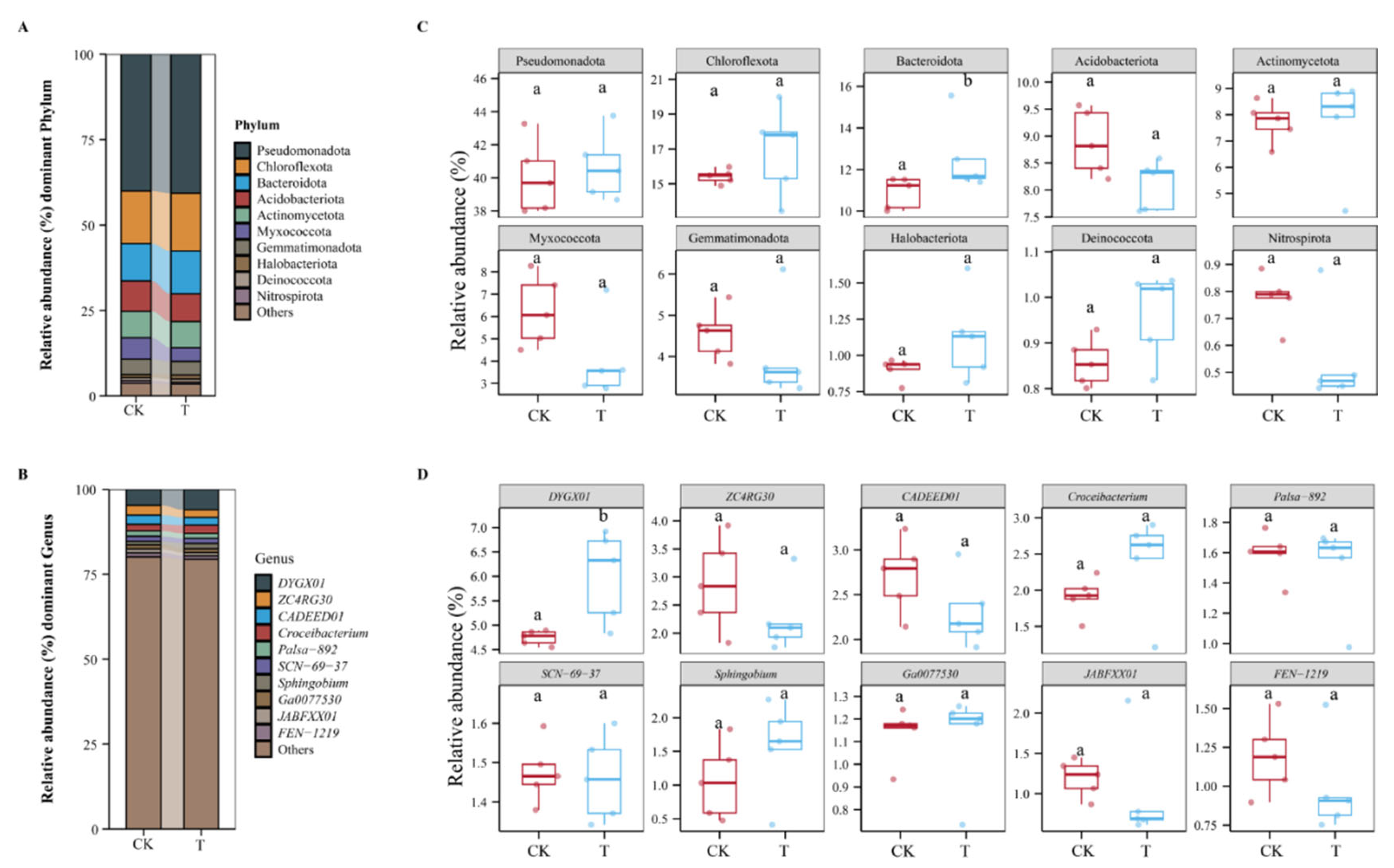
3.4. The Effect of DJ1 Polyketones on Bacterial Community Structure
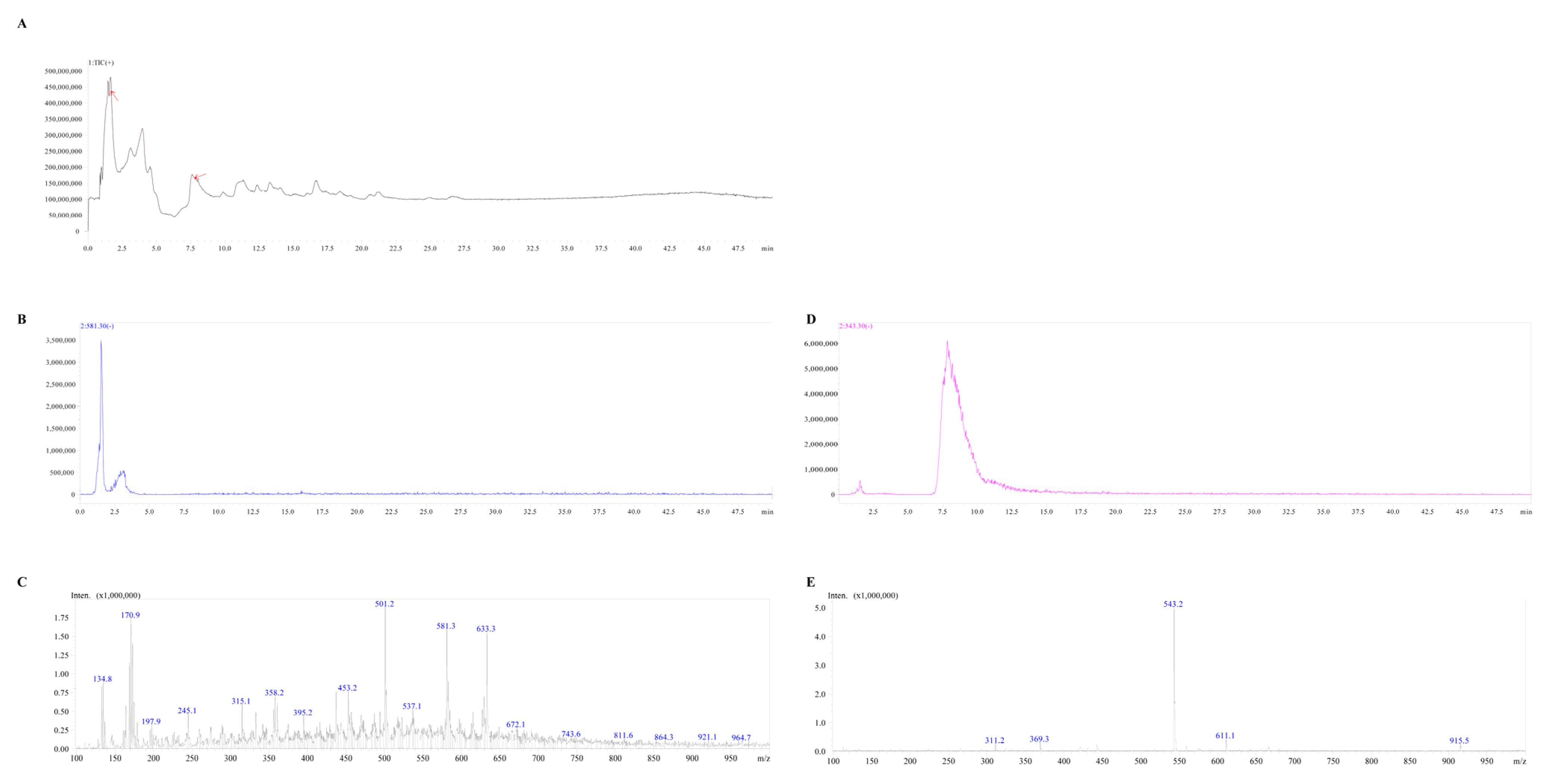
3.5. Identification of the Active Compounds
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
Appendix A
| Microbes | Target Gene | Primer Sequences (5′to 3′) |
|---|---|---|
| Bacteria | 16S rRNA | 341F-CCTACGGGNGGCWGCAG 805R-GACTACHVGGGTATCTAATCC |
| Sample | Total Reads | Total Bases | Total Reads with Ns | N Reads% | N% | Error% | Q20% | Q30% | GC% |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| CK-1 | 46,001,828 | 6,841,198,840 | 72,051 | 0.16 | 0 | 0.0239 | 98.21 | 94.79 | 61.07 |
| CK-2 | 45,867,046 | 6,820,133,424 | 75,292 | 0.16 | 0 | 0.024 | 98.19 | 94.74 | 61.05 |
| CK-3 | 42,927,794 | 6,383,065,139 | 61,364 | 0.14 | 0 | 0.024 | 98.18 | 94.7 | 61.41 |
| CK-4 | 49,209,824 | 7,316,867,623 | 70,382 | 0.14 | 0 | 0.024 | 98.15 | 94.64 | 61.52 |
| CK-5 | 45,845,230 | 6,817,708,740 | 65,531 | 0.14 | 0 | 0.0238 | 98.21 | 94.8 | 61.33 |
| T-1 | 35,992,282 | 5,349,384,452 | 53,976 | 0.15 | 0 | 0.0242 | 98.12 | 94.53 | 60.59 |
| T-2 | 49,828,222 | 7,412,718,835 | 70,156 | 0.14 | 0 | 0.0236 | 98.25 | 94.91 | 61.27 |
| T-3 | 40,778,120 | 6,068,850,552 | 53,300 | 0.13 | 0 | 0.0234 | 98.3 | 95.05 | 61.13 |
| T-4 | 44,553,116 | 6,635,128,835 | 53,605 | 0.12 | 0 | 0.0228 | 98.45 | 95.49 | 61.03 |
| T-5 | 42,919,936 | 6,385,262,071 | 59,633 | 0.14 | 0 | 0.0235 | 98.29 | 95.01 | 60.77 |
References
- Rehman, F.U.; Adnan, M.; Kalsoom, M.; Naz, N.; Husnain, M.G.; Ilahi, H.; Ilyas, M.A.; Yousaf, G.; Tahir, R.; Ahmad, U. Seed-borne fungal diseases of maize (Zea mays L.): A review. J. Agroteknologi dan Perkeb. 2021, 4, 43–60. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fu, Z.; Li, W.; Zhang, Q.; Wang, L.; Zhang, X.; Song, G.; Fu, Z.; Ding, D.; Liu, Z.; Tang, J. Quantitative trait loci for mercury accumulation in maize (Zea mays L.) identified using a RIL population. PLoS ONE 2014, 9, e107243. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, X.; Zheng, S.; Yu, M.; Xu, C.; Li, Y.; Sun, L.; Hu, G.; Yang, J.; Qiu, X. Evaluation of resistance resources and analysis of resistance mechanisms of maize to stalk rot caused by Fusarium graminearum. Plant Dis. 2024, 108, 348–358. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, J.; Han, Y.; Li, W.; Qi, T.; Zhang, J.; Li, Y. Identification of pathogens and evaluation of resistance and genetic diversity of maize inbred lines to stalk rot in Heilongjiang Province, China. Plant Dis. 2023, 107, 288–297. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.; Sun, R.; Yu, J.; Saravanakumar, K.; Chen, J. Antagonistic and Biocontrol Potential of Trichoderma asperellum ZJSX5003 Against the Maize Stalk Rot Pathogen Fusarium graminearum. Indian J. Microbiol. 2016, 56, 318–327. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, H.; Guan, Y.; Dong, Y.; Zhao, L.; Rong, S.; Chen, W.; Lv, M.; Xu, H.; Gao, X.; Chen, R.; et al. Isolation and evaluation of endophytic Bacillus tequilensis GYLH001 with potential application for biological control of Magnaporthe oryzae. PLoS ONE 2018, 13, e0203505. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xia, X.; Wei, Q.; Wu, H.; Chen, X.; Xiao, C.; Ye, Y.; Liu, C.; Yu, H.; Guo, Y.; Sun, W.; et al. Bacillus species are core microbiota of resistant maize cultivars that induce host metabolic defense against corn stalk rot. Microbiome 2024, 12, 156. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xie, S.; Jiang, L.; Wu, Q.; Wan, W.; Gan, Y.; Zhao, L.; Wen, J. Maize Root Exudates Recruit Bacillus amyloliquefaciens OR2-30 to Inhibit Fusarium graminearum Infection. Phytopathology 2022, 112, 1886–1893. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shen, S.; Yu, F.; Hao, X.; Chen, J.; Gao, H.; Lai, X. A novel Bacillus sp. with antagonistic activity against a plant pathogen, Fusarium graminearum, and its potential antagonistic mechanism. Lett. Appl. Microbiol. 2023, 76, ovad098. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liang, C.; Xu, X.X.; Sun, Y.-X.; Xin, Q.-H.; Lv, Y.-Y.; Hu, Y.-S.; Bian, K. Surfactin inhibits Fusarium graminearum by accumulating intracellular ROS and inducing apoptosis mechanisms. World J. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 2023, 39, 340. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vahidinasab, M.; Lilge, L.; Reinfurt, A.; Pfannstiel, J.; Henkel, M.; Morabbi Heravi, K.; Hausmann, R. Construction and description of a constitutive plipastatin mono-producing Bacillus subtilis. Microb. Cell Factories 2020, 19, 205. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Stubbendieck, R.M.; Brock, D.J.; Pellois, J.P.; Gill, J.J.; Straight, P.D. Linearmycins are lytic membrane-targeting antibiotics. J. Antibiot. 2018, 71, 372–381. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, M.C.; Wang, J.P.; Zhu, Y.J.; Liu, B.; Yang, W.J.; Ruan, C.Q. Antibacterial activity against Ralstonia solanacearum of the lipopeptides secreted from the Bacillus amyloliquefaciens strain FJAT-2349. J. Appl. Microbiol. 2019, 126, 1519–1529. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schneider, K.; Chen, X.H.; Vater, J.; Franke, P.; Nicholson, G.; Borriss, R.; Süssmuth, R.D. Macrolactin is the polyketide biosynthesis product of the pks2 cluster of Bacillus amyloliquefaciens FZB42. J. Nat. Prod. 2007, 70, 1417–1423. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.; Raza, W.; Jiang, G.; Yi, Z.; Fields, B.; Greenrod, S.; Friman, V.P.; Jousset, A.; Shen, Q.; Wei, Z. Bacterial volatile organic compounds attenuate pathogen virulence via evolutionary trade-offs. ISME J. 2023, 17, 443–452. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Raaijmakers, J.M.; De Bruijn, I.; Nybroe, O.; Ongena, M. Natural functions of lipopeptides from Bacillus and Pseudomonas: More than surfactants and antibiotics. FEMS Microbiol. Rev. 2010, 34, 1037–1062. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, X.-H.; Vater, J.; Piel, J.R.; Franke, P.; Scholz, R.; Schneider, K.; Koumoutsi, A.; Hitzeroth, G.; Grammel, N.; Strittmatter, A.W. Structural and functional characterization of three polyketide synthase gene clusters in Bacillus amyloliquefaciens FZB 42. J. Bacteriol. 2006, 188, 4024–4036. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miao, S.; Liang, J.; Xu, Y.; Yu, G.; Shao, M. Bacillaene, sharp objects consist in the arsenal of antibiotics produced by Bacillus. J. Cell. Physiol. 2024, 239, e30974. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chakraborty, K.; Kizhakkekalam, V.K.; Joy, M.; Dhara, S. Difficidin class of polyketide antibiotics from marine macroalga-associated Bacillus as promising antibacterial agents. Appl. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 2021, 105, 6395–6408. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, X.H.; Scholz, R.; Borriss, M.; Junge, H.; Mögel, G.; Kunz, S.; Borriss, R. Difficidin and bacilysin produced by plant-associated Bacillus amyloliquefaciens are efficient in controlling fire blight disease. J. Biotechnol. 2009, 140, 38–44. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Im, S.M.; Yu, N.H.; Joen, H.W.; Kim, S.O.; Park, H.W.; Park, A.R.; Kim, J.C. Biological control of tomato bacterial wilt by oxydifficidin and difficidin-producing Bacillus methylotrophicus DR-08. Pestic. Biochem. Physiol. 2020, 163, 130–137. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, L.; Wu, H.; Chen, L.; Yu, X.; Borriss, R.; Gao, X. Difficidin and bacilysin from Bacillus amyloliquefaciens FZB42 have antibacterial activity against Xanthomonas oryzae rice pathogens. Sci. Rep. 2015, 5, 12975. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Borah, S.N.; Goswami, D.; Sarma, H.K.; Cameotra, S.S.; Deka, S. Rhamnolipid biosurfactant against Fusarium verticillioides to control stalk and ear rot disease of maize. Front. Microbiol. 2016, 7, 1505. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, W.-B.; An, J.-X.; Jin, Y.-R.; Jing, C.-X.; Zhang, S.-Y.; Liang, H.-J.; Dai, T.-L.; Luo, X.-F.; Zhang, B.-Q.; Zhang, Z.-J. Indoloquinoline alkaloid neocryptolepine derivative inhibits Botrytis cinerea by targeting thiamine thiazole synthase. Sci. Adv. 2025, 11, eadq5329. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, C.; Qi, W.; Peng, X.; Chen, J.; Wan, C. Inhibitory effect of 7-demethoxytylophorine on Penicillium italicum and its possible mechanism. Microorganisms 2019, 7, 36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, Y.; Luo, Q.; Zhang, X.; Wang, W. Isolation and purification of a modified phenazine, griseoluteic acid, produced by Streptomyces griseoluteus P510. Res. Microbiol. 2011, 162, 311–319. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, L.; Jin, X.; Lu, X.; Guo, L.; Lu, P.; Yu, H.; Lv, B. Mechanisms of surfactin from Bacillus subtilis SF1 against Fusarium foetens: A novel pathogen inducing potato wilt. J. Fungi 2023, 9, 367. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yuan, Y.; Zhang, S.; Tan, X.; Deng, J.; Gong, S.; Zhai, X.; Xu, X.; Ruan, C.; Hu, Y.; Zhang, J. Intestinal bacterium Bacillus siamensis M54 from Allomyrina dichotoma is a potential biocontrol agent against maize stalk rot. Biol. Control 2024, 199, 105660. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheng, X.; Ji, X.; Ge, Y.; Li, J.; Qi, W.; Qiao, K. Characterization of antagonistic Bacillus methylotrophicus isolated from rhizosphere and its biocontrol effects on maize stalk rot. Phytopathology 2019, 109, 571–581. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hu, D.; Li, S.; Li, Y.; Peng, J.; Wei, X.; Ma, J.; Zhang, C.; Jia, N.; Wang, E.; Wang, Z. Streptomyces sp. strain TOR3209: A rhizosphere bacterium promoting growth of tomato by affecting the rhizosphere microbial community. Sci. Rep. 2020, 10, 20132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wilson, K.E.; Flor, J.E.; Schwartz, R.E.; Joshua, H.; Smith, J.L.; Pelak, B.A.; Liesch, J.M.; Hensens, O.D. Difficidin and oxydifficidin: Novel broad spectrum antibacterial antibiotics produced by Bacillus subtilis II. isolation and physico-chemical characterization. J. Antibiot. 1987, 40, 1682–1691. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- de Oliveira, A.J.; Ono, M.A.; Suguiura, I.M.S.; Zucareli, C.; Garcia, E.B.; Olchanheski, L.R.; Ono, E.Y.S. Potential of yeasts as biocontrol agents against Fusarium graminearum in vitro and on corn. J. Appl. Microbiol. 2023, 134, lxad296. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Coutte, F.; Lecouturier, D.; Dimitrov, K.; Guez, J.S.; Delvigne, F.; Dhulster, P.; Jacques, P. Microbial lipopeptide production and purification bioprocesses, current progress and future challenges. Biotechnol. J. 2017, 12, 1600566. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yuan, S.; Yong, X.; Zhao, T.; Li, Y.; Liu, J. Research Progress of the Biosynthesis of Natural Bio-Antibacterial Agent Pulcherriminic Acid in Bacillus. Molecules 2020, 25, 5611. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, S.; Jin, P.; Zheng, Y.; Kangkang, W.; Chen, J.; Liu, J.; Li, Y. Bacillus velezensis B105-8, a potential and efficient biocontrol agent in control of maize stalk rot caused by Fusarium graminearum. Front. Microbiol. 2024, 15, 1462992. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sun, M.; Han, C.; Meng, X.; Zeng, R.; Wang, X.; Yan, G.; Zheng, F.; Zhu, C. Biocontrol Potential of Streptomyces alboflavus LNU-CPARS28 Against Tomato Gray Mold Caused by Botrytis cinerea. Physiol. Mol. Plant Pathol. 2025, 140, 102949. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, L.-L.; Zhang, L.-F.; Xu, J.-G. Chemical composition, antibacterial activity and action mechanism of different extracts from hawthorn (Crataegus pinnatifida Bge.). Sci. Rep. 2020, 10, 8876. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yan, P.; Ahmad, S.; Xu, Z.; Jia, H.; Zhang, R.; Song, J.; Manzar, N.; Kashyap, A.S.; Zhang, W. Isolation and characterization of Bacillus sp. HSY32 and its toxin gene for potential biological control of plant parasitic nematode. Chem. Biol. Technol. Agric. 2024, 11, 191. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Toral, L.; Rodríguez, M.; Béjar, V.; Sampedro, I. Antifungal activity of lipopeptides from Bacillus XT1 CECT 8661 against Botrytis cinerea. Front. Microbiol. 2018, 9, 1315. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hyun, M.W.; Yun, Y.H.; Kim, J.Y.; Kim, S.H. Fungal and plant phenylalanine ammonia-lyase. Mycobiology 2011, 39, 257–265. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aguirre, J.; Hansberg, W.; Navarro, R. Fungal responses to reactive oxygen species. Med. Mycol. 2006, 44, 101–107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Linares-Otoya, L.; Shirkey, J.D.; Chhetri, B.K.; Mira, A.; Biswas, A.; Neff, S.L.; Linares-Otoya, M.V.; Chen, Y.; Campos-Florian, J.V.; Ganoza-Yupanqui, M.L. Discovery of a widespread chemical signalling pathway in the Bacteroidota. Nature 2025, 646, 423–432. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peng, F.; Li, X.; Wei, Z.; Han, G. Biocontrol potential and comparative genomic analysis of two Bacillus velezensis strains against sclerotinosis in mulberry fruit. Front. Microbiol. 2025, 16, 1587301. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ongena, M.; Jacques, P. Bacillus lipopeptides: Versatile weapons for plant disease biocontrol. Trends Microbiol. 2008, 16, 115–125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rabbee, M.F.; Ali, M.S.; Choi, J.; Hwang, B.S.; Jeong, S.C.; Baek, K.H. Bacillus velezensis: A Valuable Member of Bioactive Molecules within Plant Microbiomes. Molecules 2019, 24, 1046. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Adamczuk, A.; Kercheva, M.; Hristova, M.; Jozefaciuk, G. Impact of chitosan on water stability and wettability of soils. Materials 2021, 14, 7724. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yan, X.; Yu, Z.; Chen, Y.; Han, C.; Wei, Y.; Yang, F.; Qian, Y.; Wang, Y. Sodium Alginate–Montmorillonite Composite Film Coatings for Strawberry Preservation. Coatings 2024, 14, 1331. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
| Time (min) | Methanol Concentration (%) |
|---|---|
| 0–5 | 20 |
| 5–50 | 20–90 (linear gradient) |
| 50–55 | 100 |
| Treatments | Disease Incidence (%) | Diease Index | Disease Control Efficacy (%) |
|---|---|---|---|
| DJ1 polyketone | 44.89 ± 6.28 b | 23.68 ± 2.32 b | 44.33 ± 4.82 a |
| Fludioxonil | 50.62 ± 5.44 b | 24.65 ± 1.43 b | 37.22 ± 5.02 a |
| F. graminearum | 80.63 ± 2.73 a | 80.26 ± 2.82 a | -- |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Sun, M.; Du, W.; Zhang, J.; Xu, Y.; Wang, Z.; Zhou, L.; Yan, G.; Zhang, S. Isolation and Identification of Antifungal Polyketones from Bacillus velezensis DJ1 and Their Biocontrol Potential Against Corn Stalk Rot. Biology 2025, 14, 1436. https://doi.org/10.3390/biology14101436
Sun M, Du W, Zhang J, Xu Y, Wang Z, Zhou L, Yan G, Zhang S. Isolation and Identification of Antifungal Polyketones from Bacillus velezensis DJ1 and Their Biocontrol Potential Against Corn Stalk Rot. Biology. 2025; 14(10):1436. https://doi.org/10.3390/biology14101436
Chicago/Turabian StyleSun, Meng, Wanjia Du, Jialing Zhang, Yan Xu, Zixuan Wang, Lu Zhou, Gengxuan Yan, and Shumei Zhang. 2025. "Isolation and Identification of Antifungal Polyketones from Bacillus velezensis DJ1 and Their Biocontrol Potential Against Corn Stalk Rot" Biology 14, no. 10: 1436. https://doi.org/10.3390/biology14101436
APA StyleSun, M., Du, W., Zhang, J., Xu, Y., Wang, Z., Zhou, L., Yan, G., & Zhang, S. (2025). Isolation and Identification of Antifungal Polyketones from Bacillus velezensis DJ1 and Their Biocontrol Potential Against Corn Stalk Rot. Biology, 14(10), 1436. https://doi.org/10.3390/biology14101436





