Abstract
Silver nanoparticles (AgNPs) are used for their powerful antibacterial effect and their ability to adhere to surfaces due to their size; they are used in different areas of life, mainly in the area of health as medicine. More recently, in dentistry, the synthesis and characterization of AgNPs attracted significant attention due to their antibacterial properties. In this study, the AgNPs were synthesized using the most effective method on different orthodontic brackets (metallic and esthetic) and characterized by scanning electron microscopy/energy-dispersive spectroscopy (SEM/EDS) and transmission electron microscopy (TEM). Their antimicrobial effect was tested against the widely used standard human pathogens Staphylococcus aureus (Gram-negative) and Escherichia coli (Gram-positive). Our results showed that, via a simple chemical method, AgNPs can be synthesized on the surface of orthodontic brackets with good antimicrobial activity and the possibility of reducing dental decay, periodontal disease and white spots generated during orthodontic treatment.
1. Introduction
The oral microbiota has an environment that provides the proliferation of bacteria capable of producing acids, which demineralize the surfaces of tooth enamel [1]. Biofilm has a crucial role in the adhesion of these microorganisms to the dental surface in such a way that the demineralization of the enamel originates with the organic acid production of microorganisms. Streptococcus mutans is classified as the most cariogenic bacteria [1,2].
The presence of fixed orthodontic appliances, specifically brackets, bands, archwires and ties, makes dental brushing difficult and generates suitable conditions for dental biofilm accumulation and the colonization of cariogenic microorganisms, increasing the risk of enamel demineralization mainly around the brackets [3].
These acids produced by the bacteria when in contact with the surface of the tooth, if left for enough time with nutrients and an adequate environment, generate the demineralization of the enamel and the development of white spot lesions (WSL), which are considered as the first sign of caries. These lesions are characterized by their opacity, mineral loss and a decrease in fluorescence radiance when compared to healthy enamel surfaces due to an optical phenomenon cause by mineral loss in the surface that alters the refractive index, resulting in an opaque white appearance [4].
WSLs represent a major complication in patients with fixed orthodontic treatments, and their development can occur rapidly. Studies by O’Reilly et al. and Øgaard et al. showed that their development was clinically visible in patients in the first month after the placement of fixed appliances [4,5], coinciding with the study of Gorelick et al., in which the incidence ranged from 12.6% to 50% [6,7,8].
Many methods can prevent the development of these lesions and periodontal problems during orthodontics: modifying dietary habits, adequate oral hygiene and the application of topical fluoride. However, these methods rely on patient compliance, which is not reliable. Prevention of the metabolic activity of biofilm, forming fluorapatite crystals, and stimulating remineralization with fluoride-release agents are some potential methods of controlling caries. Currently, there are several forms of fluoride products (systemic forms, gels, varnishes, toothpaste and mouth-rinses) [9].
However, these products are not enough because they require the patient’s cooperation; therefore, nanotechnology was applied to improve dental materials with better properties and anti-caries potential. The decrease in biofilm accumulation is due to the great potential of nanomaterials to inhibit the demineralization process and caries-related bacteria [10]. In this sense, silver nanoparticles were synthesized and incorporated into several biomaterials.
The use of specific nanoparticles (NPs) as antimicrobial agents attracted much attention in medicine and dentistry, including Ag, Au, Ir, Pd and Pt NPs. Nanoparticles are considered as insoluble particles smaller than 100 nm in size [9]. In recent years, Ag nanoparticles were widely used due to their high cytotoxicity in a broad range of microbial and fungal species, including strains resistant to antibiotics [11,12], as well as their low toxicity in humans [13,14,15].
Several methodologies were used to synthesize silver nanoparticles (AgNPs), and they showed potent antimicrobial properties [16]. Many methods were used for the synthesis of silver nanoparticles, ranging from physical solid-state treatments (including milling, grinding and mechanical alloying techniques) [17] to gas-phase synthesis (high-temperature evaporation) [18], laser ablation [19], pyrolysis [20], plasma synthesis and liquid-phase synthesis [21]. The latter includes a variety of methods such as coprecipitation, microemulsifying, microwave irradiation, solvothermal treatments and sol-gel synthesis [22].
The nanostructured metal compounds have a high surface-to-volume ratio; it is also possible to control the size, resulting in the absence of agglomeration, thereby obtaining better properties. All these factors provide better contact with microorganisms and an increased ability to anchor them. AgNPs show efficient antimicrobial properties compared to other metallic NPs, due to their size range of 1–10 nm, and they show the highest biocidal activity against bacteria [23].
Silver has an exceptional chemical affinity for sulfhydryl groups (–SH); this causes amino acids such as cysteine present in the membranes of microorganism (MOs) to react or form a formal bond, causing the membrane to collapse, thereby causing structural changes and their death. These nanoparticles, due to their small nature, can penetrate the membrane more easily and, thus, damage the deoxyribonucleic acid (DNA) and avoid duplication [23].
The formation of free radicals by the AgNPs may be considered another mechanism via which cells die. Various studies in which electron spin resonance spectroscopy was used suggested that free radicals form when the NPs come into contact with the bacteria; these radicals can damage the cell membrane, rendering it porous, which can ultimately lead to death [24,25,26].
These studies showed that silver nanoparticles can bind directly with the cell membrane of bacteria, before damaging or altering their functionality [27,28]. This interaction may cause a series of events that interfere with the microbial processes [23,24,25,26,27,28,29]. In the oral cavity, the antibacterial properties of NPs are used through two broad mechanisms, namely, combining dental materials with NPs or coating surfaces with NPs to prevent microbial adhesion, with the overall aim of reducing biofilm formation and, subsequently, the generation of white spot lesions [11,12,13,14].
Silver compounds and NPs were already used as dental restorative materials, endodontic retrofill cement, dental implants and caries inhibitory solutions with good results; however, despite their demonstrated effectiveness, it is necessary to incorporate them into many materials in dental practice [30].
In orthodontics, the fixed orthodontic appliances act as biofilm retention sites and increase caries lesions, compromising the treatment. To reduce their incidence, fluoridated resins were proposed [4]. However, fluoridated resins showed no success in reducing the decalcification process. The development of orthodontic adhesives with antibacterial properties is necessary to decrease S. mutans adhesion at the bracket-enamel interface and to reduce demineralization at susceptible sites through various compounds such as ionic, chlorhexidine gluconate, silver nanoparticles, zinc oxide and nanoparticles of titanium dioxide. Nevertheless, the discoloration of the teeth that led to an unsightly appearance was reported for most of them [31].
When adding NPs to conventional orthodontic adhesives and appliances, the critical issue is that the physical and chemical properties should not be affected adversely, leading to less than ideal clinical performance. Furthermore, the antimicrobial and antiadhesive properties, as well as the safety of the new nanoadhesives, must be ensured over a clinically relevant time span [26,32].
The above issues are the motivation for this study, which proposes a new alternative to prevent or decrease the development of white spot lesions by adding AgNPs onto the surface of orthodontic brackets, since they represent the site where there is a greater accumulation of oral biofilm.
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Orthodontic Brackets
The orthodontic brackets can be of metal or ceramic composition, and they are attached directly to the tooth. They serve to support the active element, which is the arc correcting dental malocclusions. These, in turn, can be divided into different materials of manufacture. In the present research, we wanted to consider the two types of materials with which brackets are made (ceramic and metal materials), and evaluate the adhesion of silver nanoparticles onto both surfaces. We wanted to determine if the two types of materials were able to anchor a sufficient amount of silver nanoparticles such that they had an antibacterial effect, where the choice depends on economic and esthetic reasons by the patient.
A total of 50 commercial orthodontic bicuspid brackets (0.018 inch) with a mean base area calculated at 14.1 mm2 and a standard shape were employed (n = 10 per group), classified into 5 groups of orthodontic brackets of different materials as follows: GI InVu Roth Ceramic bracket (TP Orthodontics, LaPorte, IN, USA), GII System Alexander LTS Stainless steel bracket (American Orthodontics (AO) Sheboygan, WI, USA), GIII Gemini Roth Stainless steel bracket (3M Unitek, Corporation Monrovia, CA, USA), GIV Nu-Edge Roth Cr-Co bracket (TP Orthodontics, LaPorte, IN, USA) and GV Radiance plus Roth Sapphire bracket (American Orthodontics (AO) Sheboygan, WI, USA).
2.2. Preparation of Samples and In Situ AgNP Synthesis
In this research, the salt used was silver nitrate (AgNO3; Sigma-Aldrich, Saint Louis, MO, USA). The silver nanoparticles were synthesized with the method proposed by Bala, since in that study, the effectiveness of the aggregation of the silver nanoparticles was tested [33].
Firstly, all brackets were ultrasonically cleaned for one minute to remove impurities. Samples were allowed to dry for 12 h; they were placed in bags for sterilization and autoclaved at 121 °C, 15 psi for 15 min, and the silver nanoparticles were synthesized in situ using the method previously mentioned.
The orthodontic brackets were placed in a 10−2 M solution of oleic acid with methanol, which was stirred at 500 rpm until the total evaporation of methanol. Then, an aqueous solution of AgNO3 in a concentration of 10−2 M was added to the alumina bracket, and left in the solution for 24 h. The reduction was achieved by adding an aqueous solution of 0.04% M NaBH4, allowing it to react for 30 min. Finally, the bracket was washed with deionized water to remove any excess reagents, and dried in an oven at 100 °C for 1 h [33].
2.3. Characterization
2.3.1. Scanning Electron Microscopy and X-Ray Energy-Dispersive Spectroscopy (SEM/EDS)
The distribution and the elemental analysis of the impregnated brackets with AgNPs were evaluated by scanning electron microscopy. Each sample was placed on carbon-coated conductive tape and observed under an SEM microscope (JEOL, JSM-6510LV at 20 kV, Tokyo, Japan) with secondary electrons at 100×, 500× and 2500× magnification, operating at 20 kV. Chemical analysis was achieved by means of energy dispersion (EDS; Oxford Abingdon, UK), with a resolution of 137 eV.
2.3.2. Transmission Electron Microscopy (TEM)
Micrographs were obtained using a transmission electron microscope JEOL JEM-2100 (Tokyo, Japan) at 200 keV with LaB6 filament, with a resolution of 0.23 nm point to point and 0.14 nm line to line. The acquisition of the micrographs was carried out digitally through a Gatan charge-coupled device (CCD) camera (Pleasanton, CA, USA), model SC200.
TEM was employed to characterize the size, shape, and morphology of the synthesized AgNPs. The prepare the brackets for TEM, they were sonicated for 4 h to detach the nanoparticles from the brackets; then, a drop of the suspension was carefully placed on a copper grid (300 mesh) coated with carbon film and left to dry in ambient air.
2.3.3. Evaluation of the Antimicrobial Effect
The bacterial strains used in this study were obtained from the stock culture collection of the Microbiology Laboratory of the School of Dentistry, National Autonomous University of Mexico (UNAM, Mexico). The tests on antimicrobial activity were carried out as prescribed by the Institute of Clinical and Laboratory Standards [34].
These strains included Gram-positive and Gram-negative bacteria commonly used as standards. The antimicrobial activity of the synthesized NPs was tested against the human pathogenic bacteria Staphylococcus aureus and Escherichia coli following the Kirby–Bauer disc diffusion method against the Gram-positive and Gram-negative microorganisms and yeast [35]. The inoculations were prepared by diluting the colonies with 0.9% NaCl to 0.5 according to the McFarland scale [36], before they were applied to Muller–Hinton agar plates using sterile cotton swabs. The brackets impregnated with AgNPs were placed in each box, placing a non-impregnated bracket in the center as a positive control. After 48 h of incubation at 37 °C, the microbial susceptibility was determined by the zones of inhibition. The assays were performed in triplicate [37].
The inhibition of the antibacterial halos generated on the agar plates was measured using reflected light over the agar plate. The measured distances were rounded to the nearest millimeter with the use of the ImageJ software program (version 1.47e, National Institutes of Health, Bethesda, MD, USA). The program was calibrated using a known distance; each determination was repeated using a known distance, and each determination was repeated three times.
3. Results
3.1. Characterization of Orthodontic Brackets
3.1.1. SEM/EDS
In the micrographs made using SEM (Figure 1), the material composition of each orthodontic bracket was determined. The analysis was performed with the SEM/EDS technique, via which the anchorage on the surface of the bracket was checked. The presence of silver was confirmed using this method of synthesis, obtaining a higher concentration [33].
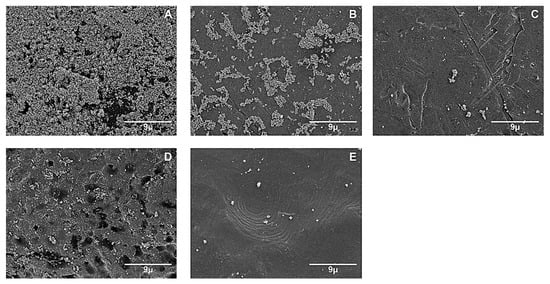
Figure 1.
Representative micrographs from the SEM of orthodontic brackets with silver nanoparticles via the method proposed in [33] (2500× magnification): (A) GI, (B) GII, (C) GIII, (D) GIV, (E) GV. For bracket names, please refer to Section 2.1.
The characterization technique was consistent with the elemental chemical mapping analysis of the nanoparticle suspension, showing absorption peaks at approximately 3 kV. Figure 2 shows the white points on the surface. The chemical mapping allowed seeing the distribution of the different elements that made up of bracket, as well as the silver which adhered to the surface (Figure 2).
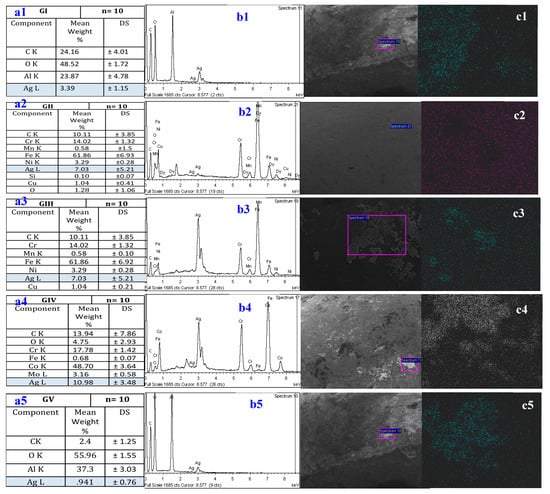
Figure 2.
(a1–a5) Mean and standard deviation by group: GI, GII, GIII, GIV and GV; (b1–b5) representative spectrum from the chemical composition of the silver nanoparticles obtained by energy-dispersive spectroscopy (EDS); (c1–c5) mapping analysis based on SEM of the silver nanoparticles on the brackets synthesized via the method proposed in [33].
3.1.2. Transmission Electron Microscopy (TEM)
In the micrographs, high-resolution transmission electron microscopy (HRTEM) showed AgNPs of 4.44 nm, representative of the average size obtained via the synthesis method described above. This corresponded to 4.69 nm in which we could observe the interplanar distance of 0.241 nm, corresponding to the (111) plane according to JCPDS-04-0783; the shape of the AgNPs tended to be spherical (Figure 3).
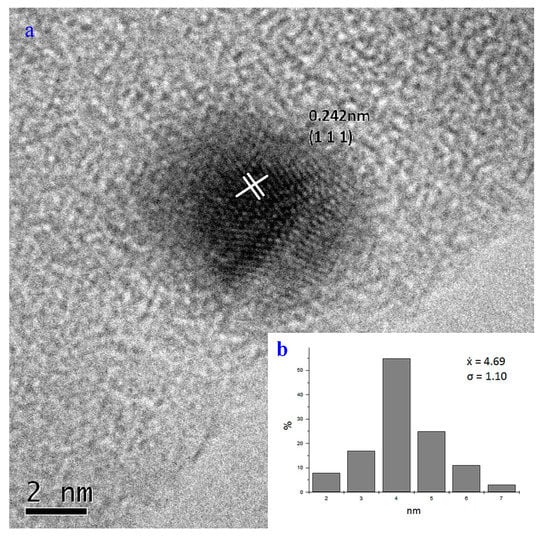
Figure 3.
(a) High-resolution TEM (HRTEM) micrograph, where it can be observed that the synthesized silver nanoparticles (AgNPs) obtained a spherical shape with an interplanar distance of 0.242 nm, corresponding to plane (111). (b) The frequency histogram reports that the average size reached was 4.69 nm with a standard deviation of ±1.10.
3.2. Evaluation of the Antimicrobial Effect
The brackets impregnated with silver nanoparticles (experimental group) were tested against Gram-positive and Gram-negative microorganisms, presenting similar zones of inhibition in all cultures. The brackets without impregnation of silver nanoparticles (control group) showed no in vitro antimicrobial effect with Staphylococcus aureus and Escherichia coli (Figure 4).
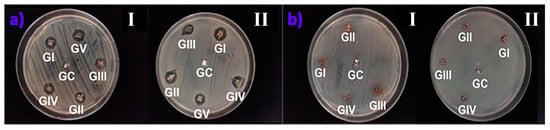
Figure 4.
(a) Representative images of brackets without AgNPs (control group) and (b) brackets with AgNPs (experimental group) when evaluated in vitro with strains of Staphylococcus aureus (I) and Escherichia coli (II).
The inhibitory halos obtained by the in vitro evaluation of the antibacterial effect, in terms of brackets with silver nanoparticles with Staphylococcus aureus and Escherichia coli, showed an excellent inhibition of microbial growth compared to the bracket control, with a diameter between 9 and 10 mm (averaged with program Image J), as shown in Table 1.

Table 1.
Results of disc diffusion test against Staphylococcus aureus and Escherichia coli in contact with silver nanoparticles (AgNPs) (mean and standard deviation). For bracket names, please refer to Section 2.1.
4. Discussion
Orthodontic brackets are attachments that are placed in the dental organs for the correction of dental malocclusions. They are fixed attachments that are in direct contact with the surface of the tooth enamel and, due to several factors such as their intricate design, the duration of the treatment, and the dental hygiene of the patient, a greater accumulation of biofilm occurs, increasing the levels of acidogenic bacteria, most notably S. mutans and Lactobacilli. These bacteria are able to lower the pH of the biofilm in orthodontic patients to a greater degree than in patients without orthodontics. Therefore, the progression of caries is faster. WSLs can become evident mainly around the brackets within one month of installation. Topical applications of sodium fluoride in rinses and varnishes, as well as the strengthening of brushing technique, are not enough to reduce the high prevalence of these lesions; this phenomenon resulted in research aimed at discovering new alternative methods. Thus, silver nanoparticles were pinpointed due to their ability to inhibit bacterial growth in aqueous and solid media as they attach to the surface of the bracket due to their large surface-to-volume ratio and their high reactivity [38].
Silver is recognized for its antimicrobial activity against Gram-positive/negative bacteria, fungi, protozoa, some viruses and antibiotic-resistant strains, as well as cariogenic Streptococcus mutans. The inhibitory effect of silver was previously determined against Gram-positive and Gram-negative cells [39,40]. DNA molecules become condensed and lose their replication ability due to a reaction following the denaturation effect of silver ions. Furthermore, silver ions interact with the thiol groups in proteins, which induces the inactivation of the bacterial proteins [41].
Several studies reported the antimicrobial effects of AgNPs on orthodontic materials, specifically orthodontic adhesives [42]. For example, Ahn et al. [43] examined the impact of adding different concentrations of silver NPs to an experimental composite adhesive containing silica nanofillers. Based on this study, the addition of silver NPs significantly reduced the adhesion of cariogenic Streptococci to orthodontic adhesives relative to conventional adhesives, without compromising physical properties (shear bond strength). Similarly, Poosti et al. [44] demonstrated that incorporating TiO2 NPs (1% w/w) into an orthodontic adhesive enhanced its antibacterial effects without compromising the physical properties.
However, the incorporation of silver nanoparticles into orthodontic brackets was not studied to know the most effective method for in situ AgNP synthesis, in addition to evaluating its antimicrobial effect against the main Gram-positive and Gram-negative strains. This gap in the literature was the reason for carrying out the present investigation.
It is important to consider the pH and reducing agent concentration used for the synthesis of the obtained NPs. The NP synthesis method is crucial to get desirable properties, such as the antibacterial activity [44]. The final size depends on the supersaturation, the fraction of metal atoms involved in the nucleation step relative to the total amount of metal in the system, and the degree of aggregation. If this process of the aggregation mechanism is prevented, an increase in size will occur via incorporation of the remaining metallic species in the solution, and the final particles will remain in the nanosize range [38].
The particle surface change arises from the adsorption of sodium borohydride, which provides repulsive electrostatic forces among the particles and prevents them from clumping together [30].
In the chemical reduction method, an additional component called a stabilizer is introduced into the reaction medium to improve the stability of the particles on the nanometer scale. The function of the stabilizer is to interact with the surface atoms and, thus, to decrease the interaction between NPs, preventing precipitation. The stabilizers are sulfur-containing compounds; surfactants and organic compounds containing polar functional groups are regularly used. Regularly, the reducing agent or its oxidation products act as stabilizers. The surfaces of NPs are covered with a layer of adsorbed components from the environment, and the composition and structure of this layer directly influence the average particle size [45]. The layer size is important; a thick layer hinders the antimicrobial capacity of the NPs and vice versa.
Silver nanoparticles maintain adhesion to the bracket surface due to the strong electrostatic bonds (van der Waals forces) achieved via anchorage with oleic acid, eliminating the possibility of detachment, resulting in selectivity for ceramic or esthetic materials. Therefore, AgNPs remain anchored for most of the time due to the strong electrostatic attraction between the electron pairs of the oxygen and the positive charge of the silver nanoparticles [30].
The results of the coaggregation of silver nanoparticles via the method proposed by Bala revealed, in most groups, a homogeneous source on the surface of the supports, as seen in the SEM and in the EDS analysis, where only GI and GII showed differences in homogeneity. This may be due to the fact that the brackets are of different material and design, respectively; however, the antimicrobial effect was high, obtaining halos of inhibition from 9 to 10 mm on average in all the groups evaluated with the strains of S. aureus and E. coli, while also decreasing the colony count of all bacterial species [33].
This research revealed that AgNPs are an effective method due to their high antimicrobial potential when analyzed with Gram-positive and Gram-negative strains, and they can be used due to their low toxicity in human tissues in low concentrations, since previous studies reported that low levels are sufficient to obtain the bactericidal effect [11,45]. However, it is necessary to perform further studies in microorganisms specific to dental caries such as S. mutans and S. sobrinus, as well as carry out more in vivo investigations in patients treated orthodontically for verification with all conditions of the oral environment [46].
The AgNPs are firmly attached to the bracket as previously mentioned, due to the electrostatic bonds which makes it difficult to detach them. To achieve detachment, it is necessary to sonicate them for 4 h in ultrasound, which is beyond the energy introduced when brushing, which should also be demonstrated in later studies [47].
In the same way, the AgNPs are unable to detach the archwire in the bracket; this will only occur to a very small degree at very specific points if the friction is very intense (slot). The only function of the slot is to support the arc of the wire, and we are more interested in AgNPs covering the external part of the bracket, which is the area where there is a greater accumulation of dentobacterial plaque and which causes the lesion of white spots around the bracket [48].
5. Conclusions
The method developed by Bala allowed observing the effective synthesis of AgNPs on the surface of orthodontic brackets; stable and well-defined halos were observed in the microbiological tests via direct contact with both Gram-positive and Gram-negative strains.
According to our study, the synthesis of AgNPs using the method previously mentioned proved to have great potential for the development of various medical and dental products.
The orthodontic brackets with AgNPs can effectively reduce the incidence and prevalence of white spot lesions due to their antibacterial effect; however, it is necessary to carry out further in vivo research in patients treated orthodontically.
Author Contributions
Experimentation, I.J.-R.; Supervision, U.V.-E. and R.J.S.-V.; Formal analysis, E.L.-C.; Review and edition of methodology, microbiology and project administration, V.H.T.-R.; Funding acquisition, R.L.-C.; Conceptualization, R.A.M.-L.
Funding
This research received no external funding.
Acknowledgments
The authors would like to thank María Citlalit Martínez Soto for technical support.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
References
- Babaahmady, K.G.; Challacombe, S.J.; Marsh, P.D.; Newman, H.N. Ecological study of Streptococcus mutans, Streptococcus sobrinus and Lactobacillus at subsites from approximal dental plaque from children. Caries Res. 1998, 32, 51–58. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hamada, S.; Slade, H.D. Biology, immunology, and cariogenicity of Streptococcus mutans. Microbiol. Rev. 1980, 44, 331–384. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Gonzalez-Perez, J.C.; Scougall-Vilchis, R.J.; Contreras-Bulnes, R.; De La Rosa-Gómez, I.; Uematsu, S.; Yamaguchi, R. Adherence of Streptococcus mutans to orthodontic band cements. Aust. Dent. J. 2012, 57, 464–469. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- O’Reilly, M.M.; Featherstone, J.D. Demineralization and remineralization around orthodontic appliances: An in vivo study. Am. J. Orthod. Dentofac. Orthop. 1987, 92, 33–40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Øgaard, B. White spot lesions during orthodontic treatment: Mechanisms and fluoride preventive aspects. Semin. Orthod. 2008, 14, 183–193. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gorelick, L.; Geiger, A.M.; Gwinnett, A.J. Incidence of white spot formation after bonding and banding. Am. J. Orthod. 1982, 81, 93–98. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Julien, K.C.; Buschang, P.H.; Campbell, P.M. Prevalence of white spot lesion formation during orthodontic treatment. Angle Orthod. 2013, 83, 641–647. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hoffman, D.A.; Clark, A.E.; Rody, W.J.; McGorray, S.P.; Wheeler, T.T. A prospective randomized clinical trial into the capacity of a toothpaste containing NovaMin to prevent white spot lesions and gingivitis during orthodontic treatment. Prog. Orthod. 2015, 16, 25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reddy, R.; Manne, R.; Sekhar, G.C.; Gupta, S.; Shivaram, N.; Nandalur, K.R. Evaluation of the efficacy of various topical fluorides on enamel demineralization adjacent to orthodontic brackets: An in vitro study. J. Contemp. Dent. Pract. 2019, 20, 89–93. [Google Scholar]
- Weir, E.; Lawlor, A.; Whelan, A.; Regan, F. The use of nanoparticles in antimicrobial materials and their characterization. Analyst 2008, 133, 835–845. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Allaker, R.P. The use of nanoparticles to control oral biofilm formation. J. Dent. Res. 2010, 89, 1175–1186. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pal, S.; Tak, Y.K.; Song, J.M. Does the antibacterial activity of silver nanoparticles depend on the shape of the nanoparticle? A study of the Gram-negative bacterium Escherichia coli. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 2007, 73, 1712–1720. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hannig, M.; Kriener, L.; Hoth-Hannig, W.; Becker-Willinger, C.; Schmidt, H. Influence of nanocomposite surface coating on biofilm formation in situ. J. Nanosci. Nanotechnol. 2007, 7, 4642–4648. [Google Scholar]
- Monteiro, D.R.; Gorup, L.F.; Takamiya, A.S.; Ruvollo-Filho, A.C.; De-Camargo, E.R.; Barbosa, D.B. The growing importance of materials that prevent microbial adhesion: Antimicrobial effect of medical devices containing silver. Int. J. Antimicrob. Agents 2009, 34, 103–110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Correa, J.M.; Mori, M.; Sanches, H.L.; Cruz, A.D.D.; Poiate, E.; Poiate, I.A.V.P. Silver nanoparticles in dental biomaterials. Int. J. Biomater. 2015, 2015, 485275. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pimpang, P.; Sutham, W.; Mangkorntong, N.; Mangkorntong, P.; Choopun, S. Effect of stabilizer on preparation of silver and gold nanoparticles using grinding method. Chiang Mai J. Sci. 2008, 35, 250–257. [Google Scholar]
- Zschech, D.; Kim, D.H.; Milenin, A.P.; Hopfe, S.; Scholz, R.; Goring, P.; Hillebrand, R.; Senz, S.; Hawker, C.J.; Russell, T.P. High-temperature resistant, ordered gold nanoparticles arrays. Nanotechnology 2006, 17, 2122–2126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Giorgetti, E.; Giusti, A.; Laza, S.; Marsili, P.; Giammanco, F. Production of colloidal gold nanoparticles by picoseconds laser ablation in liquids. Phys. Status Solidi A 2007, 204, 1693–1698. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Turner, S.; Tavernier, S.; Huyberechts, G.; Biermans, E.; Bals, S.; Batenburg, K.; Tendeloo, G. Assisted spray pyrolysis production and characterization of ZnO nanoparticles with narrow size distribution. J. Nanopart. Res. 2010, 12, 615–622. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ko, T.S.; Yang, S.; Hsu, H.C.; Chu, C.P.; Lin, H.F.; Liao, S.C.; Lu, T.C.; Kuo, H.C.; Hsieh, W.H.; Wang, S.C. ZnO nanopowders fabricated by dc thermal plasma synthesis. Mater. Sci. Eng. B 2006, 134, 54–58. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Breitwieser, D.; Moghaddam, M.M.; Spirk, S.; Baghbanzadeh, M.; Pivec, T.; Fasl, H.; Ribitsch, V.; Kappe, C.O. In situ preparation of silver nanocomposites on cellulosic fibers microwave vs conventional heating. Carbohydr. Polym. 2013, 94, 677–686. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sondi, I.; Salopek-Sondi, B. Silver nanoparticles as antimicrobial agent: A case study on E. coli as a model for Gram-negative bacteria. J. Colloid Interf. Sci. 2004, 275, 177–182. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nair, L.S.; Laurencin, C.T. Silver nanoparticles: Synthesis and therapeutic applications. J. Biomed. Nanotechnol. 2007, 3, 301–316. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rai, M.; Yadav, A.; Gade, A. Silver nanoparticles as a new generation of antimicrobials. Biotechnol. Adv. 2009, 27, 76–83. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McShan, D.; Ray, P.C.; Yu, H. Molecular toxicity mechanism of nanosilver. J. Food Drug Anal. 2014, 22, 116–127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Morones, J.R.; Elechiguerra, J.L.; Camacho, A.; Holt, K.; Kouri, J.B.; Ramirez, J.T.; Yacaman, M.J. The bactericidal effect of silver nanoparticles. Nanotechnology 2005, 16, 2346–2353. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feng, Q.L.; Wu, J.; Chen, G.Q.; Cui, F.Z.; Kim, T.N.; Kim, J.O. A mechanistic study of the antibacterial effect of silver ions on Escherichia coli and Staphylococcus aureus. J. Biomed. Mater. Res. 2000, 52, 662–668. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yuranova, T.; Rincon, A.G.; Bozzi, A.; Parra, S.; Pulgarin, C.; Albers, P.; Kiwi, J. Antibacterial textiles prepared by RF-plasma and vacuum-UV mediated deposition of silver. J. Photochem. Photobiol. A Chem. 2003, 161, 27–34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mukhopadhyay, A.; Basak, S.; Das, J.K.; Medda, S.K.; Chattopadhyay, K.; De, G. Ag-TiO2 nanoparticle codoped SiO2 films on ZrO2 barrier-coated glass substrates with antibacterial activity in ambient condition. ACS Appl. Mater. Interf. 2010, 2, 2540–2546. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- García-Contreras, R.; Argueta-Figueroa, L.; Mejía-Rubalcava, C.; Jiménez-Martínez, R.; Cuevas-Guajardo, S.; Sánchez-Reyna, P.A.; Mendieta-Zeron, H. Perspectives for the use of silver nanoparticles in dental practice. Int. Dent. J. 2011, 61, 297–301. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Garcia, I.M.; Ferreira, C.J.; de Souza, V.S.; Leitune, V.C.B.; Samuel, S.M.W.; de Souza Balbinot, G.; Collares, F.M. Ionic liquid as antibacterial agent for an experimental orthodontic adhesive. Dent. Mater. 2019, 35, 1155–1165. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Borzabadi-Farahani, A.; Borzabadi, E.; Lynch, E. Nanoparticles in orthodontics, a review of antimicrobial and anti-caries applications. Acta Odontol. Scand. 2014, 72, 413–417. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bala, T.; Armstrong, G.; Laffir, F.; Thornton, R. Titania-silver and alumina-silver composite nanoparticles: Novel, versatile synthesis, reaction mechanism and potential antimicrobial application. J Colloid Interf. Sci. 2011, 356, 395–403. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- ISO 20776-1E Clinical Laboratory Testing and In Vitro Diagnostic Test Systems—Susceptibility Testing of Infectious Agents and Evaluation of Performance of Antimicrobial Susceptibility Test Devices; Clinical and Laboratory Standards Institute: Wayne, PA, USA, 2006.
- Biemer, J.J. Antimicrobial susceptibility testing by the Kirby-Bauer disc diffusion method. Ann. Clin. Lab. Sci. 1973, 3, 135–140. [Google Scholar]
- Gold, O.G.; Jordan, H.V.; Vanhoute, J. A selective medium for Streptococcus-mutans. Arch. Oral. Biol. 1973, 11, 1357–1364. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marcotte, H.; Lavoie, M.C. Oral microbial ecology and the role of salivary immunoglobulin A. Microbiol. Molecul. Biol. Rev. 1998, 62, 71–109. [Google Scholar]
- Anhoury, P.; Nathanson, D.; Hughes, C.V.; Socransky, S.; Feres, M.; Chou, L.L. Microbial profile on metallic and ceramic bracket materials. Angle Orthod. 2002, 72, 338–343. [Google Scholar]
- Selwitz, R.H.; Ismail, A.I.; Pitts, N.B. Dental caries. Lancet 2007, 369, 51–59. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kerbusch, A.E.; Kuijpers-Jagtman, A.M.; Mulder, J.; Sanden, W.J. Methods used for prevention of white spot lesion development during orthodontic treatment with fixed appliances. Acta Odontol. Scand. 2012, 70, 564–568. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mattingly, J.A.; Sauer, G.J.; Yancey, J.M.; Arnold, R.R. Enhancement of streptococcus mutans colonization by direct bonded orthodontic appliances. J. Dent. Res. 1983, 62, 1209–1211. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bundy, K.J.; Butler, M.F.; Hochman, R.F. An investigation of the bacteriostatic properties of pure metals. J. Biomed. Mater. Res. 1980, 14, 653–663. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahn, S.J.; Lee, S.J.; Kook, J.K.; Lim, B.S. Experimental antimicrobial orthodontic adhesives using nanofillers and silver nanoparticles. Dent. Mater. 2009, 25, 206–213. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Poosti, M.; Ramazanzadeh, B.; Zebarjad, M.; Javadzadeh, P.; Naderinasab, M.; Shakeri, M.T. Shear bond strength and antibacterial effects of orthodontic composite containing TiO2 nanoparticles. Eur. J. Orthod. 2013, 35, 676–679. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baehni, P.C.; Takeuchi, Y. Anti-plaque agents in the prevention of biofilm-associated oral diseases. Oral Dis. 2003, 9, 23–29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, H.L.; Dai, S.A.; Fu, K.Y.; Hsu, S.H. Antibacterial properties of silver nanoparticles in three different sizes and their nanocomposites with a new waterborne polyurethane. Int. J. Nanomed. 2010, 5, 1017–1028. [Google Scholar]
- Mariel Murga, H.; Centeno Sanchez, R.; Sánchez Meraz, W.; González Amaro, A.M.; Arredondo Hérnandez, R.; Mariel Cárdenas, J.; Gutiérrez Cantu, F.J. Eficacia antimicrobiana del primer ortodóncico adicionado con nanopartículas de plata: Estudio transversal in vitro. Investig. Clín. 2016, 57, 321–329. [Google Scholar]
- Ochoa Ramirez, E.D. Fuerza Estática Friccional y Rugosidad de la Superficie Del Slot de Brackets de Autoligado: Estudio In Vitro. Master’s Thesis, Universidad de Cartagena, Cartagena, Colombia, 2018. [Google Scholar]
© 2019 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).