Abstract
Nine new complexes with camphor imine or camphor sulfonimine ligands were synthesized and analytically and spectroscopically characterized, aiming to identify the key parameters that drive the antibacterial activity of the complexes with metal cores and imine substituents with distinct electronic and steric characteristics. The antimicrobial activity of all complexes was evaluated by determining their minimum inhibitory concentrations (MIC) against the Gram-negative Escherichia coli ATCC25922, Pseudomonas aeruginosa 477, and Burkholderia contaminans IST408, and the Gram-positive Staphylococcus aureus Newman. Camphor imine complexes based on the hydroxyl silver center ({Ag(OH)}) typically perform better than those based on the nitrate silver center ({Ag(NO3)}), while ligands prone to establish hydrogen bonding facilitate interactions with the bacterial cell surface structures. A different trend is observed for the silver camphor sulfonimine complexes that are almost non-sensitive to the nature of the metal cores {Ag(OH)} or {Ag(NO3)} and display low sensitivity to the Y substituent. The antibacterial activities of the Ag(I) camphor sulfonimine complexes are higher than those of the camphor imine analogues. All the complexes display higher activity towards Gram-negative strains than towards the Gram-positive strain.
1. Introduction
New antimicrobials are urgently needed to overcome the increasing resistance of bacteria to existing antibiotics. In the European Union (EU), bacterial infections pose a considerable burden on health care systems, accounting for ca. 33,000 deaths in 2015 [1]. Multi-resistant Klebsiella pneumoniae, Enterobacter sp., Pseudomonas aeruginosa, or Staphylococcus aureus, members of the ESKAPE group of pathogens, deserve special attention since they are prevalent in hospitalized patients with depressed immune systems and some strains are resistant to the third generation β-lactam antibiotics, as well as carbapenems [2].
In our days, threats to human health include not only the emergence of multi-resistance among common microbial human pathogens, but of also emerging new pathogens, as is the case of SARS-COV2. These health threats create a worldwide challenge and pressure to the discovery and development of new antimicrobials, a domain that has not been intensively pursued by the pharma industry in the last decades [3].
Thus far, the library of antimicrobials relies mostly on organic compounds. However, coordination compounds may be eligible alternatives with beneficial properties [4] due to the characteristics of the metal. In addition, at the complexes the ligands may be activated towards a reactivity distinct from that they present as free organic entities or be released leaving vacant coordination positions at the metal site that may enable interactions with bacterial cell components. The redox properties of coordination compounds are among the parameters that distinguish them from the organic compounds and may play a relevant role in their mechanisms of antibacterial activity. Electron transfer processes are of utmost relevance in biological processes. Compounds that interfere with biological electron transfer processes may trigger the formation of reactive organic species (ROS), leading, for example, to the inhibition of the bacterial cell respiratory chain. The electronic and steric characteristics of coordination compounds may also switch catalytic redox processes (on/off) reducing bacteria growth, e.g., through ROS generation [4].
The antibacterial properties of silver were recognized long ago by Hippocrates (the father of medicine). During the last century, silver sulfadiazine was used to control infections on wounds and burns [5], despite some concerns raised due to possible side effects [6]. Over the two last decades, research focused on the search for potential antimicrobial properties of silver coordination compounds raised considerably. Several families of silver-based coordination compounds have been shown to display relevant antibacterial activity with acceptable toxicity [7,8,9,10,11].
Within our work, we found that several camphor imine complexes have high antibacterial activity, often combined with antifungal activity [12,13]. Such activities can be suitably engineered through the design of the camphor imine ligands and the inner sphere of the metal through co-ligands to optimize the activity of the complexes towards specific targets.
In the present work, several sets of camphor imine ([Ag(NO3)(XC10H14NY)] (X= O or N, Series a), [Ag(OC10H14NY)2((μ-O)] (Series b), [Ag(OH)(OC10H14NY)2] (Series c)), and camphor sulfonimine complexes ([Ag(NO3)(O2SNC10H14NY)2] (Series d), [Ag(OH)(O2SNC10H14NY)2] (Series e), and [Ag(OH)(O2SNC10H14NY)] (Series f)) were synthesized, analytically and spectroscopically characterized, and their antibacterial activities determined, in order to get insights into the effect of structural changes at the camphor ligand or inner sphere on the antibacterial properties of the complexes.
2. Results and Discussion
2.1. Synthesis
Six sets of silver complexes were synthesized based on camphor-type ligands, as shown in Figure 1, aiming at enhancing the antibacterial properties of Ag(I) camphor imine complexes [Ag(NO3)L2] formerly reported [12,13].
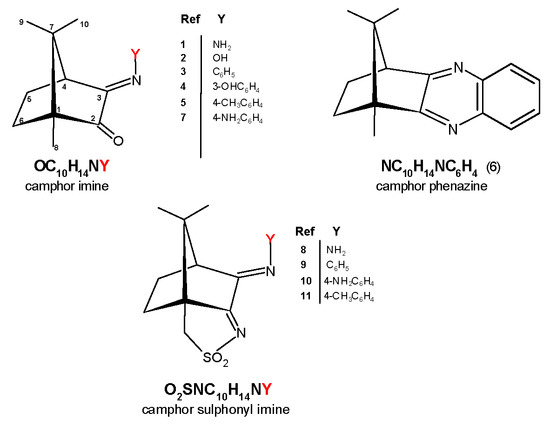
Figure 1.
Ligands used in this work: camphor imine (1−5 and 7, showing numbering scheme), camphor phenazine (6), and camphor sulfonimine (8−11).
[Ag(NO3)L] (Series a) differ on the metal to ligand ratio (1:1) from the previous nitrate complexes [Ag(NO3)L2] (1:2) and, consequently, on the structural arrangement. It was not possible to obtain suitable crystals from [Ag(NO3)(OC10H14NC6H4NH2−4)] (1a) for X-ray diffraction analysis. However, [Ag(NC10H14NC6H4)]NO3 (6a) was structurally characterized by X-ray diffraction, showing that it arranges as a coordination polymer, as shown in Figure 2.
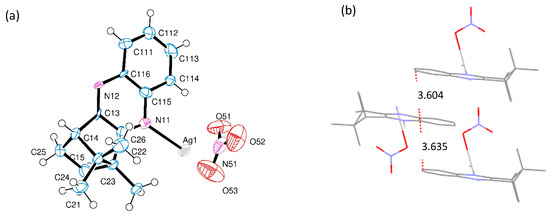
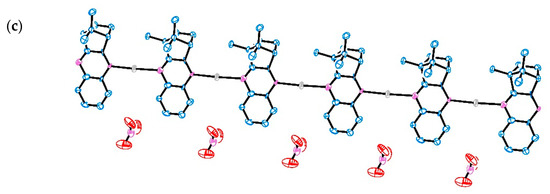
Figure 2.
(a) ORTEP drawing for [Ag(NC10H14NC6H4)]NO3 (6a) showing labelling scheme. (b) Sequential layers showing distances between parallel phenyl rings. (c) Polymeric arrangement of 6a.
The unit cell of complex 6a is formed by a silver ion (Ag(I)) coordinated to the nitrogen atom of one of the imine nitrogen atoms of the ligand. This unit bridges the Ag(I) site of a neighbor unit through the amine nitrogen atom of the ligand, forming a one-dimensional network (coordination polymer, Figure 2c) (N-Ag-N = 168.6(2) deg). A parallel 1D alignment of the nitrate ion (NO3−) equilibrates the positive charge of the silver cationic units, as shown in Figure 2c. Only one of the oxygen atoms in the nitrate anion is at nearly bonding distance from the silver atom (Ag–O51, 252.5(7) pm), occupying an orthogonal position with respect to the imine nitrogen atom (95.9(5) and 94.8(5) deg), generating a T-shaped ML3 metal center, as shown in Figure 2a.
Analytical data shows that 6a and 1a have in common the 1:1 metal to ligand ratio and conceivably the same polymeric arrangement. However, they differ in the ionic (6a, λM = 142 ohm−1 cm2 mole−1) and neutral (1a, λM = 64 ohm−1 cm2 mole−1) character, as verified through measurement of conductivity in acetonitrile solutions (1 × 10−3 M) [14]. The ionic character of 6a was confirmed by X-ray analysis. In order to get further insights into the structural differences of 1a and 6a, calculations using density functional theory (DFT) were undertaken for 1a based on an oligomer as a model compound for the coordination polymer. The oligomer was built by adding “mer” units incrementally making the chain grow. The four silver camphor units, as shown in Figure 3, can explicitly show the structural trends of the polymer as an illustrative example. Further computational details are given in Section 3.
Figure 3.
Calculated structural arrangement of [Ag(NO3)(OC10H14NNH2)] (1a) showing hydrogen bonding between the camphor imine substituent (Y = NH2) and the nitrate (NO3−) co-ligand.
Results showed that at 1a, the camphor ligand bridges two {Ag(NO3)} units—one through the imine nitrogen atom of the hydrazine moiety (NNH2), and the other through the oxygen atom (C = O) of the camphor skeleton. Additionally, the amine substituent (Y = NH2) bridges one of the oxygen atoms of the mono coordinated nitrate (NO3−) co-ligand, as shown in Figure 3, stabilizing the polymeric neutral character of the complex. These computational calculations extend the number of distinct structural arrangements found for polymeric Ag(I) camphor imine complexes, highlighting the structural versatility of the Ag(I) camphor imine system. Such versatility was also found for mononuclear complexes [Ag(NO3)(OC10H14NY)2] (Y = 2−5, Figure 1), that depending on the characteristics of the imine substituent (Y group) may display distorted octahedral to trigonal prismatic or even linear geometries [13].
In order to ascertain whether changing the co-ligand also changes the structure and properties of the complexes, nitrate was replaced by bridging oxygen or hydroxy ligands affording [{AgL}2(μ-O)] (Series b) and [Ag(OH)L] (Series c), respectively. Series b displays a dimer character with two AgIL units bridged by oxygen, while Series c keeps the 1:1 metal to ligand ratio according to a polymeric arrangement as found for 1a. The general formula found for silver hydroxy complexes follow those found for the nitrate complexes except that no complexes that fit the 1:2 metal to ligand ratio were obtained.
To check whether steric changes in the ligand affect the characteristics of the complexes, three sets of Ag(I) camphor sulphonyl imine complexes were synthesized.
Camphor sulphonyl imines (O2SNC10H13NY), as shown in Figure 1, differ from camphor imines (OC10H14NY) in an extra five members ring annulated to the camphor skeleton and presence of the sulphonyl imine group (NSO2) while keeping the imine substituent (Y, at position 3, Figure 1). For comparison purposes, a new camphor sulfonimine ligand (SO2NC10H13NC6H4CH3−4) was synthesized (see Section 3) and structurally characterized by X-ray diffraction analysis, as shown in Figure 4.
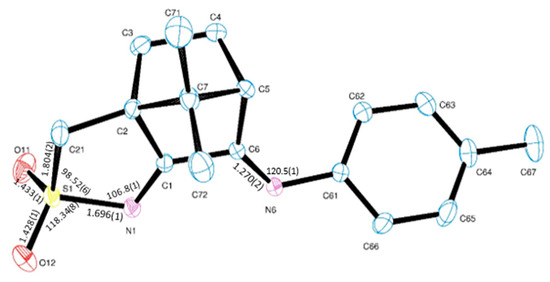
Figure 4.
ORTEP drawing for SO2NC10H13NC6H4CH3−4 (11) showing labelling scheme and selected bond lengths (angstrom) and angles (deg).
Using camphor sulphonyl imines as ligands, Ag(I) nitrate complexes [Ag(NO3)(SO2NC10H13NY)2] (Series d), bridging oxygen [{Ag(SO2NC10H13NY)2}2(μ-O)] (Series e), and hydroxy [Ag(OH)(SO2NC10H13NY)] (Series f) co-ligands were synthesized.
All the new complexes of the six families (Series a to Series f) were analytical and spectroscopically characterized by NMR (1H, 13C, DEPT, HMBC, HSQC) and FTIR (see Section 3).
2.2. Antibacterial Activity
The antibacterial activity of all complexes was evaluated against Gram-negative E. coli ATCC25922, P. aeruginosa 477, B. contaminans IST408, and Gram-positive S. aureus Newman through determination of the minimum inhibitory concentration (MIC).
Results show that all complexes are active against the bacterial strains under study. The activities against Gram-negative are considerably higher than against the Gram-positive bacterial strain, as shown in Table 1.

Table 1.
Minimum inhibitory concentration (MIC) values and AgI→Ag0 reduction potential for complexes.
Complex 1a is particularly efficient against the Gram-negative strains tested (MIC, 22−27 μg/mL), displaying a moderate activity towards the Gram-positive S. aureus strain Newman (MIC, 118 μg/mL). In contrast, complex 6a (ionic) that structurally resembles 1a (neutral) in the polymeric character displays considerably lower antibacterial activity than 1a, as shown in Table 1. Such an observation corroborates the relevance of the neutral versus ionic character of the Ag(I) camphor imine complexes on their antimicrobial activity, as previously reported for the mononuclear complexes [Ag(NO3)L2] or [AgL2]NO3 [12]. Parameters such as polarity, size, and lipophilicity are important factors for passive diffusion, affecting the partitioning and/or diffusion of a molecule into and across the membrane. In addition, highly polar groups also significantly decrease the permeability of parent compounds by orders of magnitude [15]. Since no specific transporters are known for the studied compounds, we assume that their entry into the bacterial cell mainly occurs by diffusion processes to which the basic character of the amine group at the camphor ligand (Y = NH2, 1a) and its ability to undergo hydrogen bonding in addition to the neutral character of the complex are the parameters that enhance the antibacterial performance [16]. Therefore, the differences observed in the antimicrobial activity of 1a and 6a can be attributed to the lower ability of 6a to diffuse across bacterial membranes due to its ionic character and the characteristics of the Y group.
Another parameter that, according to the previous studies, affects the biological activity of the Ag(I) camphor complexes is the co-ligand [17,18]. Replacement of nitrate by hydroxide at the inner sphere of the complexes was found to switch non-active [Ag(NO3)L] into active [Ag(OH)L] complexes against Candida albicans [14].
The herein results further corroborate the relevance of the co-ligands into the biological activity of the camphor imine complexes (Series a, b, c) by showing that complexes [Ag(OH)(OC10H14NY)] (Series c) that structurally resemble [Ag(NO3)(OC10H14NC6H4NH2−4)] (1a), in the neutral coordination polymer character, display lower MIC values, as shown in Table 1, than 1a and much lower than [{Ag(OC10H14NY)}2(μ-O)] (Series b) [19]. Thus, replacement of nitrate by hydroxide enhances the antimicrobial properties of the complexes. Complex [Ag(OH)(OC10H14NOH)] (2c) is specially active towards Gram-negative (3.4–7.2 μg/mL) and Gram-positive (9.2 μg/mL) bacterial strains, a fact that is attributed to hydrogen interactions with bacterial surface structures established through the co-ligand (OH) and/or the camphor imine substituent (Y = OH). On the contrary, the dimer character of complexes [{Ag(OC10H14NY)}2(μ-O)] (Series b) disfavors the antibacterial activity to MIC values in the range of the former reported for [Ag(NO3)L2] [12], although slightly higher than that of the ionic 6a, as shown in Table 1.
To compare the antibacterial activity of the camphor imine with the camphor sulfonimine Ag(I) complexes, the MIC values for Series d, e, and f were evaluated, as shown in Table 1. Data shows that all camphor sulfonimine complexes (except 9e) have high antibacterial activities which are comparable or even higher than that of camphor imine complexes. For example, complex 8d (camphor sulfonimine ligand) and 1a (camphor imine ligand), which have in common the metal center {Ag(NO3)} and the camphor substituent (Y = NH2) and differ on the mononuclear/polymeric character, display similar MIC values for E. coli (22 μg/mL, 1a, 27 μg/mL, 8d) while 8d performs slightly better for P. aeruginosa, B. contaminans, and S. aureus, as shown in Table 1. In what concerns the effect of the co-ligand on the MIC values of the complexes, it comes out that the camphor sulfonimine complexes are less sensitive than camphor imine complexes to changes in the silver core. Complexes of Series d and f display values in the same range for the four bacterial strains, although their metal sites are of types [Ag(NO3)L2] and [Ag(OH)L2], respectively, as shown in Table 1.
For a better rationalization of all the data it would be necessary to get the full set of complexes (with the same Y substituents) for the six families of compounds. However, undesired reactions between the metal salts and the ligand precursors prompted redox or other processes leading to the formation of Ag0 or silver oxides, instead of the coordination compounds.
A rationalization of the above MIC values, as shown in Table 1, shows that the Ag(I) complexes based on camphor imine or camphor sulfonimine behave differently in what concerns the {Ag(OH)} or {Ag(NO3)} metal cores and Y substituents. The activity of the camphor sulfonimine complexes (Series d, f, e) is basically independent of the co-ligand at silver site and slightly dependent of Y. The camphor sulfonimine ligand somehow buffers the process. A different trend is detected for the camphor imine silver complexes (Series a, b, c) that reveal activities that depend on (i) the ionic or neutral character, (ii) the characteristics of the Y substituent at the camphor imine group, and (iii) the co-ligand at metal site.
The MIC values obtained for the complexes and the precursor silver salts, as shown in Table 1, show that except 6a (ionic) and 3b, 5b, 9e (oxygen bridged), the complexes have higher activities than their precursors. The ligands by themselves are inactive.
2.3. Redox Properties
Biological processes commonly involve electron transfer and thus redox processes [20,21]. In order to evaluate whether a relationship exists between the redox characteristics and the antimicrobial properties of the complexes, their electrochemical properties were studied by cyclic voltammetry, as shown in Table 1. The results show that {Ag(NO3)} complexes (1a−6a and 8d−9d) reduce at potentials higher than {Ag(OH)} (2c, 4c, 7c, 10f, and 11f) complexes, as shown in Table 1, and both families of complexes reduce at lower potentials then their precursors Ag(NO3) ( 0.18 V) or Ag(OAc) ( −0.043 V), evidencing that the complexes are more electron rich than their precursors. In all cases, adsorption waves are observed in the reverse scan upon reduction, as shown in Figure 5a, that reveal silver metal formation (Ag0). The adsorption waves are less pronounced in the case of Ag(OH) than Ag(NO3)-based complexes, conceivably due to the fact that the {Ag(OH)}-based complexes are considerably more difficult to reduce than {Ag(NO3)}-based complexes. A peculiar feature of the silver hydroxide complexes is that Ag(I)→Ag(0) reduction occurs at potentials in the range of the ligands ( −1.46 V, 8 [22]; −1.16V, 9; −1.25 V, 10; = −1.37 V, 11).
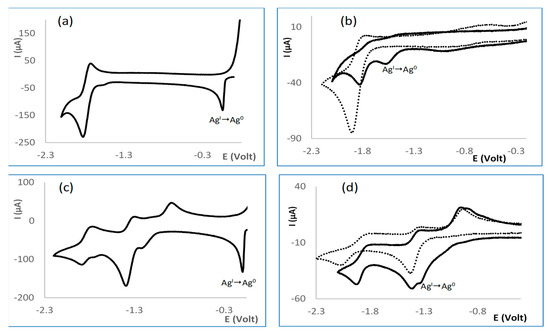
Figure 5.
Partial cyclic voltammograms for (a) [Ag(NO3)(OC10H14NC6H4CH3)2] (5a); (b) [Ag(OH)(OC10H14NC6H4NH2)] (7c); (c) [Ag(NO3)(SO2NC10H13NC6H5)2] (9d); (d) [Ag(OH)(SO2NC10H13NC6H4NH2)2] (10f). Dashed lines at (b,d) refer to free ligands.
Representative cyclic voltammograms, as shown in Figure 5, highlighting the Ag(I)→Ag(0) reduction wave are displayed for complexes 5a, 7c, 9d, and 10f. Dotted lines refer to the cyclic voltammogram of the free ligands, as shown in Figure 5b,d, evidencing proximity to metal reduction.
The rationalization of the antibacterial and electrochemical data shows that complexes which reduce at low potentials display low MIC values, except 9e that displays low potential and low activity. Additionally, complexes able to bond with hydrogen (1a, 2c, 8d) can overcome the unfavorable effect of the high Ag(I) reduction potential and display high antibacterial activity at least for some bacteria strains, as shown in Figure 6.
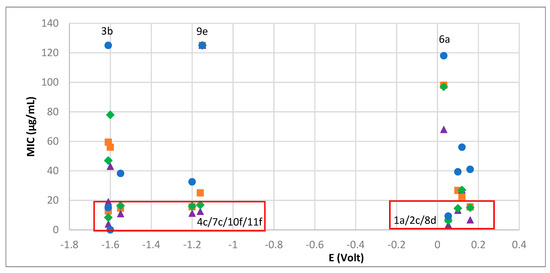
Figure 6.
MIC values versus Ag(I)→Ag(0) reduction potentials for: S. aureus (blue circles), E. coli (orange squares), B. contaminans (green losangles), P. aeruginosa (purple triangles).
We are aware that generalization must be careful. Nevertheless, low Ag(I)→Ag(0) potentials are consistent with improved resistance to reduction by electron donors in the cell (e.g., pyocyanin) [23], becoming a relevant parameter to the stability of the complexes in the biological medium and enhancement of their antibacterial activity.
3. Materials and Methods
3.1. General
The new complexes were synthesized under nitrogen using Schlenk and vacuum techniques unless stated otherwise. Camphor ligands (OC10H14NY: Y = NH2, OH, C6H5, C6H4NH2−4, C6H4CH3−4, and C6H4OH−3) were prepared according to reported procedures [24]. Silver salts, camphor, camphorsulfonic acid, the amines, and hydrazine were purchased from Sigma Aldrich. Acetonitrile (PA grade) was purchased from Carlo Erba and was purified by conventional techniques [25,26] and distilled before use. The FTIR spectra were obtained from KBr pellets using a JASCO FT/IR 4100 spectrometer. The NMR spectra (1H, 13C, DEPT, HSQC, and HMBC) were obtained from CD3CN, CD2Cl2, CDCl3, or DMSO solutions using Bruker Avance II+ (300 or 400 MHz) spectrometers. The NMR chemical shifts are referred to TMS (δ = 0 ppm).
3.2. Synthesis
3.2.1. Ligands
SO2NC10H13NC6H4NH2 (10)—Oxoimine (454 mg; 2 mmol) was dissolved in ethanol (7 mL), and the solution was acidified with CH3COOH (0.2 mL) and stirred for 20 minutes. Then, benzene−1,4-diamine (216 mg; 2 mmol) was added and the flask was saturated with N2. An orange precipitate formed upon overnight stirring at 40 °C that was filtered off solution affording the compound. Yield 77%. FTIR (KBr, cm−1): 3484 (NH2); 3384 (NH2); 1641 (C = N); 1317 (SO2); 1161 (SO2). 1H NMR (CDCl3, δppm): 7.03 (d, J = 7.6 Hz, 2H); 6.70 (d, J = 7.7 Hz, 2H); 3.90 (s, 2H); 3.36, 3.17 (2d, J = 13.5 Hz, 2H); 3.15 (d, J = 3.8 Hz, 1H); 2.33−2.17 (m, 2H); 2.04−1.97 (m, 1H); 1.87−1.79 (m, 1H); 1.10 (s, 3H); 0.90 (s, 3H).
13C NMR (CDCl3, δppm): 186.0 (C2); 161.9 (C3); 146.7 (Cipso); 139.4 (Cipso); 125.3 (CPh); 115.2 (CPh); 62.6 (C1); 52.0 (C4); 50.0 (C8); 47.4 (C7); 29.0, 23.9 (C5, C6); 20.0, 18.7 (C9, C10).
SO2NC10H13NC6H4CH3 (11)—3-oxo-camphorsulfonimide (454 mg; 2 mmol) was dissolved in ethanol (7 mL) and the solution was acidified with CH3COOH (0.2 mL). Upon stirring for 20 minutes, p-toluidine was added (268 mg; 2 mmol) and the mixture stirred at T = 40 °C overnight. A yellow precipitate formed that was filtered off affording the yellow compound. Yield 78%. FTIR (KBr, cm−1): 1658; 1633 (C = N); 1337 (SO2asym); 1161 (SO2sym). 1H NMR (CDCl3, δppm): 7.22 (d, J = 7.0 Hz, 2H); 6.91 (d, J = 7.1 Hz, 2H); 3.38, 3.18 (2d, J = 13.1 Hz, 2H); 3.05 (d, J = 3.7 Hz, 1H); 2.28−2.18 (m, 2H); 2.07−1.98 (m, 1H); 1.85−1.76 (m, 1H); 1.09 (s, 3H); 0.93 (s, 3H); 0.77 (s, 3H). 13C NMR (CDCl3, δppm): 185.5 (C2); 166.2 (C3); 146.4, 136.9 (Cipso); 129.9, 121.2 (CPh); 62.8 (C1); 51.8 (C4); 50.1 (C8); 46.9 (C7); 28.7, 24.2 (C5, C6); 20.1, 18.6 (C9, C10).
3.2.2. Complexes
Due to sensitivity of Ag(I) solutions to light, the flasks with the reaction mixtures were covered with aluminum foil. Complexes 2a, 3a, 4a, 5a, 3b, 5b, and 8d were prepared following the procedures previously reported [12,13,14].
[Ag(NO3)(OC10H14NNH2)] (1a)—The camphor imine ligand OC10H14NNH2 (1, 0.090g; 0.50 mmol) was dissolved in acetonitrile (7 mL). Then, silver nitrate (0.085 g; 0.50 mmol) was added and the mixture was stirred for ca. 8 hours. A light grey suspension (silver particles) was obtained that was filtrated off solution. The transparent solution was then evaporated under vacuum until formation of an oil to which Et2O (3 mL) was added. A white precipitate formed upon solvent evaporation. Yield 50%. Elem. Anal. (%) for AgC10H16N3O4: Found: C, 34.0; N, 11.7; H, 4.8. Calc.: C, 34.3; N, 12.0; H, 4.6. FTIR (KBr, cm−1): 3414, 3294 (NH); 1707 (C = O); 1577 (C = N); 1384 (NO3). 1H NMR (CD2Cl2, δppm): 7.40 (sl, 2H); 3.20 (d, J = 3.7 Hz, 1H); 2.04−1.95 (m, 1H); 1.79−1.70 (m, 1H); 1.60−1.43 (m, 2H); 0.95 (s, 6H); 0.77 (s, 3H). 13C NMR (CD2Cl2, δppm): 204.5 (C2); 155.0 (C3); 58.2 (C1); 46.8 (C7); 45.7 (C4); 31.2, 23.0 (C5, C6); 20.5, 17.2 (C9, C10); 8.7 (C8).
[Ag(NC10H14NC6H4)]NO3 (6a)—AgNO3 (170 mg; 1.0 mmol) and the ligand (6, C16H18N2, 238 mg; 1.0 mmol) were mixed in a Schlenk and stirred under vacuum for 15 minutes. Dried acetonitrile (10 mL) was then added, and the mixture was stirred over-night at room temperature. The suspension was filtered to remove silver particles. From the solution the complex precipitated as an off-white solid upon partial solvent evaporation of the solvent. The solid was filtered off from the colorless solution and by further evaporation of the solvent followed by a few days in the freezer, another crop of the complex was obtained that was filtered off solution. Yield 77%. Elem. Anal. (%) for AgC16H18N3O3·⅟4Et2O: Found: C, 41.0; N, 11.4; H, 5.2. Calc.: C, 41.2; N, 11.1; H, 5.5. FTIR (KBr, cm−1): 1517 (C = N); 1360 (NO3). 1H NMR (CD3CN, δppm): 7.98−7.96 (m, 2H), 7.68−7.66 (m, 2H), 3.03 (d, J = 4,4Hz, 1H), 2.37−2.27 (m, 1H), 2.14−2.04 (m, 1H), 1.98−1.92 (m, 2H), 1.38 (s, 3H), 1.12 (s, 3H), 0.58 (s, 3H). 13C NMR (CD3CN, δppm): 167.0 (C2); 165.5 (C3); 142.6, 141.6 (Cipso); 129.7, 129.5, 129.4, 129.3 (CPh); 55.1 (C1); 54.8 (C7); 54.7 (C4); 32.4, 25.1 (C5, C6); 20.4 (C9); 18.6 (C10); 10.4 (C8).
[Ag(OH)(OC10H14NOH)]· ½EtOH (2c)—A solution of the ligand NC10H14N(OH) (2, 54 mg; 0.30 mmol) in ethanol (5 mL) was added to a solution of silver acetate (50 mg; 0.30 mmol) in water (5 mL). The mixture was stirred for 2 hours at room temperature. Then, the solution was filtered to separate a slight suspension and the solution evaporated to dryness affording an off-white compound. Yield 51%. Elemental analysis for AgC10H16NO3·½EtOH, Exp.: C, 39.9; N, 3.9; H, 5.4. Calc.: C, 40.1; N, 4.3; H, 5.8. IR (KBr, cm−1): 3444 (OH), 1743 (CO), 1643 (CN). 1H NMR (DMSO, δppm): 3.08 (d, J = 3.7 Hz, 1H); 1.98−1.88 (m, 1H); 1.80 (s, 1H); 1.79−1.69 (m, 1H); 1.41−1.26 (m, 2H); 0.92 (s, 3H); 0.90 (s, 3H); 0.77 (s, 3H). 13C NMR (DMSO, δppm): 203.8 (C2); 96.6 (C3); 57.9 (C1); 45.9 (C4); 44.3 (C7); 30.1, 23.4 (C5, C6); 20.1 17.3 (C9, C10); 8.8 (C8). The chemical shifts of EtOH are omitted for clarity.
[Ag(OH)(OC10H14N(C6H4OH−3)] (4c)—A solution OC10H14NC6H4OH−3 (4, 77 mg; 0.30 mmol) in ethanol (5 mL) was added to a solution of silver acetate (50 mg; 0.30 mmol) in water (5 mL) and the mixture was stirred for 2 hours. A slight suspension formed that was filtered off and the solution evaporated to dryness providing a dark-green compound. Yield 52%. Elemental analysis for AgC16H20NO3, Exp.: C, 50.5; N, 3.5; H, 5.3. Calc.: C, 50.3; N, 3.7; H, 5.3. FTIR (KBr, cm−1): 3434 (OH); 1748 (CO); 1662 (CN). 1H NMR (CD3CN, δ ppm): 7.20 (t, J = 7.9 Hz, 1H), 6.66 (dd, J = 6.3, 1.9 Hz, 1H), 6.39 (s, 1H), 6.36 (d, J = 2.4 Hz, 1H), 2.76 (d, J = 4.8 Hz, 1H); 2.19 (s, OH); 1.91−1.84 (m, 2H); 1.63−1.56 (m, 2H); 1.03 (s, 3H); 0.97 (s, 3H); 0.85 (s, 3H). 13C NMR (CD3CN, δppm): 207.5 (C2); 173.3 (C3); 158.9, 152.4 (Cipso); 131.1, 113.0, 112.2, 107.8 (CPh); 59.0 (C1); 51.2 (C4); 45.2 (C7); 30.9, 24.9 (C5, C6); 21.2, 17.6 (C9, C10); 9.4 (C8).
[Ag(OH)(OC10H14NC6H4NH2−4)]. CH3COOH (7c)—A solution of the ligand (7, OC10H14NC6H4NH2−4, 76 mg; 0.30 mmol) in ethanol (5 mL) was added to a suspension of silver acetate (50 mg; 0.30 mmol) in water (5 mL) and N2 was fluxed through the mixture that was stirred for 5 hours at room temperature. The suspension was filtered off to remove residues and the clear solution was evaporated affording a black-bright compound. Yield 57%. Elem. Anal. for AgC16H21N2O2·CH3COOH Exp.: C, 49.3; N, 6.2; H, 5.4. Calc.: C, 49.0; N, 6.4; H, 5.7. FTIR (KBr, cm−1): 3455, 3340 (NH2); 1733 (CO); 1625 (CN); 1567 (COO). 1H NMR (CD3CN, δppm): 6.89 (d, J = 7.8 Hz, 2H); 6.67 (d, J = 7.8 Hz, 2H); 4.30 (s, 2H); 2.97 (d, J = 4.8 Hz, 1H); 1.92−1.85 (m, 1H); 1.68−1.49 (m, 3H); 1.89 (s, 3H); 1.02 (s, 3H); 0.99 (s, 3H); 0.86 (s, 3H). 13C NMR (CD3CN, δppm): 208.1 (C2); 169.4 (C3); 148.4, 139.6 (Cipso); 125.1, 115.4 (CPh); 58.7 (C1); 51.6 (C4); 45.9 (C7); 31.2, 24.6 (C5, C6); 20.9, 17.8 (C9, C10); 9.4 (C8).
[Ag(NO3)(SO2NC10H13NC6H5)2]·H2O (9d)—Ligand (9, OC10H14NC6H5, 91 mg; 0.30 mmol) in ethanol (5 mL) was added to a suspension of silver acetate (50 mg; 0.30 mmol) in water (5 mL), bubbled with N2 and stirred for 4 hours at room temperature. The suspension was filtered off to remove residues and the solution was evaporated affording a black-bright compound, that was filtered off affording the complex. Yield 57%. Elem. Anal. for AgC32H38N5O8S2·H2O Exp.: C, 48.6; N, 9.0; H, 4.7; S, 7.6. Calc.: C, 48.5; N, 8.8; H, 4.8; S, 8.0. IR (KBr, cm−1): 3434 (OH); 1667 (CN); 1637 (CN); 1384 (NO3); 1344 (SO2); 1162 (SO2). 1H NMR (DMSO, δppm): 7.46 (t, J = 7.4 Hz, 2H); 7.25 (t, J = 7.4 Hz, 1H); 6.99 (d, J = 8.4 Hz, 2H); 3.74, 3.52 (2d, J = 14 Hz, 2H); 2.88 (d, J = 4.8 Hz, 1H); 2.32−2.25 (m, 1H); 2.19–2.10 (m, 1H); 1.81−1.71 (m, 2H); 1.01 (s, 3H); 0.84 (s, 3H). 13C NMR (DMSO, δppm): 186.1 (C2); 167.8 (C3); 148.8 (Cipso); 129.3, 126.0, 120.1 (CPh); 63.0 (C1); 51.0 (C4); 49.3 (C8); 46.3 (C7); 27.7 23.4 (C5, C6); 19.2, 17.5 (C9, C10).
[{Ag(SO2NC10H13NC6H5)2}2(µ-O)]·4H2O (9e)—A solution of the ligand (9, OC10H14NC6H5, 84 mg; 0.18 mmol) in ethanol (5 mL) was added to a suspension of silver acetate (30 mg; 0.18 mmol) in water (5 mL). The mixture stirred overnight at 40 °C under N2. The suspension was filtered off affording a dark compound. Yield 64%. Elem. Anal. for Ag2C64H72N8O9S4·4H2O Exp.: C, 50.4; N, 7.3; H, 4.7; S, 8.4. Calc.: C, 50.8; N, 7.4; H, 5.3; S, 8.5. FTIR (KBr, cm−1): 3434 (OH); 1664 (CN); 1638 (CN); 1339 (SO2); 1162 (SO2). 1H NMR (DMSO, δppm): 7.45 (t, J = 7.7 Hz, 2H); 7.25 (t, J = 7.4 Hz, 1H); 6.99 (d, J = 7.7 Hz, 2H); 3.73, 3.51 (2d, J = 14 Hz, 2H); 2.87 (d, J = 4.7 Hz, 1H); 2.33 –2.24 (m, 1H); 2.19–2.09 (m, 1H); 1.82–1.70 (m, 2H); 1.01 (s, 3H); 0.83 (s, 3H). 13C NMR (DMSO, δppm): 186.2 (C2); 167.9 (C3); 148.9 (Cipso); 129.4, 126.1, 120.2 (CPh); 63.1 (C1); 51.1 (C4); 49.4 (C8); 46.4 (C7); 27.8, 23.5 (C5, C6); 19.3, 17.6 (C9, C10).
[Ag(OH)(SO2NC10H13NC6H4NH2−4)]·CH3COOH (10f)—A solution of SO2NC10H13N(C6H4)NH2 (7, 95 mg; 0.30 mmol) in ethanol (5 mL) was added to a solution of silver acetate (50 mg; 0.30 mmol) in water (5 mL) and the suspension was stirred overnight. A dark brilliant compound was obtained that was filtered and dried under vacuum. Yield 46%. Elem. Anal. for AgC18H24N3O5S, Exp.: C, 43.1; N, 8.4; H, 4.7; S, 6.5. Calc.: C, 43.0; N, 8.4; H, 4.8; S, 6.4. IR (KBr cm−1): 3437, 3366 (NH); 1743 (CO); 1643 (CN); 1564 (COO); 1335 (SO2 sym); 1160 (SO2 asym). 1H NMR (DMSO, δppm): 6.98 (d, J = 8.5 Hz, 2H); 6.64 (d, J = 8.5 Hz, 2H); 5.70 (s, 2H); 3.64, 3.41 (2d, J = 14 Hz, 2H); 3.15 (d, J = 3.9 Hz, 1H); 2.34−2.18 (m, 2H); 1.85 (s, 3H); 1.76−1.65 (m, 2H); 1.04 (s, 3H); 0.77 (s, 3H). 13C NMR (DMSO, δppm): 187.0 (C2); 159.4 (C3); 149.5 (Cipso); 136.0, 125.8, 113.8 (CPh); 62.6 (C1); 51.6 (C4); 49.2 (C8); 47.0 (C7); 28.4, 23.0 (C5, C6); 19.0, 17.8 (C9, C10).
[Ag(OH)(SO2NC10H13NC6H4CH3−4)] (11f)—A solution of SO2NC10H13N(C6H4)CH3 (11, 95 mg; 0.30 mmol) in ethanol (5 mL) was added to a solution of silver acetate (50 mg; 0.30 mmol) in water (5 mL) and the suspension was stirred overnight. A yellow compound was obtained by filtration. Yield 63%. Elem. Anal. for AgC17H21N2O3S, Exp.: C, 46.4; N, 6.5; H, 4.9; S, 7.3. Calc.: C, 46.3; N, 6.4; H, 4.8; S, 7.3. IR (KBr cm−1): 1661 (CN); 1633 (CN); 1336 (SO2 sym); 1160 (SO2 asym). 1H NMR (CD3CN, δppm): 7.26 (d, J = 8.1 Hz, 2H); 6.92 (d, J = 8.2 Hz, 2H); 3.49, 3.27 (2d, J = 14 Hz, 2H); 3.00 (d, J = 4.8 Hz, 1H); 2.36 (s, 3H); 2.34–2.16 (m, 2H); 1.90–1.74 (m, 2H); 1.06 (s, 3H); 0.86 (s, 3H). 13C NMR (CD3CN, δppm): 187.6 (C2); 168.2 (C3); 147.5, 137.4 (Cipso); 130.7, 121.8 (CPh); 64.2 (C1); 52.5 (C4); 50.6 (C8); 47.5 (C7); 29.2, 24.5 (C5, C6), 21.0 (CH3), 20.0, 18.2 (C9, C10).
3.3. Cyclic Voltammetry Studies
The redox properties of the complexes and ligands were studied by cyclic voltammetry using a three compartments cell equipped with a Pt wire electrode and interfaced with VoltaLab PST050 equipment. The cyclic voltammograms were obtained from NBu4BF4 solutions in CH3CN (0.10 M) used as electrolyte. At least ten cyclic voltammograms of each compound was obtained. The double electrode double layer was renewed between each cycle by bubbling nitrogen in the cell. The potentials were measured in volts (±10 mV) versus SCE at 200 mV/s using [Fe(η5-C5H5)2]0/+ (=0.382 V; CH3CN) as internal reference.
3.4. X-ray Diffraction Analysis
X-ray data for [Ag(NO3)(NC10H14NC6H4)] (6a) and SO2NC10H14NC6H4CH3−4 (11) were collected using a Bruker AXS-KAPPA APEX II area detector apparatus equipped with a graphite-monochromated Mo Kα (λ = 0.71073 Å) and was corrected for Lorentz polarization and, empirically, for absorption effects. The structures were solved by direct methods using SHELX97 [27] and refined by full matrix least squares against F2 using SHELX97 all included in the suite of programs WinGX v2020.1 for Windows [28]. The non-hydrogen atoms were refined anisotropically and the H atoms were inserted in idealized positions and allowed to refine riding on the parent atom. Crystal data and refinement parameters are summarized in Table 2. Illustrations of the molecular structures were made with ORTable 3. [28].

Table 2.
Crystallographic data for [Ag(NO3)(NC10H14NC6H4)] (6a) and SO2NC10H14NC6H4CH3 (11).
The Cambridge Crystallographic Data Centre (CCDC 2044258∓2044259) contains the supplementary crystallographic data for this article. The X-ray data can be obtained free of charge via www.ccdc.cam.ac.uk/conts/retrieving.html (or from the CCDC, 12, Union Road, Cambridge CB2 1EZ, UK; fax: +44 1223 336033 or deposit@ccdc.cam.ac.uk).
3.5. DFT Calculations
DFT calculations were carried out using GAMESS-US [29] version R3 with a CAMB3LYP function [30], with 65% Hartree-Fock (HF) exact exchange at long range and 19% at short range, using an SBKJC basis set. An incremental approach was used to build the oligomer chains from a single “mer” unit, by adding successive new metal centers to the seed unit. The dimeric oligomer was used to probe the conformational space of possible isomers. Once a growing trend was established (from the dimer), the new metal units were added without further probing of isomers. The four-camphor oligomer chain was included in the paper as an illustrative example. The optimized structures were confirmed as minimums by Hessians with positive eigenvalues and six near zero frequencies.
3.6. Bacterial Strains and Minimum Inhibitory Concentration Assays
The bacterial strains Staphylococcus aureus Newman, Pseudomonas aeruginosa 477, Escherichia coli ATCC25922, and Burkholderia contaminans IST408 were used in the present work and kept as frozen stock suspensions at –80 °C. When in use, bacterial cultures were maintained in Lennox Broth solid medium (Sigma-Aldrich, St. Louis, USA). Minimum inhibitory concentration (MIC) of the complexes under study were assessed by microdilution assays using Muller Hinton broth (MH) (Sigma-Aldrich, St. Louis, USA) as previously described [11,12,18,19]. Bacterial growth was assessed by measuring the cultures optical density at 640 nm (OD640). The MIC values were estimated by fitting the OD640 mean values, resulting from at least three independent experiments carried out in duplicate, with a Gompertz modified equation [12,13,14].
4. Conclusions
The antibacterial activities of the Ag(I) camphor imine (Series a, b, and c) and camphor sulfonimine imine (Series d, e, and f) complexes were evaluated against E. coli, P. aeruginosa, B. contaminans, and S. aureus through determination of MIC values. The analysis and rationalization of the results show that the imine or sulfonimine character of the camphor ligands considerably modify the behavior of the complexes in what concerns their sensitivity to the metal core and substituents on the camphor ligand. The Ag(I) camphor imine complexes are highly sensitive to nitrate or hydroxide co-ligands, showing that the {Ag(OH)} complexes are bacteriologically more active than the {Ag(NO3)} complexes. No such effect was detected on the camphor sulfonimine Ag(I) complexes. Additionally, the amine substituent (Y = NH2) at the {Ag(NO3)} camphor imine complexes (Series a) considerably enhances the antibacterial activity, while no such effect is observed for the camphor sulfonimine silver nitrate complexes (Series d).
The redox properties of the {Ag(OH)} and {Ag(NO3)} complexes are considerably different; Ag(OH) complexes reduce at much lower potentials than {Ag(NO3)} (except ([Ag(OH)(OC10H14NOH)], 2c), irrespective of the camphor imine or sulfonimine ligand. Silver hydroxy complexes resist better to Ag(I) to Ag0 reduction, and this possibly contributes to the enhancement of the complexes’ antimicrobial activity.
Overall, the herein results show that it is possible to tune the antibacterial activity of the camphor silver complexes through replacement of the co-ligand (NO3− by OH−) or re-design of the camphor ligand; camphor sulfonimine complexes tend to be more active than the related camphor imine ones. Additionally, it was also possible to verify that a relationship exists between the redox properties of the complexes and their antibacterial activity. Results herein are based on the synthesis and characterization of nine new Ag(I) complexes, the analytical and spectroscopic characteristics of which are displayed in Section 3.
Author Contributions
Conceptualization, J.H.L. and M.F.N.N.C.; data curation, J.P.C., S.A.S., A.M.G., and J.H.L.; formal analysis, S.A.S., A.M.G., J.M.M., and M.F.N.N.C.; funding acquisition, J.H.L. and M.F.N.N.C.; investigation, J.P.C., S.A.S., A.M.G., J.M.M., and M.F.N.N.C.; methodology, J.P.C., S.A.S., A.M.G., J.M.M., and M.F.N.N.C.; project administration, J.H.L. and M.F.N.N.C.; resources, A.M.G. and M.F.N.N.C.; supervision, J.H.L. and M.F.N.N.C.; writing—original draft, A.M.G. and M.F.N.N.C.; writing—review and editing, J.H.L. and M.F.N.N.C. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
The authors acknowledge financial support from Fundação para a Ciência e a Tecnologia (FCT) (projects UIDB/00100/2020 and UIDB/04565/2020) and Grant BL-CQE/2019−013. The Portuguese NMR IST–UL Centers are acknowledged for facilities.
Data Availability Statement
The X-ray data can be obtained free of charge via www.ccdc.cam.ac.uk/conts/retrieving.html (or from the CCDC, 12, Union Road, Cambridge CB2 1EZ, UK; fax: +44 1223 336033 or deposit@ccdc.cam.ac.uk).
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
References
- Cassini, A.; Högberg, L.D.; Plachouras, D.; Quattrocchi, A.; Hoxha, A.; Simonsen, G.S.; Colomb-Cotinat, M.; Kretzschmar, M.E.; Devleesschauwer, B.; Cecchini, M.; et al. Burden of AMR Collaborative Group. Attributable deaths and disability-adjusted life-years caused by infections with antibiotic-resistant bacteria in the EU and the European Economic Area in 2015: A population-level modelling analysis. Lancet Infect. Dis. 2019, 19, 56–66. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- European Centre for Disease Prevention and Control (ECDC). Summary of the Latest Data on Antibiotic Resistance in the European Union. 2012. Available online: https://www.ecdc.europa.eu/sites/default/files/documents/antibiotics-resistance-EU-data-2012.pdf (accessed on 19 November 2020).
- Theuretzbacher, U. Future antibiotics scenarios: Is the tide starting to turn? Int. J. Antimicrob. Agents 2009, 34, 15–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Frei, A.; Zuegg, J.; Elliott, A.G.; Baker, M.; Braese, S.; Brown, C.; Chen, F.; Dowson, C.G.; Dujardin, G.; Jung, N.; et al. Metal complexes as a promising source for new antibiotics. Chem. Sci. 2020, 11, 2627–2639. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alexander, J.W. History of the medical use of silver. Surg. Infect. 2009, 10, 289–292. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Atiyeh, B.S.; Costagliola, M.; Hayek, S.N.; Dibo, S.A. Effect of silver on burn wound infection control and healing: Review of the literature. Burns 2007, 33, 139–148. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Johnson, N.A.; Southerland, M.R.; Youngs, W.J. Recent Developments in the Medicinal Applications of Silver-NHC Complexes and Imidazolium Salts. Molecules 2017, 22, 1263. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Medici, S.; Peana, M.; Crisponi, G.; Nurchi, V.M.; Lachowicz, J.I.; Remelli, M.; Zoroddu, M.A. Silver coordination compounds: A new horizon in medicine. Coord. Chem. Rev. 2016, 327–328, 349–359. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liang, X.; Luan, S.; Yin, Z.; He, M.; He, C.; Yin, L.; Zou, Y.; Yuan, Z.; Li, L.; Song, X.; et al. Recent advances in the medical use of silver complex. Eur. J. Med. Chem. 2018, 157, 62–80. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Azócar, M.I.; Gómez, G.; Levín, P.; Paez, M.; Muñoz, H.; Dinamarca, N. Review: Antibacterial behavior of carboxylate silver(I) complexes. J. Coord. Chem. 2014, 67, 3840–3853. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abdulkareem, M.; Youngs, W.J. Silver and its application as an antimicrobial agent. Expert Opin. Ther. Pat. 2005, 15, 125–130. [Google Scholar]
- Cardoso, J.M.S.; Guerreiro, S.I.; Lourenço, A.; Alves, M.M.; Montemor, M.F.; Mira, N.P.; Leitão, J.H.; Carvalho, M.F.N.N. Ag(I) camphorimine complexes with antimicrobial activity towards clinically important bacteria and species of the Candida genus. PLoS ONE 2017, 12, e0177355. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Carvalho, M.F.N.N.; Leite, S.; Costa, J.P.; Galvão, A.M.; Leitão, J.H. Ag(I) camphor complexes: Antimicrobial activity by design. J. Inorg. Biochem. 2019, 199, 110791. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Costa, J.P.; Pinheiro, M.J.F.; Sousa, S.A.; Botelho do Rego, A.M.; Marques, F.; Oliveira, M.C.; Leitão, J.H.; Mira, N.; Carvalho, M.F.N.N. Antimicrobial Activity of Silver Camphorimine Complexes against Candida Strains. Antibiotics 2019, 8, 144. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Geary, W.J. The use of conductivity measurements in organic solvents for the characterisation of coordination compounds. Coord. Chem. Rev. 1971, 7, 81–122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, N.J.; Hinner, M.J. Getting across the cell membrane: An overview for small molecules, peptides, and proteins. Methods Mol. Biol. 2015, 1266, 29–53. [Google Scholar]
- Shokovaa, E.A.; Kimb, J.K.; Kovaleva, V.V. Camphor and Its Derivatives. Unusual Transformations and Biological Activity. Russ. J. Org. Chem. 2016, 52, 459–488. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Leitão, J.H.; Sousa, S.A.; Leite, S.A.; Carvalho, M.F.N.N. Silver Camphor Imine Complexes: Novel Antibacterial Compounds from Old Medicines. Antibiotics 2018, 7, 65. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cardoso, J.M.S.; Galvão, A.M.; Guerreiro, S.I.; Leitão, J.H.; Suarez, A.C.; Carvalho, M.F.N.N. Antibacterial activity of silver camphorimine coordination polymers. Dalton Trans. 2016, 45, 7114–7123. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sjulstok, E.; Olsen, J.M.H.; Solov’yov, I.A. Quantifying electron transfer reactions in biological systems: What interactions play the major role? Sci. Rep. 2015, 5, 18446. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brett, A.M. Electron Transfer Reactions in Biological Systems. In Chemistry, Molecular Sciences and Chemical Engineering; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2017; pp. 1–8. [Google Scholar]
- Carvalho, M.F.N.N. A Search for the Influence of the Electronic Characteristics of the Camphor Derived Ligands and Complexes on their Redox Properties. Port. Electrochem. Acta 2004, 22, 3–10. [Google Scholar]
- Muller, M. Bacterial Silver Resistance Gained by Cooperative Interspecies Redox Behavior. Antimicrob. Agents Chemother. 2018, 62, e00672–e00718. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Carvalho, M.F.N.N.; Costa, L.M.G.; Pombeiro, A.J.L.; Schier, A.; Scherer, W.; Harbi, S.K.; Verfürth, U.; Herrmann, R. Synthesis, structure, and electrochemistry of palladium complexes with camphor-derived chiral ligands. Inorg. Chem. 1994, 33, 6270–6277. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Armarego, W.L.F.; Chai, C.L.L. Purification of Laboratory Chemicals, 6th ed.; Elsevier Inc.: Oxford, UK, 2008. [Google Scholar]
- Weissberger, A.; Bunger, W.B.; Sakano, T.K. Organic Solvents: Physical Properties and Methods of Purification, 4th ed.; Riddick, J.A., Bunger, W.B., Eds.; Wiley-Interscience: New York, NY, USA, 1986. [Google Scholar]
- Sheldrick, G.M. SHELX-97-Programs for Crystal Structure Analysis (Release 97–2); Institüt für Anorganische Chemie der Universität: Göttingen, Germany, 1998. [Google Scholar]
- Farrugia, L.J. WINGX and ORTEP for Windows: An update. J. Appl. Crystallogr. 2012, 45, 849–854. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schmidt, M.W.; Baldridge, K.K.; Boatz, J.A.; Elbert, S.T.; Gordon, M.S.; Jensen, J.H.; Koseki, S.; Matsunaga, N.; Nguyen, K.A.; Su, S.; et al. General atomic and molecular electronic structure system. J. Comput. Chem. 1993, 14, 1347–1363. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yanai, T.; Tew, D.; Handy, N. A new hybrid exchange-correlation functional using the Coulomb-attenuating method (CAM-B3LYP). Chem. Phys. Lett. 2004, 393, 51–57. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).