Abstract
Microbial contamination of fresh berries poses a significant public health risk due to their delicate and porous structure. This study evaluated the antimicrobial efficacy of washing and coating with sodium dichloroisocyanurate (SDC) against Escherichia coli, Listeria monocytogenes, and Salmonella enterica on blackberries. Two treatment approaches were tested: washing in SDC solutions (500 ppm and 1000 ppm for 1, 4, and 8 min), and hemicellulose B-based coatings supplemented with SDC (1 and 4 min exposure). Our results demonstrated that microbial reduction was significantly influenced by SDC concentration and exposure duration; longer treatment times and higher SDC concentrations achieved greater reductions. Washing with 1000 ppm SDC for 8 min obtained reductions of 5.0 ± 0.22 Log CFU/mL for E. coli (p < 0.001), 3.6 ± 0.45 Log CFU/mL for L. monocytogenes (p < 0.01), and 4.5 ± 0.30 Log CFU/mL for S. enterica (p < 0.001). Coating treatments at 1000 ppm for 4 min achieved even greater reductions for S. enterica, reaching 6.8 ± 0.35 Log CFU/mL, which was statistically superior to the corresponding washing treatment (p < 0.001). These findings support SDC as a promising antimicrobial agent for blackberry decontamination using a washing or coating method, with potential applications in fresh produce safety.
1. Introduction
The blackberry (Rubus fruticosus) constitutes one of the many widely distributed berries among the Rubus genus, which belongs to the Rosaceae family. The berries are made up of an agglomeration of drupes, each about 1–3 cm in diameter, which vary in color from green to crimson to black as they ripen. Blackberries have been savored for centuries, cherished for their delightful flavor [1]. Berries, notably blackberries, have recently garnered popularity as “superfoods” due to their high concentration of bioactive chemicals. These include vitamins A and C, sterols, carotenoids, terpenoids, and phenolic constituents, all of which provide significant health advantages while remaining low in calories [2,3]. Blackberries contain high concentrations of bioactive components such as anthocyanins, flavonols, ellagitannins, and phenolic acids [4,5,6]. These phenolic compounds are well known for their anti-inflammatory, antioxidant, antidiabetic, and antibacterial properties [7]. Furthermore, they are thought to play a role in the prevention of chronic oxidative stress, cancer, and cardiac illnesses such myocardial cardiac disease and a fatal stroke [8]. In addition to their nutritional and therapeutic value, blackberries are particularly vulnerable to microbial contamination due to their delicate uneven surface structure, high moisture content, and minimal postharvest processing. Their frequent consumption in raw form further elevates the risk of foodborne illness, as pathogens are not eliminated through cooking. Notably, blackberries have been implicated in past contamination events, including Salmonella outbreaks traced to fresh berries in the United States and Europe, reinforcing their relevance in food safety research [9,10].
Foodborne pathogens contribute significantly to global morbidity and mortality. Each year in the United States, 31 major foodborne pathogens cause roughly 9.4 million illnesses, 56,000 hospital stays, and 1300 fatalities [9]. The most common bacterial pathogens linked to foodborne diseases are L. monocytogenes, enterohemorrhagic E. coli and S. enterica [9,10]. Bacterial contamination may take place at any stage throughout the production chain, notably through contact with contaminated water and interactions with those handling food or gear throughout harvesting and post-harvest [11]. Safeguarding the microbiological integrity of blackberries is critical for lowering the risk of foodborne diseases and preserving consumer trust. Chemical interventions, radiation exposure, and biological measures have all been investigated as ways to decontaminate fresh food [12,13]. Several studies have demonstrated the effects of chemicals such as ozone [14], sodium hypochlorite [15], lactic acid [16], and chlorine dioxide [17], on reducing the bacterial populations in berries. However, these reductions have generally not been significant [15,16,17,18]. Consequently, there is a growing demand for antimicrobial treatments that are low-cost, safe for consumption and highly effective at controlling microbes including L. monocytogenes, E. coli, and S. enterica, all of which contribute significantly to foodborne illness.
Sodium dichloroisocyanurate (SDC), a member of the N-halamine group of compounds, is a recognized biocidal agent due to its broad-spectrum antibacterial properties. The N-halamine compounds are distinguished by the presence of nitrogen-halogen covalent bonds. The antibacterial activity of SDC is attributed to the +1 oxidation state of the halide atoms in its molecular structure [19]. SDC is the sodium salt of a chlorinated hydroxy triazine and is utilized as a source of free accessible chlorine in the form of hypochlorous acid. It is extensively used as a reliable source of chlorine for swimming pool disinfection and in the food industry. It is used to disinfect drinking water, particularly in crises, since it is a convenient source of free chlorine. More recently, it has been used as a source of chlorine for point-of-use water treatment in homes [20]. SDC is less corrosive than bleach, exhibits mild toxicity, and is cost-effective, safe for humans, and environmentally benign [21,22]. Prior research has demonstrated the efficacy of SDC against prevalent food-borne intestinal protozoa, including Giardia lamblia, Entamoeba histolytica, Cyclospora, Cryptosporidium, and Microsporidia, as well as food-borne bacteria such as L. monocytogenes, E. coli and S. enterica [19,23].
Hemicellulose B, a plant-derived biopolymer, has shown promise as edible coating material for food applications due to its excellent film-forming ability, and compatibility with antimicrobial agents [24,25]. In our previous research, we developed hemicellulose-based packaging films specifically for food safety enhancement [26,27]. These formulations demonstrated improved antimicrobial retention, with notable effectiveness in reducing food borne pathogen populations during short-duration treatments.
This study systematically evaluates both washing and coating strategies using SDC as an antimicrobial agent for microbial decontamination of blackberry surfaces. Specifically, it investigates the impact of SDC concentration and exposure duration on reducing populations of three foodborne pathogens (L. monocytogenes, E. coli and S. enterica).
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Preparation of Bacterial Strains
Stock cultures of L. monocytogenes (strain 19111), E. coli (ATCC strain 20R2R, serotype O157:H7), and S. enterica (strain 53647, serotype Typhimurium) were sourced from the USDA-ARS ERRC collection in Wyndmoor, PA, USA. To preserve these bacterial strains, they were stored at −80 °C in tryptic soy broth (TSB; BBL, Sparks, MD, USA) containing 20% glycerol. To guarantee viability, each starting culture was grown for 24 h at 37 °C on tryptic soy agar (TSA; BBL) slants containing 0.6% yeast extract and stored at 4 °C for two to four weeks.
For experimental preparation, a loopful of each bacterial strain was transferred from TSA slants to individual tubes containing 20 mL TSB. The cultures were grown at 37 °C on the rotary shaker at 5.0× g for 18 h, reaching an estimated concentration of ∼9 log CFU/mL. After incubation, the bacterial cultures underwent centrifugation at 10,000× g for 10 min, after which the supernatant was removed. The resulting pellets were washed twice with 2 mL of 0.1% peptone water and subsequently reconstituted in a volume of 20 mL of 0.1% peptone water for further experimental applications. All experiments were performed in triplicate (n = 3) for each bacterial strain and treatment condition to ensure reproducibility and statistical robustness.
2.2. Preparation of Antimicrobial Solution
SDC, sourced from Sigma-Aldrich (St. Louis, MO, USA), was dissolved in sterile deionized (DI) water in precise quantities to reach the required concentrations for experimental use. The solutions were formulated at room temperature and left undisturbed for 24 h before being utilized in experiments.
2.3. Preparation of Coating Solution
Hemicellulose B was extracted from corn bran in our laboratory following the procedure detailed in our previous publications [24,26]. The coating solution was prepared by dispersing 1% (w/v) hemicellulose B into a 500 mL glass container containing sterilized deionized (DI) water supplemented with SDC at concentrations of either 500 ppm or 1000 ppm. The solution was mixed thoroughly to achieve homogeneity. For control treatments, sterilized DI water without SDC was used following the same protocol.
2.4. Disk Diffusion Assay
The disk diffusion assay was performed by inoculating TSA plates with ∼8 log CFU of individual strains of L. monocytogenes, E. coli, and S. enterica (Table 1). After inoculation, the plates were left to air dry for 5 min. A 6 mm paper disk was carefully placed on each plate, and 100 μL of SDC at concentrations of either 250 ppm or 1000 ppm was applied to the disks. The plates were then incubated for 24 to 48 h, after which the zones of inhibition surrounding the disks were measured in millimeters (mm).

Table 1.
Zones of inhibition for the different bacterial strains E. coli, L. monocytogenes, and S. enterica on TSA plates after treatment with SDC (1000 ppm). Each sample underwent testing in duplicate.
2.5. Preparation of Blackberries and Inoculum
Fresh blackberries were purchased from neighborhood stores, refrigerated at 4 °C, and consumed within a week. Berries selected for analysis measured 1–2 cm in diameter and weighed around 7–8 g. A total of 80 blackberries underwent an initial rinse with water, followed by treatment with 70% ethyl alcohol spray to eliminate microorganisms. Afterward, the berries were placed inside a biosafety cabinet and allowed to dry for 2 h.
To inoculate the blackberries with microbial contaminants, they were submerged in 100 mL of an inoculum solution, which consisted of 2 mL of each foodborne pathogens thoroughly mixed with 98 mL of 0.1% peptone water (approximately 6–7 log CFU/mL) to ensure proper suspension and distribution. After a 1 min immersion, the berries were transferred back to the biosafety cabinet and left to dry at 22 ± 2 °C for an additional 2 h to facilitate microbial attachment.
2.6. Treatment of Blackberries and Microbiological Analysis
Two treatment strategies were applied to inoculated blackberry samples: washing in SDC solutions and application of a hemicellulose B-based coating.
For SDC solution treatments, twenty blackberries per group were immersed in 500 mL of sterilized deionized (DI) water containing SDC at concentrations of either 500 ppm or 1000 ppm. The samples were agitated at room temperature (22 °C) for exposure durations of 1, 4, or 8 min. Control groups were processed identically using sterile DI water without SDC.
Following treatment, ten blackberries from each group were transferred into individual Whirl-Pak® bags with 10 mL of 0.1% peptone water and homogenized for one minute using a stomacher. Serial dilutions were performed, and aliquots were plated onto selective media to identify three pathogens, PALCAM agar (BBL/Difco, Sparks, MD, USA) (with selective supplement) for L. monocytogenes, Xylose Lysine Tergitol-4 (XLT4) agar for S. enterica, Tryptic Soy Agar (TSA, BBL/Difco) for E. coli.
For coating treatments, 20 blackberries were treated with a coating solution composed of 1% (w/v) hemicellulose B dispersed in DI water containing either 500 ppm or 1000 ppm of SDC. Samples were agitated at room temperature for durations of 1 or 4 min only. Sterile DI water was used for controls.
Microbiological analysis for the coating treatment targeted S. enterica exclusively. Ten blackberries per group were homogenized as described above, followed by serial dilutions and plating on XLT4 agar. Plates were incubated at 37 °C for up to 48 h, after which the log colony-forming units (CFU) were determined. All microbiological assays were conducted in triplicate to ensure experimental reproducibility.
2.7. Statistical Analysis
The results from triplicate tests were expressed as the mean ± standard deviation. Statistical analysis was performed using GraphPad Prism 7.0 (GraphPad Software, Inc., San Diego, CA, USA), employing a one-way analysis of variance (ANOVA), followed by a post hoc Tukey’s test. Before applying ANOVA, the normality of the data was checked using the Shapiro–Wilk test. If the data did not meet the assumptions for normal distribution, appropriate adjustments or non-parametric methods were considered. Statistically significant differences between treatment means were indicated by asterisks (* p < 0.05; ** p < 0.01; *** p < 0.001).
3. Results and Discussions
To improve the microbiological safety of blackberries, which are highly prone to contamination due to their delicate surface, this study evaluated two post-inoculation treatments: SDC washing and coating. Washing treatments targeted L. monocytogenes, E. coli, and S. enterica over varied exposure times, while the coating approach focused solely on S. enterica at shorter durations. Pathogen reductions were assessed via selective media to compare treatment efficacy.
3.1. Disk Diffusion Assays and Selection of SDC Concentration
Disk diffusion assays were conducted to evaluate the antimicrobial effectiveness of SDC on different bacterial strains. When 250 ppm of SDC was applied to sample discs on TSA plates, no inhibition zones were observed across the tested strains. However, increasing the concentration to 1000 ppm yielded inhibition zones with average diameters reaching up to 9.25 mm for the tested strains, as shown in Table 1. Consequently, for subsequent experiments on blackberries application, the SDC concentration was adjusted to 500 ppm, under the assumption that 250 ppm would be insufficient. Furthermore, the concentration was raised to 500 ppm for experiments with blackberries to account for the fruit’s porous surface, which could potentially limit the antimicrobial’s effectiveness.
3.2. Treatment of Blackberry Surfaces with SDC Solutions
The effectiveness of SDC in lowering populations of L. monocytogenes, E. coli, and S. enterica was assessed at two doses (500 ppm and 1000 ppm) as well as across three exposure durations (1 min, 4 min, & 8 min). The results demonstrated that decline in bacterial population was impacted by both the treatment concentration and the length of exposure, with longer durations and higher concentrations leading to greater decreases in microbial load (Figure 1, Figure 2 and Figure 3).
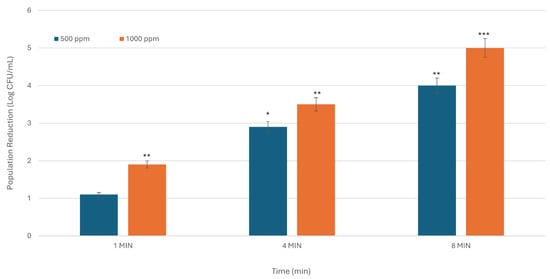
Figure 1.
The inhibitory activity of SDC against E. coli is dependent on both time and concentration. The X-axis denotes treatment duration in minutes, while the Y-axis indicates the reduction in bacterial population, expressed in Log CFU/mL. The figure presents the average results from three experiments conducted in duplicate. Asterisks indicate statistically significant differences between the means of various treatments (* p < 0.05; ** p < 0.01; *** p < 0.001).
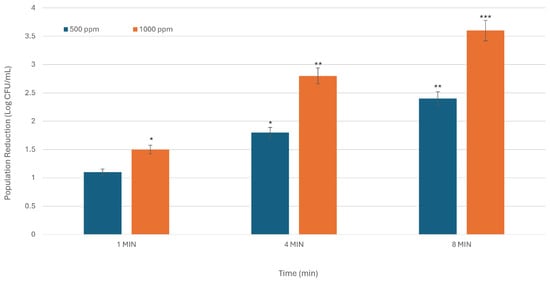
Figure 2.
The inhibitory activity of SDC against L. monocytogenes is dependent on both time and concentration. The X-axis denotes treatment duration in minutes, while the Y-axis indicates the reduction in bacterial population, expressed in Log CFU/mL. The figure presents the average results from three experiments conducted in duplicate. Asterisks indicate statistically significant differences between the means of various treatments (* p < 0.05; ** p < 0.01; *** p < 0.001).
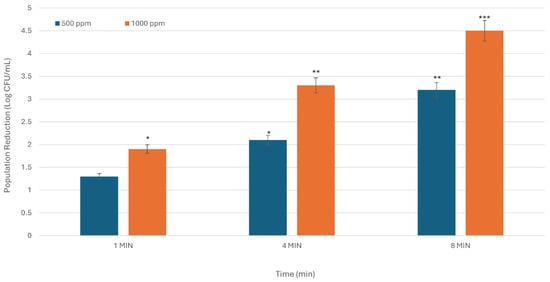
Figure 3.
The inhibitory activity of SDC against S. enterica is dependent on both time and concentration. The X-axis denotes treatment duration in minutes, while the Y-axis indicates the reduction in bacterial population, expressed in Log CFU/mL. The figure presents the average results from three experiments conducted in duplicate. Asterisks indicate statistically significant differences between the means of various treatments (* p < 0.05; ** p < 0.01; *** p < 0.001).
For E. coli, microbial reduction at 500 ppm was recorded as 1.1, 2.9, and 4.0 Log CFU/mL at exposure times of 1, 4, and 8 min, respectively. When tested at a concentration of 1000 ppm, bacterial levels showed a notable decline, with reductions of 1.9, 3.5, and 5.0 Log CFU/mL (p < 0.001) (Figure 1) in comparison to control group (i.e., sterile deionized water). These results demonstrate that higher concentrations and longer exposure times contribute to a more pronounced reduction in E. coli populations on blackberry surfaces. However, upon analysis of the data across two concentrations and three duration intervals, it was observed that a 52.6% greater reduction in microbial loads on the surface of blackberries could be attained by increasing the exposure time from 1 to 4 min, necessitating a lower dosage of 500 ppm SDC rather than 1000 ppm (2.9 Log CFU/mL at 500 ppm in 4 min; 1.9 Log CFU/mL at 1000 ppm in 1 min). In a comparable manner, a further reduction of 14.2% could be achieved with a 500 ppm solution, necessitating an extension of the exposure time by 4 min (4 Log CFU/mL at 500 ppm in 8 min; 3.5 Log CFU/mL at 1000 ppm in 4 min).
For L. monocytogenes, microbial reduction at 500 ppm was observed at 1.1, 1.8, and 2.4 Log CFU/mL for exposure durations of 1, 4, and 8 min, respectively. At 1000 ppm concentration, microbial levels reduced through 1.5, 2.8, and 3.6 Log CFU/mL (p < 0.01) over the designated time intervals when compared to the control samples (Figure 2). These results highlight the effectiveness of higher concentrations in reducing bacterial presence. These findings illustrate that increasing concentration and extending the exposure duration led to more substantial microbial reduction. Analyzing the correlation between concentration and exposure time, it was noted that a 20% and 60% greater reduction in L. monocytogenes on blackberry surfaces could be attained with a 500 ppm solution (instead of 1000 ppm), necessitating an increase in exposure time from 1 to 4 min and from 1 to 8 min, respectively. (1.8 and 2.4 Log CFU/mL at 500 ppm in 4 and 8 min, respectively; 1.5 Log CFU/mL at 1000 ppm in 1 min).
For S. enterica, microbial reductions at 500 ppm were recorded as 1.3, 2.1, and 3.2 Log CFU/mL at exposure times of 1, 4, and 8 min, respectively. When tested at 1000 ppm, microbial reductions were 1.91, 3.3, & 4.5 Log CFU/mL (p < 0.001), showing a notable increase relative to the corresponding control samples (Figure 3). These results highlight the effectiveness of higher concentrations in reducing bacterial presence. This pattern highlights the direct correlation between higher concentrations and extended exposure durations in achieving greater microbial reduction.
3.3. Treatment of Blackberry Surfaces with Hemicellulose-Based Coating Approach
The effectiveness of the hemicellulose B-based coating formulation, supplemented with SDC, was assessed for its ability to reduce S. enterica populations on blackberry surfaces. Treatments were performed using two concentrations of SDC (500 ppm and 1000 ppm) and evaluated at exposure times of 1 and 4 min.
At 500 ppm, microbial reductions were 3.2 and 5.4 Log CFU/mL for the 1 min and 4 min exposures, respectively. When tested at 1000 ppm, reductions increased to 5.2 and 6.8 Log CFU/mL (p < 0.001), across the same time intervals, indicating a clear enhancement in antimicrobial activity with higher concentration and longer contact time (Figure 4). These results demonstrate a strong positive correlation between treatment intensity (concentration and duration) and microbial reduction. Notably, the coating approach yielded substantial decreases in S. enterica, outperforming washing treatments under comparable conditions (Table 2).
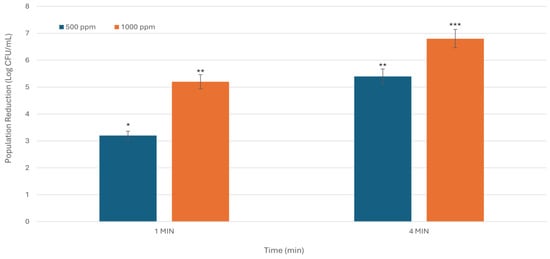
Figure 4.
The inhibitory activity of SDC hemicellulose-based coating against S. enterica is dependent on both time and concentration. The X-axis denotes treatment duration in minutes, while the Y-axis indicates the reduction in bacterial population, expressed in Log CFU/mL. The figure presents the average results from three experiments conducted in duplicate. Asterisks indicate statistically significant differences between the means of various treatments (* p < 0.05; ** p < 0.01; *** p < 0.001).

Table 2.
Demonstrates the best-performing SDC concentration and time for microbial reduction on blackberries. a Means are expressed as log CFU/mL ± SD. Asterisks to the left of the mean indicate a significant difference between treatment means. Significance was defined as * p < 0.05; ** p < 0.01; *** p < 0.001.
Overall, this intervention underscores the antimicrobial efficacy of SDC in reducing microbial contamination on blackberry surfaces through both washing and hemicellulose-based coating strategies. Across solution-based treatments, increased SDC concentration (from 500 ppm to 1000 ppm) and extended exposure times (up to 8 min) consistently improved microbial reductions for L. monocytogenes, E. coli, and S. enterica. These findings confirm that both concentration and contact time are key parameters for optimizing disinfection outcomes (Table 2), aligning with previous research highlighting the effectiveness of chlorine-based agents in fresh produce safety [28,29,30].
Interestingly, extended exposure of lower concentrations also yielded significant reductions (p < 0.05), suggesting operational flexibility depending on dosage availability and processing time constraints. For instance, the washing treatment with 500 ppm solution for 4 or 8 min could achieve comparable results, and in some cases superior reductions relative to shorter exposures at 1000 ppm. Such data offers practical insights for tailoring sanitization protocols across production environments, particularly where chemical minimization is desired without compromising efficacy [31,32].
Beyond solution washing, the hemicellulose B-based coating approach exhibited even greater efficacy, especially against S. enterica, with reductions reaching up to 6.8 Log CFU/mL at 1000 ppm within just 4 min (p < 0.001). This superior performance possibly stems from the polymer’s capacity to retain SDC on the fruit surface, promoting prolonged contact and targeted antimicrobial release. On porous produce like blackberries, such delivery systems enhance overall pathogen control and may contribute to shelf-life extension while minimizing risk of pathogen rebound.
The notable performance of hemicellulose coatings builds on previous work demonstrating their potential in food packaging and surface decontamination applications [24,25,26,27]. As a biodegradable, edible film-forming material, hemicellulose B can serve as both an antimicrobial agent and as a sustainable alternative to synthetic polymers. Although hemicellulose does not possess any antimicrobial activity, its ability to integrate with active agents like SDC enhances retention of antimicrobial activity, protects fragile surfaces, and supports post-harvest handling protocols. By integrating hemicellulose-based coating treatments, this research advances a safer, more efficient framework for fresh produce sanitation and sets the stage for developing targeted edible antimicrobial systems for commercial applications.
Despite its strengths, this study has its limitations. Microbial analyses were performed immediately post-treatment without monitoring long-term pathogen suppression, shelf-life stability, or residual activity during storage. Coating treatments were evaluated only against S. enterica, leaving efficacy against L. monocytogenes and E. coli unaddressed in that format. Additionally, parameters such as drying time, uniform coating application, and cost-effectiveness were not investigated. The absence of sensory testing [33,34], also restricts conclusions regarding consumer experience and market viability. Given that SDC is a strong oxidizing agent, future studies should assess its potential to alter fruit appearance, taste, aroma, and nutritional properties, especially at higher concentrations. Furthermore, the physical and chemical properties of the hemicellulose B-based coating, such as viscosity, thickness, homogeneity, adherence to fruit surfaces, and stability under storage conditions were not characterized in this study. We acknowledge that these attributes are essential for interpreting antimicrobial performance and assessing practical feasibility, especially in regulatory and scalability contexts. This omission limits the ability to fully evaluate the coating’s behavior in real-world applications. However, we note that this study was designed as a proof-of-concept, with a primary focus on demonstrating antimicrobial efficacy. The coating formulation was used to explore its potential as a delivery system for SDC. Although SDC is widely used and generally considered low in toxicity, its direct application to food surfaces warrants further safety evaluation to address potential risks such as skin irritation or respiratory effects at high exposure levels. The promising results observed here suggest that SDC-infused hemicellulose coatings could be integrated into commercial workflows, such as automated spray systems or edible film applications in modified atmosphere packaging. Such implementations may contribute to reducing microbial load during storage and distribution, extending shelf life, and offering a sustainable alternative to conventional antimicrobial interventions like chlorine rinses or ozone treatments. In addition, preliminary biodegradability testing confirmed that the hemicellulose-based coating is environmentally degradable, with full data to be presented in a forthcoming study. This supports its potential as a sustainable material for food safety applications.
To advance this work, future studies should explore broader pathogen coverage in coating systems, assess microbial stability under realistic storage conditions, and perform detailed sensory analyses across treated fruits. Comparative trials across different produce types, such as strawberries, grapes, or tomatoes would help verify transferability of findings. Optimization of formulation protocols, scale-up strategies, and regulatory compliance will be essential for industrial adoption. Specifically, it will be important to determine how long and at what concentration SDC remains on fruit surfaces after coating or washing, to assess the potential risk of ingesting harmful levels. Further research should also define optimal SDC concentrations and exposure durations to support practical application. As demonstrated in previous studies by Nazaruddin et al. [35], and Carpena et al. [36], integrating natural compounds into biodegradable matrices can enhance food safety through intelligent responsiveness and spoilage detection. Inspired by these approaches, combining SDC with natural antimicrobials or antioxidants may open new avenues for synergistic control and shelf-life enhancement in fresh produce management.
4. Conclusions
This study demonstrates the effectiveness of SDC in reducing microbial contamination on blackberries through two intervention strategies: washing and coatings. The antimicrobial activity of SDC was strongly influenced by concentration and contact time, with higher levels and longer exposures resulting in substantial reductions in L. monocytogenes, E. coli, and S. enterica. Notably, the hemicellulose-based coating approach achieved superior microbial reductions against S. enterica in shorter durations, suggesting enhanced retention and delivery of SDC on berry surfaces. This highlights the potential of coating-based systems for rapid and efficient pathogen control, particularly on delicate fruits like blackberries. SDC demonstrated promising antimicrobial efficacy under laboratory conditions, though its application in real-world produce safety requires further validation, including coating characterization, long-term stability, and comparative trials. The current study did not include sensory analysis, residue quantification, or simulation of commercial packaging and handling conditions. These limitations underscore the preliminary nature of the findings and highlight the need for future research to assess practical feasibility, safety, and scalability. Such efforts will be essential to determine whether SDC-infused coatings can serve as a sustainable and effective alternative to conventional antimicrobial interventions in fresh produce management.
Author Contributions
Conceptualization, S.A.H., M.I.S. and T.Z.J.; methodology, S.A.H. and M.I.S.; validation, S.A.H.; formal analysis, S.A.H.; investigation, S.A.H.; resources, M.I.S. and T.Z.J.; data curation, S.A.H., M.I.S. and T.Z.J.; writing—original draft, S.A.H.; writing—review and editing, S.A.H., M.I.S. and T.Z.J.; visualization, S.A.H.; supervision, M.I.S. and T.Z.J.; funding acquisition, T.Z.J. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This research was funded by the U.S. Department of Agriculture-Agriculture Research Services.
Institutional Review Board Statement
Not applicable.
Data Availability Statement
Data is contained within the article.
Acknowledgments
The authors acknowledge Anita Parameswaran (ERRC-ARS-USDA) for providing technical assistance.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
References
- Verma, R.; Gangrade, T.; Punasiya, R.; Ghulaxe, C. Rubus fruticosus (Blackberry) use as an herbal medicine. Pharmacogn. Rev. 2014, 8, 101–104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- D’Angelo, R.W.O.; Gonçalves, M.M.; Fachi, M.M.; Vilhena, R.d.O.; Pontarolo, R.; Maluf, D.F. UPLC–QToF-MS characterization of blackberry extracts of cultivars ‘Tupy’, ‘Guarani’, and ‘Xavante’: Development of extract-loaded niosomes. Rev. Bras. Farmacogn. 2020, 30, 519–527. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jara-Palacios, M.J.; Santisteban, A.; Gordillo, B.; Hernanz, D.; Heredia, F.J.; Escudero-Gilete, M.L. Comparative study of red berry pomaces (blueberry, red raspberry, red currant, and blackberry) as sources of antioxidants and pigments. Eur. Food Res. Technol. 2019, 245, 1–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dai, J.; Patel, J.D.; Mumper, R.J. Characterization of blackberry extract and its antiproliferative and anti-inflammatory properties. J. Med. Food 2007, 10, 258–265. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hager, T.J.; Howard, L.R.; Liyanage, R.; Lay, J.O.; Prior, R.L. Ellagitannin composition of blackberry as determined by HPLC-ESI-MS and MALDI-TOF-MS. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2008, 56, 661–669. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oszmiański, J.; Nowicka, P.; Teleszko, M.; Wojdyło, A.; Cebulak, T.; Oklejewicz, K. Analysis of phenolic compounds and antioxidant activity in wild blackberry fruits. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2015, 16, 14540–14553. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Folmer, F.; Basavaraju, U.; Jaspars, M.; Hold, G.; El-Omar, E.; Dicato, M.; Diederich, M. Anticancer effects of bioactive berry compounds. Phytochem. Rev. 2014, 13, 295–322. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zia-Ul-Haq, M.; Riaz, M.; De Feo, V.; Jaafar, H.Z.E.; Moga, M. Rubus fruticosus L.: Constituents, biological activities, and health-related uses. Molecules 2014, 19, 10998–11029. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Scallan, E.; Hoekstra, R.M.; Angulo, F.J.; Tauxe, R.V.; Widdowson, M.A.; Roy, S.L.; Jones, J.L.; Griffin, P.M. Foodborne illness acquired in the United States—Major pathogens. Emerg. Infect. Dis. 2011, 17, 7–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, W.; Chen, X.; Li, Y.; Guo, S.; Wang, Z.; Yu, X. Advances in pharmacological activities of terpenoids. Nat. Prod. Commun. 2020, 15, 1934578X20903555. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- European Food Safety Authority (EFSA). Scientific opinion on the risk posed by pathogens in food of non-animal origin. EFSA J. 2013, 11, 3025. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, W.; Zhao, W.; Sun, Y.; Sun, Y.; Wang, B.; Liu, M.; Qiu, Z.; Wang, Y.; Sun, Z.; Hu, P.; et al. Effects of multi-wavelength ultraviolet radiation on the inactivation and reactivation of E. coli in a recirculating water system. Aquac. Rep. 2025, 41, 102688. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pérez-Lavalle, L.; Carrasco, E.; Valero, A. Strategies for microbial decontamination of fresh blueberries and derived products. Foods 2020, 9, 1558. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, V.C.H.; Kim, B. Effect of a simple chlorine dioxide method for controlling five foodborne pathogens, yeasts, and molds on blueberries. Food Microbiol. 2007, 24, 794–800. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Goodburn, C.; Wallace, C.A. The microbiological efficacy of decontamination methodologies for fresh produce: A review. Food Control 2013, 32, 418–427. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tadepalli, S.; Bridges, D.F.; Driver, R.; Wu, V.C.H. Effectiveness of different antimicrobial washes combined with freezing against E. coli O157:H7, Salmonella Typhimurium, and Listeria monocytogenes inoculated on blueberries. Food Microbiol. 2018, 74, 34–39. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pangloli, P.; Hung, Y.-C. Reducing microbiological safety risk on blueberries through innovative washing technologies. Food Control 2013, 32, 621–625. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nadeem, M.; Leaks, K.; Abdullah, A.; Adamson, F.J.; Shahid, M.A. Enhancing postharvest quality of blackberries: Impact of sonicated and microwave-assisted pasteurized edible coating gels at different storage temperatures. Gels 2025, 11, 243. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Long, W., III; Sarker, M.I.; Annous, B.A.; Paoli, G.C. Evaluation of sodium dichloroisocyanurate treatment on recovered concentrations of Salmonella enterica, E. coli O157:H7, and Listeria monocytogenes from cattle hide surfaces and culture medium. J. Food Saf. 2020, 40, e12834. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- WHO. Sodium Dichloroisocyanurate in Drinking Water. Available online: https://www.who.int/docs/default-source/wash-documents/wash-chemicals/sodium-dichloroisocyanurate-2add-feb2008.pdf (accessed on 1 August 2025).
- Dong, A.; Wang, Y.J.; Gao, Y.; Gao, T.; Gao, G. Chemical insights into antibacterial N-halamines. Chem. Rev. 2017, 117, 4806–4862. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sarker, M.I.; Long, W.; Liu, C.K. Efficacy of aqueous solution of N-halamine to reduce microbiological contamination on cattle hides for meat safety with byproduct quality assurance. J. Am. Leather Chem. Assoc. 2020, 115, 330–336. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zou, Q.; Meng, W.; Wang, C.; Wang, T.; Liu, X.; Li, D. Sodium dichloroisocyanurate: Improving broiler health by reducing harmful microbial levels in the waterline. Front. Vet. Sci. 2023, 10, 1234949. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- da Silva Braga, R.; Poletto, M. Preparation and Characterization of Hemicellulose Films from Sugarcane Bagasse. Materials 2020, 13, 941. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, Y.; Sun, H.; Yang, B.; Weng, Y. Hemicellulose-Based Film: Potential Green Films for Food Packaging. Polymers 2020, 12, 1775. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hussain, S.A.; Qi, P.X.; Sharma, B.K.; Yadav, M.P.; Mainali, K.; Jin, T.Z. Valorization of corn bran-derived carbohydrate polymers for developing biodegradable packaging films. J. Polym. Environ. 2025, 33, 2552–2566. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hussain, S.A.; Sharma, B.K.; Qi, P.X.; Yadav, M.P.; Jin, T.Z. Antimicrobial and Physicochemical Properties of Hemicellulose-Based Films Incorporating Carvacrol. Polymers 2025, 17, 2073. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, J.W.; Huang, B.S.; Hsu, C.W.; Peng, C.W.; Cheng, M.L.; Kao, J.Y.; Way, T.D.; Yin, H.C.; Wang, S.S. Efficacy and safety evaluation of a chlorine dioxide solution. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2017, 14, 329. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Malka, S.K.; Park, M.H. Fresh produce safety and quality: Chlorine dioxide’s role. Front. Plant Sci. 2022, 12, 775629. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gerba, C.P. Quaternary ammonium biocides: Efficacy in application. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 2015, 81, 464–469. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luu, P.; Chhetri, V.S.; Janes, M.E.; King, J.M.; Adhikari, A. Effectiveness of aqueous chlorine dioxide in minimizing food safety risk associated with Salmonella, E. coli O157:H7, and Listeria monocytogenes on sweet potatoes. Foods 2020, 9, 1259. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, F.; Xiang, L.; Leung, K.S.-Y.; Elsner, M.; Zhang, Y.; Guo, Y.; Pan, B.; Sun, H.; An, T.; Ying, G.; et al. Emerging contaminants: A One Health perspective. Innovation 2024, 5, 100612. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martín-Diana, A.B.; Rico, D.; Barry-Ryan, C.; Frías, J.M.; Mulcahy, J.; Henehan, G.T. Comparison of calcium lactate with chlorine as a washing treatment for fresh-cut lettuce and carrots: Quality and nutritional parameters. JSFA Rep. 2005, 85, 2260–2268. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nakano, H.; Pan, X. Effects of chlorine-based antimicrobial treatments on the microbiological qualities of selected leafy vegetables and wash water. Food Sci. Technol. Res. 2014, 20, 765–774. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nazaruddin, N.; Afifah, N.; Bahi, M.; Susilawati, S.; Sani, N.D.M.; Esmaeili, C.; Iqhrammullah, M.; Murniana, M.; Hasanah, U.; Safitri, E. A simple optical pH sensor based on pectin and Ruellia tuberosa L-derived anthocyanin for fish freshness monitoring. F1000Research 2021, 10, 422. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carpena, M.; Silva, A.; Barciela, P.; Perez-Vazquez, A.; Chamorro, F.; Cassani, L.; Barroso, M.F.; Xiao, J.; Prieto, M.A.; Simal-Gandara, J. Inclusion of Natural Anthocyanins as Food Spoilage Sensors. Eng. Proc. 2023, 48, 59. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).