Deposition of Nb-Si-C Thin Films by Radio Frequency Magnetron Sputtering
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
3. Results and Discussion
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Barsoum, M.W. The Mn+1AXn Phases: A new class of solids. Progr. Solid S.T. Chem. 2000, 28, 201–281. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eklund, P.; Beckers, M.; Jansson, U.; Högberg, H.; Hultman, L. The Mn+1AXn phases: Materials science and thin-film processing. Thin Solid Film. 2010, 518, 1851–1878. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, Z.M. Progress in research and development on MAX phases: A family of layered ternary compounds. Int. Mater. Rev. 2011, 56, 143–166. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barsoum, M.W. MAX Phases: Properties of Machinable Ternary Carbides and Nitrides; Wiley-VCH Verlag GmbH & Co.: Weinheim, Germany, 2013; pp. 1–2. [Google Scholar]
- Ward, J.; Middleburgh, S.; Topping, M.; Garner, A.; Stewart, D.; Barsoum, M.W.; Preuss, M.; Frankel, P. Crystallographic evolution of max phases in proton irradiating environments. J. Nucl. Mater. 2018, 502, 220–227. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.; Zhou, Y. Recent progress in theoretical prediction, preparation, and characterization of layered ternary transition-metal carbides. Annu. Rev. Mater. Res. 2009, 39, 415–443. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Palmquist, J.-P.; Li, S.; Persson, P.O.Å.; Emmerlich, J.; Wilhelmsson, O.; Högberg, H.; Katsnelson, M.I.; Johansson, B.; Ahuja, R.; Eriksson, O.; et al. Mn+1AXn phases in the Ti-Si-C system studied by thin-film synthesis and Ab initio calculations. Phys. Rev. B 2004, 70, 165401. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eklund, P.; Beckers, M.; Frodelius, J.; Högberg, H.; Hultman, L. Magnetron sputtering of Ti3SiC2 thin films from a compound target. J. Vac. Sci. Technol. A 2007, 25, 1381–1388. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Furgeaud, C.; Brenet, F.; Nicolai, J. Multi-scale study of Ti3SiC2 thin film growth mechanisms obtained by magnetron sputtering. Materialia 2019, 7, 100369. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Palmquist, J.-P.; Jansson, U.; Seppänen, T.; Persson, P.O.Å.; Birch, J.; Hultman, L.; Isberg, P. Magnetron sputtered epitaxial single-phase Ti3SiC2 thin films. Appl. Phys. Lett. 2002, 81, 835–837. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Z.; Jin, H.; Chai, J.; Pan, J.; Seng, H.L.; Goh, G.T.W.; Wong, L.M.; Sullivan, M.B.; Wang, S.J. Temperature-dependent microstructural evolution of Ti2AlN thin films deposited by reactive magnetron sputtering. Appl. Surf. Sci. 2016, 368, 88–96. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Joelsson, T.; Flink, A.; Birch, J.; Hultman, L. Deposition of single-crystal Ti2AlN thin films by reactive magnetron sputtering from a 2Ti:Al Compound Target. J. Appl. Phys. 2007, 102, 074918. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Höglund, C.; Beckes, M.; Schell, N.; von Borany, J.; Birch, J.; Hultman, L. Topotaxial growth of Ti2AlN by solid state reaction in AlN/Ti. Appl. Phys. Lett. 2007, 90, 174106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, T.; Chen, Z.; Wang, G.; Wang, L.; Zhang, G.J. Microstructure evolution of polycrystalline Ti2AlN MAX phase film during post-deposition annealing. J. Eur. Ceram. Soc. 2018, 38, 4892–4898. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wilhelmsson, O.; Palmquist, J.-P.; Lewin, E.; Emmerlich, J.; Eklund, P.; Persson, P.O.Å.; Högberg, H.; Li, S.; Ahuja, R.; Eriksson, O.; et al. Deposition and characterization of ternary thin films within the Ti-Al-C system by DC magnetron sputtering. J. Cryst. Growth 2006, 291, 290–300. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Su, R.; Zhang, H.; O’Connor, D.J.; Shi, L.; Meng, X.; Zhang, H. Deposition and characterization of Ti2AlC MAX Phase and Ti3AlC thin films by magnetron sputtering. Mater. Lett. 2016, 179, 194–197. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Z.; Li, W.; Wang, C.; Wu, H.C.; Ke, P.L.; Wang, A.Y. Transforming the amorphous Ti-Al-C coatings to high-purity Ti2AlC MAX phase coatings by prolonged annealing at 550 °C. Mater. Lett. 2020, 261, 127160. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Högberg, H.; Eklund, P.; Emmerlich, J.; Birch, J.; Hultman, L. Epitaxial Ti2GeC, Ti3GeC2, and Ti4GeC3 MAX-phase thin films grown by magnetron sputtering. J. Mater. Res. 2005, 20, 779–782. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Crisan, O.; Crisan, A.D. Incipient low-temperature formation of MAX phase in Cr-Al-C films. J. Adv. Ceram. 2018, 7, 143–151. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grieseler, R.; Hähnlein, B.; Stubenrauch, M.; Kups, T.; Wilke, M.; Hopfeld, M.; Pezoldt, J.; Schaaf, P. Nanostructured plasma etched, magnetron sputtered nanolaminar Cr2AlC MAX phase thin films. Appl. Surf. Sci. 2014, 292, 997–1001. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, C.; Wang, B.; Li, Y.; Wang, R. First-principles study of electronic structure, mechanical and optical properties of V4AlC3. J. Phys. D: Appl. Phys. 2009, 42, 065407. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.; Qian, Y.; Zhao, G.; Xu, J.; Li, M. Preparation of Nb2AlC Coating by DC magnetron sputtering and subsequent annealing. Ceram. Int. 2017, 43, 6622–6625. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tengstrand, O.; Nedfors, N.; Andersson, M.; Lu, J.; Jansson, U.; Flink, A.; Eklund, P.; Hultman, L. Beam-induced crystallization of amorphous Me-Si-C (Me = Nb or Zr) thin films during transmission electron microscopy. Mrs Commun. 2013, 3, 151–155. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Tengstrand, O.; Nedfors, N.; Andersson, M.; Lu, J.; Jansson, U.; Flink, A.; Eklund, P.; Hultman, L. Model for electron-beam-induced crystallization of amorphous Me-Si-C (Me =Nb or Zr) thin films. J. Mater. Res. 2014, 14, 2854–2862. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Nedfors, N.; Tengstrand, O.; Flink, A.; Eklund, P.; Hultman, L.; Jansson, U. Characterization of amorphous and nanocomposite Nb-Si-C thin films deposited by DC magnetron sputtering. Thin Solid Film. 2013, 545, 272–278. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ying, G.B.; Ma, F.C.; Su, L.; He, X.D.; Zhang, C.; Dai, Z.H.; Luo, H.; Du, S.Y.; Wang, C. An ab initio prediction study of the electronic structure and elastic properties of V3GeC2. Process. Appl. Ceram. 2017, 11, 82–86. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Faraoun, H.I.; Abderrahim, F.Z.; Esling, C. First principle calculations of MAX ceramics Cr2GeC, V2GeC and their substitutional solid solutions. Comput. Mater. Sci. 2013, 74, 40–49. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yi, J.X.; Chen, P.; Li, D.L.; Xiao, X.B.; Zhang, W.B.; Tang, B.Y. Elastic and electronic properties of a new MAX compound from first-principles calculations. Solid State Commun. 2010, 150, 49–53. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ghebouli, B.; Ghebouli, M.A.; Fatmi, M.; HI, T.C.; Bouhemadou, A. First-principles calculations of structural, electronic, elastic and thermal properties of phase M2SiC (M = Ti, V, Cr, Zr, Nb, Mo, Hf, Ta and W). Trans. Nonferrous Met. Soc. China 2015, 25, 915–925. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, C.L.; Kuo, J.L.; Wang, B.; Li, Y.S.; Wang, R. A new layer compound Nb4SiC3 predicted from first-principles theory. J. Phys. D Appl. Phys. 2009, 42, 075404. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fu, Y.D.; Wang, B.C.; Teng, Y.; Zhu, X.S.; Feng, X.X.; Yan, M.F.; Korzhavyi, P.; Sun, W.W. The Role of group III, IV elements in Nb4AC3 MAX phases (A = Al, Si, Ga, Ge) and the unusual anisotropic behavior of the electronic and optical properties. Phys. Chem. Chem. Phys. 2017, 19, 15471. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Onoprienko, A.A.; Ivashchenko, V.I.; Timofeeva, I.I.; Sinelnitchenko, A.K.; Butenko, O.A. Experimental and theoretical investigation of Nb-Si-C films. Surf. Coat. Technol. 2016, 300, 35–41. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- El-Raghy, T.; Chakraborty, S.; Barsoum, M.W. Synthesis and characterization of Hf2PbC, Zr2PbC andM2SnC (M = Ti, Hf, Nb or Zr). J. Eur Ceram. Soc. 2000, 20, 2619–2625. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
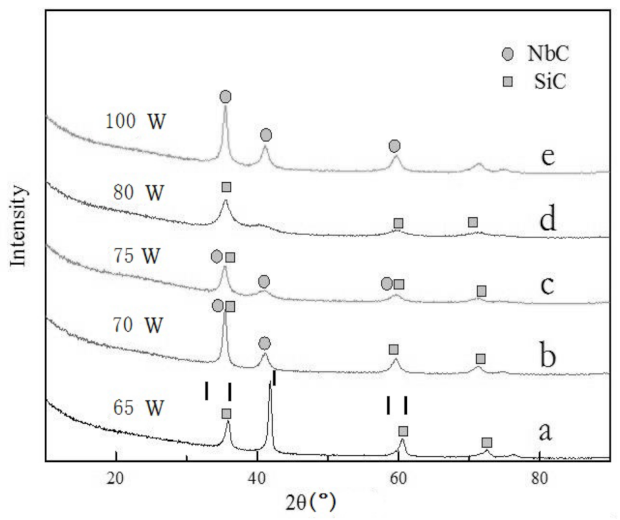
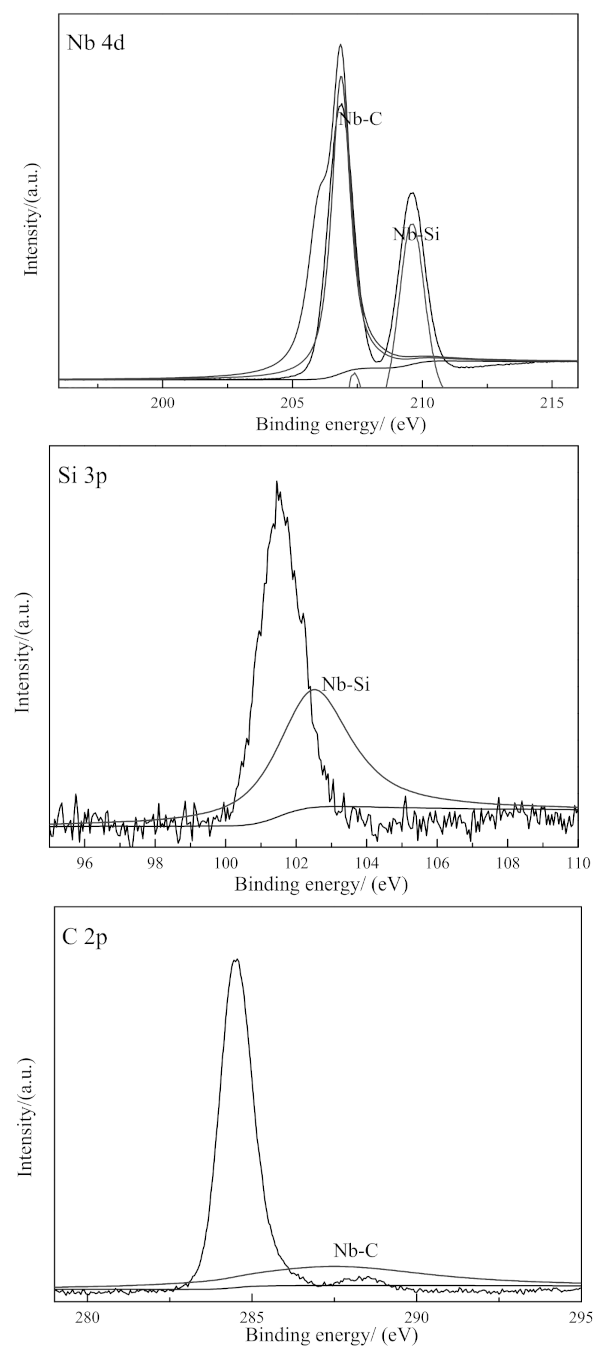
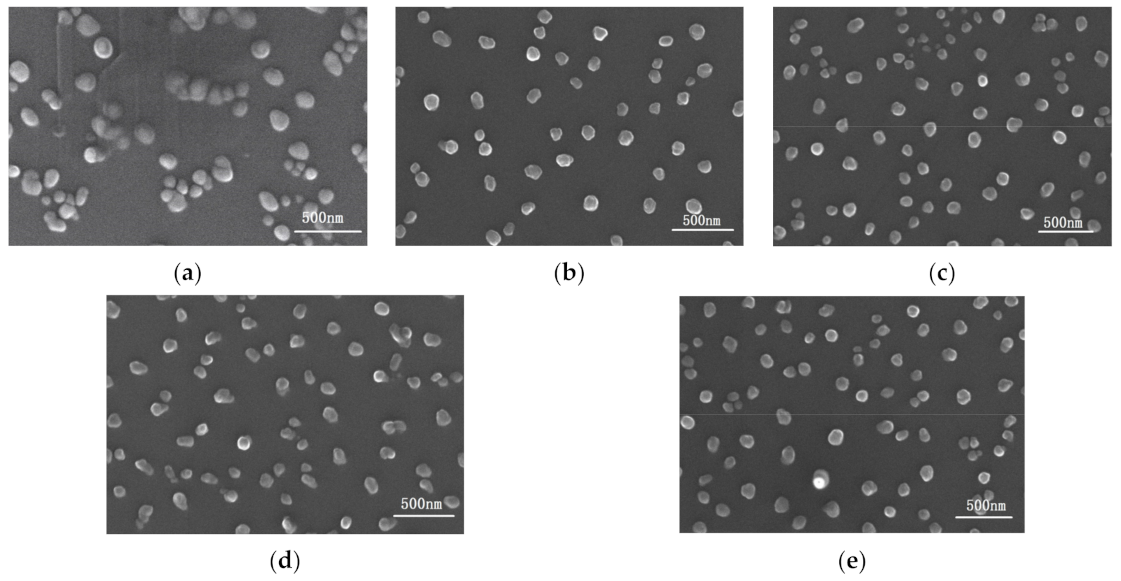


| Si/C/Nb Area Ratio | Ar Gas Flow Rate (sccm) | Sputtering Pressure (Pa) | Vacuum Degree (Pa) | Base Bias (v) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1:3:5 | 25 | 2.4 | 3 × 10−5 | −100 |
| Process Parameters | a | b | c | d | e |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Sputtering time (min) | 60 | 60 | 60 | 60 | 60 |
| Sputtering Power (W) | 65 | 70 | 75 | 80 | 100 |
| Sputtering Power (W) | C (at.%) | Si (at.%) | Nb (at.%) |
|---|---|---|---|
| 65 (a) | 30 ± 1.6 | 25 ± 1.7 | 45 ± 0.5 |
| 70 (b) | 36 ± 1.8 | 23 ± 1.3 | 41 ± 0.6 |
| 75 (c) | 42 ± 1.6 | 21 ± 1.6 | 37 ± 0.7 |
| 80 (d) | 40 ± 1.8 | 18 ± 1.5 | 42 ± 0.5 |
| 100 (e) | 44 ± 2.1 | 15 ± 1.7 | 41 ± 0.4 |
| Sputtering Power (W) | Hardness (GPa) | Elastic Modulus (GPa) | Resistivity (μΩ·m) |
|---|---|---|---|
| 65 (a) | 15 ± 1 | 200 ± 16 | 0.99 |
| 70 (b) | 18 ± 1 | 215 ± 10 | 1.95 |
| 75 (c) | 19 ± 1 | 200 ± 17 | 2.06 |
| 80 (d) | 20 ± 1 | 220 ± 15 | 1.89 |
| 100 (e) | 20 ± 2 | 215 ± 13 | 2.20 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Li, Z.; Liu, G.; Liu, G.; Zhu, X.; Fu, Y. Deposition of Nb-Si-C Thin Films by Radio Frequency Magnetron Sputtering. Coatings 2021, 11, 524. https://doi.org/10.3390/coatings11050524
Li Z, Liu G, Liu G, Zhu X, Fu Y. Deposition of Nb-Si-C Thin Films by Radio Frequency Magnetron Sputtering. Coatings. 2021; 11(5):524. https://doi.org/10.3390/coatings11050524
Chicago/Turabian StyleLi, Zifeng, Guotan Liu, Guanqi Liu, Xiaoshuo Zhu, and Yudong Fu. 2021. "Deposition of Nb-Si-C Thin Films by Radio Frequency Magnetron Sputtering" Coatings 11, no. 5: 524. https://doi.org/10.3390/coatings11050524
APA StyleLi, Z., Liu, G., Liu, G., Zhu, X., & Fu, Y. (2021). Deposition of Nb-Si-C Thin Films by Radio Frequency Magnetron Sputtering. Coatings, 11(5), 524. https://doi.org/10.3390/coatings11050524






