Abstract
The incorporation of waste polyethylene terephthalate (PET) as a modifier for asphalt presents a promising approach to addressing the environmental pollution associated with waste plastics while simultaneously extending the service life of road surfaces. This study investigates the fundamental physical properties and rheological properties of asphalt modified with waste PET at both high and low temperatures. Utilizing the theory of fractional derivatives, performance evaluation indicators, such as the deformation factor and viscoelasticity factor, have been developed for the assessment of waste PET-modified asphalt. The underlying mechanism of this modification was examined through scanning electron microscopy and Fourier transform infrared spectroscopy. The results indicate that the addition of waste PET enhances the high-temperature stability of the base asphalt but reduces its resistance to cracking at low temperatures. The fractional derivative model effectively describes the dynamic shear rheological properties of waste PET-modified asphalt, achieving a maximum correlation coefficient of 0.99991. Considering the performance of modified asphalt at both high and low temperatures, the optimal concentration of waste PET was determined to be 6%. At this concentration, the minimum creep stiffness of the PET-modified asphalt was approximately 155 MPa at −6 °C. Additionally, the rutting factor of the waste PET-modified asphalt achieved a maximum value of 527.12 KPa at 52 °C. The interaction between waste PET and base asphalt was primarily physical, with mutual adsorption leading to the formation of a spatial network structure that enhanced the deformation resistance of the asphalt. This study provides a theoretical foundation and technical support for the engineering application of waste PET as a modifier in asphalt.
1. Introduction
Plastic is extensively employed in diverse fields, including construction, medical equipment, and food packaging, owing to its characteristics of being cheap, lightweight, high-strength, and resistant to corrosion [,,]. Nonetheless, inadequate management of plastic waste can lead to significant environmental pollution [,]. Presently, the challenges associated with environmental pollution are becoming more pronounced, posing substantial threats to human survival [,,]. Consequently, the development of effective strategies for the recycling of plastic waste has emerged as an urgent issue requiring immediate attention.
There are many types of plastics, mainly including polyethylene terephthalate (PET), polyethylene, polypropylene, and other types [,]. Among them, PET is widely used in the manufacturing of food and pharmaceutical fields due to its high transparency and good barrier properties, with a global annual production and sales volume exceeding 70 million tons []. According to statistical data, fewer than 30% of PET plastic bottles are recycled, resulting in a substantial quantity of waste PET plastic bottles being disposed of in landfills. This practice significantly affects the living environments of both humans and animals [,,]. Simultaneously, the escalating incidence of extremely high-temperature conditions has led to progressively stringent demands on the thermal stability of bituminous materials within the field of road engineering [,,]. In addition, the increasingly heavy traffic load and channelized traffic have posed serious challenges to the normal use of asphalt pavements []. Traditional asphalt binders struggle to meet the needs of special weather conditions and heavy traffic [,]. Therefore, researchers have attempted to use waste PET for asphalt modification. This approach not only mitigates the environmental issues associated with waste PET but also improves the high-temperature stability of asphalt, ultimately extending the service life of pavements [,,,].
Waste PET can significantly improve the rutting resistance [,] and toughness [] of asphalt, and can also improve the aging resistance of modified asphalt [,]. In addition, Aldaigari et al. [] further investigated the anti-aging effect of functionalized waste PET on asphalt composite materials. The results showed that modified adhesives treated with waste vegetable oil had a 15.6% decrease in healing ability after long-term aging, significantly higher than the 66% decrease in healing ability of pure adhesives. In addition, waste PET was used as an additive in asphalt mixtures, and it was found that waste PET can improve the mechanical and durability properties of asphalt mixtures [,]. Arshadi M. et al. [] incorporated waste PET particles into recycled asphalt mixtures and investigated the effect of PET particles on the mechanical properties of recycled asphalt mixtures. These studies offered a crucial theoretical foundation and technical support for integrating the recycling of waste PET plastics with road engineering construction.
Nonetheless, there exists a significant gap in comprehensive research and exploration concerning the rheological properties and modification mechanisms of waste PET-modified asphalt. Such an investigation is crucial for elucidating the enhancement of high-temperature stability and the mechanical characteristics of modified bitumen and its mixtures. Furthermore, it is essential for assessing the rutting resistance of the modified materials. In recent years, the fractional derivative model has been widely applied in various engineering fields because it can overcome the drawback of the classical integer-order differential model that does not match the experimental results well [,]. Celauro et al. [] constructed a creep constitutive model describing the viscoelastic strain of viscoelastic materials using the fractional Riemann–Liouville operator and investigated the mechanical properties of the base asphalt. Li et al. [] proposed an improved fractional derivative empirical creep model and utilized this model to describe the creep characteristics of asphalt mortar. These studies provided a research basis for the extensive application of fractional derivative theory in modified asphalt and mixtures.
Therefore, this research aims to provide new perspectives and methods for evaluating and utilizing waste PET-modified asphalt. The key road performance and modification mechanism of modified bitumen with dosages of 0%, 3%, 6%, 9%, and 12% were investigated. Based on the fractional derivative theory, the dynamic shear rheological properties of waste PET-modified asphalt were analyzed, and high-temperature performance evaluation indicators for waste PET-modified asphalt are proposed. The mechanism of waste PET-modified asphalt was explored using scanning electron microscopy and Fourier transform infrared spectroscopy. This will provide a new theoretical basis and evaluation methods for the application of waste PET-modified asphalt.
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Materials
2.1.1. Asphalt
According to the technical requirements for road petroleum asphalt in JTGF40-2004, the 70 # base asphalt was provided by Alpha (Jiangyin) Asphalt Co., Ltd., Jiangyin, China. According to Chinese regulations, the main parameter indicators of the 70 # base asphalt were tested as shown in Table 1.

Table 1.
The parameter indicators of the 70 # base asphalt.
2.1.2. Preparation of Waste PET
The waste PET plastic bottles were taken from Henan Urban Construction University, as depicted in Figure 1a. The molecular weight of PET is usually between 20,000 g/mol and 30,000 g/mol, and the density of PET is about 1.15 g/cm3. The melt index of PET was 2.5 g/10 min. The PET plastic bottles were cleaned and dried after removing the bottle cap and label. Then, the bottles were sliced into plastic fragments of about 10 mm [], as shown in Figure 1b. This promoted the full integration of PET and asphalt more easily.

Figure 1.
Waste PET processing process.
2.1.3. Preparation of Waste PET-Modified Asphalt
The base asphalt was heated to 170 °C, and then waste PET plastic with masses of 3%, 6%, 9%, and 12% was added based on previous research findings []. The PET plastic was melted and mixed with the asphalt to form a mixture. The mixture was continuously stirred with a high-speed shearing instrument. The model of the high-speed shearing instrument was Shanghai Furuk Fluko-A25-2016, Shanghai, China. The cutting rate was 4000 rpm, the cutting time was 10 min, and the cutting temperature was 180 °C. This made the waste PET evenly disperse into the base asphalt.
2.2. Methods
2.2.1. Basic Physical Property Test
Basic physical properties mainly include penetration, ductility, and softening point. All experiments were conducted in three parallel trials. The error of the three sets of experiments met the standard error, and the average value of the three sets of experiments was taken as the final experimental value.
- (1)
- Penetration test
According to ASTM D 5M-13, asphalt was placed in a sample dish with an inner diameter of 55 mm and a depth of 35 mm. The penetration of waste PET-modified asphalt was tested under 25 °C by the automatic needle penetration tester SYD-280I-2020 made by Shanghai Changji Geological Instrument Co., Ltd., Shanghai, China.
- (2)
- Ductility test
According to ASTM D 113-17, asphalt was poured into the octagonal inner membrane. The ductility of waste PET-modified asphalt was tested by the asphalt low temperature elongation tester STYD-3-2018 made by Shanghai Kanglu Instrument & Equipment Co., Ltd., Shanghai, China. The temperature for the elongation test was 15 °C. The loading rate was 50 mm/min.
- (3)
- Softening point test
According to ASTM D 36M-12, asphalt was poured into a steel ring with an inner diameter of 19.8 mm and an outer diameter of 23 mm. The Ring and Ball method was used to perform the softening point of waste PET-modified asphalt by the Intelligent softening point tester SYD-2806F-2015 made by Shanghai Changji Geological Instrument Co., Ltd., Shanghai, China.
2.2.2. Frequency Scanning Test
Based on dynamic shear rheological tests, the complex shear modulus (G*) and phase angle (δ) of asphalt were measured through dynamic shear tests, which provide key parameters for PG grading. The model of the dynamic shear rheometer is SmartPave 92 (origin from Graz, Austria, 2019). According to ASTM D 7175, asphalt was poured into the grinding tool to form a circular sample with a diameter of 25 mm. The frequency range of the frequency scanning test was 1–150 rad/s, and the temperature conditions were 52 °C, 58 °C, 64 °C, and 70 °C. The experimental results were thoroughly explored and analyzed through the theory of fractional derivatives.
2.2.3. Repeated Creep Recovery Test
The Repeat Creep Recovery Test (RCR) could simulate the permanent deformation development behaviors of bitumen pavements under repeated traffic loading. The model of the dynamic shear rheometer is TA DHR-1 (Origin from New Castle, DE, USA, 2016). According to ASTM D7045-2020, asphalt was poured into the grinding tool to form a circular sample with a diameter of 8 mm. The mechanical behavior of repeated creep of asphalt under different temperature environments was tested. The test temperatures were 52 °C, 58 °C, 64 °C, and 70 °C, respectively. During the test, the load was set at 0.1 KPa, the loading time was controlled at 1 s, the unloading time was 9 s, and the cycle was repeated 10 times. The creep recovery rate was calculated according to Equation (1).
where R is the creep recovery rate;
is the total strain;
is the unrecoverable strain.
2.2.4. Flexural-Creep Stiffness Test
The bending creep stiffness test of asphalt was an important test to evaluate the crack resistance performance of the asphalt under low-temperature conditions. The bending creep stiffness was used to evaluate the stress and strain response of asphalt pavement in low-temperature environments. According to ASTM 6648, asphalt was prepared as a prism with a length of 250 mm, a width of 30 mm, and a height of 35 mm. The creep stiffness of waste PET-modified asphalt under temperature conditions of −6 °C, −12 °C, and −18 °C was measured by the asphalt bending beam rheometer (BBR) ATS-2016 made by the American ATS Company, New York, NY, USA. The load was 1N, and the loading time lasted for 240 s.
2.2.5. Scanning Electron Microscope (SEM) Test
In this study, scanning electron microscopy (origin from QUANTA-450-FEG , Eindhoven, FEI, Holland) was used to observe the microstructure of base asphalt and waste PET-modified asphalt samples, as well as the dispersion of waste PET in asphalt. The asphalt sample was gold-plated due to its weak conductivity. The spraying voltage was 10 mA. The spraying target material was gold–palladium alloy. The spraying time was 45 s. The dried asphalt sample was uniformly pasted onto the conductive adhesive for testing.
2.2.6. X-Ray Diffraction (XRD) Test
The solid phase was characterized by X-ray diffraction (XRD) utilizing an X’Pert PRO MPD instrument from PANalytical B.V., Almelo, The Netherlands. The analysis employed Cu Kα radiation and was conducted over a scanning 2θ range from 5º to 8º, with operational settings of 40 kV and 30 mA.
2.2.7. Fourier Transform Infrared Spectroscopy (FTIR) Test
The Nicolet iS10 Fourier transform infrared spectrometer, produced by Thermo Scientific in Waltham, MA, USA, was used to test and analyze the surface functional groups of waste PET-modified asphalt samples. The Nicolet iS10 Fourier Transform Infrared Spectrometer was compatible with the Thermo Scientific Smart iTRTM ATR accessory, enabling direct non-destructive testing of asphalt samples. Asphalt samples were heated to 60–80 °C and softened. A small amount of asphalt was evenly coated on the surface of attenuated total reflection (ATR) diamond crystals and cooled to solidify. The instrument was preheated for 15 min after being turned on. The blank background was scanned first, and then the asphalt sample was scanned. The ATR mode was selected, the wavelength was set to 4000–500 cm−1, the resolution was 4 cm−1, and the scanning frequency was 32.
2.2.8. Differential Scanning Calorimetry (DSC) Test
In a nitrogen environment, the heat flow curve and glass transition temperature of the samples were analyzed using a DZ-DSC300 made in Nanjing, China. The sample had a mass of 5 mg ± 0.5 mg and was placed in a crucible. The heating rate was 20 °C/min. The testing temperature range was −30–300 °C.
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. Basic Physical Properties
The physical properties of modified bitumen at different PET content levels, including penetration, softening point, and ductility, are shown in Table 2 and Figure 2.

Table 2.
The physical properties (mean ± SD) of waste PET-modified asphalt.
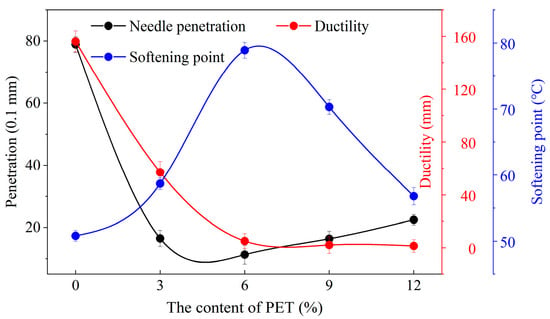
Figure 2.
The physical properties of waste PET-modified asphalt.
As the amount of waste PET increases, the penetration of asphalt shows a trend of first decreasing and then increasing. This indicates that the hardness of asphalt first increases and then decreases. Asphalt penetration can measure the consistency and softness of asphalt. The greater the penetration, the harder the asphalt []. With a waste PET content of 6%, the penetration value of PET-modified asphalt is 11.3, and its ability to resist shear failure is significantly improved.
The softening point can measure the high-temperature stability of asphalt, and the higher the softening point, the better its high-temperature stability []. With the increase in waste PET content, the softening point value of waste PET-modified asphalt shows a change of first increasing and then decreasing. The waste PET content is 6%, and the softening point of the PET-modified asphalt is 1.55 times that of the base asphalt, with a softening point value of 79 °C. This indicates that the high-temperature stability of modified asphalt at 6% content is significantly stronger than that of base asphalt.
With the increase in waste PET content, the ductility of asphalt decreases significantly, and the plasticity of asphalt decreases significantly. The ductility of PET-modified asphalt is only 1.4 cm with a waste PET content of 12%. Ductility is a plasticity index of asphalt. The larger the ductility value, the stronger the stretchability of asphalt, the better its plasticity, and the lower the Frarasis brittleness point of asphalt, which enhances the toughness of asphalt at low temperatures []. It indicates that adding waste PET weakens the low-temperature crack resistance of asphalt.
3.2. Frequency Sweep Test
A fractional derivative model applicable to asphalt materials was established. The dynamic frequency scanning test results of bitumen with various contents at several temperatures were linearly fitted to investigate the rheological behaviors of PET-modified bitumen.
3.2.1. Establishment of Fractional Derivative Model
A creep constitutive model for viscoelastic materials was created based on the fractional Riemann–Liouville fractional integral operator, as shown in Formula (2).
where
;
is the gamma function;
is the fractional integral operator of Riemann–Liouville. Formula (1) was transformed into Formula (3).
where
is a continuous function.
According to the fractional derivative theory, Formula (3) was changed to Formula (4) [].
The Riemann–Liouville fractional differential operator (
) is shown in Formula (5).
where
is a continuous function;
is a gamma function.
When
, Formula (4) can be integrated to obtain Formula (6).
According to Formula (6), the fractional derivative can be expressed by the Stieltjes convolution of
and
.
The creep constitutive equation of viscoelastic materials was constructed based on Abel clay pot elements, as shown in Formula (7).
where η was the viscosity coefficient of the material; γ was the material parameter, which was the order of the fractional derivative. When γ was equal to 0 or 1, the component degenerated into a spring or damper component, respectively. When 0 < γ < 1, the component was a composite element of a spring and a damper.
Therefore, Formula (7) was changed to Formula (8).
where
is a gamma function;
is the unit step function.
can also be expressed as
.
In addition, the stress–strain relationship of high polymer viscoelastic materials follows the Nutting formula, as shown in Formula (9).
The creep compliance (
) was calculated using Equation (10).
where A and γ are the material parameters.
From Formulas (8) and (10), it can be concluded that
. This indicated that A was inversely correlated with the viscosity coefficient of the viscoelastic material and the order of the fractional derivative.
The constitutive equation of fractional order derivative viscoelastic materials under dynamic loading was shown in Equation (11).
where
.
is the dynamic shear modulus;
is the storage modulus;
is the loss modulus.
Formula (12) was obtained by substituting
into Formula (11).
It can be obtained through simple mathematical calculations using Equation (13).
The dynamic frequency scanning test results of asphalt at different temperatures under different PET contents were linearly fitted and analyzed. The fitted parameters were calculated to obtain the values of parameters A and γ.
3.2.2. Frequency Scanning Analysis Based on Fractional Derivative Model
The frequency scanning test and linear fitting results of waste PET-modified asphalt at different temperatures are shown in Figure 3. The correlation coefficient is shown in Figure 4, and the rutting factor (G*/sinδ) is shown in Figure 5.
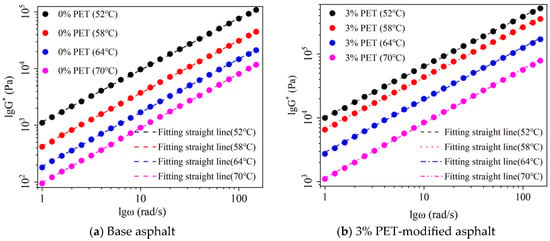
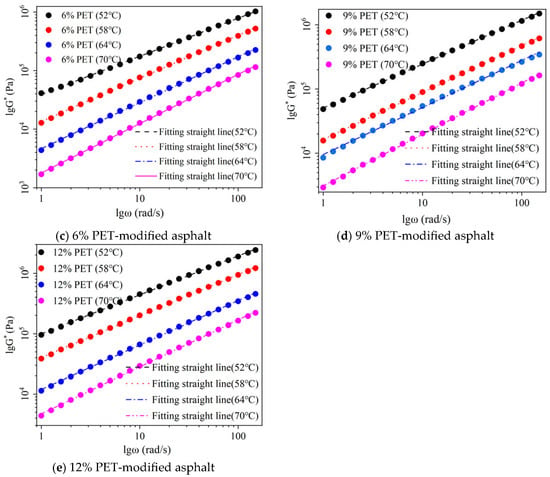
Figure 3.
Frequency scanning test and linear fitting results: (a) base asphalt, (b) 3% waste PET-modified asphalt, (c) 6% waste PET-modified asphalt, (d) 9% waste PET-modified asphalt and (e) 12% waste PET-modified asphalt.
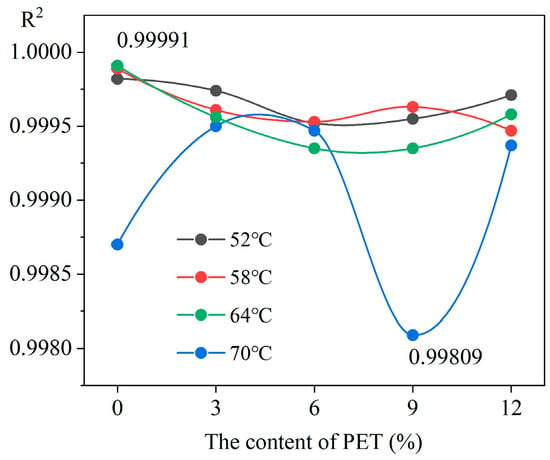
Figure 4.
Correlation coefficient.
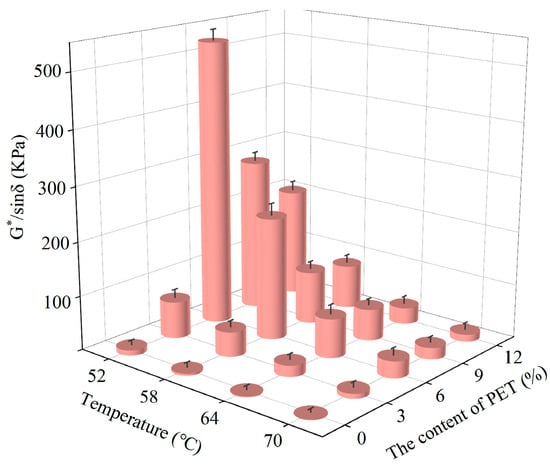
Figure 5.
Rutting factor (G*/sinδ).
As shown in Figure 3, the complex shear modulus (G*) of waste PET-modified asphalt with different dosages follows the same pattern as that of the base asphalt, increasing with the increase in angular frequency (ω). This is because the frequency of loading is increased, the internal vibration frequency of asphalt is improved, the total resistance generated by repeated shear deformation of asphalt is increased, and the complex shear modulus of asphalt is improved. The complex modulus of waste PET-modified asphalt increases with the increase in waste PET content, and the larger the complex shear modulus of asphalt, the stronger its ability to resist high-frequency loads. This indicates that increasing the waste PET content enhances the deformation resistance of waste PET-modified asphalt. The complex shear modulus of waste PET-modified asphalt increases with increasing temperature. This indicates that increasing the temperature reduces the rutting resistance of waste PET-modified asphalt.
From Figure 4, it can be seen that the range of correlation coefficient variation is relatively small, concentrated between 0.99935 and 0.99991 under 52 °C–64 °C. At higher temperatures of 70 °C, the range of variation in the correlation coefficient is relatively large, with a fluctuation range of 0.99809–0.99947. This indicates that the model is more suitable for conditions between 52 °C and 64 °C. Under 52 °C–64 °C, the correlation coefficient first decreases and then increases as the PET content increases. At higher temperatures of 70 °C, the correlation coefficient first increases, then decreases, and finally increases again as the PET content increases. At different temperatures, the correlation coefficients of 3% PET-modified asphalt reached their maximum values. This indicates that this model is more suitable for low-content PET-modified asphalt. Although the correlation coefficient fluctuates with changes in PET contents and temperature, the minimum value still exceeds 0.998. This indicates that the model can accurately describe the dynamic shear rheological properties of waste PET-modified asphalt and has good applicability.
As shown in Figure 5, it can be seen that the rutting factor gradually decreases as the temperature increases at the same waste PET content. This is because asphalt exhibits elastic properties under low temperature conditions, and the resistance required for asphalt to deform under stress is relatively high. Asphalt exhibits viscous properties under high temperature conditions, and the resistance to deformation of asphalt under stress is relatively small. Under 52 °C, the rutting factor of the 6% waste PET-modified asphalt reaches its maximum value of 527.12, which is 53.97 times that of the base asphalt under the same temperature. It indicates that the deformation resistance of waste PET-modified asphalt has been significantly improved. The rutting factor firstly increases and then decreases with the increase in waste PET content, and the rutting factor of 6% waste PET0modified asphalt is the highest, indicating that the high-temperature rutting resistance of 6% waste PET-modified asphalt is the best.
According to Equation (1), the deformation factor (A) and viscoelastic factor (γ) were calculated using the fractional derivative model, as shown in Figure 6 and Table 3, and Figure 7 and Table 4, respectively.
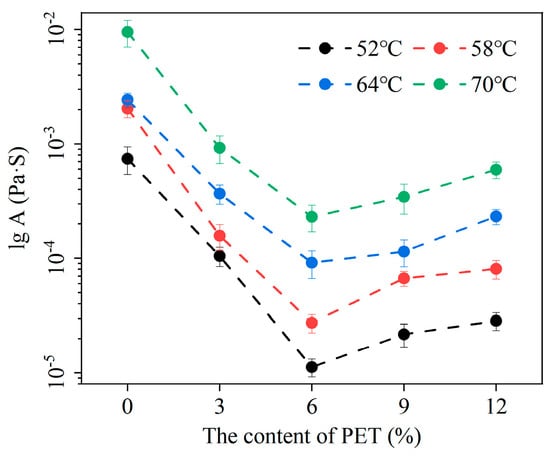
Figure 6.
Deformation factor (A).

Table 3.
The deformation factor (mean ± SD) of different contents of PET-modified asphalt.
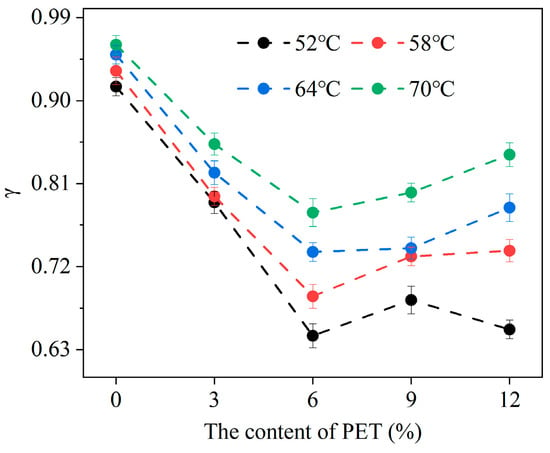
Figure 7.
Viscoelastic factor (γ).

Table 4.
The viscoelastic factor (mean ± SD) of different contents of PET-modified asphalt.
As shown in Figure 6, with the increase in waste PET content, the A value of waste PET-modified asphalt first decreases and then increases. As the experimental temperature increases, the A value gradually increases. The temperature and waste PET content have important effects on the A value. When the waste PET content is 6%, the A value at different temperatures reaches a minimum. This indicates that the waste PET-modified asphalt has the best high-temperature stability at the PET content of 6%, which is consistent with the change in rutting factor reflecting the deformation resistance of waste PET-modified asphalt.
From Figure 7, under the same temperature, the viscoelastic factor of waste PET-modified asphalt increases with the increase in waste PET content. For the same content of waste PET-modified asphalt, the viscosity component of the waste PET-modified asphalt material increases, and the viscoelastic factor value gradually increases as the temperature increases. When the content of waste PET is 6%, the viscoelastic factor of waste PET-modified asphalt with 0.6451 is the smallest at different temperature conditions. This indicates that the 6% waste PET-modified asphalt has the strongest elastic component and the strongest resistance to deformation, which is consistent with the previous analysis results.
3.3. Repeated Creep Recovery Performance
The creep recovery rate reflects the ability of asphalt to recover its original shape during repeated loading and unloading processes, and is an important parameter for evaluating the viscoelastic properties of materials. The results of repeated creep recovery tests are shown in Figure 8. The creep recovery rate of the 10th cycle calculated according to Equation (1) is shown in Figure 9.
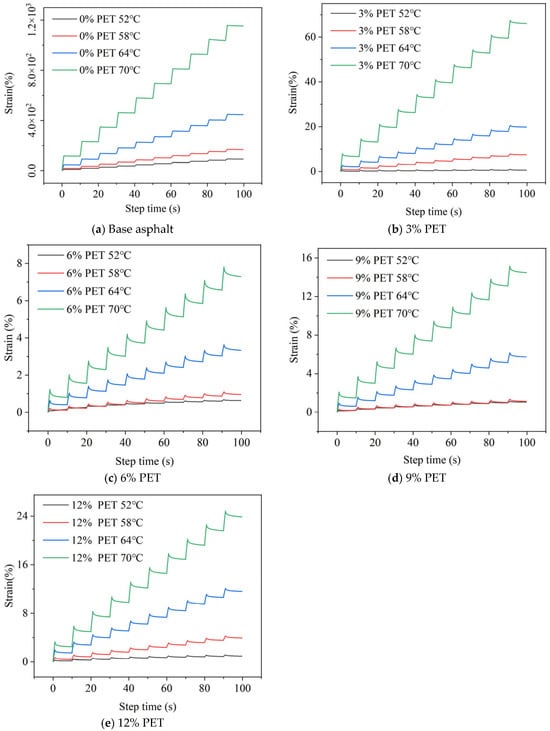
Figure 8.
Repeated creep recovery with different waste PET contents.
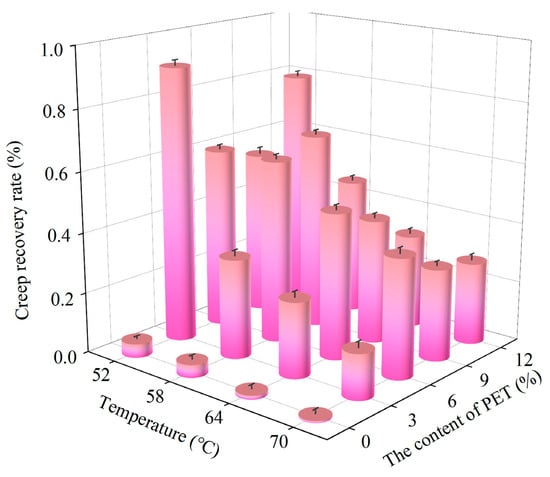
Figure 9.
Creep recovery rate.
Figure 8 shows that temperature has a significant impact on the results of repeated creep tests. As the temperature increases, the cumulative strain of asphalt increases. At 70 °C, the 20-cycle cumulative strains of waste PET-modified asphalt with 3%, 6%, 9%, and 12% additives were 5.73%, 0.63%, 1.25%, and 2.07% of the base asphalt, respectively. This indicates that the addition of waste PET can significantly improve the deformation resistance of the base asphalt, and has the minimum cumulative strain at a PET content of 6%.
From Figure 9, it can be seen that with the increase in waste PET content, the creep recovery of waste PET-modified asphalt under medium temperature conditions (52 °C) first increases, then decreases, and then increases again. The creep recovery under high-temperature conditions (58 °C, 64 °C, and 70 °C) first increases and then decreases. Under 58 °C, the creep recovery rate is the best when the content is 3%, with a creep recovery rate of 63.63%. At 64 °C and 70 °C, the modified asphalt with a dosage of 6% had the best creep recovery rates, which are 53.12% and 43.54%, respectively. Considering the high-temperature environment of asphalt pavement in the summer, 6% PET-modified asphalt has good creep recovery ability.
3.4. BBR Test
The creep stiffness (S) of waste PET-modified asphalt under different contents and temperatures is shown in Figure 10 to evaluate the low-temperature performance of PET-modified asphalt.
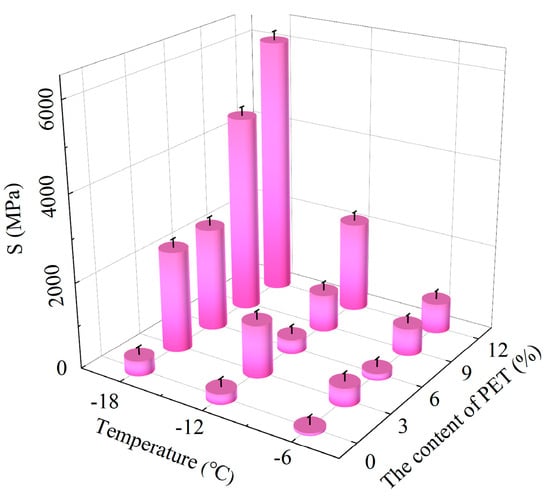
Figure 10.
The creep stiffness (S) of waste PET-modified asphalt.
The creep stiffness of waste PET-modified asphalt shows a gradually increasing trend with decreasing temperature. It indicates that the brittleness of asphalt becomes greater and cracking is more likely to occur as the temperature decreases. As the PET content increases, the creep stiffness of waste PET-modified asphalt under different temperatures shows a trend of first increasing, then decreasing, and finally increasing. The creep stiffness of waste PET-modified asphalt is the smallest with a PET content of 6%. This indicates that the brittleness of asphalt is the weakest, and the low-temperature crack resistance of asphalt is the strongest under the amount of waste PET of 6%. Considering the high-temperature and low-temperature performance of waste PET-modified asphalt, 6% is recommended as the optimal dosage for waste PET-modified asphalt.
3.5. Modification Mechanism of Waste PET-Modified Asphalt
3.5.1. SEM
Based on the principle of secondary electron imaging, the microscopic true appearance of an object can be observed through SEM. The distribution of waste PET in the matrix asphalt can be observed. The scanning electron microscopy results of waste PET-modified asphalt are shown in Figure 11.

Figure 11.
SEM image.
From Figure 11a, it can be observed the surface of the base asphalt is smooth and free of impurities. This indicates that the homogeneity of the base asphalt is good, approaching a homogeneous structure. Compared with the SEM of base asphalt, the boundary between waste PET and asphalt is more blurred. Waste PET and asphalt adhere to each other. The swollen waste PET forms a network structure in asphalt, and waste PET forms a tighter connection with asphalt (Figure 11b). This increases the dispersion of waste plastics in asphalt. The fluidity of asphalt has been reduced, which has improved the road performance of modified bitumen []. The proportion of waste PET in the asphalt area was calculated using ImageJ2, which is a scientific image analysis tool widely used in the field of biological research, and the results showed that the proportion of waste plastic area exceeded 12% []. This indicates that the swollen waste PET has been evenly distributed in the asphalt.
3.5.2. XRD
The results of the X-ray diffraction analysis are presented in Figure 12. The data reveal the presence of characteristic diffraction peaks for waste PET-modified asphalt at approximately 2θ = 20°. This observation suggests that waste PET is incorporated into the base asphalt matrix via physical adsorption. This is consistent with the analysis results of the scanning electron microscope.
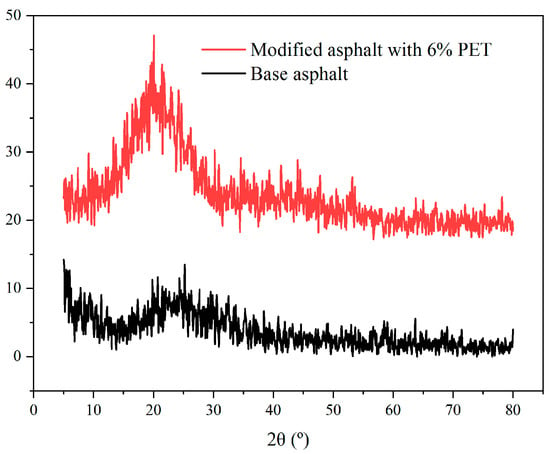
Figure 12.
X-ray diffraction of base asphalt and 6% waste PET-modified asphalt.
3.5.3. FTIR
Infrared spectra of base asphalt and PET-modified asphalt are tested separately to clarify the mechanism of PET-modified asphalt, as shown in Figure 13.
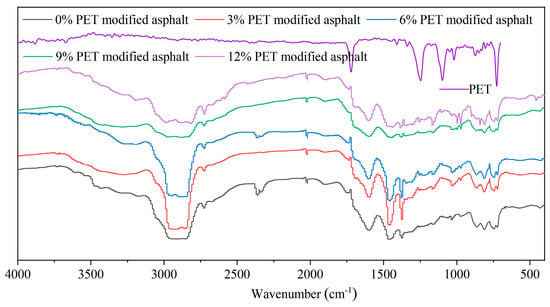
Figure 13.
FTIR spectrum for waste PET-modified asphalt.
From Figure 13, it can be observed the functional group vibration of PET mainly occurs in the low-frequency range. At 727 cm−1, there is an out-of-plane bending vibration of the C-H bond on the benzene ring. C-O undergoes stretching vibration at 1262 cm−1. At 1723 cm−1, there is a stretching vibration of the carbonyl C = O. The out-of-plane vibration of CH2 is at 1370 cm−1. Both 1018 cm−1 and 1024 cm−1 are bending vibrations in the C-H plane on the benzene ring [].
The base asphalt is mainly a mixture of elemental carbon and various hydrocarbons. The C-H stretching vibration absorption peaks of cycloalkanes and alkanes are located at 2990–2850 cm−1. The angular vibration absorption peaks of CH3 and CH2 are 1450 cm−1 and 1370 cm−1, respectively. The angular vibration absorption peaks of CH3 and CH2 are located at 900–700 cm−1. Compared with the base asphalt, the C = C double bond at 1600 cm−1 of PET-modified asphalt becomes weaker, and a new absorption peak appears at 1700 cm−1 and gradually increases. This is mainly caused by the stretching vibration of the carboxylic acid carbonyl C = O in PET. In addition, a new absorption peak appeared at 1300 cm−1, mainly caused by the stretching vibration of C-O-C in PET []. Apart from the characteristic peak of ester groups in the PET reaction mentioned above, no other new characteristic peaks are generated. This indicates that there is no chemical reaction between waste PET plastic and bitumen. The modification mainly involves physical mixing of the two materials.
3.5.4. DSC
According to Section 2.2.7, the heat flow curves of waste PET, 6% PET-modified asphalt, and asphalt mortar were tested as shown in Figure 14.
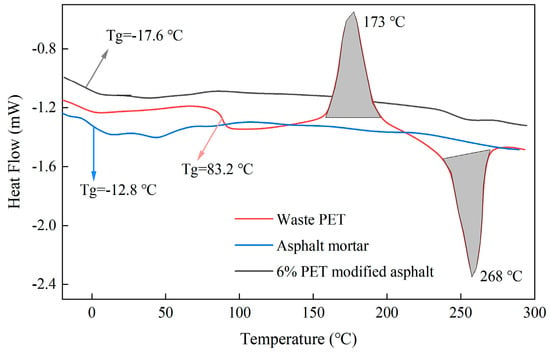
Figure 14.
DSC for waste PET-modified asphalt.
As shown in Figure 14, the glass transition temperature (Tg) of waste PET is 83.2 °C, and there is a crystallization peak and a melting peak present in the waste PET. The crystallization peak appears at 173 °C, with a heat release of 11.4 J/g. The melting peak appears at 268 °C, with a heat absorption of approximately 12.4 J/g. The glass transition temperature of asphalt emulsion is −12.8 °C, and the glass transition temperature of waste PET-modified asphalt is −17.6 °C. Compared to asphalt emulsion, the addition of waste PET reduced the glass transition temperature of asphalt by 37.5%.
4. Conclusions
To reduce environmental concerns related to PET waste and to strengthen the properties of base asphalt, the road performance and a mechanistic analysis of asphalt modified with waste PET were investigated. Rheological properties were characterized using DSR and BBR. The modification mechanisms were analyzed by SEM, XRD, FTIR, and DSC tests. Performance evaluation indicators were developed based on the theory of fractional derivatives.
The following conclusions were derived from the experimental results: (1) incorporating waste PET into asphalt enhanced its stability at elevated temperatures; however, it diminished its resistance to cracking under low temperature conditions. Taking into account the stability and resistance to cracking of modified bitumen, the best road performance was achieved with a waste PET content of 6%. (2) The deformation factor and viscoelasticity factor for waste PET-modified asphalt were developed based on the theory of fractional derivatives. A reduced deformation factor correlates with enhanced stability of modified bitumen under elevated temperatures. (3) Compared with original asphalt, the absorption peak position of waste PET-modified bitumen remained almost unchanged, and no absorption peak of new reaction compounds appeared. The mixing of waste PET with asphalt mainly involved physical adsorption and the establishment of a spatial network structure. The deformation resistance and elastic response of waste PET-modified asphalt were improved.
Although we have performed some beneficial work to expand the application scope of waste plastics, there are still some issues that need further research. For example, the fractional derivative theory should be applied to SBS-modified asphalt or rubber powder modified asphalt to expand the application scope of the fractional derivative theory in modified asphalt. In addition, validation tests should be conducted to expand the application of the fractional derivative constitutive model in asphalt mixtures or pavement performance in the future.
Author Contributions
Conceptualization, R.L. and M.W.; methodology, R.L. and Y.S.; validation, R.L., D.T. and M.W.; formal analysis, R.L., D.T., Y.S., F.M. and Y.Y.; investigation, L.L. and D.T.; writing—original draft preparation, R.L., D.T., M.W. and L.L.; writing—review and editing, R.L., M.W. and L.L. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This research was supported by the Science and Technology Research Project of Henan Province, grant number 252102230140; This project was supported by Open Research Fund Program of Henan Key Laboratory of Engineering Materials and Hydraulic Structures, grant number HNEMHS_OF202402.
Institutional Review Board Statement
Not applicable.
Informed Consent Statement
This research does not involve human beings.
Data Availability Statement
The original contributions presented in this study are included in the article. Further inquiries can be directed to the corresponding author.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
References
- Ilyas, M.; Ahmad, W.; Khan, H.; Yousaf, S.; Khan, K.; Nazir, S. Plastic waste as a significant threat to environment—A systematic literature review. Rev. Environ. Health 2018, 33, 383–406. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pan, D.; Su, F.; Liu, C.; Guo, Z. Research progress for plastic waste management and manufacture of value-added products. Adv. Compos. Hybrid. Mater. 2020, 3, 443–461. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fayshal, M.A. Current practices of plastic waste management, environmental impacts, and potential alternatives for reducing pollution and improving management. Heliyon 2024, 23, e40838. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Santos, G.; Esmizadeh, E.; Riahinezhad, M. Recycling construction, renovation, and demolition plastic waste: Review of the status quo, challenges and opportunities. J. Polym. Environ. 2024, 32, 479–509. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rafey, A.; Siddiqui, F.Z. A review of Plastic Waste Management in India–challenges and opportunities. Int. J. Environ. Anal. Chem. 2021, 103, 3971–3987. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dauvergne, P. Why is the global governance of plastic failing the oceans? NATO Adv. Sci. Inst. Ser. 2018, 51, 22–31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, C.; Nakamura, S. Approaches to solving China’s marine plastic pollution and CO2 emission problems. Econ. Syst. Res. 2019, 31, 143–157. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shu, X.; Huang, B.S. Recycling of waste tire rubber in asphalt and Portland cement concrete: An overview. Constr. Build. Mater. 2014, 67, 217–224. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Victory, W. A review on the utilization of waste material in asphalt pavements. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2022, 29, 27279–27282. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Y.; Awasthi, A.K.; Wei, F.; Tan, Q.; Li, J. Single-use plastics: Production, usage, disposal, and adverse impacts. Total Environ. 2021, 752, 141772. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tournier, V.; Topham, C.M.; Gilles, A.; David, B.; Folgoas, C.; Moya-Leclair, E.; Kamionka, E.; Desrousseaux, M.L.; Texier, H.; Gavalda, S.; et al. An engineered PET depolymerase to break down and recycle plastic bottles. Nature 2020, 580, 216–219. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Richard, C.T.; Ylvaolsen; Richard, P.M.; Anthony, D.; Steven, J.R.; Anthony, W.G.J.; Mcgonigle, D.; Russell, A.E. Lost at sea: Where is all the plastic? Science 2004, 304, 838. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jambeck, J.R.; Geyer, R.; Wilcox, C.; Theodore, R.S.; Perryman, M.; Andrady, A.; Narayan, R.; Law, K.L. Plastic waste inputs from land into the ocean. Science 2015, 347, 768–771. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Benyathiar, P.; Kumar, P.; Carpenter, G.; Brace, J.; Mishra, D.K. Polyethylene terephthalate (PET) bottle-to-bottle recycling for the beverage industry: A review. Polymers 2022, 14, 2366. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Airey, G.D.; Mohammed, M.H.; Fichter, C. Rheological characteristics of synthetic road binders. Fuel 2008, 87, 1763–1775. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, X.Y.; Shen, A.Q.; Ma, B.F. Temperature adaptability of asphalt pavement to high temperatures and significant temperature differences. Adv. Mater. Sci. Eng. 2018, 1, 9436321. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mirzaaghaeian, E.; Modarres, A. Rheological properties of bituminous mastics containing chemical warm additive at medium temperatures and its relationship to warm mix asphalt fatigue behavior. Constr. Build. Mater. 2019, 225, 44–54. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lesueur, D.; Petit, J.; Ritter, H.J. The mechanisms of hydrated lime modification of asphalt mixtures: A state-of-the-art review. Road Mater. Pavement Des. 2016, 14, 1–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Airey, G.D. Rheological properties of styrene butadiene styrene polymer modified road bitumens. Fuel 2003, 82, 1709–1719. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Raul, V.; Hussain, B. Critical factors affecting thermal cracking of asphalt pavements: Towards a comprehensive specification. Road Mater. Pavement 2013, 14, 187–200. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahmadinia, E.; Zargar, M.; Karim, M.R.; Abdelaziz, M.; Ahmadinia, M. Performance evaluation of utilization of waste polyethylene terephthalate (PET) in stone mastic asphalt. Constr. Build. Mater. 2012, 36, 984–989. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ghabchi, R.; Dharmarathna, C.P.; Mihandoust, M. Feasibility of using micronized recycled polyethylene terephthalate (PET) as an asphalt binder additive: A laboratory study. Constr. Build. Mater. 2021, 292, 123377. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oreto, C.; Russo, F.; Veropalumbo, R.; Viscione, N.; Biancardo, S.A.; Acqua, G.D. Life cycle assessment of sustainable asphalt pavement solutions involving recycled aggregates and polymers. Materials 2021, 14, 3867. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, H.; Zhang, Z.P.; Yu, X.H.; Kan, S.Y.; Luo, Y.; Han, K.B.; Liang, Y.Z.; Gao, J.P. Preparation of polyol from waste polyethylene terephthalate (PET) and its application to polyurethane (PU) modified asphalt. Constr. Build. Mater. 2024, 427, 136286. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, C.H.; Hu, K.; Chen, Y.J.; Zhang, W.G.; Chen, Y.; Chang, R. Compatibility and high temperature performance of recycled polyethylene modified asphalt using molecular simulations. Mol. Simulat. 2021, 47, 1037–1049. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mashaan, N.S.; Chegenizadeh, A.; Nikraz, H.; Rezagholilou, A. Investigating the engineering properties of asphalt binder modified with waste plastic polymer. Ain Shams Eng. J. 2021, 12, 1569–1574. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, C.W.; Jing, F.; Yang, H.C.; Li, C.X.; Xi, Z.H.; Cai, J.; Wang, Q.J.; Xie, H.F. Epoxy asphalt binder reinforced with waste polyethylene terephthalate (PET) for improving toughness. Int. J. Pavement Eng. 2024, 25, 2400547. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, H.; Zhang, S.Y.; Zhang, Z.P.; Yu, L.; Mao, Z.Y.; Kan, S.Y.; Yu, X.H.; Wang, J.J. Anti-ageing performance and mechanisms of the modified asphalt with chemically recycled products from waste polyethylene terephthalate (PET). J. Environ. Chem. Eng. 2024, 12, 114891. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mohanta, C.S.; Sreeram, A.; Yadav, V.; Padhan, R.K.; Raman, N.S.; Badoni, R.P. Synergic effect of waste PET and sebacic acid on the rheology of crumb rubber modified bitumen. Int. J. Pavement Eng. 2021, 22, 1143–1154. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aldagari, S.; Kabir, S.F.; Fini, E.H. Investigating aging properties of bitumen modified with polyethylene-terephthalate waste plastic. Resour. Conserv. Recy 2021, 173, 105687. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sajed, B.; Jamal, R.; Mahmoud, A.; Ali, M. Mechanical performance of asphalt mixture containing eco-friendly additive by recycling PET. Case Stud. Constr. Mat. 2024, 20, e02740. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Odubela, C.A.; Yaacob, H.; Warid, M.N.; Karim, K.J.; Kamaruddin, N.H.; Al-Saffar, Z.H.; Rahim, M.I. Rheological and chemical properties of reclaimed asphalt pavement using polyethylene terephthalate (PET) additive as a modifier. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2025, 32, 8025–8034. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Arshadi, M.; Hasan, T.; Saeed, Z. Laboratory investigation on the properties of asphalt concrete containing reclaimed asphalt pavement (RAP) and waste polyethylene terephthalate (PET). Int. J. Pavement Eng. 2024, 25, 2371438. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bagley, R.L. Power law and fractional calculus model of viscoelasticity. AIAA J. 1989, 27, 1412–1417. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lai, J.X.; Mao, S.; Qiu, J.L.; Fan, H.B.; Zhang, Q.; Hu, Z.N.; Chen, J.X. Investigation progresses and applications of fractional derivative model in geotechnical engineering. Math. Probl. Eng. 2016, 1, 9183296. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Celauro, C.; Fecarotti, C.; Pirrotta, A.; Collop, A.C. Experimental validation of a fractional approach for creep/recovery testing of asphalt mixtures. Constr. Build. Mater. 2012, 36, 458–466. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, R.; Yue, J.; Feng, S.; Luo, H.; Wang, T. Improved fractional order derivative empirical power function model for describing the creep of asphalt mortar. J. Build. Mater. 2015, 18, 237–242. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Assel, J.; Marat, K.; Lyazat, A.; Akpan, K.; Lailya, Z. Performance optimization approach of polymer-modified asphalt mixtures with PET and PE waste. Polymers 2024, 16, 3308. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Teyba, W.M.; Sanjaya, S.; Tewodros, G. Effect of pet size, content, and mixing process on the rheological characteristics of flexible pavement. Materials 2022, 15, 3565. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, G.F.; Ma, J.Y.; Xu, X.; Pu, T.H.; He, Y.M.; Zhang, Q. Performance evaluation of using waste polyethylene terephthalate (PET) derived additives for asphalt binder modification. Waste Biomass Valor. 2025, 16, 601–611. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Celauro, C.; Di Paola, M.; Lo Presti, D.; Pirrotta, A. Modeling of the viscoelastic behavior of paving bitumen fractional derivatives. Mecc. Dei Mater. Delle Strutt. 2009, 1, 38–51. (accessed on 5 March 2025.). [Google Scholar]
- Rabindra, K.P.; Zhen, L.; Anand, S.; Xiong, X. Compound modification of asphalt with styrene-butadiene-styrene and waste polyethylene terephthalate functionalized additives. J. Clean. Prod. 2020, 277, 124286. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vydra, M.; Kováčik, J. The use of image analysis in improving knowledge and skills on the example of teaching the biology of algae and fungi. Educ. Inf. Technol. 2025, 30, 4825–4841. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tomasz, M.M.; Krzysztof Adam, O.; Marcin, P. Research on the development of a way to modify asphalt mixtures with PET recyclates. Materials 2023, 16, 6258. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).