Fabrication of pH-Responsive PDPAEMA Thin Film Using a One-Step Environmentally Friendly Plasma Enhanced Chemical Vapor Deposition
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Materials
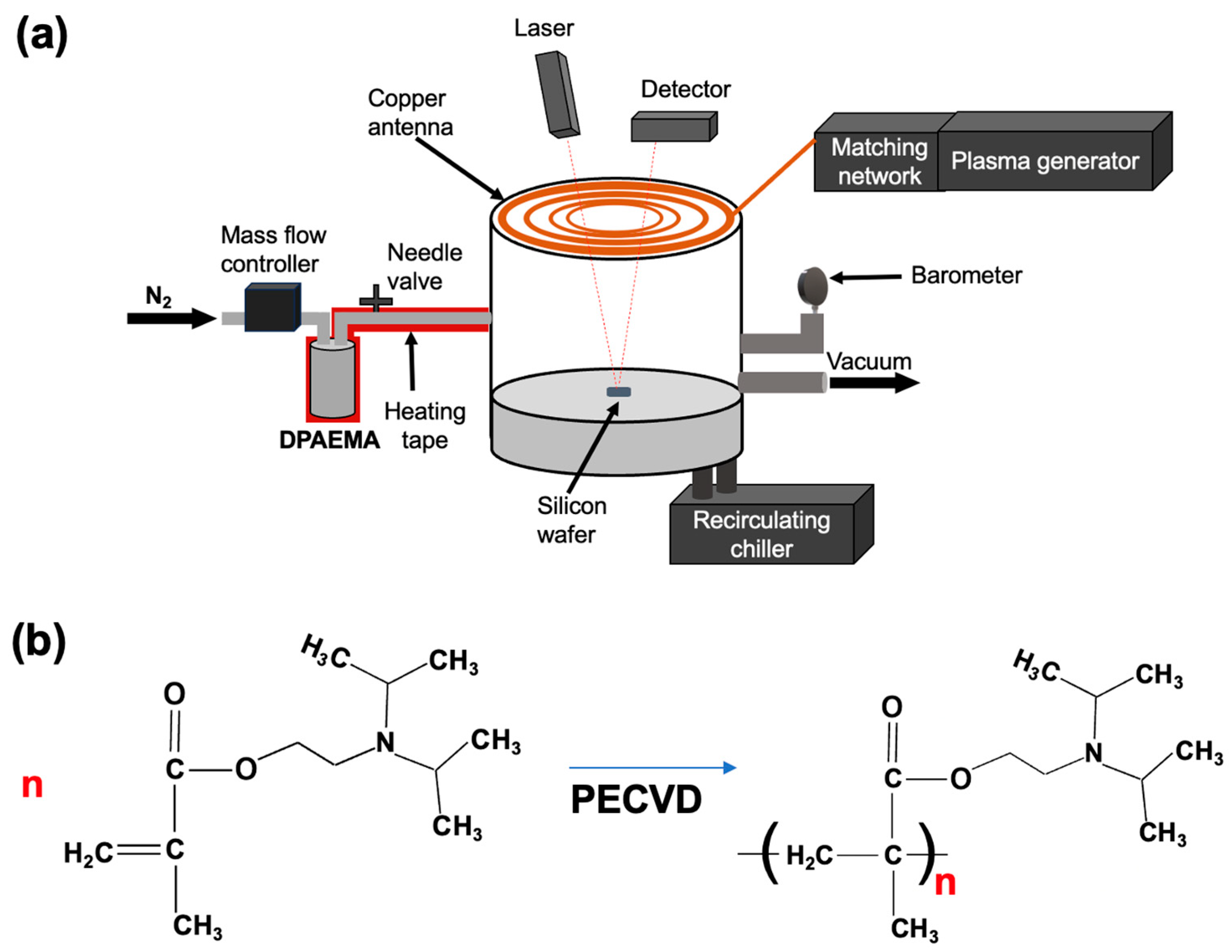
2.2. Thin Film Synthesis by PECVD
2.3. Characterizations
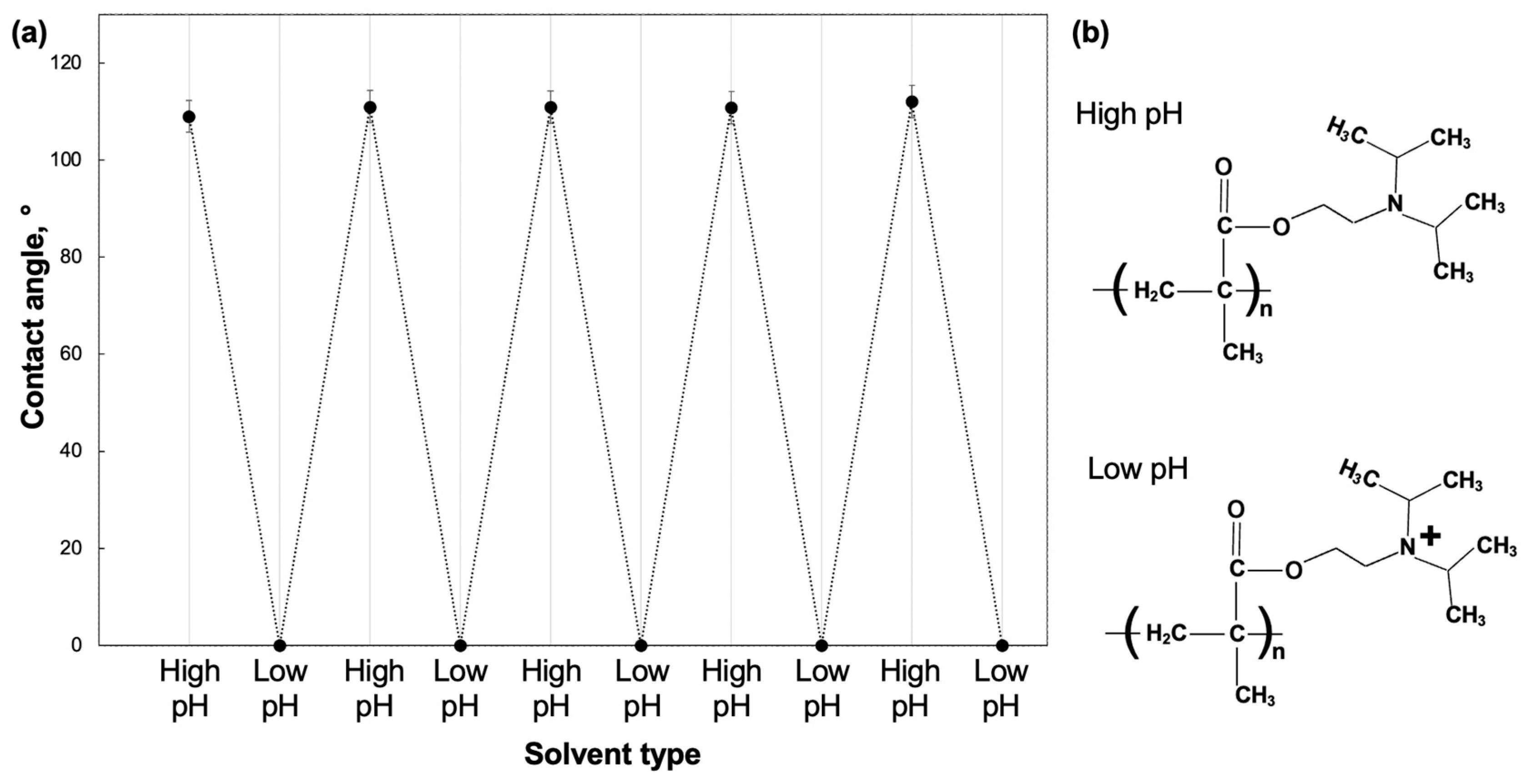
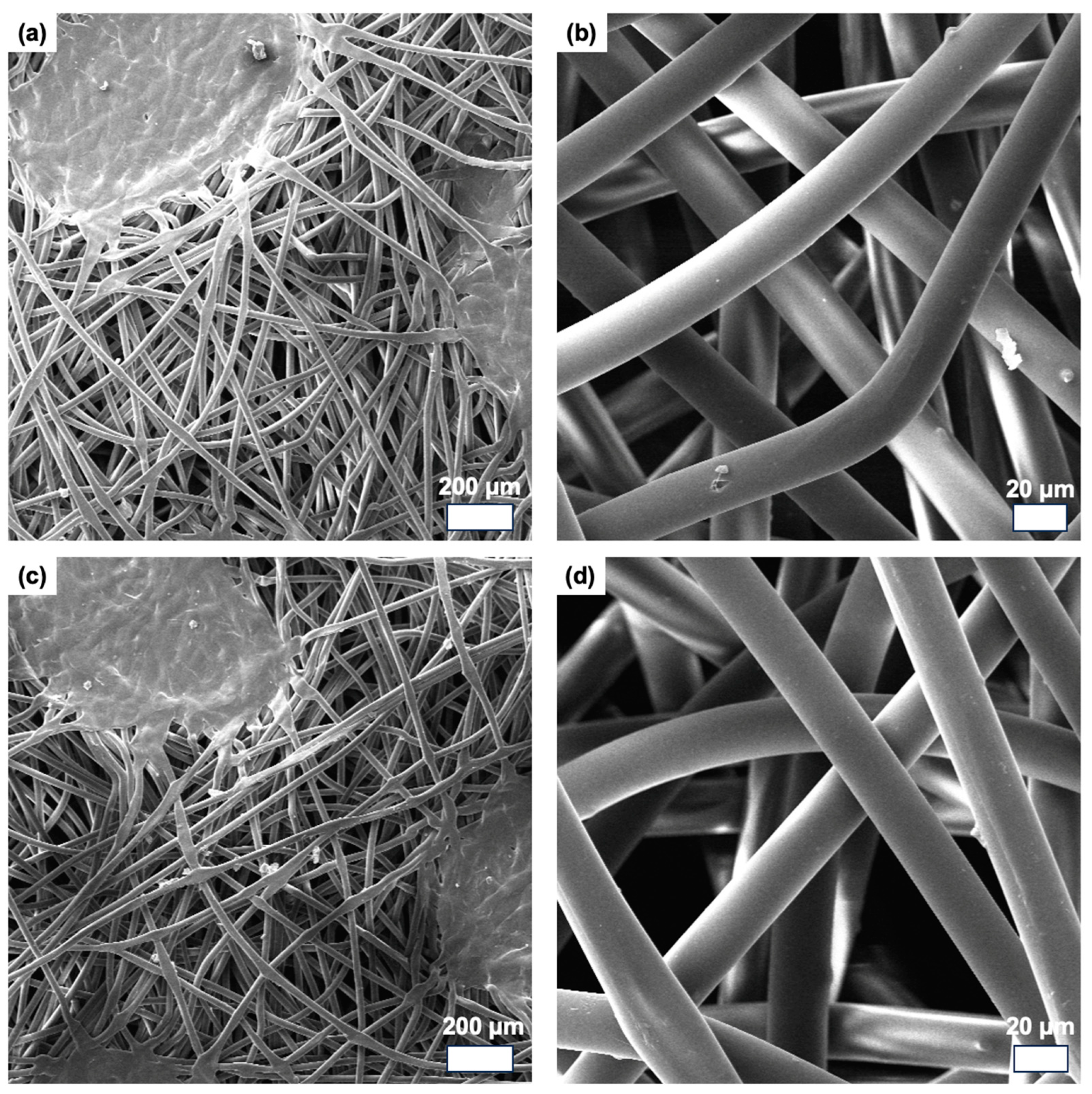
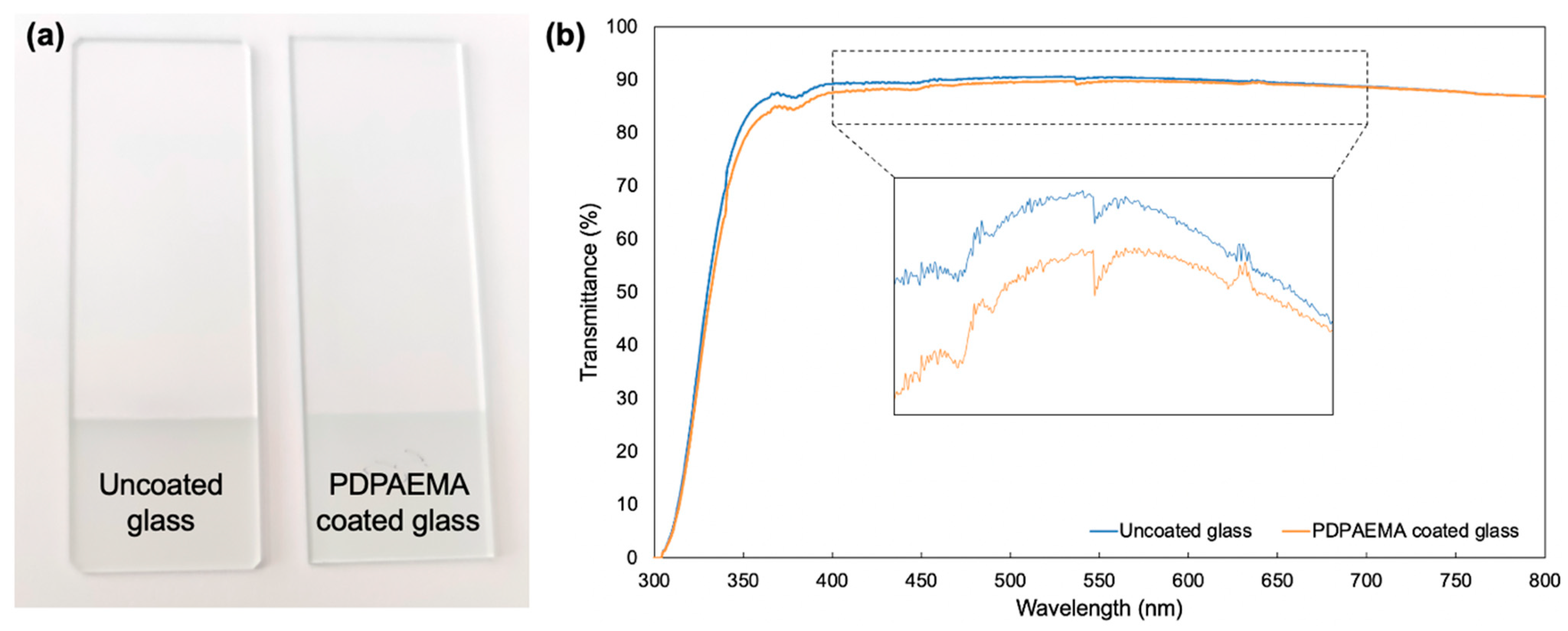
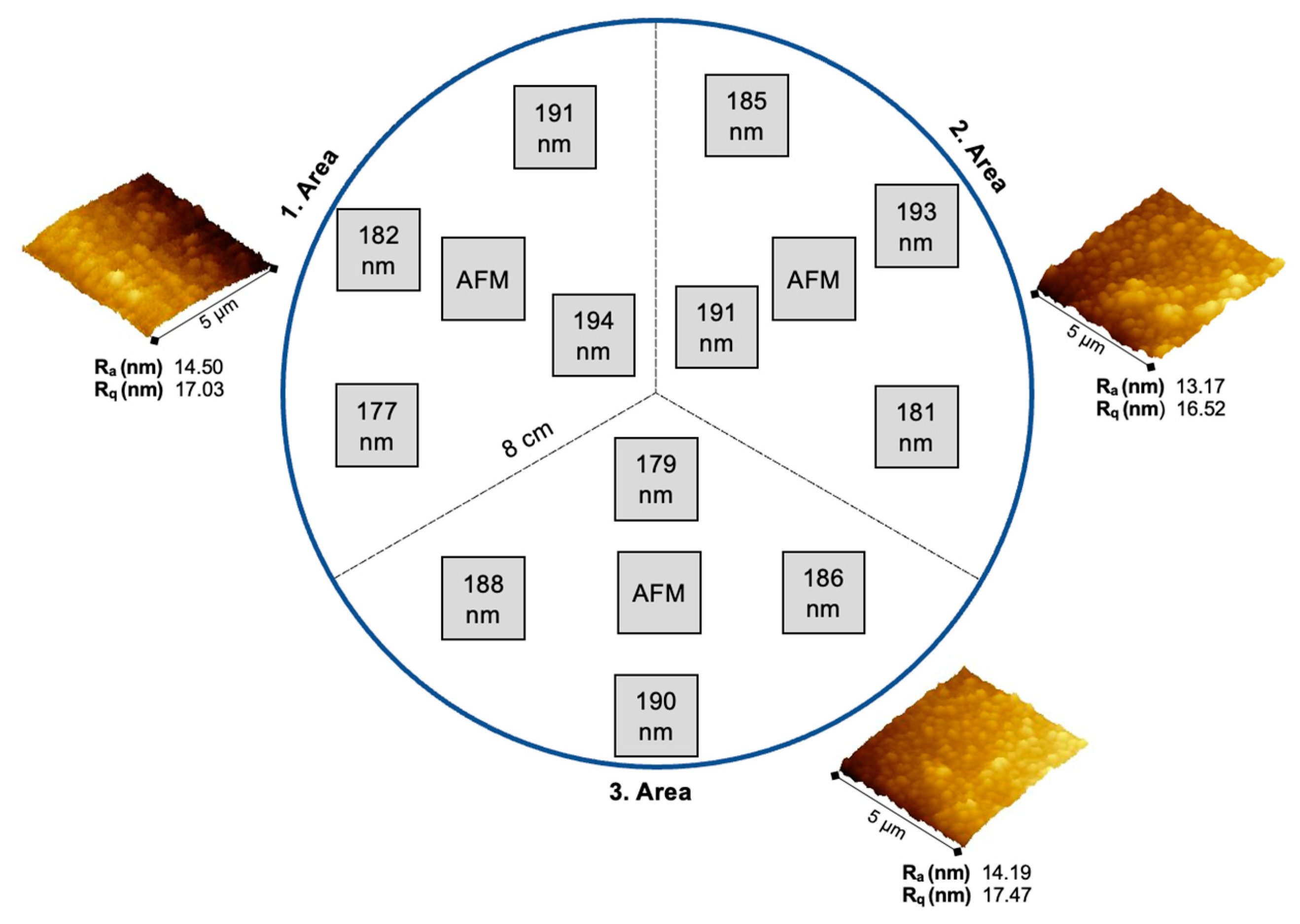
3. Results and Discussion
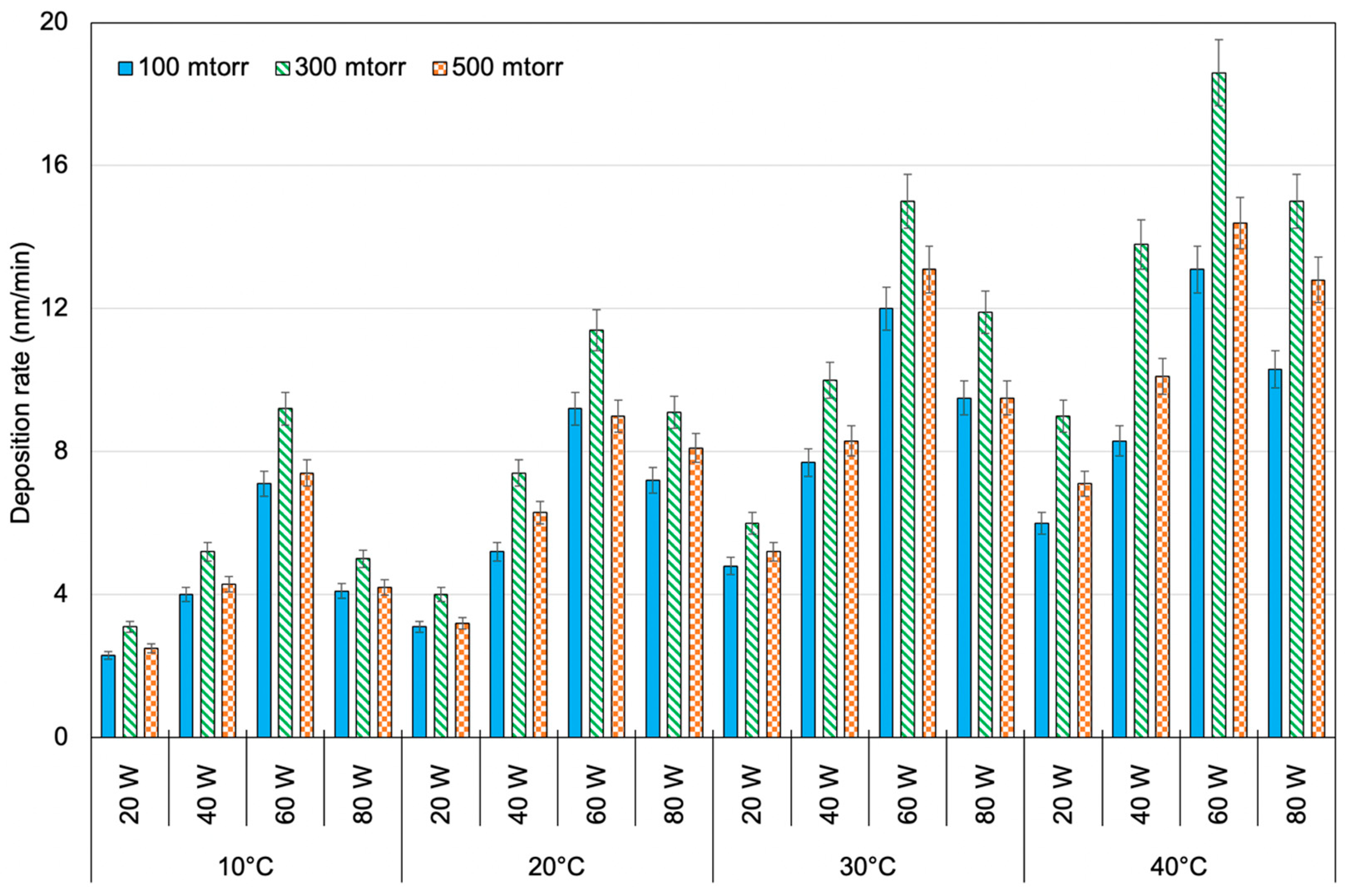
3.1. Deposition Rates
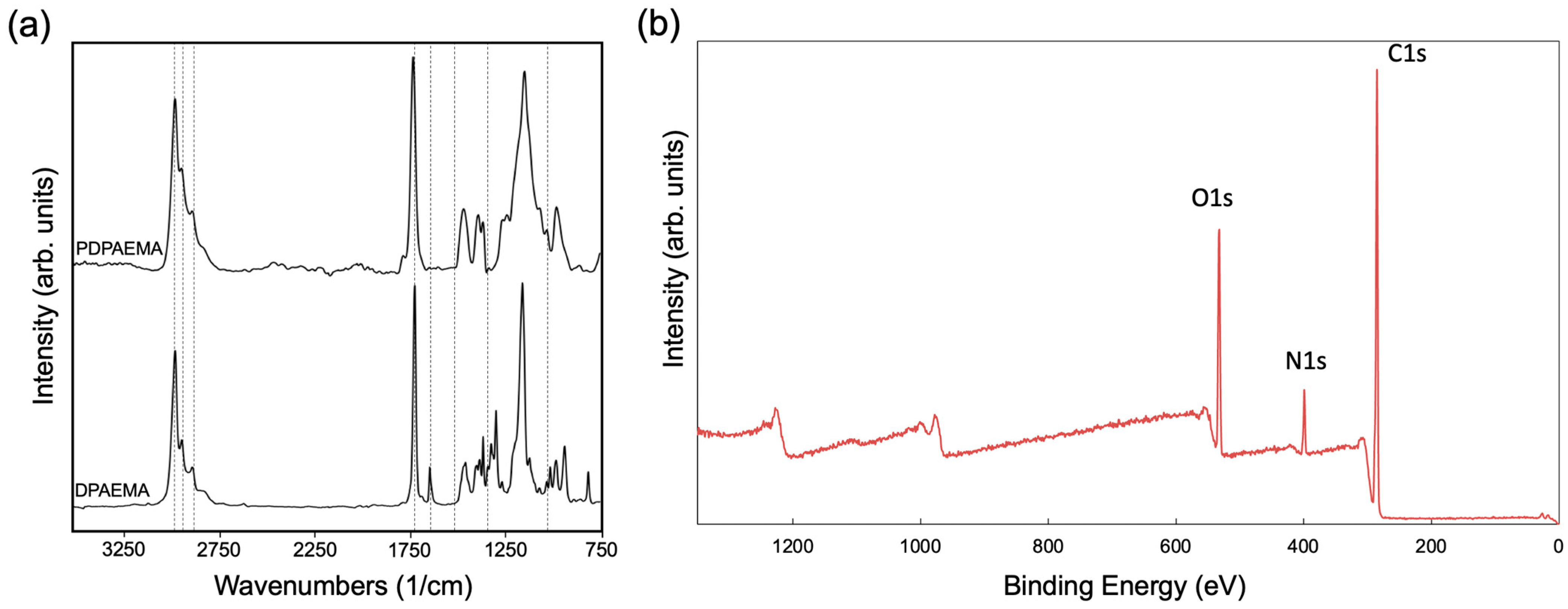
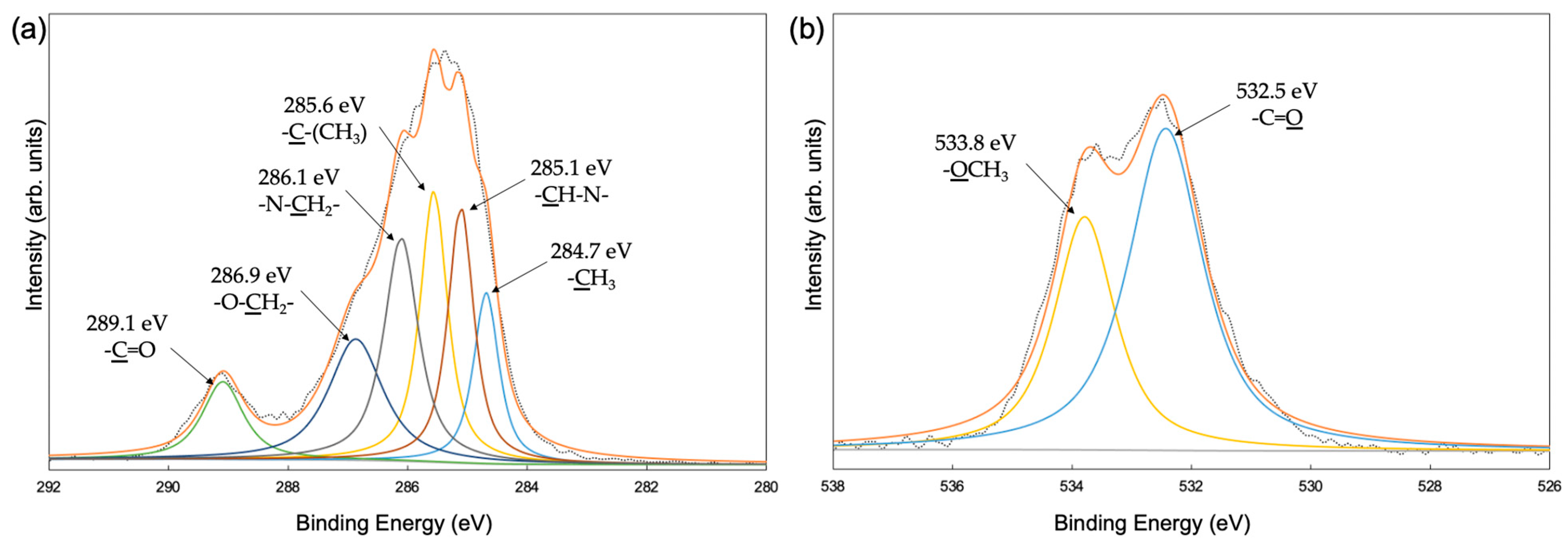
3.2. Film Structures
3.3. Large-Scale Deposition
4. Conclusions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Png, Z.M.; Wang, C.-G.; Yeo, J.; Lee, J.J.C.; Surat’man, N.E.B.; Tan, Y.L.; Liu, H.; Wang, P.; Tan, M.B.H.; Xu, J.; et al. Stimuli-responsive Structure-Property Switchable Polymer Materials. Mol. Syst. Des. Eng. 2023, 8, 1097–1129. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wurm, F.R.; Boyer, C.; Sumerlin, B.S. Progress on Stimuli-Responsive Polymers. Macromol. Rapid Commun. 2021, 42, 2100512. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gao, Y.; Wei, M.; Li, X.; Xu, W.; Ahiabu, A.; Perdiz, J.; Liu, Z.; Serpe, M.J. Stimuli-responsive polymers: Fundamental considerations and applications. Macromol. Res. 2017, 25, 513–527. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Siniscalco, D.; Pessoni, L.; Boussonnière, A.; Castanet, A.-S.; Billon, L.; Vignaud, G.; Delorme, N. Design of an Azopolymer for Photo-Switchable Adhesive Applications. Coatings 2024, 14, 275. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guisasola, E.; Baeza, A.; Talelli, M.; Arcos, D.; Moros, M.; de la Fuente, J.M.; Vallet-Regi, M. Magnetic-responsive release controlled by hot spot effect. Langmuir 2015, 31, 12777–12782. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Stamou, A.; Iatrou, H.; Tsitsilianis, C. NIPAm-based modification of poly (L-lysine): A pH-dependent LCST-type thermo-responsive biodegradable polymer. Polymers 2022, 14, 802. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jing, H.; Huang, X.; Du, X.; Mo, L.; Ma, C.; Wang, H. Facile synthesis of pH-responsive sodium alginate/carboxymethyl chitosan hydrogel beads promoted by hydrogen bond. Carbohydr. Polym. 2022, 278, 118993. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yusa, S.-I. Development and application of pH-responsive polymers. Polym. J. 2022, 54, 235–242. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ofridam, F.; Tarhini, M.; Lebaz, N.; Gagnière, É.; Mangin, D.; Elaissari, A. pH-sensitive polymers: Classification and some fine potential applications. Polym. Adv. Technol. 2021, 32, 1455–1484. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kocak, G.; Tuncer, C.; Bütün, V. pH-Responsive polymers. Polym. Chem. 2017, 8, 144–176. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bazban-Shotorbani, S.; Hasani-Sadrabadi, M.M.; Karkhaneh, A.; Serpooshan, V.; Jacob, K.I.; Moshaverinia, A.; Mahmoudi, M. Revisiting structure-property relationship of pH-responsive polymers for drug delivery applications. J. Control. Release 2017, 253, 46–63. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, L.; Ren, K.-F.; Wang, H.-B.; Wang, Y.; Ji, J. pH-sensitive controlled release of doxorubicin from polyelectrolyte multilayers. Colloids Surf. B Biointerfaces 2015, 125, 127–133. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhu, L.; Smith, P.P.; Boyes, S.G. pH-responsive polymers for imaging acidic biological environments in tumors. J. Polym. Sci. Part B Polym. Phys. 2013, 51, 1062–1067. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, J.; Zhang, G.; Ge, Z.; Liu, S. Stimuli-responsive tertiary amine methacrylate-based block copolymers: Synthesis, supramolecular self-assembly and functional applications. Prog. Polym. Sci. 2014, 39, 1096–1143. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gorji, M.; Zarbaf, D.; Mazinani, S.; Noushabadi, A.S.; Cella, M.A.; Sadeghianmaryan, A.; Ahmadi, A. Multi-responsive on-demand drug delivery PMMA-co-PDEAEMA platform based on CO2, electric potential, and pH switchable nanofibrous membranes. J. Biomater. Sci. Polym. Ed. 2023, 34, 351–371. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Eygeris, Y.; Ulery, N.; Zharov, I. pH-Responsive Membranes from Self-Assembly of Poly (2-(dimethylamino) ethyl methacrylate) Brush Silica Nanoparticles. Langmuir 2023, 39, 15792–15798. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kongkatigumjorn, N.; Smith, S.A.; Chen, M.; Fang, K.; Yang, S.; Gillies, E.R.; Johnston, A.P.; Such, G.K. Controlling endosomal escape using pH-responsive nanoparticles with tunable disassembly. ACS Appl. Nano Mater. 2018, 1, 3164–3173. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Echalier, C.; Jebors, S.; Laconde, G.; Brunel, L.; Verdié, P.; Causse, L.; Bethry, A.; Legrand, B.; Van Den Berghe, H.; Garric, X. Sol–gel synthesis of collagen-inspired peptide hydrogel. Mater. Today 2017, 20, 59–66. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Amano, M.; Uchiyama, M.; Satoh, K.; Kamigaito, M. Sulfur-Free Radical RAFT Polymerization of Methacrylates in Homogeneous Solution: Design of exo-Olefin Chain-Transfer Agents (R−CH2C(=CH2)Z). Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2022, 61, e202212633. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, X.; Wyman, I.; Zhang, G.; Lin, J.; Liu, Z.; Wang, Y.; Hu, H. Preparation of superamphiphobic polymer-based coatings via spray-and dip-coating strategies. Prog. Org. Coat. 2016, 90, 463–471. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, X.; Yang, W.; Yang, Y.; Wang, X.; Liu, X.; Zhou, F.; Zhao, Y. Subsurface-initiated atom transfer radical polymerization: Effect of graft layer thickness and surface morphology on antibiofouling properties against different foulants. J. Mater. Sci. 2020, 55, 14544–14557. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gosar, Ž.; Kovač, J.; Mozetič, M.; Primc, G.; Vesel, A.; Zaplotnik, R. Deposition of SiOxCyHz protective coatings on polymer substrates in an industrial-scale PECVD reactor. Coatings 2019, 9, 234. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gürsoy, M.; Kocadayıoğulları, B. Environmentally Friendly Approach for the Plasma Surface Modification of Fabrics for Improved Fog Harvesting Performance. Fibers Polym. 2023, 24, 3557–3567. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Karaman, M.; Gürsoy, M.; Aykül, F.; Tosun, Z.; Kars, M.D.; Yildiz, H.B. Hydrophobic coating of surfaces by plasma polymerization in an RF plasma reactor with an outer planar electrode: Synthesis, characterization and biocompatibility. Plasma Sci. Technol. 2017, 19, 085503. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gürsoy, M.; Uçar, T.; Tosun, Z.; Karaman, M. Initiation of 2-hydroxyethyl methacrylate polymerization by tert-butyl peroxide in a planar PECVD system. Plasma Process. Polym. 2016, 13, 438–446. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saenger, K.; Tong, H. Laser interferometry: A measurement technique for diffusion studies in thin polymer films. Polym. Eng. Sci. 1991, 31, 432–435. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yasuda, H.; Wang, C. Plasma polymerization investigated by the substrate temperature dependence. J. Polym. Sci. Polym. Chem. Ed. 1985, 23, 87–106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- d’Agostino, R.; Cramarossa, F.; Fracassi, F.; Illuzzi, F. Plasma polymerization of fluorocarbons. Plasma Depos. Treat. Etch. Polym. 1990, 2, 95–162. [Google Scholar]
- Gürsoy, M.; Karaman, M. Improvement of wetting properties of expanded perlite particles by an organic conformal coating. Prog. Org. Coat. 2018, 120, 190–197. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wuu, D.; Lo, W.; Chang, L.; Horng, R.-H. Properties of SiO2-like barrier layers on polyethersulfone substrates by low-temperature plasma-enhanced chemical vapor deposition. Thin Solid Films 2004, 468, 105–108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ozaydin-Ince, G.; Gleason, K.K. Transition between kinetic and mass transfer regimes in the initiated chemical vapor deposition from ethylene glycol diacrylate. J. Vac. Sci. Technol. A 2009, 27, 1135–1143. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mercan, E.S.; Karaman, M. Coating of hydrophilic poly (hydroxypropyl methacrylate) thin films via pulsed-initiated chemical vapor deposition method. J. Coat. Technol. Res. 2021, 18, 1261–1268. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Karaman, M.; Gürsoy, M.; Kuş, M.; Özel, F.; Yenel, E.; Şahin, Ö.G.; Kivrak, H.D. Chemical and physical modification of surfaces. In Surface Treatments for Biological, Chemical, and Physical Applications; Wiley: Hoboken, NJ, USA, 2017; pp. 23–66. [Google Scholar]
- Mao, Y.; Gleason, K.K. Hot filament chemical vapor deposition of poly (glycidyl methacrylate) thin films using tert-butyl peroxide as an initiator. Langmuir 2004, 20, 2484–2488. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Martin, T.P.; Gleason, K.K. Combinatorial initiated CVD for polymeric thin films. Chem. Vap. Depos. 2006, 12, 685–691. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin-Vien, D.; Colthup, N.B.; Fateley, W.G.; Grasselli, J.G. The Handbook of Infrared and Raman Characteristic Frequencies of Organic Molecules; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 1991. [Google Scholar]
- Günzler, H.; Gremlich, H.-U. IR Spectroscopy. An Introduction; IAEA: Vienna, Austria, 2002. [Google Scholar]
- Gürsoy, M. Fabrication of paper-based microfluidic devices using PECVD for selective separation. Macromol. Res. 2021, 29, 423–429. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Biederman, H.; Slavınská, D. Plasma polymer films and their future prospects. Surf. Coat. Technol. 2000, 125, 371–376. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rupper, P.; Vandenbossche, M.; Bernard, L.; Hegemann, D.; Heuberger, M. Composition and stability of plasma polymer films exhibiting vertical chemical gradients. Langmuir 2017, 33, 2340–2352. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Beamson, G. High Relution XPS of Organic Polymers. The Scienta ESCA 300 Database. ICIplc; Wiley: Chichester, UK, 1992. [Google Scholar]
- Karaman, M.; Çabuk, N. Initiated chemical vapor deposition of pH responsive poly (2-diisopropylamino) ethyl methacrylate thin films. Thin Solid Films 2012, 520, 6484–6488. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fielding, L.A.; Edmondson, S.; Armes, S.P. Synthesis of pH-responsive tertiary amine methacrylate polymer brushes and their response to acidic vapour. J. Mater. Chem. 2011, 21, 11773–11780. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Giacomelli, F.C.; Stepánek, P.; Giacomelli, C.; Schmidt, V.; Jäger, E.; Jäger, A.; Ulbrich, K. pH-triggered block copolymer micelles based on a pH-responsive PDPA (poly [2-(diisopropylamino) ethyl methacrylate]) inner core and a PEO (poly (ethylene oxide)) outer shell as a potential tool for the cancer therapy. Soft Matter 2011, 7, 9316–9325. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheng, C.; Gupta, M. Roll-to-roll surface modification of cellulose paper via initiated chemical vapor deposition. Ind. Eng. Chem. Res. 2018, 57, 11675–11680. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shrestha, S.; Parajuli, S.; Park, J.; Yang, H.; Cho, T.-Y.; Eom, J.-H.; Cho, S.-K.; Lim, J.; Cho, G.; Jung, Y. Improving Stability of Roll-to-Roll (R2R) Gravure-Printed Carbon Nanotube-Based Thin Film Transistors via R2R Plasma-Enhanced Chemical Vapor-Deposited Silicon Nitride. Nanomaterials 2023, 13, 559. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]

| Parameter | Value |
|---|---|
| Substrate temperature (°C) | 10, 20, 30, and 40 |
| Reactor pressure (mtorr) | 100, 300, and 500 |
| Plasma power (W) | 20, 40, 60, and 80 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the author. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Gürsoy, M. Fabrication of pH-Responsive PDPAEMA Thin Film Using a One-Step Environmentally Friendly Plasma Enhanced Chemical Vapor Deposition. Coatings 2024, 14, 347. https://doi.org/10.3390/coatings14030347
Gürsoy M. Fabrication of pH-Responsive PDPAEMA Thin Film Using a One-Step Environmentally Friendly Plasma Enhanced Chemical Vapor Deposition. Coatings. 2024; 14(3):347. https://doi.org/10.3390/coatings14030347
Chicago/Turabian StyleGürsoy, Mehmet. 2024. "Fabrication of pH-Responsive PDPAEMA Thin Film Using a One-Step Environmentally Friendly Plasma Enhanced Chemical Vapor Deposition" Coatings 14, no. 3: 347. https://doi.org/10.3390/coatings14030347
APA StyleGürsoy, M. (2024). Fabrication of pH-Responsive PDPAEMA Thin Film Using a One-Step Environmentally Friendly Plasma Enhanced Chemical Vapor Deposition. Coatings, 14(3), 347. https://doi.org/10.3390/coatings14030347






