Abstract
The COVID-19 pandemic and the outbreak of the locust plague in Pakistan have severely impacted grain production and trade in South Asia, thereby posing serious threats to global grain security. This study formulated a comprehensive analysis of crop yield and trade restrictions consequent to the combined impact of COVID-19 and the locust plague with the GTAP model and quantitatively simulated the characteristics and mechanisms of changes in the production and trade patterns of major grain crops (paddy rice and wheat) in South Asia. Results indicate that COVID-19 and the locust plague affected global grain production and imports and exports to varying degrees. Grain production was reduced by 15% and global trade shrank sharply, with total imports and exports shrinking by 5.79% and 1.41%, respectively. This also led to international food prices changing significantly, which further influenced the food affordability and accessibility, especially for developing countries that are heavily dependent on imports. Nepal, Sri Lanka, and Bangladesh were the regions that experienced the highest rises in grain import prices, which caused the processed rice imports of Sri Lanka, Nepal, Bhutan and Maldives, and Bangladesh to drop by 81%, 77%, 80%, and 89%, respectively. Furthermore, the global grain trade patterns were also severely affected. South Asian countries’ grain trade links with China, Europe, Africa, and Latin America were weakened. Grain exports mainly converged in Africa, with Australia, the United States, and Latin America being the main exporters. The findings of this paper are helpful to identify countries facing high grain security risks and can shed light on policy measures to address the dual challenge for guaranteeing global grain security in the post-epidemic era.
1. Introduction
Both food production and trade are important components of food security. Food production strongly correlates with food trade where changes in food production will lead to significant fluctuations and strong uncertainty in food trade, such as restrictive food trade policies and exacerbating international food price fluctuations, which will affect global food affordability and availability. The novel coronavirus (COVID-19) pandemic has had far-reaching impacts on many aspects of daily life, including the global food trade. With lockdowns, border closures, and disrupted supply chains, the pandemic has caused significant disruptions to global food systems, affecting food production, distribution, and trade [1]. As a result, countries around the world are grappling with issues such as food insecurity, rising food prices, and reduced access to essential food products [2]. With more than 1.9 billion people, South Asia is home to one-fourth of the world’s population and has the highest number of people living in poverty. As an important region in global grain production and trade, the Bangladesh–India–Myanmar region contributes one-third of the global paddy rice yield [3]. India contributes 20% of the global paddy rice supply and 12% of the global wheat supply. As the fourth largest paddy rice exporter, Pakistan contributes about 9.2% of global paddy rice exports [4]. The pandemic has caused disruptions in the food supply chain, affecting the availability and affordability of food in South Asia. The outbreak of the locust plague in Pakistan has exacerbated the existing challenges in the food and agricultural sector in South Asia [5]. Because of the dual challenge of COVID-19 and the locust plague, some South Asian countries are expected to experience further reductions in grain production and impose further restrictions on exports, thus severely affecting global grain trade patterns and security [6]. As the pandemic continues to evolve, it is essential to address the challenges facing South Asia’s food systems and understand the extent of the COVID-19 impact on world food trade and the measures being taken to address these challenges.
Natural disasters such as droughts, floods, hurricanes, earthquakes, and extreme weather events pose a major challenge to global food security by causing sharp drops in crop yield and supply [7,8]. For example, the 2011 floods in Thailand disrupted rice production, causing a global rice shortage and increasing the price of rice by 25%. Similarly, the 2010 earthquake in Haiti destroyed much of the country’s infrastructure, including ports and warehouses, disrupting food imports and causing food prices to skyrocket. A considerable amount of literature has been published to examine the impacts of natural disasters on world food trade [9,10,11]. Cheng et al. [12] analyzed the threat posed by temperature anomalies on the agriculture sector and found that the threat goes beyond agricultural production to all aspects across food supply and demand channels, further amplifying volatility in food markets. Vishwakarma et al. [13] analyzed the impact of extreme weather stress on global wheat trade and suggested that the current international trade network should be enhanced by considering the patterns of extreme weather stress to yield synchrony among countries. Feng et al. [14] explored the impact of the Russia–Ukraine crisis on food security and trade pattern with a structural general equilibrium trade model. Overall, these studies suggest that natural disasters can have significant and far-reaching impacts on world food trade, affecting both production and consumption patterns and leading to price volatility and supply chain disruptions [8,11,15,16].
With the uncertainty of the COVID-19 pandemic, the evolution of grain production and trade patterns has become fluctuant and unstable. There have been several studies examining the impact of COVID-19 on world food trade since the outbreak of the pandemic in early 2020. Previous studies have reported how the pandemic has disrupted global supply chains, affected trade flows and prices, and impacted food security [17,18,19]. Glauber et al. [6] found that the COVID-19 pandemic exacerbated the labor shortages worldwide, and the logistical restrictions also escalated the reduction in grain yields. Several studies also documented that the pandemic disrupted global food supply chains, causing significant losses for farmers and processors, and led to reduced availability and increased prices for food in many countries [19,20,21]. It has been noted that COVID-19 motivated some countries to formulate restrictive policies on grain exports, which would reduce trade, exacerbate the fluctuations in international grain prices [22], and destroy current global grain trade patterns [23]. Recent evidence suggests that these restrictions have already affected the global grain supply chain and caused great losses to developing countries that rely on grain imports [24,25,26].
The GTAP (Global Trade Analysis Project) model is a widely used tool for analyzing the impacts of international trade policies and economic developments on different sectors of the economy. One of the key strengths of the GTAP model is its ability to capture the complex interdependencies among different sectors of the economy, including agriculture, manufacturing, and services [27]. This allows researchers to analyze the effects of changes in food trade policies on a range of economic outcomes, including prices, output, and employment. Moreover, the model is capable of simulating different scenarios, which enables policymakers and researchers to assess the impacts of various policy options. The GTAP model has been widely used in analyzing the impacts of tariff policies, trade restrictions, climate change, and infectious disease on global food trade [28,29,30]. Hoang et al. [31] used the GTAP model to analyze the impacts of trade policies on food security in developing countries and found that trade liberalization could have both positive and negative impacts on food security. Xie et al. [32] analyzed the regional and global impact of the grain trade ban and found that it will end in an increase in global food prices and a sharp drop in food trade. Guan et al. [33] simulated the impact of the strictness and duration of the control measures on the economy during the epidemic period, and found that the length of time for the implementation of prevention and control measures will lead to different economic costs. Zhai et al. [34] uses the GTAP model to evaluate the impact of grain export restrictions on world food security during the COVID-19 pandemic. Studies also simulated how cooperation programs such as trade cooperation, production cooperation, and prevention and control cooperation will help to better deal with the COVID-19 pandemic [35,36]. Therefore, with flexibility, transparency, and openness, the GTAP model has been widely used to analyze a variety of trade-related issues, allowing for a comprehensive analysis of trade flows and their effects on different sectors and countries.
The COVID-19 pandemic has brought unprecedented challenges to the global food system, and the evolution of the locust plague in Pakistan will exacerbate the vulnerabilities to global food supply chains, thus affecting the global food security and trade [25]. Although previous studies explored how the COVID-19 pandemic has affected grain trade patterns or how the natural disasters will affect the grain production, the influence of COVID-19 pandemic stress and synchronous crop yield anomalies due to natural disasters such as the locust plague on trade linkages among countries remains unexplored. Moreover, only a few studies have probed into their combined impacts [37]. South Asia is one of the largest contributors to the world’s paddy rice and wheat production; the COVID-19 pandemic and the locust plague have severely affected the food production system and led to lockdown and trade restrictions which have severely impacted the international grain trade and undermined grain security. Considering the complex relationships between grain production change and grain trade patterns in the context of the COVID-19 pandemic accompanied by the locust plague, both have adversely and simultaneously affected global grain trade patterns. This study focused on the changes in paddy rice and wheat production due to the trade restrictions caused by COVID-19 and the locust plague in the South Asia. The GTAP model was introduced to comprehensively and quantitatively analyze their effects on grain production, prices, and trade patterns in South Asian countries. The purpose was to identify countries facing high grain security risks, propose policy measures addressing the dual challenge, and provide a scientific basis for guaranteeing global grain security in the post-epidemic era.
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Research Framework
In 2020, the impact of COVID-19 on the global grain supply and the destruction of crop production by the locust plague posed serious threats to the grain trade patterns of South Asian countries. The effects of the labor shortages and logistical restrictions caused by COVID-19 on grain production were complicated by the locust plague sweeping some South Asian countries. Moreover, the export restrictions imposed by the major grain-producing countries in South Asia aggravated the damage caused by COVID-19 to the supply of grain. The theoretical framework of the combined impacts of COVID-19 and locust plague on grain trade patterns in South Asia is shown in Figure 1.
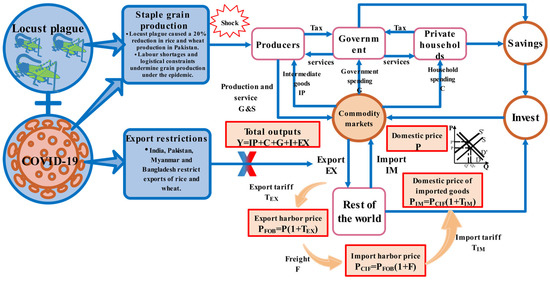
Figure 1.
Theoretical framework to analyze combined impacts of COVID-19 and locust plague on grain trade patterns in South Asia.
In the short term, the locust plague directly shocked grain production in some South Asian countries, leading to large-scale crop losses for food producers. At the same time, the COVID-19 outbreak resulted in labor shortages and logistical constraints, triggering a secondary attack on grain production. Under the dual pressure, the policy of restricting grain exports was able to secure domestic grain supplies to some extent, but caused domestic grain prices to fall. Lower domestic grain prices reversely harmed the producers’ economic interests, resulted in reduced crop yields, and weakened incentives for agricultural production. In the long run, trade restrictions blocked the channels of grain outflow and hindered the necessary production inputs for producers, thus reducing the availability of grain markets. Although the final domestic price was lower than the international price (after price increases), it was still higher than it would have been in the absence of trade restrictions. For countries that relied on grain imports, the trade restrictions, risks, and uncertainties of the international grain market, reduction in grain exports, and the reduced grain supply in international grain markets led to panic purchases by grain importers and increased demand for grain commodities. As a result, the import prices of grain commodities increased drastically and exacerbated grain insecurity for developing countries that relied on grain imports.
2.2. The GTAP Model
The GTAP model is a multi-country and multisector economic equilibrium model developed by Purdue University in the United States. Being a comparative static analytical model, it assumes that markets are perfectly competitive and that the returns to production scale are constant [38]. The sub-models for the production, consumption, government expenditures, and other economic behaviors were constructed for each country. These sub-models were connected via the trade sector. The equilibrium between total supply and total demand was achieved to maximize producer profits and consumer utilities, which jointly determine the values of endogenous variables (prices, wages, etc.). The GTAP database tracks reconciled bilateral trade data between countries. All countries are linked together by commodity trading. The model can analyze the effects of different policies on the production, price changes, GDP, and import and export trading of each sector in each country.
In the model, the production structure is a nested constant elasticity of substitution (CES) function (Figure 2). Each product is a combination of intermediate products and factors of production. There are five types of production factors: land, capital, skilled labor, unskilled labor, and natural resources. Intermediate products comprise domestic and foreign products in the CES function, where different foreign products are aggregated into a single imported product. For the factor market, the model allows flows of capital and labor between production sectors, as well as the partial flow of land between crop production sectors.
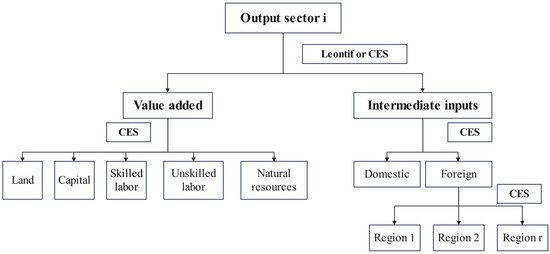
Figure 2.
Production structure for the GTAP model.
Each country in the model has only one national account, which accumulates all tax revenues and endowment incomes. The total income is distributed to private expenditures, savings, and government expenditures via the Cobb–Douglas function. Private and government expenditures are incorporated into a nonhomogeneous constant difference elasticity (CDE) function and Cobb–Douglas function, respectively. The sub-utility function of investment expenditures (total investment) is based on the Leontief effect parameter. The total investment is derived from the identical equation between nominal investment and savings, which are the sum of domestic savings and net capital inflows from foreign economic entities. Then, the investment expenditures on composite commodities are decomposed into the demands for domestic commodities and imported commodities by a CES sub-utility preference function. The Cobb–Douglas equation has the following form:
where is utility, A is the technology level parameter, X and Y are products, and α denotes the share of X gained in .
There are two international sectors, which are the international bank and the international transport sector, in the GTAP model. The savings of various countries are aggregated into the international bank and distributed among countries according to the return on invested capital (ROIC). The international transport sector is mainly responsible for transporting products between regions, striking a balance among cost, insurance and freight (CIF), and free on board (FOB), while linking up countries around the world through bilateral trade.
The GTAP model uses a series of price equations to connect various regions and departments around the world:
where is the FOB price, is the CIF price, is the domestic market price of the export countries, is the domestic market price of the import countries, is the export tariff, is the import tariff, and is the iceberg cost in international trade.
In the GTAP model, due to production reduction and trade restrictions, the domestic price of grain and the imposing tariffs will increase, leading to an uncertain demand and supply of the grain trade. This study performed a simulation using data from 2014 as the benchmark year in the GTAP Model Version 10 Database [39] and quantitatively analyzed the combined effects of COVID-19 and the locust plague on grain production, prices, and trade patterns in South Asian countries.
2.3. Model Specification
Driven by multiple factors of grain production and trade policies, grain trade patterns in South Asia are constantly evolving. Their evolution is closely related to national grain security. Affected by the global pandemic, India, Myanmar, Pakistan, and Bangladesh imposed restrictions on processed rice exports to all countries in the world. The locust plague of Pakistan has invaded 38% of the land and reduced wheat production by 15% [40]. South Asia as a whole has a sound crop growth status, and some South Asian countries have seen increases in grain yields. The wheat yield of India in 2020 was about 4% more than that in 2019. The wheat yields of Bhutan and Nepal also have been increasing, but those of Bangladesh and Myanmar in 2020 were almost the same as those in 2019 [2]. This study constructed a comprehensive scenario analysis of crop yields and trade restrictions affected by COVID-19 and the locust plague considering the grain production status in South Asia countries. Specifically, for paddy rice and wheat, Pakistan saw a 20% reduction in crop yield, but India, Bhutan, and Nepal reported increases of 10%, 5%, and 5%, respectively, while the crop yields of Myanmar and Bangladesh remained unchanged. Furthermore, India, Pakistan, Myanmar, and Bangladesh restricted their exports of these crops. The specific scenarios were defined and the GTAP model parameters were quantified as shown in Table 1.

Table 1.
Parameter assignment of scenarios.
The GTAP database (Version 10) covers 121 countries and 65 aggregate regions of the world for each reference year [39]. The dimensionally large input–output tables and the detailed trade and investment information make the GTAP model capable of tackling any regional setting or aggregation level, while keeping the size of the intertemporal model manageable. In this study, the 121 countries were merged into 23 regional sets, and 65 production sectors were merged into 20 industrial sectors, as shown in Table 2.

Table 2.
Regional sets and industrial sectors in GTAP database (Version 10).
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. Changes in the Scale of Grain Trade
Only India, Myanmar, Bangladesh, Pakistan, and Nepal saw declines in paddy rice, processed rice, and wheat exports, whereas other regions in the world all experienced increases in grain exports. There were regional differences in the intensity of changes (Figure 3a). India, Myanmar, Bangladesh, and Pakistan imposed restrictions on grain exports, which led to a sharp shrinkage in their exports. Nepal was highly dependent on grain imports from India; thus, India’s restrictions on grain exports caused a reduction in Nepal’s grain imports and the decline in the domestic grain supply led to a rise in domestic grain prices [41]. The domestic prices of paddy rice, processed rice, and wheat rose by 9.94%, 10.56%, and 7.48%, respectively (Figure 4). The rise in domestic grain prices further weakened the competitiveness of its grain exports on the international grain market and decreased its paddy rice, processed rice, and wheat exports by 33.00%, 15.39%, and 58.90%, respectively (Table S1). In contrast, Bhutan’s increase in grain yield ensured a sufficient supply of domestic grain, and the drop in its domestic grain prices strengthened its comparative advantages in grain export. Its paddy rice, processed rice, and wheat exports increased by 44.11%, 71.60%, and 47.08%, respectively. In addition, the processed rice exports of the United States, Europe, and China increased by 101%, 62%, and 41%, respectively, while their paddy rice exports increased by 2%, 16%, and 40%, respectively (Table S1).
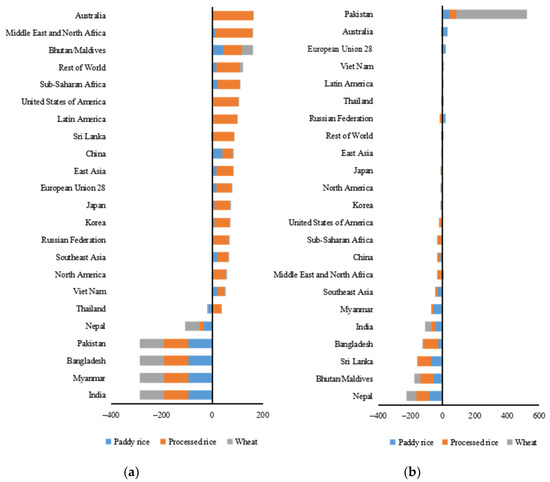
Figure 3.
Percentage changes in (a) exports and (b) imports of grain by country.
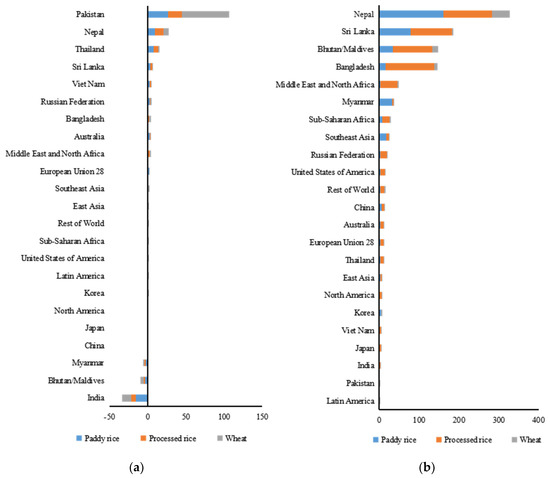
Figure 4.
Percentage changes in (a) domestic and (b) import prices of grains by country.
All South Asian countries, except Pakistan, saw a significant decline in grain imports (Figure 3b). The restrictive policies on grain exports led to a reduction in the international grain supply and aggravated the upward pressure on international grain prices [42]. The paddy rice and wheat import prices of Nepal, Bhutan, the Maldives, Bangladesh, Sri Lanka, and other countries increased sharply. For instance, the paddy rice, processed rice, and wheat import prices of Nepal increased by 162%, 121%, and 44%, respectively (Figure 4, Table S2). The general rise in grain import prices led to reduced grain imports. The paddy rice and processed rice imports of Sri Lanka, Nepal, Bhutan and Maldives, and Bangladesh dropped significantly. Their processed rice imports dropped by 81%, 77%, 80%, and 89%, respectively. In contrast, Pakistan experienced a reduction in domestic grain yield due to the locust plague. Thus, the reduced domestic supply led to a surge in demand for imports [43]. The paddy rice, processed rice, and wheat imports of Pakistan increased by 44%, 42%, and 438%, respectively.
3.2. Changes in Grain Trade Patterns
As can be seen from the changes in the grain exports of the major regions (Figure 5a–c), COVID-19 and the locust plague greatly affected global grain trade patterns in 2020. The trade links of South Asian countries with China, Europe, Africa, and Latin America were weakened while global grain exports mainly converged in Africa. Moreover, the scale of the grain trade declined among South Asian countries. After India imposed restrictions on paddy rice and wheat exports, its paddy rice exports to Nepal declined markedly by 46.67%, and its wheat exports to Bangladesh declined by 31.28%. The substantial rise in the domestic grain prices of Pakistan further weakened the competitiveness of its grain exports, thus reducing the export volumes. Pakistan’s wheat exports to Bhutan declined markedly by 68.25%. The restrictions on grain exports imposed by some countries in South Asia (an important region in global grain production and trade) accelerated the adjustments of grain trade patterns by other regions. Myanmar’s paddy rice exports to China and processed rice exports to Europe declined markedly by 78.28% and 33.39%, respectively. The processed rice exports of India, Pakistan, and Bangladesh to the Central, Eastern, and Northern African region decreased by 51.95%, 26.99%, and 25.15%, respectively. The wheat exports of India to the same region decreased by 34.54%, and the wheat exports of Bangladesh to Latin America declined markedly by 84.73%. Not receiving the same volume of grain exports from South Asia as before, Africa began to import grain from other regions; thus, the processed rice exports from Australia, the United States, and Latin America to the African region increased by 144.98%, 88.36%, and 76.56%, respectively. In contrast, the increases in the grain yields of Bhutan and the Maldives led to lower domestic grain prices, which heightened their competitiveness in the international grain market. Their paddy rice exports to Europe and wheat exports to Central, Eastern, and Northern Africa increased by 19.50% and 23.26%, respectively. The export restrictions imposed by some countries because of COVID-19 disrupted the trade flows of staple food grains such as paddy rice and wheat [44], affected the sustainability of the supply chain between major grain importers and exporters [30], and weakened the intensity of trade between South Asian countries. Such restrictions also significantly and negatively affected the grain exports of China, Africa, Europe, Latin America, and other regions.
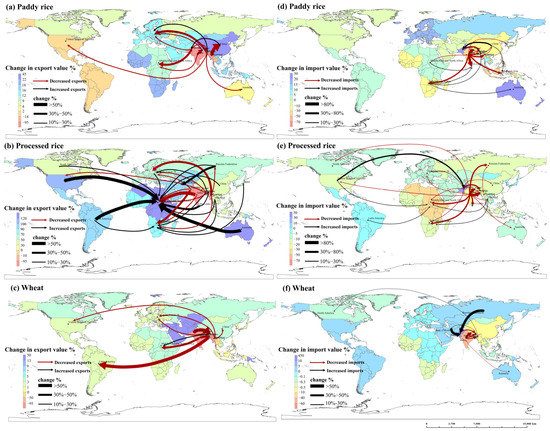
Figure 5.
Changes in (a–c) exports and (d–f) imports of major countries and regions after grain export restrictions in South Asian countries. Note: Countries with absolute value changes in exports greater than 10% were selected.
The changes in the grain imports of the major regions (Figure 5d–f) shifted the focus of global grain imports to the United States, China, and Russia. The grain imports of South Asia were significantly affected by COVID-19 and the locust plague. A substantial rise in grain imports was observed only in Pakistan, whereas the other countries had shrinking grain imports. Sri Lanka, Nepal, and Bangladesh were highly dependent on grain imports from India [45,46]; thus, India’s restrictions on grain exports weakened the intensity of their grain trade. The paddy rice imports of Sri Lanka and Nepal from India declined significantly by 97.31% and 91.62%, respectively. The processed rice imports of Nepal and Bangladesh from India declined by 80.01% and 86.28%, respectively, and their wheat imports from India declined by 65.83% and 48.10%, respectively. The domestic paddy rice and processed rice prices of Pakistan rose more than those of other regions in the world; hence, Pakistan’s competitiveness in grain exports further weakened. It is worth noting that Bhutan’s paddy rice and Pakistan’s processed rice imports declined markedly by 58.05% and 74.45%, respectively. The locust plague also severely affected the domestic grain yield of Pakistan, whose rise in domestic grain prices relative to the prices of imported grain weakened its comparative advantages in domestic grain production. Hence, consumers and producers in the domestic grain production and processing industry began to utilize imported grain instead of domestic grain. Consequently, Pakistan increased its wheat imports from Russia by 138.60%, paddy rice imports from China by 45.36%, and processed rice imports from the United States by 36.97%.
3.3. Discussion
The COVID-19 pandemic and the constant outbreak of natural disasters or geopolitical conflicts have made the international situation more uncertain and complex. This has led to pessimistic expectations of future food supply and panic hoarding of food around the world. Affected by this, international food prices have increased significantly and further destabilized the international agricultural product market. As a result of the uncertainties induced by COVID-19 and the locust plague, some South Asian countries have taken restrictive measures on international flows, thereby intensifying the deglobalization trend, severely impacting the international grain trade, and undermining grain security [45,47]. This study analyzed the combined impact of COVID-19 and the locust plague on the grain trade patterns of South Asian countries in 2020. The results showed that grain supply interruptions and grain price increases in South Asian countries were particularly prominent and seriously threatening to their national grain security.
South Asia is an important region in global grain production and trade. Its restrictive policies on grain exports have led to a reduction in the international grain supply and aggravated the upward pressure on international grain prices in developing countries, such as Nepal, Sri Lanka, and Bangladesh, that rely on grain imports. Countries such as Nepal and Sri Lanka are highly dependent on processed rice imports from India and are vulnerable to the effects of export restrictions imposed by India because such restrictions would directly affect their domestic grain supplies and lead to fluctuations in their domestic grain prices. To cope with these consequences, South Asian countries require regional and global cooperation. Firstly, the role of the South Asian Association for Regional Cooperation (SAARC) Food Bank should be strengthened [48] to provide grain reserves and buffers, as well as guarantee to the regional grain security, in the short term. Secondly, active efforts should be made to achieve legally effective trade agreements with grain exporters to overcome grain trade barriers in order to maintain long-term, stable grain trade relations [49]. Therefore, efforts should be made to expand import channels and avoid dependence on imports from individual countries in order to enhance the stability of national grain trades, guarantee uninterrupted supply chains of staple food grains, and guard against grain shortages and soaring prices [45].
In addition, it is necessary to strengthen mutual assistance and cooperation with countries outside the region in the whole agricultural chain, including production, consumption, reserving and trading. For example, the national grain reserve system in South Asian countries should be improved to alleviate the impacts of emergencies such as COVID-19 and the locust plague on domestic grain supplies. Although there are established national grain reserve systems in some South Asia countries, such as the Food Corporation of India in India and the Pakistan Agricultural Storage and Services Corporation in Pakistan, the quality of storage facilities and the management of the stocks have been a cause of concern. Other countries in South Asia, such as Nepal, Sri Lanka, and Bhutan, do not have well-established national grain reserve systems, and the countries rely heavily on imports to meet their food requirements.
Locusts are known to be one of the most destructive pests for crops, and the current outbreak in Pakistan has resulted in a significant decrease in agricultural yields [50]. According to reports, the locust in Pakistan resulted in a loss of approximately 40% of the wheat crop in some areas, while, in other regions, the yield losses were as high as 70% [40]. The locust plague in Pakistan has not only affected the country’s grain production and trade but has also had a significant impact on South Asia’s overall grain production and trade. Pakistan is a significant exporter of wheat, and the decrease in production has led to a decrease in exports. This has resulted in a shortage of wheat supply in the region, leading to higher wheat prices in neighboring countries such as Afghanistan, India, and Bangladesh. The long-term effects of the outbreak are yet to be seen, but it is clear that efforts must be made to control the locust population and prevent future infestations to safeguard the region’s food security. For Pakistan, it is necessary to engage in the China–Pakistan Economic Corridor initiative and cooperate with China in establishing an expert group to provide technical support for closely tracking and monitoring the locust plague in targeted regional prevention in order to control the plague’s effects on grain production and guarantee national grain security.
4. Conclusions
The outbreak of locusts has caused extensive crop losses in affected areas, which has seriously damaged food production. At the same time, labor shortages and logistical constraints under the COVID-19 epidemic led to a decline in food production. South Asia is one of the largest contributors to world’s paddy rice and wheat production. The COVID-19 pandemic and the locust plague have severely affected the food production system and led to lockdown and trade restrictions, thereby intensifying the deglobalization trend, severely impacting the international grain trade, and undermining grain security. Our study focused on the food trade issue in the context of paddy rice and wheat production reduction in South Asia caused by COVID-19 epidemic and locusts plague, which significantly exacerbated the vulnerabilities to global food supply chains. This study formulated a scenario of paddy rice and wheat yields with trade restrictions imposed in response to the combined impact of COVID-19 and the locust plague in 2020, and then applied the GTAP model to investigate the characteristics and mechanisms of changes in the grain trade patterns of South Asia.
In this research, the grain production, grain imports and exports, and domestic and trade prices were comprehensively analyzed. As for grain production, we found that the locust plague of Pakistan has invaded 38% of the land and reduced wheat production by 15%. The overlaid restrictive policies on grain exports during COVID-19 have led to a reduction in the international grain supply and aggravated the upward pressure on international grain prices. Global grain imports and exports have been affected to varying degrees. After India, Myanmar, Bangladesh, and Pakistan imposed restrictions on their grain exports, and global trade shrank sharply, with total imports and exports shrinking by 5.79% and 1.41%, respectively. This also led to international food prices changing significantly. For instance, the paddy rice, processed rice, and wheat import prices of Nepal increased by 162%, 121%, and 44%. The increased food price will significantly influence the food affordability and accessibility, especially for developing countries that are heavily dependent on imports. Nepal, Sri Lanka, and Bangladesh saw substantial rises in the import prices of grain (especially processed rice, whose import prices rose more than 100%) and were among the regions that saw the highest rise in grain import prices. The general rise in grain import prices led to a reduction in grain imports. The processed rice imports of Sri Lanka, Nepal, Bhutan and Maldives, and Bangladesh dropped by 81%, 77%, 80%, and 89%, respectively. Because of the severe impact of the locust plague, Pakistan experienced a reduction in domestic grain yield, which further reduced its domestic supply and led to a surge in imports.
The effects of COVID-19 and the locust plague on the supply chain caused a shortage of staple food grains in vulnerable countries and harmed the grain trade relations of the world, thus accelerating the adjustments of global trade patterns. South Asia’s trade links with China, Europe, Africa, and Latin America were weakened; hence, global grain exports have mainly converged in Africa. The processed rice exports from Australia, the United States, and Latin America to the Central, Eastern, and Northern Africa increased by 144.98%, 88.36%, and 76.56%, respectively. The changes in the grain imports of South Asia were significantly impacted by COVID-19 and the locust plague. A substantial rise in grain imports was observed only in Pakistan, whereas reduced grain imports were observed in other countries. Because of the severe impact of the locust plague, Pakistan saw a substantial rise in wheat imports from Russia by 138.60%, paddy rice imports from China by 45.36%, and processed rice imports from the United States by 36.97%.
The outbreak and spread of COVID-19 and the locust plague are highly uncertain. This study probed into the combined impacts COVID-19 pandemic stress and synchronous crop yield anomalies due to natural disasters such as the locust plague on food production and trade which were rarely discussed in previous studies. By analyzing the combined impacts of COVID-19 and the locust plague on grain production, prices, and trade patterns in South Asian countries, we can identify the bottleneck factors restricting grain security and provide a scientific basis for formulating strategies to guarantee global grain security. The main limitation of this research is that the scenario design was mainly focused on production change and export restriction, which was the main influence of COVID-19 and the locust plague. However, many other factors such as inflation or geopolitical conflicts that can influence the trade patterns were not considered in our study. Therefore, more comprehensive and refined scenario simulations are needed in the future.
Supplementary Materials
The following supporting information can be downloaded at: https://www.mdpi.com/article/10.3390/agriculture13061212/s1, Table S1: Percentage changes in imports and exports of grain by country; Table S2: Percentage changes in domestic prices and import prices of grains by country.
Author Contributions
Conceptualization, Q.Z. and Y.Z.; methodology, Q.Z. and S.L.; software, S.L.; formal analysis and validation, Q.Z., S.L. and Y.Z.; manuscript writing, Q.Z. and S.L., revising, Y.Z. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This research was funded by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (Grant No. 31861143015 and Grant No. 72004074).
Institutional Review Board Statement
Not applicable.
Data Availability Statement
The data presented in this study are available on request from the corresponding author.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
References
- Laborde, D.; Martin, W.; Swinnen, J.; Vos, R. COVID-19 Risks to Global Food Security. Science 2020, 369, 500–502. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Crop Prospects and Food Situation|GIEWS—Global Information and Early Warning System on Food and Agriculture|Food and Agriculture Organization of the United Nations. Available online: https://www.fao.org/giews/reports/crop-prospects/en/ (accessed on 25 March 2023).
- Cagliarini, A.; Rush, A. Economic Development and Agriculture in India. RBA Bull. 2011, 15–22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Azam, A.; Shafique, M. Agriculture in Pakistan and Its Impact on Economy. A Review. Inter. J. Adv. Sci. Technol. 2017, 103, 47–60. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peng, W.; Ma, N.L.; Zhang, D.; Zhou, Q.; Yue, X.; Khoo, S.C.; Yang, H.; Guan, R.; Chen, H.; Zhang, X. A Review of Historical and Recent Locust Outbreaks: Links to Global Warming, Food Security and Mitigation Strategies. Environ. Res. 2020, 191, 110046. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Glauber, J.; Laborde Debucquet, D.; Martin, W.; Vos, R. COVID-19: Trade Restrictions Are Worst Possible Response to Safeguard Food Security. In COVID-19 and Global Food Security; IFPRI: Washington, DC, USA, 2020; pp. 66–68. [Google Scholar]
- Puma, M.J.; Bose, S.; Chon, S.Y.; Cook, B.I. Assessing the Evolving Fragility of the Global Food System. Environ. Res. Lett. 2015, 10, 024007. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Davis, K.F.; Downs, S.; Gephart, J.A. Towards Food Supply Chain Resilience to Environmental Shocks. Nat. Food 2021, 2, 54–65. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Faling, M. Framing Agriculture and Climate in Kenyan Policies: A Longitudinal Perspective. Environ. Sci. Policy 2020, 106, 228–239. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fair, K.; Bauch, C.; Anand, M. Dynamics of the Global Wheat Trade Network and Resilience to Shocks. Sci. Rep. 2017, 7, 7177. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ozer, O.O.; Ozden, A.; Kan, M. Impact of Global Climate Change on Agricultural Production: Balkan Countries in 2050. J. Environ. Prot. Ecol. 2020, 21, 151–158. [Google Scholar]
- Cheng, S.; Li, X.; Cao, Y. Global Evidence of the Exposure-Lag-Response Associations between Temperature Anomalies and Food Markets. J. Environ. Manag. 2023, 325, 116592. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vishwakarma, S.; Zhang, X.; Lyubchich, V. Wheat Trade Tends to Happen between Countries with Contrasting Extreme Weather Stress and Synchronous Yield Variation. Commun. Earth Environ. 2022, 3, 1–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feng, F.; Jia, N.; Lin, F. Quantifying the Impact of Russia-Ukraine Crisis on Food Security and Trade Pattern: Evidence from a Structural General Equilibrium Trade Model. China Agric. Econ. Rev. 2023, 15, 241–258. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sam, A.S.; Abbas, A.; Padmaja, S.S.; Sathyan, A.R.; Vijayan, D.; Kaechele, H.; Kumar, R.; Mueller, K. Flood Vulnerability and Food Security in Eastern India: A Threat to the Achievement of the Sustainable Development Goals. Int. J. Disaster Risk Reduct. 2021, 66, 102589. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wood, S.A.; Smith, M.R.; Fanzo, J.; Remans, R.; DeFries, R.S. Trade and the Equitability of Global Food Nutrient Distribution. Nat. Sustain. 2018, 1, 34–37. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wells, C.R.; Sah, P.; Moghadas, S.M.; Pandey, A.; Shoukat, A.; Wang, Y.; Wang, Z.; Meyers, L.A.; Singer, B.H.; Galvani, A.P. Impact of International Travel and Border Control Measures on the Global Spread of the Novel 2019 Coronavirus Outbreak. PNAS 2020, 117, 7504–7509. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Udmale, P.; Pal, I.; Szabo, S.; Pramanik, M.; Large, A. Global Food Security in the Context of COVID-19: A Scenario-Based Exploratory Analysis. Prog. Disaster Sci. 2020, 7, 100120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Toffolutti, V.; Stuckler, D.; McKee, M. Is the COVID-19 Pandemic Turning into a European Food Crisis? Eur. J. Public Health 2020, 30, 626–627. [Google Scholar]
- Aday, S.; Aday, M.S. Impact of COVID-19 on the Food Supply Chain. Food Qual. Saf. 2020, 4, 167–180. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Erokhin, V.; Gao, T. Impacts of COVID-19 on Trade and Economic Aspects of Food Security: Evidence from 45 Developing Countries. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2020, 17, 5775. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cao, L.; Li, T.; Wang, R.; Zhu, J. Impact of COVID-19 on China’s Agricultural Trade. China Agric. Econ. Rev. 2020, 13, 1–21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barua, S. COVID-19 Pandemic and World Trade: Some Analytical Notes. SSRN Electron. J. 2020. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reardon, T.; Bellemare, M.F.; Zilberman, D. How COVID-19 May Disrupt Food Supply Chains in Developing Countries. In COVID-19 and Global Food Security; IFPRI: Washington, DC, USA, 2020; pp. 78–80. [Google Scholar]
- Falkendal, T.; Otto, C.; Schewe, J.; Jägermeyr, J.; Konar, M.; Kummu, M.; Watkins, B.; Puma, M.J. Grain Export Restrictions during COVID-19 Risk Food Insecurity in Many Low-and Middle-Income Countries. Nat. Food 2021, 2, 11–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Anderson, K. Trade-Related Food Policies in a More Volatile Climate and Trade Environment. Food Policy 2022, 109, 102253. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hertel, T.W. Global Trade Analysis: Modeling and Applications; Cambridge University Press: Cambridge, UK, 1997. [Google Scholar]
- Siriwardana, M.; Yang, J. GTAP Model Analysis of the Economic Effects of an Australia-China FTA: Welfare and Sectoral Aspects. Glob. Econ. Rev. 2008, 37, 341–362. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peters, G.P.; Andrew, R.; Lennox, J. Constructing an Environmentally-Extended Multi-Regional Input-Output Table Using the Gtap Database. Econ. Syst. Res. 2011, 23, 131–152. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arouna, A.; Soullier, G.; del Villar, P.M.; Demont, M. Policy Options for Mitigating Impacts of COVID-19 on Domestic Rice Value Chains and Food Security in West Africa. Glob. Food Secur.-Agric. Policy 2020, 26, 100405. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hoang, H.K.; Meyers, W.H. Price Stabilization and Impacts of Trade Liberalization in the Southeast Asian Rice Market. Food Policy 2015, 57, 26–39. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xie, W.; Huang, J.; Wang, J.; Cui, Q.; Robertson, R.; Chen, K. Climate Change Impacts on China’s Agriculture: The Responses from Market and Trade. China Econ. Rev. 2020, 62, 101256. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guan, D.; Wang, D.; Hallegatte, S.; Davis, S.J.; Huo, J.; Li, S.; Bai, Y.; Lei, T.; Xue, Q.; Coffman, D. Global Supply-Chain Effects of COVID-19 Control Measures. Nat. Hum. Behav. 2020, 4, 577–587. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhai, L.; Yuan, S.; Feng, Y. The Economic Effects of Export Restrictions Imposed by Major Grain Producers. Agric. Econ. 2022, 68, 11–19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, Y.; Hao, X.; Hu, Y.; Lu, Z. The Impact of the COVID-19 Pandemic on China’s Manufacturing Sector: A Global Value Chain Perspective. Front. Public Health 2021, 9, 683821. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thube, S.D.; Delzeit, R.; Henning, C.H. Economic Gains from Global Cooperation in Fulfilling Climate Pledges. Energy Policy 2022, 160, 112673. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, Z.; Elomri, A.; El Omri, A.; Kerbache, L.; Liu, H. The Compounded Effects of COVID-19 Pandemic and Desert Locust Outbreak on Food Security and Food Supply Chain. Sustainability 2021, 13, 1063. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hertel, T.; Powell, A.; Frisvold, G.; Gehlhar, M.; Gray, D.; Hanslow, K.; Huff, K.; Ianchovichina, E.; Kuhn, B.; Lanclos, D.K. Global Trade Analysis: Modeling and Applications; Cambridge University Press: Cambridge, UK, 2015. [Google Scholar]
- Desert Locust Situation In Pakistan|FAO in Pakistan|Food and Agriculture Organization of the United Nations. Available online: https://www.fao.org/pakistan/resources/in-depth/desert-locust-situation-in-pakistan/en/ (accessed on 25 March 2023).
- The GTAP Data Base: Version 10. Available online: https://ideas.repec.org/a/gta/jnlgea/v4y2019i1p1-27.html (accessed on 25 March 2023).
- Ceylan, F.; Özkan, B. Assessing Impacts of COVID-19 on Agricultural Production and Food Systems in the World and in Turkey. Gaziantep Univ. J. Soc. Sci. 2020, 19, 472–485. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fan, S.; Si, W.; Zhang, Y. How to Prevent a Global Food and Nutrition Security Crisis under COVID-19? China Agric. Econ. Rev. 2020, 12, 471–480. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Amanta, F.; Aprilianti, I. Indonesian Food Trade Policy during COVID-19. Policy Brief 2020, 1–7. [Google Scholar]
- Lin, B.-X.; Zhang, Y.Y. Impact of the COVID-19 Pandemic on Agricultural Exports. J. Integr. Agric. 2020, 19, 2937–2945. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Amjath-Babu, T.S.; Krupnik, T.J.; Thilsted, S.H.; McDonald, A.J. Key Indicators for Monitoring Food System Disruptions Caused by the COVID-19 Pandemic: Insights from Bangladesh towards Effective Response. Food Secur. 2020, 12, 761–768. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rasul, G. Twin Challenges of COVID-19 Pandemic and Climate Change for Agriculture and Food Security in South Asia. Environ. Chall. 2021, 2, 100027. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Evenett, S.; Fiorini, M.; Fritz, J.; Hoekman, B.; Lukaszuk, P.; Rocha, N.; Ruta, M.; Santi, F.; Shingal, A. Trade Policy Responses to the COVID-19 Pandemic Crisis: Evidence from a New Data Set. World Econ. 2022, 45, 342–364. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Giap, B.M. COVID-19 Pandemic Impacts on Food Security in Central and West Asia: Key Issues and Strategic Options. Asian Dev. Bank 2020, 9, 1–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Paul, R.K.; Yeasin, M. COVID-19 and Prices of Pulses in Major Markets of India: Impact of Nationwide Lockdown. PLoS ONE 2022, 17, e0272999. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Showler, A.T.; Shah, S.; Khan, S.; Ullah, S.; Degola, F. Desert Locust Episode in Pakistan, 2018–2021, and the Current Status of Integrated Desert Locust Management. J. Integr. Pest Manag. 2022, 13, 1. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).