Abstract
Grafting of paramagnetic transition and rare earth metal ions onto the surface of detonation nanodiamonds (DNDs) was successfully implemented in the recent decade and opened new opportunities in the biomedical application of these compounds, particularly as novel contrast agents for magnetic resonance imaging. The grafting was studied mainly using EPR, NMR, and magnetic measurements. Such a highly surface-sensitive, quantitative, chemical analytic technique as X-ray photoelectron spectroscopy (XPS) was very rarely used. In this paper, we report the XPS study of grafting transition and rare-earth metal ions (Cu2+, Co2+, Mn2+, and Gd3+) onto the surface of DNDs. Binding energies for metal, carbon, oxygen, and nitrogen atoms were determined and attributed to the corresponding ion states and atomic groups. Comparing XPS and EPR findings, we showed that the developed synthesis route resulted in almost complete grafting of manganese and gadolinium atoms in the form of paramagnetic ions Mn2+ and Gd3+ to the diamond surface, while only 30% of the copper atoms on the surface are in the paramagnetic state Cu2+, and the rest 70% are in the non-magnetic Cu+ state. It was not possible to draw a similar conclusion regarding Co2+ ions due to the lack of data on the amount of these paramagnetic ions on the DND surface.
1. Introduction
Diamond nanoparticles produced by the detonation method (detonation nanodiamonds, DNDs) have attracted great interest due to their numerous applications and commercial availability [1,2,3,4,5,6,7,8,9,10,11,12,13,14,15,16,17,18,19]. Among the recent attractive areas of the nanodiamond applications, one could mention nanodiamonds as catalyst support substances including putting them to use as single-atom catalysts [20,21,22], and mostly as contrast agents in the magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) [23,24,25,26,27]. To implement the latter, paramagnetic ions were initially chemically bound to the surface of diamond nanoparticles, mainly in organogadolinium fragments conjugated to the ND surface [23,24,25,26,27]. In the last decade, the direct grafting of paramagnetic ions of transition and rare earth metals onto the DND surface has been successfully implemented [28,29,30,31,32,33,34,35,36,37]. Such grafting results in an increase in the relaxation rate of nuclear spins of carbon and hydrogen atoms in the DND structure [28,29,30,31,32,33,34]. Furthermore, it significantly accelerates both spin-lattice and spin-spin relaxation of hydrogen spins of the solvent in aqueous suspensions of metal-grafted DNDs [35,36,37]. The latter demonstrate very high relaxivity, an order of magnitude higher than that of Dotarem, used as a contrast agent in the clinics, and are therefore very promising as new contrast agents for magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) [35,36,37].
Ionic grafting is performed by mixing the aqueous suspensions of purified DNDs with aqueous solutions of copper, cobalt, manganese, and gadolinium salt nitrates containing paramagnetic ions of these elements [28,29,30,31,32,33]. It would seem that the more paramagnetic ions are grafted to the surface, the more effective the resulting contrast agent should be. However, it has been established that the grafting of such ions is limited. The matter is that transition and rare earth ions are coupled to the DND surface via exchange with protons of closely located surface carboxyl (−COOH) groups [28,29,30,31,32,33,34], and the incorporation of ions is limited by the number of corresponding surface COOH groups. It should be noted that among the hydrocarbon and hydroxyl groups that each nanodiamond surface possesses, the number of carboxyl groups is not very large. Estimates by Comet et al. [38] showed that a DND particle with a diameter of 5 nm exhibits ∼67 −COOH groups. This means that no more than 33 doubly charged ions (or less than 22 triply charged ones) can be grafted to such a particle. Magnetic (SQUID) measurement data [31,39,40] indicate the presence of ∼18 Gd3+ ions incorporated into the surface of a 5 nm DND particle at a maximum nominal Gd concentration of ∼3.28 wt%. This means that not all metal atoms would be grafted to the DND surface, and increasing the metal concentration in the solution would not necessarily result in an increase in the grafted ions. Moreover, the question is whether all these metals are in paramagnetic Cu2+, Co2+, Mn2+ and Gd3+ states. For example, it has been recently suggested [41,42] that grafting DNDs with copper may result not only in DNDs with surface paramagnetic Cu2+ ions but also in DND complexes with diamagnetic Cu+ ions and even in neutral clusters of several Cu0 atoms located in the space between DND particles. Their fixation on the DND surface (if it exists) is unknown. XPS shows from 39 to 64 Cu atoms on the surface of a 5 nm DND particle [41], while EPR shows only 20 Cu2+ ions in such a particle [42]. The difference may be due to the presence of the above-mentioned diamagnetic ions and copper atoms.
To address this issue, in this paper, we investigated DNDs grafted with paramagnetic Cu2+, Co2+, Mn2+, and Gd3+ ions using X-ray photoelectron spectroscopy (XPS). XPS is a highly surface-sensitive quantitative chemical analysis technique that can be used to address a wide range of material problems. The sampling depth for XPS measurements is 5–10 nm from the top of the surface, which can in principle cover the entire volume of a DND particle with a diameter of 4.5–5 nm. We analyze the formation of metal complexes on the DND surface and consider them with the published EPR findings [28,29,30,31,32] and recent theoretical calculations on the fixation of transition metal ions on the surface of DND particles.
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Samples
The initial nanodiamond material (DND powder) was repeatedly purified in boiled hydrochloric acid, then washed in boiled water [28,29,30,31,32,33,34] for removal of non-diamond sp2 carbon, iron-containing complexes and other para- and ferromagnetic impurities. This was carefully controlled for impurities using NMR, EPR and superconducting quantum interference device (SQUID) [30,31,32,43], and then precisely chemically modified with transition metal ions at Ioffe Institute (St. Petersburg, Russia). Chemical modification of the nanodiamond surface was done by mixing a suspension of DND particles with a water solution of copper acetate, cobalt or gadolinium nitrate, and manganese sulfate, respectively [28,29,30,31,32,33,34,35,36,37,44,45]. The concentration of DND suspension was about 0.5 wt%, and the concentration of a metal salt solution was 0.1 M.
The resulting mixture was subjected to intense and prolonged ultrasonic irradiation, which promoted disaggregation of DND particles and ion exchange in an aqueous solution between two- or three-charged metal ions (Cu2+, Co2+, Mn2+ or Gd3+) and two or three protons of the nearest carboxyl groups, terminated on the DND surface in many places. As a result, transition or rare earth metal ions form a metal-DND complex with the nanodiamond surface. This has repeatedly been experimentally confirmed [29,30,31,32,33,34,35,36,37,39,40,41,42,44,45]. After synthesis, the powder was removed from the suspension and dried. The number of carboxyl groups on the nanodiamond surface is about 60 [38] and in the case of trivalent ions, up to 20 metal ions could be bound with the nanodiamond particle surface. This number has been confirmed in experiments using electron paramagnetic resonance and static magnetization measurement [39]. The examined highly purified DNDs grafted with copper, cobalt, manganese, and gadolinium were studied, as summarized in Table 1. The metal content (wt.%) in the DND particle was determined by energy-dispersive X-ray analysis [28,29,30,31,32,33,34].

Table 1.
List of samples examined. S is the electron spin of the paramagnetic ion, NA is the weighting percent of the transition and rare-earth elements in the DND particle, N is the number of paramagnetic ions per DND particle, and NS is the paramagnetic ion concentration.
The average particle size in the suspension, determined by dynamic light scattering (DLS), ranged from 4.5 to 5 nm [28,29,30,31,32,33,34]. The interaction of hydrogen atoms of the surface carboxyl groups of a DND particle with metal ions leads to a decrease in the surface charge of the nanodiamond particle, resulting in a reduction of the z-potential of the surface (to −20 mV ÷ −15 mV in the case of Co2+, Cu2+, Mn2+ and almost to zero in the case of Gd3+ [45].
2.2. XPS Measurements
XPS data were collected using an ESCALAB -Xi+ ultra-high vacuum (5 × 10−10 mbar) X-ray photoelectron spectrometer equipped with an AlKα X-ray source and a monochromator. The X-ray beam size was 500 μm. Survey spectra were recorded with a pass energy of 150 eV, and high-energy resolution spectra were recorded with a pass energy of 20 eV. To correct for charging effects, all spectra were calibrated relative to the carbon C 1s peak positioned at 284.8 eV. Atomic ratios were calculated from peak intensity ratios and reported atomic sensitivity factors.
The AVANTAGE v6.6.0 Build 00114 Thermo Fisher Scientific software was used for data acquisition and analysis. For identification of the element’s chemical state, high-energy resolution measurements of the Cu2p Co2p, Mn2p, Gd3d, and Gd4d lines were performed with a pass energy of 50eV and a step size of 0.1 eV. For band deconvolution and fitting, the corresponding peaks for each element were fitted by using Lorentzian/Gaussian 30% function mixture and taking FWHM (full width at half maximum) in the range 1–2.5 eV. The XPS spectra were recorded at different acquisition times to get XPS high-resolution spectra. For Cu, Mn, and Co, electrons from the 2p level were measured, and for Gd, electrons from the 4d and 3d levels were measured. All these levels show spin-orbit splitting, which results in two states with different binding energies. Relative intensities were calculated taking into account sensitivity factors for each element.
3. Results and Discussion
Let us first discuss our XPS data on paramagnetic ions listed in Table 2, together with the data received from EPR and SQUID measurements.

Table 2.
XPS bands of paramagnetic ions in Cu-, Co-, Mn- and Gd-DNDs. Here BE is the binding energy, and at% is the atomic percent according to the XPS, EPR and SQUID measurements.
3.1. XPS of Cu-DND Powder
The recent literature XPS data for copper-grafted DNDs [41,42] show two bands determined by the spin-orbit splitting of the Cu 2p level (Δ ~ 19.8 eV). The symmetric 2p1/2 peak was observed at the binding energy of 952.7 eV, while the asymmetric 2p3/2 peak appeared to be composed of two products at the binding energies of 932.6 and 935 eV, attributed to Cu+ and Cu2+ ions, respectively. Our Cu 2p3/2 XPS spectrum (Figure 1) shows two bands at the binding energies of 932.09 eV and 933.94 eV, attributed to the non-magnetic Cu+ and paramagnetic Cu2+ ions, respectively [46,47,48,49,50,51,52]. 2p1/2 XPS spectrum (Figure 1) also shows two bands at the binding energies of 951.6 eV and 953.37 eV, assigned to the aforementioned Cu+ and Cu2+ ions [46,47,48,49,50,51,52]. The spectra also show two satellites of the above lines at 943.04 and 957.51 eV, correspondingly.
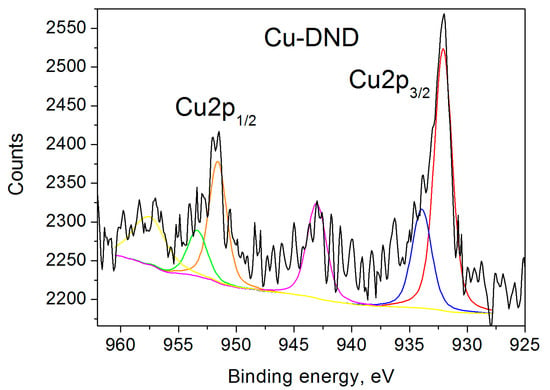
Figure 1.
Cu 2p XPS spectra of Cu-DND sample. The black line is the experimental spectrum. Deconvolutions into two components are shown by red and blue lines for 2p3/2 bands and orange and green for 2p1/2 bands, correspondingly. The satellites are shown by magenta and yellow lines.
One can find from Table 2 that the atomic percentage of the paramagnetic divalent copper ions measured by XPS and the atomic percent of the paramagnetic Cu2+ ions measured by EPR practically coincide within the experimental errors. Thus we can conclude that around 30% of the grafted copper ions are paramagnetic and 70% are diamagnetic. The previous studies of Cu-DNDs mentioned above [41,42] do not provide percentages of Cu+ and Cu2+ ions, but their XPS spectra are very similar to ours.
In addition, we also measured the Auger spectra of copper (Figure 2), which show two peaks of kinetic energy, Cu LM2 at 917.99 eV and Cu LM2 at 915.37 with atomic % of 29.41 and 70.59%, corresponding to Cu2+ and Cu+ bands. The data are in good agreement with the XPS and EPR results.
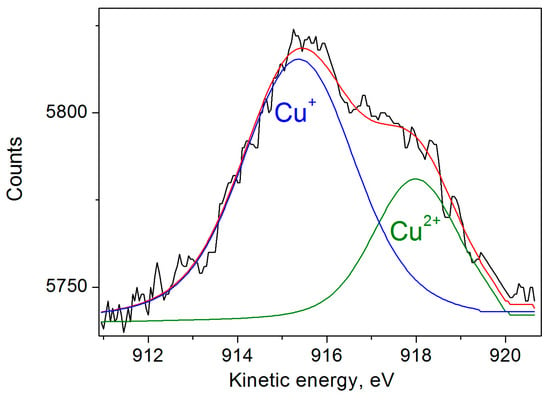
Figure 2.
Auger spectrum of Cu-DND particles. Deconvolutions into two components is shown by blue and olive lines.
Grafting of paramagnetic ions to nanodiamonds utilizes the exchange between protons of surface carboxyl groups and charged copper ions [28,29,30,31,32,33]. The presence of Cu+ on the diamond surface means a 70% reduction of Cu2+ in the parent copper acetate to Cu+ in Cu-DND occurs.
3.2. XPS of Co-DND Powder
The XPS spectrum of Co-DND is shown in Figure 3. It consists of two main spin-orbit split bands (Co2p3/2 at 779.86 eV and Co2p1/2 at 795.15 eV, Δ = 15.3 eV) and two satellites at 785.16 and 801.20 eV for the above bands, respectively [50,53]. The binding energies of 779.86 eV and 795.15 eV are characteristic of the Co2p3/2 and Co2p1/2 bands of divalent Co2+ ions in CoO [47]. Close to these binding energy values are also observed in the oxides Co2O3 and Co3O4. Herewith, it is generally accepted that the energy gap between the main Co 2p peak and the satellite peak is closely related to the oxidation states. When the energy gap is ∼6.0 eV, the valence of the Co cation is assigned to 2+. If this energy gap is 9–10 eV, the spectrum is associated with Co cations having a valence of 3+ [54,55]. Our XPS data show the above gap as 5.3 and 6.05 eV for Co2p3/2 and Co2p1/2, respectively, confirming the existence of Co2+ ions in our sample, as previously obtained by EPR measurements [28].
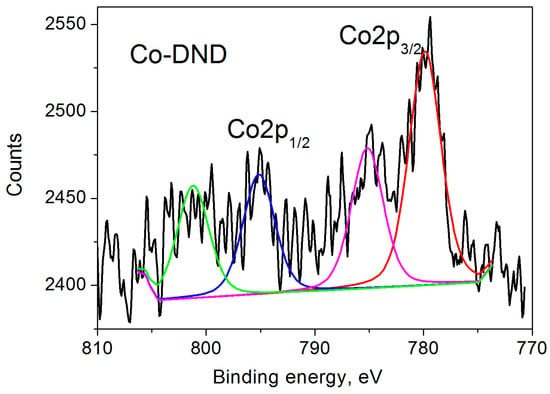
Figure 3.
Co 2p XPS spectrum of Co-DND sample. 2p3/2 and 2p1/2 bands are shown by red and blue lines, and satellites are shown by magenta and green lines.
Unfortunately, it was not possible to determine the Co2+ ion content in our Co-DND sample using EPR measurements [28]. Therefore, we cannot give a quantitative correspondence between the cobalt ions measured by XPS and EPR methods. However, both methods clearly show the presence of Co2+ ions on the surface of our Co-DND sample.
3.3. XPS of Mn-DND Powder
The XPS spectra of our Mn-DND sample (Figure 4) show binding energies of 639.7 and 641.4 eV for Mn2p3/2 and 651.1 and 653.2 eV for Mn2p1/2, both characteristic of Mn2p transitions with a separation of 11.5–11.8 eV between the spin-orbit split primary peaks. Each band shows a two-component structure. The data included in the XPS database [47] do not show satellite peaks for Mn, so it can be assumed that the doublet detection is caused by nonequivalent manganese ions. The non-equivalence can be caused by different valences of the ions or different atomic configurations of the neighboring oxygen ions.
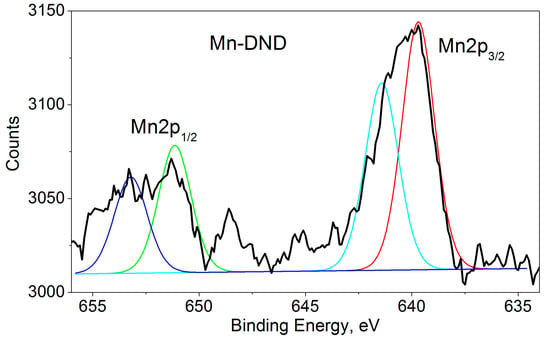
Figure 4.
Mn 2p XPS of Mn-DND sample. Deconvolutions of the 2p1/2 and 2p3/2 bands into two components are shown by red, cyan, green, and blue lines.
Note that manganese has six oxidation states (0, II, III, IV, VI, and VIII) with overlapping binding energy ranges, which poses a serious challenge for qualitative and quantitative analysis. Numerous XPS studies of Mn oxidation demonstrate difficulties in differentiating between the contributions of Mn2+, Mn3+, and Mn4+ ions [56,57,58,59,60], since similar binding energies are obtained for the oxides MnO, Mn2O3, Mn3O4, and MnO2, and the separation of the peaks leaves much to be desired. This is also true for our case.
We address this issue by comparing the manganese content of our sample, as determined from the XPS measurements presented here (0.07 at%), and previous EPR data showing 0.085 at% of Mn2+ ions [32] (Table 2). These numbers are virtually identical within experimental errors, leading us to conclude that all the manganese is Mn2+, located in various atomic configurations of neighboring oxygen ions.
3.4. XPS of Gd-DND Powder
The results of our XPS measurements of Gd-DND powder are shown in Figure 5 and Figure 6. According to the literature [61,62,63,64,65,66,67,68,69], the Gd 3d core level spectra are split by spin-orbital coupling at the doublet (1187.3 eV for the 3d5/2 part and 1220 eV for the 3d3/2 part) with an energy difference of Δ = 32.7 eV. Note that we could not measure the Gd3d3/2 band with our equipment because it overlapped with the carbon Auger band and was hidden by it. The 3d5/2 band we measured is shown in Figure 5. One can find that this band consists of two components observed at 1185.4 and 1187.9 eV, which originate from two inequivalent Gd atoms.
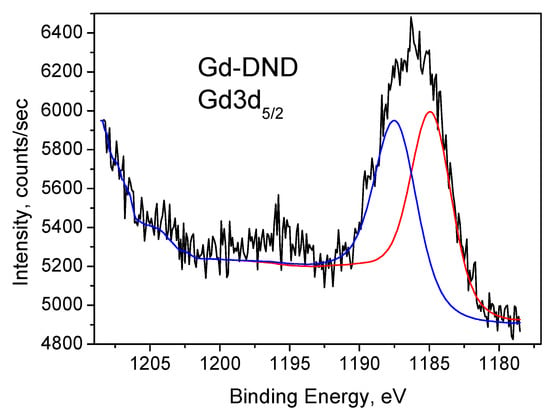
Figure 5.
Gd3d5/2 XPS of Gd-DND sample. Deconvolution into two components is shown by red and blue lines.
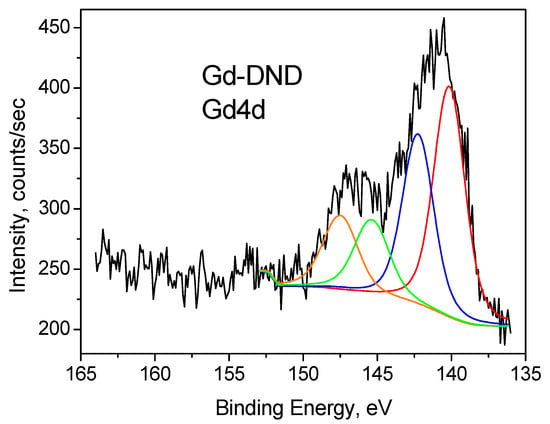
Figure 6.
Gd4d XPS spectrum of Gd-DND sample. Deconvolution into four components is shown by red, blue, green and orange lines.
Similarly, the Gd 4d core level spectra are split by the spin-orbit coupling into Gd4d5/2 and Gd4d3/2 bands with an energy difference of Δ = 5.3–5.4 eV (Figure 6). Each of these bands consists of two components, namely 139.9 eV and 142.2 eV for the 4d5/2 band and 145.2 eV and 147.5 eV for the 4d3/2 band. This finding is in good qualitative agreement with what is reported in the literature [61,62,63,64,65,66,67,68,69] and with our measurements of Gd2O3 powder, which contains only Gd3+ ions.
The way the sample was prepared should result in the formation of Gd3+ ions. This option is also supported by the fact that the atomic percentage of gadolinium measured by XPS is almost identical to that of paramagnetic Gd3+ ions measured by EPR (Table 2). Therefore the obtained bands refer to two nonequivalent Gd3+ ions bound to oxygen atoms and having different specific configurations.
To this end, recent DFT calculations [70,71] revealed two possible configurations of the Gd3+ chelate complexes on the diamond (111) surface. For the first configuration, the distances between the gadolinium atom and the three nearest oxygen atoms are 0.2281, 0.2182, and 0.2126 nm, respectively. For the second configuration of the Gd3+ chelate complex, the calculated distances between Gd and the three nearest oxygen atoms are 0.2281, 0.2384, and 0.2515 nm, and the distances to the other three more distant oxygen atoms are 0.2553, 0.2665, and 0.3588 nm, respectively.
3.5. C1s, N1s and O1s XPS
All XPS spectra of carbon, nitrogen and oxygen atoms and their quantization are given in Supplementary Materials.
4. Conclusions
In this paper, we report on the study of grafting transition and rare earth metal ions (Cu2+, Co2+, Mn2+, and Gd3+) to the surface of detonation nanodiamonds using the X-ray photoelectron spectroscopy (XPS) technique. The binding energies of metal, carbon, oxygen, and nitrogen atoms were determined and assigned to the corresponding ionic states and atomic groups. By analyzing the XPS data and comparing them with the EPR findings, we showed that the developed synthesis route leads to almost complete grafting of manganese and gadolinium atoms in the form of paramagnetic ions Mn2+ and Gd3+ to the diamond surface, while only 30% of the copper atoms on the surface are in the paramagnetic state Cu2+, and the rest 70% are in the non-magnetic Cu+ state.
Supplementary Materials
The following supporting information can be downloaded at: https://www.mdpi.com/article/10.3390/nano15040260/s1.
Author Contributions
Conceptualization, A.P. and N.F.; methodology, A.A., A.C., N.F. and A.P.; investigation, N.F. and A.P.; resources, N.F., A.P., A.C. and A.A.; data curation, N.F. and A.P.; writing—original draft preparation, A.P. and N.F.; writing—review and editing, A.P. and N.F.; supervision, A.P.; project administration, A.P. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This research was carried out within the framework of State Task No. FFUG-2024-0019.
Data Availability Statement
Data are contained within the article.
Acknowledgments
The authors thank Alexander Vul’ and Alexander Shames for useful discussions.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
References
- Dolmatov, V.Y.; Ozerin, A.N.; Kulakova, I.I.; Bochechka, O.O.; Lapchuk, N.M.; Myllymaki, V.; Vehanen, A. Detonation nanodiamonds: New aspects in the theory and practice of synthesis, properties and applications. Russ. Chem. Rev. 2020, 89, 1428–1462. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vul’, A.Y.; Shenderova, O.A. (Eds.) Detonation Nanodiamonds: Science and Applications; Pan Stanford Publishing: Singapore, 2014; pp. 181–204. [Google Scholar]
- Shenderova, O.A.; McGuire, G.E. Science and Engineering of Nanodiamond Particle Surfaces for Biological Applications (Review). Biointerphases 2015, 10, 030802. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arnault, J.-C. (Ed.) Nanodiamonds. Advanced Material Analysis, Properties and Applications; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2017; 488p, Available online: https://www.elsevier.com/books/nanodiamonds/arnault/978-0-323-43029-6 (accessed on 17 April 2024).
- Aharonovich, I.; Neu, E. Diamond Nanophotonics. Adv. Opt. Mater. 2014, 2, 911–928. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tegafaw, T.; Liu, S.; Ahmad, M.Y.; Saidi, A.K.A.A.; Zhao, D.; Liu, Y.; Yue, H.; Nam, S.W.; Chang, Y.; Lee, G.H. Production, surface modification, physicochemical properties, biocompatibility, and bioimaging applications of nanodiamonds. RSC Adv. 2023, 13, 32381. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chang, S.L.Y.; Reineck, P.; Krueger, A.; Mochalin, V.N. Ultrasmall Nanodiamonds: Perspectives and Questions. ACS Nano 2022, 16, 8513–8524. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Panich, A.M.; Shames, A.I.; Mogilyansky, D.; Goren, S.D.; Dolmatov, V.Y. Detonation Nanodiamonds Fabricated from Tetryl: Synthesis, NMR, EPR and XRD study. Diam. Relat. Mater. 2020, 108, 107918. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shames, A.I.; Panich, A.M.; Friedlander, L.; Dolmatov, V.Y. Magnetic resonance study of novel detonation nanodiamonds originated from non-conventional explosives. Diam. Relat. Mater. 2023, 136, 110059. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wrachtrup, J.; Jelezko, F. Processing Quantum Information in Diamond. J. Phys. Condens. Matter 2006, 18, S807–S824. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Doherty, M.W.; Manson, N.B.; Delaney, P.; Jelezko, F.; Wrachtrupe, J.; Hollenberg, L.C.L. The Nitrogen-Vacancy Color Centre in Diamond. Phys. Rep. 2013, 528, 1–45. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nunn, N.; d’Amora, M.; Prabhakar, N.; Panich, A.M.; Froumin, N.; Torelli, M.D.; Vlasov, I.; Reineck, P.; Gibson, B.; Rosenholm, J.M.; et al. Fluorescent Single-Digit Detonation Nanodiamond for Biomedical Applications. Methods Appl. Fluoresc. 2018, 6, 035010. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shenderova, O.A.; Shames, A.I.; Nunn, N.A.; Torelli, M.D.; Vlasov, I.; Zaitsev, A. Review Article: Synthesis, Properties, and Applications of Fluorescent Diamond Particles. J. Vac. Sci. Technol. B 2019, 37, 030802. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pezzagna, S.; Meijer, J. Quantum Computer Based on Color Centers in Diamond. Appl. Phys. Rev. 2021, 8, 011308. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nunn, N.; Shames, A.I.; Torelli, M.; Smirnov, A.I.; Shenderova, O. Luminescent diamond: A platform for next generation nanoscale optically driven quantum sensors. In Luminescent Nanomaterials; Jenny Stanford Publishing: Singapore, 2022; pp. 1–95. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shames, A.; Panich, A.; Friedlander, L.; Cohen, H.; Butler, J.; Moreh, R. Magnetic Resonance Study of Bulky CVD Diamond Disc. Materials 2024, 17, 1871. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shames, A.I.; Panich, A.M.; Kempiński, W.; Alexenskii, A.E.; Baidakova, M.V.; Dideikin, A.T.; Osipov, V.Y.; Siklitski, V.I.; Osawa, E.; Ozawa, M.; et al. Defects and impurities in nanodiamonds: EPR, NMR and TEM study. J. Phys. Chem. Solids 2002, 63, 1993–2001. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dey, T.; Ghosh, A.; Sanya, A.; Charles, C.J.S.; Pokharel, S.; Nair, L.; Singh, M.; Kaity, S.; Ravichandiran, V.; Kaur, K.; et al. Surface engineered nanodiamonds: Mechanistic intervention in biomedical applications for diagnosis and treatment of cancer. Biomed. Mater. 2024, 19, 032003. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Francis, S.J.; Torelli, M.D.; Nunn, N.A.; Arepally, G.M.; Shenderova, O.A. Clot Imaging Using Photostable Nanodiamond. Nanomaterials 2023, 13, 961. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bogdanowicz, R. Functionalized nanodiamonds as a perspective green carbo-catalyst for removal of emerging organic pollutants. Curr. Opin. Solid State Mater. Sci. 2022, 26, 100991. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Navalon, S.; Dhakshinamoorthy, A.; Álvaro, M.; García, H. Diamond Nanoparticles in Heterogeneous Catalysis. Chem. Mater. 2020, 32, 4116–4143. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gawande, M.B.; Fornasiero, P.; Zbořil, R. Carbon-Based Single-Atom Catalysts for Advanced Applications. ACS Catal. 2020, 10, 2231–2259. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Manus, L.M.; Mastarone, D.J.; Waters, E.A.; Zhang, X.-Q.; Schultz-Sikma, E.A.; MacRenaris, K.W.; Ho, D.; Meade, T.J. Gd(III)-Nanodiamond Conjugates for MRI Contrast Enhancement. Nano Lett. 2010, 10, 484–489. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rammohan, N.; MacRenaris, K.W.; Moore, L.K.; Parigi, G.; Mastarone, D.J.; Manus, L.M.; Lilley, L.M.; Preslar, A.T.; Waters, E.A.; Filicko, A.; et al. Nanodiamond-Gadolinium(III) Aggregates for Tracking Cancer Growth In Vivo at High Field. Nano Lett. 2016, 16, 7551–7564. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nakamura, T.; Ohana, T.; Yabuno, H.; Kasai, R.; Suzuki, T.; Hasebe, T. Simple Fabrication of Gd(III)-DTPA-Nanodiamond Particles by Chemical Modification for Use as Magnetic Resonance Imaging (MRI) Contrast Agent. Appl. Phys. Express 2013, 6, 015001. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, L.; Shiino, A.; Qin, H.; Kimura, T.; Komatsu, N. Synthesis, Characterization, and Magnetic Resonance Evaluation of Polyglycerol-Functionalized Detonation Nanodiamond Conjugated with Gadolinium(III) Complex. J. Nanosci. Nanotechnol. 2015, 15, 1076–1082. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hou, W.; Toh, T.B.; Abdullah, L.N.; Yvonne, T.W.Z.; Lee, K.J.; Guenther, I.; Chow, E.K.H. Nanodiamond–Manganese dual mode MRI contrast agents for enhanced liver tumor detection. Nanomed. Nanotech. Biol. Med. 2017, 13, 783–793. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Panich, A.M.; Shames, A.I.; Medvedev, O.; Osipov, V.Y.; Alexenskii, A.E.; Vul’, A.Y. Magnetic Resonance Study of Detonation Nanodiamonds with Surface Chemically Modified by Transition Metal Ions. Appl. Magn. Reson. 2009, 36, 317–329. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Panich, A.M.; Altman, A.; Shames, A.I.; Osipov, V.Y.; Alexenskiy, A.E.; Vul’, A.Y. Proton magnetic resonance study of diamond nanoparticles decorated by transition metal ions. J. Phys. D Appl. Phys. 2011, 44, 125303. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shames, A.I.; Panich, A.M.; Osipov, V.Y.; Aleksenskiy, A.E.; Vul’, A.Y.; Enoki, T.; Takai, K. Structure and Magnetic Properties of Detonation Nanodiamond Chemically Modified by Copper. J. Appl. Phys. 2010, 107, 014318. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Panich, A.M.; Shames, A.I.; Sergeev, N.A.; Osipov, V.Y.; Alexenskiy, A.E.; Vul’, A.Y. Magnetic Resonance Study of Gadolinium-Grafted Nanodiamonds. J. Phys. Chem. C 2016, 120, 19804–19811. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Panich, A.M.; Shames, A.I.; Aleksenskii, A.E.; Yudina, E.B.; Vul’, A.Y. Manganese-grafted detonation nanodiamond, a novel potential MRI contrast agent. Diam. Relat. Mater. 2021, 119, 108590. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Panich, A.M. Nuclear Magnetic Resonance Studies of Nanodiamond Surface Modification. Diam. Relat. Mater. 2017, 79, 21–31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Panich, A.M.; Aleksenskii, A.E.; Yudina, E.B.; Vul’, A.Y. Spatially Resolved Spin−Lattice Relaxation Times and Line Widths in Manganese-Grafted Detonation Nanodiamonds. J. Phys. Chem. C 2022, 126, 1489–1495. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Panich, A.M.; Salti, M.; Goren, S.D.; Yudina, E.B.; Alexenskii, A.E.; Vul’, A.Y.; Shames, A.I. Gd(III)-Grafted Detonation Nanodiamonds for MRI Contrast Enhancement. J. Phys. Chem. C 2019, 123, 2627–2631. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Panich, A.M.; Salti, M.; Prager, O.; Swissa, E.; Kulvelis, Y.V.; Yudina, E.B.; Aleksenskii, A.E.; Goren, S.D.; Vul’, A.Y.; Alexander, I. Shames, PVP-coated Gd-grafted nanodiamonds as a novel and potentially safer contrast agent for in-vivo MRI. Magn. Reson. Med. 2021, 86, 935–942. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Panich, A.M.; Salti, M.; Aleksenskii, A.E.; Kulvelis, Y.V.; Chizhikova, A.; Vul’, A.Y.; Shames, A.I. Suspensions of manganese-grafted nanodiamonds: Preparation, NMR, and MRI study. Diam. Relat. Mater. 2023, 131, 109591. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Comet, M.; Pichot, V.; Siegert, B.; Britz, F.; Spitzer, D. Detonation Nanodiamonds for Doping Kevlar. J. Nanosci. Nanotechnol. 2010, 10, 4286–4292. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Osipov, V.Y.; Aleksenskiy, A.E.; Takai, K.; Vul’, A.Y. Magnetic Studies of a Detonation Nanodiamond with the Surface Modified by Gadolinium Ions. Phys. Solid State 2015, 57, 2314–2319. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Osipov, V.Y.; Boukhvalov, D.W.; Takai, K. Gadolinium ion bonding on the surface of carboxylated detonation nanodiamond in terms of magnetochemistry and density functional theory. Mendeleev Commun. 2020, 30, 436–438. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Osipov, V.Y.; Romanov, N.M.; Suvorkova, I.E.; Osipova, E.V.; Tsuji, T.; Ishiguro, Y.; Takai, K. Magnetic resonance tracking of copper ion fixation on the surface of carboxylated nanodiamonds from viewpoint of changes in carbon-inherited paramagnetism. Mendeleev Commun. 2022, 32, 132–135. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gridnev, I.D.; Osipov, V.Y. Transition metal atoms grafted on the nanodiamonds surface: Identification and guest–host spin–spin interactions. Mendeleev Commun. 2022, 32, 143–151. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Osipov, V.Y.; Shames, A.I.; Enoki, T.; Takai, K.; Baidakova, M.V.; Vul’, A.Y. Paramagnetic defects and exchange coupled spins in pristine ultrananocrystalline diamonds. Diam. Relat. Mater. 2007, 16, 2035–2038. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aleksenski, A.E.; Yagovkina, M.A.; Vul’, A.Y. Intercalation of Ultrafine-Dispersed Diamond in Aqueous Suspensions. Phys. Solid State 2004, 46, 685–686. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yudina, E.B.; Aleksenskii, A.E.; Fomina, I.G.; Shvidchenko, A.V.; Danilovich, D.P.; Eremenko, I.L.; Vul, A.Y. Interaction of Carboxyl Groups with Rare Metal Ions on the Surface of Detonation Nanodiamonds. Eur. J. Inorg. Chem. 2019, 2019, 4345–4349. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Biesinger, M.C.; Lau, L.W.M.; Gerson, A.R.; Smart, R.S.C. Resolving surface chemical states in XPS analysis of first row transition metals, oxides and hydroxides: Sc, Ti, V, Cu and Zn. Appl. Surf. Sci. 2010, 257, 887–898. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Naumkin, A.V.; Kraut-Vass, A.; Gaarenstroom, S.W.; Powell, C.J. NIST X-ray Photoelectron Spectroscopy Database, Version 5.0 (Last Update to Data Content: 2023). Available online: https://srdata.nist.gov/xps/ (accessed on 23 December 2024).
- Bui, N.T.; Kang, H.; Teat, S.J.; Su, G.M.; Pao, C.W.; Liu, Y.S.; Zaia, E.W.; Guo, J.; Chen, J.L.; Meihaus, K.R.; et al. A nature-inspired hydrogen-bonded supramolecular complex for selective copper ion removal from water. Nat. Commun. 2020, 11, 3947. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- de Sousa, P.V.F.; de Oliveira, A.F.; da Silva, A.A.; Lopes, R.P. Environmental remediation processes by zero valence copper: Reaction mechanisms. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2019, 26, 14883–14903. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lázaro-Martínez, J.M.; Lupano, L.V.L.; Piehl, L.L.; Rodríguez-Castellón, E.; Orto, V.C.D. New Insights about the Selectivity in the Activation of Hydrogen Peroxide by Cobalt or Copper Hydrogel Heterogeneous Catalysts in the Generation of Reactive Oxygen Species. J. Phys. Chem. C 2016, 120, 29332–29347. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, X.; Ai, S.; Huang, Y.; Huang, C.; Yu, W.; Mao, Z. Fast and reversible adsorption for dibenzothiophene in fuel oils with metallic nano-copper supported on mesoporous silica. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2021, 28, 2741–2752. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Varma, K.S.; Shukla, A.D.; Tayade, R.J.; Joshi, P.A.; Das, A.K.; Modi, K.B.; Gandhi, V.G. Photocatalytic performance and interaction mechanism of reverse micelle synthesized Cu-TiO2 nanomaterials towards levofloxacin under visible LED light. Photochem. Photobiol. Sci. 2022, 21, 77–89. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thermo Fisher Scientific. Cobalt X-ray Photoelectron Spectra, Cobalt Electron Configuration, and Other Elemental Information. Available online: https://www.thermofisher.com/il/en/home/materials-science/learning-center/periodic-table/transition-metal/cobalt.html (accessed on 23 December 2024).
- Wei, W.F.; Chen, W.X.; Ivey, D.G. Rock. Salt-Spinel Structural Transformation in Anodically Electrodeposited Mn-Co-O Nanocrystals. Chem. Mater. 2008, 20, 1941–1947. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, W.; Wu, J.; Ouyang, C.; Gao, Y.; Xu, X.; Huang, Z. Optical properties of Mn-Co-Ni-O thin films prepared by radio frequency sputtering deposition. J. Appl. Phys. 2014, 115, 093512. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Murray, J.W.; Dillard, J.G.; Giovanoly, R.; Moers, H.; Stumm, W. Oxidation of Mn(I1): Initial mineralogy, oxidation state and ageing. Geochim. Cosmochim. Acta Vol. 1985, 49, 463–470. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nesbitt, H.W.; Banerjee, D. Interpretation of XPS Mn(2p) spectra of Mn oxyhydroxides and constraints on the mechanism of MnO2 precipitation. Am. Mineral. 1998, 83, 305–315. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Biesinger, M.C.; Payne, B.P.; Grosvenor, A.P.; Lau, L.W.M.; Gerson, A.R.; Smart, R.S.C. Resolving surface chemical states in XPS analysis of first row transition metals, oxides and hydroxides: Cr, Mn, Fe, Co and Ni. Appl. Surf. Sci. 2011, 257, 2717–2730. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ilton, E.S.; Post, J.E.; Heaney, P.J.; Ling, F.T.; Kerisit, S.N. XPS determination of Mn oxidation states in Mn (hydr)oxides. Appl. Surf. Sci. 2016, 366, 475–485. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moulder, J.F.; Stickle, W.F.; Sobol, P.E.; Bomben, K.D. Handbook of X-ray Photoelectron Spectroscopy. A Reference Book of Standard Spectra for Identification and Interpretation of XPS Data; Chastain, J., Ed.; Perkin-Elmer Corporation: Eden Prairie, MN, USA, 1992. [Google Scholar]
- Brunckova, H.; Kolev, H.; Rocha, L.A. XPS characterization and luminescent properties of GdNbO4 and GdTaO4 thin Films. Appl. Surf. Sci. 2020, 504, 144358. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barreca, D.; Gasparotto, A.; Milanov, A.; Tondello, E.; Devi, A.; Fischer, R.A. Gd2O3 Nanostructured Thin Films Analyzed by XPS. Surf. Sci. Spectr. 2007, 14, 60–67. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Haunsbhavi, K.; Kumar, A.; Ubaidullah, M.; Shaikh, S.F.; Venkatesh, R.; Alagarasan, D.; Murahari, P.; Angadi, B. The effect of rare-earth element (Gd, Nd, La) doping of NiO films on UV photodetector. Phys. Scr. 2022, 97, 055815. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khan, S.A.; Gambhir, S.; Ahmad, A. Extracellular biosynthesis of gadolinium oxide (Gd2O3) nanoparticles, their biodistribution and bioconjugation with the chemically modified anticancer drug taxol. Beilstein J. Nanotechnol. 2014, 5, 249–257. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Milanov, A.P.; Toader, T.; Parala, H.; Barreca, D.; Gasparotto, A.; Bock, C.; Becker, H.W.; Ngwashi, D.K.; Cross, R.; Paul, S.; et al. Lanthanide Oxide Thin Films by Metalorganic Chemical Vapor Deposition Employing Volatile Guanidinate Precursors. Chem. Mater. 2009, 21, 5443–5455. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vijayaprasath, G.; Habibulla, I.; Dharuman, V.; Balasubramanian, S.; Ganesan, R. Fabrication of Gd2O3 Nanosheet-Modified Glassy Carbon Electrode for Nonenzymatic Highly Selective Electrochemical Detection of Vitamin B2. ACS Omega 2020, 5, 17892–17899. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Raiser, D.; Deville, J.P. Study of XPS photoemission of some gadolinium compounds. J. Electron Spectrosc. Relat. Phenom. 1991, 57, 91–97. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Majeed, S.; Shivashankar, S.A. Rapid, microwave-assisted synthesis of Gd2O3 and Eu:Gd2O3 nanocrystals: Characterization, magnetic, optical and biological studies. J. Mater. Chem. B 2014, 2, 5585–5593. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Datta, P.; Majewski, P.; Aldinger, F. Study of gadolinia-doped ceria solid electrolyte surface by XPS. Mater. Charact. 2009, 60, 138–143. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Osipov, V.Y.; Boukhvalov, D.W.; Takai, K. Isolated Spin-7/2 Species of Gadolinium (III) Chelate Complexes on the Surface of 5-nm Diamond Particles. Nanomaterials 2023, 13, 1995. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Boukhvalov, D.W.; Osipov, V.Y.; Serikkanov, A.; Takai, K. Unveiling the Structure of Metal–Nanodiamonds Bonds: Experiment and Theory. C J. Carbon Res. 2024, 10, 63. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).