Abstract
Surface ozone (O3) pollution is an emerging environmental abiotic stress that poses substantial risks to crop yield losses and food security worldwide, and especially in China. However, the O3-induced detrimental effects on double-season rice have rarely been investigated at large scales and over relatively long temporal spans. In this study, we estimated the crop production reductions and associated economic losses for double-season rice across southern China during 2013–2019, using a high spatial resolution surface ozone reanalysis dataset and rice distribution maps, and county-level production data, in combination with a locally derived exposure-response function for rice. Results show that AOT40 (cumulative hourly O3 exposure above 40 ppb) presented generally increasing trends over growing seasons in 2013–2019, spanning from 4.0 to 7.1 ppm h and 6.1 to 10.5 ppm h for double-early rice and double-late rice, respectively. Moreover, O3-induced relative yield losses ranged from 4.0% to 6.6% for double-early rice and 6.3% to 11.1% for double-late rice. Over the seven years, ambient O3 exposure resulted in crop production losses of 1951.5 × 104 tons and economic losses of 8,081.03 million USD in total. To combat the O3-induced agricultural risks, measures such as stringent precursors emission reductions and breeding O3-resistant cultivars should be continuously implemented in the future.
1. Introduction
Surface ozone (O3) is a secondary air pollutant, mainly generated by complicated photochemical reactions of precursors such as volatile organic compounds (VOCs), nitrogen oxides (NOx), carbon monoxide (CO) and methane (CH4) [1]. With the excessive burning of fossil fuels and accelerated urbanization process since the Industrial Revolution, surface O3 concentration has experienced a substantial increase worldwide [2]. Model simulations indicate that the global average O3 concentration in the summer is predicted to progressively increase to 80 ppb by 2100 as a consequence of a three-fold increase in precursors emissions [3]. In recent years, both modeling and observational data demonstrate that the hourly peak of surface O3 concentration has declined in Europe and North America. In contrast, the temporal evolution trend of O3 is the contrary in Asia, especially in China [4]. During the past three decades, with sustained economic growth and accelerating urbanization, the ground-level O3 concentration in China has become increasingly serious, with a growth rate of 2.4 ppb per year [5] which has exceeded the pollution level of developed nations in Europe and the United States. At present, the concentration of ambient O3 in China has far surpassed the critical concentration threshold for human health and plant damages [6]. Spatially, the most seriously polluted areas are mainly concentrated in highly developed regions such as Beijing–Tianjin–Hebei, the Yangtze River Delta and the Pearl River Delta [7].
A high concentration of surface O3 would decrease crops’ chlorophyll content [8], accompanied by weakened photosynthesis [9] and accelerated leaf senescence [10,11], thus leading to a reduction in crop yields [12,13,14]. A recent global modeling study showed that the global production of crops including rice, corn, wheat and soybean was on average reduced by 4.4%, 6.1%, 7.1% and 12.4%, respectively, each year due to surface O3 pollution for the period 2010–2012 [15]. Notably, China suffered extremely serious crop losses, including 8.1% (21.5 million tons), 10.2% (25.5 million tons), 9.8% (13.6 million tons) and 19.4% (3.1 million tons) losses for rice, corn, wheat and soybeans, respectively. Meanwhile, Feng et al. [6] used observational O3 data provided by more than 1400 ground stations and also reported that the rice and wheat production decreased by 8.0% and 6.0%, respectively, due to O3 pollution over China in 2015, resulting in economic losses of up to USD 18.6 billion. In the future, the continued socioeconomic development in China would bring about increases in the emissions of O3 precursors (NOX and VOCs), in combination with the promotion of global warming to the formation of O3 [16], leading to a further increase in China’s surface O3 pollution in the coming decades. Therefore, the adverse influence of ambient O3 pollution is expected to worsen in China, and a special focus needs to be devoted to evaluating the potential impact of O3 on agricultural losses.
Rice is one of the most important staple crops in the world, serving as a primary source of food for over 40% of the global population [17]. China is the world’s largest rice producer, accounting for 30% of the global total rice production. Due to the population growth and the reduction of farmland during the rapid urbanization and industrialization process, the demand for rice yield and quality continues to rise. However, in recent years, numerous studies have shown that rice is a crop variety sensitive to O3 pollution [10,18,19]. Crucially, O3-induced rice yield loss has imposed great risks for food security, which is contrary to the sustainable development goal of ending hunger by 2030 proposed by the United Nations (SDG 2). Notably, southern China is the primary rice-planting region, especially for double cropping rice, contributing to more than 85% of rice production in China [20]. Since southern China is recognized as a hotspot of surface ozone pollution [4,21], the quantitative assessment of O3-induced rice yield reductions and associated economic losses in this region is urgently needed.
Over the past decades, scholars have employed open-top chambers (OTC) and free-air gas enrichment (FACE) facilities to quantitatively investigate crop yield loss in response to elevated O3 concentration gradients [22,23]. During the process, researchers have gradually established the O3-yield response relationships between O3 exposure dose and relative yield of many crops [24,25,26,27,28], which laid foundations for the assessment of ozone-induced crop losses at large scales. Among O3 exposure metrics, AOT40 (cumulative daytime O3 exposure exceeding an hourly threshold of 40 ppb) is the most widely used in reality since it takes into account both the ozone exposure concentration and exposure accumulation period. Additionally, AOT40 has the advantages of simple calculation and displaying significant linear correlations with crop yield losses [14], which promote its applicability in the regional assessment of agricultural losses induced by ozone stress. For instance, Sinha et al. [29] adopted AOT40-based exposure-yield response functions to quantify the crop losses caused by ozone pollution, and estimated relative yield losses of 27–41% for wheat, 21–26% for rice, 3–5% for maize and 47–58% for cotton in the Punjab and Haryana states of India. They also reported that Asian crop cultivars presented considerably higher sensitivities to O3-induced yield reductions in contrast with their counterparts in Europe and US. Likewise, Emberson et al. [30] also revealed that experimentally derived exposure-response functions established in North America led to an underestimation of the detrimental impacts of O3 on agricultural production in Asia. Therefore, directly using exposure-response functions from other countries may be problematic since crop responses to ozone stress could be differentiated due to the discrepancies in crop varieties and climatic conditions in various regions [24]. In other words, the establishment of AOT40-yield response functions for local crop cultivars provides a good prerequisite for crop yield reduction assessment caused by O3 pollution in the region [31]. For assessing the crop yield reductions in China, Wang et al. [26] employed OTC experiments to establish AOT40-relative-yield response relationships for Chinese wheat and rice cultivars. On this basis, Zhao et al. [32] utilized the AOT40-based response functions established by Wang et al. [26] and assessed that surface O3 pollution gave rise to the relative yield loss of wheat and rice of 9.86–36.05% and 7.25–23.87%, respectively, in the Yangtze River Delta region, and the total economic loss was USD 209.31 × 107 and USD 237.03 × 107.
Regional quantification of the impact of O3 pollution on crop yield requires the estimation of O3 exposure. Due to the frequent absence of O3 observational data, a large amount of research has relied on atmospheric chemical transport models (CTM) to simulate the concentration of O3 [33,34]. Avnery et al. [9] employed simulated ozone gridded data modeled by MOZART-2 to assess crop losses, and estimated O3-induced global yield losses of 3.9–15% for wheat, 8.5–14% for soybean and 2.2–5.5% for maize in 2000. However, the simulated O3 data based on the CTM models have substantial uncertainties in spatial resolution, emission inventories, chemistry and model parameterization [35,36], resulting in great discrepancies in estimated O3 exposure and associated crop loss estimates on the regional scale when using different chemical transport models [37,38]. Since 2013, China has established air quality monitoring stations across the country and provides hourly ambient ozone concentration monitoring data in each city. Therefore, some researchers turned to using ozone observational data to assess the impact of ambient O3 pollution on crop yield reduction instead of model-simulated data [6,39]. Although station-based O3 monitoring data increased the reliability of crop losses estimates in comparison with model-simulated counterparts, the spatial and temporal coverage of ground monitoring stations is limited, which masks the variability of ambient O3 over space and time [40]. Moreover, the distribution of monitoring stations is spatially uneven, and most of the stations are located in urban areas. Many studies have shown that O3 concentration in rural areas is higher than that over urban areas [41,42]. Hence, O3 observational data based on site monitoring may underestimate the pollution level in the rural areas where the crops are planted.
In addition, when calculating the O3 exposure, most of the existing studies took regional administrative units (province or city-levels) as the evaluation units and used the averaged O3 of all monitoring stations within the administrative boundary to represent the O3 exposure of crops. Finer evaluations at the county scale are relatively scarce, especially in south China where there is a highly spatially heterogenous region with a contribution of 99% of the double cropping paddy area in China [43]. It is generally considered by previous studies that the smaller the administrative units applied (e.g., assessment at the county level), the higher the accuracy of the yield loss estimates would be [44]. Nevertheless, the division of administrative boundaries is not able to delineate the locations of planted crops, thereby decreasing the accuracy of O3-induced crop loss estimates. Furthermore, considering the differences in O3 concentration along the rural–urban gradients as mentioned above, as well as the limited density of monitoring stations, the ozone pollution conditions over a region may not be well characterized by the averaged values of the observational data derived from the ground stations in that region. Consequently, using regional administrative boundaries instead of cropland maps could generate large uncertainties in crop loss estimates [20]. In other words, the introduction of cropland distribution data, especially for high-resolution crop type maps with sufficient spatial details, contributes to improving the accuracy of estimates in heterogeneous regions. Finally, previous studies were mostly conducted at short time periods or for a specific year, and it was thus hard to produce reflections of the temporal change trends of O3-induced agricultural losses and associated food security over a longer time frame.
To fill the knowledge gaps as aforementioned, the present study employed a high spatial resolution hourly surface ozone reanalysis dataset that optimally combined the ground observations and nested air quality prediction via a data assimilation technique, which outperformed both the measured and model simulated O3 data in estimating regional O3 concentration. Moreover, a high-resolution (10 × 10 m) double-season paddy rice distribution dataset was also used to identify the locations of crops in the heterogeneous farmlands of south China, which added to the improved accuracy of the estimated O3 exposure of crops when in combination with the ozone reanalysis dataset. Additionally, a locally derived exposure-response function for rice was incorporated and the county-level rice production data were adopted to assess the O3-induced crop losses on the finest scales possible (i.e., county-scale), so as to raise the estimate accuracy. The analysis was conducted for seven consecutive years from 2013 to 2019 to promote the estimates’ temporal representativeness. The specific objectives are to (1) investigate the spatial and temporal evolutions of the AOT40 exposure metric of double-cropping rice (early rice and late season rice) in south China during the relatively long term (2013–2019); (2) estimate the yield reductions and economic losses caused by ozone exposure in south China spanning from 2013 to 2019. It is expected that the present study will increase the accuracy of O3-induced crop loss estimates, and contribute to an improved understanding of the food security risks posed by air pollution.
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Data Sources
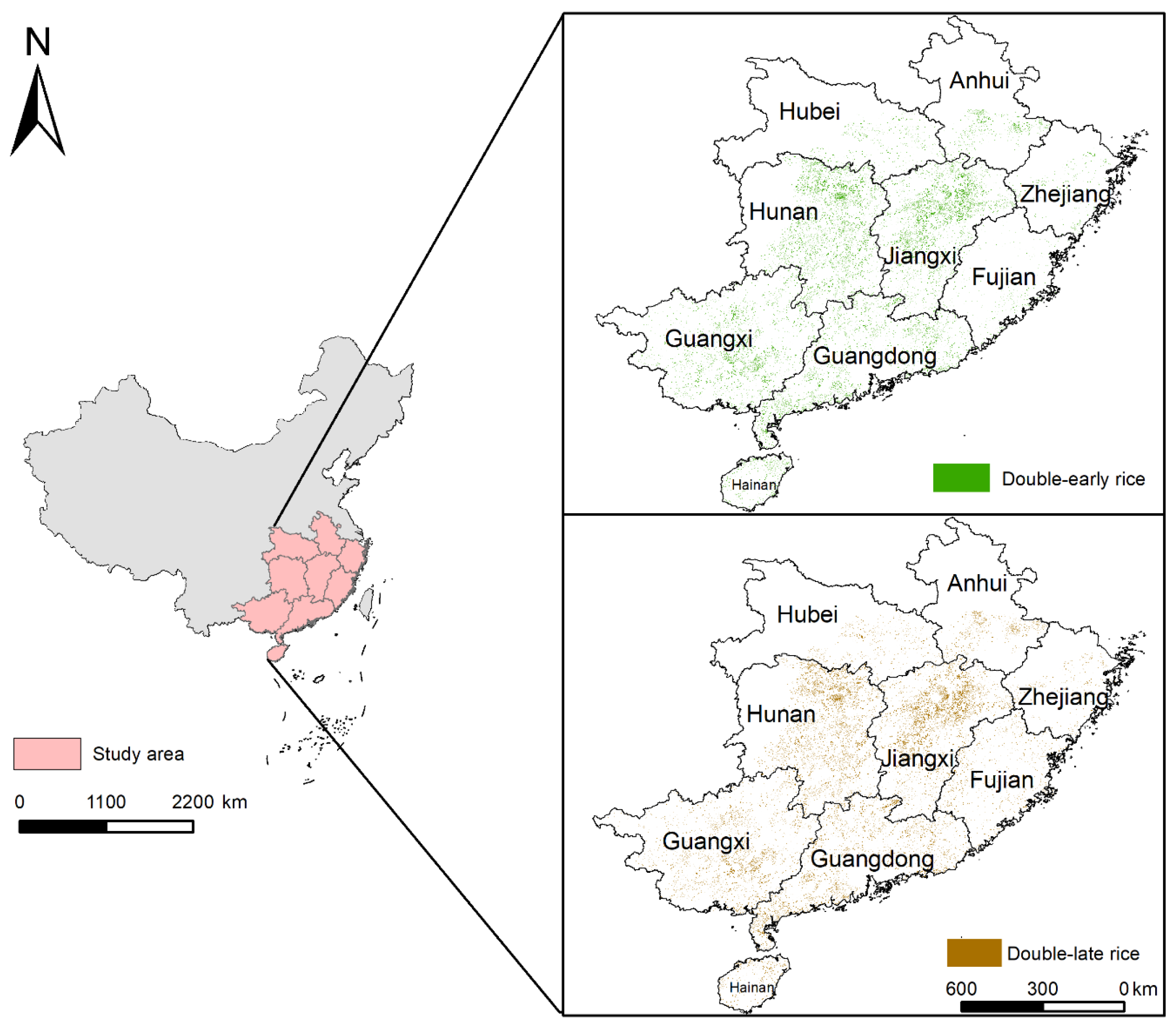
This study involves 286 counties and districts in nine southern provinces of China, of which the specific planting regions of double cropping rice are shown in Figure 1. The spatial distribution of double-season rice in South China at the resolution of 10 m was derived from our previous study [43]. The early rice and late season rice maps were produced using time-series Sentinel-1 SAR images and a time-weighted dynamic time warping (TWDTW) algorithm, achieving an overall accuracy of over 90%.
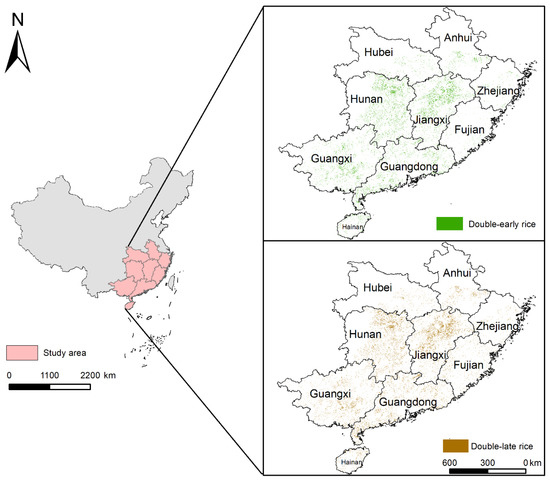
Figure 1.
Study area and spatial distribution of double cropping rice in south China.
The hourly ground-level ozone concentration data from 2013 to 2019 were acquired from the Chinese Air Quality Reanalysis (CAQRA) dataset [45], which was generated by the Institute of Atmospheric Physics, Chinese Academy of Sciences (IAP, CAS). The CAQRA dataset provided the surface gridded fields of six conventional air pollutants (i.e., PM2.5, PM10, SO2, NO2, CO and O3) at high spatial and temporal resolutions of 15km and 1 h, respectively. Specifically, the dataset was produced through the assimilation of more than 1000 ground-based observations provided by the China National Environmental Monitoring Centre (CNEMC) using the chemical data assimilation system (ChemDAS) developed by the IAP, which comprised the Nested Air Quality Prediction Modeling System (NAQPMS, a three-dimensional chemical transport model); and an ensemble Kalman filter (EnKF, the assimilation algorithm). Through the five-fold cross-validation with ground observations and by comparing with the Copernicus Atmosphere Monitoring Service Reanalysis (CAMSRA) dataset developed by the European Centre for Medium-Range Weather Forecasts (ECMWF), the validation result demonstrated that the CAQRA dataset achieved high accuracy in characterizing the magnitude and spatiotemporal variability of China’s air pollutants at ground level [7], which renders it more applicable for regional-scale air quality studies. To date, the dataset has been widely used in related research on environmental risk assessment by air pollution [40,46,47,48].
Yields of early rice and late rice in 286 counties and districts of south China during 2013–2019 were derived from the China Statistical Yearbook (2014–2020) (http://www.stats.gov.cn/, accessed on 17 February 2022). Administrative zoning vector data were acquired from the National Geomatics Center of China (http://www.ngcc.cn/ngcc/, accessed on 17 February 2022).
2.2. The Calculation of AOT40
The widely used AOT40 exposure metric was employed in this study to assess the O3-induced yield losses of double-season rice during their respective growing seasons from 2013 to 2019. The AOT40 is defined as the critical cumulative [O3] level exceeding the threshold value of 40 ppb under effective light conditions during crop growth season, which was calculated using the formula below:
where is hourly concentration (ppb) of daytime hours and is the number of hours during the growing season. Note that the threshold of 40 ppb was considered as the critical level at which ozone imposed damages on crop growth based on the field control studies [24,26]. Based on the previous research [20,39] and the range of growing seasons provided by the China National Rice Research Institute (https://cnrri.caas.cn/, accessed on 10 March 2022), we determined the accumulation periods for double-season rice, which were 20 April to 20 July for double-early rice and 25 July to 25 October for double-late rice, respectively.
AOT40 was calculated based on the hourly O3 reanalysis CAQRA dataset. Subsequently, AOT40 data were re-gridded to 1 × 1 km horizontal resolution using the Kriging interpolation method [40]. Next, AOT40 exposure metric values were spatially extracted for double-season rice based on the paddy maps. Lastly, the extracted AOT40 was aggregated to the county level for the subsequent rice yield loss assessment.
2.3. Relative Yield and Relative Yield Loss
To estimate the crop yield losses by ground-level O3 pollution in a quantitative manner, scholars established the exposure-response relationships between O3 exposure dose and relative crop yields based on the O3-enrichment experiments, which laid the foundations for the regional assessment of O3-induced production reduction risks. Among them, Wang et al. [26] developed an O3 exposure-response function for rice in China using the open top field chamber (OTC) facility, which has been widely used for rice yield losses estimation in China [31,49,50]. The modeled relative yield (RY) was calculated as shown below:
The relative yield loss (RYL) of rice is subsequently calculated as:
2.4. Estimated Production and Economic Losses
Rice production reduction and economic losses induced by O3 pollution were estimated for each county on the basis of the method proposed by Sinha et al. [29].
where is the estimated crop production loss and represents crop production in county . The economic cost loss (ECL) is determined by the CPL and the crop production purchase price (CPP), which was derived from the National Development and Reform Commission (NDRC) (http://www.ndrc.gov.cn/, accessed on 1 October 2022). The CPP for rice during 2013–2019 was converted to U.S. dollars (USD) using the average exchange rate of that year.
3. Results
3.1. Spatiotemporal Change Patterns of Ozone Pollution across South China
The average daytime ozone concentration [O3] in the entire region of southern China in the stage of double-early rice ranged from 33.2 ppb to 40.4 ppb, and in the stage of double-late rice it was 34.4 ppb to 50.0 ppb for years 2013–2019 (Table 1). Overall, the ozone concentration in the double-late rice was higher than that accumulated over the double-early rice period. From the perspective of temporal trends, the ozone concentration demonstrated a change pattern of a U-shaped curve in most provinces, with the lowest value being around 2016. Among them, Anhui province suffered the most evident uptrend in ozone concentration over the growing seasons of double-early rice (+2.3 ppb/yr) and double-late rice (+1.6 ppb/yr). In the spatial domain, ozone pollution in Hubei province was the most severe for the double-early rice stage, with the highest ozone level in the average of seven years (45.8 ppb), followed by Anhui (41.9 ppb) and Zhejiang provinces (40.7 ppb). On the other hand, in the double-late rice stage the annual average ozone concentration in Guangdong province was the highest (48.4 ppb), and was significantly higher as compared with that in the double-early rice stage (34.9 ppb), indicating that O3-induced damage to crop growth would be more serious in the late rice growing season. A similar change pattern was also observed in the neighboring Guangxi province.

Table 1.
Average daytime ozone concentration during the rice growing seasons.
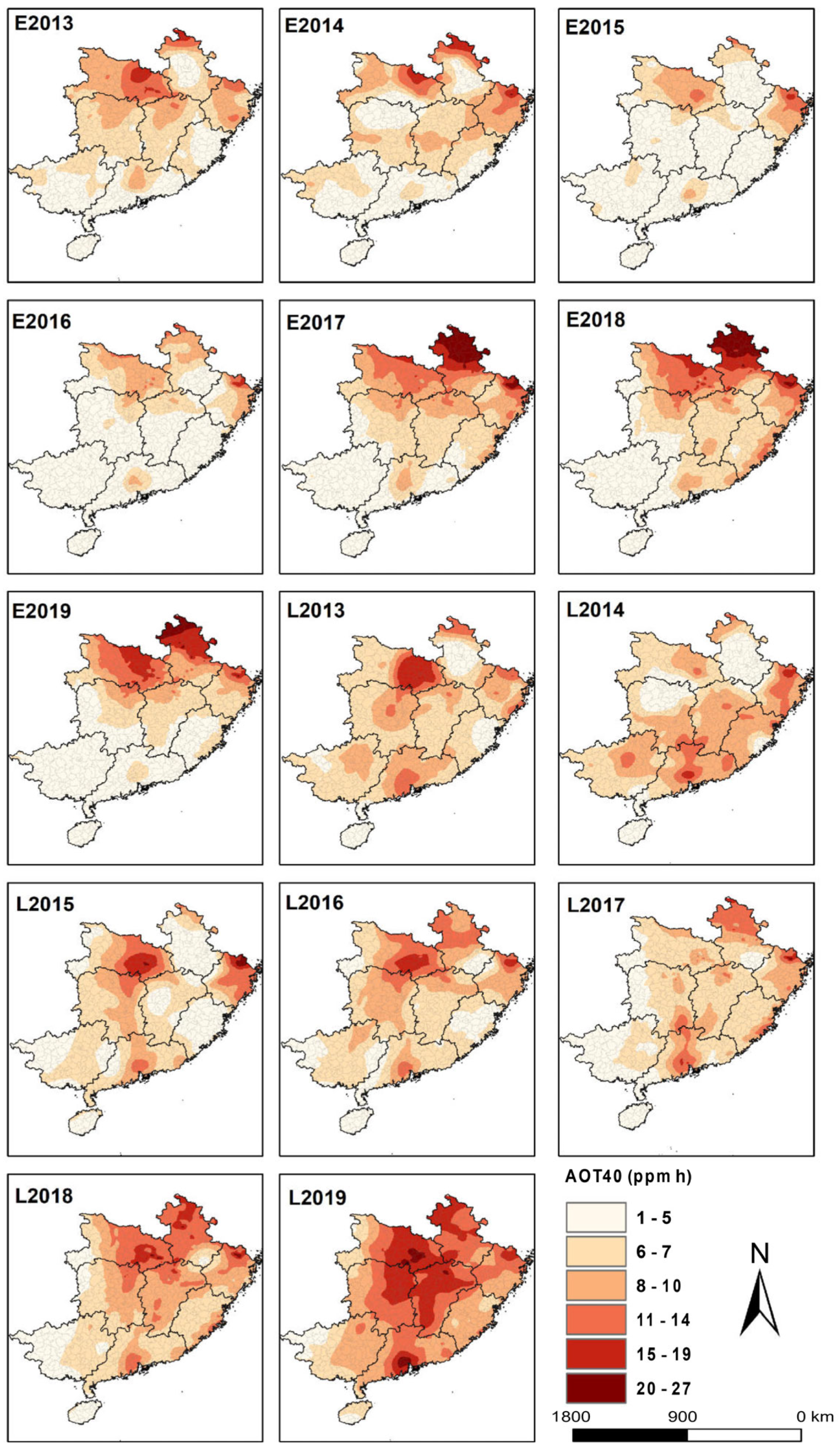
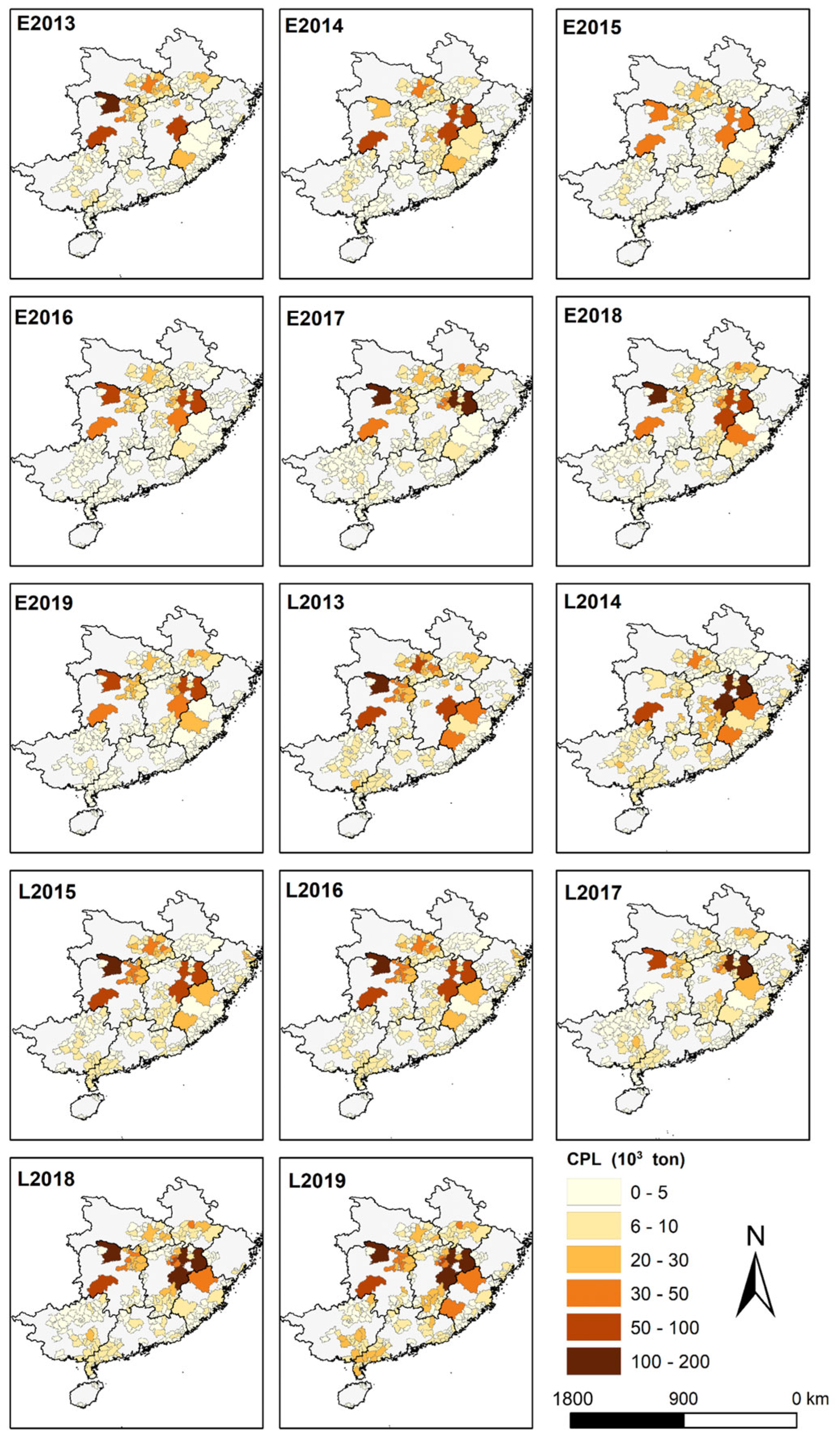
Focusing on the exposure-based AOT40 metric (Figure 2), the annually averaged AOT40 values across the whole southern China region over 2013–2019 were 4.0–7.1 ppm h and 6.1–10.5 ppm h for the growing periods of double-early and double-late rice, respectively. In general, during the late rice growing season, the ozone exposure level was 28.1% higher than that over the double-early rice growing period over the seven years. In terms of temporal evolution, although both early and late rice showed generally increasing trends in AOT40 values from 2013 to 2019, the annual increase rate of AOT40 in the growing season of late rice (0.47 ppm h/yr) was nearly double the amount of early rice (0.25 ppm h/yr). In particular, O3 exposure increased at an annual increase of 2.2 ppm h (36.5% growth per year) during the late rice growing season for the three consecutive years of 2017 to 2019. These findings implied that ozone pollution imposed greater risks on late rice production in the region. Regarding the spatial distribution, AOT40 values featured evident spatial heterogeneity across southern China. The AOT40 indexes of Anhui (9.6 ppm h), Hubei (9.2 ppm h), and Zhejiang (8.7 ppm h) were ranking the highest at the double-early rice stage, while those of Zhejiang (9.4 ppm h), Hubei (9.1 ppm h) and Jiangxi (8.2 ppm h) took the highest place at the double-late rice stage. In contrast, the minimum AOT40 values were largely observed in Hainan and Guangxi during the entire double rice stage, with 0.85 ppm h and 2.9 ppm h in Hainan for the early rice and late rice, while 3.2 ppm h and 5.5 ppm h were observed in Guangxi for early rice and late rice, respectively. As depicted in Figure 2, it can be seen that AOT40 increased significantly during the double rice growing seasons. Specifically, during the growing period of early rice, the hotspots of O3 exposure (corresponding to AOT40 of over 15 ppm h) expanded from small proportions mainly in northeast Hubei in 2013 to larger proportions of the northern part of the south China region in 2017 and 2018, especially for northern Anhui’s Huaibei Plain. Likewise, during the growing period of late rice, the hotspots of O3 exposure expanded from small areal proportions mainly in the Jianghan Plain in eastern Hubei in 2013 to significantly larger parts in the central south China region (also the intensively farmed area) in 2019. In addition, considerable increases of AOT40 also occurred over the Pearl River Delta in southern Guangdong throughout the study period, and the O3 exposure was significantly elevated during the late rice period compared with the counterpart over the early rice stage in this area.
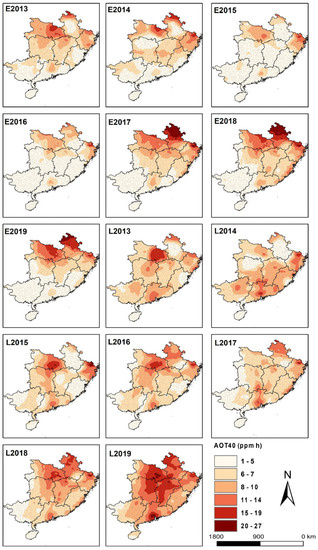
Figure 2.
Spatial distribution of AOT40 values over the growing season stages of early rice and late rice from 2013 to 2019. The E and L in the part-labels represent early rice and late rice, respectively.
3.2. Relative Yield Loss
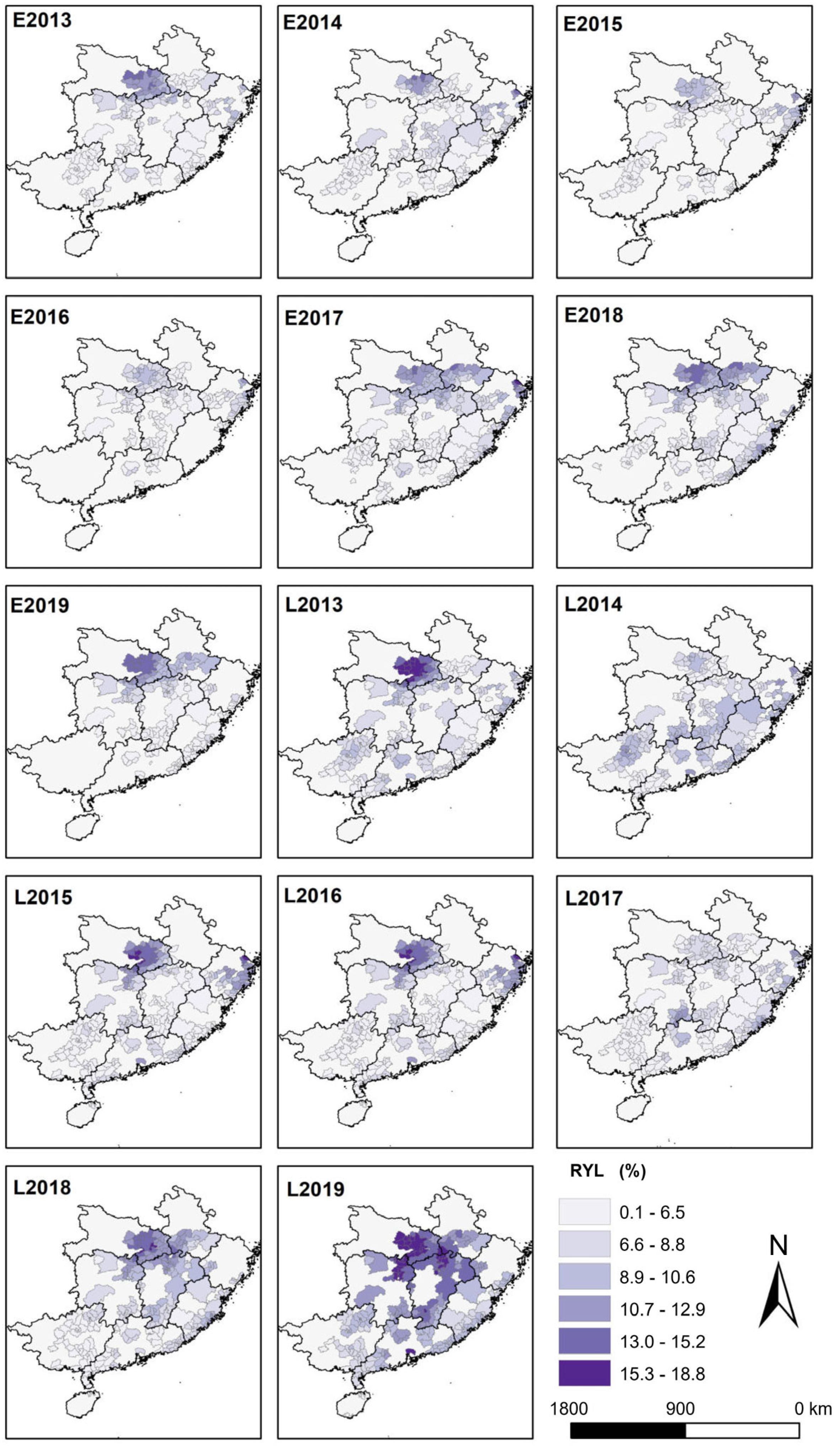
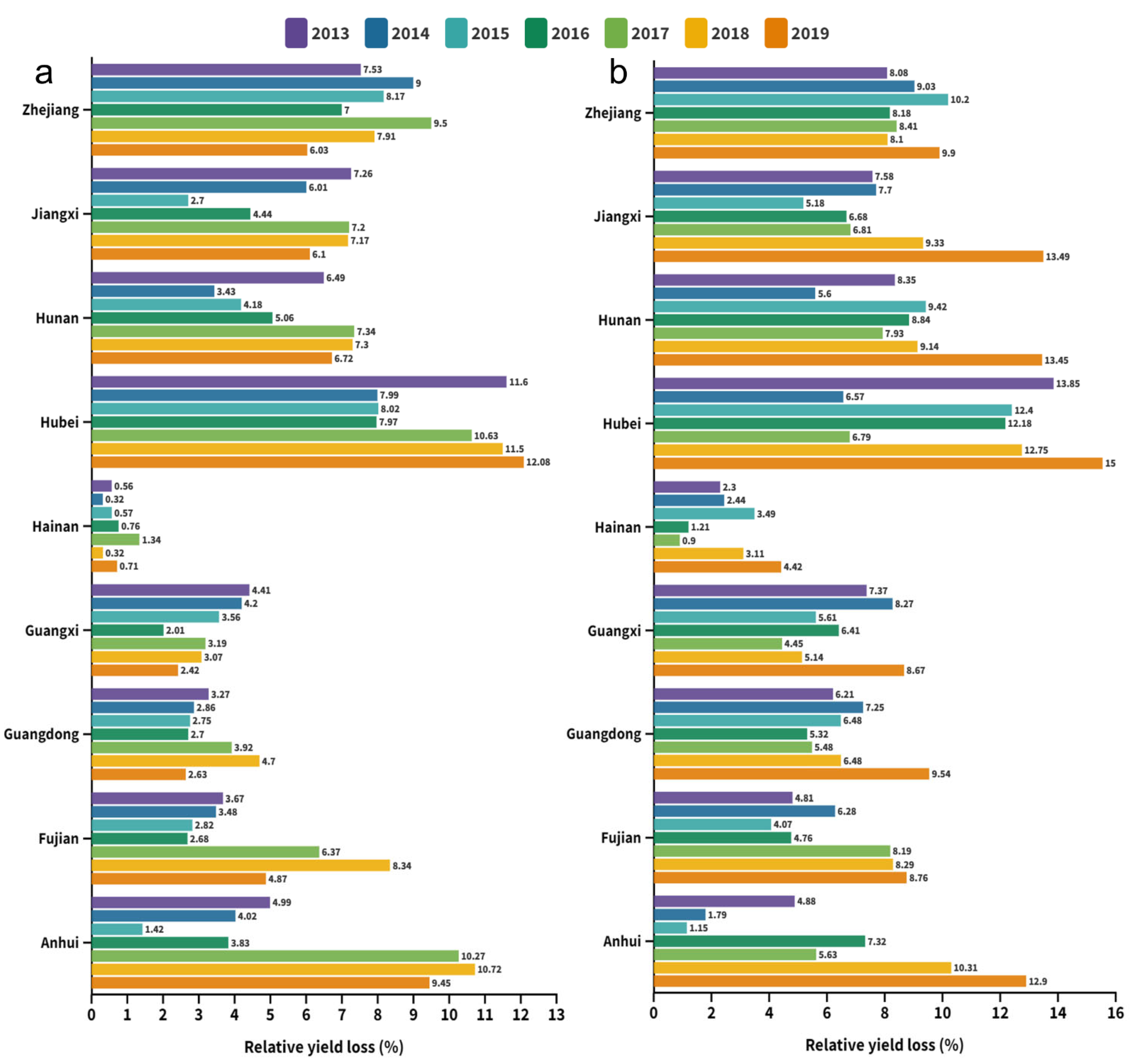
The spatially averaged relative yield losses of early rice due to ozone exposure during the growing periods over 2013–2019 were 5.5%, 4.7%, 4.0%, 4.1%, 6.3%, 6.6% and 5.4%, respectively (Figure 3). Among the nine provinces in southern China, Hubei, one of China’s primary rice production provinces, suffered the highest multi-year average of RYL (10.0%) over the study period and had the peak of 12.08% in 2019 (Figure 4). Following Hubei, Zhejiang and Anhui provinces had average RYL of 7.9% and 6.4%, respectively. In contrast, Hainan province had an average RYL of merely 0.65% during 2013–2019. The county-level regions with the highest RYL were the regions with higher O3 exposure levels since the relative yield loss was linearly correlated with AOT40 values. Specifically, the regional maximum RYL was largely observed in Hubei counties (14.3%, 13.9%, 14.2% in Xiaochang in 2013, 2014 and 2018, respectively; 15.0% in Yunmeng in 2019) as well as Zhejiang counties (11.9%, 12.4% and 15.2% in Cixi of Ningbo city for years 2015–2017).
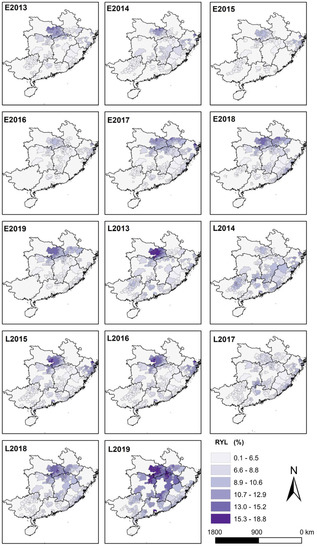
Figure 3.
Spatial distribution of relative yield loss (RYL) of early rice and late rice over growing seasons from 2013 to 2019. The E and L in the part-labels represent early rice and late rice, respectively.
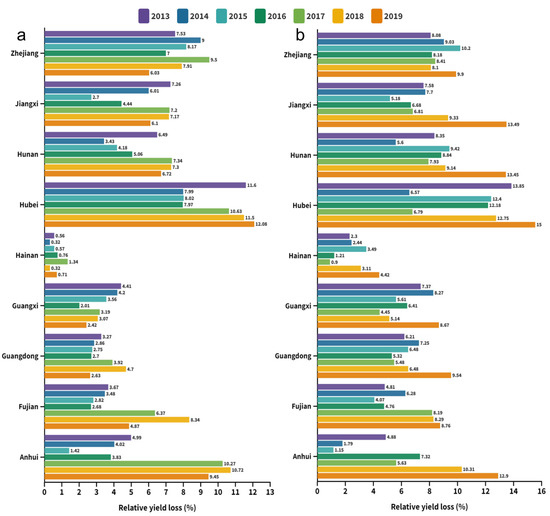
Figure 4.
Regional statistics on the relative yield loss from 2013 to 2019. (a) Double-early rice period and (b) double-late rice period.
For double-late rice, the average values of RYL over the growing seasons were 7.3%, 6.8%, 6.8%, 7.0%, 6.3%, 8.0% and 11.1% for 2013, 2014, 2015, 2016, 2017, 2018 and 2019, respectively (Figure 3). It was obviously seen that the RYL of late rice stayed relatively stable in the entire southern China region between 2013 and 2017, while it increased rapidly beyond 2017 (more than double in 2019 compared with 2017), which was in line with the temporal changes of AOT40. From the perspective of regional differentiation, in the double-late rice stage the RYL of South China varied considerably (0.9–15.0%) (Figure 4). Hubei suffered the highest RYL of 11.4% by average over the growing periods of late rice, followed by Hunan (9.0%) and Zhejiang (8.8%). By comparison, the lowest RYL was observed in Hainan province (2.6%). Generally speaking, crop relative yield loss was comparatively higher for late rice than early rice for all southern provinces. Focusing on the 286 counties, the maximum RYL values during the growing season of late rice were observed in Jiayu of Hubei (16.7%) for 2013, Liunan of Guangxi (12.9%) for 2014, Cixi of Zhejiang (16.5%) for 2015, Hanchuan of Hubei (14.8%) for 2016, Cixi of Zhejiang (12.4%) for 2017, and Jiayu of Hubei (15.5% and 18.8%) for 2018 and 2019, respectively.
3.3. Crop Production Loss and Economic Cost Loss
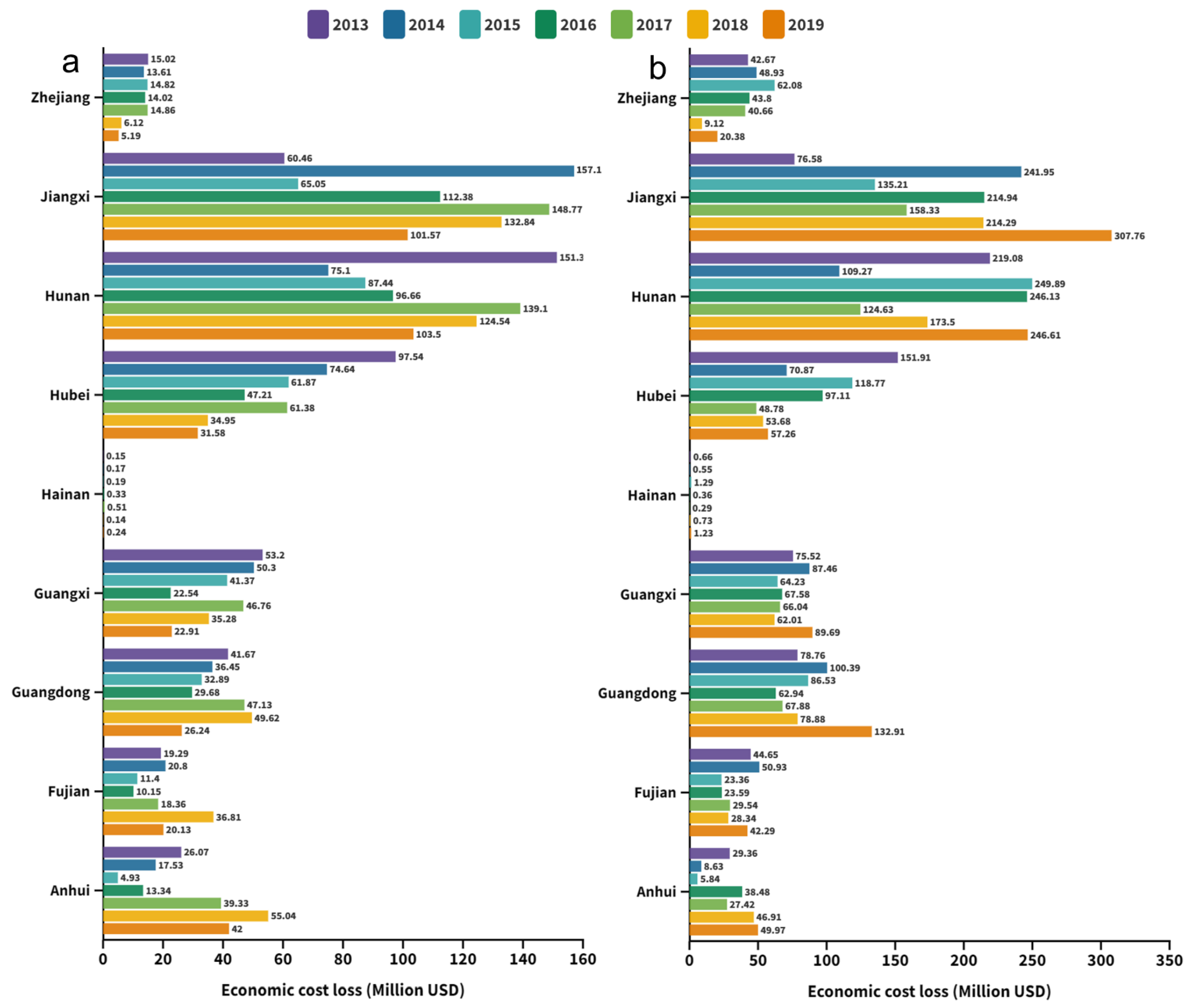
As illustrated in Figure 5, we evaluated the crop production losses (CPL) of double-cropping rice per county in southern China during 2013–2019. From 2013 to 2019, the annual estimated total CPL in the double-early rice period ranged from 75.8 × 104 t to 123.1 × 104 t, and in the double-late rice period it was between 134.4 × 104 t and 241.7 × 104 t. It is clearly seen that double-late rice suffered more yield losses induced by ambient ozone pollution. It should be emphasized that CPL depends not only on RYL, but also on total crop production. For example, Hubei province had the highest average RYL (11.4%) at the double-late rice stage during the study period, but the county-level average CPL in Hubei province was much lower than in that in Hunan and Jiangxi provinces. In fact, higher CPL regions were largely located in Hunan and Jiangxi provinces, which totaled 187.9 × 104 t and 187.4 × 104 t over the study period for early rice (together representing 53.3% of the total loss in south China), and 332.0 × 104 t and 327.4 × 104 t for late rice, representing 52.8% of the total yield loss in the whole region altogether. It is noteworthy that these two provinces are the top producers of double season rice in China, which contribute to a large part (e.g., 49.1% in 2019) of national total double season rice production. Correspondingly, ambient ozone pollution has introduced considerable risks of yield reduction in these areas.
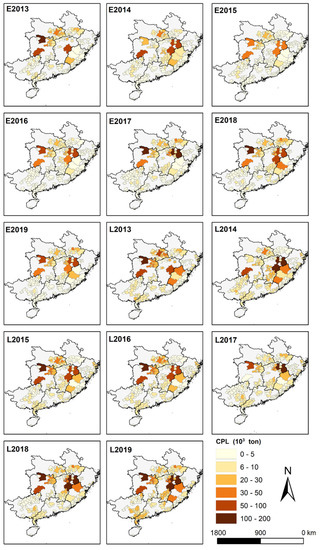
Figure 5.
Crop production losses of double-season rice during the growing seasons from 2013 to 2019. The E and L in the part-labels represent early rice and late rice, respectively.
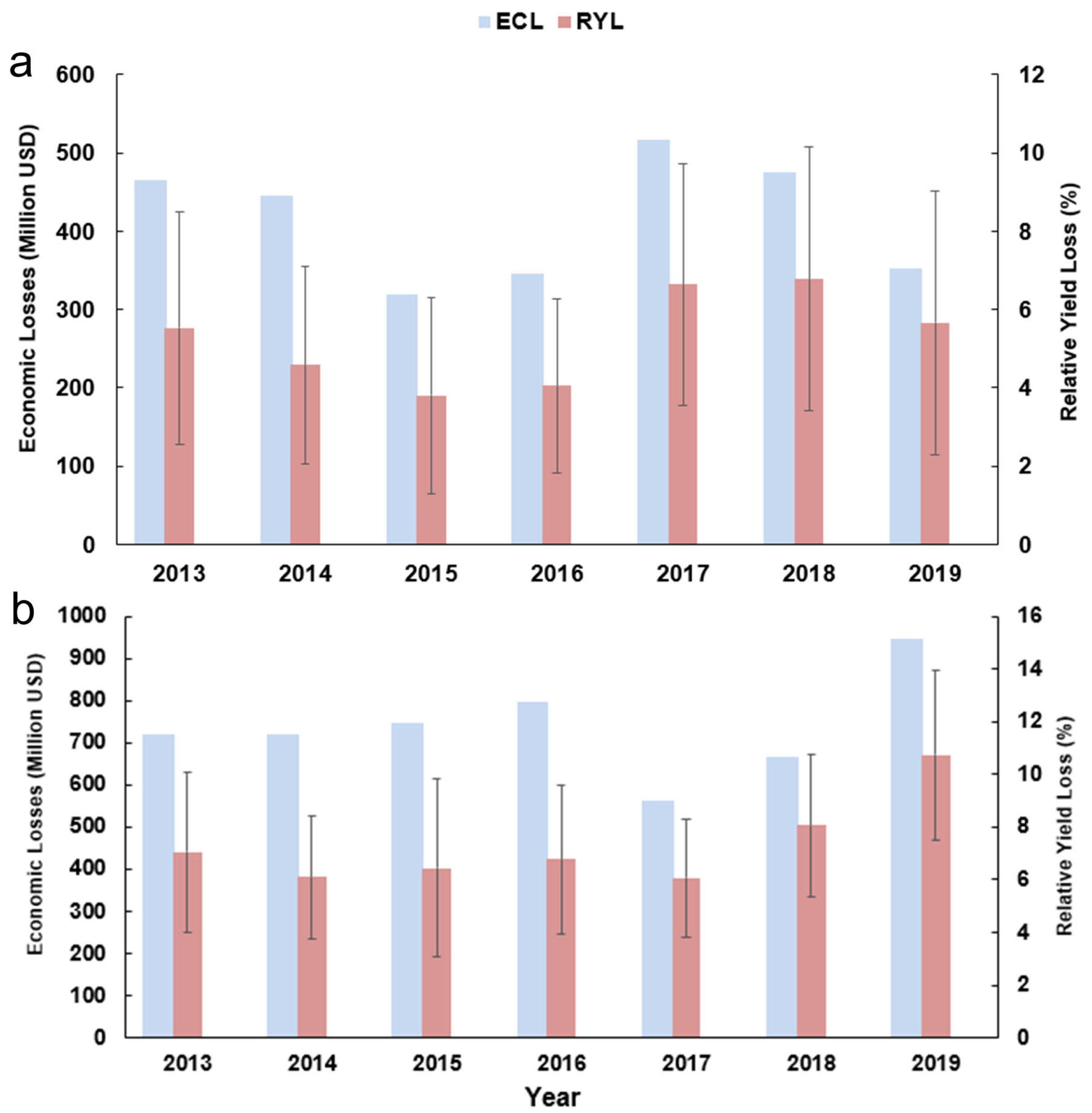
The economic cost losses (ECL) were estimated on the basis of the CPL as well as the purchase price of rice for the respective years (Figure 6). For double-early rice, the ECL value of the regional sum in south China spanned from USD 320.0 million to USD 516.2 million over 2013–2019, whereas in the double-late rice growing period the ECL was estimated to be between USD 563.6 million and USD 948.1 million. Taken together, the ECL of the early rice and late rice combined peaked at USD 1301.46 million in 2019, while achieving the minimum of USD 1067.16 million in 2015. Similar to CPL, the ECL is also a function of RYL and crop production. Therefore, a combination of high crop production and high RYL led to high economic losses (Figure 7). To sum up, the total economic losses of double season rice due to ozone exposure were assessed to be USD 8081.03 million in the whole of south China across seven years. It is noted that over half of the economic losses were contributed by Hunan and Jiangxi provinces.
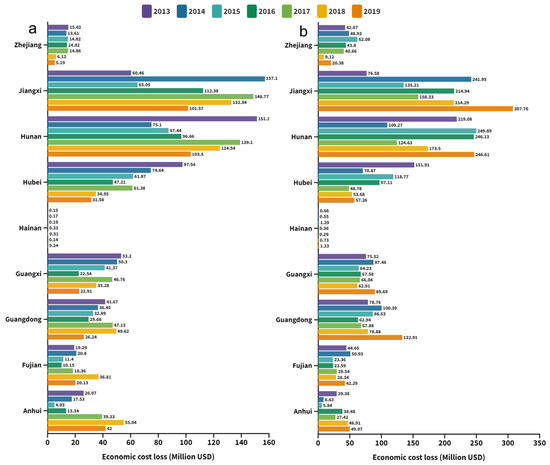
Figure 6.
Regional statistics on the economic cost loss by ozone exposure from 2013 to 2019. (a) Double-early rice period and (b) double-late rice period.
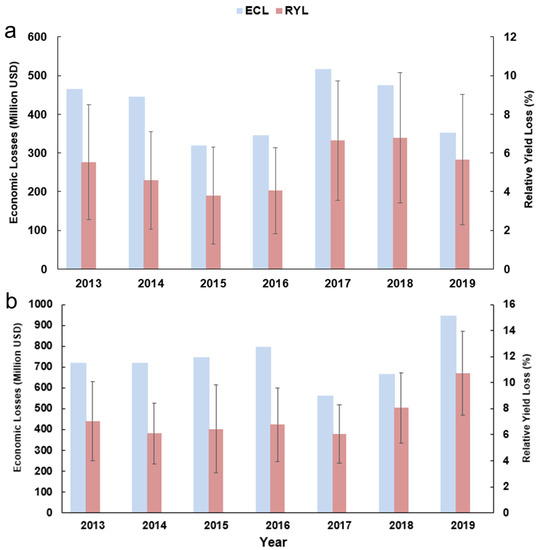
Figure 7.
Economic loss and relative yield loss of double-season rice caused by ozone exposure in the whole of south China over 2013–2019. (a) Double-early rice and (b) double-late rice. The error bar indicates the standard deviation. Note that the ECL (economic cost loss, in Million USD) is a regionally summed indicator (not regionally averaged) and thus no error bars are applied.
4. Discussion
4.1. Ozone Pollution in South China
Increasing studies reveal that fine particulate matter PM2.5 has been well contained in China due to the nation-wide implementation of stringent control measures [51]. However, accompanying the sustained economic growth and the accelerating process of urbanization in recent years, the emissions of O3 precursors (e.g., NOX, VOCs) in China also increased considerably, leading to rapidly increasing O3 concentration in many regions, especially in densely populated and economically developed regions such as the Yangtze River Delta and Pearl River Delta regions in south China [52]. Several studies show that surface O3 has replaced PM2.5 as the main atmospheric pollutant in these regions [4,53]. Regarding south China as a major double-season rice producer and also a hotspot of ozone pollution, mounting research has been carried out on the assessment of crop yield loss induced by O3 pollution in this region [18,20,32,49]. Since 2013, China has established over 1000 ambient air quality monitoring stations around the country, which provide foundations for yield reduction estimates induced by ozone pollution. However, many studies directly utilized ground station-based O3 observation data to evaluate the production loss. For instance, Zhao et al. [39] reported that the average O3 concentration ranged from 35.9 to 39.1 ppb during the double-late rice growing season, which was apparently lower than our result. The underestimation of O3 concentration inevitably introduced more uncertainties into the crop production losses assessment. The reason for the underestimation is that the distribution of air quality ground stations is spatially uneven, primarily located in urban areas, and O3 concentration in rural and suburban areas is often higher than that in urban areas [41,54]. This is highly relevant to the proportion of the two primary ozone precursors (NOX and VOCs) [55]. In urban areas, the concentration of O3 decreases through the NOx titration process. By contrast, the volatile organic compounds emitted by plants in rural and suburban areas promote the formation of ambient ozone. Under this context, in spite of the establishment of monitoring stations nationwide, the ozone monitoring network does not cover vast agricultural areas which fails to characterize the actual level of crop exposure to surface ozone, and may possibly underestimate the risks of crop yield reductions.
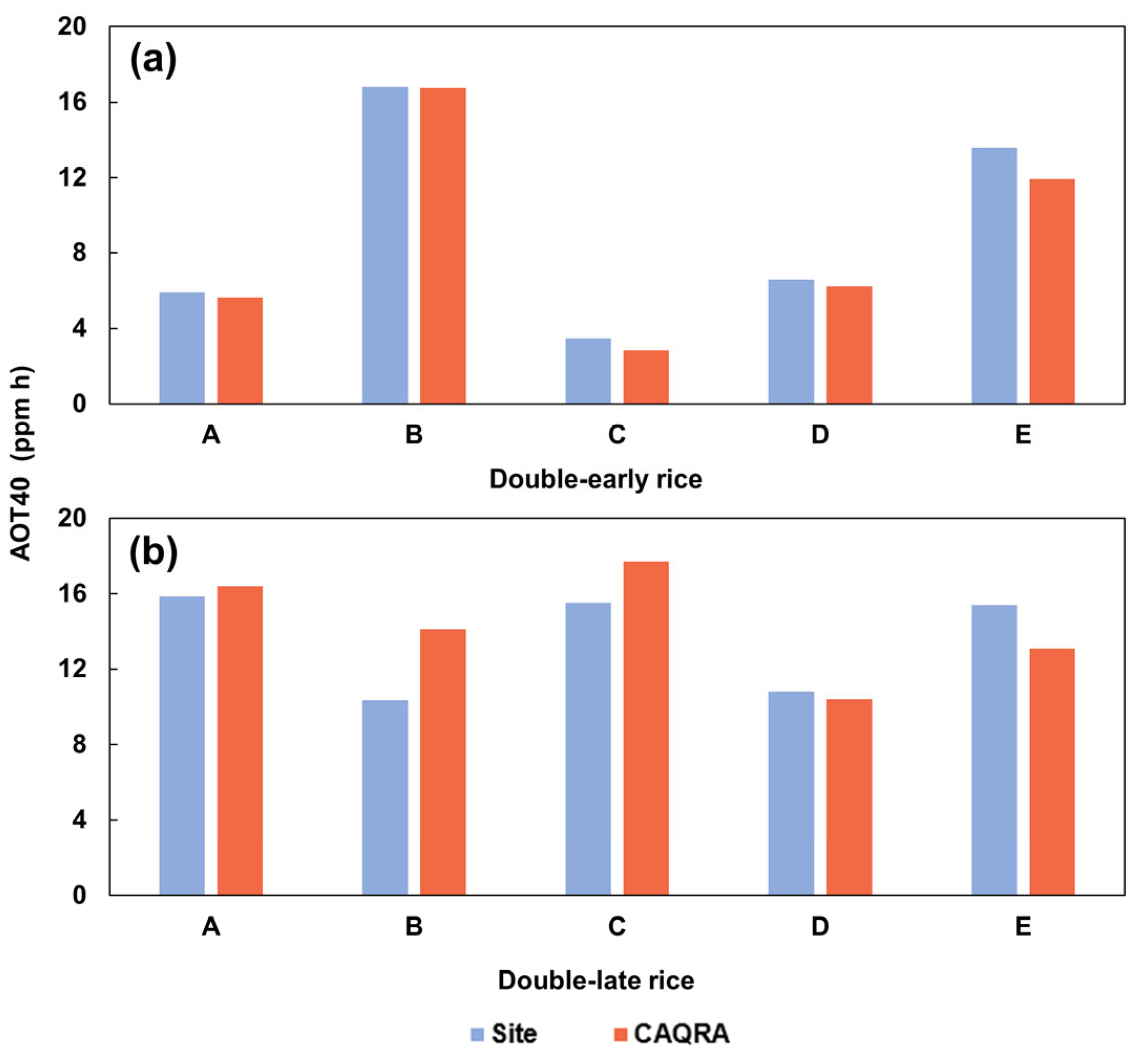
A few studies have adopted geostatistical methods to spatially extend the point-based O3 station observations to spatially continuous surface ozone distribution data [36,49,56]. Although the spatial interpolation can resolve the issue of spatial-temporal discontinuity of the monitoring stations, it should be pointed out that the interpolation is still a fitting approach in essence, which fails to obtain the actual O3 exposure but gives rise to the uncertainty caused by the density and spatial distribution of observation sites. Research showed that the prediction error was more significant in areas distant from the monitoring sites and with sparse distribution of sites [49]. Additionally, the lack of high-resolution crop distribution maps further increased the uncertainties of O3 estimates since most studies simply employed the regional average to represent crop exposure to ozone pollution without considering the actual planting extent of crops. In contrast with previous research, this study adopted a high-resolution hourly ozone reanalysis dataset (i.e., CAQRA) to more accurately quantify the threat of ozone pollution to crops by optimally combining the observation results and air quality prediction via data assimilation [40]. Evaluation at rural sites indicate an averaged bias of 9.5% and 12.8% for double-early rice and double-late rice, respectively (Figure 8). Furthermore, spatially detailed double-season rice distribution maps were also used in combination with the CAQRA dataset to better reflect the spatial and temporal variability of crop exposure to ambient ozone at a fine scale, which provided a prerequisite for an accurate and reliable crop yield reductions estimate.
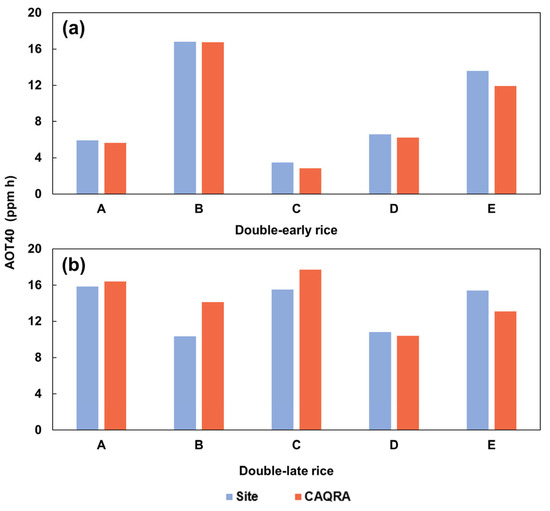
Figure 8.
Comparison of AOT40 between rural sites and the used CAQRA ozone reanalysis dataset. (a) Double-early rice and (b) double-late rice. Note that site A: Tongtianyan, B: Jiaoganghu, C: Zhongshan, D: Qiandaohu and E: Xixi.
It is generally believed that when the concentration of ambient O3 is higher than a certain threshold (usually set at 40 ppb) it will cause damages to crops [24]. All regions of south China except for Anhui province had a yearly average O3 concentration exceeding 40 ppb during the double-late rice growing season for the years 2013–2015 and 2018–2019. Recent research demonstrated that from 2013 to 2019 China’s O3 pollution has shown a rapidly increasing trend in general, with the continuous expansion of high-medium O3 concentration areas [5], which was in line with our findings. This study indicated that the AOT40 metric presented an overall aggravating trend over time (Figure 2). It is noted that AOT40 during the late rice growing season increased at an annual growth rate of 36.5% over 2017–2019, during which the concentration of PM2.5 was observed to continuously decline [50]. Furthermore, it is found that hotspots of O3 pollution (AOT40 > 15 ppm h) have been expanding spatially during the study period, especially in 2019 when the areas of severe pollution occupied the widespread central regions of South China, which was also an intensively farmed region, posing grave risks to regional food security. Moreover, our study also found that ozone exposure was more significant in double-late rice growing seasons compared with the counterpart over the double-early rice growing seasons, especially in southern provinces of the south China region (e.g., Guangdong, Hunan, Jiangxi provinces), which was consistent with previous studies [18,20]. Particularly, Guangdong ranked first among the nine provinces in terms of ozone concentration during the late rice growing periods (Table 1). Recent research showed that the primary factors affecting the O3 concentration were the precursors (mainly NOX, VOCs) concentration, solar ultraviolet intensity, temperature and atmospheric transparency [57]. Guangdong province has considerable amounts of both anthropogenic and natural source VOCs emissions due to its vast economic growth and high forest cover, and the meteorological conditions of high temperature, strong sunshine, less cloud cover and weak wind led by the subtropical high in autumn are conducive to ozone generation in this region [58]. In contrast to the northern provinces, O3 concentration peaked in autumn around October in Guangdong province, which corresponds to the growing season of late rice. It is thus suggested to harvest crops in advance appropriately to avoid potentially greater rice yield losses caused by accumulated ozone exposure [40].
4.2. Comparison of RYL with Other Research
In this study, we employed a field experimentally derived O3 exposure-response (E-R) function for assessing the effect of O3 on rice yield. Our result found that double-late rice was more prone to yield reductions compared with double-early rice since ozone exposure peaked in autumn, corresponding to the late rice growing period. In parallel with AOT40 increment during the studied years 2013–2019, the relative yield loss (RYL) also progressively increased from 7.3% in 2013 to 11.1% in 2019 since RYL was linearly correlated with AOT40. A recent study pointed out that ambient ozone pollution reduced rice production by 4.4% on a yearly basis worldwide [15]. Numerous studies indicated that Chinese crop cultivars are more sensitive to O3 pollution than those in the United States and Europe, leading to a relatively higher ozone yield gap [59,60]. A global modelling study showed that China suffered a rice yield reduction of 8.1% each year [15], which was comparable with our analysis. Although China has not formally proposed a critical level of O3 for crop protection, 5% of yield loss is generally considered as an appropriate critical level for crop production [24,36,49]. In our studied south China region, the critical level of 5% yield loss was exceeded for the double-early rice season in four years out of seven, the exception being 2014–2016, whereas for the double-late rice growing season the relative yield loss exceeded this critical level in all years. Especially in 2019, the relative yield loss of late rice was more than two-fold this critical level. It is inferred that the detrimental impact of ambient O3 pollution on double-cropping rice in south China cannot be ignored.
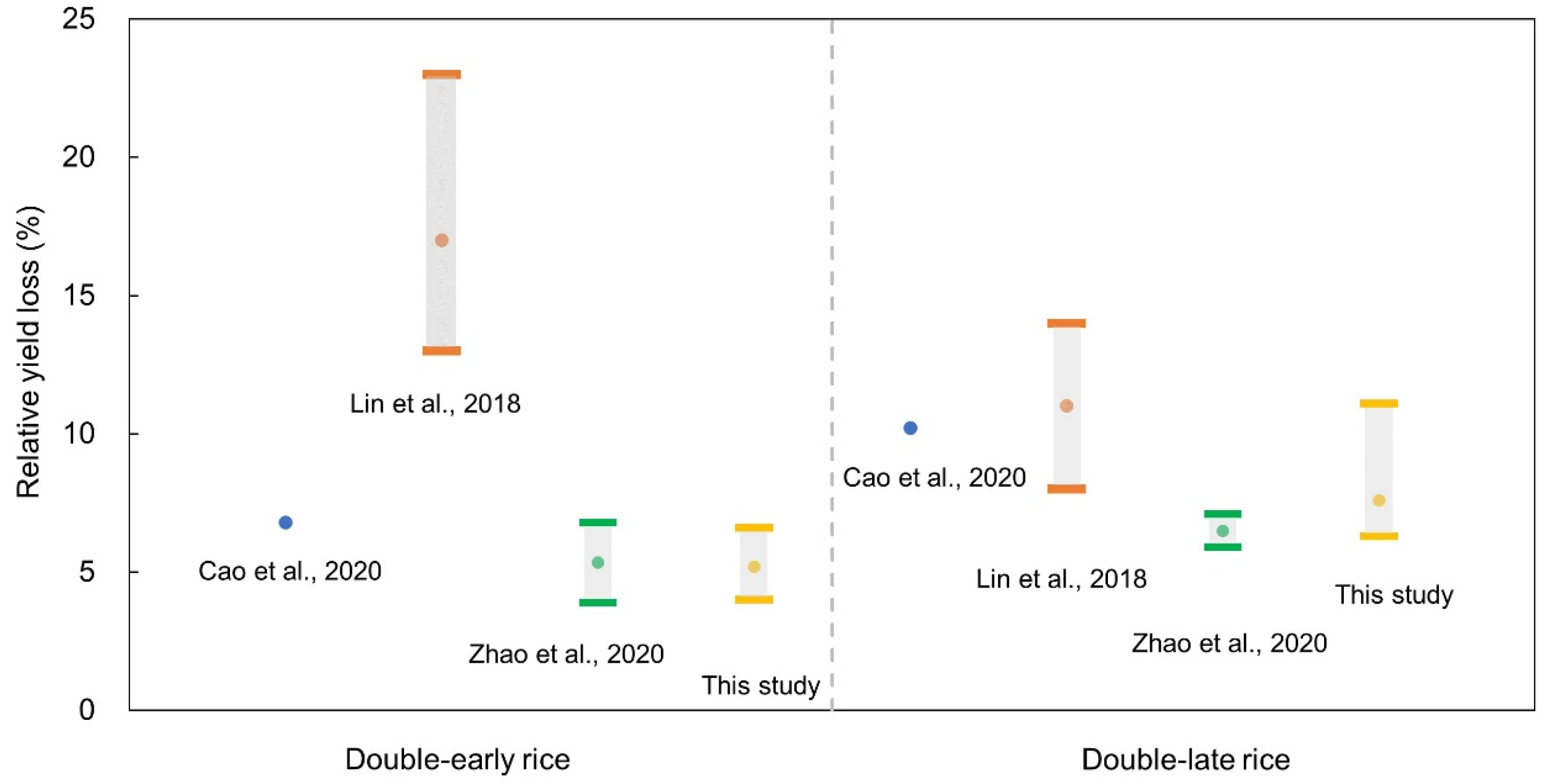
We also compared our results with other related studies conducted in China (Figure 9). For instance, the research by Cao et al. [20] reported that ambient ozone exposure induced 6.8% and 10.2% of relative yield loss for double-early rice and double-late rice in 2015, using an observation data-based AOT40 metric. Zhao et al. [39] showed the RYL estimate for double-early and double-late rice at 5.4% and 6.5% during 2015–2018, which was also based on observational AOT40. It is noted that the relative yield loss estimate from this study is generally within the range of values revealed by the above studies. Similar to our findings, these studies also demonstrated that double-late rice was more vulnerable to yield reductions by ambient ozone pollution. In contrast, Lin et al. [18] revealed a higher evaluation of the RYL, estimated at 17% and 11% for double-early rice and double-late rice in 2014, which was higher than the abovementioned studies and our research. Previous reports indicated that the estimated yield reductions may vary due to the discrepancies in estimated O3 exposure, the use of differing exposure-response functions, and diverse estimation units (county-level, city-level and provincial-level) [40,49]. Lin et al. [18] obtained the RYLs by employing three exposure-response functions derived from different field experiments designed for Chinese and European cultivars, and then combining the results. As mentioned above, there exist considerable differences in the sensitivity to ambient ozone exposure between Chinese and European crop cultivars. The combination of such differently sourced E-R functions may introduce large uncertainties. In addition, uncertainty may also derive from the modelled estimation of ozone concentrations based on an atmospheric chemical transport model, which is considered to suffer uncertainties from the emission inventory, meteorology and chemical mechanisms as well as spatial resolution [35]. Moreover, the estimation unit used in the study by Lin et al. [18] was limited to provincial level, which may conceal the spatial heterogeneity in RYL [31]. By contrast, our study estimated the RYLs at a fine scale using a high-resolution rice distribution dataset and county-level yield data. In fact, it is preferable to base the study on the smaller spatial unit for calculation to acquire a more accurate estimate of yield losses [36].
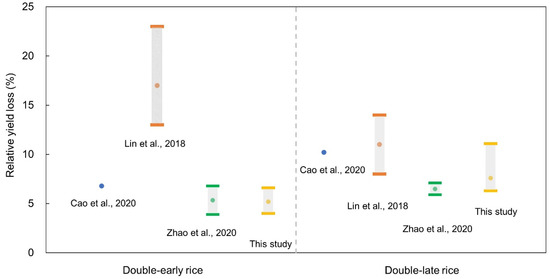
Figure 9.
Comparison of relative yield loss between this study and other related research. Note that the cited literature in the figure have been listed in the references, namely Cao et al. [20], Lin et al. [18], and Zhao et al. [39].
4.3. Limitations and Suggestions for Future Perspectives
As mentioned above, in this study we adopted a Chinese-specific exposure-response function based on the AOT40 index for the assessment of yield reductions induced by ambient ozone pollution. The AOT40 metric concerns O3 concentration and exposure time simultaneously, and has the advantages of simple calculation and being easy to use, and it was also commonly adopted in the previous literature [28,30,60]. However, the impact of O3 on plants depends not only on the ambient O3 concentration but also on the stomatal conductance of plant leaves that determine the absorption of O3 [13]. In recent years, the flux-based metric PODY (Phytotoxic O3 dose over an hourly flux threshold of Y nmol m–2 · s–1) was proposed which further considered the effects of biological and environmental factors (phenology, temperature, photosynthetically active radiation, vapor pressure deficit and soil water potential) on plant stomatal O3 absorption [25]. Research showed that, in comparison with flux-based metrics, the ambient O3 exposure-based AOT40 metric overestimated crop yield reductions [61,62]. Hence, the flux-based PODY index is regarded to be more suitable for O3-induced yield losses estimate. Nevertheless, the calculation of the PODY stomatal uptake metric requires hourly observation data for meteorological factors, soil moisture and other variables. Additionally, the threshold Y will alter with the change of crop varieties, growth periods and environmental factors, and no model can fully simulate the dynamic change process of parameter Y [14]. These limiting factors make it difficult to apply to large-scale yield loss assessment. In the future, more attention should be directed to the study on stomatal ozone flux-response functions established for Chinese crop cultivars, improving the estimation accuracy of regional rice yield losses.
Moreover, in the present study the AOT40 exposure-response function was derived using the open-top chambers (OTC) facility. It was reported that the evaluation of crop O3 sensitivity also relies on the selection of exposure modes [33]. Research showed that crops displayed a higher sensitivity to ozone pollution using the free-air controlled exposure (O3-FACE) in contrast with enclosed OTC experiments, which suffered the defect that the microclimates (e.g., temperature, water, radiation and winds) within the chamber were not comparable with the free air conditions outside the chamber [62]. Consequently, actual yield loss may be slightly higher than the current estimate.
As revealed in the present study, ambient ground-level O3 pollution has adversely impacted rice production in double-cropping rice planting areas of south China, causing yield reductions totaling 19.52 million tons and economic losses of USD 8081.03 million during 2013–2019. Given that O3 concentration is projected to increase continuously during the growing seasons in the farming areas, ambient O3 pollution intensively threatens food security in China. Moreover, the resulting crop yield loss may increase China’s grain imports, thus affecting the grain prices on the international market, thereby influencing global food security [63]. Hence, in this study, we propose several suggestions to alleviate the negative impacts of O3 on crop production for policymakers. Firstly, it is recommended to continuously implement rigorous policies on the emission reduction of ozone precursors. The “Three-year Action Plan for Cleaner Air” promulgated during the period 2018–2020 has been proven a success in suppressing O3 pollution by reducing the emissions of NOX and anthropogenic VOCs in the last few years [50]. Accordingly, it is a priority to establish more air quality ground stations in rural areas, which are currently underrepresented in the national ozone measurement network, in order to promote the monitoring and early warning of ambient O3 and its precursors emissions in major grain producing areas, and raise the accuracy of O3-induced yield reductions assessment [64]. Secondly, it is suggested to reasonably schedule the growth period of crops to avoid the peak season of O3 and reduce the cumulative exposure to ambient O3 during the crop growth periods. For instance, local farmers could consider expanding the planting area of double-early rice in the middle and lower reaches of the Yangtze River and Guangdong province, taking into account the relatively smaller ozone exposure risk during the growth season of double-early rice, as our analysis pointed out in the present study. Thirdly, with regard to the continued severity of surface ozone in the coming years, breeding O3-resistant crop varieties through advanced molecular biotechnology provides an alternative to improving the resistance of crops to O3 exposure risks. Finally, the application of antioxidants (e.g., ethylenediurea, EDU) has been validated as an effective approach to mitigate O3 damage to crops [65]. Consequently, rationally applying EDU is conducive to countering the adverse impacts of agricultural losses by high O3 pollution levels in future climate and emission scenarios.
5. Conclusions
In this study, we estimated the rice yield and economic losses by ambient ozone exposure on the county scale for the time series of 2013 to 2019 in the main double-cropping regions of southern China. The joint application of a full-coverage and high-resolution ground-level ozone reanalysis dataset and a high-resolution double-season rice distribution dataset, in combination with a Chinese-specific crop exposure-response function, guarantees the reliability of the analysis results in the present study. The main conclusions are summarized as follows:
(1) The AOT40 exposure metric presented generally increasing trends in both double-early and double-late rice growing seasons from 2013 to 2019. However, the annual growth rate of the latter was two-fold the counterpart of the former. In particular, AOT40 increased at an annual increase of 2.2 ppm h (36.5% growth per year) during the late rice growing season for the three consecutive years of 2017 to 2019, indicating more aggravated ozone exposure imposed on rice production during the double-late rice season.
(2) The relative yield losses caused by ambient ozone exposure ranged from 4.0% to 6.6% for double-early rice and 6.3% to 11.1% for double-late rice, exceeding the critical level of 5%. The associated crop production loss and economic loss totaled 703.7 × 104 t and USD 2921.6 million for double-early rice and 1247.8 × 104 t and USD 5159.4 million for double-late rice over the last seven years. Priorities should be devoted to Hunan and Jiangxi provinces, which altogether contributed over 50% of the total yield reductions out of nine provinces in the whole of southern China.
(3) Overall, our analysis highlighted the severity of O3-induced crop loss in southern China. With continued economic growth, it is projected that surface O3 concentrations will continuously rise in the future. In this context, it is prioritized to establish more stations for surface-level O3 monitoring in rural areas and thereby reduce the uncertainties in estimated crop O3 exposure. Moreover, government departments should formulate more stringent policies on O3 precursors emission reduction. O3-resistant crop cultivars and the application of antioxidants in fields are also urgently necessary to reduce O3-induced agricultural losses in the future.
Author Contributions
Conceptualization, J.P.; methodology, J.P. and P.L.; software, P.L., X.G. and H.G.; validation, P.L. and X.G.; formal analysis, J.P., P.L., X.G., B.P., H.L., H.G., F.Z. and H.F.; investigation, P.L. and X.G.; resources, J.P.; data curation, P.L., X.G. and B.P.; writing—original draft preparation, J.P.; writing—review and editing, J.P., P.L. and H.F.; visualization, P.L.; supervision, J.P.; project administration, J.P. and H.F.; funding acquisition, J.P. and H.F. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This research was funded by the Guangdong Basic and Applied Basic Research Foundation (Nos. 2021A1515110442, 2020A1515110172), the “Unveiling the List of Hanging” Science and Technology Project of Jinggangshan Agricultural High-tech Industrial Demonstration Zone (No. 20222-051244), Natural Science Foundation of Guangdong Province (Grants No. 2023A1515030122), the Foundation of the President of the Zhongke-Ji’an Institute for Eco-Environmental Sciences (ZJIEES-2022-02), and the Science and Technology Project of Jinggangshan Agricultural High-Tech Industrial Demonstration Zone (No. 202151).
Acknowledgments
The authors would like to thank the editors and anonymous reviewers for their constructive suggestions and comments to improve the quality of this paper, and special gratitude should be given to the contributors of the Chinese Air Quality Reanalysis (CAQRA) dataset used in this research.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
References
- Vingarzan, R. A review of surface ozone background levels and trends. Atmos. Environ. 2004, 38, 3431–3442. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cooper, O.R.; Parrish, D.; Ziemke, J.; Balashov, N.; Cupeiro, M.; Galbally, I.; Gilge, S.; Horowitz, L.; Jensen, N.; Lamarque, J.-F. Global distribution and trends of tropospheric ozone: An observation-based review. Elem. Sci. Anthr. 2014, 2, 000029. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fiscus, E.L.; Booker, F.L.; Burkey, K.O. Crop responses to ozone: Uptake, modes of action, carbon assimilation and partitioning. Plant Cell Environ. 2005, 28, 997–1011. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, T.; Xue, L.; Brimblecombe, P.; Lam, Y.F.; Li, L.; Zhang, L. Ozone pollution in China: A review of concentrations, meteorological influences, chemical precursors, and effects. Sci. Total Environ. 2017, 575, 1582–1596. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lu, X.; Zhang, L.; Wang, X.; Gao, M.; Li, K.; Zhang, Y.; Yue, X.; Zhang, Y. Rapid increases in warm-season surface ozone and resulting health impact in China since 2013. Environ. Sci. Technol. Lett. 2020, 7, 240–247. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feng, Z.; De Marco, A.; Anav, A.; Gualtieri, M.; Sicard, P.; Tian, H.; Fornasier, F.; Tao, F.; Guo, A.; Paoletti, E. Economic losses due to ozone impacts on human health, forest productivity and crop yield across China. Environ. Int. 2019, 131, 104966. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kong, L.; Tang, X.; Zhu, J.; Wang, Z.; Li, J.; Wu, H.; Wu, Q.; Chen, H.; Zhu, L.; Wang, W. A 6-year-long (2013–2018) high-resolution air quality reanalysis dataset in China based on the assimilation of surface observations from CNEMC. Earth Syst. Sci. Data 2021, 13, 529–570. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feng, Z.; Kobayashi, K.; Ainsworth, E.A. Impact of elevated ozone concentration on growth, physiology, and yield of wheat (Triticum aestivum L.): A meta-analysis. Glob. Change Biol. 2008, 14, 2696–2708. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Avnery, S.; Mauzerall, D.L.; Liu, J.; Horowitz, L.W. Global crop yield reductions due to surface ozone exposure: 1. Year 2000 crop production losses and economic damage. Atmos. Environ. 2011, 45, 2284–2296. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feng, Z.; Kobayashi, K. Assessing the impacts of current and future concentrations of surface ozone on crop yield with meta-analysis. Atmos. Environ. 2009, 43, 1510–1519. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singh, A.A.; Agrawal, S.; Shahi, J.; Agrawal, M. Investigating the response of tropical maize (Zea mays L.) cultivars against elevated levels of O3 at two developmental stages. Ecotoxicology 2014, 23, 1447–1463. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wilkinson, S.; Mills, G.; Illidge, R.; Davies, W.J. How is ozone pollution reducing our food supply? J. Exp. Bot. 2012, 63, 527–536. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ainsworth, E.A. Understanding and improving global crop response to ozone pollution. Plant J. 2017, 90, 886–897. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Peng, J.; Shang, B.; Xu, Y.; Feng, Z.; Calatayud, V. Effects of ozone on maize (Zea mays L.) photosynthetic physiology, biomass and yield components based on exposure-and flux-response relationships. Environ. Pollut. 2020, 256, 113466. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mills, G.; Sharps, K.; Simpson, D.; Pleijel, H.; Frei, M.; Burkey, K.; Emberson, L.; Uddling, J.; Broberg, M.; Feng, Z. Closing the global ozone yield gap: Quantification and cobenefits for multistress tolerance. Glob. Change Biol. 2018, 24, 4869–4893. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Shen, L.; Wu, S.; Mickley, L.; He, J.; Hao, J. Sensitivity of surface ozone over China to 2000–2050 global changes of climate and emissions. Atmos. Environ. 2013, 75, 374–382. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, T.; Yang, X.; Fu, W.; Li, G.; Feng, B.; Fu, G.; Tao, L. Strengthened Assimilate Transport Improves Yield and Quality of Super Rice. Agronomy 2022, 12, 753. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, Y.; Jiang, F.; Zhao, J.; Zhu, G.; He, X.; Ma, X.; Li, S.; Sabel, C.E.; Wang, H. Impacts of O3 on premature mortality and crop yield loss across China. Atmos. Environ. 2018, 194, 41–47. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ramya, A.; Dhevagi, P.; Priyatharshini, S.; Saraswathi, R.; Avudainayagam, S.; Venkataramani, S. Response of rice (Oryza sativa L.) cultivars to elevated ozone stress. Environ. Monit. Assess. 2021, 193, 808. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cao, J.; Wang, X.; Zhao, H.; Ma, M.; Chang, M. Evaluating the effects of ground-level O3 on rice yield and economic losses in Southern China. Environ. Pollut. 2020, 267, 115694. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, X.-B.; Yuan, B.; Parrish, D.D.; Chen, D.; Song, Y.; Yang, S.; Liu, Z.; Shao, M. Long-term trend of ozone in southern China reveals future mitigation strategy for air pollution. Atmos. Environ. 2022, 269, 118869. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pleijel, H.; Danielsson, H.; Ojanperä, K.; De Temmerman, L.; Högy, P.; Badiani, M.; Karlsson, P. Relationships between ozone exposure and yield loss in European wheat and potato—A comparison of concentration-and flux-based exposure indices. Atmos. Environ. 2004, 38, 2259–2269. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, X.; Feng, Z.; Sun, T.; Liu, X.; Tang, H.; Zhu, J.; Guo, W.; Kobayashi, K. Effects of elevated ozone concentration on yield of four Chinese cultivars of winter wheat under fully open-air field conditions. Glob. Change Biol. 2011, 17, 2697–2706. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mills, G.; Buse, A.; Gimeno, B.; Bermejo, V.; Holland, M.; Emberson, L.; Pleijel, H. A synthesis of AOT40-based response functions and critical levels of ozone for agricultural and horticultural crops. Atmos. Environ. 2007, 41, 2630–2643. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feng, Z.; Tang, H.; Uddling, J.; Pleijel, H.; Kobayashi, K.; Zhu, J.; Oue, H.; Guo, W. A stomatal ozone flux–response relationship to assess ozone-induced yield loss of winter wheat in subtropical China. Environ. Pollut. 2012, 164, 16–23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, X.; Zhang, Q.; Zheng, F.; Zheng, Q.; Yao, F.; Chen, Z.; Zhang, W.; Hou, P.; Feng, Z.; Song, W. Effects of elevated O3 concentration on winter wheat and rice yields in the Yangtze River Delta, China. Environ. Pollut. 2012, 171, 118–125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singh, A.A.; Agrawal, S.; Shahi, J.; Agrawal, M. Assessment of growth and yield losses in two Zea mays L. cultivars (quality protein maize and nonquality protein maize) under projected levels of ozone. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2014, 21, 2628–2641. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peng, J.; Shang, B.; Xu, Y.; Feng, Z.; Pleijel, H.; Calatayud, V. Ozone exposure-and flux-yield response relationships for maize. Environ. Pollut. 2019, 252, 1–7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sinha, B.; Singh Sangwan, K.; Maurya, Y.; Kumar, V.; Sarkar, C.; Chandra, B.; Sinha, V. Assessment of crop yield losses in Punjab and Haryana using 2 years of continuous in situ ozone measurements. Atmos. Chem. Phys. 2015, 15, 9555–9576. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Emberson, L.; Büker, P.; Ashmore, M.; Mills, G.; Jackson, L.; Agrawal, M.; Atikuzzaman, M.; Cinderby, S.; Engardt, M.; Jamir, C. A comparison of North American and Asian exposure–response data for ozone effects on crop yields. Atmos. Environ. 2009, 43, 1945–1953. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, M.; Yao, Q.; Chen, D.; Li, M.; Li, R.; Gao, B.; Zhao, B.; Chen, Z. Estimating the impact of ground ozone concentrations on crop yields across China from 2014 to 2018: A multi-model comparison. Environ. Pollut. 2021, 283, 117099. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhao, H.; Zheng, Y.; Wu, X. Assessment of yield and economic losses for wheat and rice due to ground-level O3 exposure in the Yangtze River Delta, China. Atmos. Environ. 2018, 191, 241–248. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Van Dingenen, R.; Dentener, F.J.; Raes, F.; Krol, M.C.; Emberson, L.; Cofala, J. The global impact of ozone on agricultural crop yields under current and future air quality legislation. Atmos. Environ. 2009, 43, 604–618. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Silva, R.A.; West, J.J.; Zhang, Y.; Anenberg, S.C.; Lamarque, J.-F.; Shindell, D.T.; Collins, W.J.; Dalsoren, S.; Faluvegi, G.; Folberth, G. Global premature mortality due to anthropogenic outdoor air pollution and the contribution of past climate change. Environ. Res. Lett. 2013, 8, 034005. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Seltzer, K.M.; Shindell, D.T.; Kasibhatla, P.; Malley, C.S. Magnitude, trends, and impacts of ambient long-term ozone exposure in the United States from 2000 to 2015. Atmos. Chem. Phys. 2020, 20, 1757–1775. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, T.; Liu, S.; Xu, Y.; Feng, Z.; Calatayud, V. Assessment of O3-induced yield and economic losses for wheat in the North China Plain from 2014 to 2017, China. Environ. Pollut. 2020, 258, 113828. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Aunan, K.; Berntsen, T.K.; Seip, H.M. Surface ozone in China and its possible impact on agricultural crop yields. AMBIO A J. Hum. Environ. 2000, 29, 294–301. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tang, H.; Takigawa, M.; Liu, G.; Zhu, J.; Kobayashi, K. A projection of ozone-induced wheat production loss in China and India for the years 2000 and 2020 with exposure-based and flux-based approaches. Glob. Change Biol. 2013, 19, 2739–2752. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, H.; Zheng, Y.; Zhang, Y.; Li, T. Evaluating the effects of surface O3 on three main food crops across China during 2015–2018. Environ. Pollut. 2020, 258, 113794. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dong, C.; Gao, R.; Zhang, X.; Li, H.; Wang, W.; Xue, L. Assessment of O3-induced crop yield losses in northern China during 2013–2018 using high-resolution air quality reanalysis data. Atmos. Environ. 2021, 259, 118527. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sicard, P.; Serra, R.; Rossello, P. Spatiotemporal trends in ground-level ozone concentrations and metrics in France over the time period 1999–2012. Environ. Res. 2016, 149, 122–144. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zeng, X.; Gao, Y.; Wang, Y.; Ma, M.; Zhang, J.; Sheng, L. Characterizing the distinct modulation of future emissions on summer ozone concentrations between urban and rural areas over China. Sci. Total Environ. 2022, 820, 153324. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pan, B.; Zheng, Y.; Shen, R.; Ye, T.; Zhao, W.; Dong, J.; Ma, H.; Yuan, W. High resolution distribution dataset of double-season paddy rice in china. Remote Sens. 2021, 13, 4609. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feng, Z.; Hu, T.; Tai, A.P.; Calatayud, V. Yield and economic losses in maize caused by ambient ozone in the North China Plain (2014–2017). Sci. Total Environ. 2020, 722, 137958. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tang, X.; Kong, L.; Zhu, J.; Wang, Z.; Li, J.; Wu, H.; Wu, Q.; Chen, H.; Zhu, L.; Wang, W. A High-Resolution Air Quality Reanalysis Dataset over China (CAQRA); Science Data Bank: Beijing, China, 2021. [Google Scholar]
- Chen, M.; Qin, Q.; Liu, F.; Wang, Y.; Wu, C.; Yan, Y.; Xiang, H. How long-term air pollution and its metal constituents affect type 2 diabetes mellitus prevalence? Results from Wuhan Chronic Disease Cohort. Environ. Res. 2022, 212, 113158. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, H.; Li, M.; Zhang, S.; Qian, Z.M.; Zhang, Z.; Zhang, K.; Wang, C.; Arnold, L.D.; McMillin, S.E.; Wu, S. Interactive effects of cold spell and air pollution on outpatient visits for anxiety in three subtropical Chinese cities. Sci. Total Environ. 2022, 817, 152789. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, H.; Zhang, X.; Zhang, H.; Luo, H.; Feng, Y.; Wang, J.; Huang, C.; Yu, Z. Assessing the effect of fine particulate matter on adverse birth outcomes in Huai River Basin, Henan, China, 2013–2018. Environ. Pollut. 2022, 306, 119357. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ren, X.; Shang, B.; Feng, Z.; Calatayud, V. Yield and economic losses of winter wheat and rice due to ozone in the Yangtze River Delta during 2014–2019. Sci. Total Environ. 2020, 745, 140847. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, H.; Wang, L.; Zhang, Z.; Qi, Q.; Zhang, H. Quantifying ecological and health risks of ground-level O3 across China during the implementation of the “Three-year Action Plan for Cleaner Air”. Sci. Total Environ. 2022, 817, 153011. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Gao, W.; Wang, S.; Song, T.; Gong, Z.; Ji, D.; Wang, L.; Liu, Z.; Tang, G.; Huo, Y. Contrasting trends of PM2.5 and surface-ozone concentrations in China from 2013 to 2017. Natl. Sci. Rev. 2020, 7, 1331–1339. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, X.; Hong, J.; Zhang, L.; Cooper, O.R.; Schultz, M.G.; Xu, X.; Wang, T.; Gao, M.; Zhao, Y.; Zhang, Y. Severe surface ozone pollution in China: A global perspective. Environ. Sci. Technol. Lett. 2018, 5, 487–494. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shen, F.; Zhang, L.; Jiang, L.; Tang, M.; Gai, X.; Chen, M.; Ge, X. Temporal variations of six ambient criteria air pollutants from 2015 to 2018, their spatial distributions, health risks and relationships with socioeconomic factors during 2018 in China. Environ. Int. 2020, 137, 105556. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sousa, S.; Alvim-Ferraz, M.; Martins, F. Identification and origin of nocturnal ozone maxima at urban and rural areas of Northern Portugal–Influence of horizontal transport. Atmos. Environ. 2011, 45, 942–956. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tong, L.; Zhang, H.; Yu, J.; He, M.; Xu, N.; Zhang, J.; Qian, F.; Feng, J.; Xiao, H. Characteristics of surface ozone and nitrogen oxides at urban, suburban and rural sites in Ningbo, China. Atmos. Res. 2017, 187, 57–68. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Seltzer, K.M.; Shindell, D.T.; Malley, C.S. Measurement-based assessment of health burdens from long-term ozone exposure in the United States, Europe, and China. Environ. Res. Lett. 2018, 13, 104018. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, K.; Jacob, D.J.; Shen, L.; Lu, X.; De Smedt, I.; Liao, H. Increases in surface ozone pollution in China from 2013 to 2019: Anthropogenic and meteorological influences. Atmos. Chem. Phys. 2020, 20, 11423–11433. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shen, J.; Zhang, Y.; Wang, X.; Li, J.; Chen, H.; Liu, R.; Zhong, L.; Jiang, M.; Yue, D.; Chen, D. An ozone episode over the Pearl River Delta in October 2008. Atmos. Environ. 2015, 122, 852–863. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pleijel, H.; Broberg, M.C.; Uddling, J. Ozone impact on wheat in Europe, Asia and North America–A comparison. Sci. Total Environ. 2019, 664, 908–914. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feng, Z.; Xu, Y.; Kobayashi, K.; Dai, L.; Zhang, T.; Agathokleous, E.; Calatayud, V.; Paoletti, E.; Mukherjee, A.; Agrawal, M. Ozone pollution threatens the production of major staple crops in East Asia. Nat. Food 2022, 3, 47–56. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tang, H.; Pang, J.; Zhang, G.; Takigawa, M.; Liu, G.; Zhu, J.; Kobayashi, K. Mapping ozone risks for rice in China for years 2000 and 2020 with flux-based and exposure-based doses. Atmos. Environ. 2014, 86, 74–83. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feng, Z.; Calatayud, V.; Zhu, J.; Kobayashi, K. Ozone exposure- and flux-based response relationships with photosynthesis of winter wheat under fully open air condition. Sci. Total Environ. 2018, 619–620, 1538–1544. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tai, A.P.K.; Martin, M.V.; Heald, C.L. Threat to future global food security from climate change and ozone air pollution. Nat. Clim. Change 2014, 4, 817–821. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feng, Z.; Hu, E.; Wang, X.; Jiang, L.; Liu, X. Ground-level O3 pollution and its impacts on food crops in China: A review. Environ. Pollut. 2015, 199, 42–48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shang, B.; Fu, R.; Agathokleous, E.; Dai, L.; Zhang, G.; Wu, R.; Feng, Z. Ethylenediurea offers moderate protection against ozone-induced rice yield loss under high ozone pollution. Sci. Total Environ. 2022, 806, 151341. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).