Probabilistic Prediction of Spudcan Bearing Capacity in Stiff-over-Soft Clay Based on Bayes’ Theorem
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Uncertainties of Empirical Prediction
3. Bayesian Prediction of Peak Resistance
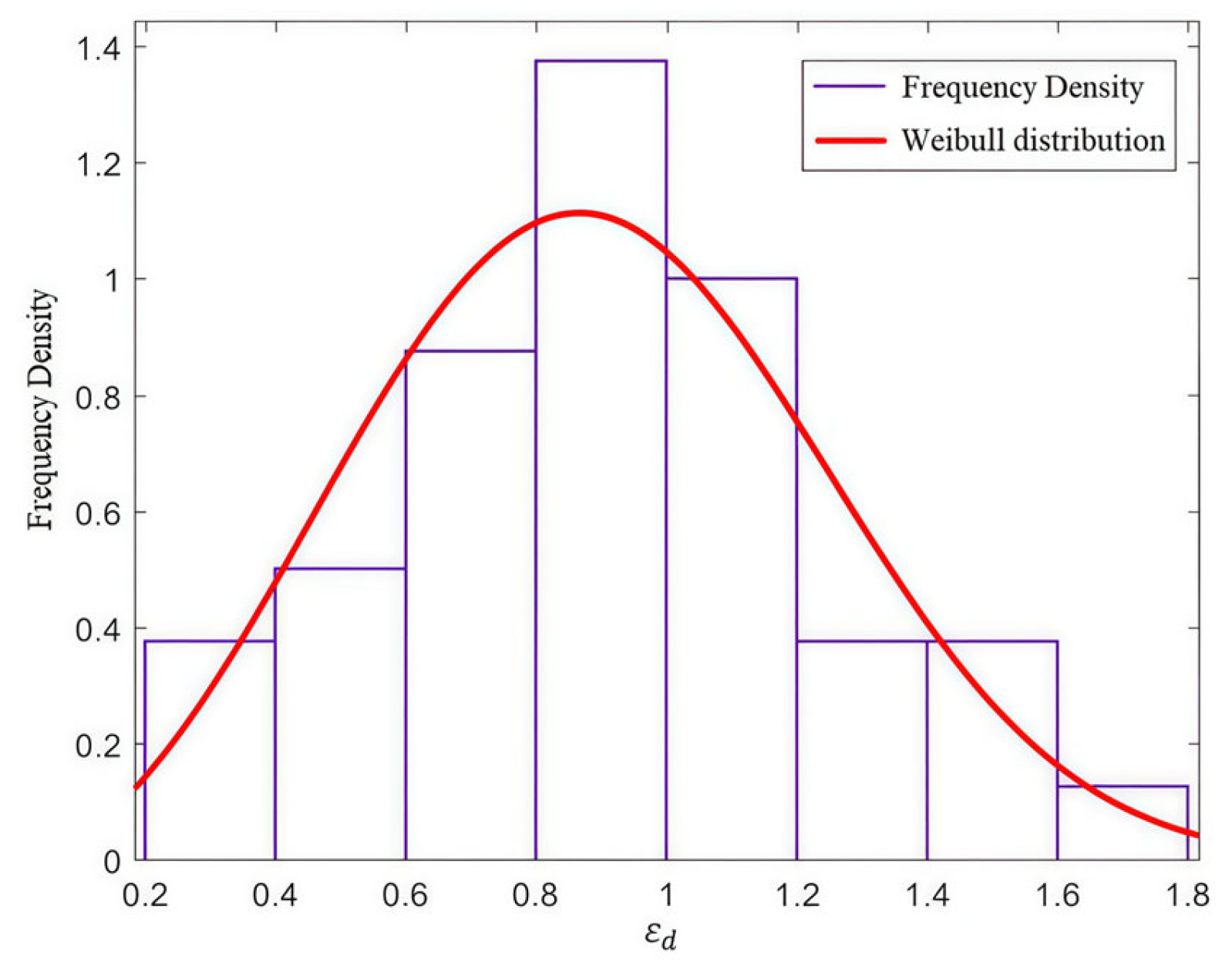
3.1. Prior Probability
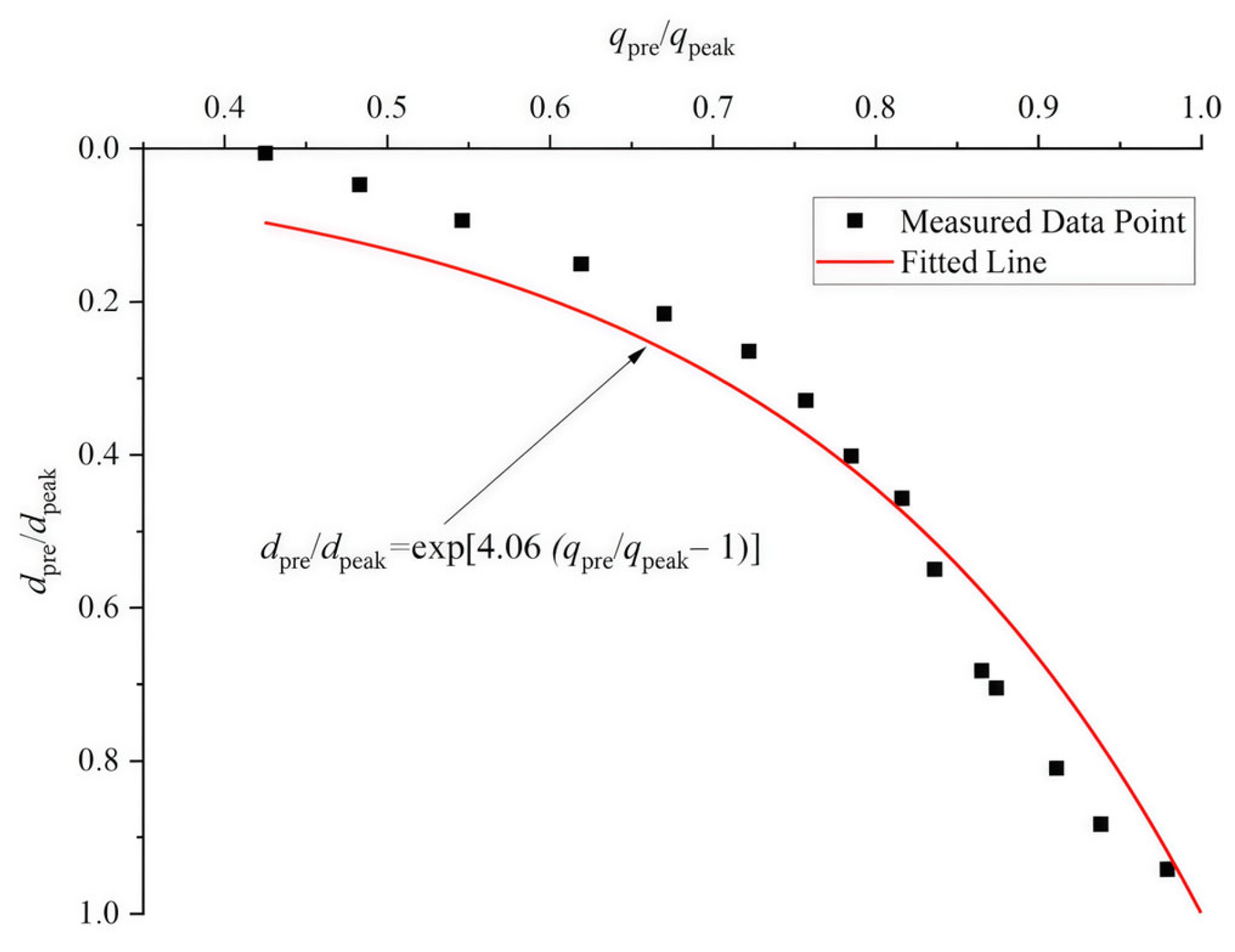
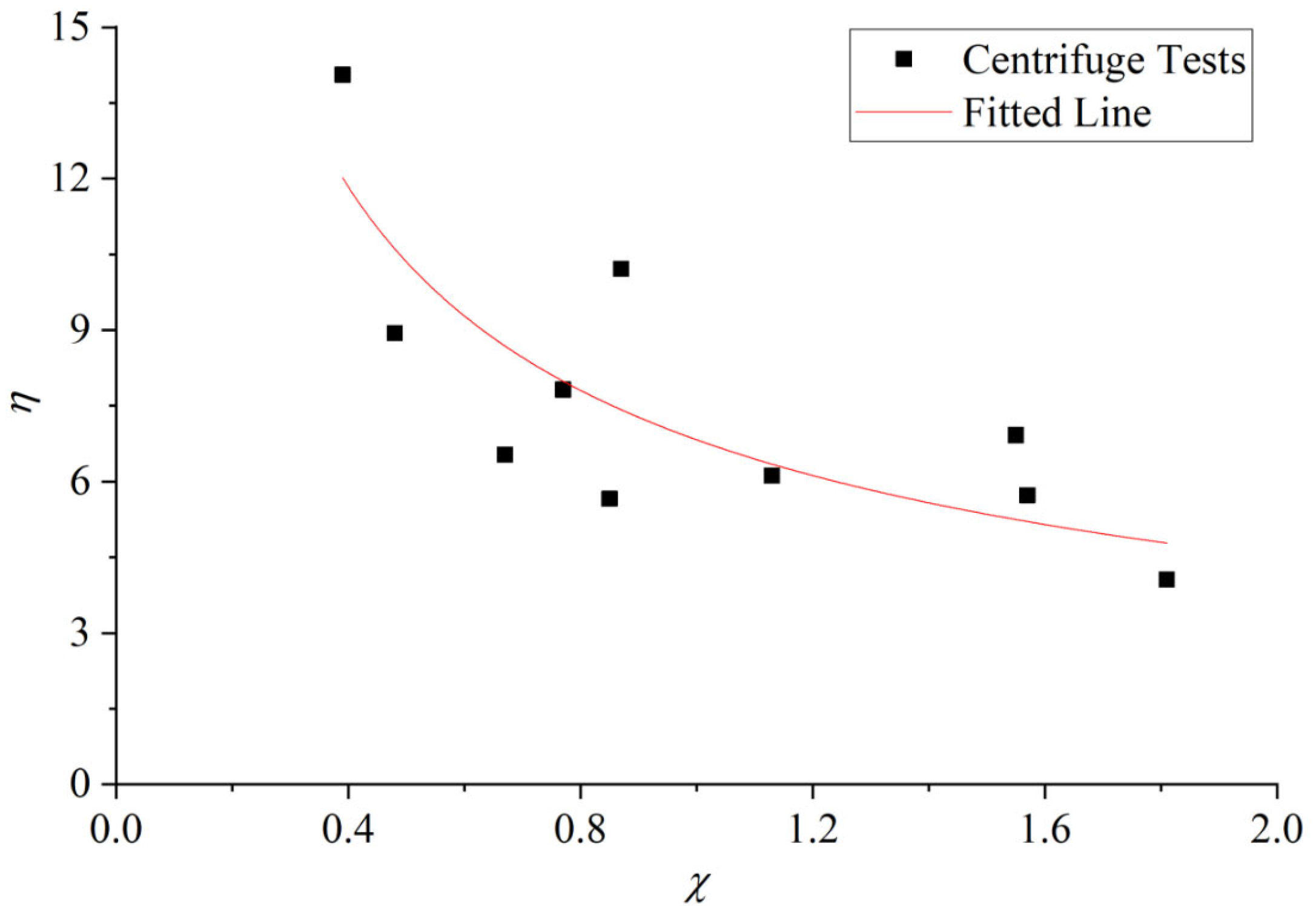
3.2. Likelihood Probability
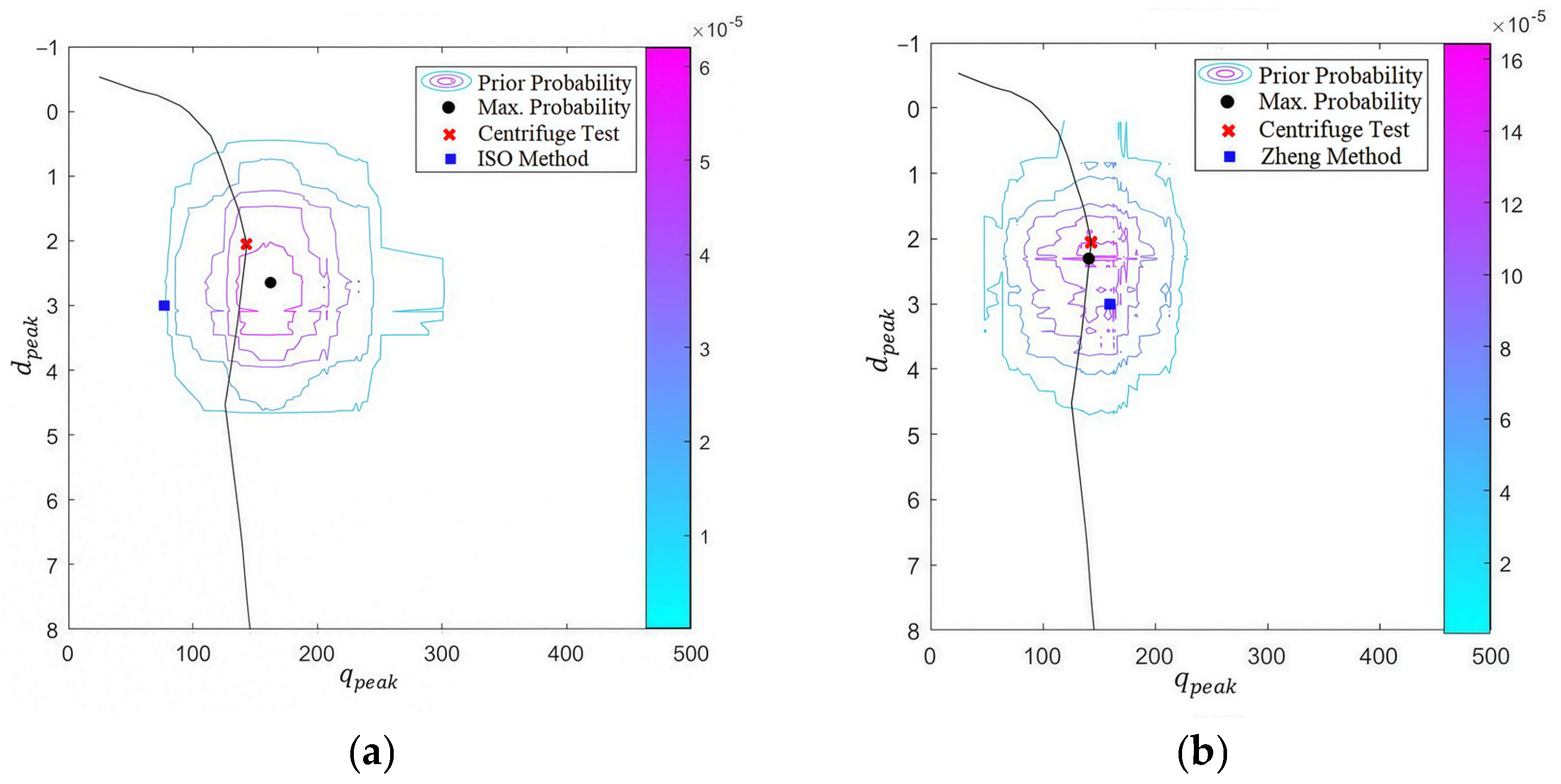
3.3. Posterior Probability
4. Results and Discussion
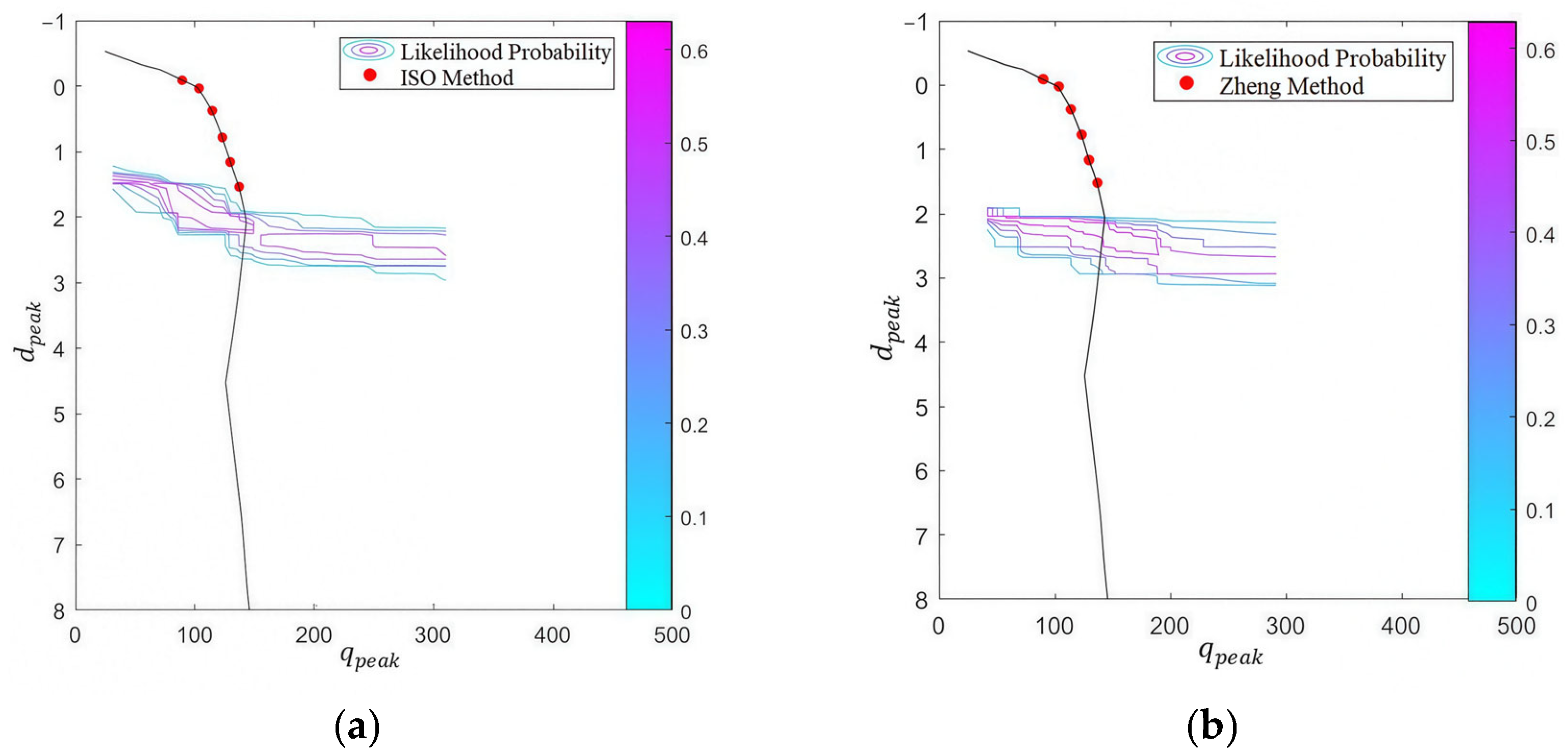
4.1. Effect of the Empirical Formula Choice
4.1.1. Prediction from Empirical Formulas
4.1.2. Prior Probability Analysis
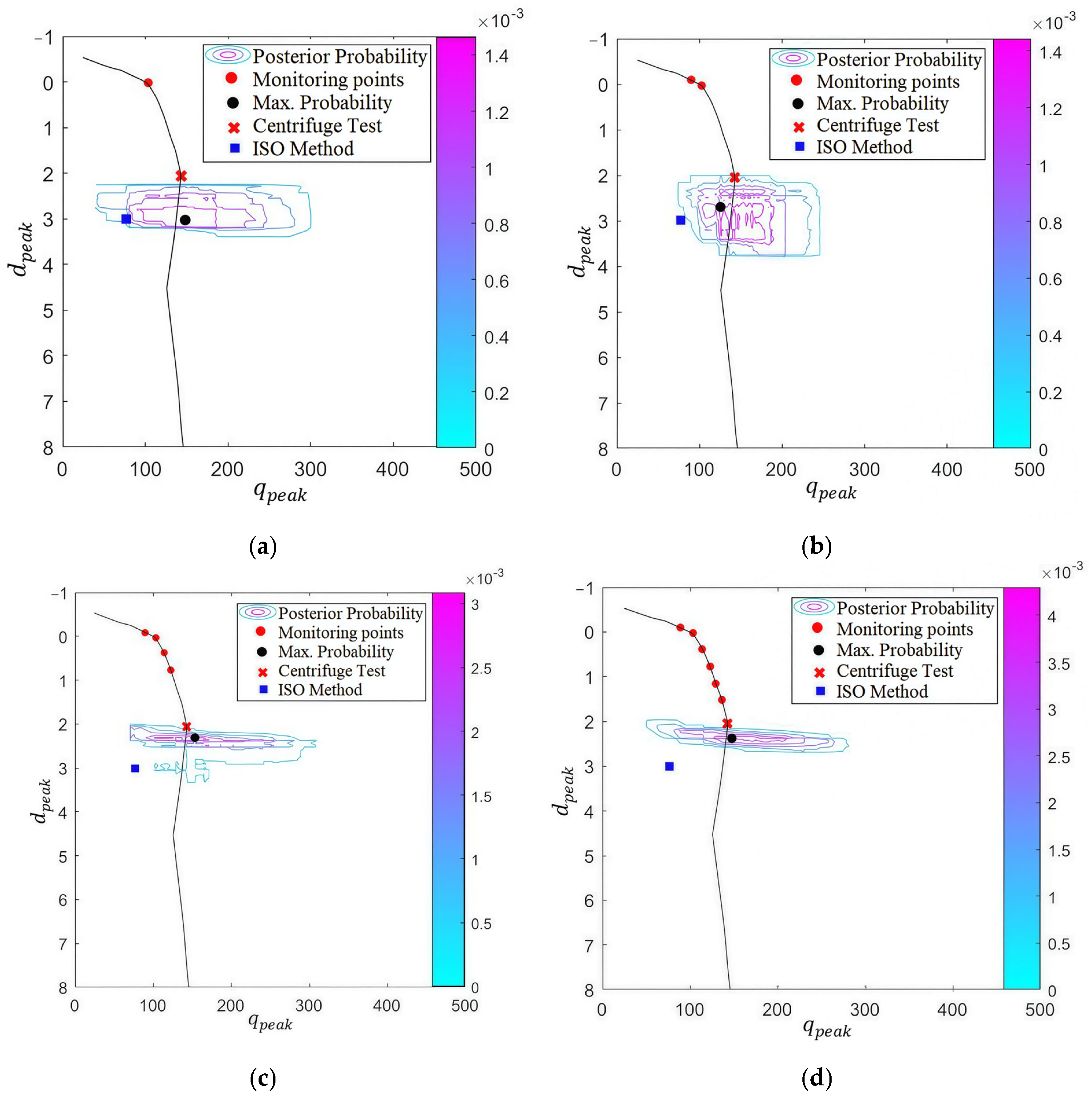
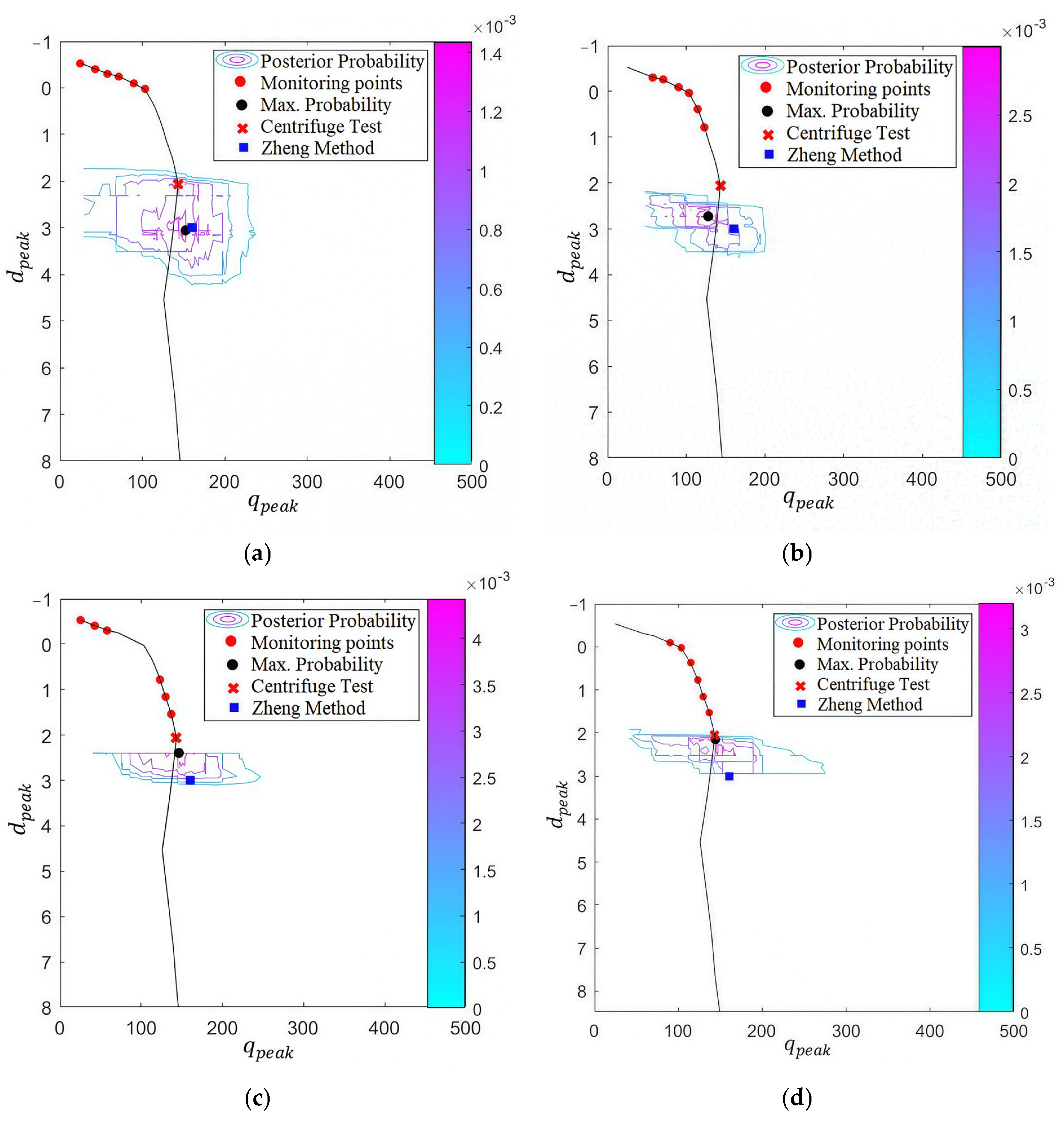
4.1.3. Likelihood and Posterior Probability Analysis
4.2. Effect of the Monitored Point Number
4.3. Effect of the Monitored Point Position
5. Conclusions
- (1)
- The Bayesian approach significantly improves prediction accuracy compared with deterministic methods. The integration of monitoring data progressively narrows the uncertainty bounds, enabling the most probable failure zone to converge toward the actual punch-through point. This dynamic updating mechanism mitigates the limitations of static empirical models, which lack adaptability to site-specific conditions.
- (2)
- Although the selection of empirical formulas directly influences the prior distributions, it has a limited influence on the posterior probability. This is because the formulas all take into account the undrained shear strength ratio between the two layers and the thickness of the stiff layer, which are the two most sensitive parameters to the prediction of the peak resistance.
- (3)
- Increasing the number of monitored penetration points and the proximity of monitored points to the peak resistance point enhances the probabilistic prediction accuracy, whereas distant points provide limited diagnostic value.
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Hu, P.; Xiao, Z.; Leo, C. Advances in the prediction of spudcan punch-through in double-layered soils. Mar. Struct. 2021, 79, 103038. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- ISO 19905-1:2016; Iso Petroleum and Natural Gas Industries—Site-Specific Assessment of Mobile Offshore Units–Part 1: Jack-Ups. ISO: Geneva, Switzerland, 2016.
- SNAMET. T&R Bulletin, 5-05 A: Guidelines for Site Specific Assessment of Mobile Jack-Up Units. 2008. Available online: https://sname.org/node/1810 (accessed on 15 May 2025).
- Van Dijk, B.; Yetginer, A.G. Findings of the Issmge Jack-Up Leg Penetration Prediction Event. In Proceedings of the 3rd International Symposium on Frontiers in Offshore Geotechnics, Oslo, Norway, 10–12 June 2015; pp. 1267–1274. [Google Scholar]
- Rohani, M.J.; Sha’Ari, F.A.; Rahman, A.A.; Wan Ismail, W.M.; Chan, N.; Tho, K.K. Improving Jack-Up Rig Spudcan Penetration Predictions in Malaysian Waters. In Proceedings of the Offshore Technology Conference Asia, Kuala Lumpur, Malaysia, 22–25 March 2016; pp. 2183–2190. [Google Scholar]
- Hossain, M.S.; Randolph, M.F. Deep-penetrating spudcan foundations on layered clays: Centrifuge tests. Géotechnique 2010, 60, 157–170. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hossain, M.S.; Randolph, M.F. Deep-penetrating spudcan foundations on layered clays: Numerical analysis. Géotechnique 2010, 60, 171–184. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tjahyono, S. Experimental and Numerical Modelling of Spudcan Penetration in Stiff Clay Overlying Soft Clay. Ph.D. Thesis, University of Western Australia, Perth, Australia, 2011. [Google Scholar]
- Zheng, J.; Hossain, M.S.; Wang, D. Prediction of spudcan penetration resistance profile in stiff-over-soft clays. Can. Geotech. J. 2016, 53, 1978–1990. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zheng, J.; Hossain, M.S.; Wang, D. Estimating spudcan penetration resistance in stiff-soft-stiff clay. J. Geotech. Geoenviron. 2018, 144, 04018001. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, X.; Meng, X.; Zhang, Q. A new method for predicting the penetration curve of spudcan on stiff-over-soft clay. Ocean Eng. 2024, 310, 118649. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, X.; Zhang, A.; Zhang, Q.; Li, D. Predicting the ultimate bearing capacity of spudcan in stiff-over-soft clay based on a failure model varying with soil parameter. Appl. Ocean Res. 2024, 148, 104026. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Uzielli, M.; Cassidy, M.J.; Hossain, M.S. Bayesian prediction of punch-through probability for spudcans in stiff-over-soft clay. In Geotechnical Safety and Reliability; American Society of Civil Engineers: Reston, VA, USA, 2017; pp. 247–265. [Google Scholar]
- Li, J.; Hu, P.; Uzielli, M.; Cassidy, M.J. Bayesian prediction of peak resistance of a spudcan penetrating sand-over-clay. Géotechnique 2018, 68, 905–917. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Hu, P.; Li, J. Probabilistic prediction of the spudcan extraction from sand-over-clay based on monitored data. Ocean Eng. 2023, 281, 114787. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, F. A Novel Approach for Probabilistic Prediction of Offshore Jack-Up Installation. Ph.D. Thesis, The University of Western Australia, Perth, Australia, 2020. [Google Scholar]
- Yang, F.; Li, J.; Cassidy, M.J. Probabilistic site characterisation using monitored spudcan installation data. Géotechnique 2023, 73, 353–373. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, F.; Li, J.; Cassidy, M.J. Probabilistic punch-through distance for a spudcan penetrating sand-over-clay. Geo-Risk 2017, 2017, 569–577. [Google Scholar]
- Jiang, J.; Wang, D.; Zhang, S. Improved prediction of spudcan penetration resistance by an observation-optimized model. J. Geotech. Geoenviron. 2020, 146, 06020014. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zheng, J.; Zhang, S.; Wang, D.; Jiang, J. Optimization for the assessment of spudcan peak resistance in clay–sand–clay deposits. J. Mar. Sci. Eng. 2021, 9, 698. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, X.; Wang, D.; Zhang, S. Probabilistic prediction of spudcan peak penetration resistance based on parameter estimation and sectionalized adaptive linear simplification. Ocean Eng. 2024, 298, 117228. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fallah, S.; Gavin, K.; Moradabadi, E. Estimation of Spudcan Penetration Using a Probabilistic Eulerian finite Element Analysis; CRC Press: Boca Raton, FL, USA, 2015; pp. 1281–1286. [Google Scholar]
- Vinay, K.; Avijit, B.; Portelinha, F.; Manish, K.; Guru, D. Influence of variation of soil properties in bearing capacity and settlement analysis of a strip footing using random finite element method. Civ. Eng. Infrastruct. 2024, 57, 383–403. [Google Scholar]
- Gao, P.; Liu, Z.; Zeng, J.; Zhan, Y.; Wang, F. A random forest model for the prediction of spudcan penetration in stiff-over-soft clays. Pol. Marit. Res. 2020, 27, 130–138. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eslami, A.; Valikhah, F.; Veiskarami, M. Cpt-based investigation for pile toe and shaft resistances distribution. Geotech. Geol. Eng. 2017, 35, 2891–2905. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ghorbani, J.; Aghdasi, S.; Nazem, M.; McCartney, J.S.; Kodikara, J. Augmented intelligence framework for real-time ground assessment under significant uncertainty. Eng. Comput. 2025, 1–22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tordesillas, A.; Zheng, H.; Qian, G.; Bellett, P.; Saunders, P. Augmented intelligence forecasting and what-if-scenario analytics with quantified uncertainty for big real-time slope monitoring data. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sci. 2024, 62, 5209429. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]



| No. | Centrifuge Test | Empirical Methods | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Zheng Method | ISO Method | Zheng Method | |||
| (kPa) | (m) | kPa | kPa | m | |
| 1 | 118.36 | 2.16 | 98.18 | 60.67 | 1.76 |
| 2 | 115.47 | 1.59 | 94.35 | 62.08 | 1.81 |
| 3 | 143.29 | 2.06 | 160.14 | 76.84 | 3.00 |
| 4 | 136.96 | 3.86 | 177.65 | 233.00 | 3.82 |
| 5 | 191.88 | 2.28 | 167.53 | 137.02 | 3.76 |
| 6 | 173.98 | 3.39 | 180.00 | 340.94 | 5.37 |
| 7 | 165.29 | 3.35 | 190.46 | 197.40 | 5.47 |
| 8 | 185.29 | 7.05 | 218.62 | 541.53 | 6.03 |
| 9 | 128.78 | 0.60 | 137.37 | 75.56 | 0.75 |
| 10 | 138.61 | 0.63 | 144.36 | 90.97 | 1.26 |
| 11 | 179.73 | 0.88 | 191.58 | 93.67 | 0.90 |
| 12 | 185.10 | 1.58 | 209.87 | 231.14 | 2.15 |
| 13 | 252.90 | 0.79 | 249.55 | 150.39 | 1.39 |
| 14 | 253.07 | 2.44 | 257.38 | 399.22 | 2.88 |
| 15 | 321.98 | 1.41 | 298.96 | 213.37 | 1.69 |
| 16 | 272.64 | 4.10 | 316.91 | 724.88 | 4.74 |
| 17 | 108.29 | 1.20 | 70.83 | 31.99 | 0.99 |
| 18 | 101.15 | 0.30 | 64.11 | 19.30 | 0.32 |
| 19 | 58.52 | 0.93 | 73.91 | 38.51 | 1.16 |
| 20 | 49.00 | 0.39 | 57.19 | 16.60 | 0.29 |
| 21 | 164.82 | 2.62 | 158.65 | 70.67 | 2.56 |
| 22 | 227.96 | 0.96 | 229.89 | 97.92 | 1.11 |
| 23 | 147.41 | 3.48 | 144.09 | 149.12 | 3.57 |
| 24 | 229.30 | 1.74 | 200.50 | 139.80 | 1.09 |
| 25 | 205.50 | 3.06 | 155.70 | 111.40 | 1.85 |
| 26 | 119.54 | 0.45 | 209.22 | 72.41 | 0.30 |
| 27 | 166.24 | 1.68 | 161.01 | 116.12 | 1.66 |
| 28 | 167.40 | 1.25 | 214.96 | 130.64 | 1.08 |
| 29 | 128.23 | 1.42 | 409.00 | 200.52 | 1.29 |
| 30 | 182.52 | 1.36 | 409.00 | 200.52 | 1.29 |
| 31 | 193.18 | 1.34 | 409.00 | 200.52 | 1.29 |
| 32 | 234.52 | 0.96 | 409.00 | 200.52 | 1.29 |
| 33 | 273.73 | 0.51 | 409.00 | 200.52 | 1.29 |
| 34 | 335.03 | 0.30 | 409.00 | 200.52 | 1.29 |
| 35 | 109.23 | 1.70 | 393.36 | 184.09 | 1.11 |
| 36 | 81.70 | 0.79 | 393.36 | 184.09 | 1.11 |
| 37 | 144.83 | 1.06 | 393.36 | 184.09 | 1.11 |
| 38 | 180.33 | 0.48 | 393.36 | 184.09 | 1.11 |
| 39 | 281.14 | 0.30 | 393.36 | 184.09 | 1.11 |
| 40 | 332.25 | 0.48 | 393.36 | 184.09 | 1.11 |
| Uncertainty Factor | Empirical Method | ||
|---|---|---|---|
| ISO-recommended method | 1.5889 | 2.3240 | |
| Zheng method | 0.9613 | 3.0549 | |
| / | 1.0090 | 2.8450 |
| Empirical Method | Peak Resistance/kPa | Punch-Through Failure Depth/m |
|---|---|---|
| ISO method | 76.84 | 3 |
| Zheng method | 160.14 | 3 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Sun, Z.; Gao, P.; Gao, Y.; Bi, J.; Gao, Q. Probabilistic Prediction of Spudcan Bearing Capacity in Stiff-over-Soft Clay Based on Bayes’ Theorem. J. Mar. Sci. Eng. 2025, 13, 1344. https://doi.org/10.3390/jmse13071344
Sun Z, Gao P, Gao Y, Bi J, Gao Q. Probabilistic Prediction of Spudcan Bearing Capacity in Stiff-over-Soft Clay Based on Bayes’ Theorem. Journal of Marine Science and Engineering. 2025; 13(7):1344. https://doi.org/10.3390/jmse13071344
Chicago/Turabian StyleSun, Zhaoyu, Pan Gao, Yanling Gao, Jianze Bi, and Qiang Gao. 2025. "Probabilistic Prediction of Spudcan Bearing Capacity in Stiff-over-Soft Clay Based on Bayes’ Theorem" Journal of Marine Science and Engineering 13, no. 7: 1344. https://doi.org/10.3390/jmse13071344
APA StyleSun, Z., Gao, P., Gao, Y., Bi, J., & Gao, Q. (2025). Probabilistic Prediction of Spudcan Bearing Capacity in Stiff-over-Soft Clay Based on Bayes’ Theorem. Journal of Marine Science and Engineering, 13(7), 1344. https://doi.org/10.3390/jmse13071344





