Abstract
Introduction: The recent Zika virus(ZIKV) epidemic in Brazil was characterized by a range of different clinical presentations, particularly microcephaly, Guillain-Barré syndrome, and death. In this context, we determined the causal relationship between fatal microcephaly cases and ZIKV infection. Methods: Twelve fatal cases of neonates, whose mothers were infected with ZIKV during pregnancy, were examined; cases included nine neonatal deaths due to microcephaly, one miscarriage, and two stillbirths. Tissue samples were obtained from all cases at necropsy and were submitted for virological investigation (RT-qPCR and virus isolation) and/or histopathology (hematoxylin and eosin staining) and immunohistochemical assay for the detection of ZIKV antigens. Results: ZIKV antigens and/or ZIKV RNA were detected in tissue samples of all 12 cases examined. ZIKV was recovered in one case. Results of the virological and immunohistochemical analyses, as well as the anatomic abnormalities and histopathologic changes observed at necropsy on the 12 fatal cases, are presented. Conclusions: Data from these 12 cases provide strong evidence of the causal relationship between ZIKV and congenital disease in fetuses of women who were infected with the virus during pregnancy.
1. Introduction
Zika virus (ZIKV), a mosquito-borne agent belonging to the genus Flavivirus family Flaviviridae, was originally isolated in Uganda in 1947 [1]. Subsequently, ZIKV has spread globally [2]. In 2013, the virus was associated with a large epidemic in French Polynesia [3]; and since 2015, 47 countries and territories have confirmed the local transmission of ZIKV disease. Further, 27 countries and territories in the Americas have reported confirmed cases of congenital disease associated with ZIKV infection [4]. In 2015, ZIKV infections were detected in the Brazilian state of Bahia [5,6]. However, a later study reported that the introduction of the virus into Brazil actually occurred in 2013, suggesting the failure of early recognition contributed to the extensive and silent spread of the virus throughout the country [7].
The ZIKV epidemic in Brazil was characterized by a range of different clinical presentations, particularly microcephaly, Guillain-Barré syndrome, and death in individuals with autoimmune disorders [8]. The Brazilian Ministry of Health and the Pan American Health Organization (PAHO) confirmed the causal relationship between microcephaly and ZIKV after diagnosis at the Evandro Chagas Institute (Ministry of Health) of a case of microcephaly and other neurological manifestations in a newborn that died 5 min after birth. In this case, ZIKV was isolated from the brain and viral RNA was detected by real-time RT-PCR in the brain and other organs, including lungs, heart, liver and kidney [7,9]. In the present article virological, histological and immunohistochemical studies were done on 12 fatal cases, including nine newborn cases of microcephaly, one miscarriage, and two stillbirths caused by ZIKV infection. The purpose of this report is to use these confirmed cases of fatal microcephaly to demonstrate the clinical, virological, and histopathological findings associated with ZIKV infection.
2. Material and Methods
2.1. Patients
The study included 12 cases of fatal ZIKV infection that occurred between November 2015 and January 2016 from the northeast region of Brazil (states of Ceará-CE (n = 5), Paraíba-PB (n = 1), Pernambuco-PE (n = 1), and Rio Grande do Norte-RN (n = 4)), as well as from the southeast (state of Espírito Santo-ES (n = 1)). Table 1 summarizes the demographic and clinical characteristics and Table 2 gives the laboratory and necropsy findings on the 12 cases.

Table 1.
Information about the 12 fatal cases of Zika virus (ZIKV) infection.

Table 2.
Results of Histopathology, Immunohistochemistry (IHC) and Real Time PCR (RT-qPCR) in the 12 fatal cases of ZIKV infection.
Microcephaly was diagnosed in the cases investigated after stillbirth (n = 2) and in newborns that had died after delivery (n = 9). An additional case of abortion was also included in the study, totaling 12 cases. The cases described are shown in Table 1.
2.2. Ethics Statement
Biological samples of the patients were obtained and processed in the context of the emergency definition by the Ministry of Health during surveillance activities of the ZIKV epidemic in Brazil. This study was approved (opinion number 1.888.946) by the Research Ethics Committee (CEP) of the Evandro Chagas Institute (IEC). Photograph of case 10 was authorized by parents (See authorization as appendix).
2.3. Real Time RT-PCR (RT-qPCR) and Virus Isolation
Attempts to isolate virus were performed using C6/36 cell cultures [10]. Briefly, blood and tissue fragments were triturated in phosphate-buffered saline containing 10% fetal bovine serum and antibiotics. After centrifugation at 2100× g for 10 min at 4 °C, 100 µL of the supernatant was inoculated into a 25-cm2 tissue culture flask with a monolayer of mosquito cells. After incubation for 2 h at 28 °C, medium was added and the cells were incubated at room temperature (~25 °C) for 10 days. The cells were first examined by an indirect immunofluorescent assay using a flavivirus group hyperimmune polyclonal mouse antibody. Next, cells that did not react to dengue and yellow fever virus monoclonal antibodies produced by Biomanguinhos/FIOCRUZ (DENV1-041118FDEN1P, DENV2-070109FDEN2P, DENV3-070910FDEN3P, 041005FDEN4P and foy YFV-111108FFAD2PB lots, Biomanguinhos/FIOCRUZ, Rio de Janeiro, Brazil) were tested by real-time RT-PCR (RT-qPCR) [11,12]. Supernatants of tissue homogenates and, when available serum samples, were used for RNA extraction with the Trizol Plus RNA Extraction kit (Ambion, Thermo-FischerScientific, Waltham, MA, USA), according to manufacturer instructions. The RT-qPCR assays were carried out in a 7500 Real Time PCR System (Applied Biotechnologies, Thermo-Fischer Scientific, Waltham, MA, USA) using the Superscript III Platinum One-Step RT-qPCR kit (Invitrogen, Thermo-Fischer Scientific, Waltham, MA, USA) and two different primer/probe sets targeting the NS5 and E regions of the ZIKV genome.All clinical samples were simultaneously tested by RT-qPCR against dengue virus (DENV) and chikungunya virus.
2.4. Histopathology and Immunohistochemistry
Paraffin-embedded tissue samples were processed for histopathology and stained with hematoxylin and eosin (HE). For immunohistochemistry (IHC), an adapted Streptavidin Alkaline Phosphatase (SAAP) assay [8,13,14,15,16,17,18] with anti-ZIKV polyclonal mouse antibody. The polyclonal anti-ZIKV antibody used in the IHC assay was prepared at the Instituto Evandro Chagas (IEC, Ananindeua, Brazil) in young Swiss mice using a ZIKV strain isolated in cell culture (C6/36 cells). This polyclonal serum was tested against antigens of ZIKV and several other circulating flaviviruses (dengue virus—DENV, yellow fever virus–YFV, Saint Louis encephalitis virus—SLEV, etc.) in Brazil and was only positive for ZIKV. All clinical samples were simultaneously tested by IHC against ZIKV and the most important flaviviruses occurring in Brazil (DENV and Yellow fever virus-YFV) using monoclonal antibodies.
3. Results
Table 2 shows the results of the RT-qPCR, histopathology, and immunohistochemistry assays for ZIKV in tissues taken at necropsy from the 12 cases. A single ZIKV strain was isolated from the brain, heart, kidney, and lungs of Case 10. The clinical specimens were also subjected to RT-qPCR for the detection of dengue and chikungunya, and all of the specimens tested negative. In addition, immunohistochemistry assays for dengue, yellow fever, and chikungunya viruses were also negative in all examined clinical specimens. In contrast, ZIKV antigens were detected in the tissues of all 12 cases, with the brain and liver tissues showing the strongest positive (and ZIKV load titers) results (Table 2).
Case 1 showed necrotic lesions in fetal tissues and calcifications in the placenta. ZIKV antigens were detected in both tissues (Figure 1A–D). Fresh tissues were not obtained.
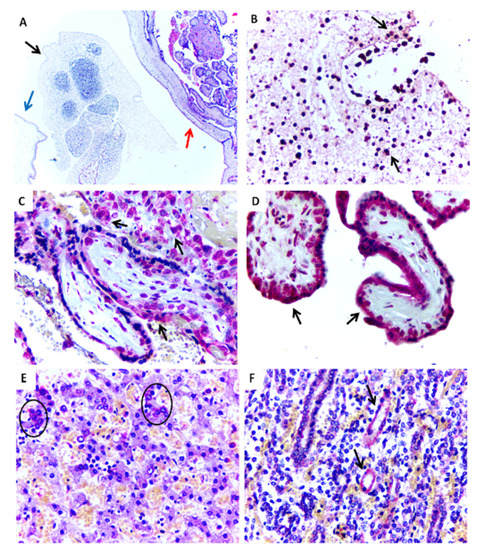
Figure 1.
Histopathological aspects and positive immunostaining of the ZIKV-infectedmiscarriage (Case 1). (A) Embryonic tissue (black arrow) within the yolk sac (blue arrow) and placenta (red arrow) (HE, 100×). (B) Positive immunostaining for ZIKV antigens in embryonic tissue (IHC, SAAP, 400×). (C,D) Positive immunostaining for ZIKV in placental chorionic villi (IHC, SAAP, 400×). (E) Positive immunostaining to ZIKV observed in the liver in hepatocytes (circle) (Case 3) (IHC, SAAP, 400×). (F) Positive immunostaining to ZIKV observed in the kidney in renal tubule (black arrows) (Case 3) (IHC, SAAP, 400×).
Case 2 showed large areas of cerebral necrosis, apoptosis, focal areas with calcifications, gliosis, vascular proliferation, and edema. ZIKV antigens, detected by immunohistochemistry and viral RNA, were found in all tissues studied (brain, liver, kidney, and lungs) (Table 2). In Case 3, histopathology revealed apoptotic neurons, diffuse vascular congestion and edema in the brain. Similarly, alterations were seen in the liver (congestion and steatosis), placenta (multifocal calcification areas), and lungs (congestion). Immunohistochemistry was ZIKV-positive only in the brain, liver, and kidney (Table 2) (Figure 1E,F).
Amniotic fluid and meconium were found in the lungs, strongly suggesting fetal distress and aspiration. Fresh tissues were not obtained (Table 2). Histopathological changes were observed in almost all examined tissues. The central nervous system (CNS) was the most affected tissue, but several changes were also found in sections of viscera, mainly liver, kidney, and lungs (Table 2).
Case 4 only survived for 4 hbut had microcephaly and other malformations (nasopalatine fissure, low set ears, and congenital clubfoot). Vascular congestion was observed in all examined tissues (brain, liver, kidney, and lungs). Edema in the brain, focal areas of steatosis in the liver, and focal hemorrhage in the kidney and lungs were frequently found. Immunohistochemistry exams were positive in the brain (Figure 2A,B) and other tissues, except for the lungs (Table 2).
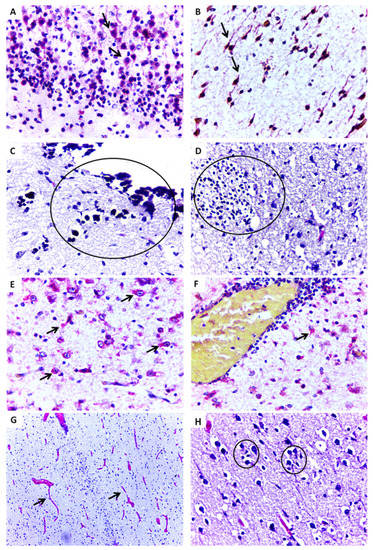
Figure 2.
Representative histopathological changes and positive immunostaining in central nervous tissue of ZIKV-positive microcephaly cases by ZIKV. (A,B) Cellular disorganization in the cortical layer and positive immunostaining (arrow) for ZIKV antigen in neurons (Case 4) (IHC, SAAP, 400×). (C) Foci of dystrophic calcification in parenchyma with degenerative necrotic lesion (Case 6) (HE, 400×). (D) Gliosis in parenchyma with degenerative necrotic lesion (Case 6) (HE, 400×). (E,F) Positive immunostaining for ZIKV in neurons and astrocytes with perivascular inflammatory infiltrate (Case 6) (IHC, SAAP, 400×). (G) Significant vascular proliferation, edema and vessel congestion (arrows) (Case 11) (HE, 100×). (H) Pyramidal neurons of the cerebral cortex with neuronophagy, satelitosis, and gliosis (circles) (Case 11) (HE, 400×).
Case 5 survived for 6 hand had microcephaly, arthrogryposis, and other malformations. The mother had a confirmed ZIKV infection during pregnancy; and brain fragments of the infant tested positive for the virus by RT-qPCR (RNA detection) and immunohistochemistry (antigen detection). In addition to relevant histopathological findings observed in the brainstem (edema, vascular congestion, and degenerative neuronal lesions), significant changes were found in the liver (subcapsular bleeding, steatosis, and inflammatory infiltrate), kidney, and lungs (focal hemorrhage and vascular congestion) (Table 2).
Case 6 had microcephaly, arthrogryposis, other congenital malformations and survived for 14 h. Histopathological analysis revealed intense brain damage characterized by necrosis, apoptosis, gliosis, calcifications, ventriculomegaly, edema, intense vascular congestion, and inflammatory infiltration (Figure 2C,D). Like the other cases, vascular congestion was observed in the liver, kidney, and lungs, as well as hepatic steatosis, pulmonary bleeding, and edema. Immunohistochemistry was positive for ZIKV antigen (Figure 2E,F) and viral RNA was detected by RT-qPCR in the brain (Table 2).
Case 7 died 1 day after birth. Intense histological changes were observed in neuronal tissue, including meningeal thickening, as well as edema, hyperemia, intense vascularization, and an inflammatory infiltrate in all CNS structures examined. Intense vascular proliferation and focal necrotic lesions were frequent. In the lung, an inflammatory infiltrate mainly consisting of lymphocytes was detected in the bronchioles and interstitial septa, accompanied by alveolar collapse. Immunohistochemistry was only positive for ZIKV antigen in the brain, while the ZIKV genome was detected in the brain, liver, spleen, heart, kidney, and lungs (Table 2).
Case 8 survived for 2 days and had microcephaly. Histological changes were mainly found in the CNS and included intense vascular congestion, edema, vascular proliferation, neuronal necrosis, focal neuronal depopulation, and multiple calcification foci. Aspiration of amniotic fluid was observed in the lungs, suggesting fetal distress. Immunohistochemistry was positive for ZIKV antigens in all tissues examined (Table 2).
Case 9 survived for 1 day and had microcephaly and other severe congenital malformations (congenital clubfoot and agenesis of the fingers). In the brain, multiple areas of cortical calcifications were observed, as well as neuronal depopulation, edema, necrosis, focal gliosis, vascular proliferation and residual necrotic neurons. Immunohistochemistry was positive in the brain, liver, and kidney. ZIKV RNA was detected in the brain, kidney, and lungs (Table 2).
Case 10 (Figure 3) survived for only 5 min and had microcephaly, arthrogryposis and other congenital malformations includingatresia of esophagus and insipient trachea. ZIKV RNA was detected by RT-qPCR in cerebrospinal fluid, brain, heart, kidney, and lungs. ZIKV was isolated in C6/36 cells from the brain, heart, kidney, and lungs. Formalin-fixed samples were not obtained (Table 2).
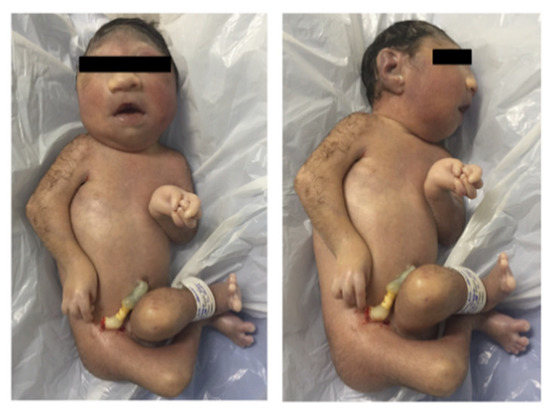
Figure 3.
Newborn with 29 weeks gestational age showing microcephaly and arthrogryposis. The infantdied 5 min after birth (Case 10).
Case 11 survived for 1 day and had microcephaly and arthrogryposis. Important changes were observed in CNS tissues, including meningeal thickening, intense vascular proliferation, edema, neuronal destruction followed by depopulation, and focal gliosis in the cortex (Figure 2G,H). Viral RNA was detected in all tissue samples (brain, liver, spleen, heart and kidney), and immunohistochemistry identified ZIKV antigens in the brain, liver, heart and kidney (Table 2).
Case 12 survived for 1 day. Placental tissue contained several foci ofcalcification and immunohistochemistry was positive for ZIKV antigens. ZIKV RNA was detected by real-time PCR in the placenta and in a neonatal serum sample. Fresh and formalin-fixed tissues samples were not collected from this case (Table 2).
4. Discussion
Until recently, ZIKV was not considered a serious threat or important public health problem. However, with the onset of Zika fever outbreaks and the microcephaly epidemic in Brazil and other countries, reports of microcephaly and other congenital malformations started to appear with cases of ZIKV infection, and the term “congenital ZIKV syndrome” was proposed [19,20,21,22]. In view of the severity of some cases with intense brain damage and other malformations, the Brazilian Government, and thereafter the WHO, classified the ZIKV epidemic as a public health emergency of international concern [23].
The first link between ZIKV and microcephaly in Brazil was established at the Evandro Chagas Institute with the detection of the ZIKV genome in the brain and other visceral fragmentsof a fatal case [9], and later in follow-ups of pregnant women infected with ZIKV in Rio de Janeiro [24,25]. These reports and others [21,26,27] demonstrated the need for clinical and laboratory evaluation of as many microcephaly cases as possible. Neonates who have died with microcephaly shouldbe examined to demonstrate the presence of ZIKV antigens by immunohistochemistry in paraffin-embedded tissues, or of ZIKV RNA by RT-qPCR in fresh tissues, cerebrospinal fluid, and serum samples, as previously reported [7,8,27,28].
In the present study, all 12 cases presented with severe and intense CNS involvement, which was characterized by necrosis, apoptosis, diffuse vascular congestion and proliferation, edema, inflammatory infiltration, gliosis, and calcifications. The predominance of lesions typical of neuronal tissue destruction is almost pathognomonic of the congenital ZIKV syndrome. In almost all of the cases, neuronal destruction (depopulation) was observed, which was well illustrated in our Cases 8, 9 and 11 of microcephaly.
In Case 1, ZIKV antigens were detected in embryonic tissues, neuronal cells, hepatocytes, and tubular renal cells. This case was a miscarriage that occurred at 8 weeks of gestation, demonstrating the destructive potential of ZIKV and characterizing the intense neurotropism of the virus. In addition, these findings emphasize the devastating fetal CNS injury following infection of the mother with ZIKV during pregnancy.
Important alterations were also detected in hepatic tissues, including steatosis, vascular congestion, focal erythropoiesis, and inflammatory infiltrates, similar to the descriptions of changes seen with other arboviruses, such as yellow fever and dengue virus [29,30,31]. In addition, renal changes were also found in our cases, especially vascular congestion, a finding also reported with dengue virus infection [32]. ZIKV RNA and/or antigens were detected in all cases, even in the child that died only 5 min after birth, as well as in the cases of microcephaly, stillbirth, and miscarriage, whose mothers were infected in the first or second trimester of gestation. These findings reinforce the capacity of ZIKV to persist in tissues of miscarriages, stillbirths, and neonates.
This case series demonstrates the potential of ZIKV to cause intrauterine infection, resultingine death at birth. The CNS lesions observed in our cases of miscarriage, stillbirth and newborn infections were predominantly characterized by neuronal death (necrosis and apoptosis), gliosis and calcifications;whereas lesions observed in the fatal adult cases have been predominantly inflammatory [8,13,14,15,16,17]. In conclusion, this study provides important new information on the relationship of ZIKV infection with microcephaly and other congenital defects in cases of congenital ZIKV syndrome. The detection of ZIKV antigens and viral RNA in CNS cells, especially neurons, and also in other cells of viscera in fetal and neonatal cases suggests that ZIKV persists in these cells. In our case series, the presence of ZIKV antigens and/or RNA in the 12 cases in Brazil was confirmed, indicating the causative role of ZIKV in nine neonate deaths, two stillbirths, and one miscarriage (ZIKV detected in placenta). In addition, cases 10 and 12 demonstrate that congenital ZIKV infection persisted for several months since the motherswere infected in the first and second trimesters, respectively. The stage and duration of infection were likely responsible for the severe clinical presentation and destruction of neurons, and, consequently, the depopulation of neurons in large areas of the cerebral cortex. This study provides strong evidence that ZIKV was the causative agent of microcephaly and other severe congenital malformations in the patients, resulting in fetal and neonatal deaths, as well as miscarriage.
Author Contributions
Conceptualization, R.S.S.A. and P.F.C.V.; methodology, M.T.A., A.J.M.F., B.T.D.N., D.F.H., E.V.P.S., V.L.C., J.O.C., L.C.M., B.C.B.V., J.R.S., F.M.C.A., M.G.L.d.Q., M.R.T.N., A.C.R.C., S.G.R. and J.A.S.Q.; formal analysis, R.S.S.A., J.S.A.Q., R.B.T. and P.F.C.V.; investigation of cases, F.M.C.A., E.M.R., A.R.P.C. and C.S.O.; resources, P.F.C.V.; writing—original draft preparation, R.S.S.A., J.A.S.Q., R.B.T. and P.F.C.V.; writing—review and editing, R.S.S.A., J.R.S., P.Y.S., J.A.S.Q., R.B.T. and P.F.C.V.; funding acquisition, P.F.C.V.; revision of final version, all authors.
Funding
This study is supported by the Evandro Chagas Institute, Ministry of Health of Brazil, CNPq by PFCV (303999/2016-0, 439971/2016-0 and 440405/2016-5), CAPES by PFCV (Zika Fast-track).
Acknowledgments
We are grateful for the staff of the Department of Pathology at the IEC, especially Valter Miranda Campos and Maria de Lourdes Gomes Lima, personal of the Department of Arbovirology and Hemorrhagic Fevers at the IEC, and Adlai Raimundo Sousa for their technical support, as well as staff of the Public Health Laboratories of Ceará, Espírito Santo, Pernambuco, and Rio Grande do Norte States.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
References
- Dick, G.W.; Kitchen, S.; Haddow, A. Zika Virus (I). Isolations and serological specificity. Trans. R. Soc. Trop. Med. Hyg. 1952, 46, 509–520. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hayes, E.B. Zika Virus Outside Africa. Emerg. Infect. Dis. 2009, 15, 1347–1350. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Oehler, E.; Watrin, L.; Larre, P.; Leparc-Goffart, I.; Lastere, S.; Valour, F.; Baudouin, L.; Mallet, H.; Musso, D.; Ghawche, F. Zika virus infection complicated by Guillain-Barre syndrome—Case report, French Polynesia, December 2013. Euro Surveill. 2014, 19, 7–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pan American Health Organization (PAHO)/World Health Organization (WHO). Zika—Epidemiological Update, 25 August 2017; PAHO/WHO: Washington, DC, USA, 2017. [Google Scholar]
- Campos, G.S.; Bandeira, A.C.; Sardi, S.I. Zika Virus Outbreak, Bahia, Brazil. Emerg. Infect. Dis. 2015, 21, 1885–1886. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zanluca, C.; de Melo, V.C.A.; Mosimann, A.L.P.; dos Santos, G.I.V.; dos Santos, C.N.D.; Luz, K. First report of autochthonous transmission of Zika virus in Brazil. Mem. Inst. Oswaldo Cruz 2015, 110, 569–572. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Faria, N.R.; Azevedo, R.S.S.; Kraemer, M.U.G.; Souza, R.; Cunha, M.S.; Hill, S.C.; Theze, J.; Bonsall, M.B.; Bowden, T.A.; Rissanen, I.; et al. Zika virus in the Americas: Early epidemiological and genetic findings. Science 2016, 352, 345–349. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Azevedo, R.S.S.; Araujo, M.T.; Martins Filho, A.J.; Oliveira, C.S.; Nunes, B.T.D.; Cruz, A.C.R.; Nascimento, A.G.P.; Medeiros, R.C.; Caldas, C.A.M.; Araujo, F.C.; et al. Zika virus epidemic in Brazil. I. Fatal disease in adults: Clinical and laboratorial aspects. J. Clin. Virol. 2016, 85, 56–64. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pan American Health Organization (PAHO)/World Health Organization (WHO). Epidemiological Alert—Neurological Syndrome, Congenital Malformations, and Zika Virus Infection. Implications for Public Health in the Americas—1 December 2015; PAHO/WHO: Washington, DC, USA, 2015. [Google Scholar]
- Tesh, R.B. A method for the isolation and identification of dengue viruses, using mosquito cell cultures. Am. J. Trop. Med. Hyg. 1979, 28, 1053–1059. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Faye, O.; Faye, O.; Dupressoir, A.; Weidmann, M.; Ndiaye, M.; Sall, A.A. One-step RT-PCR for detection of Zika virus. J. Clin. Virol. 2008, 43, 96–101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lanciotti, R.S.; Kosoy, O.L.; Laven, J.J.; Velez, J.O.; Lambert, A.J.; Johnson, A.J.; Stanfield, S.M.; Duffy, M.R. Genetic and Serologic Properties of Zika Virus Associated with an Epidemic, Yap State, Micronesia, 2007. Emerg. Infect. Dis. 2008, 14, 1232–1239. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martines, R.B.; Bhatnagar, J.; de Oliveira Ramos, A.M.; Davi, H.P.F.; Iglezias, S.D.A.; Kanamura, C.T.; Keating, M.K.; Hale, G.; Silva-Flannery, L.; Muehlenbachs, A.; et al. Pathology of congenital Zika syndrome in Brazil: A case series. Lancet 2016, 388, 898–904. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chimelli, L.; Melo, A.S.O.; Avvad-Portari, E.; Wiley, C.A.; Camacho, A.H.S.; Lopes, V.S.; Machado, H.N.; Andrade, C.V.; Dock, D.C.A.; Moreira, M.E.; et al. The spectrum of neuropathological changes associated with congenital Zika virus infection. Acta Neuropathol. 2017, 133, 983–999. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Azevedo, R.S.S.; de Sousa, J.R.; Araujo, M.T.F.; Martins Filho, A.J.; de Alcantara, B.N.; Araujo, F.M.C.; Queiroz, M.G.L.; Cruz, A.C.R.; Vasconcelos, B.H.B.; Chiang, J.O.; et al. In situ immune response and mechanisms of cell damage in central nervous system of fatal cases microcephaly by Zika virus. Sci. Rep. 2018, 8, 1–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- de Sousa, J.R.; Azevedo, R.S.S.; Martins Filho, A.J.; de Araujo, M.T.F.; Moutinho, E.R.C.; Baldez Vasconcelos, B.C.; Cruz, A.C.R.; Oliveira, C.S.; Martins, L.C.; Baldez Vasconcelos, B.H.; et al. Correlation between apoptosis and in situ immune response in fatal cases of microcephaly caused by Zika virus. Am. J. Pathol. 2018, 188. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- de Sousa, J.R.; da Silva Azevedo, R.D.S.; Martins Filho, A.J.; de Araujo, M.T.F.; Cruz, E.D.R.M.; Vasconcelos, B.C.B.; Cruz, A.C.R.; de Oliveira, C.S.; Martins, L.C.; Vasconcelos, B.H.B.; et al. In situ inflammasome activation results in severe damage to the central nervous system in fatal Zika virus microcephaly cases. Cytokine 2018, 111, 255–264. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bollweg, B.C.; Silva-flannery, L.; Spivey, P.; Hale, G.L.; Hale, G.L. Optimization of commercially available Zika virus antibodies for use in a laboratory-developed immunohistochemical assay. J. Pathol. Clin. Res. 2017, 4, 19–25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pan American Health Organization (PAHO)/World Health Organization (WHO). Zika—Epidemiological Update, 8 April 2016; PAHO/WHO: Washington, DC, USA, 2016. [Google Scholar]
- PAHO/WHO-Case Definitions. Zika Resources: Case Definitions. Available online: https://www.paho.org/hq/index.php?option = com_content&view = article&id = 11117:zika-resources-case-definitions&Itemid = 41532&lang = en (accessed on 20 September 2018).
- Moore, C.A.; Staples, J.E.; Dobyns, W.B.; Pessoa, A.; Ventura, C.V.; da Fonseca, E.B.; Ribeiro, E.M.; Ventura, L.O.; Neto, N.N.; Arena, J.F.; et al. Characterizing the Pattern of Anomalies in Congenital Zika Syndrome for Pediatric Clinicians. JAMA Pediatr. 2016. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miranda-Filho, D.D.B.; Martelli, C.M.T.; Ximenes, R.A.D.A.; Araújo, T.V.B.; Rocha, M.A.W.; Ramos, R.C.F.; Dhalia, R.; França, R.F.D.O.; Marques Júnior, E.T.D.A.; Rodrigues, L.C. Initial Description of the Presumed Congenital Zika Syndrome. Am. J. Public Health 2016, 106, 598–600. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Heymann, D.L.; Hodgson, A.; Sall, A.A.; Freedman, D.O.; Staples, J.E.; Althabe, F.; Baruah, K.; Mahmud, G.; Kandun, N.; Vasconcelos, P.F.C.; et al. Zika virus and microcephaly: Why is this situation a PHEIC? Lancet 2016, 387, 719–721. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Calvet, G.; Aguiar, R.S.; Melo, A.S.O.; Sampaio, S.A.; de Filippis, I.; Fabri, A.; Araujo, E.S.M.; de Sequeira, P.C.; de Mendonça, M.C.L.; de Oliveira, L.; et al. Detection and sequencing of Zika virus from amniotic fluid of fetuses with microcephaly in Brazil: A case study. Lancet Infect. Dis. 2016, 16, 653–660. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oliveira Melo, A.S.; Malinger, G.; Ximenes, R.; Szejnfeld, P.O.; Alves Sampaio, S.; Bispo de Filippis, A.M. Zika virus intrauterine infection causes fetal brain abnormality and microcephaly: Tip of the iceberg? Ultrasound Obstet. Gynecol. 2016, 47, 6–7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schuler-Faccini, L.; Ribeiro, E.M.; Feitosa, I.M.L.; Horovitz, D.D.G.; Cavalcanti, D.P.; Pessoa, A.; Doriqui, M.J.R.; Neri, J.I.; de Pina Neto, J.M.; Wanderley, H.Y.C.; et al. Possible Association Between Zika Virus Infection and Microcephaly—Brazil, 2015. MMWR. Morb. Mortal. Wkly. Rep. 2016, 65, 59–62. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mlakar, J.; Korva, M.; Tul, N.; Popović, M.; Poljšak-Prijatelj, M.; Mraz, J.; Kolenc, M.; Resman Rus, K.; Vesnaver Vipotnik, T.; Fabjan Vodušek, V.; et al. Zika Virus Associated with Microcephaly. N. Engl. J. Med. 2016, 374, 951–958. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Arzuza-Ortega, L.; Polo, A.; Pérez-Tatis, G.; López-García, H.; Parra, E.; Pardo-Herrera, L.C.; Rico-Turca, A.M.; Villamil-Gómez, W.; Rodríguez-Morales, A.J. Fatal Sickle Cell Disease and Zika Virus Infection in Girl from Colombia. Emerg. Infect. Dis. 2016, 22, 925–927. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Monath, T.P.; Vasconcelos, P.F.C. Yellow fever. J. Clin. Virol. 2015, 64, 160–173. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Quaresma, J.A.S.; Barros, V.L.R.S.; Fernandes, E.R.; Pagliari, C.; Takakura, C.; da Costa Vasconcelos, P.F.; de Andrade, H.F.; Duarte, M.I.S. Reconsideration of histopathology and ultrastructural aspects of the human liver in yellow fever. Acta Trop. 2005, 94, 116–127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pagliari, C.; Quaresma, J.A.S.; Fernandes, E.R.; Stegun, F.W.; Brasil, R.A.; de Andrade, H.F.; Barros, V.; Vasconcelos, P.F.C.; Duarte, M.I.S. Immunopathogenesis of dengue hemorrhagic fever: Contribution to the study of human liver lesions. J. Med. Virol. 2014, 86, 1193–1197. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pagliari, C.; Simões Quaresma, J.A.; Kanashiro-Galo, L.; de Carvalho, L.V.; Vitoria, W.O.; da Silva, W.L.F.; Penny, R.; Vasconcelos, B.C.B.; da Costa Vasconcelos, P.F.; Duarte, M.I.S. Human kidney damage in fatal dengue hemorrhagic fever results of glomeruli injury mainly induced by IL17. J. Clin. Virol. 2016, 75, 16–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
© 2018 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).