Abstract
Methyltrimethyltridecylchromans (MTTCs), a class of oxygen-containing aromatic derivatives, have been used as indicators of paleosalinity in source rocks and crude oils. However, the reliability of these compounds as indicators in mature organic matter remains unclear, hindering a definitive assessment of their significance for oil–oil or oil–source rock correlation. In this study, a suite of mature oils and associated source rocks from the Paleogene Shahejie (E2s) Formation in the Machang area, Dongpu Depression, Bohai Bay Basin, were analyzed. The distribution of bulk compositions and biomarkers in the oils and source rock extracts suggests a genetic relationship, indicating that the oils were derived from similar organic matter (predominantly algae and aquatic macrophytes) and depositional environments (low salinity), with comparable maturity levels (within the middle oil window). The β/γ-MTTC ratio, a proposed maturity indicator, appears unreliable in mature organic matter, as evidenced by its poor correlation with established maturity proxies (e.g., C29 24-ethylcholestanes αββ/(ααα + αββ)) in the studied samples. In contrast, MTTC-based salinity paraments (α/δ, α/γ, MTTCI, and the cross-plot of MTTCI versus Pr/Ph) consistently reflect a low-salinity depositional environment for these crude oils and source rocks, except in the ternary diagram of relative alkylation abundances. These findings suggest that MTTC-derived paleosalinity indicators may serve as effective tools for oil–oil or oil–source rock correlation within the middle oil window. This study provides evidence supporting the broader applicability of MTTC-based proxies for paleosalinity reconstruction and correlation studies, particularly in mature organic matter under geological conditions. The results also offer insights for regional petroleum exploration in saline lacustrine basins.
1. Introduction
Methyltrimethyltridecylchromans (MTTCs), characterized by a carbon skeleton of 2-methyl-2-(4,8,12-trimethyltridecyl)-chromans, are structurally derived from vitamin E through the removal of the C-6 hydroxyl group. Based on the number and position of substituents on the benzene ring, these compounds can be classified into five homolog types [1,2,3].
MTTCs were first identified in geological sediments by Sinninghe Damsté et al. [1] and have since been frequently detected in Permian, Cretaceous, Paleogene, and Neogene source rocks, as well as in associated crude oils [4,5], with particularly high concentrations in Cretaceous, Paleogene, and Neogene samples [6,7,8,9,10].
However, the origin and formation mechanisms of MTTCs remain debated. Structurally analogous to tocopherols (vitamin E) and their derivatives (e.g., α-tocopherol, α-tocopherol quinones, and trimethylphytylbenzoquinone), MTTCs exhibit varying degrees of positive correlation with α-MTTC [11,12]. These observations suggest that MTTCs may derive from the diagenetic alteration of tocopherol derivatives [11,12]. However, chemical reaction analyses indicate that direct conversion of vitamin E into MTTCs via hydroxyl elimination is unlikely during early diagenesis [13].
An alternative hypothesis proposes that MTTCs form through the cyclization of alkylated phenols—structurally related compounds also detected in sediments—as suggested by Barakat et al. [14]. Meanwhile, Sinninghe Damsté et al. argued for a biosynthetic origin based on carbon isotopic similarities between MTTCs and biomarkers of primary photosynthesizers (e.g., algae or Calvin-cycle-utilizing bacteria) [13,15,16,17,18,19,20]. In contrast, Li et al. proposed that MTTCs could arise from condensation reactions between chlorophyll and alkylphenols during diagenesis [2]. Tulipani et al. provided further support for this mechanism by analyzing stable carbon isotopes of pyrolyzed fragments (trimethylphenol and pristenes) from 5,7,8-trimethyl-MTTC using online pyrolysis–gas chromatography–isotope ratio mass spectrometry (Py-GC-irMS) [8]. Nevertheless, this hypothesis fails to explain the limited diversity of MTTC isomers observed in geological samples [21].
Consequently, several proxies have been proposed to reconstruct paleosalinity in the upper water column, including: (1) the α/δ and α/γ ratios [15], (2) the MTTC index (MTTCI = α-MTTC/total MTTCs) [16], (3) a cross-plot of MTTCI versus the Pr/Ph ratio [5], and (4) a ternary diagram of the relative abundances of MTTCs with varying degrees of alkylation [5]. Additionally, the chroman ratio (α-MTTC/sum of all MTTCs) has been proposed as a molecular paleoproxy for identifying freshwater incursions that drive salinity stratification [9]. This ratio has been effectively employed to trace temporal and spatial variations in freshwater input and its control on salinity stratification during the deposition of black shales in the Lower Permian Irati Formation [22]. Due to their high specificity and widespread use in paleosalinity reconstruction, these MTTC-based indicators have been successfully applied to oil–source rock correlation studies. Notable examples include analyses of immature to low-maturity organic matter from the Huanghekou Sag (Bohai Bay Basin, eastern China) and the Songliao Basin (northeastern China) [23,24].
However, the influence of thermal maturity on MTTCs remains poorly constrained [3,25]. Notably, these compounds are predominantly detected in immature to low-maturity sediments and crude oils, establishing their presence as a reliable indicator for organic matter within this maturity range [21,26,27]. In particular, the β/γ-MTTC ratio serves as an effective maturity proxy for source rocks and oils within the immature to marginal maturity stage (vitrinite reflectance, Ro < 0.65%) [28]. Furthermore, Jiang et al. suggested that the characteristic chemical structure of MTTCs renders them susceptible to thermal degradation; with increasing maturity, these compounds undergo decomposition through either side-chain cleavage or dihydropyran ring opening [5,6].
However, multiple studies have documented the occurrence of these compounds in thermally mature organic matter [5,29,30,31,32]. Current understanding suggests their presence is primarily governed by the depositional environment of organic matter rather than maturity levels [3]. Supporting this view, Koopmans et al. conducted artificial maturation experiments (0–300 °C) on immature to low-maturity sediments and found that neither the distribution of dimethyl-MTTCs nor the chroman ratio showed significant variation with thermal maturity [16,33]. Similarly, Jiang et al. reported that (β + γ)-MTTC% and β/γ-MTTC ratios remain essentially unaffected by thermal maturity in immature to low-maturity sediments under geological conditions [5,30].
Despite their established utility in immature systems, MTTCs are rarely documented in mature organic matter studies, and the reliability of associated geochemical parameters remains uncertain [28]. Furthermore, the effectiveness of these compounds as indicators for oil–oil or oil–source rock correlation remains unresolved. In this study, the distributions of MTTCs in mature crude oils and source rocks from the Paleogene Shahejie Formation (E2s3) in the Machang area of the Dongpu Depression, Bohai Bay Basin, are investigated. Through comprehensive geochemical characterization—including organic matter source analysis, paleosalinity assessment, and maturity evaluation using bulk compositional data and multiple biomarker parameters—this study aims to (1) evaluate the applicability of MTTC-derived indicators for maturity and paleosalinity assessment in mature organic matter and (2) assess their potential for oil–oil and oil–source rock correlation studies.
2. Geological Setting
The Dongpu Depression, a marginal NNE-trending Cenozoic rift basin, is situated in the southwestern Bohai Bay Basin of northeastern China (Figure 1) [34]. This structural depression spans approximately 5300 km2. The depression’s internal structure comprises four distinct NNE-trending fault-bounded tectonic units arranged sequentially from west to east: (1) the Western Slope Belt, (2) Western Sag Belt, (3) Central Anticlinal Belt, and (4) Eastern Sag Belt [35].
The Machang area occupies the southern portion of the Central Anticlinal Belt in the Dongpu Depression, Bohai Bay Basin. This structural domain is bounded by the Gegangji Southern Sag to the east and demarcated by the Machang Fault to the west, with approximate dimensions of 4 km (E-W) × 30 km (N-S) [36].
The Cenozoic stratigraphy drilled in the Machang area includes the Shahejie (E2s), Dongying (E1d), Guantao (N1g), Minghuazhen (N1m), and Pingyuan (Qp) Formations. Based on lithological characteristics and fossil assemblages, the Shahejie Formation can be stratigraphically subdivided into four distinct members, designated in ascending order as E2s4, E2s3, E2s2, and E2s1 [37]. E2s3 can be also further subdivided into lower (E2s3L), middle (E2s3M), and upper (E2s3U) sections, whereas E2s4 and E2s2 only consist of lower (E2s4L, E2s2L) and upper (E2s4U, E2s2U) sections (Figure 2). Moreover, E2s3, the target member, consists of mudstone, shale siltstone, and sandstone, the main source rocks in the Machang area [36,38].
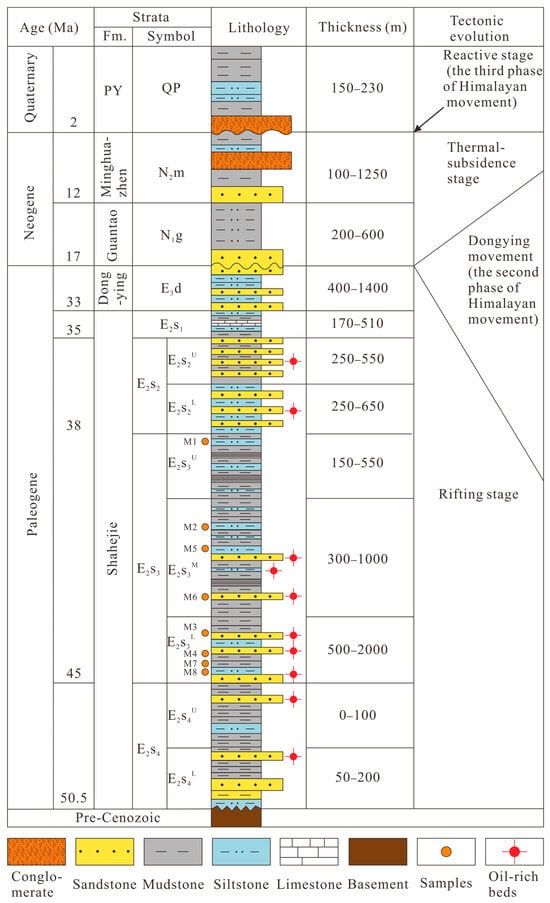
Figure 2.
Generalized stratigraphy of the southern Dongpu depression (modified from Liu et al. and Tang et al. [36,39]); Fm.: Formation; PY: Pingyuan.
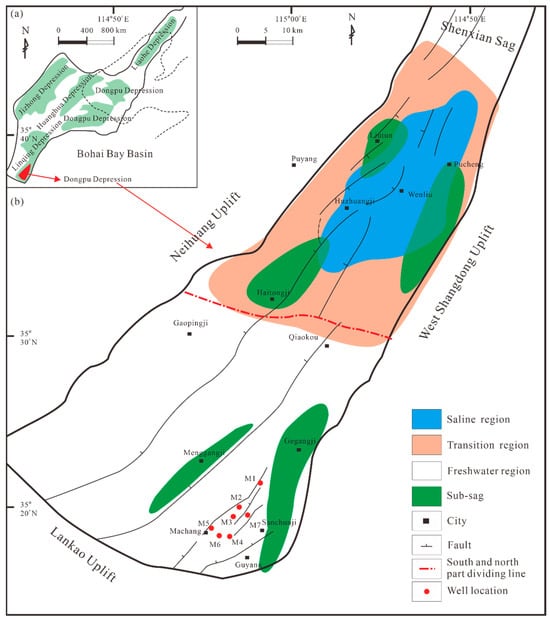
Figure 1.
The geographical location of the study area (a) and the structural units with sampling well locations (b) in the Machang area, Dongpu Depression, Bohai Bay Basin, Eastern China (modified from Gao et al. [38]).
3. Samples and Methods
3.1. Samples
Six crude oil and two source rock samples were collected from the Shahejie Formation (depths: 2451.9–3379.1 m) in the northeastern Machang area of the Dongpu Depression, Bohai Bay Basin. The crude oils exhibit a characteristic brown coloration, low API gravity (11–21°), and high wax content, typical of continental lacustrine systems [36]. Source rocks from the E2s3ᴸ member, identified as the potential source of these oils [40], show TOC values ranging from 1.16% to 1.43%. Bulk composition analysis reveals similar distributions across all samples (Table 1), characterized by (1) high saturated hydrocarbon fractions (55–68%), (2) low aromatic fractions (12–18%), and (3) minimal resin and asphaltene content (15–25%)—a pattern consistent with extracts from the source rocks.

Table 1.
Bulk physical properties and calculated MTTC parameters of the studied crude oils and associated source rocks in the study area.
3.2. Methods
Following established protocols [41], source rock samples were processed by first removing exterior portions (1–3 cm) and cutting the interior into chips. The chips were sequentially rinsed with dichloromethane (DCM), dried, and ground to a fine powder (<100 mesh) using a stainless-steel puck mill. Between samples, the mill was rigorously cleaned by: (1) triple grinding with quartz sand (pre-baked at 550 °C for ≥8 h), (2) sequential washing with tap and deionized water, and (3) multiple DCM rinses.
Powdered rock aliquots (30–50 g) were subjected to Soxhlet extraction using 250 mL of a dichloromethane–methanol azeotropic mixture (9:1 v/v) to obtain total lipid extracts. During subsequent rotary evaporation, active copper wire (pre-cleaned with dilute HCl and acetone) was introduced to each extract for elemental sulfur removal through in situ copper sulfide formation.
Following sulfur removal, both the extracts and crude oil samples underwent fractionation into asphaltenes and maltenes through precipitation with excess n-hexane (40:1 v/v) at room temperature for 24 h. The maltene fraction was subsequently separated into saturated hydrocarbons, aromatic hydrocarbons, and polar resins using column chromatography with a silica gel/alumina (3:1 w/w) stationary phase that had been activated at 150 °C for 6 h. The elution sequence employed (1) n-hexane (15 mL/g stationary phase) to isolate saturated hydrocarbons; (2) n-hexane/dichloromethane (1:1 v/v; 15 mL/g) for aromatic hydrocarbons; and dichloromethane/methanol (98:2 v/v; 10 mL/g) to recover polar resins.
The saturated and aromatic fractions were dried under nitrogen and immediately sealed in amber vials to prevent degradation prior to analysis. Compound separation and identification were conducted using an Agilent 7890A/5975C GC-MS (Agilent Technologies, CA, USA) system equipped with a DB-5 MS fused silica capillary column (Agilent Technologies, CA, USA) (60 m × 0.25 mm i.d., 0.25 μm film thickness). The injector temperature was maintained at 280 °C, and helium was used as the carrier gas at a constant flow rate of 1 mL min−1. For the saturated fractions, the GC oven temperature was initially held at 50 °C for 1 min, then increased to 100 °C at a rate of 20 °C/min, followed by a gradient rise to 310 °C at 3 °C/min, and finally held at 310 °C for 16 min. For the aromatic fractions, the oven temperature program began at 60 °C (held for 2 min), ramped to 150 °C at 8 °C/min, then to 315 °C at 4 °C/min, and maintained 315 °C for 10 min. The mass selective detector (MSD) was operated in full-scan acquisition mode with a scan range of 50–550 Da. The relative abundances of molecular markers were determined based on peak areas in the corresponding mass chromatograms. Response factors were not applied to correct for variations in ionization efficiencies among different compounds.
4. Results
4.1. Composition and Occurrence of MTTCs
Five isomers were unambiguously identified in the aromatic fractions of the crude oil and source rock samples [1,5] (Figure 3). Specifically, δ-MTTC and α-MTTC were identified from m/z 121 and m/z 149 ion chromatograms, respectively, whereas β-MTTC, γ-MTTC, and ζ-MTTC eluted sequentially and were detected in m/z 135 ion chromatograms (Figure 3). Among these isomers, α-MTTC was the most abundant in both the oils and source rocks, with MTTC index (MTTCI) values ranging from 0.60 to 0.68 and 0.62 to 0.66, respectively (Table 1). The β/γ-MTTC ratio, a well-established maturity parameter, exhibited significant variation, ranging from 4.32 to 31.30 in the oils and from 3.92 to 4.82 in the source rocks (Table 1). Paleosalinity indicators, including the α/δ-MTTC and α/γ-MTTC ratios, ranged from 6.28 to 15.34 and 12.55 to 110.04 in the oils, respectively. In contrast, the corresponding values in the source rocks were more constrained, ranging from 13.10 to 14.29 and 11.08 to 18.82 (Table 1).
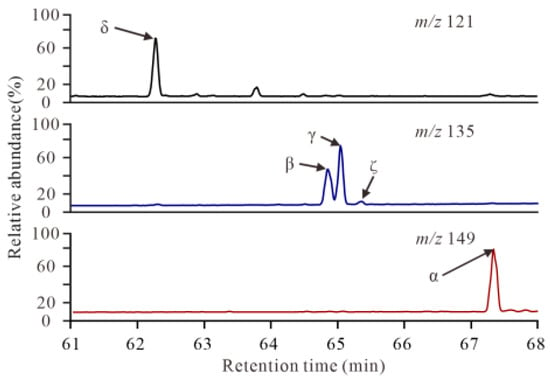
Figure 3.
Mass chromatograms of the distribution of mono- (m/z 121), di- (m/z 135), and trimethyl-MTTCs (m/z 149) in M1 crude oils typical for identifying MTTCs in the aromatic fractions of crude oil samples from the Machang area, Dongpu Depression, Bohai Bay Basin (δ: δ-MTTC; β: β-MTTC; γ: γ-MTTC; ζ: ζ-MTTC; α: α-MTTC).
4.2. Saturated Hydrocarbon Molecular Markers
N-alkanes ranging from n-C12 to n-C37 were detected in the crude oils and source rocks (Figure 4a,d,g). The relative proportions of n-alkanes in the ranges of C15–C20, C21–C25, and C27–C31 in the crude oils ranged from 37.1% to 47.4%, 34.8% to 47.5%, and 6.6% to 25.3%, respectively; in the source rocks, they ranged from 54.5% to 56.2%, 36.0% to 36.1%, and 7.7% to 9.6%, respectively (Table 2). The carbon preference index (CPI) and odd–even predominance (OEP) values for the crude oils ranged from 1.03 to 1.23 and 0.99 to 1.06, respectively, similar to the values in the source rocks (Table 2). This indicates a lack of significant odd or even carbon number preference in the n-alkanes. Furthermore, the Pr/Ph ratios in the crude oils varied from 1.05 to 1.21, while those in the source rocks ranged from 1.11 to 1.45 (Table 2). Additionally, the Pr/n-C17 and Ph/n-C18 ratios in the crude oil samples ranged from 0.26 to 1.37 and 0.25 to 1.29, respectively; in the source rocks, these ratios ranged from 0.82 to 0.83 and 0.59 to 0.83, respectively (Table 2).
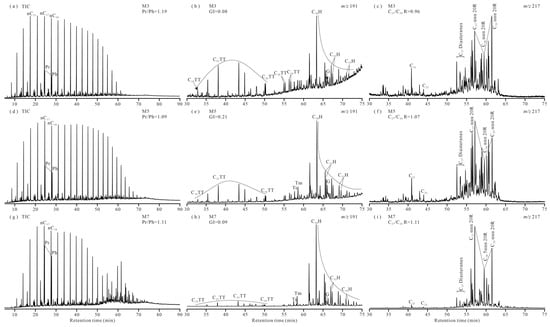
Figure 4.
Total ion chromatograms (TICs) (a,d,g) of saturate fractions and mass chromatograms (m/z 191 for tricyclic terpanes and hopanes (b,e,h); m/z 217 for steranes (c,f,i)) applied to show oil–oil and oil–source rock correlations in the studied crude oils and associated source rocks from the Machang area, Dongpu Depression, Bohai Bay Basin. (Pr: pristane; Ph: phytane; C19–29 TT: C19–C29 tricyclic terpanes; C30–35 H: C30–C35 hopanes; C21: pregnane; C22: homopregnane; C27 ααα 20R: 20R-C27 5α, 7α, 14α sterane; C28 ααα 20R: 20R-C28 5α, 7α, 14α sterane; C29 ααα 20R: 20R-C29 5α, 7α, 14α sterane).

Table 2.
Depositional environment parameters of saturated and aromatic hydrocarbons for the crude oils and associated source rocks in the study area.
(C19 + C21)/C23 TT ratios in oils ranged from 0.73 to 0.85 versus 0.56 to 0.62 in source rocks (Figure 4b,e,h; Table 2). Hopanoid pentacyclic terpanes (C27–C35) exhibited dominance of C30 hopane (C30H). C31–35 homohopane distributions displayed maximum abundance at C31, with a progressive decline toward C35. C35/C31–35 H ratios ranged from 0.00 to 0.13 in oils and 0.09 to 0.11 in source rocks (Figure 4b,e,h; Table 2). Additionally, gammacerane (Ga) occurred at a low relative abundance, with Ga/C30 H (GI) ratios of 0.08–0.45 in oils and 0.05–0.09 in source rocks (Figure 4b,e,h; Table 2). Steranes detected in all samples included pregnane, homopregnane, C27–29 regular steranes, and C27/C29 diasteranes. C21–22/C27–29 sterane ratios averaged 0.03 in oils and 0.01 in source rocks. Diasterane/regular sterane ratios (C27) ranged from 0.19 to 0.42 in oils and 0.16 to 0.17 in source rocks, while C27/C29 regular sterane ratios averaged 1.07 in oils and 1.17 in source rocks ((Figure 4c,f,i; Table 2).
4.3. Aromatic Hydrocarbon Molecular Markers
Naphthalene, phenanthrene, and benzothiophene series compounds were relatively abundant in aromatic fractions of all samples. Maturity parameters associated with naphthalene series compounds (DNR and TNR-2) in oils ranged from 2.93 to 4.96 and 0.79 to 0.92, respectively, while corresponding values in source rocks ranged from 2.63 to 3.29 and 0.60 to 0.67, respectively (Table 3). Equivalent vitrinite reflectance values (Rc-1 and Rc-2) for oils ranged from 0.75 to 0.92 and 0.88 to 0.95, respectively, versus 0.73–0.79 and 0.76–0.80 in source rocks (Table 3). Phenanthrene series maturity parameters (MPI1, F1, and F2) in crude oils ranged from 0.48 to 1.39, 0.40 to 0.47, and 0.22 to 0.26, respectively, compared to 0.41–0.45, 0.41–0.42, and 0.23–0.24 in source rocks (Table 3). Additionally, benzothiophene series parameters served as significant maturity indicators. Mean 4,6-DMDBT/1,4-DMDBT ratios and corresponding Rc-4 values in oils were 1.85 and 0.83, respectively, versus 0.64 and 0.66 in source rocks. DBT/P ratios, used as paleosalinity indicators, ranged from 0.08 to 0.11 in oils and 0.02 to 0.04 in source rocks (Table 2).

Table 3.
Maturity parameters of saturated and aromatic hydrocarbons for the studied oils and associated source rocks in the study area.
5. Discussion
5.1. Origin of Crude Oils and Source Rocks
5.1.1. Sources of Organic Matter
The distribution patterns of n-alkanes may also reflect the precursor sources of crude oils and source rocks. Short-chain alkanes (with a carbon number less than 20) predominantly originate from algae [42,43], while medium-chain alkanes (with a carbon number ranging from 21 to 25) are mainly derived from aquatic macrophytes [44], and long-chain alkanes (with a carbon number greater than 27) containing a predominance of odd carbon numbers are mainly derived from land plants [43,45]. n-Alkanes were characterized by relatively high proportions of C15–20 and C21–25 alkanes (37.13 to 56.24% and 34.75 to 47.45%, respectively) and a lower proportion of C27–31 alkanes (6.60 to 25.34%), which suggested that these oils and rocks, in particular, may be mainly derived from algae and aquatic macrophytes, with a smaller contribution from higher plants.
Previous studies found that a Pr/n-C17-vs.-Ph/n-C18 cross-plot can be used to determine the organic matter types of source rocks or related oils [46]. Figure 5a shows that the crude oils and source rocks from the Machang area, Dongpu Depression were composed of mixed organic matter.
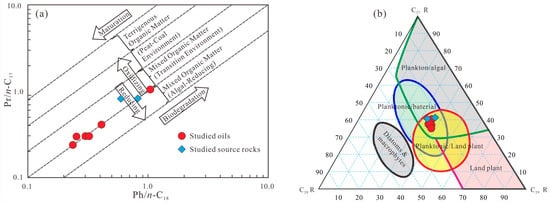
Figure 5.
(a) Pr/n-C17 vs. Ph/n-C18 plot (modified after [44]) and (b) relationship between regular sterane compositions (modified after [46]) of crude oils and associated source rocks from the Machang area, Dongpu Depression, Bohai Bay Basin (C27–29 R: C27–C29 regular steranes) [10,12].
The C19 + 20/C21 ratio is usually used to indicate land plant input in organic matter [47]. In this study, these ratios ranged from 0.56 to 0.85, with a mean of less than 1, suggesting that the studied oils and rocks received a small contribution from land plants.
The distribution of regular steranes, notably, also has the potential to indicate the sources of organic matter. Extensive previous studies have attributed C27 steranes to algae and C29 steranes to land plants [48]. All studied samples are plotted in the plankton/algal, planktonic/bacterial, and planktonic/land plant intersection areas (Figure 5b), suggesting that the oils and rocks were both derived from similar organic matter.
5.1.2. Depositional Environments
The Pr/Ph ratio, a conventional molecular marker for depositional environment determination, has been extensively applied to sediments and associated crude oils [4,49]. Pr/Ph ratios < 1.0 indicate anoxic conditions, whereas ratios >3.0 suggest oxic depositional environments [50]. However, Pr/Ph ratio reliability as a redox proxy can be compromised by organic matter maturity variations [51] and differential pristane/phytane precursors [52]. Nevertheless, our results indicate shared biological precursors (algae and aquatic macrophytes; Section 5.1.1) and consistent thermal maturity levels across samples (Section 5.1.3), supporting Pr/Ph ratios as reliable redox indicators. Consequently, the observed Pr/Ph ratios (1.05–1.45) reliably record dysoxic to anoxic conditions.
Gammacerane (Ga) serves as a robust indicator of water column stratification, primarily linked to paleosalinity variations during deposition [21]. Thus, variations in both the Gammacerane index (GI = 0.05–0.45; mean 0.17) and Pr/Ph ratios indicate fluctuating water stratification under relatively low salinity.
Wang et al. demonstrated that pregnane and homopregnane distributions correlate significantly with depositional environments [53]. Accordingly, they proposed a cross-plot of C21–22/C27–29 steranes versus diasterane/regular sterane C27 ratios for environmental diagnosis. As shown in Figure 6a, all samples plot within the open environment field.
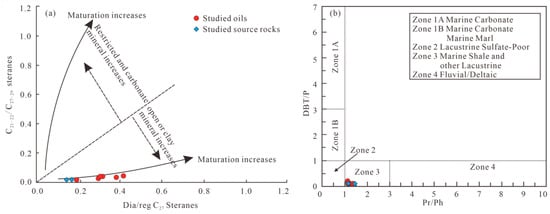
Figure 6.
(a) Cross-plot of C21–22/C27–29 sterane vs. dia/reg C27 sterane ratios (modified after [13]) and (b) cross-plot of DBT/P vs. Pr/Ph ratios (modified after Barakat, A.O. [14]) showing the sedimentary environment of crude oils and associated source rocks from the Machang area, Dongpu Depression, Bohai Bay Basin. (DBT/P: dibenzothiophenes/phenanthrene; Pr/Ph: pristane/phytane; C21–22/C27–29 ste = (pregnane + homopregnane)/C27–C29 regular steranes; Dia/reg C27 = (βα + αβ) diacholestanes/(αα + ββ) cholestanes)).
The dibenzothiophene/phenanthrene (DBT/P) ratio effectively constrains depositional environments and source rock lithology [54,55,56,57]. All Machang area samples (Dongpu Depression, Bohai Bay Basin) exhibit characteristics of sulfate-poor lacustrine environments, with DBT/P ratios consistently < 1.0 (Figure 6b).
5.1.3. Maturity Levels
As detailed in Section 3.1, Machang-area crude oils exhibit anomalously low densities and high saturated hydrocarbon contents (Table 1), contrasting with typical low-maturity terrestrial oils. Elevated maturity diminishes odd–even carbon preference in n-alkanes, reflected by CPI and OEP values approaching 1.00 [58,59]. Mean CPI and OEP values of 1.06 and 1.01, respectively, indicate consistent mid-oil window maturity across samples. Hopane and sterane isomerization progresses systematically with increasing thermal maturity. The 22S/(22S + 22R) ratios for C31 17α,21β(H)-homohopanes and ββ/(αα + ββ) ratios for C29 steranes effectively gauge thermal maturity [43,60,61]. All samples plot within the mature field (Figure 7a). With increasing maturity, thermally stable isomers accumulate preferentially, enabling alkyl-naphthalene distributions to represent thermal maturity [62,63]. α-Substituted alkyl-naphthalene exhibits greater steric hindrance than β-substituted isomers [62,63]. Consequently, α-substituted isomers display lower thermal stability. Thus, β/α alkyl-naphthalene ratios serve as robust maturity parameters [18].
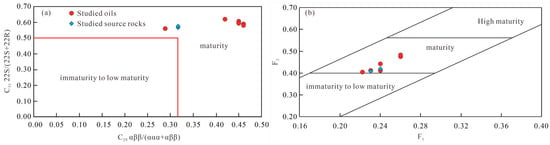
Figure 7.
(a) Cross-plot of C29 ββ/(αα + ββ) vs. C31 22S/(22S + 22R); (b) cross-plot of (a) the methyl-phenanthrene distribution fraction (MPDF) F1 vs. F2 (modified after Bao et al. [64]).
Previous studies have established alkyl-naphthalene series as molecular maturity indicators. This study employs DNR and TNR-2 parameters and their equivalent vitrinite reflectance values (Rc-1, Rc-2; formulae in Table 3) to assess sample maturity [62,63]. Rc-1 and Rc-2 values range from 0.73 to 0.94 and 0.76 to 0.95, respectively (Table 3), confirming maturity across all samples. Parameters F1 and F2, derived from methylphenanthrene isomer distributions (Table 3), provide robust maturity assessments [64]. All samples plot within the mature domain (Figure 7b).
Dibenzothiophene (DBT) compounds, sulfur-containing aromatic hydrocarbons, are ubiquitous in sedimentary systems and crude oils. Extensive research demonstrates that relative DMDBT abundances are primarily maturity-dependent [65,66]. Owing to biodegradation resistance, the 4,6-/1,4-DMDBT ratio effectively evaluates organic matter maturity [65,66]. Luo et al. developed the equivalent vitrinite reflectance parameter Rc-3 based on 4,6-/1,4-DMDBT ratios (formula in Table 3) [67]. Rc-3 values of 0.66–0.85 indicate maturation within the oil window.
Both saturated and aromatic hydrocarbon maturity parameters consistently indicate mid-oil window maturation. Analyzed compounds span low to high molecular weights. Analogous thermodynamic behaviors across compound classes validate parameter reliability.
Collectively, bulk composition distributions and biomarker signatures demonstrate genetic relationships between oils and source rock extracts, indicating shared origins from predominantly algal and aquatic macrophyte organic matter deposited in low-salinity environments at consistent mid-oil window maturity.
5.2. Availability of MTTC-Associated Parameters
The β/γ-MTTC ratio has been proposed to assess thermal maturity in sediments and crude oils [28]. However, β/γ-MTTC ratios showed no significant correlation with established maturity parameters, including C29 ββ/(αα + ββ) steranes and equivalent vitrinite reflectance values (Rc-2, Rc-3; Figure 8), demonstrating their unreliability as a maturity indicator in thermally mature systems. This observation aligns with findings from equivalent strata in the Laizhou Bay Sag and northern Bohai Bay Basin [30].
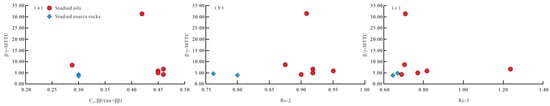
Figure 8.
Cross-plot of β/γ-MTTC with C29 ββ/(αα + ββ) (a), Rc-2 (b) and Rc-3 (c) expressing increasing maturity in crude oils and associated source rocks from the Machang area, Dongpu Depression, Bohai Bay Basin.
The parameter’s limitations likely stem from compromised thermodynamic stability differences between β- and γ-MTTCs, resulting from clay mineral abundance/composition changes associated with organic matter at moderate burial depths [36,68]. Targeted thermal simulation experiments should validate this mechanism, particularly through controlled mineralogical assemblages representing different depositional conditions incorporated into discrete experimental sets [68].
Elevated δ-MTTC abundance in hypersaline environments led Sinninghe Damsté et al. [15] to propose α/δ-MTTC ratios as paleosalinity indicators, where α/δ-MTTC > 100 indicates non-hypersaline conditions and values <2 signify hypersaline environments [16,19,20]. The observed α/δ-MTTC values (>2 to <100; Table 1) align with relatively low GI and elevated Pr/Ph ratios, consistent with formation in low-salinity environments. δ-MTTC is typically undetectable or trace in oxic, low-salinity settings due to redox sensitivity [3]. Wang et al. [3] therefore proposed α/γ-MTTC as an alternative indicator: α/γ-MTTC values < 2 indicate mesosaline conditions, values of 2–15 signify normal marine environments, and values >15 reflect freshwater to brackish systems. Measured α/γ-MTTC ratios (12.55–110.04; Table 1) suggest depositional environments spanning normal marine to freshwater/brackish conditions. Similarly, MTTCI serves as another salinity indicator [69], where values < 0.5 suggest hypersaline environments and ratios > 0.5 indicate lower-salinity conditions [3,69,70,71]. MTTCI values of 0.60–0.68 (Table 1) indicate relatively low salinity. A cross-plot of MTTCI versus Pr/Ph ratios effectively assesses paleosalinity [3,69,72], with all samples plotting within the normal marine salinity field (Figure 9a). Collectively, MTTC-related parameters (α/δ-MTTC, α/γ-MTTC, MTTCI) remain effective paleosalinity proxies for mature organic matter, consistent with independent indicators (Pr/Ph, GI, DBT/P).
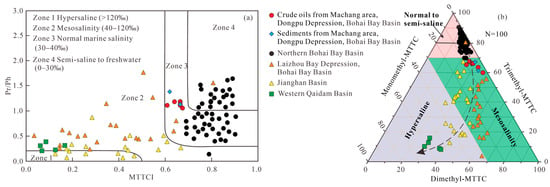
Figure 9.
(a) MTTCI values vs. Pr/Ph ratios (modified after [3]), showing the inferred paleosalinity differences for crude oils and associated sediments from the studied area and lacustrine sediments from the western Qaidam Basin [17], Jianghan Basin [28], Laizhou Bay Depression, and the northern Bohai Bay Basin (Zones 1, 2, 3, and 4 modified from Schwark et al. and Wang et al. [3,69]); (b) ternary plot of mono-, di-, and trimethyl-MTTCs (modified after [31]) for crude oils and associated sediments from the Machang area, Dongpu Depression, Bohai Bay Basin (this study) and lacustrine sediments from the western Qaidam Basin [17], Jianghan Basin [28], Laizhou Bay Depression [30], and northern Bohai Bay Basin [31]. The arrow in the figure indicates increasing paleosalinity, ranging from brackish water conditions to hypersaline environments (N = sample size).
These findings align with biomarker applications in thermally mature organic matter from (a) the Upper Cretaceous Nenjiang Formation (SK-1 South borehole, Songliao Basin) and (b) Paleogene Shahejie Formation lacustrine sediments (Northern Bohai Bay Basin) [3,31]. Thermally-driven demethylation during early diagenesis (Ro < 0.6%) establishes predictable conversion pathways from α to γ and δ-MTTC isomers, predicting progressive decreases in α/δ-MTTC, α/γ-MTTC, and MTTCI ratios with advancing maturity. However, no significant negative correlations exist with established maturity proxies (e.g., C29 αββ/(ααα + αββ) steranes; Supplemental Material), indicating disrupted conversion pathways in thermally mature systems. Discrepancies between low-maturity Qianjiang Formation (Tertiary, Jianghan Basin) and mature Shahejie Formation samples arise from (a) distinct depositional settings (variable clay mineralogy), and (b) maturity-dependent thermal effects on MTTCs [68].
Jiang et al. [6] developed a ternary diagram using relative abundances of (a) trimethyl-MTTC (α-MTTC), (b) dimethyl-MTTCs (β-, γ-, ζ-MTTC), and (c) monomethyl-MTTC (δ-MTTC) to classify paleosalinity environments. All samples plot within the normal–mesosaline field (Figure 9b), contradicting low-salinity diagnoses from independent proxies. This discrepancy arises from the selective loss or transformation of δ-MTTC in mature settings and likely reflects limited salinity resolution in the ternary method. Consequently, integrated multi-proxy approaches provide superior paleosalinity constraints.
5.3. Application in Oil–Oil and Oil–Source Rock Correlation
MTTCs have also been reported in mature organic matter from the Nenjiang Formation (Upper Cretaceous) from the SK-l southern borehole in Songliao Basin, China [3]; the Paleogene Shahejie Formation in the northern Bohai Bay Basin, China [31]; the Neogene Čučale unit in the northwest part of the Toplica Basin, Serbia [32]; and the Neogene Guantao and Minghuazhen Formations in the Miaoxi Depression, eastern Bohai Bay Basin, China [73,74].
In this study, similar distribution patterns of MTTCs associated with paleosalinity indicators indicate that all the studied oils are genetically related to the source rocks (Table 1, Figure 9), in agreement with diagnoses made using the other source-related proxies. These associated indicators, therefore, may offer a robust method for oil family classification and oil–source correlation in the middle oil window, although there is a migration effect on these compounds in crude oils. Among these methods, the cross-plot of the MTTC index (MTTCI) versus pristane/phytane (Pr/Ph) ratios, combined with a ternary diagram illustrating the relative abundances of differently alkylated MTTC compounds, provides an effective and visually intuitive approach for oil–oil and oil–source rock correlations (Figure 9).
6. Conclusions
All studied crude oils exhibit a clear genetic affinity for their source rocks, evidenced by shared organic precursors (primarily algal and aquatic macrophyte-derived), consistent deposition in low-salinity environments, and uniform thermal maturity within the mid-oil window, while β/γ-MTTC ratios proved unreliable for maturity assessment in thermally mature systems.
This study confirms that MTTC-derived paleosalinity parameters (α/δ, α/γ, MTTCI, and MTTCI/Pr/Ph cross-plots) reliably indicate low-salinity depositional environments across all samples, with oil–oil and oil–source correlations strongly supported by independent biomarker data. Notably, MTTCI/Pr/Ph cross-plots and alkylation-degree ternary diagrams emerge as the most effective tools for robust oil–oil and oil–source rock correlation, providing a more precise and geochemically consistent framework than traditional maturity indicators in thermally mature systems. These findings underscore the utility of MTTC paleosalinity parameters as diagnostic tools for the genetic classification and correlation of crude oils.
Author Contributions
Y.T.: Writing—original draft, Conceptualization, Supervision, Project administration. M.H.: Writing—original draft, Software, Formal analysis, Data curation. X.Y.: Writing—review & editing, Methodology. K.L.: Software, Validation. Y.M.: Writing—review and editing. Y.H.: Writing—review and editing. T.X.: Resources, Data curation. C.Z.: Resources, Data curation. L.C.: Resources. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
The work was funded by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (No. 42072174).
Data Availability Statement
The original contributions presented in this study are included in the article. Further inquiries can be directed to the corresponding author.
Conflicts of Interest
Tianwu Xu and Chengfu Zhang was employed by Exploration and Development Research Institute, Zhongyuan Oilfield Company, SINOPEC. The remaining authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
References
- Sinninghe Damsté, J.S.; Kock-Van Dalen, A.C.; De Leeuw, J.W.; Schenck, P.A.; Guoying, S.; Brassell, S.C. The identification of mono-, di- and trimethyl 2-methyl-2-(4,8,12-trimethyltridecyl)chromans and their occurrence in the geosphere. Geochim. Cosmochim. Acta 1987, 51, 2393–2400. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, M.W.; Larter, S.R.; Taylor, P.; Jones, D.M.; Bowler, B.; Bjorøy, M. Biomarkers or not biomarkers? A new hypothesis for the origin of pristane involving derivation from methyltrimethyltridecylchromans (MTTCs) formed during diagenesis from chlorophyll and alkylphenols. Org. Geochem. 1995, 23, 159–167. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, L.; Song, Z.G.; Yin, Q.; George, S.C. Paleosalinity significance of occurrence and distribution of methyltrimethyltridecyl chromans in the Upper Cretaceous Nenjiang Formation, Songliao Basin, China. Org. Geochem. 2011, 42, 1411–1419. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luo, G.M.; Yang, H.; Algeo, T.J.; Hallmann, C.; Xie, S.C. Lipid biomarkers for the reconstruction of deep-time environmental conditions. Earth Sci. Rev. 2019, 189, 99–124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, X.Y.; Tang, Y.J.; Yang, Y.; Yang, H.F.; Wang, F.L.; Lü, X.X. Impact of biodegradation on methyltrimethyltridecylchromans (MTTCs) in crude oils from the Bohai Bay Basin, China. Org. Geochem. 2023, 184, 140669. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, K.X.; Lin, C.M.; Cai, C.F.; Zhang, X.; Huang, S.Y.; Fan, Z.C. Current Status and Challenges of Methyltrimethyltridecylchromans Research in Source Rocks and Crude Oils. ACS Omega 2019, 4, 9835–9842. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dutta, S.; Bhattacharya, S.; Raju, S.V. Biomarker signatures from Neoproterozoic–Early Cambrian oil, western India. Org. Geochem. 2013, 56, 68–80. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tulipani, S.; Grice, K.; Greenwood, P.; Schwark, L. A pyrolysis and stable isotopic approach to investigate the origin of methyltrimethyltridecylchromans (MTTCs). Org. Geochem. 2013, 61, 1–5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tulipani, S.; Grice, K.; Greenwood, P.F.; Haines, P.W.; Sauer, P.E.; Schimmelmann, A.; Summons, R.E.; Foster, C.B.; Böttcher, M.E.; Playton, T.; et al. Changes of palaeoenvironmental conditions recorded in Late Devonian reef systems from the Canning Basin, Western Australia: A biomarker and stable isotope approach. Gondwana Res. 2015, 28, 1500–1515. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tulipani, S.; Grice, K.; Greenwood, P.F.; Schwark, L.; Böttcher, M.E.; Summons, R.E.; Foster, C.B. Molecular proxies as indicators of freshwater incursion-driven salinity stratification. Chem. Geol. 2015, 409, 61–68. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sheng, G.Y.; Fu, J.M.; Jiang, J.G.; Liang, D.G.; Brassell, S.C.; Eglinton, G. The discovery and significance of MTTCs in crude oil and source rocks. Sci. China 1987, 4, 423–428. [Google Scholar]
- Connock, G.T.; Liu, X.-L. Tocopherols and associated derivatives track the phytoplanktonic response to evolving pelagic redox conditions spanning Oceanic Anoxic Event 2. Geobiology 2023, 21, 743–757. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, H.; Hou, L.H.; Chen, T.S.; Peng, P.A.; Sheng, G.Y. Stable Carbon Isotopic Compositions of Methylated-MTTC in Crude Oils from Saline Lacustrine Depositional Environment: Source Implications. Acta Geol. Sin. Engl. 2007, 6, 1041–1048. [Google Scholar]
- Barakat, A.O.; Rullkötter, J. A Comparative Study of Molecular Paleosalinity Indicators: Chromans, Tocopherols and C20 Isoprenoid Thiophenes in Miocene Lake Sediments (Nördlinger Ries, Southern Germany). Aquat. Geochem. 1997, 3, 169–190. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sinninghe Damsté, J.S.; Rijpstra, W.I.C.; De Leeuw, J.W.; Schenck, P.A. The occurrence and identification of series of organic sulphur compounds in oils and sediment extracts: II. Their presence in samples from hypersaline and non-hypersaline palaeoenvironments and possible application as source, palaeoenvironmental and maturity indicators. Geochim. Cosmochim. Acta 1989, 53, 1323–1341. [Google Scholar]
- Sinninghe Damsté, J.S.; Keely, B.J.; Betts, S.E.; Baas, M.; Maxwell, J.R.; de Leeuw, J.W. Variations in abundances and distributions of isoprenoid chromans and long-chain alkylbenzenes in sediments of the Mulhouse Basin: A molecular sedimentary record of palaeosalinity. Org. Geochem. 1993, 20, 1201–1215. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.D.; Jiang, A.Z.; Sun, Y.G.; Xie, L.J.; Chai, P.X. Stable carbon isotope compositions of isoprenoid chromans in Cenozoic saline lacustrine source rocks from the Western Qaidam Basin, NW China: Source implications. Chin. Sci. Bull. 2012, 57, 657–667. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- van Aarssen, B.G.K.; Bastow, T.P.; Alexander, R.; Kagi, R.I. Distributions of methylated naphthalenes in crude oils: Indicators of maturity, biodegradation and mixing. Org. Geochem. 1999, 30, 1213–1227. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grice, K.; Schouten, S.; Nissenbaum, A.; Charrach, J.; Sinninghe Damsté, J.S. A remarkable paradox: Sulfurised freshwater algal (Botryococcus braunii) lipids in an ancient hypersaline euxinic ecosystem. Org. Geochem. 1998, 28, 195–216. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grice, K.; Schouten, S.; Peters, K.E.; Sinninghe Damsté, J.S. Molecular isotopic characterisation of hydrocarbon biomarkers in Palaeocene–Eocene evaporitic, lacustrine source rocks from the Jianghan Basin, China. Org. Geochem. 1998, 29, 1745–1764. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sinninghe Damsté, J.S.; Kenig, F.; Koopmans, M.P.; Koster, J.; Schouten, S.; Hayes, J.M.; de Leeuw, J.W. Evidence for gammacerane as an indicator of water column stratification. Geochim. Cosmochim. Acta 1995, 59, 1895–1900. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martins, L.L.; Schulz, H.M.; Severiano Ribeiro, H.J.P.; Nascimento, C.A.; Souza, E.S.; da Cruz, G.F. Organic geochemical signals of controlling freshwater dynamics on salinity stratification in organic-rich shales in the Lower Permian Irati Formation (Paraná Basin, Brazil). Org. Geochem. 2020, 140, 103958. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lan, X.D.; Liu, H. The geochemical characteristics of the Paleogene lacustrine source rock and Cenozoic oil in the eastern Huanghekou Sag, Bohai Bay Basin, China: An oil–source rock correlation. J. Pet. Sci. Eng. 2022, 214, 110434. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bechtel, A.; Jia, J.; Strobl, S.A.I.; Sachsenhofer, R.F.; Liu, Z.J.; Gratzer, R.; Püttmann, W. Palaeoenvironmental conditions during deposition of the Upper Cretaceous oil shale sequences in the Songliao Basin (NE China): Implications from geochemical analysis. Org. Geochem. 2012, 46, 76–95. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, Y.M.; Weng, H.X.; Su, A.G.; Liang, D.G.; Peng, D.H. Geochemical characteristics of Tertiary saline lacustrine oils in the Western Qaidam Basin, northwest China. Appl. Geochem. 2005, 20, 1875–1889. [Google Scholar]
- Bao, J.P.; Wang, T.G.; Gan, Y.N. Dehydroxytocopherol and its geochemical significances. J. Jianghan Pet. Inst. 1989, 11, 11–18. [Google Scholar]
- Jirman, P.; Geršlová, E.; Bubík, M.; Sachsenhofer, R.F.; Bechtel, A.; Więcław, D. Depositional environment and hydrocarbon potential of the Oligocene Menilite Formation in the Western Carpathians: A case study from the Loučka section (Czech Republic). Mar. Pet. Geol. 2019, 107, 334–350. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bao, J.P.; Zhu, C.S.; Ma, A.L. The relationship between methylated chromans and maturity of organic matter in the source rocks from Jianghan hypersaline basin. Sci. China Ser. D 2009, 52, 34–41. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, K.; Lin, C.; Li, H.; Chen, Q. Effect of paleosalinity and maturity on the distribution of dimethyl-MTTCs. Petrol. Sci. Technol. 2018, 36, 2037–2042. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, K.X.; Lin, C.M.; Zhang, X.; Cai, C.F.; Xiao, F.; He, W.X.; Peng, L. Variations in abundance and distribution of methyltrimethyltridecylchromans (MTTCs) in sediments from saline lacustrine settings in Cenozoic lacustrine basins, China. Org. Geochem. 2018, 121, 58–67. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, K.X.; Lin, C.M.; Peng, L.; Zhang, X.; Cai, C.F. Methyltrimethyltridecylchromans (MTTCs) in lacustrine sediments in the northern Bohai Bay Basin, China. Org. Geochem. 2019, 133, 1–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Burazer, N.; Šajnović, A.; Vasić, N.; Kašanin-Grubin, M.; Životić, D.; Mendonça Filho, J.G.; Vulić, P.; Jovančićević, B. Influence of paleoenvironmental conditions on distribution and relative abundance of saturated and aromatic hydrocarbons in sediments from the NW part of the Toplica basin, Serbia. Mar. Pet. Geol. 2020, 115, 104252. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Koopmans, M.P.; Rijpstra, W.I.C.; de Leeuw, J.W.; Lewan, M.D.; Damsté, J.S.S. Artificial maturation of an immature sulfur- and organic matter-rich limestone from the Ghareb Formation, Jordan. Org. Geochem. 1998, 28, 503–521. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zuo, Y.H.; Ye, B.; Wu, W.T.; Zhang, Y.X.; Ma, W.X.; Tang, S.L.; Zhou, Y.S. Present temperature field and Cenozoic thermal history in the Dongpu depression, Bohai Bay Basin, North China. Mar. Pet. Geol. 2017, 88, 696–711. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, D.L.; Tang, Y.J.; Li, H.B.; Xu, T.W.; Wang, T. Methyltrimethyltridecylchromans in Mature Oils from Saline Lacustrine Settings in the Dongpu Depression, Bohai Bay Basin, East China. ACS Omega 2021, 6, 17400–17412. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tang, Y.J.; Jing, Y.R.; Xu, T.W.; Zhang, C.F.; Lü, L.S.; Yang, X.Y.; Pei, B.B. Detection and potential geochemical significance of methyltrimethyltridecylchromans in mature crude oils. J. Nat. Gas Geosci. 2023, 8, 127–141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, M.; Chen, H.H.; Huang, C.J.; Kemp, D.B.; Xu, T.W.; Zhang, H.G.; Li, M.S. Astronomical forcing and sedimentary noise modeling of lake-level changes in the Paleogene Dongpu Depression of North China. Earth Planet. Sci. Lett. 2020, 535, 116116. [Google Scholar]
- Gao, G.H.; Cao, J.; Xu, T.W.; Zhang, H.G.; Zhang, Y.X.; Hu, K. Nuclear magnetic resonance spectroscopy of crude oil as proxies for oil source and thermal maturity based on 1H and 13C spectra. Fuel 2020, 271, 117622. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, X.Y.; Chen, H.H.; Mu, X.S.; Zhang, H.A.; Fan, J.J.; Huang, Y.H.; Zhao, K.; Mansour, A.; Gentzis, T.; Ostadhassan, M. Organic matter preservation conditions in the third member of the Shahejie Formation (Dongpu Depression, China). Int. J. Coal Geol. 2023, 277, 104334. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, J.D.; Xu, T.W.; Tang, Y.J.; Lu, K. Geochemical characteristics and source correlation of crude oil in Machang area, Dongpu Depression. Fault Block Oil Gas. Field 2019, 26, 426–428+479. [Google Scholar]
- Wu, J.Q.; Chu, D.L.; Luo, G.; Wignall, P.B.; Algeo, T.J.; Xie, S.C. Stepwise deforestation during the Permian-Triassic boundary crisis linked to rising temperatures. Earth Planet. Sci. Lett. 2023, 620, 118350. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cranwell, P.A. Organic geochemistry of Cam Loch (Sutherland) sediments. Chem. Geol. 1977, 20, 205–221. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tong, X.N.; Hu, J.F.; Xi, D.P.; Zhu, M.B.; Song, J.Z.; Peng, P.A. Depositional environment of the Late Santonian lacustrine source rocks in the Songliao Basin (NE China): Implications from organic geochemical analyses. Org. Geochem. 2018, 124, 215–227. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ficken, K.J.; Li, B.; Swain, D.L.; Eglinton, G. An n-alkane proxy for the sedimentary input of submerged/floating freshwater aquatic macrophytes. Org. Geochem. 2000, 31, 745–749. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eglinton, G.; Hamilton, R.J. Leaf epicuticular waxes. Science 1967, 156, 1322–1335. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shanmugam, G.N. Significance of Coniferous Rain Forests and Related Organic Matter in Generating Commercial Quantities of Oil, Gippsland Basin, Australia. AAPG (Am. Assoc. Pet. Geol.) Bull. 1985, 69, 1241–1254. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiao, H.; Li, M.J.; Yang, Z.; Zhu, Z.L. Distribution patterns and geochemical implications of Ci-C23 tricyclic terpanes insource rocks and crude oils occurring in various depositional environments. Geochemica 2019, 48, 161–170. [Google Scholar]
- Huang, W.Y.; Meinschein, W.G. Sterols as ecological indicators. Geochim. Cosmochim. Acta 1979, 43, 739–745. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Diasty, W.S.E.; Moldowan, J.M.; Peters, K.E.; Hammad, M.M.; Essa, G.I. Organic geochemistry of possible Middle Miocene–Pliocene source rocks in the west and northwest Nile Delta, Egypt. J. Pet. Sci. Eng. 2021, 208, 109357. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peters, K.E.; Walters, C.C.; Moldowan, J.M. The Biomarker Guide 2. In Biomarkers and Isotopes in Petroleum Exploration and Earth History; Cambridge University Press: New York, NY, USA, 2005. [Google Scholar]
- ten Haven, H.L.; de Leeuw, J.W.; Rullkötter, J.; Damsté, J.S.S. Restricted utility of the pristane/phytane ratio as a palaeoenvironmental indicator. Nature 1987, 330, 641–643. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rowland, S.J. Production of acyclic isoprenoid hydrocarbons by laboratory maturation of methanogenic bacteria. Org. Geochem. 1990, 15, 9–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, G.L.; Chang, X.C.; Wang, T.G.; Simoneit, B.R.T. Pregnanes as molecular indicators for depositional environments of sediments and petroleum source rocks. Org. Geochem. 2015, 78, 110–120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hughes, W.B.; Holba, A.G.; Dzou, L.I.P. The ratios of dibenzothiophene to phenanthrene and pristane to phytane as indicators of depositional environment and lithology of petroleum source rocks. Geochim. Cosmochim. Acta 1995, 59, 3581–3598. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cui, Y.; Kump, L.R.; Ridgwell, A.J.; Charles, A.J.; Junium, C.K.; Diefendorf, A.F.; Freeman, K.H.; Urban, N.M.; Harding, I.C. Slow release of fossil carbon during the Palaeocene–Eocene Thermal Maximum. Nat. Geosci. 2011, 4, 481–485. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Witkowski, C.R.; Weijers, J.W.H.; Blais, B.; Schouten, S.; Sinninghe Damsté, J.S. Molecular fossils from phytoplankton reveal secular Pco2 trend over the Phanerozoic. Sci. Adv. 2018, 4, 4556. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, H.Y.; Liu, Q.Y.; Jin, Z.J.; Zhu, D.Y.; Meng, Q.Q.; Wu, X.Q.; Li, P.P.; Zhu, B.Q. Organic compounds in geological hydrothermal systems: A critical review of molecular transformation and distribution. Earth Sci. Rev. 2024, 252, 104757. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bray, E.E.; Evans, E.D. Distribution of n-paraffins as a clue to recognition of source beds. Geochim. Cosmochim. Acta 1961, 22, 2–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Scalan, E.S.; Smith, J.E. An improved measure of the odd-even predominance in the normal alkanes of sediment extracts and petroleum. Geochim. Cosmochim. Acta 1970, 34, 611–620. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ensminger, A.; Albrecht, P.; Ourisson, G.; Tissot, B. Evolution of polycyclic alkanes under the effect of burial (Early Toarcian shales, Paris Basin). Adv. Geochem. 1977, 1975, 45–52. [Google Scholar]
- Seifert, W.K.; Moldowan, J.M. Use of biological markers in petroleum exploration. Methods Geochem. Geophys. 1986, 24, 261–290. [Google Scholar]
- Radke, M.; Welte, D.H.; Willsch, H. Geochemical study on a well in the Western Canada Basin: Relation of the aromatic distribution pattern to maturity of organic matter. Geochim. Cosmochim. Acta 1982, 46, 1–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Radke, M.; Rullkötter, J.; Vriend, S.P. Distribution of naphthalenes in crude oils from the Java Sea: Source and maturation effects. Geochim. Cosmochim. Acta 1994, 58, 3675–3689. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bao, J.P.; Wang, T.G.; Zhou, Y.Q.; Yu, F.X.; Wang, J.Y.; Zhou, Q.L.; Chen, F.J. The Relationship between Methyl Phenanthrene Ratiosand the Evolution of Organic Matter. J. Jianghan Pet. Inst. 1992, 14, 8–13+19. [Google Scholar]
- Hughes, W.B. Use of thiophenic organosulfur compounds in characterizing crude oils derived from carbonate versus siliciclastic sources. AAPG Bull. 1984, 18, 181–196. [Google Scholar]
- Li, M.J.; Simoneit, B.R.T.; Zhong, N.N.; Fang, R.H. The distribution and origin of dimethyldibenzothiophenes in sediment extracts from the Liaohe Basin, East China. Org. Geochem. 2013, 65, 63–73. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luo, J.; Cheng, K.M.; Fu, L.X.; Hu, Y.J.; Jiang, N.H. Alkylated dibenzothiophene index-a new method to assess thermal, maturity of source rocks. Acta Pet. Sin. 2001, 22, 27–31. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, X.X.; Cai, J.G.; Bao, Y.J. Catalysis of Clay Mineral to Organic Matter in Hydrocarbon Genesis. Mar. Pet. Geol. 2006, 11, 27–38. [Google Scholar]
- Schwark, L.; Vliex, M.; Schaeffer, P. Geochemical characterization of Malm Zeta laminated carbonates from the Franconian Alb, SW-Germany (II). Org. Geochem. 1998, 29, 1921–1952. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sachsenhofer, R.F.; Hentschke, J.; Bechtel, A.; Coric, S.; Gratzer, R.; Gross, D.; Horsfield, B.; Rachetti, A.; Soliman, A. Hydrocarbon potential and depositional environments of Oligo-Miocene rocks in the Eastern Carpathians (Vrancea Nappe, Romania). Mar. Pet. Geol. 2015, 34, 611–620. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, H.; Shen, C.C.; Zhang, Z.R.; Liu, M.; Sheng, G.Y.; Peng, P.a.; Hsu, C.S. 2,3,6-/2,3,4-Aryl Isoprenoids in Paleocene Crude Oils from Chinese Jianghan Basin: Constrained by Water Column Stratification. Energy Fuels 2015, 29, 4690–4700. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, Z.B.; Grohmann, S.; Zieger, L.; Dai, W.; Littke, R. Evolution of organic matter quantity and quality in a warm, hypersaline, alkaline lake: The example of the Miocene Nördlinger Ries impact crater, Germany. Front. Earth Sci. 2022, 10, 989478. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, X.Y.; Lv, X.X.; Huang, Y.H.; He, Y.L.; Yang, R.; Wang, R.Y.; Peng, P. The depositional environment of the lacustrine source rocks in the Eocene middle number of the Liushagang Formation of the Weixinan Sag, Beibuwan Basin, China: Implications from organic geochemical analyses. Minerals 2023, 13, 575. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, X.Y.; Tang, Y.J.; Sun, P.; Hu, Y.M.; Yang, H.F.; Wang, F.L. Aryl isoprenoids in severe biodegradation oils from the Miaoxi Depression, Bohai Bay Basin. Org. Geochem. 2025, 207, 105014. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).