Effect of a Herbal Therapy on Clinical Symptoms of Acute Lower Uncomplicated Urinary Tract Infections in Women: Secondary Analysis from a Randomized Controlled Trial
Abstract
1. Introduction
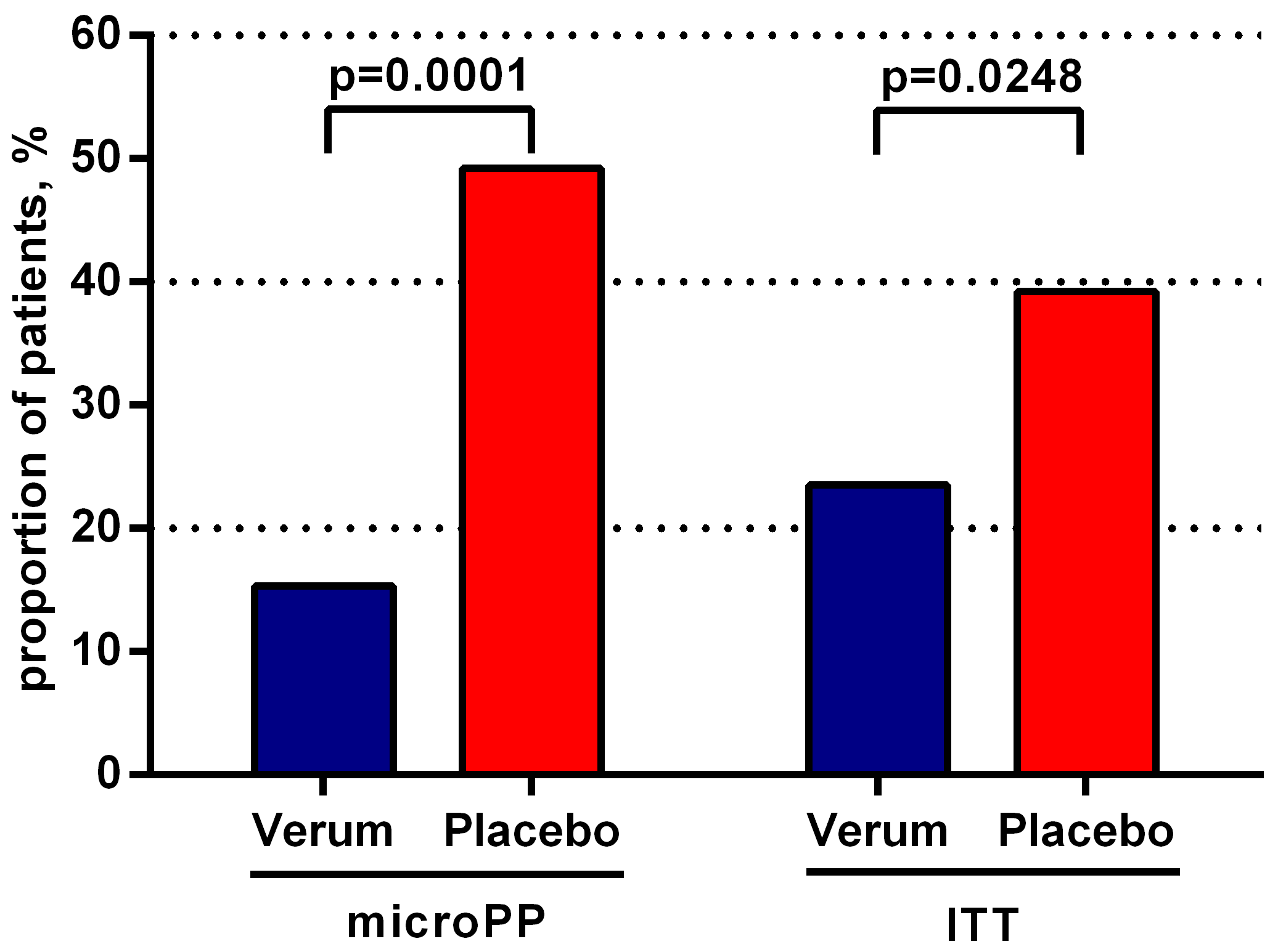
2. Results
3. Discussion
4. Material and Methods
4.1. Trial Design
4.2. Patients
4.3. Randomization and Masking
4.4. Procedures
4.5. Outcomes
- patients whose bacterial count was less than 104 CFU/mL at the time of inclusion
- patients whose urine cultures were contaminated and, therefore, not evaluable
- patients who took concomitant medication that could influence the results of the urine cultures. For this secondary analysis, we defined a new patient-relevant clinical endpoint (i.e., clinical improvement of symptoms) based on the Acute Cystitis Symptom Score (ACSS) (Table S3), a validated, standardized self-reporting questionnaire used to evaluate the symptoms of acute uncomplicated cystitis in women [22,23,24,25,26]. In addition, we analyzed whether the herbal combination reduced the rate of antibiotic use.
4.6. Statistical Analysis
4.7. Ethics Approval and Consent to Participate
4.8. Consent for Publication
4.9. Availability of Data and Material
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
List of Abbreviations
| ACSS | Acute Cystitis Symptom Score |
| CFU | Colony Forming Units |
| E.coli | Escherichia coli |
| EMA | European Medicines Agency |
| FDA | Food and Drug Administration |
| HMPC | Committee on Herbal Medicinal Products |
| ITT | Itention-To-Treat |
| microPP | Population of Patients with evaluable microbiologic data |
| NSAID | Nonsteroidal Anti-Inflammatory Drugs |
| QOL | Quality of Life |
| UPEC | Uropathogenic Escherichia coli |
| UTI | Urinary Tract Infection |
| uUTI | Uncomplicated Urinary Tract Infection |
References
- Foxman, B. The epidemiology of urinary tract infection. Nat. Rev. Urol. 2010, 7, 653–660. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- The European Association of Urology (EAU) Guidelines. Edn. Presented at the EAU Annual Congress Copenhagen. 2018. Available online: http://uroweb.org/guideline/urological-infections/ (accessed on 10 October 2019).
- Goossens, H.; Ferech, M.; Vander Stichele, R.; Elseviers, M.; ESAC Project Group. Outpatient antibiotic use in Europe and association with resistance: A cross-national database study. Lancet 2005, 365, 579–587. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tandogdu, Z.; Cek, M.; Wagenlehner, F.; Naber, K.; Tenke, P.; van Ostrum, E.; Johansen, T.B. Resistance patterns of nosocomial urinary tract infections in urology departments: 8-year results of the global prevalence of infections in urology study. World J. Urol. 2014, 32, 791–801. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schito, G.C.; Naber, K.G.; Botto, H.; Palou, J.; Mazzei, T.; Gualco, L.; Marchese, A. The ARESC study: An international survey on the antimicrobial resistance of pathogens involved in uncomplicated urinary tract infections. Int. J. Antimicrob. Agents. 2009, 34, 407–413. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kahlmeter, G.; ECO.SENS. An international survey of the antimicrobial susceptibility of pathogens from uncomplicated urinary tract infections: The ECO.SENS Project. J. Antimicrob. Chemother. 2003, 51, 69–76. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Leitlinienprogramm, DGU. AWMF: Interdisziplinäre S3 Leitlinie: Epidemiologie, Diagnostik, Therapie, Prävention und Management Unkomplizierter, Bakterieller, Ambulant Erworbener Harnwegsinfektionen bei Erwachsenen Patienten. Kurzversion 1.1.-2. 2017 AWMF Registernummer: 043/044. Available online: https://www.awmf.org/uploads/tx_szleitlinien/043-044k_S3_Harnwegsinfektionen_2017-05.pdf (accessed on 4 December 2019).
- Kronenberg, A.; Butikofer, L.; Odutayo, A.; Muhlemann, K.; da Costa, B.R.; Battaglia, M.; Meli, D.N.; Frey, P.; Limacher, A.; Reichenbach, S.; et al. Symptomatic treatment of uncomplicated lower urinary tract infections in the ambulatory setting: Randomised, double blind trial. BMJ 2017, 359, j4784. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gagyor, I.; Bleidorn, J.; Kochen, M.M.; Schmiemann, G.; Wegscheider, K.; Hummers-Pradier, E. Ibuprofen versus fosfomycin for uncomplicated urinary tract infection in women: Randomised controlled trial. BMJ 2015, 351, h6544. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vik, I.; Bollestad, M.; Grude, N.; Baerheim, A.; Damsgaard, E.; Neumark, T.; Bjerrum, L.; Cordoba, G.; Olsen, I.C.; Lindbæk, M. Ibuprofen versus pivmecillinam for uncomplicated urinary tract infection in women—A double-blind, randomized non-inferiority trial. PLoS Med. 2018, 15, e1002569. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Afshar, K.; Fleischmann, N.; Schmiemann, G.; Bleidorn, J.; Hummers-Pradier, E.; Friede, T.; Wegscheider, K.; Moore, M.; Gágyor, I. Reducing antibiotic use for uncomplicated urinary tract infection in general practice by treatment with uva-ursi (REGATTA)—A double-blind, randomized, controlled comparative effectiveness trial. BMC Complement. Altern. Med. 2018, 18, 203. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wagenlehner, F.M.; Abramov-Sommariva, D.; Holler, M.; Steindl, H.; Naber, K.G. Non-Antibiotic Herbal Therapy (BNO 1045) versus Antibiotic Therapy (Fosfomycin Trometamol) for the Treatment of Acute Lower Uncomplicated Urinary Tract Infections in Women: A Double-Blind, Parallel-Group, Randomized, Multicentre, Non-Inferiority Phase III Trial. Urol. Int. 2018, 101, 327–336. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- European Medicines Agency. Assessment Report on Orthosiphon stamineus Benth., folium. 2011. Available online: https://www.ema.europa.eu/en/documents/herbal-report/final-assessment-report-orthosiphon-stamineus-benth-folium_en.pdf (accessed on 4 December 2019).
- European Medicines Agency. Assessment Report on Ononis spinosa L., radix. 2014. Available online: https://www.ema.europa.eu/en/documents/herbal-report/final-assessment-report-ononis-spinosa-l-radix_en.pdf (accessed on 4 December 2019).
- European Medicines Agency. Assessment Report on Solidago virgaurea L., herba. 2008. Available online: https://www.ema.europa.eu/en/documents/herbal-report/assessment-report-solidago-virgaurea-l-herba_en.pdf (accessed on 4 December 2019).
- Sarshar, S.; Asadi Karam, M.R.; Habibi, M.; Bouzari, S.; Qin, X.; Goycoolea, F.M.; Brandt, S.; Hensel, A. Cytoprotective and antiadhesive effects of aqueous leaf extract from Orthosiphon aristatus against uropathogenic E. coli. Planta Med. 2016, 81, S1–S381. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sarshar, S.; Brandt, S.; Asadi Karam, M.R.; Habibi, M.; Bouzari, S.; Lechtenberg, M.; Dobrindt, U.; Qin, X.; Goycoolea, F.M.; Hensel, A. Aqueous extract from Orthosiphon stamineus leaves prevents bladder and kidney infection in mice. Phytomedicine 2017, 28, 1–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fischer, R.; Kotzolt, B. Therapie unkomplizierter Harnwegsinfektionen mit einem pflanzlichen Aquaretikum: Ergebnisse einer offenen Verlaufsstudie. Der Kassenarzt. 1998, 38, 39–43. [Google Scholar]
- Fischer, R.; Kühnau, S.; Widey, K.D.; Braun, R. Wirksamkeit einer Phytotherapeutikakombination bei Harnwegsinfekten. Der Allgemeinarzt. 1994, 11, 863–869. [Google Scholar]
- EMA. Guideline on the Evaluation of Medicinal Products Indicated for Treatment of Bacterial Infections, Rev 3 Draft. 2018. Available online: https://www.ema.europa.eu/en/documents/scientific-guideline/draft-guideline-evaluation-medicinal-products-indicated-treatment-bacterial-infections-revision-3_en.pdf (accessed on 4 December 2019).
- FDA. Uncomplicated Urinary Tract Infections—Developing Drugs for Treatment. Guidance for Industry. 2019. Available online: https://www.fda.gov/media/129531/download (accessed on 4 December 2019).
- Alidjanov, J.F.; Naber, K.G.; Abdufattaev, U.A.; Pilatz, A.; Wagenlehner, F.M.E. Reevaluation of the Acute Cystitis Symptom Score, a Self-Reporting Questionnaire. Part I. Development, Diagnosis and Differential Diagnosis. Antibiotics 2018, 7, 6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Alidjanov, J.F.; Naber, K.G.; Abdufattaev, U.A.; Pilatz, A.; Wagenlehner, F.M. Reevaluation of the Acute Cystitis Symptom Score, a Self-Reporting Questionnaire. Part II. Patient-Reported Outcome Assessment. Antibiotics 2018, 7, 43. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Alidjanov, J.F.; Naber, K.G.; Pilatz, A.; Radzhabov, A.; Zamuddinov, M.; Magyar, A.; Tenke, P.; Wagenlehner, F.M. Evaluation of the draft guidelines proposed by EMA and FDA for the clinical diagnosis of acute uncomplicated cystitis in women. World J. Urol. 2019. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Alidjanov, J.F.; Naber, K.G.; Pilatz, A.; Radzhabov, A.; Zamuddinov, M.; Magyar, A.; Tenke, P.; Wagenlehner, F.M. Additional assessment of Acute Cystitis Symptom Score questionnaire for patient-reported outcome measure in female patients with acute uncomplicated cystitis: Part II. World J. Urol. 2019. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Alidjanov, J.F.; Lima, H.A.; Pilatz, A.; Pickard, R.; Naber, K.G.; Safaev, Y.U.; Wagenlehner, F.M. Preliminary Clinical Validation of the English Language Version of the Acute Cystitis Symptom Score. JOJ Urol. Nephron. 2017, 1, 55561. Available online: https://juniperpublishers.com/jojun/pdf/JOJUN.MS.ID.555561.pdf (accessed on 4 December 2019).
- Diggle, P.J.; Heagerty, P.; Liang, K.; Zeger, S.L. Analysis of Longitudinal Data, 2nd ed.; Oxford University Press: Oxford, UK, 2005. [Google Scholar]
- Pocock, S.J. Clinical Trials, A Practical Approach; Wiley: Hoboken, NJ, USA, 1991; pp. 50–63, 187–242. [Google Scholar]
- The R Project for Statistical Computing. Version 3.3.2. Available online: https://www.r-project.org/ (accessed on 4 December 2019).



| A | ACSS-Adjusted Symptom Score (microPP) | ||||
| Day | Verum | Placebo | Difference | 95% CI | |
| Day 0 | 4.9 | 5.0 | −0.1 | [−0.4, +0.4] | p = 0.9519 |
| Day 1 | 4.2 | 4.8 | −0.6 | [−1.1, −0.2] | p = 0.0086 |
| Day 7 | 2.1 | 3.2 | −1.1 | [−1.6, −0.4] | p < 0.0001 |
| B | ACSS-Adjusted Symptom Score (ITT) | ||||
| Day | Verum | Placebo | Difference | 95% CI | |
| Day 0 | 4.7 | 4.9 | −0.2 | [−0.7, +0.2] | p = 0.9519 |
| Day 1 | 3.9 | 4.6 | −0.7 | [−1.3, −0.2] | p = 0.0081 |
| Day 7 | 1.6 | 3.5 | −1.9 | [−2.6, −1.1] | p = 0.0008 |
© 2019 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Vahlensieck, W.; Lorenz, H.; Schumacher-Stimpfl, A.; Fischer, R.; Naber, K.G. Effect of a Herbal Therapy on Clinical Symptoms of Acute Lower Uncomplicated Urinary Tract Infections in Women: Secondary Analysis from a Randomized Controlled Trial. Antibiotics 2019, 8, 256. https://doi.org/10.3390/antibiotics8040256
Vahlensieck W, Lorenz H, Schumacher-Stimpfl A, Fischer R, Naber KG. Effect of a Herbal Therapy on Clinical Symptoms of Acute Lower Uncomplicated Urinary Tract Infections in Women: Secondary Analysis from a Randomized Controlled Trial. Antibiotics. 2019; 8(4):256. https://doi.org/10.3390/antibiotics8040256
Chicago/Turabian StyleVahlensieck, Winfried, Horst Lorenz, Anne Schumacher-Stimpfl, Roland Fischer, and Kurt G. Naber. 2019. "Effect of a Herbal Therapy on Clinical Symptoms of Acute Lower Uncomplicated Urinary Tract Infections in Women: Secondary Analysis from a Randomized Controlled Trial" Antibiotics 8, no. 4: 256. https://doi.org/10.3390/antibiotics8040256
APA StyleVahlensieck, W., Lorenz, H., Schumacher-Stimpfl, A., Fischer, R., & Naber, K. G. (2019). Effect of a Herbal Therapy on Clinical Symptoms of Acute Lower Uncomplicated Urinary Tract Infections in Women: Secondary Analysis from a Randomized Controlled Trial. Antibiotics, 8(4), 256. https://doi.org/10.3390/antibiotics8040256




