Abstract
Tetracycline resistance in streptococci is mainly due to ribosomal protection mediated by the tet(M) gene that is usually located in the integrative and conjugative elements (ICEs) of the Tn916-family. In this study, we analyzed the genes involved in tetracycline resistance and the associated mobile genetic elements (MGEs) in Streptococcus dysgalactiae subsp. equisimilis (SDSE) causing invasive disease. SDSE resistant to tetracycline collected from 2012 to 2019 in a single hospital and from 2018 in three other hospitals were analyzed by whole genome sequencing. Out of a total of 84 SDSE isolates, 24 (28.5%) were resistant to tetracycline due to the presence of tet(M) (n = 22), tet(W) (n = 1), or tet(L) plus tet(W) (n = 1). The tet(M) genes were found in the ICEs of the Tn916-family (n = 10) and in a new integrative and mobilizable element (IME; n = 12). Phylogenetic analysis showed a higher genetic diversity among the strains carrying Tn916 than those having the new IME, which were closely related, and all belonged to CC15. In conclusion, tetracycline resistance in SDSE is mostly due to the tet(M) gene associated with ICEs belonging to the Tn916-family and a new IME. This new IME is a major cause of tetracycline resistance in invasive Streptococcus dysgalactiae subsp. equisimilis in our settings.
1. Introduction
Streptococcus dysgalactiae subsp. equisimilis (SDSE) are beta-hemolytic streptococci that possess cell wall carbohydrate serogroup antigens C and G and sometimes A or L. SDSE are present in the microbiota of the respiratory, gastrointestinal, and female genital tract and the skin of humans [1,2]. It usually causes mild to severe infections in humans as Streptococcus pyogenes, ranging from pharyngitis and skin infections to necrotizing fasciitis and streptococcal toxic shock-like syndrome [2,3]. These two species are phylogenetically closely related and share many virulence factors, such as the M-protein, involved in the adhesion and immune system evasion, and used for epidemiological typing [4]. In recent years, two important facts related to SDSE have been described: first, the global emergence of invasive disease due to SDSE [5,6,7,8] and second, the description of the horizontal DNA transfer from SDSE to S. pyogenes, such as pbp2X gene, leading S. pyogenes to have a decreased susceptibility to beta-lactams [9].
Tetracycline resistance can be mediated by three main mechanisms: active efflux pumps, ribosomal protection, and enzymatic inactivation. Within the genus Streptococcus, ribosomal protection is the most important mechanism, and the tet(M) gene the most frequent. This gene is mostly found in the integrative and conjugative elements (ICEs), mainly of the Tn916-family, which can spread through horizontal transmission by conjugation [10]. In fact, having all the requirements for self-transmission is a hallmark of ICEs. On the other hand, integrative and mobilizable elements (IMEs) are elements that encode their own excision and integration, possess only some sequence and genes involved in conjugation, and hijack the conjugation apparatus of conjugative plasmids or ICEs to promote their own transfer [11]. Despite the fact that IMEs’ prevalence is still underestimated, many of them encode resistance to antibiotics and altogether confer resistance to a large variety of antibiotics [11]. Considering resistance to tetracycline, several IMEs from Streptococcus suis were found to carry the tet(O) gene and one a tet(40) gene [12,13,14]. However, no IME carrying tet(M) had ever been identified in Firmicutes. During a surveillance study of tetracycline resistance in SDSE we found a new IME carrying the tet(M) gene. Hence, the aim of the present study was to describe this new element and to analyze the epidemiology of tetracycline resistance in SDSE.
2. Results and Discussion
Out of a total of 84 SDSE isolates causing invasive disease (iSDSE), 24 (28.5%) were resistant to tetracycline. In order to analyze the trends in the iSDSE over the study period, we analyzed data from the Hospital Universitari de Bellvitge (HUB) covering the whole period. Even though the number of isolates collected per year was low, tetracycline resistance rates remained stable among the iSDSE collected from HUB from 37.5% (3/8) in 2012–2015 to 30.2% (16/53) in 2016–2019.
The genome analysis showed that tetracycline resistance was associated with the presence of the tet(M) (n = 22), tet(W) (n = 1), or tet(L) plus tet(W) (n = 1) genes. This gene distribution among the iSDSE agreed with previous results from other regions [15,16]. Nevertheless, exploring the genetic environment of the tet(M) gene, we found that it was carried by two different types of elements transferable by conjugation. In ten isolates, the tet(M) gene was carried by an ICE belonging to the Tn916-family [Tn916 (n = 9) and Tn3872 (n = 1, also having the erm(B) gene)], as previously described. On the other hand, 12 isolates had the tet(M) gene in a new IME (IME_SDSE_HUB-4529; Figure 1 and Figure 2) that was identical (100% nucleotide identity) in all 12 isolates. The IME_SDSE_HUB-4529 encodes a tyrosine integrase and a relaxase of the MOBT superfamily. All of them are integrated in the same site located in an intergenic region between the genes encoding for the alpha subunit of ribonucleotide reductase of class Ib (aerobic) and the Na+-dependent branched-chain amino acid transporter (Figure 2). A BLASTN search identified identical IMEs (100% identity) in the Enterococcus faecium (Acc. num AP019408.1) and Clostridioides difficile (Acc. num CP016102.1) genomes. The insertion sites of the element in the three species were different suggesting that the integrase is not site-specific. This fact together with the 100% identity of the IMEs and with the clustering of the strains on the phylogenetic tree suggests the clonality of the 12 strains and a recent acquisition of the IME by a common ancestor to these strains. A further BLASTN search identified similar structures in other Gram-positive bacteria (E. faecalis, C. innocuum, and Catenibacterium sp.) commonly found in the gut microbiota with an identity above 95% (Supplementary Figure S1). The presence of IME structures in iSDSE with a putative origin from other bacterial species is a cause for concern, especially for E. faecium which is known to be associated with vancomycin and multidrug resistance. In fact, transfer of the van(A) gene from enterococcal species to S. aureus has already been described [17]. The chance of DNA exchanges is more plausible in the current scenario, with an increasing frequency of SDSE which is a cause of human infection.
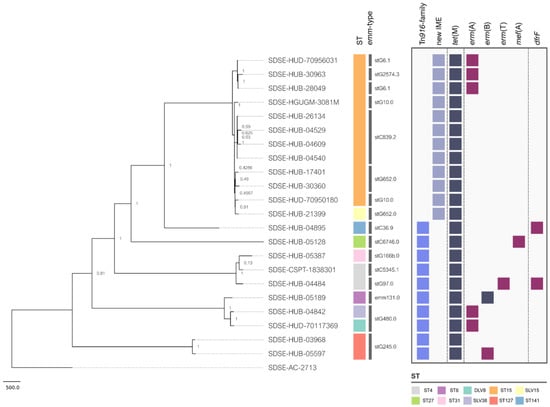
Figure 1.
Phylogenetic tree and presence/absence matrix depicting the acquired resistance genes of iSDSE carrying tet(M). The strain names are shown on the tree branches. The colored squares in the first column represent the ST (Sequence-Type). The second column shows the emm-types. The two first columns of light blue and grey squares represent the mobile genetic elements (MGEs) in which the tet(M) gene is found. The following columns represent a presence/absence matrix of tet(M) and other acquired resistance genes indicating in dark blue when present in the same element as tet(M) and in dark red when present in a different element.
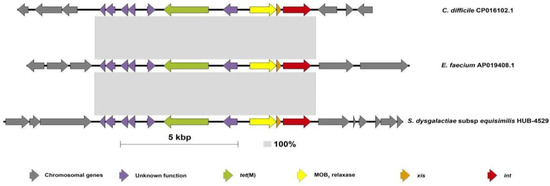
Figure 2.
Schematic representation of the IME containing tet(M) in the SDSE compared with the sequence from E. faecium and C. difficile. This figure shows the structure of the IME containing the tet(M) gene found in twelve strains of the present study (HUB, HUD, HGUGM) compared with the previously described isolates in the literature for E. faecium (Acc. num AP019408.1) and C. difficile (Acc. num CP016102.1). The size of this IME is 9352 bp. The grey-shaded areas connect identical regions (100% identity). Each arrow represents a gene. Colors represent different genes. Grey: chromosomal genes (compared in SDSE with reference strain (AC-2713) (Acc num HE858529.1)). Red: integrase; orange: excisionase; yellow: MOBT relaxase; green: tet(M) gene; purple: unknown function genes.
Aside from the elements carrying tetracycline resistance, most of the isolates also had other resistance mechanisms carried by other elements (Figure 1). Among isolates carrying Tn916, one strain had the erm(T) gene in a non-self-transmissible plasmid and the dfr(F) in a different IME; two isolates had the Tn916 inserted into a larger ICE belonging to the Tn1549-family that also had erm(TR); a single isolate had the dfr(F) in a different IME; one isolate had the macrolide efflux genetic assembly (MEGA) element carrying the mef(E) gene; and finally, one isolate also had erm(B) located near an insertion sequence. On the other hand, three out of 12 isolates carrying the IME_SDSE_HUB-4529 also had the erm(TR) gene located in a Tn1549-family of ICE.
Table 1 shows the antibiotic susceptibility of the tetracycline-resistant SDSE. Beta-lactams (penicillin and cefotaxime), vancomycin, and linezolid were active against all the strains. In fact, beta-lactams are the first-line treatment of SDSE infections, and linezolid could be used as an alternative treatment in case of allergy. Regarding levofloxacin, all strains were “susceptible, increased exposure” following the EUCAST criteria. Nevertheless, one strain had a D83A substitution in ParC and had a MIC of levofloxacin of 2 mg/L which, as has occurred in other streptococci, could be the first step to achieving high-level fluroquinolone resistance under antibiotic pressure. Other resistance rates could be explained by the transferable resistance mechanisms described above.

Table 1.
The antibiotic susceptibility of 24 tetracycline-resistant SDSE strains.
The phylogenetic analysis of the tetracycline-resistant isolates showed a high STs’ and emm-type diversity. We found 10 different STs (ST15 n = 11, ST4 n = 2, ST127 n = 2, and ST8, ST27, ST31, ST141, DLV8, SLV15, SLV38 n = 1), and 13 different emm-types (stC839.2 n = 4, stG652.0 n = 3, stG480.0 n = 2, stG6.1 n = 2, stG10.0 n = 2, stG245.0 n = 2, and stG2574.3, stG166b.0, stG6746.0, stC36.9, emm131.0, stC5345.1, stG97.0 n = 1) among tetracycline-resistant strains harboring the tet(M). These STs and emm-types have been previously described as a cause of disease in humans [15,16,18,19,20,21,22]. Figure 1 shows the phylogenetic relatedness of the SDSE strains carrying tet(M) regardless of the MGEs carrying this gene. Of note, the isolates carrying the tet(M) gene in the ICEs of the Tn916 family were genetically more distinct (Figure 1) than the strains carrying tet(M) in the novel IME. In fact, all isolates carrying the IME_SDSE_HUB-4529 belonged to the same clonal complex (CC15) suggesting a clonal spread of resistance. Nevertheless, these strains of CC15 had different emm-types. In fact, no clear relationship between emm-type and clonal complex has been established for SDSE, as occurs for S. pyogenes, highlighting the more accurate role of CC to differentiate SDSE lineages. Some tetracycline-resistant isolates were also resistant to macrolides, lincosamides, and trimethoprim–sulfamethoxazole. These co-resistances were more frequent in the strains carrying Tn916 (7/10) than in the ones that carry the IME_SDSE_HUB-4529 (3/12) (Figure 1).
MGEs are a frequent cause of resistance dissemination in streptococci. Among them, the ICEs had all the genes required for conjugation and could easily spread intra- and interspecies [23]. In this way, we found a high clonal diversity of tetracycline-resistant strains harboring the tet(M) gene in the Tn916. Furthermore, this element has been associated with resistance in streptococci since the late 1990s, enhancing the opportunities to spread among different strains and species [24]. In contrast, we found a high genetic relatedness among isolates having the tet(M) gene in the new IME (ST15), highlighting that the increase in the prevalence of this new element could be associated preferably to clonal spread of the successful lineages having them. Nevertheless, the presence of ICEs harboring other resistance genes in some of the strains suggests a putative scenario of co-dissemination among other streptococci. Furthermore, it is important to note that other ICEs lacking resistance determinants could also be found among strains and could play a role in the spreading of IMEs [11].
In conclusion, the spread of tetracycline resistance in Streptococcus dysgalactiae subsp. equisimilis is mediated by both the horizontal spread of mobile genetic elements among different strains and by the clonal spread of tetracycline-resistant lineages harboring tet(M). We described a new integrative mobilizable element in Streptococcus dysgalactiae subsp. equisimilis with a putative origin from E. faecium or C. difficile, which highlights the importance of interspecies transfer of resistance determinants.
3. Materials and Methods
This was a retrospective study from 2012 to 2019 including all tetracycline-resistant iSDSE in the Hospital Universitari de Bellvitge (HUB), an adult tertiary teaching hospital located in the Southern Barcelona area, Spain. Furthermore, in order to understand the spread of MGEs and tetracycline-resistant lineages around the country, isolates causing iSDSE in three other hospitals during 2018 were also included. These additional hospitals were in the Center (H. Universitario Gregorio Marañón, Madrid, HGUGM), North (H. Universitario Donostia, Donostia, HUD), and East (Consorci Sanitari Parc Taulí, Sabadell, CSPT) of Spain.
The strains were identified by Matrix-Assisted Laser Desorption/Ionization—Time of Flight (MALDI-TOF, Bruker-Daltonics, Bremen, Germany) and tested by both disc-diffusion and broth microdilution methods for antimicrobial susceptibility following the EUCAST recommendations and criteria (www.eucast.org (accessed on 10 October 2022)). For microdilution, the commercially available plates were used (STRHAE, Sensititre, ThermoFisher Scientific, Waltham, MA, USA). The following antibiotics were tested: penicillin, ampicillin, cefotaxime, erythromycin, clindamycin, linezolid, tetracycline, chloramphenicol, ciprofloxacin, levofloxacin, vancomycin, and trimethoprim–sulfamethoxazole.
The molecular characterization of tetracycline-resistant strains was performed by whole genome sequencing. Genomic DNA was extracted using a QIAamp DNA Mini Kit (Qiagen) and quantified with the QuantiFluor dsDNA System (Promega Corporation, Madison, WI, USA). The libraries were prepared using Nextera XT and sequenced by paired-end sequencing (2 × 150 bp) on an Illumina MiSeq Platform (Illumina Inc., San Diego, CA, USA), following the manufacturer’s instructions. The read quality assessment and genome assembly was conducted using the INNUca v4.2 pipeline (github.com/B-UMMI/INNUca (accessed on 10 October 2021)). The multilocus sequence type (MLST) was in silico deduced using the MLST v2.4 software (github.com/tseemann/mlst (accessed on 10 October 2021)) and the PubMLST database (pubmlst.org/organisms/streptococcus-dysgalactiae (accessed on 0 October 12021)) and the emm-type by the CDC databases (www2.cdc.gov/vaccines/biotech/strepblast.asp (accessed on 10 October 2021)). The final assemblies were annotated with Prokka v1.13.7, whereas genes related to conjugative or mobilizable genetic elements were annotated with ICEscreen (Lao et al., unpublished results), a tool to detect ICEs and integrative mobilizable elements (IMEs) in Firmicute genomes. The resistance genes were found using the ResFinder database [25]. The genetic environment of the tet(M) gene was studied through comparison with previously described sequences present in public databases using Geneious 9.1.7 (Biomatters, Auckland, New Zealand). For phylogenetic analysis, a single nucleotide polymorphism alignment with Snippy v4.4.0 (github.com/tseemann/snippy (accessed on 11 January 2023)) was performed, the recombination was removed by Gubbins v2.4 [26], and subsequently, a final phylogenetic tree was constructed with RAxML-NG and 100 bootstrap replicates [27], represented using Microreact (microreact.org/ (accessed on 11 January 2023)). The sequence comparisons between the new IME described in this work and those available on NCBI were displayed using Easyfig program. The sequence data were deposited in the European Nucleotide Archive under the project accession number PRJEB55810 (Supplementary Material Table S1).
Supplementary Materials
The following supporting information can be downloaded at: https://www.mdpi.com/article/10.3390/antibiotics12030579/s1, Table S1: Antibiotic resistance and mobile genetic elements in the 24 tetracycline-resistant strains. Figure S1; Schematic representation of the IME containing tet(M) in SDSE (SDSE-HUB-4529) compared with different sequences from E. faecium, C. difficile, Clostridium innocuum, E. faecalis, and Catenibacterium sp.
Author Contributions
Conceptualization, C.A., G.L.d.E. and N.L.-B.; methodology, G.L.d.E., A.G.-D., D.B., G.G. and J.L.; software, A.G.-D., J.L., H.C., T.L. and N.L.-B.; validation: G.L.d.E., A.G.-D. and C.A.; formal analysis, A.G.-D., G.G., J.L., N.L.-B., H.C. and T.L.; investigation, G.L.d.E., A.G.-D., D.B., A.C., E.C., J.M.M. and L.F.-D.; resources, M.Á.D. and C.A.; data curation, G.L.d.E., A.G.-D., G.G. and J.L.; writing—original draft, preparation, G.L.d.E., A.G.-D. and C.A.; writing—review and editing, G.L.d.E., A.G.-D., G.G., J.L., D.B., A.C., J.M.M., E.C., L.F.-D., H.C., T.L., M.Á.D., N.L.-B. and C.A.; visualization, D.B. and G.L.d.E.; supervision, C.A. and N.L.-B.; project administration, C.A.; funding acquisition, C.A. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This study was supported through the Projects PI21/01000, “Centro de Investigación Biomédica en Red (CIBER) de Enfermedades Respiratorias (CB06/06/0037)” and “CIBER de Enfermededes Infecciosas (CB21/13/0009)”, an initiative of the Instituto de Salud Carlos III, Madrid, Spain. It was co-funded by the European Regional Development Fund/European Social Fund (ERDF/ESF, “Investing in your future”). We thank the CERCA Programme/Generalitat de Catalunya for institutional support.
Institutional Review Board Statement
This study was in accordance with the Declaration of Helsinki from the World Medical Association. It was approved by the Clinical Research Ethics Committee of Bellvitge University Hospital (PR283/21). Written informed consent was not required as this was a retrospective and observational study with isolates obtained as part of routine microbiological tests. Patient confidentiality was always protected, and all personal data were anonymized following the current legal normative in Spain (LOPD 15/1999 and RD 1720/2007). Moreover, this project followed Law 14/2007 on Biomedical Research for the management of biological samples in clinical research.
Informed Consent Statement
Patient consent was waived because acces to electronic clinical records of patients was retrospective, the study involved no intervention, and the results would not be accurate without the collection of all episodes.
Data Availability Statement
Sequence data were deposited in the European Nucleotide Archive under the project accession number PRJEB55810.
Acknowledgments
We wish to thank the past and present staff of the Microbiology Departments who contributed to this project on a daily basis. This study was partially presented as a poster at the 21st Lancefield International Symposium for Streptococci and Streptococcal Diseases 2022, Stockholm.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
References
- Vandamme, P.; Pot, B.; Falsen, E.; Kersters, K.; Devriese, L.A. Taxonomic Study of Lancefield Streptococcal Groups C, G, and L (Streptococcus dysgalactiae) and Proposal of S. dysgalactiae subsp. equisimilis subsp. Nov. Int. J. Syst. Bacteriol. 1996, 46, 774–781. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Efstratiou, A. Pyogenic Streptococci of Lancefield Groups C and G as Pathogens in Man. J. Appl. Microbiol. 1997, 83, 72S–79S. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brandt, C.M.; Spellerberg, B. Human Infections Due to Streptococcus dysgalactiae subspecies equisimilis. Clin. Infect. Dis. 2009, 49, 766–772. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jensen, A.; Kilian, M. Delineation of Streptococcus dysgalactiae, Its Subspecies, and Its Clinical and Phylogenetic Relationship to Streptococcus pyogenes. J. Clin. Microbiol. 2012, 50, 113–126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lambertsen, L.M.; Ingels, H.; Schønheyder, H.C.; Hoffmann, S.; Hoffmann, S.; Ingels, H.; Lambertsen, L.; Christensen, J.J.; Dessau, R.; Lomborg, S.; et al. Nationwide Laboratory-Based Surveillance of Invasive Beta-Haemolytic Streptococci in Denmark from 2005 to 2011. Clin. Microbiol. Infect. 2014, 20, O216–O223. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Anonymous. Voluntary Surveillance of Pyogenic and Non-Pyogenic Streptococcal Bacteraemia in England, Wales and Northern Ireland: 2020. Health Prot. Rep. 2021, 15, 1–23. [Google Scholar]
- Wajima, T.; Morozumi, M.; Hanada, S.; Sunaoshi, K.; Chiba, N.; Iwata, S.; Ubukata, K. Molecular Characterization of Invasive Streptococcus dysgalactiae subsp. equisimilis, Japan. Emerg. Infect. Dis. 2016, 22, 247–254. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rantala, S.; Vuopio-Varkila, J.; Vuento, R.; Huhtala, H.; Syrjänen, J. Clinical Presentations and Epidemiology of β-Haemolytic Streptococcal Bacteraemia: A Population-Based Study. Clin. Microbiol. Infect. 2009, 15, 286–288. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Beres, S.B.; Zhu, L.; Pruitt, L.; Olsen, R.J.; Faili, A.; Kayal, S.; Musser, J.M. Integrative Reverse Genetic Analysis Identifies Polymorphisms Contributing to Decreased Antimicrobial Agent Susceptibility in Streptococcus pyogenes. mBio 2022, 13, e0361821. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chopra, I.; Roberts, M. Tetracycline Antibiotics: Mode of Action, Applications, Molecular Biology, and Epidemiology of Bacterial Resistance. Microbiol. Mol. Biol. Rev. 2001, 65, 232–260. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guédon, G.; Libante, V.; Coluzzi, C.; Payot, S.; Leblond-Bourget, N. The Obscure World of Integrative and Mobilizable Elements, Highly Widespread Elements That Pirate Bacterial Conjugative Systems. Genes 2017, 8, 337. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Libante, V.; Nombre, Y.; Coluzzi, C.; Staub, J.; Guédon, G.; Gottschalk, M.; Teatero, S.; Fittipaldi, N.; Leblond-bourget, N.; Payot, S. Chromosomal Conjugative and Mobilizable Elements in Streptococcus suis: Major Actors in the Spreading of Antimicrobial Resistance and Bacteriocin Synthesis Genes. Pathogens 2019, 9, 22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liang, P.; Wang, M.; Gottschalk, M.; Vela, A.I.; Estrada, A.A.; Wang, J.; Du, P.; Luo, M.; Zheng, H.; Wu, Z. Genomic and Pathogenic Investigations of Streptococcus suis Serotype 7 Population Derived from a Human Patient and Pigs. Emerg. Microbes. Infect. 2021, 10, 1960–1974. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.; Qi, K.; Bai, X.; Wu, Z.; Kang, W.; Liang, P.; Zheng, H.; Xu, J. Characterization of Integrative and Conjugative Elements Carrying Antibiotic Resistance Genes of Streptococcus suis Isolated in China. Front. Microbiol. 2022, 13, 1074844. [Google Scholar]
- Lu, B.; Fang, Y.; Huang, L.; Diao, B.; Du, X.; Kan, B.; Cui, Y.; Zhu, F.; Li, D.; Wang, D. Molecular Characterization and Antibiotic Resistance of Clinical Streptococcus dysgalactiae subsp. equisimilis in Beijing, China. Infect. Genet. Evol. 2016, 40, 119–125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rojo-Bezares, B.; Toca, L.; Manuel Azcona-Gutiérrez, J.; Ortega-Unanue, N.; Toledano, P.; Sáenz, Y. Streptococcus dysgalactiae subsp. equisimilis from Invasive and Non-Invasive Infections in Spain: Combining Epidemiology, Molecular Characterization, and Genetic Diversity. Eur. J. Clin. Microbiol. Infect. Dis. 2021, 40, 1013–1021. [Google Scholar]
- Mcguinness, W.A.; Malachowa, N.; Deleo, F.R. Vancomycin Resistance in Staphylococcus aureus. Yale J. Biol. Med. 2017, 90, 269–281. [Google Scholar]
- Gherardi, G.; Imperi, M.; Palmieri, C.; Magi, G.; Facinelli, B.; Baldassarri, L.; Pataracchia, M.; Creti, R. Genetic Diversity and Virulence Properties of Streptococcus dysgalactiae subsp. equisimilis from Different Sources. J. Med. Microbiol. 2013, 63, 90–98. [Google Scholar]
- de Souza, J.P.; Santos, A.R.; de Paula, G.R.; Barros, R.R. Antimicrobial Susceptibility and Genetic Relationships among Streptococcus dysgalactiae subsp. equisimilis Isolates in Rio de Janeiro. Infect. Dis. 2016, 48, 676–681. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Leitner, E.; Zollner-Schwetz, I.; Zarfel, G.; Masoud-Landgraf, L.; Gehrer, M.; Wagner-Eibel, U.; Grisold, A.J.; Feierl, G. Prevalence of Emm Types and Antimicrobial Susceptibility of Streptococcus dysgalactiae subsp. equisimilis in Austria. Int. J. Med. Microbiol. 2015, 305, 918–924. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Traverso, F.; Blanco, A.; Villalón, P.; Beratz, N.; Sáez Nieto, J.A.; Lopardo, H. Molecular Characterization of Invasive Streptococcus dysgalactiae subsp. equisimilis. Multicenter Study: Argentina 2011–2012. Rev. Argent. Microbiol. 2016, 48, 279–289. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Loubinoux, J.; Plainvert, C.; Collobert, G.; Touak, G.; Bouvet, A.; Poyart, C. Adult Invasive and Noninvasive Infections Due to Streptococcus dysgalactiae subsp. equisimilis in France from 2006 to 2010. J. Clin. Microbiol. 2013, 51, 2724–2727. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ambroset, C.; Coluzzi, C.; Guédon, G.; Devignes, M.D.; Loux, V.; Lacroix, T.; Payot, S.; Leblond-Bourget, N. New Insights into the Classification and Integration Specificity of Streptococcus Integrative Conjugative Elements through Extensive Genome Exploration. Front. Microbiol. 2016, 6, 1483. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rice, L.B. Tn916 Family Conjugative Transposons and Dissemination of Antimicrobial Resistance Determinants. Antimicrob. Agents Chemother. 1998, 42, 1871–1877. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zankari, E.; Hasman, H.; Cosentino, S.; Vestergaard, M.; Rasmussen, S.; Lund, O.; Aarestrup, F.M.; Larsen, M.V. Identification of Acquired Antimicrobial Resistance Genes. J. Antimicrob. Chemother. 2012, 67, 2640–2644. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Croucher, N.J.; Page, A.J.; Connor, T.R.; Delaney, A.J.; Keane, J.A.; Bentley, S.D.; Parkhill, J.; Harris, S.R. Rapid Phylogenetic Analysis of Large Samples of Recombinant Bacterial Whole Genome Sequences Using Gubbins. Nucleic Acids Res. 2015, 43, e15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kozlov, A.M.; Darriba, D.; Flouri, T.; Morel, B.; Stamatakis, A. RAxML-NG: A Fast, Scalable and User-friendly Tool for Maximum Likelihood Phylogenetic Inference. Bioinformatics 2019, 35, 4453–4455. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).