Systemic and Pulmonary Inflammation/Oxidative Damage: Implications of General and Respiratory Muscle Training in Chronic Spinal-Cord-Injured Patients
Abstract
Simple Summary
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. General Context of Spinal Cord Injury
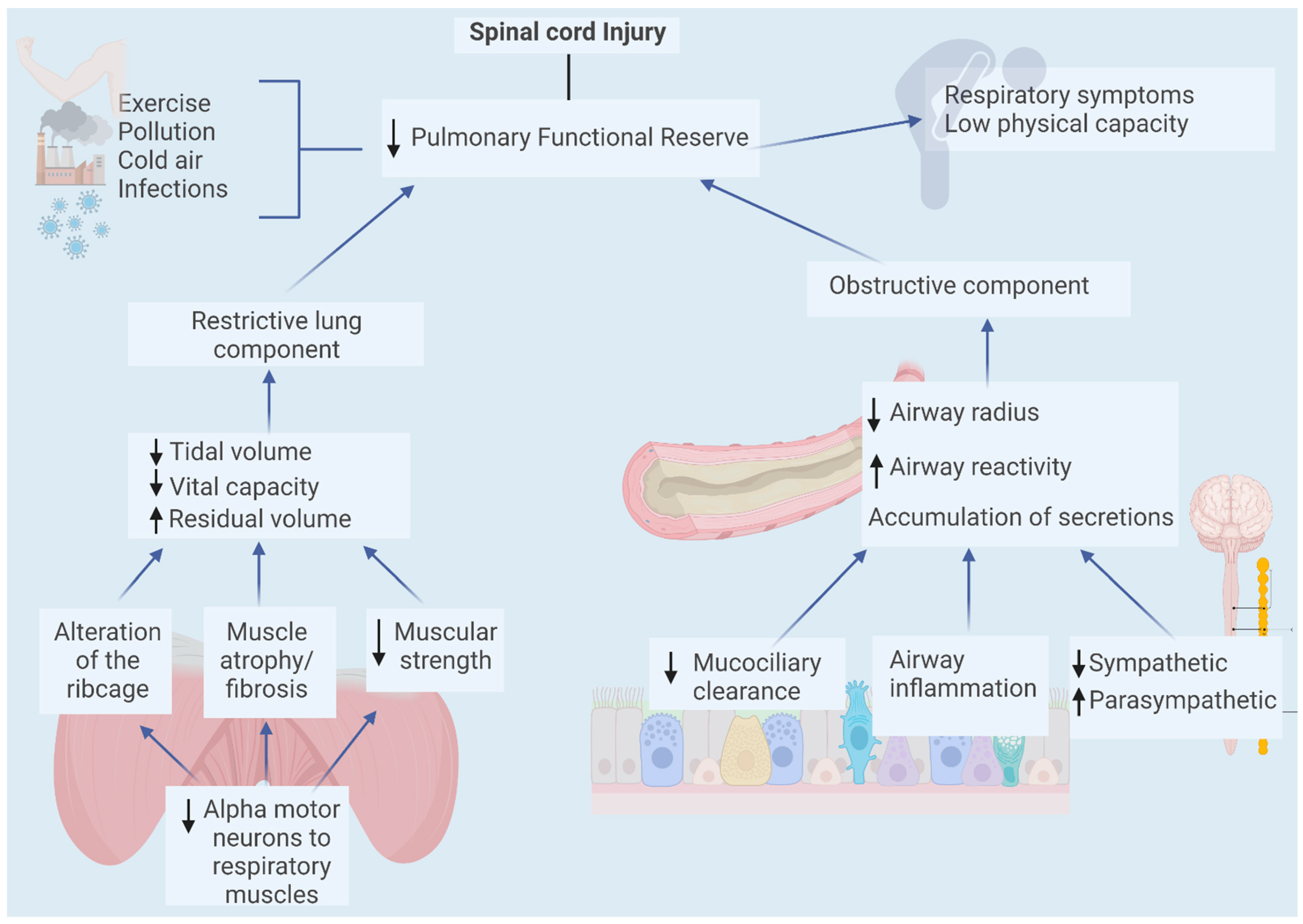
3. Pulmonary Effects of Spinal Cord Injury
4. Cardiorespiratory Response of Spinal Cord Injury Patients to Acute Exercise
5. Systemic Inflammation in Spinal Cord Injury Patients
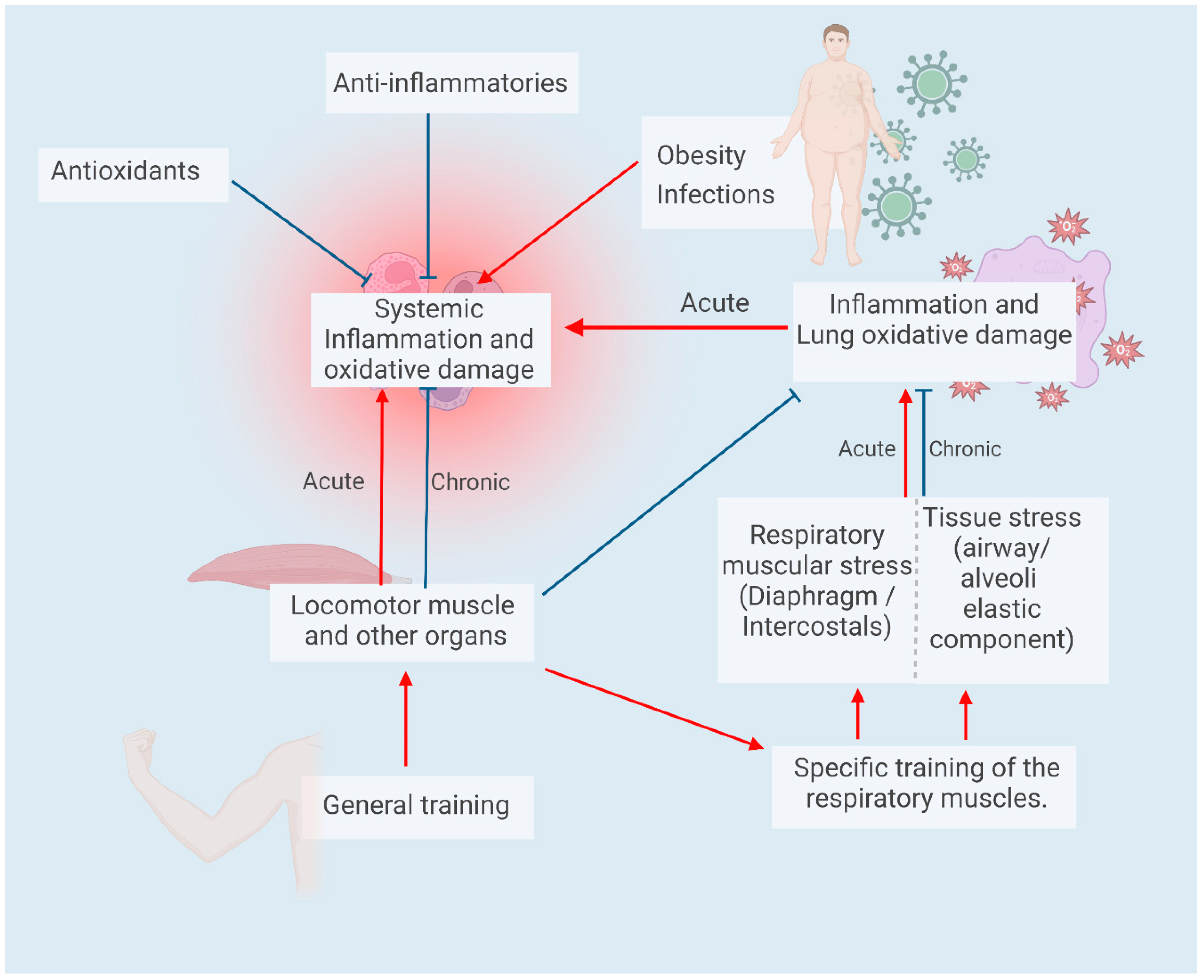
6. Inflammation/Pulmonary Oxidative Damage in Spinal Cord Injuries
7. Inflammation and Oxidative Damage in Acute and Chronic Exercise (Training)
8. Respiratory Muscle Training for Spinal Cord Injury Patients: A Strategy to Improve Lung Function and Physical Performance: Can It Also Diminish Lung Inflammation?
9. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- DeVivo, M.J. Sir Ludwig Guttmann Lecture: Trends in spinal cord injury rehabilitation outcomes from model systems in the United States: 1973–2006. Spinal Cord 2007, 45, 713–721. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Middleton, J.W.; Dayton, A.; Walsh, J.; Rutkowski, S.B.; Leong, G.; Duong, S. Life expectancy after spinal cord injury: A 50-year study. Spinal Cord 2012, 50, 803–811. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Krause, J.S.; Newman, J.C.; Clark, J.M.R.; Dunn, M. The natural course of spinal cord injury: Changes over 40 years among those with exceptional survival. Spinal Cord 2016, 55, 502–508. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kraft, R.; Dorstyn, D. Psychosocial correlates of depression following spinal injury: A systematic review. J. Spinal Cord Med. 2015, 38, 571–583. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chuang, C.-H.; Chen, P.-C.; Bai, C.-H.; Wu, Y.-L.; Tsai, M.-C.; Li, C.-Y. Association between Spinal Cord Injury and Alcohol Dependence: A Population-Based Retrospective Cohort Study. J. Pers. Med. 2022, 12, 473. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lüthi, H.; Geyh, S.; Baumberger, M.E.; Dokladal, P.; Scheuringer, M.; Mäder, M.; Cieza, A. The individual experience of functioning and disability in Switzerland—Patient perspective and person-centeredness in spinal cord injury. Spinal Cord 2011, 49, 1173–1181. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Siddall, P.J.; Middleton, J.W. Spinal cord injury-induced pain: Mechanisms and treatments. Pain Manag. 2015, 5, 493–507. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Courtois, F.; Alexander, M.; McLain, A.B. (. Women’s Sexual Health and Reproductive Function After SCI. Top. Spinal Cord Inj. Rehabil. 2017, 23, 20–30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- West, C.; Bellantoni, A.; Krassioukov, A.V. Cardiovascular Function in Individuals with Incomplete Spinal Cord Injury: A Systematic Review. Top. Spinal Cord Inj. Rehabil. 2013, 19, 267–278. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Smith, D.L.; Yarar-Fisher, C. Contributors to Metabolic Disease Risk Following Spinal Cord Injury. Curr. Phys. Med. Rehabil. Rep. 2016, 4, 190–199. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Farkas, G.J.; Burton, A.M.; McMillan, D.W.; Sneij, A.; Gater, D.R. The Diagnosis and Management of Cardiometabolic Risk and Cardiometabolic Syndrome after Spinal Cord Injury. J. Pers. Med. 2022, 12, 1088. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gibbs, J.C.; Patsakos, E.M.; Maltais, D.B.; Wolfe, D.L.; Gagnon, D.H.; Craven, B.C. Rehabilitation interventions to modify endocrine-metabolic disease risk in individuals with chronic spinal cord injury living in the community (RIISC): A systematic search and review of prospective cohort and case–control studies. J. Spinal Cord Med. 2021, 46, 6–25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- LaVela, S.L.; Burkhart, E.; Jones, K.; Pellegrini, C. Health care provider views on the magnitude of overweight/obesity in spinal cord injury and awareness of evidence-based guidance for weight management. PMR 2021, 15, 20–30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fuller, D.D.; Lee, K.-Z.; Tester, N.J. The impact of spinal cord injury on breathing during sleep. Respir. Physiol. Neurobiol. 2013, 188, 344–354. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schilero, G.J.; Bauman, W.A.; Radulovic, M. Traumatic Spinal Cord Injury. Clin. Chest Med. 2018, 39, 411–425. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Alizadeh, A.; Dyck, S.M.; Karimi-Abdolrezaee, S. Traumatic spinal cord injury: An overview of pathophysiology, models and acute injury mechanisms. Front. Neurol. 2019, 10, 282. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- WHO. Spinal Cord Injury. 2013. Available online: https://www.who.int/news-room/fact-sheets/detail/spinal-cord-injury (accessed on 28 April 2023).
- Wyndaele, M.; Wyndaele, J.J. Incidence, prevalence and epidemiology of spinal cord injury: What learns a worldwide literature survey? Spinal Cord 2006, 44, 523–529. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Burns, A.S.; Marino, R.J.; Flanders, A.E.; Flett, H. Clinical diagnosis and prognosis following spinal cord injury. Handb. Clin. Neurol. 2012, 109, 47–62. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reyes, M.R.L.; Elmo, M.J.; Menachem, B.; Granda, S.M. A Primary Care Provider’s Guide to Managing Respiratory Health in Subacute and Chronic Spinal Cord Injury. Top. Spinal Cord Inj. Rehabil. 2020, 26, 116–122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Raab, A.M.; Mueller, G.; Elsig, S.; Gandevia, S.C.; Zwahlen, M.; Hopman, M.T.E.; Hilfiker, R. Systematic Review of Incidence Studies of Pneumonia in Persons with Spinal Cord Injury. J. Clin. Med. 2021, 11, 211. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Troyer, A.; Heilporn, A. Respiratory mechanics in quadriplegia. The respiratory function of the intercostal muscles. Am. Rev. Respir. Dis. 1980, 122, 569–600. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Estenne, M.; De Troyer, A. The effects of tetraplegia on chest wall statics. Am. Rev. Respir. Dis. 1986, 134, 121–124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Radulovic, M.; Schilero, G.J.; Wecht, J.M.; Weir, J.P.; Spungen, A.M.; Bauman, W.A.; Lesser, M. Airflow Obstruction and Reversibility in Spinal Cord Injury: Evidence for Functional Sympathetic Innervation. Arch. Phys. Med. Rehabil. 2008, 89, 2349–2353. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schilero, G.J.; Hobson, J.C.; Singh, K.; Spungen, A.M.; Bauman, W.A.; Radulovic, M. Bronchodilator effects of ipratropium bromide and albuterol sulfate among subjects with tetraplegia. J. Spinal Cord Med. 2016, 41, 42–47. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Brown, R.; DiMarco, A.F.; Hoit, J.D.; Garshick, E. Respiratory dysfunction and management in spinal cord injury. Respir. Care 2006, 51, 853–870. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Rosales-Antequera, C.; Viscor, G.; Araneda, O.F. Inflammation and Oxidative Stress as Common Mechanisms of Pulmonary, Autonomic and Musculoskeletal Dysfunction after Spinal Cord Injury. Biology 2022, 11, 550. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eerden, S.; Dekker, R.; Hettinga, F.J. Maximal and submaximal aerobic tests for wheelchair-dependent persons with spinal cord injury: A systematic review to summarize and identify useful applications for clinical rehabilitation. Disabil. Rehabil. 2017, 40, 497–521. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shaw, D.; Crawford, M.H.; Karliner, J.S.; DiDonna, G.; Carleton, R.M.; Ross, J.; O’Rourke, R.A. Arm-crank ergometry: A new method for the evaluation of coronary artery disease. Am. J. Cardiol. 1974, 33, 801–805. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gee, C.M.; Currie, K.D.; Phillips, A.A.; Squair, J.W.; Krassioukov, A.V. Spinal Cord Injury Impairs Cardiovascular Capacity in Elite Wheelchair Rugby Athletes. Clin. J. Sport Med. 2017, 30, 33–39. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hopman, M.T.E. Circulatory Responses During Arm Exercise in Individuals with Paraplegia. Int. J. Sports Med. 1994, 15, 126–131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Spengler, C.; Hostettler, S.; Leuthold, L.; Brechbühl, J.; Mueller, G.; Illi, S. Maximal cardiac output during arm exercise in the sitting position after cervical spinal cord injury. J. Rehabil. Med. 2012, 44, 131–136. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vivodtzev, I.; Taylor, J.A. Cardiac, Autonomic, and Cardiometabolic Impact of Exercise Training in Spinal Cord Injury. J. Cardiopulm. Rehabil. Prev. 2021, 41, 6–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Houtman, S.; Oeseburg, B.; Hopman, M.T.E. Blood Volume and Hemoglobin After Spinal Cord Injury. Am. J. Phys. Med. Rehabil. 2000, 79, 260–265. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Phillips, W.T.; Kiratli, B.J.; Sarkarati, M.; Weraarchakul, G.; Myers, J.; Franklin, B.A.; Parkash, I.; Froelicher, V. Effect of spinal cord injury on the heart and cardiovascular fitness. Curr. Probl. Cardiol. 1998, 23, 641–716. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wheeler, G.; Cumming, D.; Burnham, R.; Maclean, I.; Sloley, B.D.; Bhambhani, Y.; Steadward, R.D. Testosterone, cortisol and catecholamine responses to exercise stress and autonomic dysreflexia in elite quadriplegic athletes. Spinal Cord 1994, 32, 292–299. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Webborn, A.D. “Boosting” performance in disability sport. Br. J. Sports Med. 1999, 33, 74–75. [Google Scholar]
- Flett, S.; Garcia, J.; Cowley, K.C. Spinal electrical stimulation to improve sympathetic autonomic functions needed for movement and exercise after spinal cord injury: A scoping clinical review. J. Neurophysiol. 2022, 128, 649–670. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bhambhani, Y. Physiology of wheelchair racing in athletes with spinal cord injury. Sports Med. 2002, 32, 23–51. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Theisen, D. Cardiovascular determinants of exercise capacity in the Paralympic athlete with spinal cord injury. Exp. Physiol. 2012, 97, 319–324. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fugl-Meyer, A.R. Effects of respiratory muscle paralysis in tetraplegic and paraplegic patients. Scand. J. Rehabil. Med. 1971, 3, 141–150. [Google Scholar]
- Bergofsky, E.H. Mechanism for Respiratory Insufficiency After Cervical Cord Injury. Ann. Intern. Med. 1964, 61, 435–447. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gee, C.; Eves, N.; Sheel, A.; West, C. How does cervical spinal cord injury impact the cardiopulmonary response to exercise? Respir. Physiol. Neurobiol. 2021, 293, 103714. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jain, N.B.; Brown, R.; Tun, C.G.; Gagnon, D.; Garshick, E. Determinants of Forced Expiratory Volume in 1 Second (FEV1), Forced Vital Capacity (FVC), and FEV1/FVC in Chronic Spinal Cord Injury. Arch. Phys. Med. Rehabil. 2006, 87, 1327–1333. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hooker, S.P.; Figoni, S.F.; Glaser, R.M.; Rodgers, M.M.; Ezenwa, B.N.; Faghri, P.D. Physiologic responses to prolonged electrically stimulated leg-cycle exercise in the spinal cord injured. Arch. Phys. Med. Rehabil. 1990, 71, 863–869. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Jin, Y.; Song, Y.; Lin, J.; Liu, T.; Li, G.; Lai, B.; Gu, Y.; Chen, G.; Xing, L. Role of inflammation in neurological damage and regeneration following spinal cord injury and its therapeutic implications. Burn. Trauma 2023, 11, tkac054. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Albayar, A.A.; Roche, A.; Swiatkowski, P.; Antar, S.; Ouda, N.; Emara, E.; Smith, D.H.; Ozturk, A.K.; Awad, B.I. Biomarkers in Spinal Cord Injury: Prognostic Insights and Future Potentials. Front. Neurol. 2019, 10, 27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sterner, R.C.; Sterner, R.M. Immune response following traumatic spinal cord injury: Pathophysiology and therapies. Front. Immunol. 2023, 13, 1084101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, H.; Peng, H.; Wang, P.-C.; Zou, T.; Feng, X.-M.; Wan, B.-W. Role of regulatory T cells in spinal cord injury. Eur. J. Med. Res. 2023, 28, 163. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Orr, M.B.; Gensel, J.C. Spinal Cord Injury Scarring and Inflammation: Therapies Targeting Glial and Inflammatory Responses. Neurotherapeutics 2018, 15, 541–553. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Prüss, H.; Kopp, M.A.; Brommer, B.; Gatzemeier, N.; Laginha, I.; Dirnagl, U.; Schwab, J.M. Non-Resolving Aspects of Acute Inflammation after Spinal Cord Injury (SCI): Indices and Resolution Plateau. Brain Pathol. 2011, 21, 652–660. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schwab, J.M.; Zhang, Y.; Kopp, M.A.; Brommer, B.; Popovich, P.G. The paradox of chronic neuroinflammation, systemic immune suppression, autoimmunity after traumatic chronic spinal cord injury. Exp. Neurol. 2014, 258, 121–129. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yates, A.G.; Jogia, T.; Gillespie, E.R.; Couch, Y.; Ruitenberg, M.J.; Anthony, D.C. Acute IL-1RA treatment suppresses the peripheral and central inflammatory response to spinal cord injury. J. Neuroinflamm. 2021, 18, 15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Farkas, G.J.; Gorgey, A.S.; Dolbow, D.R.; Berg, A.S.; Gater, D.R. The influence of level of spinal cord injury on adipose tissue and its relationship to inflammatory adipokines and cardiometabolic profiles. J. Spinal Cord Med. 2017, 41, 407–415. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sun, X.; Jones, Z.B.; Chen, X.-M.; Zhou, L.; So, K.-F.; Ren, Y. Multiple organ dysfunction and systemic inflammation after spinal cord injury: A complex relationship. J. Neuroinflamm. 2016, 13, 260. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Segal, J.L.; Gonzales, E.; Yousefi, S.; Jamshidipour, L.; Brunnemann, S.R. Circulating levels of IL-2R, ICAM-1, and IL-6 in spinal cord injuries. Arch. Phys. Med. Rehabil. 1997, 78, 44–47. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Frost, F.; Roach, M.J.; Kushner, I.; Schreiber, P. Inflammatory C-reactive protein and cytokine levels in asymptomatic people with chronic spinal cord injury. Arch. Phys. Med. Rehabil. 2005, 86, 312–317. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Morse, L.R.; Stolzmann, K.; Nguyen, H.P.; Jain, N.B.; Zayac, C.; Gagnon, D.R.; Tun, C.G.; Garshick, E. Association Between Mobility Mode and C-Reactive Protein Levels in Men with Chronic Spinal Cord Injury. Arch. Phys. Med. Rehabil. 2008, 89, 726–731. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Manns, P.J.; McCubbin, J.A.; Williams, D.P. Fitness, Inflammation, and the Metabolic Syndrome in Men with Paraplegia. Arch. Phys. Med. Rehabil. 2005, 86, 1176–1181. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, T.-D.; Wang, Y.-H.; Huang, T.-S.; Su, T.-C.; Pan, S.-L.; Chen, S.-Y. Circulating Levels of Markers of Inflammation and Endothelial Activation are Increased in Men with Chronic Spinal Cord Injury. J. Formos. Med. Assoc. 2007, 106, 919–928. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schwartz, K.; Henzel, M.K.; Richmond, M.A.; Zindle, J.K.; Seton, J.M.; Lemmer, D.P.; Alvarado, N.; Bogie, K.M. Biomarkers for recurrent pressure injury risk in persons with spinal cord injury. J. Spinal Cord Med. 2019, 43, 696–703. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Park, A.; Anderson, D.; Battaglino, R.A.; Nguyen, N.; Morse, L.R. Ibuprofen use is associated with reduced C-reactive protein and interleukin-6 levels in chronic spinal cord injury. J. Spinal Cord Med. 2020, 45, 117–125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bernardi, M.; Fedullo, A.L.; Bernardi, E.; Munzi, D.; Peluso, I.; Myers, J.; Lista, F.R.; Sciarra, T. Diet in neurogenic bowel management: A viewpoint on spinal cord injury. World J. Gastroenterol. 2020, 26, 2479–2497. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Goldsmith, J.A.; Ennasr, A.N.; Farkas, G.J.; Gater, D.R.; Gorgey, A.S. Role of exercise on visceral adiposity after spinal cord injury: A cardiometabolic risk factor. Eur. J. Appl. Physiol. 2021, 121, 2143–2163. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McMillan, D.W.; Maher, J.L.; Jacobs, K.A.; Nash, M.S.; Gater, D.R. Exercise Interventions Targeting Obesity in Persons with Spinal Cord Injury. Top. Spinal Cord Inj. Rehabil. 2021, 27, 109–120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Santos, L.V.; Pereira, E.T.; Reguera-García, M.M.; de Oliveira, C.E.P.; Moreira, O.C. Resistance Training and Muscle Strength in people with Spinal cord injury: A systematic review and meta-analysis. J. Bodyw. Mov. Ther. 2021, 29, 154–160. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Savikj, M.; Kostovski, E.; Lundell, L.S.; Iversen, P.O.; Massart, J.; Widegren, U. Altered oxidative stress and antioxidant defence in skeletal muscle during the first year following spinal cord injury. Physiol. Rep. 2019, 7, e14218. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Michaeloudes, C.; Abubakar-Waziri, H.; Lakhdar, R.; Raby, K.; Dixey, P.; Adcock, I.M.; Mumby, S.; Bhavsar, P.K.; Chung, K.F. Molecular mechanisms of oxidative stress in asthma. Mol. Asp. Med. 2022, 85, 101026. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cui, X.; Zhang, Y.; Lu, Y.; Xiang, M. ROS and Endoplasmic Reticulum Stress in Pulmonary Disease. Front. Pharmacol. 2022, 13, 879204. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Radulovic, M.; Schilero, G.J.; Wecht, J.M.; La Fountaine, M.; Rosado-Rivera, D.; Bauman, W.A. Exhaled Nitric Oxide Levels Are Elevated in Persons with Tetraplegia and Comparable to that in Mild Asthmatics. Lung 2009, 188, 259–262. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Radulovic, M.; Bauman, W.A.; Wecht, J.M.; LaFountaine, M.; Kahn, N.; Hobson, J.; Singh, K.; Renzi, C.; Yen, C.; Schilero, G.J. Biomarkers of inflammation in persons with chronic tetraplegia. J. Breath Res. 2015, 9, 036001. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Araneda, O.F.; Carbonell, T.; Tuesta, M. Update on the Mechanisms of Pulmonary Inflammation and Oxidative Imbalance Induced by Exercise. Oxidative Med. Cell. Longev. 2016, 2016, 4868536. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kouda, K.; Furusawa, K.; Sugiyama, H.; Sumiya, T.; Ito, T.; Tajima, F.; Shimizu, K. Does 20-min arm crank ergometer exercise increase plasma interleukin-6 in individuals with cervical spinal cord injury? Eur. J. Appl. Physiol. 2011, 112, 597–604. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Umemoto, Y.; Furusawa, K.; Kouda, K.; Sasaki, Y.; Kanno, N.; Kojima, D.; Tajima, F. Plasma IL-6 levels during arm exercise in persons with spinal cord injury. Spinal Cord 2011, 49, 1182–1187. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ogawa, T.; Nakamura, T.; Banno, M.; Sasaki, Y.; Umemoto, Y.; Kouda, K.; Kawasaki, T.; Tajima, F. Elevation of interleukin-6 and attenuation of tumor necrosis factor-α during wheelchair half marathon in athletes with cervical spinal cord injuries. Spinal Cord 2014, 52, 601–605. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Paulson, T.A.; Goosey-Tolfrey, V.L.; Lenton, J.P.; Leicht, C.A.; Bishop, N.C. Spinal Cord Injury Level and the Circulating Cytokine Response to Strenuous Exercise. Med. Sci. Sports Exerc. 2013, 45, 1649–1655. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peake, J.M.; Markworth, J.F.; Nosaka, K.; Raastad, T.; Wadley, G.D.; Coffey, V.G. Modulating exercise-induced hormesis: Does less equal more? J. Appl. Physiol. 2015, 119, 172–189. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tu, W.; Wang, H.; Li, S.; Liu, Q.; Sha, H. The Anti-Inflammatory and Anti-Oxidant Mechanisms of the Keap1/Nrf2/ARE Signaling Pathway in Chronic Diseases. Aging Dis. 2019, 10, 637–651. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Souza, J.; da Silva, R.A.; Scheffer, D.D.L.; Penteado, R.; Solano, A.; Barros, L.; Budde, H.; Trostchansky, A.; Latini, A. Physical-Exercise-Induced Antioxidant Effects on the Brain and Skeletal Muscle. Antioxidants 2022, 11, 826. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Allison, D.J.; Chapman, B.; Wolfe, D.; Sequeira, K.; Hayes, K.; Ditor, D.S. Effects of a Functional Electrical Stimulation–Assisted Cycling Program on Immune and Cardiovascular Health in Persons with Spinal Cord Injury. Top. Spinal Cord Inj. Rehabil. 2016, 22, 71–78. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- van Duijnhoven, N.; Hesse, E.; Janssen, T.; Wodzig, W.; Scheffer, P.; Hopman, M. Impact of exercise training on oxidative stress in individuals with a spinal cord injury. Eur. J. Appl. Physiol. 2010, 109, 1059–1066. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yates, B.A.; Brown, R.; Picard, G.; Taylor, J.A. Improved pulmonary function is associated with reduced inflammation after hybrid whole-body exercise training in persons with spinal cord injury. Exp. Physiol. 2023, 108, 353–360. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hart, J.E.; Morse, L.; Tun, C.G.; Brown, R.; Garshick, E. Cross-sectional associations of pulmonary function with systemic inflammation and oxidative stress in individuals with chronic spinal cord injury. J. Spinal Cord Med. 2015, 39, 344–352. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hart, J.E.; Goldstein, R.; Walia, P.; Teylan, M.; Lazzari, A.; Tun, C.G.; Garshick, E. FEV1 and FVC and systemic inflammation in a spinal cord injury cohort. BMC Pulm. Med. 2017, 17, 113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nas, K. Rehabilitation of spinal cord injuries. World J. Orthop. 2015, 6, 8–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xiang, X.-N.; Zong, H.-Y.; Ou, Y.; Yu, X.; Cheng, H.; Du, C.-P.; He, H.-C. Exoskeleton-assisted walking improves pulmonary function and walking parameters among individuals with spinal cord injury: A randomized controlled pilot study. J. Neuroeng. Rehabil. 2021, 18, 86. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Battikha, M.; Sà, L.; Porter, A.; Taylor, J.A. Relationship Between Pulmonary Function and Exercise Capacity in Individuals with Spinal Cord Injury. Am. J. Phys. Med. Rehabil. 2014, 93, 413–421. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yasar, F.; Tasci, C.; Savci, S.; Tozkoparan, E.; Deniz, O.; Balkan, A.; Bilgic, H. Pulmonary Rehabilitation Using Modified Threshold Inspiratory Muscle Trainer (IMT) in Patients with Tetraplegia. Case Rep. Med. 2012, 2012, 587901. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boswell-Ruys, C.L.; Lewis, C.R.H.; Wijeysuriya, N.S.; McBain, R.A.; Lee, B.B.; McKenzie, D.K.; Gandevia, S.C.; Butler, J.E. Impact of respiratory muscle training on respiratory muscle strength, respiratory function and quality of life in individuals with tetraplegia: A randomised clinical trial. Thorax 2020, 75, 279–288. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, C.-Y.; Lee, J.-S.; Kim, H.-D.; Lee, D.-J. Short-term effects of respiratory muscle training combined with the abdominal drawing-in maneuver on the decreased pulmonary function of individuals with chronic spinal cord injury: A pilot randomized controlled trial. J. Spinal Cord Med. 2016, 40, 17–25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shin, J.C.; Han, E.Y.; Cho, K.H.; Im, S.H. Improvement in Pulmonary Function with Short-term Rehabilitation Treatment in Spinal Cord Injury Patients. Sci. Rep. 2019, 9, 17091. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Postma, K.; Bussmann, J.; Haisma, J.; van der Woude, L.; Bergen, M.; Stam, H. Predicting respiratory infection one year after inpatient rehabilitation with pulmonary function measured at discharge in persons with spinal cord injury. J. Rehabil. Med. 2009, 41, 729–733. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fabero-Garrido, R.; del Corral, T.; Angulo-Díaz-Parreño, S.; Plaza-Manzano, G.; Martín-Casas, P.; Cleland, J.A.; Fernández-De-Las-Peñas, C.; López-De-Uralde-Villanueva, I. Respiratory muscle training improves exercise tolerance and respiratory muscle function/structure post-stroke at short term: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Ann. Phys. Rehabil. Med. 2021, 65, 101596. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dar, J.A.; Mujaddadi, A.; Moiz, J.A. Effects of inspiratory muscle training in patients with obstructive sleep apnoea syndrome: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Sleep Sci. 2022, 15, 480–489. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fernández-Lázaro, D.; Corchete, L.A.; García, J.F.; Donoso, D.J.; Lantarón-Caeiro, E.; Mielgo, R.C.; Mielgo-Ayuso, J.; Gallego-Gallego, D.; Seco-Calvo, J. Effects on Respiratory Pressures, Spirometry Biomarkers, and Sports Performance after Inspiratory Muscle Training in a Physically Active Population by Powerbreath®: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. Biology 2022, 12, 56. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McCaughey, E.; Butler, J.; McBain, R.; Boswell-Ruys, C.; Hudson, A.; Gandevia, S.; Lee, B. Abdominal Functional Electrical Stimulation to Augment Respiratory Function in Spinal Cord Injury. Top. Spinal Cord Inj. Rehabil. 2019, 25, 105–111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Butler, J.; Lim, J.; Gorman, R.B.; Boswell-Ruys, C.; Saboisky, J.; Lee, B.; Gandevia, S.C. Posterolateral Surface Electrical Stimulation of Abdominal Expiratory Muscles to Enhance Cough in Spinal Cord Injury. Neurorehabili. Neural Repair 2010, 25, 158–167. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Koppers, R.J.; Vos, P.J.; Folgering, H.T. Tube breathing as a new potential method to perform respiratory muscle training: Safety in healthy volunteers. Respir. Med. 2006, 100, 714–720. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Szczepan, S.; Michalik, K.; Borkowski, J.; Zatoń, K. Effects of Swimming with Added Respiratory Dead Space on Cardiorespiratory Fitness and Lipid Metabolism. J. Sports Sci. Med. 2020, 19, 95–101. [Google Scholar]
- Danek, N.; Michalik, K.; Smolarek, M.; Zatoń, M. Acute Effects of Using Added Respiratory Dead Space Volume in a Cycling Sprint Interval Exercise Protocol: A Cross-Over Study. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2020, 17, 9485. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gross, D.; Ladd, H.; Riley, E.; Macklem, P.; Grassino, A. The effect of training on strength and endurance of the diaphragm in quadriplegia. Am. J. Med. 1980, 68, 27–35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Uijl, S.G.; Houtman, S.; Folgering, H.T.; Hopman, M.T.E. Training of the respiratory muscles in individuals with tetraplegia. Spinal Cord 1999, 37, 575–579. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Soumyashree, S.; Kaur, J. Effect of inspiratory muscle training (IMT) on aerobic capacity, respiratory muscle strength and rate of perceived exertion in paraplegics. J. Spinal Cord Med. 2018, 43, 53–59. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- West, C.R.; Taylor, B.J.; Campbell, I.G.; Romer, L.M. Effects of inspiratory muscle training on exercise responses in Paralympic athletes with cervical spinal cord injury. Scand. J. Med. Sci. Sports 2013, 24, 764–772. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Litchke, L.G.; Russian, C.J.; Lloyd, L.K.; Schmidt, E.A.; Price, L.; Walker, J.L. Effects of Respiratory Resistance Training with a Concurrent Flow Device on Wheelchair Athletes. J. Spinal Cord Med. 2008, 31, 65–71. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gee, C.M.; Williams, A.M.; Sheel, A.W.; Eves, N.D.; West, C.R. Respiratory muscle training in athletes with cervical spinal cord injury: Effects on cardiopulmonary function and exercise capacity. J. Physiol. 2019, 597, 3673–3685. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Denguezli, M.; Ben Chiekh, I.; Ben Saad, H.; Zaouali-Ajina, M.; Tabka, Z.; Zbidi, A. One-year endurance training: Effects on lung function and airway inflammation. J. Sports Sci. 2008, 26, 1351–1359. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Araneda, O.F.; Urbina-Stagno, R.; Tuesta, M.; Haichelis, D.; Alvear, M.; Salazar, M.P.; García, C. Increase of pro-oxidants with no evidence of lipid peroxidation in exhaled breath condensate after a 10-km race in non-athletes. J. Physiol. Biochem. 2013, 70, 107–115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Araneda, O.F.; Guevara, A.J.; Contreras, C.; Lagos, N.; Berral, F.J. Exhaled Breath Condensate Analysis after Long Distance Races. Int. J. Sports Med. 2012, 33, 955–961. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Araneda, O.F.; Rosales-Antequera, C.; Contreras-Briceño, F.; Tuesta, M.; Rossi-Serrano, R.; Magalhães, J.; Viscor, G. Systemic and Pulmonary Inflammation/Oxidative Damage: Implications of General and Respiratory Muscle Training in Chronic Spinal-Cord-Injured Patients. Biology 2023, 12, 828. https://doi.org/10.3390/biology12060828
Araneda OF, Rosales-Antequera C, Contreras-Briceño F, Tuesta M, Rossi-Serrano R, Magalhães J, Viscor G. Systemic and Pulmonary Inflammation/Oxidative Damage: Implications of General and Respiratory Muscle Training in Chronic Spinal-Cord-Injured Patients. Biology. 2023; 12(6):828. https://doi.org/10.3390/biology12060828
Chicago/Turabian StyleAraneda, Oscar F., Cristián Rosales-Antequera, Felipe Contreras-Briceño, Marcelo Tuesta, Rafael Rossi-Serrano, José Magalhães, and Ginés Viscor. 2023. "Systemic and Pulmonary Inflammation/Oxidative Damage: Implications of General and Respiratory Muscle Training in Chronic Spinal-Cord-Injured Patients" Biology 12, no. 6: 828. https://doi.org/10.3390/biology12060828
APA StyleAraneda, O. F., Rosales-Antequera, C., Contreras-Briceño, F., Tuesta, M., Rossi-Serrano, R., Magalhães, J., & Viscor, G. (2023). Systemic and Pulmonary Inflammation/Oxidative Damage: Implications of General and Respiratory Muscle Training in Chronic Spinal-Cord-Injured Patients. Biology, 12(6), 828. https://doi.org/10.3390/biology12060828








