Abstract
This study investigated the effects of harvest time, cellulase, lactic acid bacteria, and ensiling with alfalfa hay on the chemical parameters, bacterial community composition, and fermentation of corn stalk silage. Corn stalks were ensiled after the ear harvest at 0 days (D0) and 20 days (D20). Each harvest was treated with alfalfa hay [AL, 5% of fresh matter (FM)], Lactobacillus plantarum (Lp) (1 × 106 CFU/g of FM), Trichoderma cellulase (TC) (100 mg/kg of FM), or both Lp and TC (Lp+TC). The silos were opened after 60 days of fermentation. The dry matter (DM) content of raw materials increased from 18.79% to 28.32% with the harvest time. The acid detergent fiber (ADF) content also significantly increased (p < 0.05), while water-soluble carbohydrates (WSCs) and in vitro dry matter digestibility (IVDMD) significantly decreased (p < 0.05). After 60 days, the neutral detergent fiber (NDF) and ADF contents increased, and all chemical composition and fermentation state parameters of silages had significant differences (p < 0.05) with the harvest time. Compared with the control group, the AL treatment resulted in higher (p < 0.05) DM and crude protein (CP) contents, and the Lp+TC treatment resulted in a lower NDF (p < 0.05) content. For D0, the TC and Lp+TC treatments resulted in a higher WSC content and lower NDF and ADF contents than in D20. Meanwhile, the ammonia-nitrogen (NH3-N) content in each treatment was less than 10% of the DM. The pH values were all approximately 3.70. The AL treatment significantly increased the lactic acid (LA) content and lactic/acetic acid ratio (LA/AA). Additionally, the silages had a similar microbial environment before and after fermentation. We recommend harvesting corn stalks for silage immediately after the corn ear harvest. Adding cellulase improved the corn stalk feed value, and ensiling with alfalfa hay improved its fermentation quality.
1. Introduction
Corn is considered a crucial forage grain crop with diverse applications, ranging from consuming corn ears to utilizing stalks as animal fodder and producing derivative products through extensive processing. Worldwide corn production has been abundant, reaching 1151.36 million metric tons by the year 2022 [1]. This substantial corn yield results in a significant generation of corn stalks. Unfortunately, many farmers opt to burn corn stalks, leading to resource wastage, air pollution, and exacerbating environmental challenges [2].
While corn stalks are abundant, their complex structure, composed of cellulose, lignin, and hemicellulose tightly bound by covalent bonds [3], presents challenges in using them as feed [4]. This results in a rough texture, poor palatability, and low digestibility. Enhancing the effective utilization of corn stalks as feed becomes crucial, particularly in the winter when forage for herbivores becomes scarce, and animals compete with humans for grain for food [5].
Ensiling is an effective preservation method that can improve forage palatability, digestibility, and nutrient retention for long-term storage [6]. However, leaving corn stalks in the field, a common practice, leads to nutrient loss [7]. Previous studies have explored the use of additives, such as cellulase and lactic acid bacteria (LAB), to enhance corn stalk silage quality [8,9]. Cellulase has become a popular additive for silage in recent years [10]. It can convert cellulose to glucose, which is better for silage fermentation and can be more easily digested. Lactic acid bacteria (LAB) have also been used as additives in many studies [11,12,13]. They can convert carbohydrates in raw materials into lactic acid, lower the pH, and inhibit the growth of harmful microorganisms, thereby achieving long-term preservation and maintaining nutrients. At the same time, the activity of microorganisms can improve palatability. Alfalfa hay is frequently used in mixed ensiling due to its rich protein content and good palatability. It can improve the moisture of raw materials, which is an important issue in silage making.
While many studies have focused on additives and mixed ensiling, the impact of harvest time and ensiling duration on corn stalk silage quality remains underexplored. Compared to whole-plant corn silage, corn stalks, often considered waste, present an opportunity to improve feed selectivity and environmental sustainability. Identifying the optimal time for harvest, silage-making, and storage is crucial for farmers [14]. Therefore, our study aims to investigate the effects of harvest time, cellulase, lactic acid bacteria, and mixed ensiling with alfalfa on the chemical parameters, bacterial community compositions, and fermentation characteristics of corn stalk silage.
2. Methods and Materials
2.1. Material Preparation and Ensiling
In this experiment, “Mi-baek 2-ho” corn (Zea mays L.) was sown on 27 April 2022 at Seoul National University, Pyeongchang campus (latitude: 37°32′46.10″ N, longitude: 128°26′17.90″ E, Pyeongchang-gun, Gangwon-do, Republic of Korea). The corn ears were harvested on 1 August 2022. The corn stalks were harvested at 0 days (D0) and 20 days (D0) after the ear harvest and made directly into silage. The stalks were chopped into 2–3 cm pieces (SC-7000, Agricultural Machinery, Inc., Daegu, Republic of Korea) and then sprayed with different additives: (1) alfalfa hay, (2) Lactobacillus plantarum NLRI-101 (1.5 × 1010 CFU/g of FM, ChungMi Bio Co., Ltd., Ansong City, Gyeonggi-do, Republic of Korea), and (3) Trichoderma cellulase (6.3 units/mg, Merck KGaA Co., Ltd., Darmstadt, Germany). According to previous studies1 [15,16], we set the treatments as 10 mL/kg FM distilled water (control); alfalfa hay [AL, 5% of fresh matter (FM)]; Lactobacillus plantarum NLRI-101 (Lp) (1 × 106 CFU/g of FM), Trichoderma cellulase (TC) (100 mg/kg of FM), or both Lp and TC (Lp+TC).
Approximately 400 g of chopped corn stalks treated with additives were placed into plastic bags and sealed with a vacuum packer (QV-100, BlueTec Co., Ltd., Ansong City, Gyeonggi-do, Republic of Korea). Treatments were replicated three times. The D0 and D20 silages were opened after 60 days. Samples of each silage were then taken to analyze the quality of the chemical parameters, bacterial community composition, and fermentation characteristics.
2.2. Chemical and Microbiological Analysis
The dry matter (DM) content of fresh samples and silages was determined by drying in an oven at 65 °C for 72 h. Then, the dried samples were passed through a 0.20 mm sieve (Thomas Scientific, Inc., Swedesboro, NJ, USA) and ground into a powder for chemical analysis. Water soluble carbohydrate (WSC) content was determined by modifying the anthrone method [17]. Crude protein (CP) content was analyzed according to the Association of Official Agricultural Chemists (AOAC) method [18]. Acid detergent fiber (ADF) and neutral detergent fiber (NDF) contents were determined using an Ankom2000 fiber analyzer (Ankom Technologies, Inc., Fairport, NY, USA) following the method of Van Soest et al. [19]. In vitro DM digestibility (IVDMD) was determined by placing the nylon sample filter bags (50 × 55 mm, ANKOM F57, ANKOM Tech., Fairport, NY, USA, 0.5 ± 0.09 g/sample) into bottles with buffer solutions and ruminal gastric juice from cows, and keeping them in a digester at 39 °C for 48 h. Samples were then analyzed using the same method as that used for the NDF analysis [20].
The forage nutritive value was expressed as the total digestible nutrient (TDN) and relative feed value (RFV), which were calculated as follows [21]:
TDN: TDN% = 88.9 − 0.79 × ADF%
RFV: DDM% = 88.9 − 0.779 × ADF%
DMI% = 120/NDF%
RFV = (DMI% × DDM%)/1.29
RFV: DDM% = 88.9 − 0.779 × ADF%
DMI% = 120/NDF%
RFV = (DMI% × DDM%)/1.29
Next, 10 g of fresh silage samples were homogenized in 90 mL sterile saline (0.85% NaCl solution), shaken for 1 h in a mechanical shaker, and refrigerated for 24 h. Samples were then filtered through a filter paper (Whatman No. 1, AVANTE C, Toyo Roshi Kaisha, Ltd., Tokyo, Japan). The extract was serially diluted 102−105 times with 0.85% NaCl, and 10 µL of each extract was evenly spread on an agar surface using a plastic spreader followed by incubation. The LAB number was counted after growing on De Man, Rogosa, and Sharpe agar (MRS) medium incubated at 37 °C for 24−48 h. Total microorganisms (TMs) were counted on plate count agar (PCA) medium incubated at 37 °C for 48−72 h. Mold and yeast were counted on potato dextrose agar (PDA) medium incubated at 25 °C for 48−72 h. After incubating, the colony-forming units per gram (cfu/g) of microorganisms were counted on the agar plates, calculated according to the dilution factor, and converted to a log10 value.
2.3. Fermentation Analysis
The silage samples (10 g) were blended with 90 mL of distilled water in conical flasks on a mechanical shaker for 1 h, kept in a refrigerator for 24 h, and filtered through a filter paper (Whatman No. 6, AVANTEC, Toyo Roshi Kaisha, Ltd., Tokyo, Japan). The pH value, ammonia-nitrogen (NH3-N), and organic acid contents were analyzed using these silage filtrates. The pH value was measured with a pH meter (AB 150, Fisher Scientific International, Inc., Pittsburgh, PA, USA) as described by Kaiser et al. (2003) [22]. The NH3-N content was determined according to the modified phenol-hypochlorite reaction method described by Broderick and Kang (1980) [23]. Lactic acid (LA), acetic acid (AA), propionic acid (PA), and butyric acid (BA) contents were analyzed using high-performance liquid chromatography [Agilent HPLC 1260, column: Agilent Hi-Plex H, 7.7 × 300 mm, 8 µm (p/n PL1170-6830); mobile phase: 0.005 M H2SO4; flow rate: 0.7 mL/min: Agilent, Santa Clara, CA, USA].
2.4. Statistical Analysis
This study had one control and four treatment groups, which were analyzed using statistical methods. The data were analyzed as a 5 × 3 factorial arrangement in a completely randomized design. Further analysis was conducted using a general linear model (GLM) in Statistical Product and Service Solution (SPSS) version 26. The fixed effects of harvest time and additives were analyzed via one-way ANOVA, and their interaction was analyzed via univariate two-way analysis. The differences among treatments were determined using a least significant difference (LSD) test with a significant difference at p < 0.05. All figures were produced using GraphPad Prism 8 version 8.0.2 (263) software.
3. Results
3.1. Microbial Counts and Chemical Composition of Raw Materials
The microorganism counts and chemical composition of corn stalks are presented in Table 1 and Table 2. The LAB, TM, and yeast and mold (YM) counts were in the ranges of 5.47 to 5.39, 5.73 to 5.41, and 3.50 to 3.65 log10 cfu/g FM, respectively. The LAB and YM counts were not significantly affected by harvest time (p > 0.05), while the TM count in D0 was significantly higher than that of D20 (p < 0.05).

Table 1.
Microorganism population of corn stalks before ensiling.

Table 2.
Chemical compositions of corn stalks treated with additives before ensiling.
Harvest time had effects on DM, WSC, ADF, and IVDMD contents significantly (p < 0.05). The DM content was averaged from 18.79% to 28.32%, and the WSC content of corn stalks was greater than 13.0% of DM on average at D0 and greater than 12.0% of DM on average at D20. All corn stalks had a CP content greater than 6.0% of DM, while the AL treatment had the highest CP content. The NDF content was from 47.18~50.35% of DM at D0 and from 47.74~51.43% of DM at D20. ADF content was higher at D20 than at D0, which was 28.72% of DM on average. Meanwhile, D0 had higher IVDMD content than D20 (averaged from 72.44% of DM to 66.65% of DM).
3.2. Chemical Composition of Corn Stalk Silage
The chemical compositions of corn stalk silages treated with additives for 60 days are shown in Table 3. After 60 days of ensiling, there were significant differences (p < 0.05) in all chemical parameters due to the harvest time, additives, and their interactions, except the ADF contents; the additives had no significant effect(p = 0.05) on it, which averages 32.99 at D0 and 33.30 at D20. Additionally, also the CP content showed no significant differences due to interactions (p > 0.05). The DM, NDF, and ADF contents increased significantly with harvest time (p < 0.001), while the WSC, CP, and IVDMD contents decreased significantly (p < 0.001). Compared to the raw materials, the DM content was reduced (average from 18.79% to 17.17% at D0 and from 28.32% to 26.09% at D20), the WSC content declined sharply, more than 85.0%, and the CP content also decreased. Moreover, the digestibility of the feed deteriorated, with an increase in the NDF and ADF contents and a decrease in the IVDMD content. After the ensiling process, the effects of additives on the chemical compositions of D0 and D20 displayed similar changes. Compared with the control group, the AL treatment had a higher CP content, which was 7.56 at D0 and 6.77 at D20, the TC treatment had a higher DM content, and the Lp+TC treatment had a higher WSC content and lower NDF and ADF contents.

Table 3.
Chemical compositions of corn stalks silage treated with additives after 60 days.
The TDN content and RFV of corn stalk silage are shown in Figure 1 and Figure 2, respectively. D0 had higher TND and RFV values than D20, while the additives resulted in no significant difference compared to the control group. The fermentation indicators, pH, and the NH3-N and organic acid contents are shown in Table 4. There were significant differences in the NH3-N, LA, and LA/AA contents with a delayed harvest time, and there were significant differences in pH and NH3-N, LA, and LA/AA contents when additives were supplied. There were also significant differences in pH and the NH3-N and LA contents due to the interactions between delayed harvest time and additives. The additive treatments had a similar pH at D0 and D20, which were all around 3.70. The NH3-N content was significantly increased with harvest time (p < 0.001), with average 4.50% of total N at D0 and 7.37% of total N at D20, while the LA and LA/AA contents decreased (p < 0.001). The NH3-N content was lower in the TC treatment than in other treatments (p > 0.05). The effect of additives on LA and the LA/AA ratio was similar at D0 and D20, with the AL treatment having the highest content (3.64% of DM, 6.28 at D0 and 2.98% of DM, 4.89 at D20, respectively) but the differences with the other treatments were not significant.
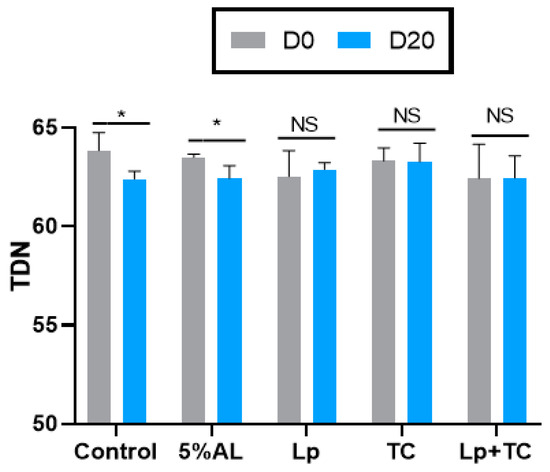
Figure 1.
Total digestible nutrients (TDN) of corn stalk silages treated with additives after 60 days. AL, corn stalk co-ensiling with alfalfa hay; Lp, corn stalk with the addition of lactic acid bacteria (LAB); TC, corn stalk with the addition of cellulase; Lp+TC, corn stalk with the addition of LAB and cellulase; SEM, standard error of the mean. D0 and D20 indicated corn stalks at 0 and 20 days after ear harvest, respectively; bars labeled with * are significantly different (p < 0.05); NS means no significant.
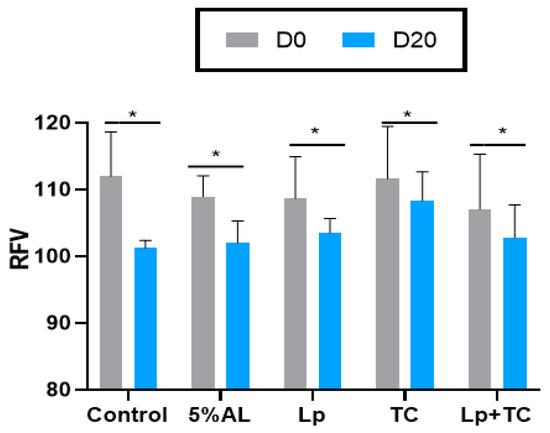
Figure 2.
Relative feed value (RFV) of corn stalk silages treated with additives after 60 days. AL, corn stalk co-ensiling with alfalfa hay; Lp, corn stalk with the addition of lactic acid bacteria (LAB); TC, corn stalk with the addition of cellulase; Lp+TC, corn stalk with the addition of LAB and cellulase; SEM, standard error of the mean. D0 and D20 indicated corn stalks at 0 and 20 days after ear harvest, respectively; bars labeled with * are significantly different (p < 0.05).

Table 4.
pH and NH3-N and fermentation acid contents in corn stalk silages treated with additives after 60 days.
3.3. Microbial Population of Corn Stalk Silage
The microbial composition of corn stalk silage on D0 and D20 is shown in Figure 3. At the same harvest time, there were no significant differences in the microorganism populations under the different additive treatments. There were significant differences in the LAB counts for the AL, Lp, and Lp+TC treatments at D0 and D20, with larger LAB populations in the AL, Lp, and Lp+TC treatments at D0 than at D20. Neither additives nor harvest time had a significant effect on the YM populations. For the TM count, only the Lp treatment had a significant difference in D0 and D20, with a higher population at D20.
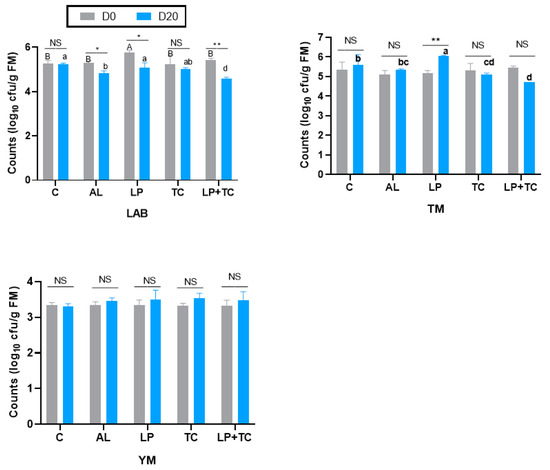
Figure 3.
Microbial composition of corn stalk silages treated with additives after 60 days. AL, corn stalk co-ensiling with alfalfa hay; Lp, corn stalk with the addition of lactic acid bacteria (LAB); TC, corn stalk with the addition of cellulase; Lp+TC, corn stalk with the addition of LAB and cellulase; TM, total microorganisms; YM, yeasts and molds; C = control; AL = alfalfa; LP = Lactobacillus plantarum; TC = Trichoderma cellulase; LP+TC = L. plantarum + T. cellulase; and SEM, standard error of the mean. D0 and D20 indicate corn stalks at 0 and 20 days after ear harvest; bars labeled with * are significantly different (p < 0.05); bars labeled with ** are significantly different (p < 0.001); NS means no significant; and different superscripts in different letters indicate that additives differ (p < 0.05).
4. Discussion
4.1. Chemical Composition, Digestion Index, and Microbial Population of Corn Stalks and Their Silages
Increasing the development and use of non-grain feed resources, such as grass and stalks, is an effective measure to resolve the conflict between the development of animal husbandry and human competition for grain [24]. Corn stalks are the by-products of corn after the ears are consumed. If they can be used effectively, both economic and environmental benefits could be achieved. Farmers usually harvest the corn ears before they are fully mature (more reproductive) to ensure the best flavor, but the harvest date for the remaining stalks is not certain. It is, therefore, important to determine the optimal stalk harvest date to produce good silage and to establish methods that can improve the quality of stalk silage.
Previous studies have shown that leaving stalks in the field after the ear harvest could decrease the CP content, increase the DM and fiber contents of the stalks, and reduce the dry matter digestibility [16,25,26,27]. The DM content in stalks left in the field has been shown to increase by more than 50%, which may be due to the ears of corn harvested at an earlier stage being more vegetative and the corn stalks still growing to some extent after the ears were harvested [28]. The CP content decreased after 60 days ensiling. In the fresh stalk (D0) silage, it decreased by nearly 5.0%, while in the D20 silage, it was nearly 16.0% lower. This was consistent with the results of previous studies. It has been reported that the CP content decreases after ensiling [29,30], although in some good-quality silages, the CP content can be maintained without significant changes [31]. In this study, the silages from the D0 treatment groups maintained their CP content well, while there was an obvious loss in the D20 treatment groups, indicating that ensiling fresh stalks immediately could maintain their nutritional content and produce higher quality silage. In previous studies, the water loss of corn stalks and the proportion of DM increased significantly after field exposure; the NDF and ADF contents also increased sharply [28]. Our results were similar. Compared with the D0 stalks, the D20 stalks had higher NDF and ADF contents and a lower IVDMD content.
The LAB and WSC contents play important roles in the fermentation process before ensiling. The LAB counts in this study ranged from 5.39 to 5.47 log10 cfu/g FM. Guo et al. (2021) [25] also reported similar counts, indicating that harvest time could reduce the fermentation quality of corn stalk silage. This was also evidenced by the TM population, which decreased significantly in D20 stalks. The WSC content, which ranged from 6.0% to 8.0% of DM, was more likely to produce high-quality silage [32]. In this study, the average WSC content was 11.96 to 13.09% of DM and, therefore, contributed to the production of good silage. After ensiling, the LAB population only increased in the D20 silages, while the YM population decreased, but it was similar in D0 and D20. Furthermore, additives had no significant effect on the various bacterial populations in the silages. These were similar to the results of Sun et al. (2019) [33]. It may be due to LAB dominating the microbial population of raw materials. The raw materials contained high WSC and LAB contents, enabling strong fermentation effects to be achieved even without additives. LAB produce a large amount of lactic acid at the beginning of fermentation, creating an acidic environment, thereby inhibiting the growth of mold, yeast and other harmful bacteria. If the epiphytic LAB of corn stalks are homofermentative LAB, it will promote the dominance of homolactic fermentation and achieve a better silage effect [34].
Using alfalfa hay as an additive to mix with corn stalks for ensiling can not only increase the CP content of corn stalks but also realize the ensiling possibility of alfalfa. In terms of chemical compositions, the alfalfa treatment significantly increased the CP content, but there were no significant differences with the control group for the other parameters.
4.2. pH and Organic Acid and NH3-N Contents of Corn Stalk Silage
Among the different fermentation states, the pH of all the treatments was similar, but all pH values were less than 4.2. As reported by Guo et al. (2021) [25], successful silage requires a pH lower than 4.2. Guan et al. [35] said that the rapid decrease in pH value is caused by the proliferation and fermentation of lactic acid bacteria to produce more lactic acid, thereby inhibiting the growth of harmful bacteria and forming a high-quality fermentation environment. The high WSC content in the raw materials can provide enough nutrition for LAB so that lactic acid fermentation can dominate at the beginning of fermentation and drop the pH rapidly. Therefore, the microbial community and WSC content in the raw materials will have an impact on pH [36]. If the fermentation microbial communities in different treatment groups are similar, similar pH changes will result. In this experiment, there were similar counts of microorganisms before ensiling, and the WSC content in raw materials was high, which may be the reason why the pH values of each treatment group were similar. McDonald (1991) [37] reported that the NH3-N content was less than 10% of the total N, indicating that the silage preserved the N content, and NH3-N is an iconic parameter for indicating protein degradation. In this study, the AL treatment had the lowest NH3-N content in both the D0 and D20 silages, indicating their proteolysis was relatively low. The NH3-N content in the D20 silage was nearly twice that of the D0 silage, which indicated that the fermentation effect of D0 was better than that of D20. This was also confirmed using the LA content, which was higher in D0 silage.
Both LA and AA are important indicators of the quality of silage. During the fermentation process, LA contributes most to the decrease in pH. Kilic (1986) [38] reported that an LA content higher than 2.0% on a DM basis was required to produce high-quality silage. The higher the LA content, the better the quality of silage, while AA has an inhibitory effect on fungi and a positive effect on aerobic stability [37]. The LA/AA is an indication of homolactic dominant fermentation. If the LA/AA content is more than 3, the fermentation process is homolactic dominant fermentation [39]. In this study, the LA content and LA/AA ratio in the AL treatment were significantly higher than in the control group, indicating that the AL treatment group had better fermentation than the control group. This may be due to the addition of alfalfa hay, which controlled the moisture content of the raw material, allowing it to achieve better silage results [40].
Silage inoculated with LAB is considered an effective method to improve the quality of silage fermentation [15]. Epiphytic LAB occurs naturally in forage crops, participates in silage fermentation, and has an impact on silage quality. The LAB count determines if microbial additions to raw materials are required [33]. The homofermentative LAB in corn silage uses glucose during fermentation to produce LA and some AA, formic acid (FA), and PA, and therefore, the pH drops rapidly to approximately 4.0, thereby inhibiting the activities of other microorganisms [41]. When the pH drops to 3.8, the growth of LAB is also inhibited, and the biochemical processes in the silage are stopped.
If LAB cannot quickly become the dominant flora during fermentation, a large number of spoilage microorganisms will grow rapidly and affect the quality of silage [42]. Therefore, adding LAB to silaged raw materials can increase the LAB population in silage raw materials, enabling LAB to quickly become the dominant flora and thereby improving the nutritional value and quality of silage [15]. In this study, the pH value of the LAB treatment was less than 4.2, the NH3-N content was less than 10%, the LA content was greater than 2% on a DM basis, and the LA/AA ratio was higher than 3. This indicated that the silage quality resulting from the LAB treatment was good. However, compared with the control group, it did not significantly improve the fermentation effect, nor was it significantly different from the control group in terms of chemical composition. This was similar to the results of Khota et al. (2018) [43]; this may be because the effect of the natural epiphytic LAB population on the raw materials was large enough to allow homolactic fermentation to occur at the beginning of the fermentation process, thereby achieving a strong fermentation effect. Thus, for the raw materials in our study, LAB inoculation cannot improve silage quality, and it is therefore not necessary to add an LAB inoculation when making silage.
Cellulase is a frequently used silage additive. Li et al. (2018) [44] reported that the addition of cellulase can increase the amount of LAB in the substrate, and the mixed-use of cellulase and LAB could be an effective way to enhance fermentation. Cellulase acts on the β-1,4-glucosidic bonds in cellulose macromolecules to decompose them into monosaccharides or disaccharides, which are directly absorbed by animals and can improve feed utilization [45]. In addition, more sugars can be released for fermentation by LAB via the action of enzymes that help break down carbohydrates into sugars [46]. Our results showed that the NDF and ADF contents in the TC and Lp+TC treatments were lower than those in the control group, while the WSC content was much higher. This shows that the addition of cellulase decomposes the cellulose in corn stalks into WSCs, which can degrade fiber and improve the quality of silage. This is also supported by other studies [47]. The NH3-N content in the TC treatment was lower than that in the control group (<10% DM), which indicated that the addition of cellulase was beneficial to the fermentation of silage, limited the decomposition of proteins, and better-preserved nutrients. Furthermore, the LA content (>2% DM) and LA/AA ratio (>3.0) in the TC and Lp+TC treatments reached the standard required for good silage, but their contents were not improved compared with the control group. The inability of these treatments to improve the fermentative properties of silage may be due to the inability of the inoculum to compete with the epiphytic microbial population in the raw material [48].
5. Conclusions
In this study, we found that all treatments improved the chemical composition value and resulted in good fermentation effects. However, delaying the harvest time of corn stalks resulted in a decrease in their chemical composition value and fermentation effects. Among the fresh stalk silage treatments, the TC and Lp+TC additives produced a better chemical composition value, while the AL treatment resulted in a better fermentation effect. Therefore, harvesting fresh corn stalks for silage immediately after a corn ear harvest could result in better chemical composition value and fermentation effects. In terms of the materials suitable for making silage, the additives tested here may not produce significant effects. However, if additives are recommended, they would be most effective for raw materials with a low nutritional content, such as the addition of cellulase or LAB and cellulase. For high-moisture raw materials, it is recommended to add hay additives, such as alfalfa hay.
Author Contributions
Conceptualization, L.-L.W.; Methodology, L.-L.W., Y.-F.L., Y.-S.Y., H.-J.K. and W.-J.L.; Software, L.-L.W.; Formal analysis, L.-L.W.; Investigation, L.-L.W.; Data curation, L.-L.W.; Writing—original draft, L.-L.W.; Writing—review & editing, Y.-F.L. and J.-G.K.; Supervision, J.-G.K.; Project administration, J.-G.K.; Funding acquisition, J.-G.K. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This study was financially supported by the Cooperative Research Program for Agriculture Science & Technology Development (Project No. PJ01575202).
Institutional Review Board Statement
Caring for animals was according to the guidelines of the Animal Ethical Committee (Seoul National University, Republic of Korea) under the approval number of SNU-160105-1.
Data Availability Statement
The authors confirm that the data supporting the findings of this study are available within the article.
Conflicts of Interest
We certify that there is no conflict of interest with any financial organization regarding the material discussed in the manuscript.
References
- Global Corn Production from 2014/2015 to 2022/2023 (in Million Metric Tons)* [Graph]. 2023. Available online: https://www.statista.com/statistics/1156213/global-corn-production/ (accessed on 25 December 2023).
- Bhuvaneshwari, S.; Hettiarachchi, H.; Meegoda, J.N. Crop Residue Burning in India: Policy Challenges and Potential Solutions. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2019, 16, 832. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jin, Z.; Katsumata, K.; Lam, T.; Iiyama, K. Covalent linkages between cellulose and lignin in cell walls of coniferous and nonconiferous woods. Biopolymers 2006, 83, 103–110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, D.; Xu, C.; Ye, H.; Shi, Y.; Sheng, Y.; Ge, S.; Zhang, M.; Wang, H. New Poplar-Derived Biocomposites via Single-Step Thermoforming Assisted by Phosphoric Acid Pretreatment. Polymers 2022, 14, 3636. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Steinfeld, H.G.; Gerber, P.; Wassenaar, T.D. Livestock’s Long Shadow: Environmental Issues and Options; Food and Agriculture Organization of the United Nations (FAO): Rome, Italy, 2006. [Google Scholar]
- Xin, Y.; Chen, C.; Zhong, Y.; Bu, X.; Huang, S.; Tahir, M.; Du, Z.; Liu, W.; Yang, W.; Li, J.; et al. Effect of storage time on the silage quality and microbial community of mixed maize and faba bean in the Qinghai-Tibet Plateau. Front. Microbiol. 2022, 13, 1090401. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Clark, A. Managing Cover Crops Profitably; Diane Publishing: Darby, PA, USA, 2008. [Google Scholar]
- Kung, L. A review on silage additives and enzymes. In Proceedings of the 59th Minneapolis Nutrition Conference, Minneapolis, MN, USA, 23 September 1998; pp. 121–135. Available online: http://cdn.canr.udel.edu/wp-content/uploads/2014/02/A-REVIEW-ON-SILAGE-ADDITIVES-AND-ENZYMES.pdf (accessed on 25 December 2023).
- Oladosu, Y.; Rafii, M.Y.; Abdullah, N.; Magaji, U.; Hussin, G.; Ramli, A.; Miah, G. Fermentation quality and additives: A case of rice straw silage. BioMed Res. Int. 2016, 2016, 7985167. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hu, Z.; Ma, D.; Niu, H.; Chang, J.; Yu, J.; Tong, Q.; Li, S. Enzyme additives influence bacterial communities of Medicago sativa silage as determined by Illumina sequencing. AMB Express 2021, 11, 5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, D.; Lee, K.D.; Choi, K.C. Role of LAB in silage fermentation: Effect on nutritional quality and organic acid production—An overview. AIMS Agric. Food 2021, 6, 216–234. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mathur, H.; Beresford, T.P.; Cotter, P.D. Health Benefits of Lactic Acid Bacteria (LAB) Fermentates. Nutrients 2020, 12, 1679. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Raman, J.; Kim, J.-S.; Choi, K.R.; Eun, H.; Yang, D.; Ko, Y.-J.; Kim, S.-J. Application of Lactic Acid Bacteria (LAB) in Sustainable Agriculture: Advantages and Limitations. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2022, 23, 7784. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Weinberg, Z.G.; Ashbell, G. Engineering aspects of ensiling. Biochem. Eng. J. 2003, 13, 181–188. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheng, Q.; Li, P.; Xiao, B.; Yang, F.; Li, D.; Ge, G.; Jia, Y.; Bai, S. Effects of LAB inoculant and cellulase on the fermentation quality and chemical composition of forage soybean silage prepared with corn stover. Grassl. Sci. 2021, 67, 83–90. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, J.L.; Wang, P.; Zhou, C.H.; Li, P.; Tang, H.Y.; Zhang, J.B.; Cai, Y. Chemical composition and in vitro digestibility of corn stover during field exposure and the fermentation characteristics of silage prepared with microbial additives. Asian-Australas. J. Anim. Sci. 2019, 32, 1854–1863. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yemm, E.W.; Willis, A.J. The estimation of carbohydrates in plant extracts by anthrone. Biochem. J. 1954, 57, 508–514. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gonthier, P.; Visentin, I.; Valentino, D.; Tamietti, G.; Cardinale, F. The Legitimate Name of a Fungal Plant Pathogen and the Ethics of Publication in the Era of Traceability. Sci. Eng. Ethics 2017, 23, 631–633. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Van Soest, P.J.; Robertson, J.B.; Lewis, B.A. Methods for Dietary Fiber, Neutral Detergent Fiber, and Nonstarch Polysaccharides in Relation to Animal Nutrition. J. Dairy Sci. 1991, 74, 3583–3597. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tilley, J.M.A.; Terry, R.A. A Two-Stage Technique for The In Vitro Digestion Of Forage Crops. Grass Forage Sci. 1963, 18, 104–111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rohweder, D.A.; Barnes, R.F.; Jorgensen, N. Proposed Hay Grading Standards Based on Laboratory Analyses for Evaluating Quality. J. Anim. Sci. 1978, 47, 747–759. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kaiser, A.; Piltz, J.; Burns, H. Topfodder silage-a silage extension package for the grazing industries. In Proceedings of the Beef Products Program: Technology-Our Future, Tocal College, Paterson, Australia, 13 May 2003; pp. 95–97. [Google Scholar]
- Broderick, G.A.; Kang, J.H. Automated Simultaneous Determination of Ammonia and Total Amino Acids in Ruminal Fluid and In Vitro Media1. J. Dairy Sci. 1980, 63, 64–75. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, C.; Wang, G.; Yang, H. Study on the Coupling System of Grain-Grass-Livestock of Herbivorous Animal Husbandry in Agricultural Areas: A Case Study of Najitun Farm of Hulunbuir Agricultural Reclamation in China. Land 2022, 11, 691. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, L.; Lu, Y.; Li, P.; Chen, L.; Gou, W.; Zhang, C. Effects of Delayed Harvest and Additives on Fermentation Quality and Bacterial Community of Corn Stalk Silage. Front. Microbiol. 2021, 12, 687481. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cai, Y.; Du, Z.; Yamasaki, S.; Nguluve, D.; Tinga, B.; Macome, F.; Oya, T. Influence of microbial additive on microbial populations, ensiling characteristics, and spoilage loss of delayed sealing silage of Napier grass. Asian-Australas. J. Anim. Sci. 2020, 33, 1103–1112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Horst, E.H.; Bumbieris Junior, V.H.; Neumann, M.; López, S. Effects of the Harvest Stage of Maize Hybrids on the Chemical Composition of Plant Fractions: An Analysis of the Different Types of Silage. Agriculture 2021, 11, 786. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McEniry, J.; King, C.; O’Kiely, P. Silage fermentation characteristics of three common grassland species in response to advancing stage of maturity and additive application. Grass Forage Sci. 2014, 69, 393–404. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, Y.; Liang, L.; Dai, S.; Wu, C.; Chen, C.; Hao, J. Effect of Different Regions and Ensiling Periods on Fermentation Quality and the Bacterial Community of Whole-Plant Maize Silage. Front. Microbiol. 2021, 12, 743695. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wan, J.C.; Xie, K.Y.; Wang, Y.X.; Liu, L.; Yu, Z.; Wang, B. Effects of wilting and additives on the ensiling quality and in vitro rumen fermentation characteristics of sudangrass silage. Anim. Biosci. 2021, 34, 56–65. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Desta, S.T.; Yuan, X.; Li, J.; Shao, T. Ensiling characteristics, structural and nonstructural carbohydrate composition and enzymatic digestibility of Napier grass ensiled with additives. Bioresour. Technol. 2016, 221, 447–454. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Amer, S.; Hassanat, F.; Berthiaume, R.; Seguin, P.; Mustafa, A.F. Effects of water soluble carbohydrate content on ensiling characteristics, chemical composition and in vitro gas production of forage millet and forage sorghum silages. Anim. Feed. Sci. Technol. 2012, 177, 23–29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, L.; Wang, Z.; Gentu, G.; Jia, Y.; Hou, M.; Cai, Y. Changes in microbial population and chemical composition of corn stover during field exposure and effects on silage fermentation and in vitro digestibility. Asian-Australas. J. Anim. Sci. 2019, 32, 815–825. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pholsen, S.; Khota, W.; Pang, H.; Higgs, D.; Cai, Y. Characterization and application of lactic acid bacteria for tropical silage preparation. Anim. Sci. J. 2016, 87, 1202–1211. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guan, Y.; Lv, H.; Wu, G.; Chen, J.; Wang, M.; Zhang, M.; Pang, H.; Duan, Y.; Wang, L.; Tan, Z. Effects of Lactic Acid Bacteria Reducing the Content of Harmful Fungi and Mycotoxins on the Quality of Mixed Fermented Feed. Toxins 2023, 15, 226. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, J.; Li, Z.; Shang, S.; Zhao, X.; Zhang, W.; Zhang, X.; Bai, J.; Yang, Z.; Guo, K. Effect of additives and moisture on the fermentation quality and bacterial community of high moisture ear corn. Front. Microbiol. 2023, 14, 1251946. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- McDonald, P.; Henderson, A.R.; Heron, S.J.E. The Biochemistry of Silage; Chalcombe Publications: Shedfield, UK, 1991. [Google Scholar]
- Kilic, A. Silo Feed (Instruction, Education and Application Proposals); Bilgehan Press: Izmir, Turkey, 1986. [Google Scholar]
- Kung, L., Jr.; Stokes, M.R. Analyzing silages for fermentation end products. Univ. Del. Coll. Agric. Nat. Resour. 2001, 11–17. [Google Scholar]
- Zou, Y.; Dong, S.; Du, Y.; Li, S.; Wang, Y.; Cao, Z. Effects of moisture content or particle size on the in situ degradability of maize silage and alfalfa haylage in lactating dairy cows. Anim. Nutr. 2016, 2, 249–252. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Muck, R.E.; Nadeau, E.M.G.; McAllister, T.A.; Contreras-Govea, F.E.; Santos, M.C.; Kung, L. Silage review: Recent advances and future uses of silage additives. J. Dairy Sci. 2018, 101, 3980–4000. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sa, D.W.; Lu, Q.; Wang, Z.; Ge, G.; Sun, L.; Jia, Y. The potential and effects of saline-alkali alfalfa microbiota under salt stress on the fermentation quality and microbial. BMC Microbiol. 2021, 21, 149. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Khota, W.; Pholsen, S.; Higgs, D.; Cai, Y. Comparative analysis of silage fermentation and in vitro digestibility of tropical grass prepared with Acremonium and Tricoderma species producing cellulases. Asian-Australas. J. Anim. Sci. 2018, 31, 1913–1922. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, D.-X.; Ni, K.-K.; Zhang, Y.-C.; Lin, Y.-L.; Yang, F.-Y. Influence of lactic acid bacteria, cellulase, cellulase-producing Bacillus pumilus and their combinations on alfalfa silage quality. J. Integr. Agric. 2018, 17, 2768–2782. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lynd, L.R.; Weimer, P.J.; van Zyl, W.H.; Pretorius, I.S. Microbial cellulose utilization: Fundamentals and biotechnology. Microbiol. Mol. Biol. Rev. 2002, 66, 506–577. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nkhata, S.G.; Ayua, E.; Kamau, E.H.; Shingiro, J.B. Fermentation and germination improve nutritional value of cereals and legumes through activation of endogenous enzymes. Food Sci. Nutr. 2018, 6, 2446–2458. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiong, H.; Zhu, Y.; Wen, Z.; Liu, G.; Guo, Y.; Sun, B. Effects of Cellulase, Lactobacillus plantarum, and Sucrose on Fermentation Parameters, Chemical Composition, and Bacterial Community of Hybrid Pennisetum Silage. Fermentation 2022, 8, 356. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kung, L., Jr.; Stokes, M.R.; Lin, C.J. Silage Additives. In Silage Science and Technology; Wiley: Hoboken, NJ, USA, 2003; pp. 305–360. [Google Scholar]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).