Abstract
Aluminum alloy (AA6061)-based hybrid metal matrix composites (HMMCs) are manufactured using a dual stir casting method, with varying volume percentages of B4C (5%, 10%, and 15%) and Gr (10%, 15%, and 20%) incorporated. The resulting HMMC and reinforcement elements are uniformly dispersed within the main matrix, forming a mechanically mixed layer with interfacial reactions. This layer reduces wear loss and friction coefficient compared to AA6061, especially with higher amounts of B4C and Gr, as they demonstrate little aggregation of reinforced material. The presence of Gr particles enabled the impact of different wear parameters (applied load, sliding speed, and distance) to be combined. Micro-hardness studies demonstrate that the hardness of HMMC increases as the volume fraction of reinforced particles and sliding distance increase. The compression test revealed a 22% improvement over AA6061. As a result, adding reinforcing materials to the matrix contributes to inducing greater strength by increasing wear resistance with a Gr-imparted lubrication effect.
1. Introduction
When aluminum alloy (AA) metal matrix composites (MMC) replace heavy ferrous metals, they exhibit desirable properties such as lightweight, high specific strength, elastic modulus, improved high-temperature performance, and antifriction behavior [1]. Hybrid composites, such as AA6061 matrix reinforced with B4C, have become increasingly important due to their improved mechanical and tribological properties, resulting from the synergistic effects of the constituent materials [2]. B4C is an effective reinforcing material because of its high hardness, stiffness, and low density. Combining B4C with AA results in a high-specific-strength product with superior wear resistance and thermal stability. However, the challenge lies in achieving good wetting between B4C particulates and molten AA at low temperatures, as this would enhance mechanical and physical properties such as stiffness, density, wear resistance, and hardness. Studies have shown that using larger particle sizes of B4C leads to improved microstructures without particle agglomeration [3]. Examining the interface of B4C particle-reinforced AA2024 MMCs reveals a refined microstructure with sub-grains as small as 400 nm [4]. As the volume percentage of particles increased in stir-cast A206/silica sand composites, the dendritic arm spacing decreased [5]. AA-B4C composites produced through accumulative roll bonding exhibit a uniform dispersion of B4C particles in the aluminum matrix [6]. The wear coefficient of AA6061 composites was calculated using Archard’s model, which closely aligns with experimental values compared to Yang’s model [7]. The sliding wear behavior of cast AA6061 composites with added Al2O3 particles shows that increasing the volume % of Al2O3 reduces both heat conductivity and friction coefficient [8]. The porosity level does not impact the composites’ wear rate (WR), as the hardness decreases with increasing porosity in AA composites reinforced with B4C, titanium boride, and silicon nitride ceramics [9].
The addition of graphite (Gr) to AA6061 increases wear resistance but reduces the mechanical strength of AA, despite Gr’s low strength [10]. Incorporating B4C into AA6061 results in increased corrosion resistance [11]. The mechanical and tribological behavior of AA7075-SiC with neem leaf ashes (containing high carbon content) is also examined, where the WR decreases. At the same time, the material strength increases due to the presence of silicon carbide [12]. The microstructure of AA 7075 undergoes significant changes when carbon nanoparticles are added, resulting in notable improvements in mechanical characteristics such as tensile and compression strength [13]. The wear characteristics of hybrid AA matrix composites reinforced with Gr and SiC particulates were found to be superior, along with their mechanical properties [14]. Adding 10% B4C in the AA MMC enhanced mechanical strength and reduced the wear rate [15]. The tribological behavior of AA6061 was analyzed by adjusting the weight percentages of carbon nanotube (CNT) and SiC using the stir casting process (SCP) [16]. The friction behavior of Al 6061-SiC-MWCNT was significantly affected by varying the load [17]. A scanning electron microscope (SEM) was used to perform a wear track microstructure analysis of AA5052 reinforced with 5% tungsten carbide, revealing that adding tungsten carbide reduced wear while maintaining constant input parameters [18]. AA6061-B4C powders with different concentrations of B4C (5, 10, and 15 wt.%) at 5% Gr were examined, and the sample containing 15 wt.% B4C exhibited the best wear characteristics, with a hardness value of 164 HV, significantly higher than the 33 HV for pure AA. The coefficient of friction was influenced by load and sliding speed, with higher loads and sliding speeds leading to increased friction. Regarding cost-effectiveness, SCP is superior to alternative treatments, costing thirty times less [19]. The wear characteristics of hyper eutectic Al-silicon alloys produced through partial solid metal processing were investigated under conditions of 0.2 m/s sliding rate and 10–40 N load, with prolonged cooling on steel and cast iron wheels, and compared to typical cast alloys. Using borax as a wet medium, mixed with 50% SiCp after heating at 250 °C for 20 min, resulting in a smooth dispersion of SiCp [20]. The (CoCrNi)88Mo12 dual-phase MEA, a ductile face-centered cubic matrix, and hard phase, was designed to improve cryogenic wear performance, with a friction-induced amorphous layer lowering wear by 73% at 113 K [21].
The tribological behavior of hydrocarbon produced with 2.5% to 10% equivalent weight of SiCp and graphite (Gr) particles was investigated using design of experiments approaches. The wear was influenced by favorable parameters such as force and sliding distance [22]. The dry-sliding wear behavior of AA reinforced with 5% SiCp and B4C hybrid was investigated using a pin-on-disk tribometer (PODT). The hybrid composites maintained their resistance qualities under 60 N loads and falling rate ranges of 1–4 m/s. The cooperative impact of reinforcement particles enhanced wear resistance with a small amount of SiCp and B4C [23]. SCP was used to synthesize various weight percentages of B4C and a constant 3% of BN reinforcements in AA-7075 HC. This increased micro-hardness, tensile strength, compression, and reduced corrosion rate by 18.5% to 22.4% [24].
Adding B4C ceramic with Gr substance and to aluminum-based MM composites (MMC) through SCP increased microhardness and decreased weight loss (WL) as the concentrations of B4C and graphite increased. The maximum wear resistance was observed at 15 wt.% B4C and 10 wt.% Gr [25]. Response surface analysis (RSM) and artificial neural network (ANN) were utilized to evaluate the tests’ impact and determine their significance level. The Taguchi model, in conjunction with an ANN, was employed to ascertain the wear behavior of the hybridized mixture and estimate the influential factors on the degradation rate of composites [26]. While data are scarce regarding the effects of dry sliding wear on multi-ceramic reinforced composites, the findings from this study will contribute to defining the role of hybridized composites (AA6061 + B4C + Gr) in functional settings [27,28]. The addition of Gr particles to aluminum alloys significantly enhances wear resistance and reduces the coefficient of friction.
Additionally, forming a tribo-layer on the composite surface improves material integrity by providing lubrication [29]. For composites incorporating 40% SiC/5% Gr/AA with varying sizes of graphite particles using the squeeze casting method, adding Gr particles decreased the friction coefficient and increased wear resistance by a substantial margin of 170 to 340 times. Furthermore, wear resistance displayed an upward trend with increasing graphite particle size, indicating enhanced lubricating properties [30].
Aluminum-based hybrid metal matrix composites (HMMCs) are gaining popularity in the automotive and aircraft sectors due to their increased strength, hardness, stiffness, wear and corrosive resistance, and thermal characteristics. To further enhance their mechanical properties and resistance to wear, boron carbide (B4C) and graphite (Gr) are added to the aluminum HMMCs. This combination overcomes the brittleness and machinability issues associated with using B4C alone and the strength loss in composites reinforced with Gr. Despite pertinent research in the literature, detailed instructions on how to use the dual-stage SCP for the complete flowing phase technique to incorporate variable volume percentages of B4C and Gr that were previously added in insufficient volume % into an AA-6061 alloy matrix are lacking. This limitation hinders our ability to characterize the morphological, hardness, and tribological behavior fully. By adjusting the volume percentage, Gr, a moderately lubricating material with brittle properties, can enhance the mechanical and tribological behavior of AA-MMCs. In this study, we aimed to fabricate B4C- and Gr-reinforced AA6061 HCs by varying their volume percentages (5, 10, and 15 for B4C, and relatively higher amounts of 10, 15, and 20 for Gr) using the dual-stage SCP method. Furthermore, we sought to analyze their morphological, mechanical, and tribological behavior under different parameter conditions.
2. Materials and Methodology
AA6061 was chosen as the matrix for generating AA HCs using SCP in this study. AA HC has a high strength-to-weight ratio, is sufficiently strong, has the lowest density, is reasonable, and is of exceptional quality commonly used in automotive and marine fields (refer to composition Table 1). Only by using low-density reinforcements such as B4C (1 μm) of 2500 kg/m3 and Gr (10 μm) of 2100 kg/m3 can lower the HC density than AA6061 (2700 kg/m3) and other ceramic-reinforced materials. High thermal conductivity, excellent workability, and machinability may all be improved by combining B4C and Gr with Al [31]. Adding these reinforceable components in volume % improves specific AA’s physical characteristics (high strength-to-weight ratio, reducing density, high stiffness, lubrication, etc.). The Gr enhances the wear resistance of the HC at higher temperatures, while B4C is wettable, thermally stable, and chemically inert [32]. The Al-HCs are made with different percentages of B4C (5, 10, and 15%) and the Gr (10, 15 and 20%) in higher content. B4C is a more rigid material than Gr, and Gr has good bonding to AA for microstructure uniformity and stability. The SEM microstructure of B4C and Gr raw materials is presented in Figure 1a,b. Figure 1a displays the topographic SEM image of B4C, revealing that the particles have flat, hexagonal platelet shapes varying in size from 1 to 2 μm, with no other elements detected. On the other hand, Figure 1b shows that the powder particles, ranging in size from 9 to 10 μm, are agglomerated, giving rise to irregular shapes resembling flakes of various sizes [33]. At high and extremely low temperatures, AA provides strength and damage resistance. Pure (AA6061) and three types of composites (AA6061/B4C/Gr) were developed in this study (AA6061). AA6061 has tensile and yield strengths of 290 and 248 MPa, respectively [34].

Table 1.
Composition of Al6061 HC in wt.%.
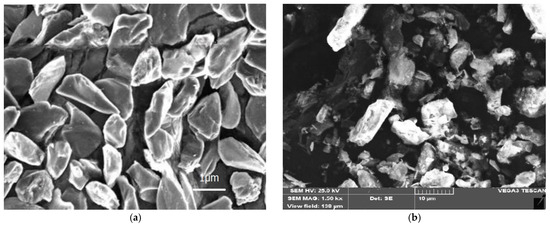
Figure 1.
Morphological view of (a) B4C (b) Gr.
2.1. Manufacturing Using SCP
Stir casting has been shown to be the most cost-effective of practically all well-established MMC manufacturing procedures, and it has mainly been used to produce Al-HCs. Gr and B4C were carefully cleaned with water and then heated to 200 and 600 °C, respectively, to remove dust, moisture, and carbonaceous material. This combination is ready to use in the main procedure when the color changes from black to grey. In a double stirring casting method, 85, 75, and 65% AA6061 specimens are produced at a molten temperature of 750 °C. Gr (10, 15, and 20%) and B4C (5, 10, and 15%) were preheated at 548 °C for specimen preparation. Preheated Gr and B4C are combined with the slurry at a consistent pace (at 745 °C) such that the volume, shape, and location of the reinforcing particles and the construction procedure change in accomplishing critical features for both elements. The mixture is agitated for around 5–10 min to ensure consistent mixing of ingredients. After stirring, it is poured into molds that [33] are stored at 450 °C for 45 min to solidify uniformly. Transferring the produced Al-HC slurry into a preheated (at 350 °C) steel die and cooling it to ambient temperature prevents a lot of heterogeneity and rapid cooling [35].
2.2. Microhardness Tests of AA6061/B4C/Gr
The Vickers microhardness tester was utilized for evaluating hardness following the guidelines outlined in ASTM E384-10 [36]. Specifically, microhardness tests were conducted on the samples of the AA6061 alloy and their composites after interval of 2 m/s. In the beginning, pin surface was achieved with a surface finish of 0.3 μm by employing finer diamond abrasives. All samples were subjected to a 500 g load for 10 s. The test was performed at five distinct locations to ensure accuracy, thereby minimizing the likelihood of the indenter resting on the hard reinforcement particles [37].
2.3. Density Measurement
The mass density of the unreinforced AA and Al HCs was determined based on Archimedes’ principle. The specimen was initially suspended freely in the air and weighed. Then it was immersed fully in distilled water, and its mass was determined. The mass of the specimen fully immersed in water will be less than its mass in air. The mass density (kg/m3) of the specimen was calculated using the expression (1) [33]:
where m1 and m2 are the specimen’s masses in air and water (kg/m3), and ρw is the mass density of water. Whereas the theoretical density () was evaluated by using expression (2) with Vas total volume of composite:
2.4. Measuring of Compressive Strength
Uniaxial compressive test specimens were prepared following the ASTM-E9 [38] guidelines for the AA matrix material incorporated with its reinforcement. The specimens were sized at 5 × 3 × 3 mm3. These specimens underwent a compression test conducted on an INSTRON 5985 model computerized universal testing machine to evaluate their compressive properties. The test was conducted at room temperature with a 0.5 mm/min crosshead speed. To determine the compressive strength of each specimen, they were compressed up to 25% of their initial height, and the applied force corresponding to the deformation was calculated [39]. A total of five specimens were subjected to compression testing at room temperature.
2.5. Measurement of Tribological Behavior of Al-MMCs and Their Morphology
The morphological evaluation of produced Al-MMCs is investigated to show the more insightful microstructural properties. The samples were sliced to prepare for metallography processes using ASTM standards so that the microstructural pattern of HC samples could be investigated using an SEM (Make: VEGA 3 TESCAN, Brno, Czech Republic). Before utilizing a scanning electron microscope to verify the microstructural pattern and distribution of particles (B4C and Gr) in HCs, an etching solution of HCl + HF + HNO3 (known as Keller’s reagent) was utilized. Wear tests (dry sliding) were carried out using an Al HC pin specimen with a diameter of 12 mm and a length of 30 mm (ASTM-G099 standard [40]), which was held against a revolving disk face (EN31 steel disc) with a track diameter of 60 mm. To ensure that contact faces are clean and horizontal, the pin sample surfaces were treated using emery (80 grit size). Before and after each examination, the specimens and used tracks were cleaned with acetone. The load (10, 20, and 40 N), speed (2 and 4 m/s), and sliding distance (2000 m, 4000 m, and 8000 m) were all tested [3,37,41].
3. Results and Discussion
By adjusting the percent weight of B4C- and Gr-reinforced AA-HCs using the stir casting process, we could manufacture B4C- and Gr-reinforced AA-HCs in this study. This paper examines and investigates the microstructure, hardness, tribological characteristics, worn surface morphology, and compressive strength of manufactured HCs.
3.1. Morphological Characterization of B4C and Gr Reinforced Al-HCs
Figure 2a–c are illustrative SEM figures of cast samples after etching, exhibiting the wear surfaces of AA6061/5% B4C/10% Gr, 10% B4C/15% Gr, and 15% B4C/20% Gr HC at specified magnification using a scanning electron microscope (VEGA 3 TESCAN, Czech Republic). According to microstructural investigations of these specimens, B4C and Gr (reinforcements) are consistently spread across the cross-section in the AA-MMC. The cluster of reinforced particles was discovered aggregating in a specific area and along the granule borders of the main AA6061 matrix, displaying smooth interdendritic arrangement through precipitated reinforcing particles at the grain boundary junction. The distribution of black-colored reinforcing particles (opaque and does not reflect) in the reflecting AA6061 matrix was discovered in the HC specimens. As a result, Gr seems to have granules of a regular form [13].
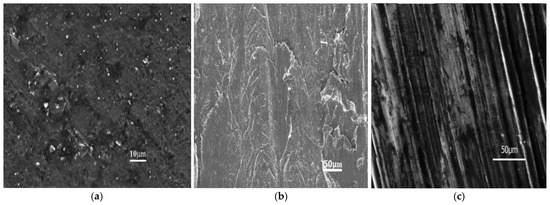
Figure 2.
Microstructural view of AA6061+ (a) 5% B4C/10% Gr, (b) 10% B4C/15% Gr, and (c) 15% B4C/20% Gr HCs.
It was discovered that many reinforcing particles formed the granule peripheries of the leading Al matrix. In contrast, only a few tiny spotted particles began the granule peripheries in the AA matrix [33,37]. The reinforcing particles do not thaw to their full extent despite rising melt temperature; instead, they emerge as tiny round-type reinforcing particles in selected regions with regular reinforcing particle distribution in the AA matrix alloy, as illustrated in Figure 2a–c. Compared to the AA matrix, these reinforcing particles have a higher hardness and melting point. On the other hand, unmelted reinforcing particles play an important role in determining the compression intensity of HCs through dampening. Spherical shapes B4C particles and slightly skewed Gr particles are detected in the HC’s dendritic aluminum matrix. The patterns of the distribution of reinforced particles were found to be randomly orientated [42,43]. Figure 3 illustrates the EDS results of the HMMC composite conforming the Mg and Si grains in AA6061, whereas other elements are not seen like Gr and B4C, which indicates that the phase has been changed.
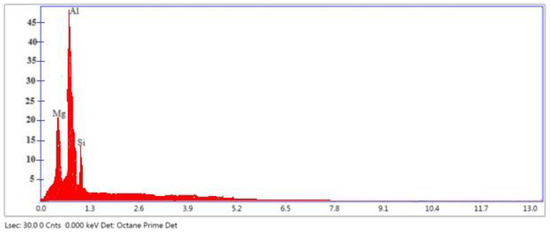
Figure 3.
EDS results of AA6061 + 15% B4C/20% Gr HCs after stir casting.
3.2. Micro-Hardness of Al6061/B4C/Gr Composites
Figure 4 illustrates the average values obtained from these readings of the Vickers test for assessing micro-hardness utilized for cast and HC samples. The existence of equal dispersal of B4C and Gr in the AA matrix alloy and granules alteration found in the microstructural view demonstrates the amplified hardness of generated HCs (Figure 4). Increased B4C weight percent is a barrier to disarticulation, resulting in higher hardness than AA [25]. The hardness achieved by modifying the sliding distance was examined at each of these sliding distances and presented to verify which HC has excellent wear properties with various wt.% of Gr and B4C particles.
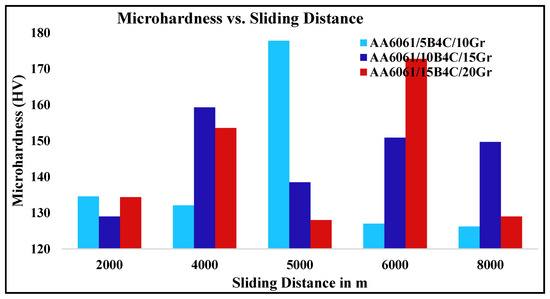
Figure 4.
Microhardness of AA6061/B4C/Gr with varying combinations of B4C (5, 10, and 15%) and Gr (10, 15, and 20%) HCs vs. sliding distance.
The microhardness of AA6061/B4C/Gr composites increased as the sliding distance increased up to 5000 m. After that, it decreased and stabilized after reaching 6000 m [27]. This behavior change was attributed to strain hardening initially, followed by softening due to wear and the accumulation of reinforcement debris. Creating a transfer layer on the worn surface, also known as the mechanically mixed layer, was responsible for this effect as it enhanced the microhardness values. However, when the sliding distance increased, the MML got saturated, causing the microhardness levels to stabilize.
Additionally, the microhardness decreased due to deformation of the matrix, fracture of B4C and Gr particles, and wear-induced damage [34]. The reinforcements’ content also enhanced the microhardness values, with B4C content ranging from 5% to 15% and Gr content ranging from 10% to 20%. The lower particle size of B4C and the finer particle size of Gr substantially improved hardness. The increased hardness of the composite was primarily attributed to the high hardness of B4C reinforcing particles, their uniform distribution within the composites, and increased density [42].
The higher hardness value can be attributed to the expansion of Gr and B4C particulate matter, which is evident by the even dispersion of B4C particulate matter in the AA matrix and the strengthening influence of the MMC. The presence of rigid reinforcement particulate matter protects against plastic distortion, resulting in the improved hardness of the metal matrix when combined with the optional inclusion of particulate matter in the composites. Among the compositions studied the AA6061 + 10% B4C + 15% Gr composite exhibited the highest hardness value. Sliding distance (SD) affects the distribution of reinforcing material on the worn surface of MMCs, consequently impacting the microhardness (HV). The contact between the surface and counter-surface of AA-MMCs subjects the material to significant stress and distortion. Initially, the microhardness of MMCs decreases due to substantial plastic deformation and grain refinement during the sliding process. However, as the SD increases, the microhardness begins to rise again. Eventually, it stabilizes after a certain sliding distance due to the generation of in situ wear debris and regrowth of the worn surface through enhanced diffusion caused by slag impact [43].
3.3. Results of AA HCs Density
The mass density of the AA HCs was determined using Archimedes’ principle, and the results are presented in Table 2 as observed or actual density whereas the rule of mixture was used for theoretical density. Mass densities of AA6061/B4C/Gr composites decrease as the percentage of reinforcement increases and are slightly lower than that of the unreinforced aluminum alloy. The AA/15% B4C/20% Gr hybrid composite exhibits the lowest density among all the hybrid composites. The addition of boron carbide and graphite particles reduces the density of the hybrid composites, making them lightweight and suitable for automobile applications. The density of boron carbide (2.51 g/cm3) and graphite (2.13 g/cm3) is lower than that of aluminum alloy (2.65 g/cm3), resulting in a lower density value for the hybrid composites [33]. Three trials were conducted.

Table 2.
Density of AA6061 and composites.
3.4. Ultimate Compressive Strength (UCS) of AA6061/B4C/Gr
Observations indicate that the UCS of HCs increased due to the dampening/cushioning effect and the even dispersion of B4C and Gr reinforcing particles and their changed phases in the AA matrix alloy. By increasing particle storage, the reinforcing particles were detained in the AA matrix, decreasing granule size in the microstructure. The area of interface borders between the B4C and AA matrix also increased with an increase in B4C wt. percent in the AA matrix, and particles gathered at these borders rather than granular boundaries.
Figure 5 illustrates the UCS of AA6061 with reinforced materials Gr and B4C and the UCS value of AA with nine weight percent of supporting materials. Increasing the weight percentage of reinforced material raises the MMC’s UCS. Since HCs are superior to the base alloy, high UCS values were observed with 20% Gr and B4C—5%, 10%, and 15% of the reinforcement components with AA6061 matrix [33]. Furthermore, increasing the weight percent of Gr leads to a larger granule size, generating a large dislocation population in the AA matrix and a high compression capacity of AA HCs (Figure 5). AA-Gr and B4C fine-sized ceramics are more complex than the matrix, resulting in excellent compression stability. As a result, the strong ceramic particulate materials can withstand deformation while enhancing AA strength [37,39,41].
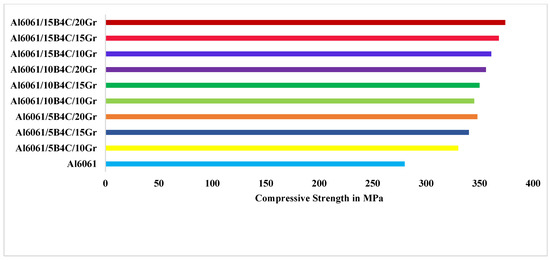
Figure 5.
Compressive strength of AA6061/B4C/Gr with varying combinations of B4C (5, 10, and 15%) and Gr (10, 15, and 20%) HCs.
3.5. Tribological Characteristics of AA6061/B4C/Gr
Table 3 displays the cumulative wear values in grams (WL) of the base metal and HC specimens after the addition of reinforced materials produced by SCP. Compared to the matrix metal, wear (dry sliding type) significantly decreased as WL decreased. The WL of the specimens was examined using a PODT, with variations in weight percent of B4C and Gr, applied average axial load (ANL), sliding velocity (SV), and SD. The hybridized matrix AA6061/5% B4C/10% Gr had a lower WL than AA6061/15% B4C/20% Gr, making it less prone to wear. The lower WL formed a fine layer on the surface. All specimens showed a rising WR pattern when the load was more than 30 N, and the SV was four m/s [34]. The gradient between wear and reinforcing percent dropped as the load rose since the matrix kept the filler material sliding reasonably. The WR and load remained the same for all percent reinforcing until 40 N as the SV increased from 2 to 4 m/s. SEM shots illustrated that the WL increased as the load climbed over 30 N due to the debonding of plasticized surfaces. The same pattern was observed when ANL was 40 N, with increasing SD and SV (Figure 6). All samples showed MML deformation, with the reinforced alloy being more stable than the unreinforced one. There were minimal improvements in sample AA6061/5% B4C/10% Gr (7.6%) at a higher load than AA samples [33,44,45].

Table 3.
Cumulative weight loss values of AA and Al-HC.
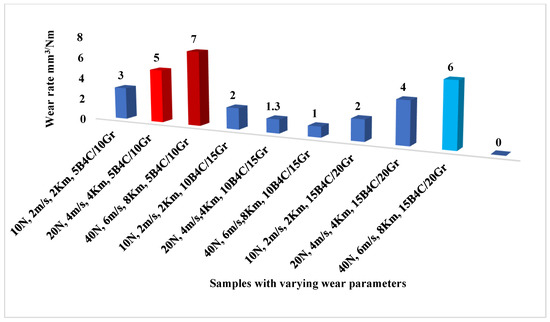
Figure 6.
WR vs. load, SV, and SD for AA6061/5% B4C/10% Gr, 10% B4C/15% Gr and 15% B4C/20% Gr composites.
Micrographs of the worn surfaces of the HCs, as shown in Figure 7a–c, after applying an applied average axial load (ANL) of 30 N at a sliding distance of 2000 m and a sliding speed of 3 m/s, exhibited adhesive wear. The wear behavior of AA and HCs under various loads is observed, with the worn pin surface of the AA displaying more debris. In contrast, the abraded wear surfaces displayed coarse and deep grooves in the sliding direction. The application of load enhances the production of coarse grooves, wear debris, and surface delamination. Significant plastic stresses were directly applied to the pin’s surface, and the harsh asperities on the steel counter face plowed or cut into the pin, generating wear by removing tiny pieces of matrix material [33,45,46,47,48].
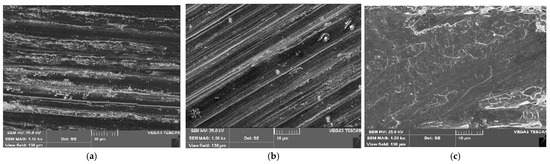
Figure 7.
SEM micrographs of the worn surface at 30 N at a speed of 3 m/s and at a sliding distance of 2000 m (a) AA6061/5% B4C/10% Gr; (b) AA6061/10% B4C/15% Gr; and (c) AA6061/15% B4C/20% Gr composites.
The surface of pin materials underwent a displacement up to a radius of 0.5 mm on one side of the specimen, while the remaining surface remained flat. This type of fracture is considered to occur due to wear debris.
3.6. Worn Surface Morphology and COF under Various Parameters
When conducting the wear test on the AA/5B4C/10Gr HC, fine and shallow grooves were observed in the sliding direction with tiny debris at a load of 10 N. The incorporation of strong B4C reinforcement resulted in reduced groove width and debris development, leading to lower wear rates (WRs). The composite’s load-bearing capacity improvements also enhanced abrasion resistance, lowering WR. However, when the applied axial load was increased to 20 N, delamination became the dominant characteristic due to subsurface plastic deformation and the creation of subsurface crack propagation. Alongside broader grooves, a more significant amount of debris was also observed. The stress caused by repetitive sliding on inclusions or other flaws in the aluminum alloy leads to the nucleation of subsurface fractures, which eventually spread parallel to the surface and reach the surface. Generating long and thin flake-like sheets or plate-like debris, as shown in Figure 8a,b.
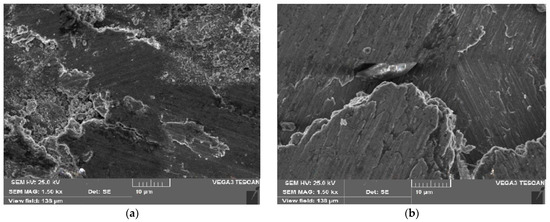
Figure 8.
SEM pictures of worn-out surface of the AA6061/5 B4C/10 Gr vs. applied axial load (a) 10 N and (b) 20 N.
AA’s wear rates (WRs) rose consistently as applied axial loads increased, with a particularly sharp increase at 30 N. At this load, the worn pin surface exhibited delamination, wider grooves with more debris, and a combination of adhesive and abrasive wear. Figure 7 illustrates the creation of rows of furrows on the worn pin surface (it can produce or generate holes by removing particles and covering the created holes with free particles because of the presence of two different sizes and the lubricating nature of Gr). Evidence of material transfer and plastic deformation could be observed on the pin surface. The increased load caused the breakdown of the oxide layer due to metallic contact, resulting in significant plastic deformation of the surface irregularities. Fractures were created and propagated across the asperities when the deformation in each shear band reached a critical limit, eventually removing particles from the deformed asperity. The wear resistance increased with increasing B4C reinforcement in composites up to 10%, but wear resistance diminished when B4C was combined over 10%. The highest wear resistance was reported in the case of HCs with AA/5B4C/10Gr. However, when stress increased, a higher degree of B4C reinforcement (15%) was equal to 20% Gr reinforcement. Among all SS and load levels, the AA/15B4C/20Gr HC exhibited the lowest wear resistance, as shown in Figure 9a,b [33,49,50].
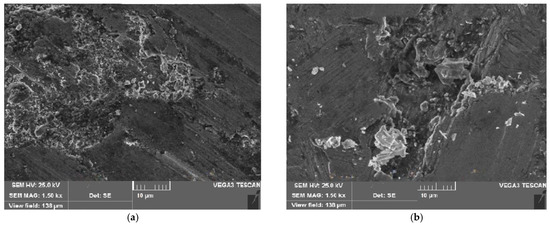
Figure 9.
SEM pictures of worn-out surface of the AA6061/10% B4C/15% Gr vs. sliding speed of (a) 2 m/s and (b) 3 m/s.
The applied axial load resulted in the production of fine grooves and shallow cracks in B4C-reinforced HCs. Additionally, graphite smears and spreads across the surface under load, creating a smeared layer that functions as a lubricant. With greater load, this oxide layer and the scattered graphite layers remain stable, allowing B4C particles to form a protective mixed matrix layer (MML), as depicted in Figure 10a,b.
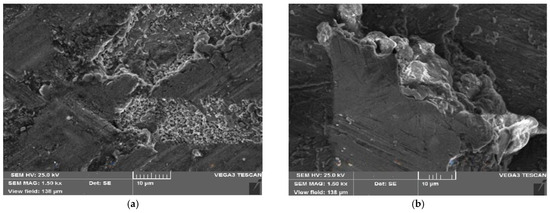
Figure 10.
SEM pictures of worn-out surface of the AA6061/15% B4C/20% Gr vs. applied axial load of (a) 10 N and (b) 20 N.
The worn surfaces of the parent AA and AA/15% B4C/20% Gr HC specimens, tested at SS of 1–3 m/s, revealed that even at a lower SS, the unreinforced parent AA displayed abrasive wear with the formation of coarse and deep grooves in the sliding direction. As the SS increased, significant abrasive wear occurred, resulting in material pulling away from the surface, leading to loose abrasive debris. With an increased sliding speed, material removal through delamination and defoliation caused deeper and wider grooves. The thin oxide films on the unworn AA surfaces quickly degraded under the influence of abrasion, facilitating direct metallic contact between the sliding contacts and resulting in higher wear rates for AA; however, at a constant sliding speed of 3 m/s, oxide wear debris filled troughs on the pin surface, compacting into a protective layer that limited metallic contact and reduced the wear rate of AA [37,51].
Oxidative wear in AA/15% B4C/20% Gr HCs leads to the production of mechanically mixed layers (MMLs). MMLs produce a work-hardened layer between the HC pin and the counter face, isolating the wearing surfaces and preventing asperity interactions with the pin surfaces, leading to decreases in the wear resistance of the HC. As the B4C concentration increases, a stable MML layer forms, significantly reducing the wear rate of AA/15% B4C/20% Gr HC compared to other composites. MML has also been observed in AA6061 MMCs. As the sliding speed increases, the asperities on the softer AA surfaces deform and shatter, resulting in a smoother surface. Strain in the material beneath the worn surface reaches significant levels, although it does not immediately contribute to fracture formation. When fractures reach the surface, long and thin wear sheets separate, forming large delamination craters, as depicted in Figure 11a–c [48,49,50,51,52,53,54].
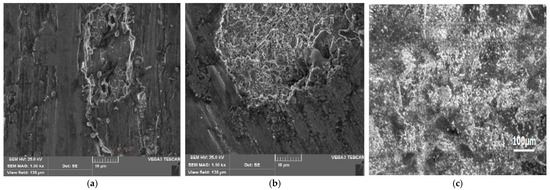
Figure 11.
SEM pictures of worn-out surface of the AA6061/15% B4C/20% Gr vs. sliding speed of (a) 2 m/s and (b) 3 m/s (c) at 3 m/s with low magnification.
The coefficients of friction (COF) of composites and unreinforced alloys were calculated in order to evaluate their friction behavior. Figure 12a shows that as the applied load grew, so did the COF of the AA and their HCs. As the load rises due to wear, debris accumulation increases, which may affect the true area of contact and hence the COF. This might be because the dry sliding wear testing employed a larger load range and sliding speed. With the addition of Gr particles, the COF in AA6061 alloy dropped, reaching a minimum at 15% Gr content. This is twice as cheap as the basic alloy. The addition of 15% Gr to the basal matrix material has no discernible effect on the COF. The lubricating layer thickness and Gr content both rise, lowering the COF and reducing shear stress at the subsurface. The composite has better tribological properties than the matrix alloy, keeping the wear rate and COF low at an acceptable Gr content. The existence of a smeared graphite layer at the tribosurface, serving as a solid lubricant, can be attributed to the lower COF. As the B4C percentage is increased, the COF lowers until it reaches a minimum value for 10% of the AA6061 alloy. The COF rises with further B4C addition as a result of the composite developing a thicker MML. Figure 12b illustrates the EDS results of the worn-out face where element Gr is missing, indicating that it might have changed phase (lubricant).
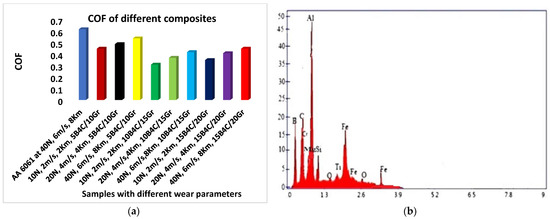
Figure 12.
(a) COF of various HMMCs under variation of parameters and (b) EDS results after wear-out.
4. Conclusions
The study found that SCP was a successful method for producing AA6061 HCs with B4C and Gr reinforcing components. The reinforcing components were evenly distributed throughout the AA matrix, creating interface boundaries.
- The inclusion of B4C and Gr elements prevented dislocation and increased the material’s hardness, wear resistance, and compressive characteristics.
- The mixed layer containing B4C and Gr decreased WL more effectively.
- The composites with 15 vol.% B4C and 20 vol.% Gr exhibited improved morphological, mechanical, and tribological characteristics.
- Wearing resistance was found to be related to hardness. Because of the inhomogeneous distribution of reinforcing elements on the worn surface, microhardness changes with SD.
- The distribution of the reinforcing components was uniform throughout the AA matrix, creating interface boundaries between them.
- The inclusion of B4C and Gr elements helped to prevent dislocation.
- The low wear loss and reduced COF of the composites mixed with B4C, and Gr layers demonstrated little aggregation of reinforced material, a dispersed graphite layer functioning as a solid lubricant, and higher B4C content producing thicker MML.
However, corrosion tests must be conducted, and future research should aim to minimize the drawbacks of these composites during machining.
Author Contributions
Conceptualization, M.Y. and R.A.; Methodology, M.Y.; Software, R.A.; Validation, M.Y. and R.A.; Formal analysis, M.Y. and R.A.; Investigation, M.Y.; Resources, R.A.; Data curation, R.A.; Writing—original draft, M.Y.; Writing—review & editing, M.Y. and R.A.; Visualization, R.A.; Supervision, M.Y.; Project administration, M.Y. and R.A.; Funding acquisition, R.A. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This research was funded by the Deputyship for Research and Innovation, Ministry of Education in Saudi Arabia through project number: IFP22UQU4310022DSR096.
Institutional Review Board Statement
Not applicable.
Informed Consent Statement
Not applicable.
Data Availability Statement
The data analyzed in this manuscript are part of our research work and are available for public use.
Acknowledgments
The authors extend their appreciation to the Deputyship for Research and Innovation, Ministry of Education in Saudi Arabia for funding this research work through project number: IFP22UQU4310022DSR096.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
References
- Singh, J.; Chauhan, A. Characterization of hybrid aluminum matrix composites for advanced applications—A review. J. Mater. Res. Technol. 2016, 5, 159–169. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kala, H.; Mer, K.K.S.; Kumar, S. A Review on Mechanical and Tribological Behaviors of Stir Cast Aluminum Matrix Composites. Procedia Mater. Sci. 2014, 6, 1951–1960. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bujari, S.S.; Kurahatti, R. Microstructure and Wear Behavior of B4C Particulates Reinforced Al-4.5%Cu Alloy Composites. IOSR J. Mech Civ. Eng. 2017, 4, 4–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nie, C.; Gu, J.; Liu, J.; Zhang, D. Production of Boron Carbide Reinforced 2024 Aluminum Matrix Composites by Mechanical Alloying. Composites 2007, 48, 990–995. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rohatgi, P.; Schultz, B.; Daoud, A.; Zhang, W. Tribological performance of A206 aluminum alloy containing silica sand particles. Tribol. Int. 2010, 43, 455–466. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alizadeh, M. Effects of temperature and B4C content on the bonding properties of roll-bonded aluminum strips. J. Mater. Sci. 2012, 47, 4689–4695. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ramesh, C.S.; Khan, A.R.A.; Ravikumar, N.; Savanprabhu, P. Prediction of wear coefficient of Al6061–TiO2 composites. Wear 2005, 259, 602–608. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yilmaz, O.; Buytoz, S. Abrasive wear of Al2O3-reinforced aluminium-based MMCs. Compos. Sci. Technol. 2001, 61, 2381–2392. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oñoro, J.; Salvador, M.D.; Cambronero, L.E.G. High-temperature mechanical properties of aluminium alloys reinforced with boron carbide particles. Mater. Sci. Eng. A 2009, 499, 421–426. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chegini, M.; Fallahi, A.; Shaeri, M.H. Effect of Equal Channel Angular Pressing (ECAP) on Wear Behavior of Al-7075 Alloy. Procedia Mater. Sci. 2015, 11, 95–100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shanbhag, V.V.; Yalamoori, N.N.; Karthikeyan, S.; Ramanujam, R.; Venkatesan, K. Fabrication, Surface Morphology and Corrosion Investigation of Al 7075-Al2O3 Matrix Composite in Sea Water and Industrial Environment. Procedia Eng. 2014, 97, 607–613. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Prasanna, S.C.; Ramesh, C.; Manivel, R.; Manikandan, A. Preparation of Al6061-SiC with neem leaf ash in AMMCs by using stir casting method and evaluation of mechanical, wear properties and investigation on microstructures. Appl. Mech. Mater. 2017, 854, 115–120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alvandi, H.; Farmanesh, K. Microstructural and Mechanical Properties of Nano/Ultra-fine Structured 7075 Aluminum Alloy by Accumulative Roll-Bonding Process. Procedia Mater. Sci. 2015, 11, 17–23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Suresh, S.; Moorthi, N.S.V. Process Development in Stir Casting and Investigation on Microstructures and Wear Behavior of TiB2 on Al6061 MMC. Procedia Eng. 2013, 64, 1183–1190. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rana, H.G.; Badheka, V.J.; Kumar, A. Fabrication of Al7075/B4C Surface Composite by Novel Friction Stir Processing (FSP) and Investigation on Wear Properties. Procedia Technol. 2016, 23, 519–528. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ramesh, C.S.; Swamy, N.R.P.; Chandrashekar, T. Effect of heat treatment on strength and abrasive wear behaviour of Al6061-SiCp composites. Bull. Mater. Sci. 2010, 33, 49–54. [Google Scholar]
- Umanath, K.; Selvamani, S.T.; Palanikumar, K.; Sabarikreeshwaran, R. Dry Sliding Wear Behaviour of AA6061-T6 Reinforced SiC and Al2O3 Particulate Hybrid Composites. Procedia Eng. 2014, 97, 694–702. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yoo, S.C.; Kang, B.; Van Trinh, P.; Phuong, D.D.; Hong, S.H. Enhanced mechanical and wear properties of Al6061 alloy nanocomposite reinforced by CNT-template-grown core–shell CNT/SiC nanotubes. Sci. Rep. 2020, 10, 12896. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sharif, E.M.; Karimzadeh, F.; Enayati, M.H. Fabrication and evaluation of mechanical and tribological properties of boron carbide reinforced aluminum matrix nanocomposites. Mater. Des. 2011, 32, 3263–3271. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lawrance, C.A.; Prabhu, P.S. Stir Casting of in-situ Al 6061TiB2 Metal Matrix Composite Synthesized with Different Reaction Holding Times. Int. J. Eng. Res. Technol. IJERT 2015, 4, 449–453. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ren, Y.; Huang, Z.; Wang, Y.; Zhou, Q.; Yang, T.; Li, Q.; Jia, Q.; Wang, H. Friction-induced rapid amorphization in a wear-resistant (CoCrNi)88Mo12 dual-phase medium-entropy alloy at cryogenic temperature. Compos. Part B Eng. 2023, 263, 110833. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alaneme, K.K.; Aluko, A.O. Production and Age-Hardening Behavior of Borax Premixed SiC reinforced Al-Mg-Si alloy Composites developed by Double Stir-Casting Technique. West Indian J. Eng. 2012, 34, 80–85. [Google Scholar]
- Suresha, S.; Sridhara, B. Wear characteristics of hybrid aluminium matrix composites reinforced with graphite and silicon carbide particulates. Compos. Sci. Technol. 2010, 70, 1652–1659. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Uthayakumar, M.; Aravindan, S.; Rajkumar, K. Wear performance of Al–SiC–B4C hybrid composites under dry sliding conditions. Mater. Des. 2013, 47, 456–464. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumar, V.; Raja, K.; Chandrasekar, V.S.; Thulasiram, R. Thrust force evaluation and microstructure characterization of hybrid composites (Al7075/B4C/BN) processed by conventional casting technique. J. Braz. Soc. Mech. Sci. Eng. 2019, 41, 228. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Prabagaran SChandramohan, G.; Sundaram, P.S. Influence of Graphite on the Hardness and Wear behavior of AA6061–B4C Composite. Mater. Technol. 2018, 48, 661–667. [Google Scholar]
- Sharath, B.N.; Venkatesh, C.V.; Afzal, A.; Aslfattahi, N.; Aabid, A.; Baig, M.; Saleh, B. Multi Ceramic Particles Inclusion in the Aluminium Matrix and Wear Characterization through Experimental and Response Surface-Artificial Neural Networks. Materials 2021, 14, 2895. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ravindranath, V.M.; Shankar, G.S.S.; Basavarajappa, S.; Kumar, N.G.S. Dry sliding Wear Behavior of Hybrid aluminum Metal Matrix composite reinforced with Boron carbide and graphite particles. Mater. Today Proc. 2017, 4, 11163–11167. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sharath, B.; Madhu, K.; Venkatesh, C. Experimental Study on Dry Sliding Wear Behavior of Al-B4C-Gr Metal Matrix Composite at Different Temperatures. Appl. Mech. Mater. 2019, 895, 96–101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Venkataraman, B.; Sundararajan, G. Correlation between the characteristics of the mechanically mixed layer and wear behavior of aluminium, Al-7075 alloy and Al-MMCs. Wear 2000, 245, 22–38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Leng, J.; Jiang, L.; Wu, G.; Tian, S.; Chen, G. Effect of Graphite Particle Reinforcement on Dry Sliding Wear of SiC/Gr/Al Composites. Rare Met. Mater. Eng. 2009, 38, 1894–1898. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nagaraju, S.B.; Somashekara, M.K.; Puttegowda, M.; Manjulaiah, H.; Kini, C.R.; Venkataramaiah, V.C. Effect of B4C/Gr on Hardness and Wear Behavior of Al2618 Based Hybrid Composites through Taguchi and Artificial Neural Network Analysis. Catalysts 2022, 12, 1654. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ramanathan, A.; Krishnan, P.K.; Muraliraja, N. A review on the production of wear resistance model for the metal matrix composites, through stir casting, furnace design, properties, challenges, and research opportunities. J. Manuf. Process. 2019, 42, 213–245. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thiyagarajan, T.; Subramanian, R.; Somasundaram Dharmalingam Achiappan Radhika, N.; Gowrisankar, A. Wear behavior of B4C reinforced hybrid aluminum matrix composites. Mater. Technol. 2014, 46, 497–501. [Google Scholar]
- Baradeswaran, A.; Vettivel, S.C.; Perumal, A.E.; Selvakumar, N.; Issac, R.F. Experimental investigation on mechanical behavior, modelling and optimization of wear parameters of B4C and graphite reinforced aluminium hybrid composites. Mater. Des. 2014, 63, 620–632. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- ASTM E384-10; Standard Test Method for Microindentation Hardness of Materials. ASTM: West Conshohocken, PA, USA, 2010.
- Thirumalai, T.; Subramanian, R.; Kumaran, S. Production and characterization of hybrid aluminum matrix composites reinforced with boron carbide (B4C) and graphite. J. Sci. Ind. Res. 2014, 73, 667–670. [Google Scholar]
- ASTM-E9; International. Standard Test Methods of Compression Testing of Metallic Mate Rials at Room Temperature. ASTM: West Conshohocken, PA, USA, 2009.
- Karthe, M.; Karuppusamy, S.; Sureshkumar, B.; Ali, A.N. Mechanical and wear properties of Al7075-B4C–Gr metal matrix composites fabricated by the using stir casting method. Mater. Today Proc. 2023, 77, 389–393. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- ASTM G99-17; Standard Test Method for Wear Testing with a Pin-on-Disk Apparatus. ASTM: West Conshohocken, PA, USA, 2017.
- Narayan, S.; Rajeshkannan, A. Hardness, tensile and impact behaviour of hot forged aluminium metal matrix composites. J. Mater. Res. Technol. 2017, 6, 213–219. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bodunrin, M.O.; Alaneme, K.K.; Chown, L.H. Aluminium matrix hybrid composites: A review of reinforcement philosophies; mechanical, corrosion and tribological characteristics. J. Mater. Res. Technol. 2015, 4, 434–445. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ramadoss, N.; Pazhanivel, K.; Anbuchezhiyan, G. Synthesis of B4C and BN reinforced Al7075 hybrid composites using stir casting method. J. Mater. Res. Technol. 2020, 9, 6297–6304. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nasr, A.A. Thermal protection of a vertical plate using ethylene glycol film cooling flowing down on a vertical plate. J. Umm Al-Qura Univ. Eng. Archit. 2023, 14, 135–141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shorowordi, K.M.; Laoui, T.; Haseeb, A.S.M.A.; Celis, J.P.; Froyen, L. Microstructure and interface characteristics of B4C, SiC and Al2O3 reinforced Al matrix composites: A comparative study. J. Mater. Process. Technol. 2003, 142, 738–743. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Basavarajappa, S.; Chandramohan, G. Wear Studies on Metal Matrix Composites: A Taguchi Approach. J. Mater. Sci. Technol. 2009, 21, 845–850. [Google Scholar]
- Canakci, A.; Arslan, F.; Yasar, I. Pre-treatment process of B4C particles to improve incorporation into molten AA2014 alloy. J. Mater. Sci. 2007, 42, 9536–9542. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Patdar, D.; Rana, R.S. Effect of B4C particle reinforcement on the various properties of aluminium matrix composites: A survey paper. Mater. Today Proc. 2017, 4, 2981–2988. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alam, M.T.; Ansari, A.H. X-ray diffraction analysis and microstructural examination of Al-SiC composite fabricated by stir casting. Int. J. Sci. Technol. Manag. 2015, 4, 941–956. [Google Scholar]
- Singh, N.; Belokar, R.M. Tribological behavior of aluminum and magnesium-based hybrid metal matrix composites: A state-of-art review. Mater. Today Proc. 2021, 44, 460–466. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baradeswaran, A. Elaya Perumal Influence of B4C on the tribological and mechanical properties of Al 7075-B4C composites. Compos. Part B Eng. 2013, 54, 146–152. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sharma, S.; Goyal, A.; Bharadwaj, P.; Oza, A.D.; Pandey, A. Application of metal matrix composite fabricated by reinforcement materials—A review. Mater. Today Proc. 2023, in press. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, H.; Jiang, L.; Balog, M.; Krizik, P.; Schoenung, J.M. Reinforcement Size Dependence of Load Bearing Capacity in Ultrafine-Grained Metal Matrix Composites. Metall. Mater. Trans. A 2017, 48, 4385–4392. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Softah, G.J. Characterization and Performance Study of DCMD in Different Configurations after Membrane Thermal 505 Treatment. J. Umm Al-Qura Univ. Eng. Archit. 2020, 11, 33–38. [Google Scholar]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).