A New Cell Line Derived from the Caudal Fin of the Dwarf Gourami (Trichogaster lalius) and Its Susceptibility to Fish Viruses
Abstract
Simple Summary
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Primary Culture and Subculture of Dwarf Gourami Fin Cells
2.2. Cell Growth Optimization
2.3. Chromosome Analysis
2.4. Species Confirmation of DGF Cells
2.5. Transfection of GFP Vector
2.6. Propagation of Viruses
2.6.1. Virus Susceptibility and Viral Multiplication
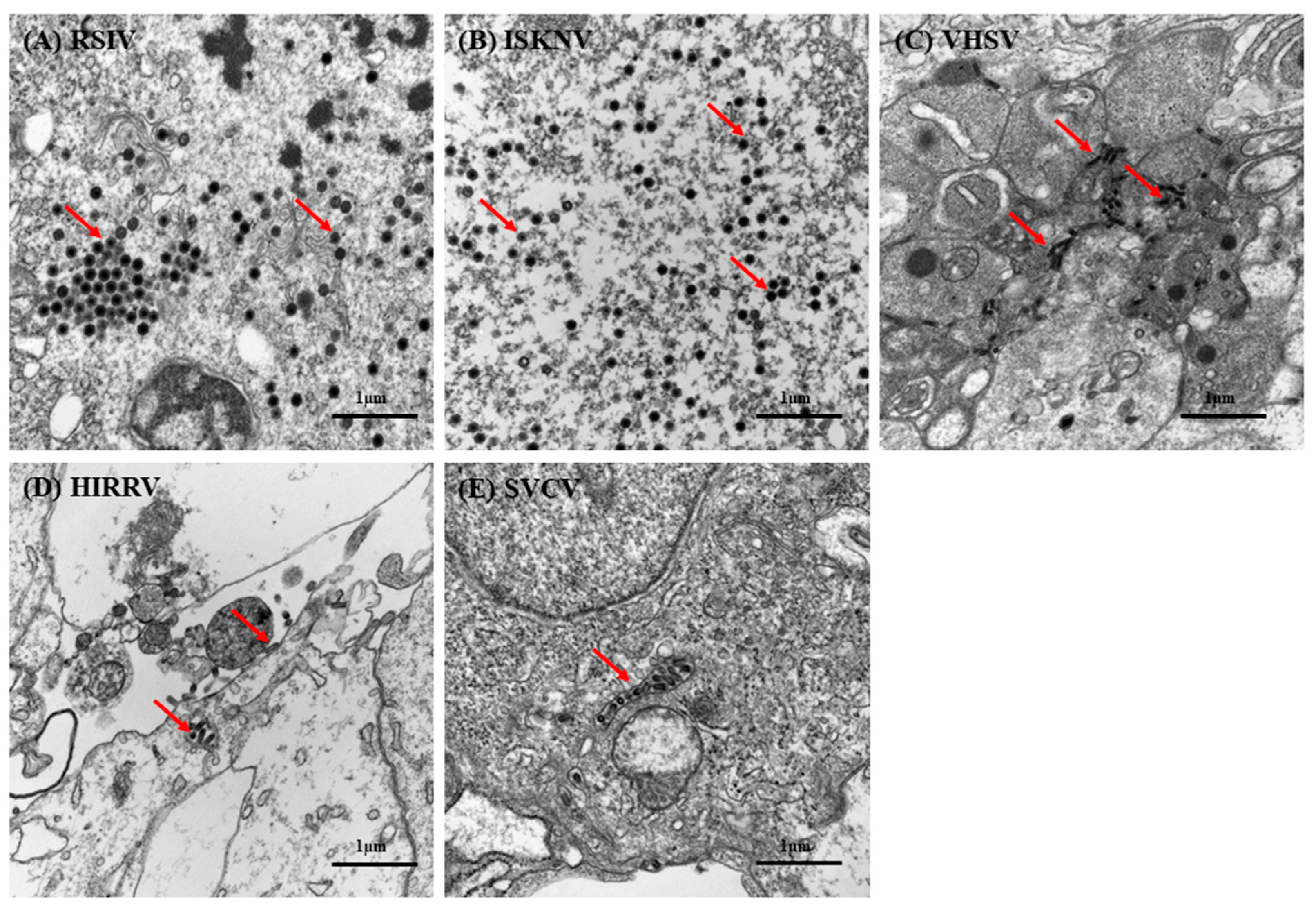
2.6.2. Transmission Electron Microscopy
2.7. Characteristics of RSIV and ISKNV Replication in DGF Cells
2.7.1. Extracellular Virus Propagated in DGF Cells
2.7.2. Comparison of DGF and Other Cell Lines for Megalocytivirus Propagation
2.7.3. Viral Gene Expression
3. Results
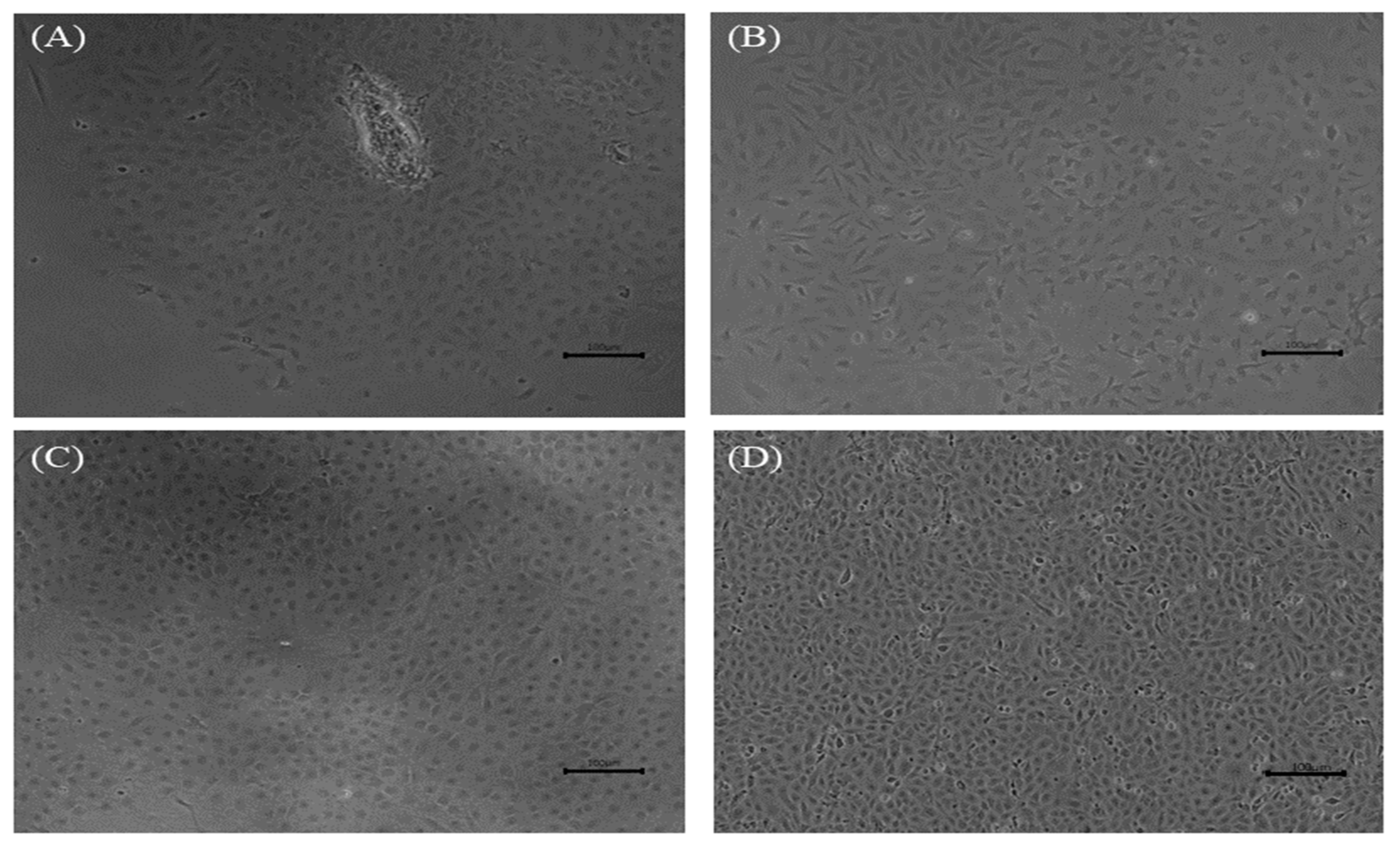
3.1. Development of DGF Cells
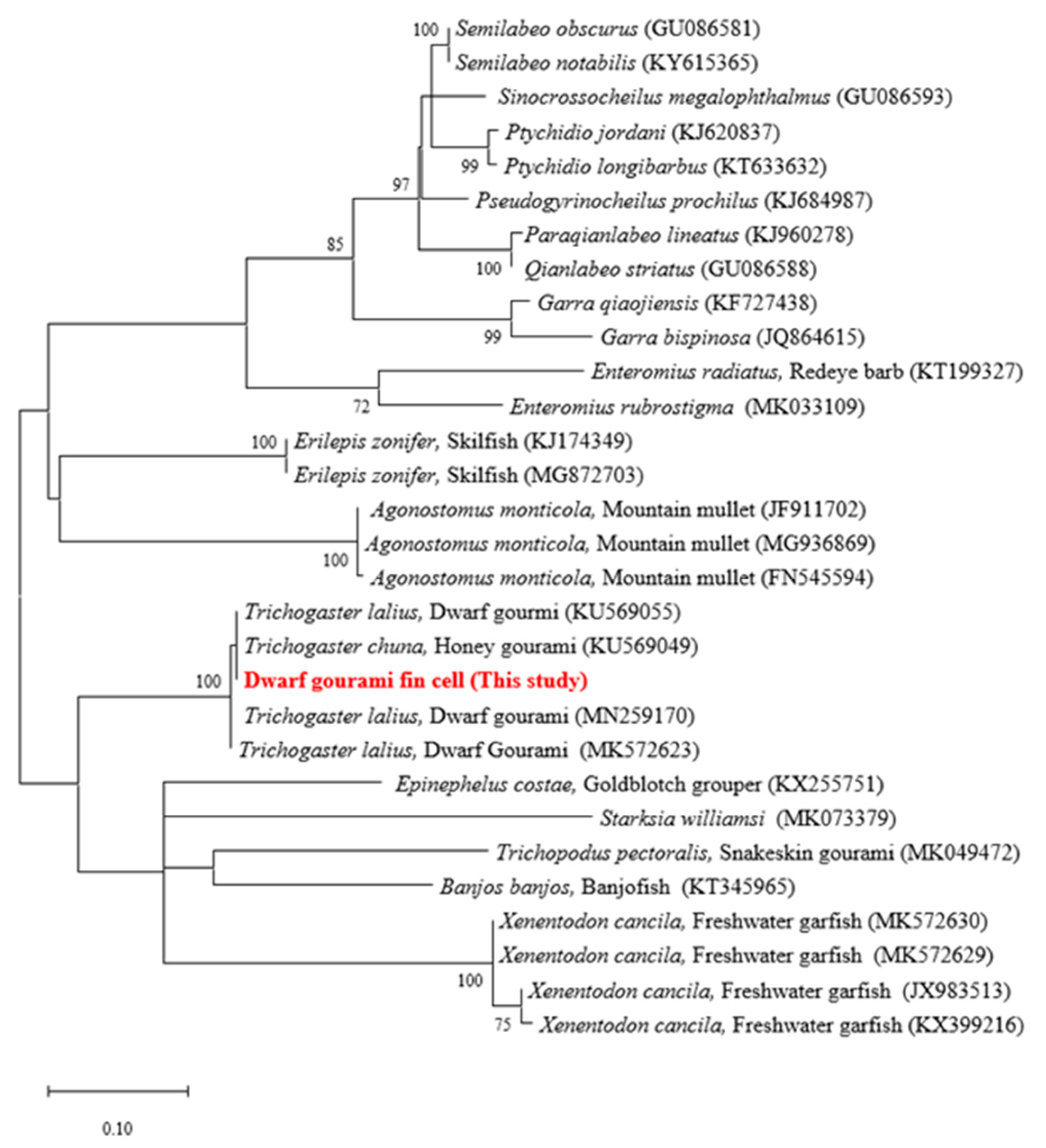
3.2. Species Confirmation of DGF Cells
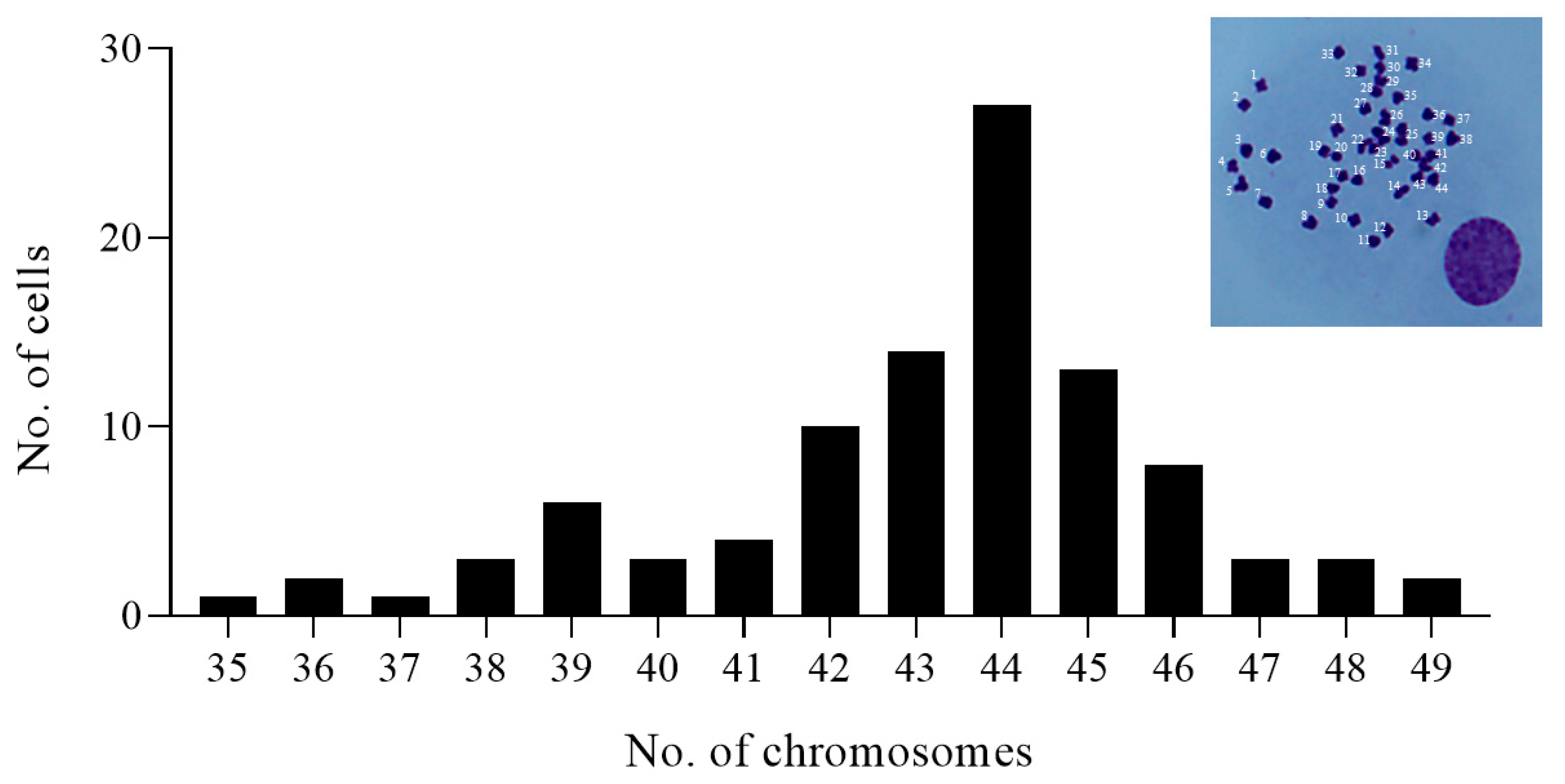
3.3. Chromosome Number
3.4. Growth Characteristics of DGF Cells
3.5. DGF Cell Transfection
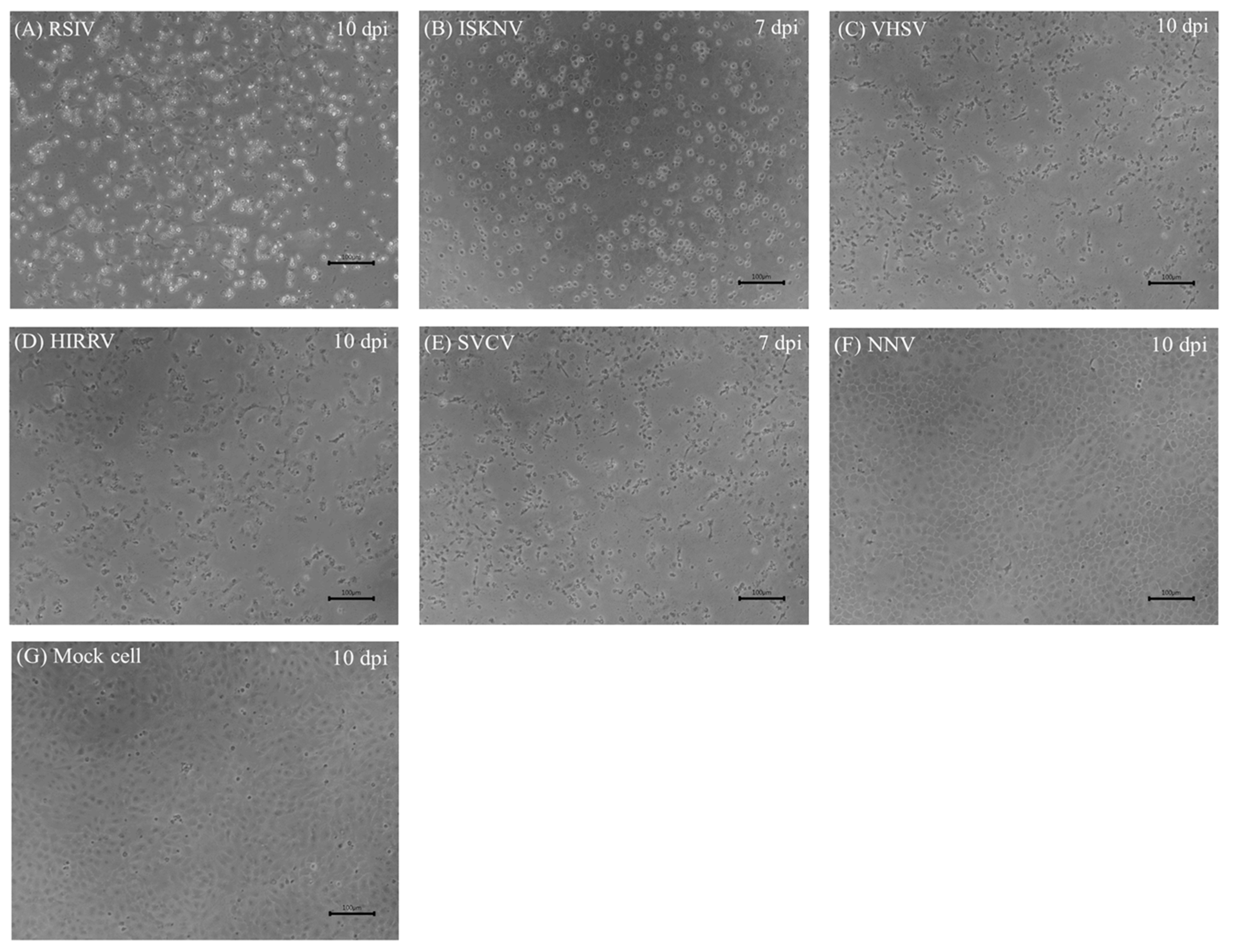
3.6. Virus Susceptibility
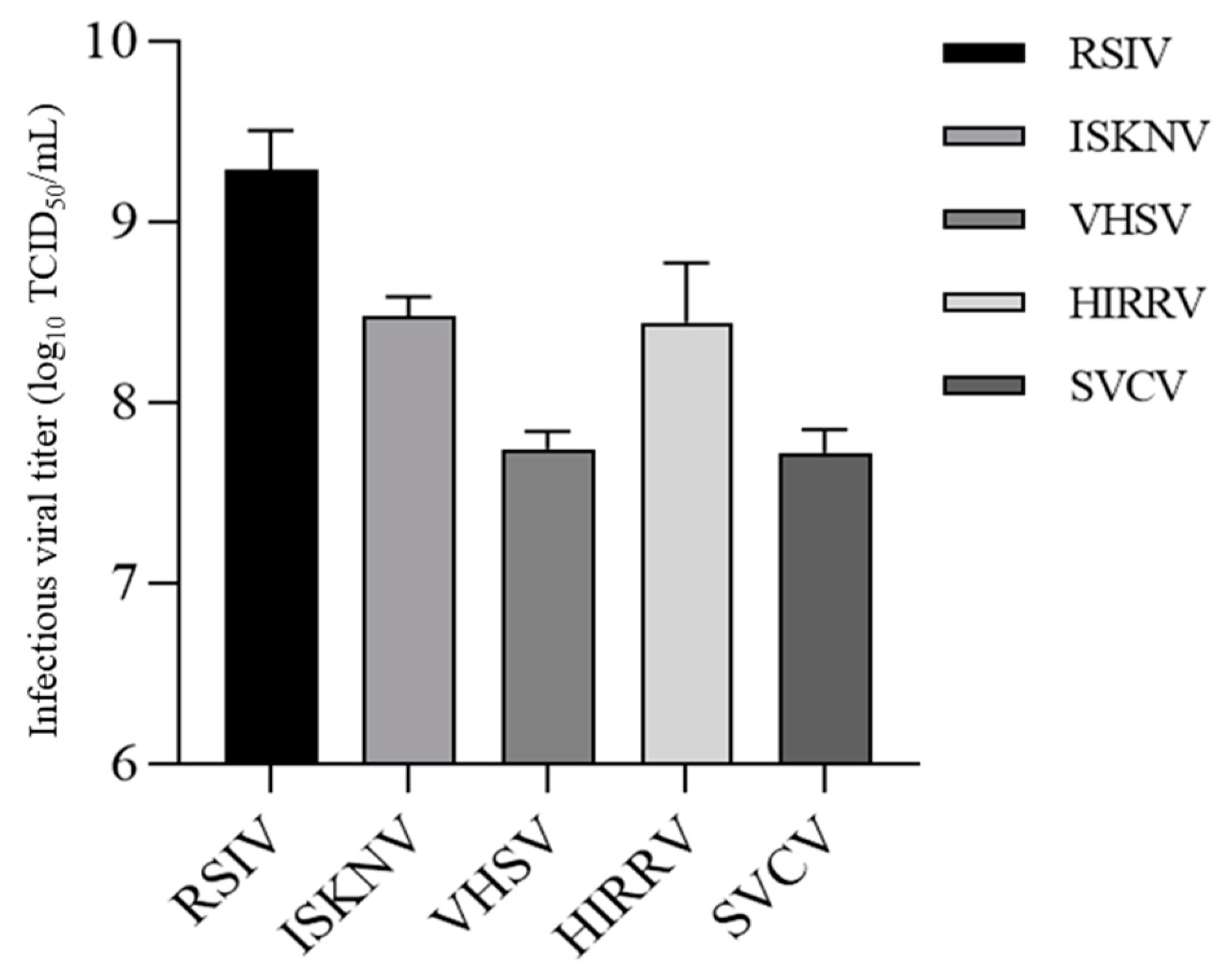
3.7. Viral Multiplication
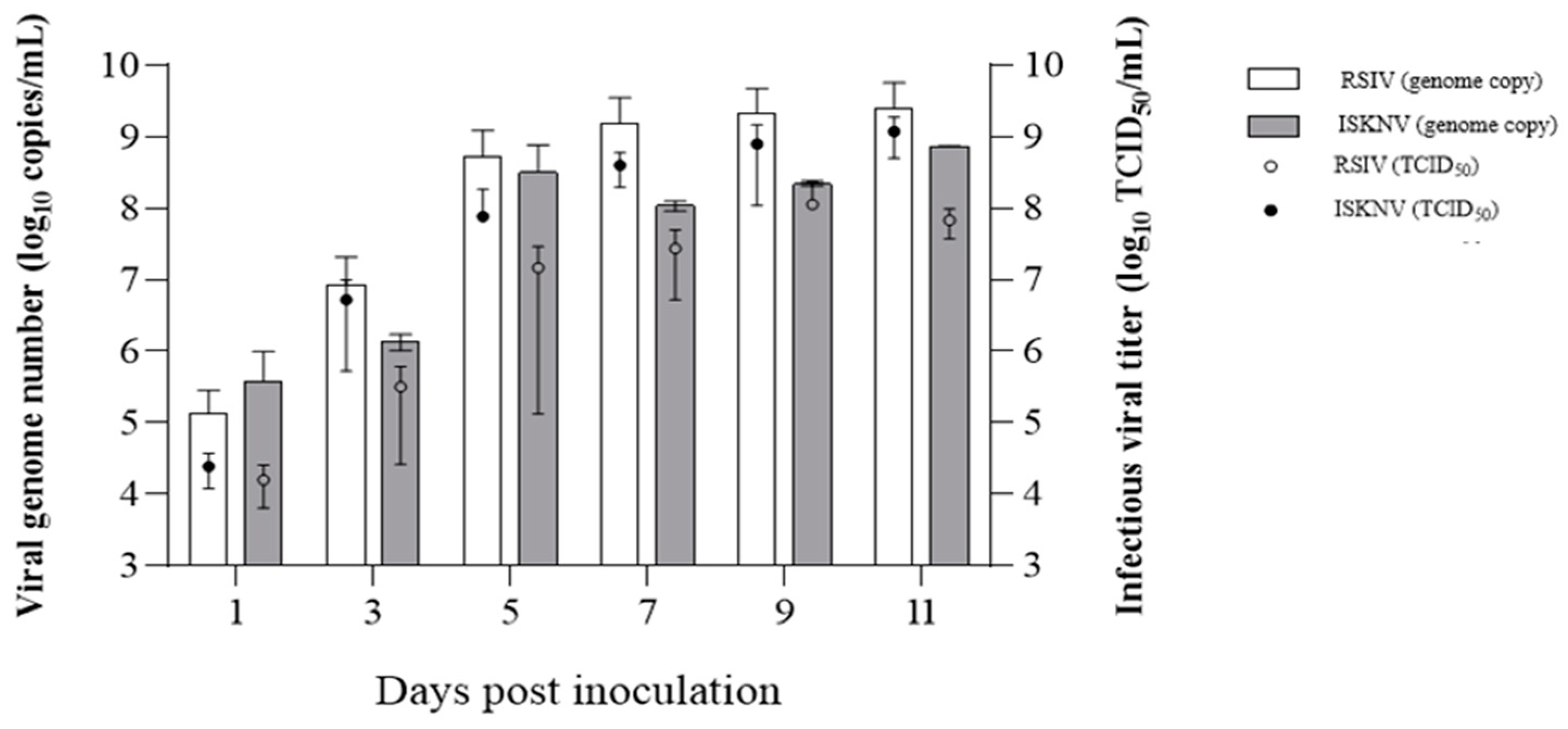
3.8. Propagation of RSIV and ISKNV
3.9. Comparison of DGF and Other Cell Lines for RSIV and ISKNV Propagation
3.10. Viral Gene Expression
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Olivier, K. World trade in ornamental species. In Marine Ornamental Species–Collection, Culture & Conservation; Wiley: Hoboken, NJ, USA, 2003; pp. 49–63. [Google Scholar]
- Raja, K.; Aanand, P.; Padmavathy, S.; Sampathkumar, J.S. Present and future market trends of Indian ornamental fish sector. Int. J. Fish. Aquat. Stud. 2019, 7, 6–15. [Google Scholar]
- Johan, C.A.C.; Zainathan, S.C. Megalocytiviruses in ornamental fish: A review. Vet. World 2020, 13, 2565. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- de Groof, A.; Guelen, L.; Deijs, M.; van der Wal, Y.; Miyata, M.; Ng, K.S.; van Grinsven, L.; Simmelink, B.; Biermann, Y.; Grisez, L.; et al. A Novel Virus Causes Scale Drop Disease in Lates calcarifer. PLoS Pathog. 2015, 11, e1005074. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- WOAH (World Organization for Animal Health). Manual of Diagnostic Tests for Aquatic Animal. Chapter 2.3.7. Red Sea Bream Iridoviral Disease. Available online: https://www.oie.int/fileadmin/Home/eng/Health_standards/aahm/current/2.3.07_RSIVD.pdf (accessed on 13 March 2023).
- Go, J.; Lancaster, M.; Deece, K.; Dhungyel, O.; Whittington, R. The molecular epidemiology of iridovirus in Murray cod (Mac-cullochella peelii peelii) and dwarf gourami (Colisa lalia) from distant biogeographical regions suggests a link between trade in ornamental fish and emerging iridoviral diseases. Mol. Cell. 2016, 20, 212–222. [Google Scholar]
- Jeong, J.B.; Kim, H.Y.; Jun, L.J.; Lyu, J.H.; Park, N.G.; Kim, J.K.; Do Jeong, H. Outbreaks and risks of infectious spleen and kidney necrosis virus disease in freshwater ornamental fishes. Dis. Aquat. Org. 2008, 78, 209–215. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rimmer, A.E.; Becker, J.A.; Tweedie, A.; Lintermans, M.; Landos, M.; Stephens, F.; Whittington, R.J. Detection of dwarf gourami iridovirus (Infectious spleen and kidney necrosis virus) in populations of ornamental fish prior to and after importation into Australia, with the first evidence of infection in domestically farmed Platy (Xiphophorus maculatus). Prev. Vet. Med. 2015, 122, 181–194. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hood, Y.; Sadler, J.; Poldy, J.; Starkey, C.S.; Robinson, A.P. Biosecurity system reforms and the development of a risk-based surveillance and pathway analysis system for ornamental fish imported into Australia. Prev. Vet. Med. 2019, 167, 159–168. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Thangaraj, R.S.; Narendrakumar, L.; Prasannan Geetha, P.; Shanmuganathan, A.R.; Dharmaratnam, A.; Nithianantham, S.R. Comprehensive update on inventory of finfish cell lines developed during the last decade (2010–2020). Rev. Aquac. 2021, 13, 2248–2288. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dong, C.; Weng, S.; Shi, X.; Xu, X.; Shi, N.; He, J. Development of a mandarin fish Siniperca chuatsi fry cell line suitable for the study of infectious spleen and kidney necrosis virus (ISKNV). Virus Res. 2008, 135, 273–281. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Imajoh, M.; Sugiura, H.; Oshima, S.I. Morphological changes contribute to apoptotic cell death and are affected by caspase-3 and caspase-6 inhibitors during red sea bream iridovirus permissive replication. Virology 2004, 322, 220–230. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ku, C.C.; Lu, C.H.; Wang, C.S. Establishment and characterization of a fibroblast cell line derived from the dorsal fin of red sea bream, Pagrus major (Temminck & Schlegel). J. Fish Dis. 2010, 33, 187–196. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Oh, S.Y.; Nishizawa, T. Establishment of rock bream Oplegnathus fasciatus embryo (RoBE-4) cells with cytolytic infection of red seabream iridovirus (RSIV). J. Virol. Methods 2016, 238, 1–5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kawato, Y.; Yamashita, H.; Yuasa, K.; Miwa, S.; Nakajima, K. Development of a highly permissive cell line from spotted knifejaw (Oplegnathus punctatus) for red sea bream iridovirus. Aquaculture 2017, 473, 291–298. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yeh, S.W.; Cheng, Y.H.; Nan, F.N.; Wen, C.M. Characterization and virus susceptibility of a continuous cell line derived from the brain of Aequidens rivulatus (Günther). J. Fish Dis. 2018, 41, 635–641. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gardenia, L.; Sukenda, S.; Junior, M.Z.; Lusiastuti, A.; Alimuddin, A. Development of primary cell culture from spleen of giant gourami Osphronemus goramy for propagation of giant gourami iridovirus (GGIV). J. Fish Dis. 2020, 43, 829–838. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kwon, W.J.; Yoon, M.J.; Jin, J.W.; Kim, K.I.; Kim, Y.C.; Hong, S.; Jeong, J.B.; Do Jeong, H. Development and characterization of megalocytivirus persistently-infected cell cultures for high yield of virus. Tissue Cell 2020, 66, 101387. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kurita, J.; Nakajima, K.; Hirono, I.; Aoki, T. Polymerase chain reaction (PCR) amplification of DNA of red sea bream iridovirus (RSIV). Fish Pathol. 1998, 33, 17–23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, G.H.; Kim, M.J.; Choi, H.J.; Koo, M.J.; Kim, M.J.; Min, J.G.; Kim, K.I. Evaluation of a novel TaqMan probe-based real-time PCR assay for detection and quantitation of red sea bream iridovirus. Fish. Aquat. Sci. 2021, 24, 351–359. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dalla Valle, L.; Zanella, L.; Patarnello, P.; Paolucci, L.; Belvedere, P.; Colombo, L. Development of a sensitive diagnostic assay for fish nervous necrosis virus based on RT-PCR plus nested PCR. J. Fish Dis. 2000, 23, 321–327. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, H.J.; Cuenca, A.; Olesen, N.J. Validation of a novel one-step reverse transcription polymerase chain reaction method for detecting viral haemorrhagic septicaemia virus. Aquaculture 2018, 492, 170–183. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cho, M.Y.; Lee, D.C.; Kim, J.W.; Cha, S.J.; Park, S.H.; Park, M. Monitoring of diseases in wild marine fish stocks collected in June 2006 by a trawl in the Southern Korean waters. J. Fish Dis. 2006, 19, 215–225. [Google Scholar]
- Stone, D.M.; Ahne, W.; Denham, K.L.; Dixon, P.F.; Liu, C.Y.; Sheppard, A.M.; Tayloar, G.R.; Way, K. Nucleotide sequence analysis of the glycoprotein gene of putative spring viraemia of carp virus and pike fry rhabdovirus isolates reveals four genogroups. Dis. Aquat. Org. 2003, 53, 203–210. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jeong, M.A.; Jeong, Y.J.; Kim, K.I. Complete genome sequences and pathogenicity analysis of two red sea bream iridoviruses isolated from cultured fish in Korea. Fishes 2021, 6, 82. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, K.I.; Kwon, W.J.; Kim, Y.C.; Kim, M.S.; Hong, S.; Do Jeong, H. Surveillance of aquatic animal viruses in seawater and shellfish in Korea. Aquaculture 2016, 461, 17–24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Byun, J.H. Detected SVCV in Carp and Its Culturing Characteristics in New Cell Lines. Master’s Thesis, Pukyong National University, Busan, Republic of Korea, 27 February 2015. [Google Scholar]
- Jeong, Y.J.; Kim, Y.C.; Min, J.G.; Jeong, M.A.; Kim, K.I. Characterization of rock bream (Oplegnathus fasciatus) fin cells and its susceptibility to different genotypes of megalocytiviruses. Fish Pathol. 2021, 34, 149–159. [Google Scholar]
- Jin, J.W.; Kim, Y.K.; Hong, S.; Kim, Y.C.; Kwon, W.J.; Jeong, H.D. Identification and characterization of Megalocytivirus type 3 infection with low mortality in starry flounder, Platichthys stellatus, in Korea. J. World Aquac. Soc. 2018, 49, 229–239. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Supiwong, W.; Tanomtong, A.; Kenthao, A.; Seetapan, K.; Kaewsri, S.; Sanoamuang, L.O. Standardized karyotype of the three-spot gourami, Trichogaster trichopterus (Perciformes, Belontidae) from Thailand by conventional and Ag-NOR staining technique. Nucleus 2010, 53, 103–107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, Y.; Ren, Y.; Zhang, Y.; Wang, G.; He, Z.; Liu, Y.; Cao, W.; Wang, Y.; Chen, S.; Fu, Y.; et al. A New Cell Line Derived from the Spleen of the Japanese Flounder (Paralichthys olivaceus) and Its Application in Viral Study. Biology 2022, 11, 1697. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kang, M.S.; Oh, M.J.; Kim, Y.J.; Kawai, K.; Jung, S.J. Establishment and characterization of two new cell lines derived from flounder, Paralichthys olivaceus (Temminck & Schlegel). J. Fish Dis. 2003, 26, 657–665. [Google Scholar]
- Sun, Z.; Ren, Y.; Zhang, Y.; Yang, Y.; Wang, G.; He, Z.; Liu, Y.; Cao, W.; Wang, F.; Fu, Y.; et al. Establishment and characterization of a cell line from the brain of the Japanese flounder (Paralichthys olivaceus) and its application in the study of viral infection. Aquaculture 2023, 562, 738825. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lakra, W.S.; Swaminathan, T.R.; Joy, K.P. Development, characterization, conservation and storage of fish cell lines: A review. Fish Physiol. Biochem. 2011, 37, 1–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rastogi, A.; Yadav, M.K.; Joaquin, M.P.C.; Verma, D.K.; Swaminathan, T.R.; Kushwaha, B.; Paria, A.; Pradhan, P.K.; Sood, N. Development of cell lines from brain, spleen and heart of ornamental blood parrot cichlid and their susceptibility to Tilapia ti-lapinevirus. Aquaculture 2022, 561, 738711. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kibenge, F.S.; Godoy, M.G. (Eds.) Aquaculture Virology; Academic Press: Cambridge, MA, USA, 2016. [Google Scholar]
- Ito, T.; Yoshiura, Y.; Kamaishi, T.; Yoshida, K.; Nakajima, K. Prevalence of red sea bream iridovirus among organs of Japanese amberjack (Seriola quinqueradiata) exposed to cultured red sea bream iridovirus. J. Gen. Virol. 2013, 94, 2094–2101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kurita, J.; Nakajima, K. Megalocytiviruses. Viruses 2012, 4, 521–538. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jung, M.H.; Nikapitiya, C.; Jung, S.J. DNA vaccine encoding myristoylated membrane protein (MMP) of rock bream iridovirus (RBIV) induces protective immunity in rock bream (Oplegnathus fasciatus). Vaccine 2018, 36, 802–810. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]




| Target Virus | Object | Primers | Sequence | Reference |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Megalocytiviruses a (RSIV and ISKNV) | Detection | 1-F | CTCAAACACTCTGGCTCATC | [19] |
| 1-R | GCACCAACACATCTCCTATC | |||
| Detection and quantification | RSIV 1094F | CCAGCATGCCTGAGATGGA | [20] | |
| RSIV 1221R | GTCCGACACCTTACATGACAGG | |||
| RSIV 1177 Probe | FAM-TACGGCCGCCTGTCCAACG-BHQ1 | |||
| NNV b | Detection | VNN1 | ACACTGGAGTTTGAAATTCA | [21] |
| VNN2 | GTCTTGTTGAAGTTGTCCCA | |||
| VHSV c | Detection | VHSV 3F | GGGACAGGAATGACCATGAT | [22] |
| VHSV 2R | TCTGTCACCTTGATCCCCTCCAG | |||
| HIRRV d | Detection | HRV-F | ACCCTGGGATTCCTTGATTC | [23] |
| HRV-R | TCTGGTGGGCACGATAAGTT | |||
| SVCV e | Detection | SVCV F1 | TCTTGGAGCCAAATAGCTCARRTC | [24] |
| SVCV R2 | AGATGGTATGGACCCCAATACATHACNCAY |
| Target Gene | Primer Name | Primer Sequence (5′ to 3′) | Condition | Product Size (bp) | Reference |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| MCP | qM1F | GGCGACTACCTCATTAATGT | 95 °C, 10 min (95 °C, 10 s, 60 °C, 1 min) × 40 cycles | 141 | [29] |
| qM1R | CCACCAGGTCGTTAAATGA | ||||
| ATPase | qATPase1F | AACAAGCCAGACATGTGTG | 95 °C, 10 min, (95 °C, 15 sec, 60 °C, 1 min) × 40 cycles | 165 | In this study |
| qATPase1R | TGTAGTAGCGCACCATGTC | ||||
| Polymerase | qPoly1F | GTTTATGGCGGGGGCAAT | 136 | ||
| qPoly1R | TGGCCCAGCTGTATGTAGC | ||||
| Ring finger protein | qRFP1F | TGTGCAGAGTGCCGTTCAA | 161 | ||
| qRFP1R | TGTGTGCCTGTACACACAGT | ||||
| Myristoylated membrane protein | qMyristmem1F | TGCGGGACTGGGAGTTG | 146 | ||
| qMyristmem1R | TGCCATAAAAGGCGGCC | ||||
| β-actin | qDwBactin_F | TAGCCACGCTCTGTCAGGAT | 152 | ||
| qDwBactin_R | ACCACCGGTATTGTCATGGA |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Jeong, Y.-J.; Kim, K.-I. A New Cell Line Derived from the Caudal Fin of the Dwarf Gourami (Trichogaster lalius) and Its Susceptibility to Fish Viruses. Biology 2023, 12, 829. https://doi.org/10.3390/biology12060829
Jeong Y-J, Kim K-I. A New Cell Line Derived from the Caudal Fin of the Dwarf Gourami (Trichogaster lalius) and Its Susceptibility to Fish Viruses. Biology. 2023; 12(6):829. https://doi.org/10.3390/biology12060829
Chicago/Turabian StyleJeong, Ye-Jin, and Kwang-Il Kim. 2023. "A New Cell Line Derived from the Caudal Fin of the Dwarf Gourami (Trichogaster lalius) and Its Susceptibility to Fish Viruses" Biology 12, no. 6: 829. https://doi.org/10.3390/biology12060829
APA StyleJeong, Y.-J., & Kim, K.-I. (2023). A New Cell Line Derived from the Caudal Fin of the Dwarf Gourami (Trichogaster lalius) and Its Susceptibility to Fish Viruses. Biology, 12(6), 829. https://doi.org/10.3390/biology12060829





