A Review on N-Doped Carbon-Based Materials for the NH3-SCR Reaction
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Reaction Mechanism of NH3-SCR
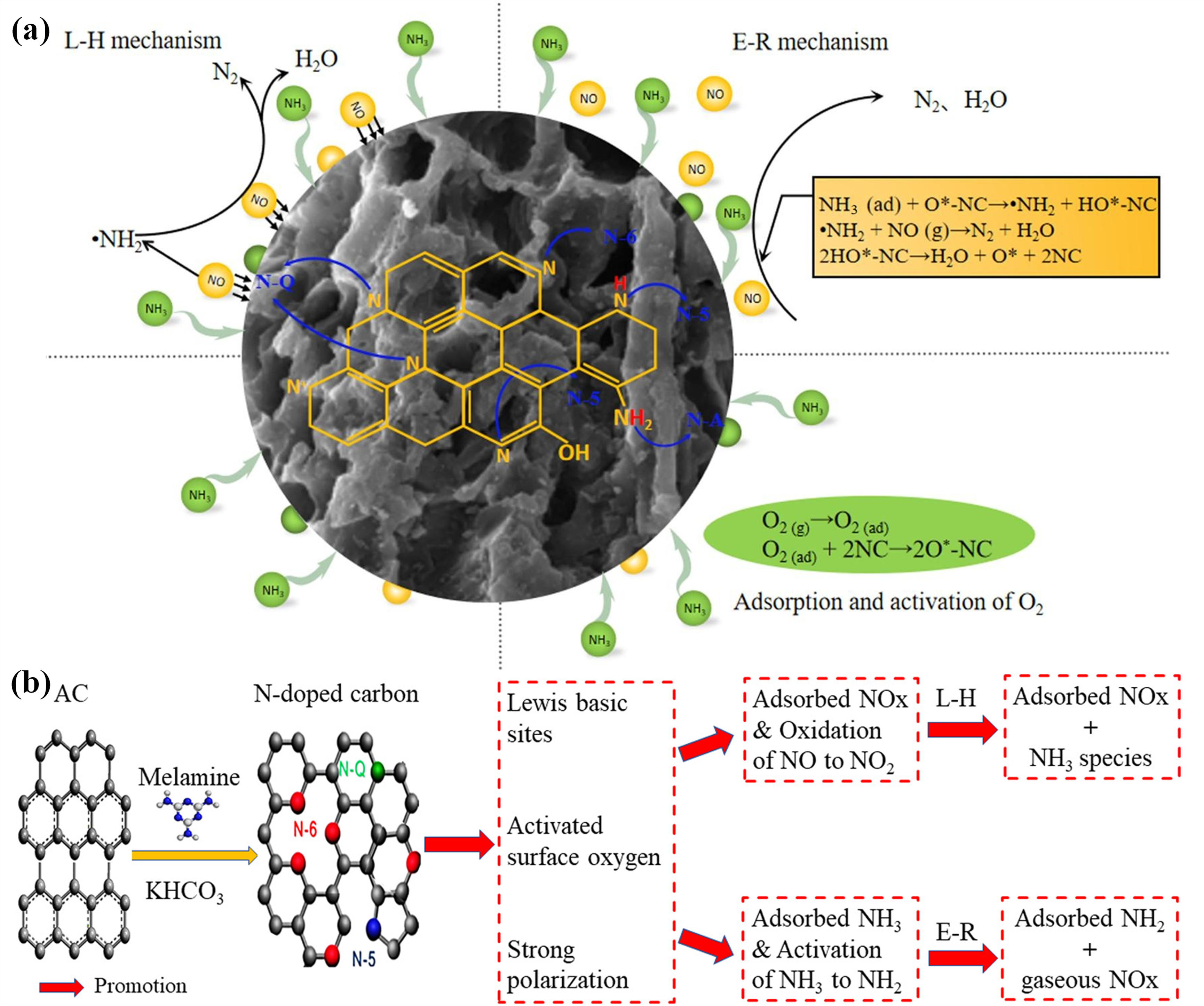
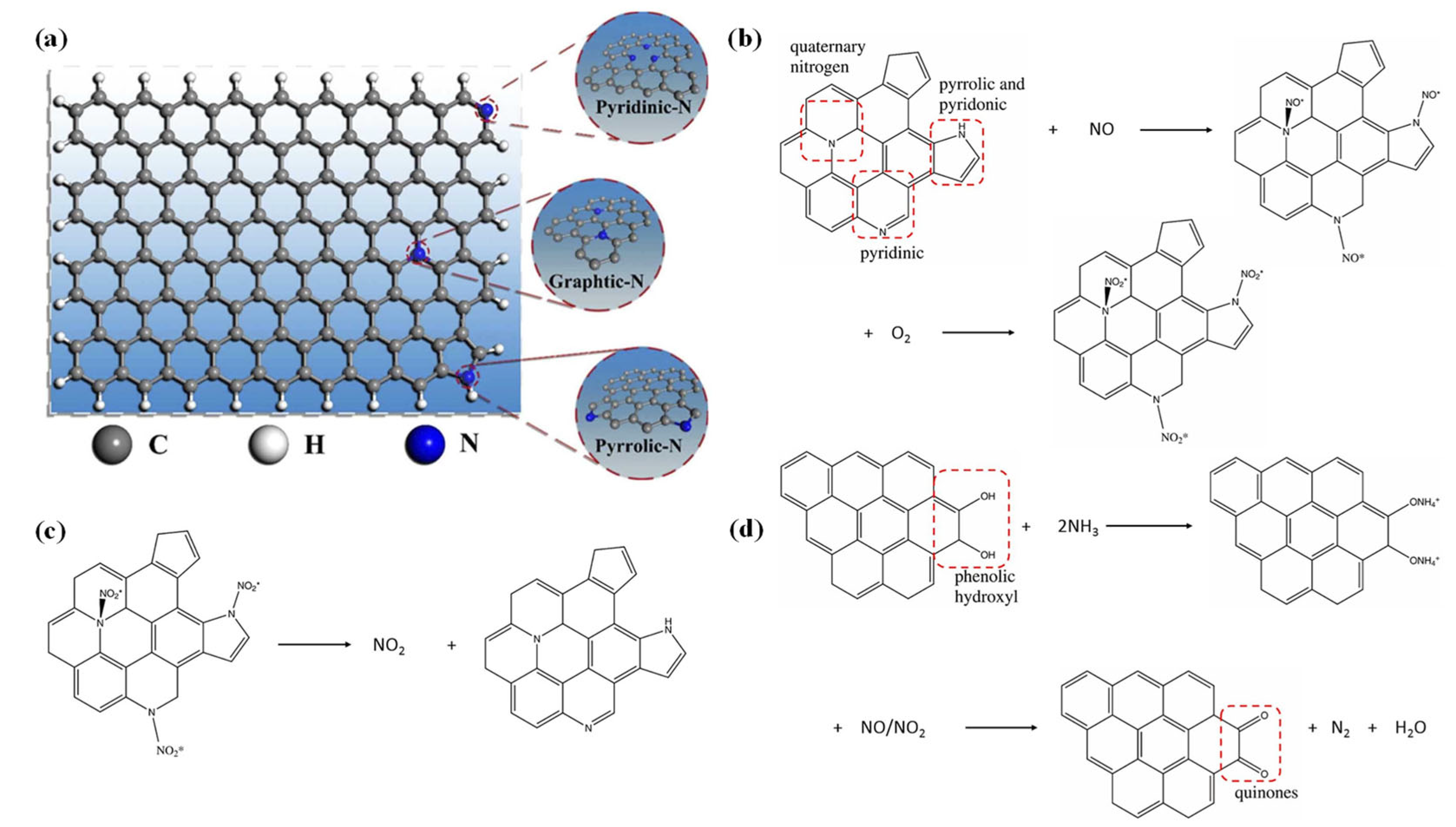
3. The Functional Mechanism of NC
4. Nitrogen-Doped Carbon as Metal-Free Catalysts
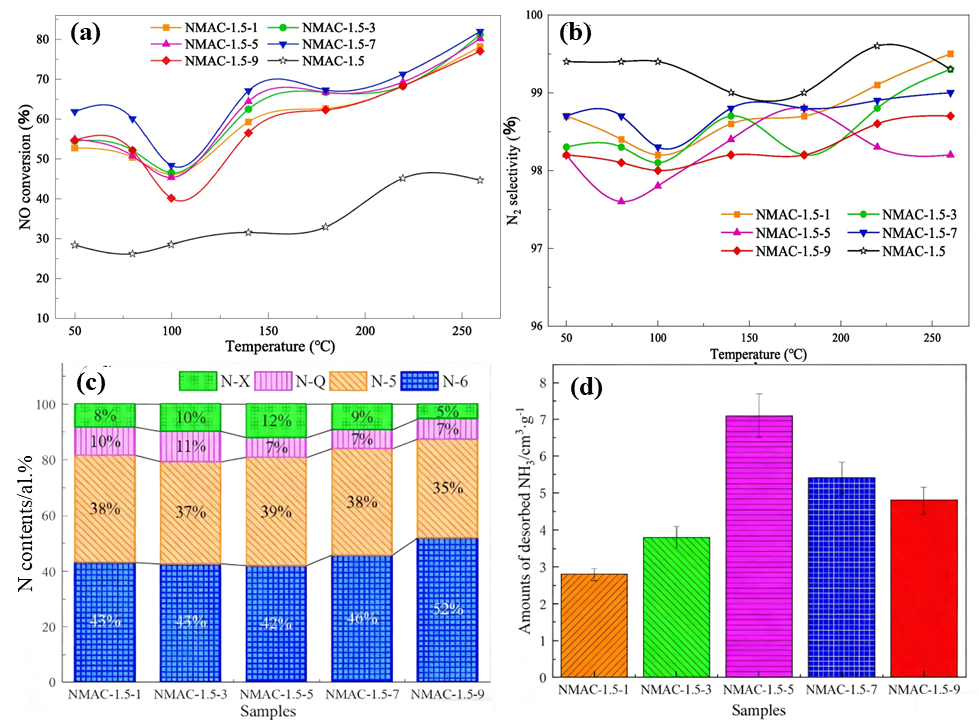
4.1. Regulating the Concentration and Types of Nitrogen Doping
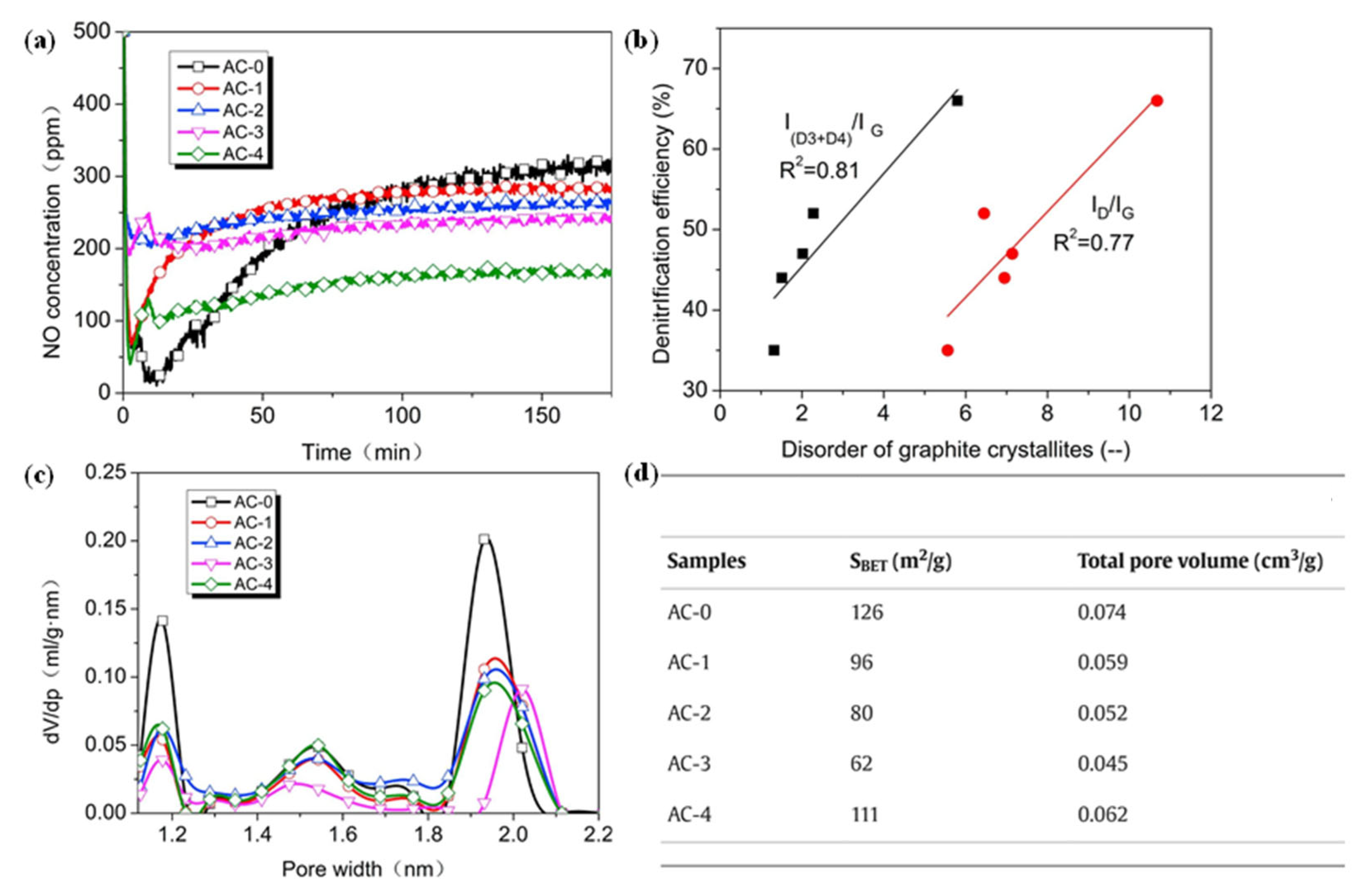
4.2. Optimizing the Pore Structure of NC
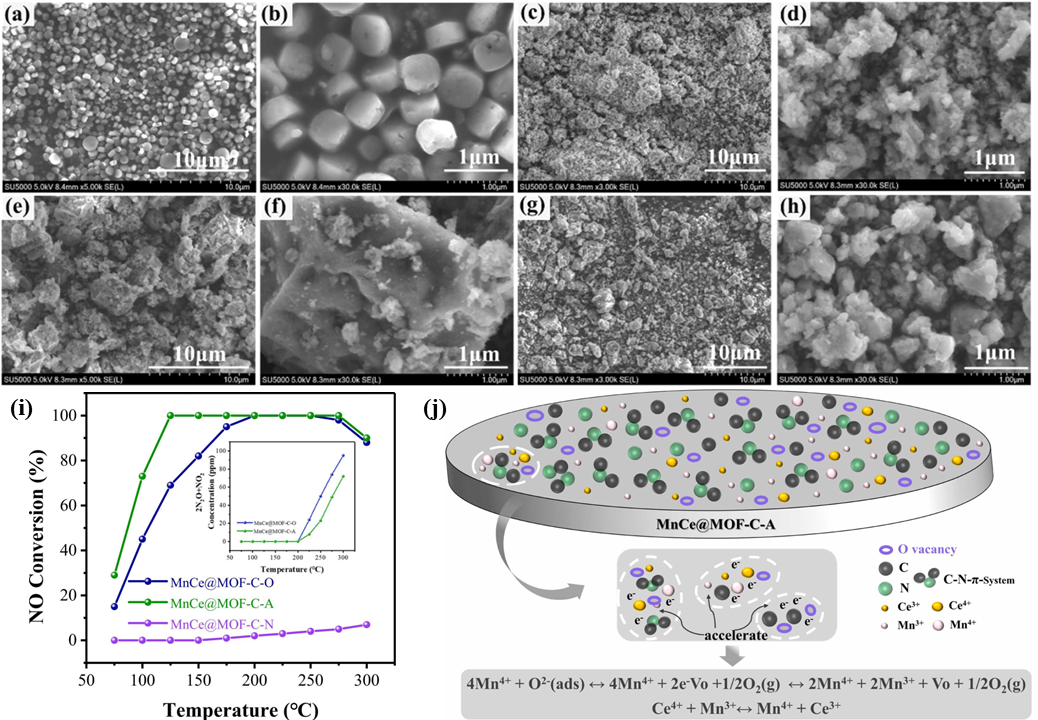
5. Nitrogen-Doped Carbon Materials as Support for Metal Catalysts
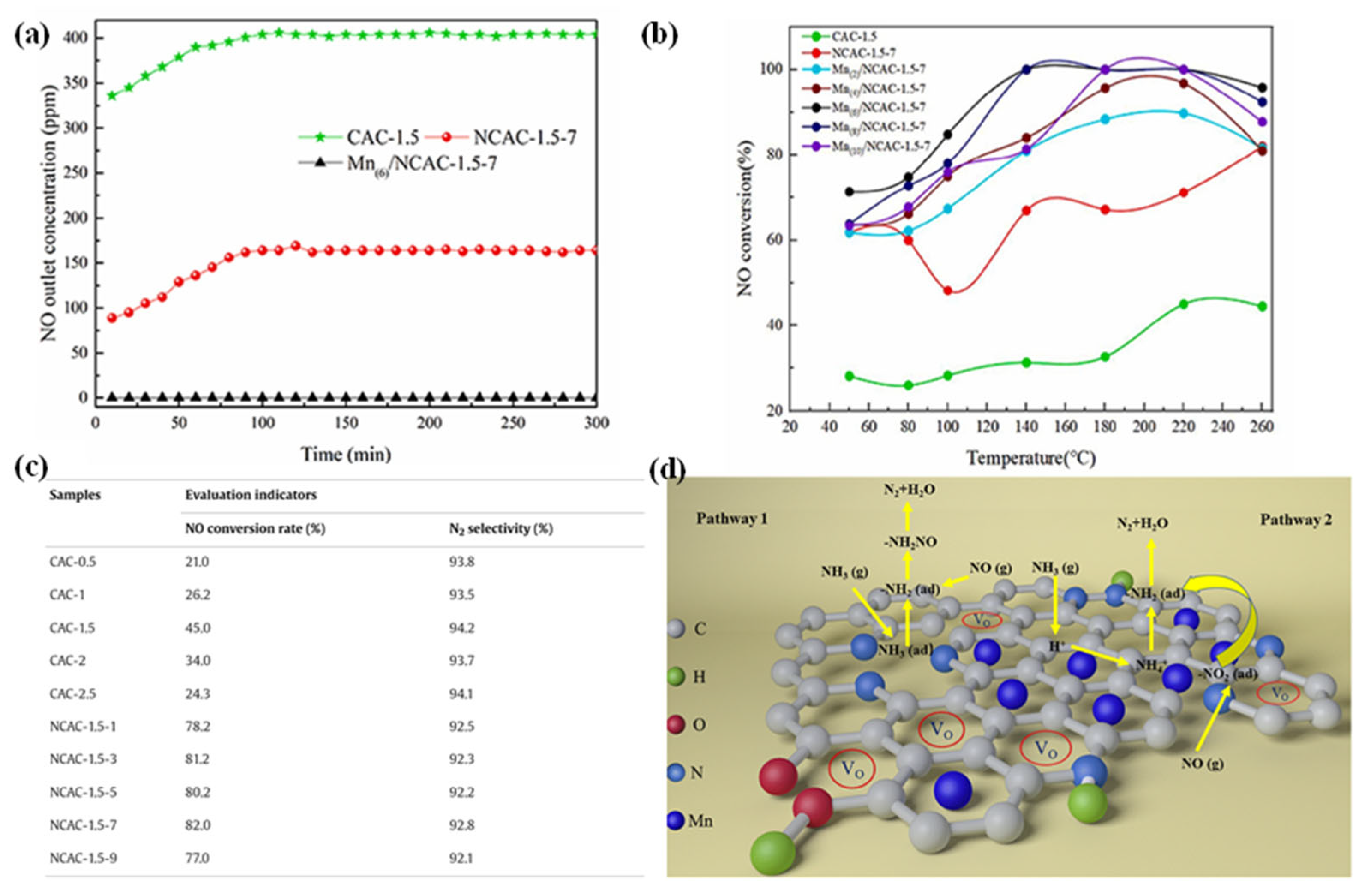
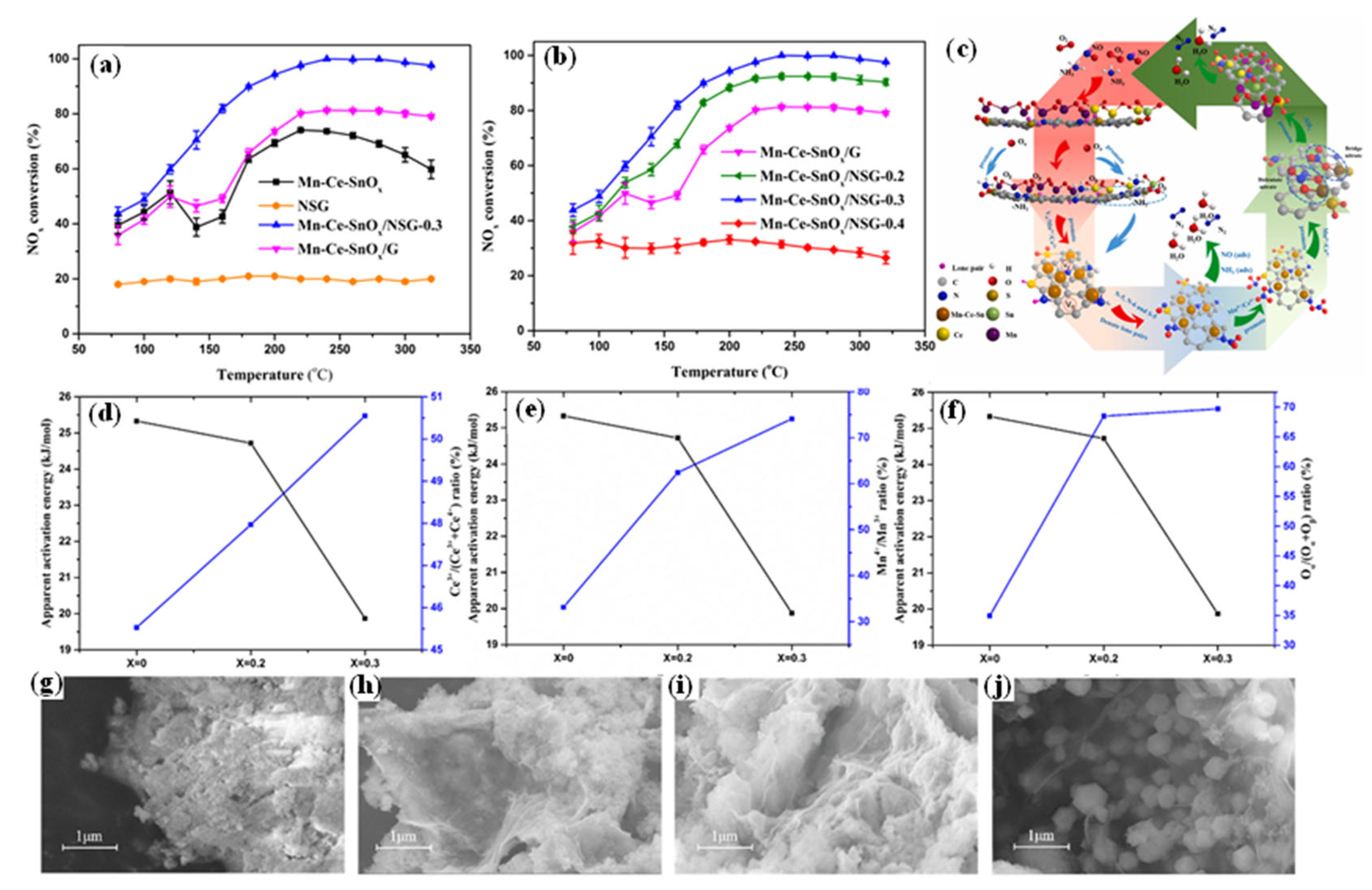
5.1. The Synergistic Interaction Between Transition Metals and Nitrogen-Doped Carbon
5.2. Dual-Atom-Doped Carbon as the Support
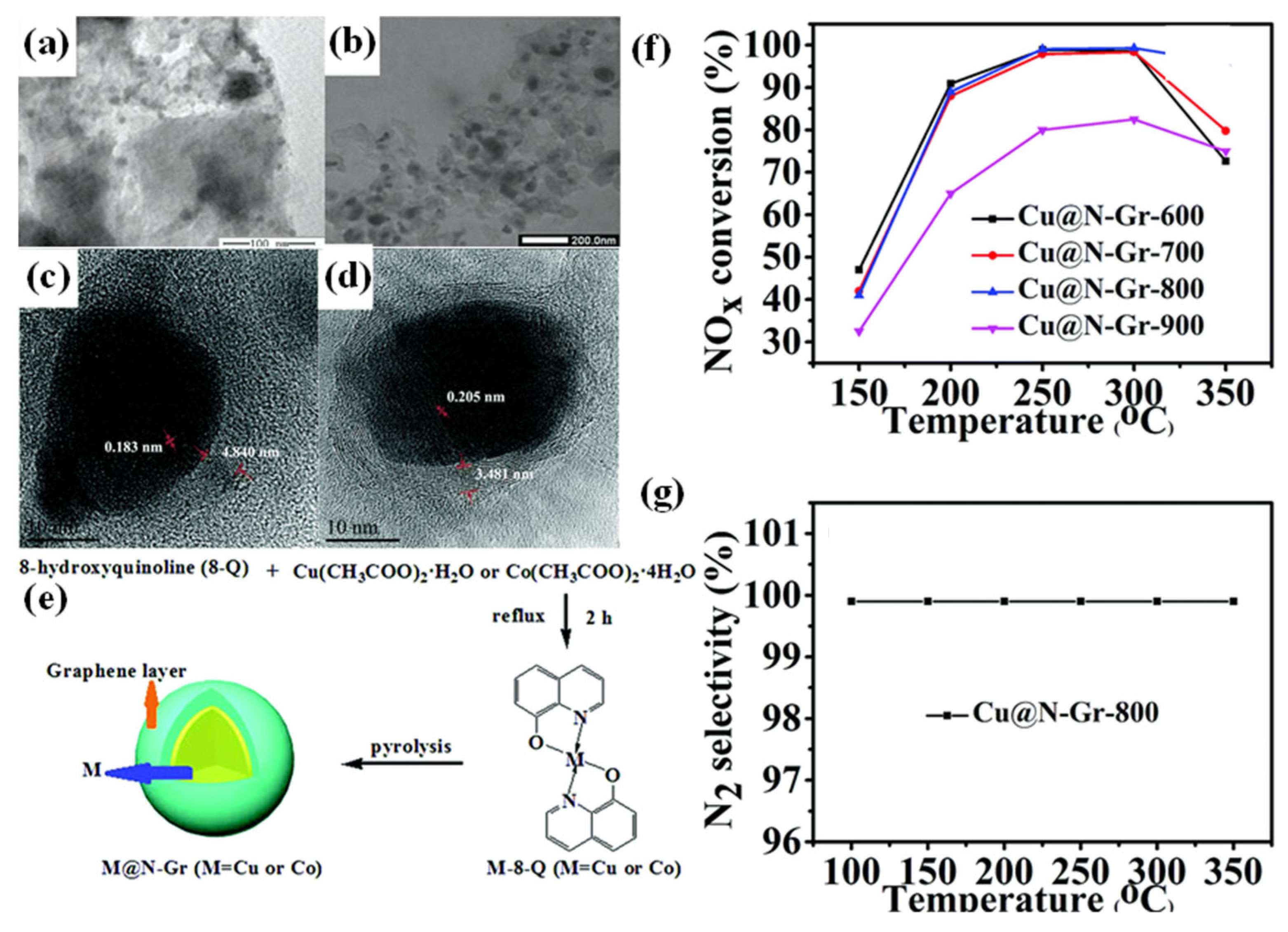
5.3. Encapsulation Strategy
6. Discussion Regarding the Stability of NC
7. Future Prospects and Challenges Ahead
- Carbon materials are prone to sintering at high temperatures, thus losing their catalytic activity. The nitrogen sites on carbon materials are especially susceptible to deactivation in high-temperature environments. Meanwhile, nitrogen-doped carbon materials are prone to deactivation and poisoning by SO2 and H2O after long-term SCR reactions. Future improvements are required in this aspect, such as optimizing the nitrogen doping mode or introducing appropriate carriers to enhance the thermal stability of the catalyst.
- The homogeneity of nitrogen doping exerts a crucial influence on the performance of the catalyst. Nevertheless, the current nitrogen doping approaches still exhibit a certain degree of inhomogeneity. In the future, it is necessary to explore and develop more efficient nitrogen doping technologies to improve the homogeneity of the catalyst, with the aim of achieving a higher nitrogen doping amount and a more uniform nitrogen distribution, thereby enhancing the catalytic performance.
- Despite the existence of numerous and outstanding modification approaches for nitrogen-doped carbon materials at present, the catalytic mechanism still requires in-depth investigation; in particular, the specific functions of different types of nitrogen sites in catalytic reactions remain ambiguous. Future studies need to profoundly explore the catalytic mechanism of nitrogen-doped carbon catalysts and deeply analyze the specific roles of different nitrogen sites in the SCR reaction.
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Sun, Y.; Zwolinska, E.; Chmielewski, A.G. Abatement technologies for high concentrations of NOx and SO2 removal from exhaust gases: A review. Crit. Rev. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2016, 46, 119–142. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shahbazi, H.; Abolmaali, A.M.; Alizadeh, H.; Salavati, H.; Zokaei, H.; Zandavi, R.; Torbatian, S.; Yazgi, D.; Hosseini, V. An emission inventory update for Tehran: The difference between air pollution and greenhouse gas source contributions. Atmos. Res. 2022, 275, 106240. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Panigrahi, T.H.; Sahoo, S.R.; Murmu, G.; Maity, D.; Saha, S. Current challenges and developments of inorganic/organic materials for the abatement of toxic nitrogen oxides (NOx)—A critical review. Prog. Solid State Chem. 2022, 68, 100380. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hui, J.; Zhu, S.; Li, Z.; Cao, X.; Lyu, Q. Mechanism of preheating modification on NOx emission reduction during peak shaving of different coal ranks. Process Saf. Environ. Prot. 2025, 193, 432–445. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Van Caneghem, J.; De Greef, J.; Block, C.; Vandecasteele, C. NOx reduction in waste incinerators by selective catalytic reduction (SCR) instead of selective non catalytic reduction (SNCR) compared from a life cycle perspective: A case study. J. Clean. Prod. 2016, 112, 4452–4460. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Si, M.; Shen, B.; Adwek, G.; Xiong, L.; Liu, L.; Yuan, P.; Gao, H.; Liang, C.; Guo, Q. Review on the NO removal from flue gas by oxidation methods. J. Environ. Sci. 2021, 101, 49–71. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Luo, C.; Ma, S.; Feng, Y.; Wang, C.; Zhao, G.; Feng, H.; Liu, J. Research status and development of flue gas denitrification technology in selective non-catalytic reduction. Electr. Power Technol. Environ. Prot. 2024, 40, 603–614. [Google Scholar]
- Shin, Y.; Jung, Y.; Cho, C.P.; Pyo, Y.D.; Jang, J.; Kim, G.; Kim, T.M. NOx abatement and N2O formation over urea-SCR systems with zeolite supported Fe and Cu catalysts in a nonroad diesel engine. Chem. Eng. J. 2020, 381, 122751. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Tang, T.; Zhou, Q.; Xu, L.; Tang, C. Research progress in high-temperature SCR denitration: From catalyst innovations to reaction mechanism exploration. Electr. Power Technol. Environ. Prot. 2025, 41, 343–356. [Google Scholar]
- Li, F.; Liu, J.; Wang, R.; Ma, J. Research progress of manganese-based low-temperature SCR denitrification catalysts. Electr. Power Technol. Environ. Prot. 2025, 41, 383–392. [Google Scholar]
- Li, N.; Wang, Z.; Zhao, K.; Shi, Z.; Gu, Z.; Xu, S. Large scale synthesis of N-doped multi-layered graphene sheets by simple arc-discharge method. Carbon 2010, 48, 255–259. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zheng, D.; Cheng, P.; Yao, Q.; Fang, Y.; Yang, M.; Zhu, L.; Zhang, L. Excess Se-doped MoSe2 and nitrogen-doped reduced graphene oxide composite as electrocatalyst for hydrogen evolution and oxygen reduction reaction. J. Alloys Compd. 2020, 848, 156588. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, M.; Tong, S.; Jiang, L.; Hou, B.; Li, X.; Zhang, Y.; Yue, J.; Jiang, M.; Sheng, L. Nitrogen-doped porous carbon composite with three-dimensional conducting network for high rate supercapacitors. J. Alloys Compd. 2020, 844, 156217. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pan, H.; Zhang, Y.; Pan, Y.; Lin, W.; Tu, W.; Zhang, H. Nitrogen-doped porous carbon with interconnected tubular structure for supercapacitors operating at sub-ambient temperatures. Chem. Eng. J. 2020, 401, 126083. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, L.; Chen, S.; Hei, J.; Gao, R.; Liu, L.; Su, L.; Li, G.; Chen, Z. Ultrafine, high-loading and oxygen-deficient cerium oxide embedded on mesoporous carbon nanosheets for superior lithium–oxygen batteries. Nano Energy 2020, 71, 104570. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maldonado, S.; Stevenson, K.J. Influence of Nitrogen Doping on Oxygen Reduction Electrocatalysis at Carbon Nanofiber Electrodes. J. Phys. Chem. B 2005, 109, 4707–4716. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Majeed, S.; Zhao, J.; Zhang, L.; Anjum, S.; Liu, Z.; Xu, G. Synthesis and electrochemical applications of nitrogen-doped carbon nanomaterials. Nanotechnol. Rev. 2013, 2, 615–635. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, G.; Yang, J.; Lv, C.; Li, D.; Fang, D. Research progress of NH3-SCR over carbon-based catalysts for NO removal. J. Environ. Chem. Eng. 2023, 11, 110966. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pérez-Cadenas, M.; Moreno-Castilla, C.; Carrasco-Marín, F.; Pérez-Cadenas, A.F. Surface Chemistry, Porous Texture, and Morphology of N-Doped Carbon Xerogels. Langmuir 2009, 25, 466–470. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, H.; Liu, Y.; Gao, R.; Dong, T.; Hou, Z.; Jing, L.; Duan, E.; Deng, J.; Dai, H. N-doped carbon-modified palladium catalysts with superior water resistant performance for the oxidative removal of toxic aromatics. J. Hazard. Mater. 2022, 437, 129358. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Z.; Li, D.; Lan, G.; Yin, Z.; Pan, M.; Jiang, F.; Li, J.; Tan, D. Development and evaluation of mechanistic model for standard SCR, fast SCR, and NO2 SCR of NH3-SCR over Cu-ZSM-5. Energy 2024, 306, 132544. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, C.; Malta, G.; Kubota, H.; Toyao, T.; Maeno, Z.; Shimizu, K.-i. Mechanism of NH3 Selective Catalytic Reduction (SCR) of NO/NO2 (Fast SCR) over Cu-CHA Zeolites Studied by In Situ/Operando Infrared Spectroscopy and Density Functional Theory. J. Phys. Chem. C 2021, 125, 21975–21987. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cao, L.; Chen, L.; Wu, X.; Ran, R.; Xu, T.; Chen, Z.; Weng, D. TRA and DRIFTS studies of the fast SCR reaction over CeO2/TiO2 catalyst at low temperatures. Appl. Catal. A-Gen. 2018, 557, 46–54. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bendrich, M.; Scheuer, A.; Hayes, R.E.; Votsmeier, M. Unified mechanistic model for Standard SCR, Fast SCR, and NO2 SCR over a copper chabazite catalyst. Appl. Catal. B Environ. 2018, 222, 76–87. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, Y.; Liu, J.; Liu, F.; Wang, Z.; Ding, J.; Huang, H. Reaction mechanism for NH3-SCR of NOx over CuMn2O4 catalyst. Chem. Eng. J. 2019, 361, 578–587. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Adapa, S.; Gaur, V.; Verma, N. Catalytic oxidation of NO by activated carbon fiber (ACF). Chem. Eng. J. 2006, 116, 25–37. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Elkaee, S.; Phule, A.D.; Yang, J.H. Advancements in (SCR) technologies for NOx reduction: A comprehensive review of reducing agents. Process Saf. Environ. Prot. 2024, 184, 854–880. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shi, Y.; Zhao, T.; Du, J.; Feng, B.; Tang, Q.; Shan, S.; Zhang, M.; Wang, Q.; Zhao, J. Low temperature NH3 selective catalytic reduction of NOx over CeOx-biochar catalyst prepared by air oxidation. J. Energy Inst. 2024, 112, 101484. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, M.; Chen, J.; Wu, F.; Wang, Y.; Chen, K.; Xiong, C.; Zhu, R. Unraveling the anti-poisoning mechanism of highly dispersed Ni atoms enhanced porous MnOx catalysts in the selective reduction of NOx by NH3. J. Colloid Interface Sci. 2025, 694, 137662. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eigenmann, F.; Maciejewski, M.; Baiker, A. Selective reduction of NO by NH3 over manganese-cerium mixed oxides: Relation between adsorption, redox and catalytic behavior. Appl. Catal. B Environ. 2006, 62, 311–318. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, X.; Li, B.; Wang, Y.; Wei, T.; Li, S.; Li, W. Insight into the dynamic behaviors of reactants with temperature over a TiOx-based catalyst for NOx removal via NH3-SCR. Appl. Surf. Sci. 2022, 605, 154689. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, S.; Feng, X.; Liu, Z.; Zhao, W.; Li, Y.; Zhang, J. Nitrogen doping in porous biochar from cotton stalk with H3PO4 activation for reduction of NOx with NH3-SCR at low temperatures: Characteristics and catalytic activity analysis. Fuel 2023, 332, 126256. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jia, Y.; Jiang, J.; Zheng, R.; Guo, L.; Yuan, J.; Zhang, S.; Gu, M. Insight into the reaction mechanism over PMoA for low temperature NH3-SCR: A combined In-situ DRIFTs and DFT transition state calculations. J. Hazard. Mater. 2021, 412, 125258. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Q.; Hou, Y.; Xiang, N.; Liu, Y.; Huang, Z. A new insight into the promotional effect of nitrogen-doping in activated carbon for selective catalytic reduction of NOx with NH3. Sci. Total Environ. 2020, 740, 140158. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yue, K.; Liu, S.; Yan, S.; Bi, D.; Liu, Z.; Xu, S. Analysis of the reaction mechanism of N/S co-doped carbon-based catalysts for low-temperature NH3-SCR reduction of Nox. Sep. Purif. Technol. 2024, 344, 127302. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, N.; Cheng, Q.; Wang, M.; He, Y.; Ji, H.; Rosei, F. Triggering synergistic electronic promoting effect through oxygen doping to promote electrochemical nitrogen reduction on metal-free electrocatalyst. Inorg. Chem. Front. 2023, 10, 7010–7017. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Si, Z.; Weng, D.; Wu, X.; Jiang, Y. Roles of Lewis and Bronsted acid sites in NO reduction with ammonia on CeO2-ZrO2-NiO-SO4−2 catalyst. J. Rare Earths 2010, 28, 727–731. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, W.; Zhang, Q.; Zhu, Y.; Zhao, P.; Chen, B.; Peng, W.; Li, Y.; Zhang, F.; Fan, X. Boosting Reaction Kinetics and Mass Transfer of Bifunctional Co-Based Oxygen Electrocatalyst Prepared from CoAl-LDH. Adv. Energy Mater. 2023, 13, 2301580. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, X.; Pan, X.; Yu, L.; Ren, P.; Wu, X.; Sun, L.; Jiao, F.; Bao, X. Silicon carbide-derived carbon nanocomposite as a substitute for mercury in the catalytic hydrochlorination of acetylene. Nat. Commun. 2014, 5, 3688. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Trovarelli, A. Catalytic Properties of Ceria and CeO2-Containing Materials. Catal. Rev. 1996, 38, 439–520. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, Q.; Jing, W.; Hou, Y.; Huang, Z.; Ma, G.; Han, X.; Sun, D. On the nature of oxygen groups for NH3-SCR of NO over carbon at low temperatures. Chem. Eng. J. 2015, 270, 41–49. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tian, W.; Zhang, H.; Duan, X.; Sun, H.; Shao, G.; Wang, S. Porous Carbons: Structure-Oriented Design and Versatile Applications. Adv. Funct. Mater. 2020, 30, 1909265. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- You, F.-T.; Yu, G.-W.; Xing, Z.-J.; Li, J.; Xie, S.-Y.; Li, C.-X.; Wang, G.; Ren, H.-Y.; Wang, Y. Enhancement of NO catalytic oxidation on activated carbon at room temperature by nitric acid hydrothermal treatment. Appl. Surf. Sci. 2019, 471, 633–644. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, Y.; Bu, Y.; Zhong, Q.; Cai, W. Catalytic oxidation of NO by g-C3N4-assisted electrospun porous carbon nanofibers at room temperature: Structure-activity relationship and mechanism study. Catal. Commun. 2016, 87, 62–65. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, X.; Lu, Z.; Tang, Y.; Ma, D.; Yang, Z. Depletion NOx Made Easy by Nitrogen Doped Graphene. Catal. Lett. 2014, 144, 1016–1022. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, M.-C.; Teng, H. Nitrogen-containing carbons from phenol–formaldehyde resins and their catalytic activity in NO reduction with NH3. Carbon 2003, 41, 951–957. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, Z.; Wang, M.; Huang, Z.-H.; Kang, F. Preparation of graphene/carbon hybrid nanofibers and their performance for NO oxidation. Carbon 2015, 87, 282–291. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qu, Z.; Sun, F.; Pi, X.; Li, X.; Wu, D.; Gao, J.; Zhao, G. One-step synergistic optimization of hierarchical pore topology and nitrogen dopants in activated coke for efficient catalytic oxidation of nitric oxide. J. Clean. Prod. 2022, 335, 130360. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, K.X.; Ling, L.C.; Lu, C.X.; Qiao, W.M.; Liu, Z.Y.; Liu, L.; Mochida, I. Catalytic removal of SO2 over ammonia-activated carbon fibers. Carbon 2001, 39, 1803–1808. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hong, Z.; Wang, Z.; Li, X. Catalytic oxidation of nitric oxide (NO) over different catalysts: An overview. Catal. Sci. Technol. 2017, 7, 3440–3452. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grzybek, T.; Klinik, J.; Samojeden, B.; Suprun, V.; Papp, H. Nitrogen-promoted active carbons as DeNOx catalysts. Catal. Today 2008, 137, 228–234. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, S.; Xu, S.; Tong, J.; Ding, D.; Wang, G.; Chen, R.; Jin, P.; Wang, X.C. Overlooked role of nitrogen dopant in carbon catalysts for peroxymonosulfate activation: Intrinsic defects or extrinsic defects? Appl. Catal. B Environ. 2021, 295, 120291. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ismagilov, Z.R.; Shalagina, A.E.; Podyacheva, O.Y.; Ischenko, A.V.; Kibis, L.S.; Boronin, A.I.; Chesalov, Y.A.; Kochubey, D.I.; Romanenko, A.I.; Anikeeva, O.B.; et al. Structure and electrical conductivity of nitrogen-doped carbon nanofibers. Carbon 2009, 47, 1922–1929. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Szymański, G.S.; Grzybek, T.; Papp, H. Influence of nitrogen surface functionalities on the catalytic activity of activated carbon in low temperature SCR of NO with NH3. Catal. Today 2004, 90, 51–59. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, Z.; Wei, J.; Lv, E.; Sheng, L.; Liu, D.; Lei, W.; Gao, W.; Guo, Y.; Li, X.; Zhang, H. Reinforcing cementitious composites with nitrogen-doped graphene: Insights into molecular interactions and interfacial behavior. Mater. Today Commun. 2024, 40, 109468. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, Y.; Li, Y.; Xu, Z.; Xiong, J.; Zhu, T. Transformation of functional groups in the reduction of NO with NH3 over nitrogen-enriched activated carbons. Fuel 2018, 223, 312–323. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sousa, J.P.S.; Pereira, M.F.R.; Figueiredo, J.L. NO oxidation over nitrogen doped carbon xerogels. Appl. Catal. B Environ. 2012, 125, 398–408. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Q.; Hou, Y.; Wang, J.; Liu, Y.; Xiang, N.; Huang, Z. Superiority of Raw Biomass and Potassium Hydroxide in Preparation of Ultrahigh Nitrogen Doping of Carbon for NH3-SCR Reaction. ACS Sustain. Chem. Eng. 2020, 8, 11308–11316. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sousa, J.P.S.; Pereira, M.F.R.; Figueiredo, J.L. Modified activated carbon as catalyst for NO oxidation. Fuel Process. Technol. 2013, 106, 727–733. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vinu, A. Two-Dimensional Hexagonally-Ordered Mesoporous Carbon Nitrides with Tunable Pore Diameter, Surface Area and Nitrogen Content. Adv. Funct. Mater. 2008, 18, 816–827. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, B.; Huang, R.; Jin, D.; Ye, D. Low temperature SCR of NO with NH3 over carbon nanotubes supported vanadium oxides. Catal. Today 2007, 126, 279–283. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, C.; Wu, Y.; Liang, H.; Chen, X.; Tang, J.; Wang, X. N-doped graphene and TiO2 supported manganese and cerium oxides on low-temperature selective catalytic reduction of NOx with NH3. J. Adv. Ceram. 2018, 7, 197–206. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, P.; Li, Z.; Cui, J.; Geng, C.; Kang, Y.; Zhang, C.; Yang, C. N-doped graphene/CoFe2O4 catalysts for the selective catalytic reduction of NOx by NH3. RSC Adv. 2019, 9, 15791–15797. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, Y.; Jia, L.; Hou, B.; Li, D.; Wang, J.; Sun, Y. The Correlation of Interfacial Interaction and Catalytic Performance of N-Doped Mesoporous Carbon Supported Cobalt Nanoparticles for Fischer–Tropsch Synthesis. J. Phys. Chem. C 2013, 118, 268–277. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, X.H. Antonietti, M. Metal nanoparticles at mesoporous N-doped carbons and carbon nitrides: Functional Mott-Schottky heterojunctions for catalysis. Chem. Soc. Rev. 2013, 42, 6593–6604. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, W.; Guo, S.; Zhang, H.; Pan, X.; Bao, X. Enhanced Ammonia Synthesis Activity of Ru Supported on Nitrogen-Doped Carbon Nanotubes. Chin. J. Catal. (Chin. Version) 2014, 32, 1418–1423. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, J.; Mo, D.; Tao, L.; Li, J.; Fu, S.; Dong, L.; Li, B.; Chen, Z.; Fan, M. N-doped porous carbon material derived by MOFs calcined in proper oxygen atmosphere as high-performance catalyst for the low-temperature NH3-SCR. J. Environ. Chem. Eng. 2023, 11, 111218. [Google Scholar]
- Choi, S.Y.; Purbia, R.; Kim, H.J.; Kim, J.-K.; Kim, S.-W.; Mo, J.; Ye, B.; Jeong, B.; Lee, D.H.; Kim, D.; et al. Low temperature selective catalytic reduction of NOx with NH3 with improved SO2 and water resistance by using N-doped graphene dots-CuO–CeO2 nano-heterostructures modified vanadate catalysts. Appl. Surf. Sci. 2023, 623, 157088. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, J.; Shen, H.; Zhou, X.; Zheng, T.; Guo, F.; Zhang, Q.; Duan, M. Enhancement low-temperature NH3-SCR activity of the Fe-Mn-Mo/TiO2 catalyst and its DFT calculations and kinetics. Mol. Catal. 2023, 551, 113657. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feng, X.; Liu, S.; Yue, K.; Wei, H.; Bi, D.; Zhao, W. Insight into the promotional effect of Mn-modified nitrogenous biochar on the NH3-SCR denitrification activity at low temperatures. Energy 2023, 285, 129323. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Białas, A.; Szlendak, J.; Czosnek, C.; Motak, M. Activated Carbon as a Support of Catalysts for the Removal of Nitrogen Oxides. Mineralogia 2020, 51, 9–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Spadaro, L.; Arena, F.; Granados, M.; Ojeda, M.; Fierro, J.; Frusteri, F. Metal–support interactions and reactivity of Co/CeO2 catalysts in the Fischer–Tropsch synthesis reaction. J. Catal. 2005, 234, 451–462. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zheng, W.; Zhang, X.; Zheng, Y.; Yue, Y. “Oxynitride trap” over N/S co-doped graphene-supported catalysts promoting low temperature NH3-SCR performance: Insight into the structure and mechanisms. J. Hazard. Mater. 2022, 423, 127187. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Z.; Yang, J.; Ma, X.; Cui, J.; Ma, Y.; Geng, C.; Kang, Y.; Yang, C. In situdesign of Cu and Co nanoparticles encapsulated in N-doped graphene with core–shell structure-derived 8-hydroxyquinoline complexes for the selective catalytic reduction of NOx by NH3. New J. Chem. 2020, 44, 12639–12645. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yao, L.; Lu, Y.; Pan, H.; Xiang, G.; Zhou, X.; Liu, W.; Liu, Q.; Kong, M.; Cao, J. Promotion effect of nitrogen doping on the low-temperature NH3-SCR of NO over activated carbon: Characterization and mechanism analysis. J. Environ. Chem. Eng. 2024, 12, 114381. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, S.; Wang, J.; Wang, Z.; Zhang, L.; Xu, H. The effect of pyrrolic nitrogen on corrosion inhibition performance of N-doped carbon dots. Surf. Interfaces 2024, 44, 103740. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Sun, X.; Li, F.; Xu, Y.; Zhang, Q.; Ma, J. A Review on N-Doped Carbon-Based Materials for the NH3-SCR Reaction. Nanomaterials 2025, 15, 1566. https://doi.org/10.3390/nano15201566
Sun X, Li F, Xu Y, Zhang Q, Ma J. A Review on N-Doped Carbon-Based Materials for the NH3-SCR Reaction. Nanomaterials. 2025; 15(20):1566. https://doi.org/10.3390/nano15201566
Chicago/Turabian StyleSun, Xueli, Fangxiao Li, Yun Xu, Qian Zhang, and Jingwen Ma. 2025. "A Review on N-Doped Carbon-Based Materials for the NH3-SCR Reaction" Nanomaterials 15, no. 20: 1566. https://doi.org/10.3390/nano15201566
APA StyleSun, X., Li, F., Xu, Y., Zhang, Q., & Ma, J. (2025). A Review on N-Doped Carbon-Based Materials for the NH3-SCR Reaction. Nanomaterials, 15(20), 1566. https://doi.org/10.3390/nano15201566




