Abstract
Background: Managing pain with intrathecal infusion pumps has significantly improved the treatment of individuals whose pain is uncontrollable by other methods. Using ultrasound to locate the refill port of these infusion pumps may offer an improvement over traditional methods. Objective: The objective of this systematic review is to update existing knowledge on the use of ultrasound for locating the refill port in intrathecal infusion pumps. Methods: The PRISMA review protocol was followed, and the review was registered in PROSPERO under registration number CRD 42024595671. Results: The main findings indicate that this technique is primarily used only in complex cases where access is difficult. Pain assessment, patient satisfaction, and recharge time compared to the traditional method are crucial factors for selecting the type of process to implement. Conclusions: No conclusive data are presented regarding the technique’s effect on pain reduction, patient satisfaction, reduction in time spent refilling the pump, or the prior experience level of the professional performing it, but notable improvements in these aspects are observed in certain situations.
1. Introduction
1.1. Background
Pain is an unpleasant sensory and emotional experience associated with, or resembling that associated with, actual or potential tissue damage [1]. It is prevalent in numerous clinical settings across various specialties, which leads to a significant demand for medical care. However, pain management is often limited. Among these limitations is the difficulty in measuring pain, as it is an experience strongly influenced by subjectivity.
Many types of pain exist. Patients who have intrathecal infusion pumps typically suffer from chronic pain that has not responded to other treatment modalities. These pumps are also used in oncological patients or those requiring palliative care.
Intrathecal infusion devices are an excellent method for treating individuals with refractory chronic pain, as stated by Rey-Ares et al. [2]. Patients report an improved quality of life due to the use of these devices, as shown by Narváez Sarmiento et al. in their study [3]. Recharge intervals typically range from one to three months, as indicated in the report by Karri J et al. [4], depending on the dose and concentration of the analgesic drug [5].
Traditionally, a template provided in refill kits was used to recharge intrathecal infusion pumps. These plastic templates simulate the pump’s size and feature a central hole that, when correctly positioned on the patient’s abdomen, should align with the refill port. This method is prone to localization errors, especially in overweight patients with thickened abdominal walls due to lipid deposits. Patients undergoing this technique sometimes report discomfort associated with repeated needle sticks to locate the refill port. More severe and potentially life-threatening complications can also occur, such as depositing high-concentration drugs outside the pump, as argued by Grape S et al. [6].
The use of ultrasound has expanded to a multitude of healthcare interventions. It is employed in the management of pregnant women, for ultrasound-guided infiltrations, and for screening and diagnosing certain cardiac and digestive pathologies, and increasingly for critical care patient management. Notably, it is a harmless and easy-to-use method. When using ultrasound for a refill, the refill port is first located with the ultrasound device. Since the port is a silicone structure, it appears as a vertical anechoic area on the screen. The pump itself is metal, so it will look hyperechoic. The surrounding tissues, such as muscle fibers, produce few return echoes and create a hypoechoic image.
The pump is located by palpation, and with a skin marker, the refill port is marked using the ultrasound. In more complex cases, such as when the device is not well-anchored to the internal tissue, the ultrasound can be used throughout the refill procedure with a sterile cover. Potential drawbacks of this technique include access to an ultrasound machine and the experience level of the professionals [2].
However, ultrasound devices are typically available within pain units, so they do not represent an extra cost.
By locating the exact position of the refill port, it is possible to access the reservoir with a single puncture. Regarding complications, ultrasound is harmless and does not increase the risks associated with the technique. As mentioned, in some cases, it can actually reduce complications by preventing multiple punctures or changes in the needle’s angle within the skin [4].
This technique can reduce recharge time and enhance patient safety. This could lead to increased satisfaction for both the professionals performing the procedure and the patients receiving care [3].
1.2. Objective
Given the above, the objective of this systematic review is to update existing knowledge on the use of ultrasound for locating the refill port of intrathecal infusion pumps.
2. Methodology
The methodology employed for this report was a systematic review of the scientific literature published on the ultrasound-guided refill of intrathecal infusion pumps. This review followed the Preferred Reporting Items for Systematic reviews and Meta-Analyses (PRISMA) protocol, which consists of a 27-item checklist covering the most representative sections of an original article, along with guidelines for their development. This systematic review was conducted according to a predefined protocol, available at http://www.crd.york.ac.uk/PROSPERO/ with the registration number CRD 42024595671, accessed on 11 September 2025.
2.1. Eligibility Criteria
We selected randomized clinical trials (RCTs), descriptive studies, and case reports—including those from both living and deceased subjects, if they belonged to preclinical feasibility studies and provided relevant data for this systematic review. All were published within the last twenty years (2004–2024). This broad timeframe was chosen because the topic under study is uncommon, and the goal was to compile all available published information. Articles had to provide information on the refill of intrathecal infusion pumps using ultrasound, with no restrictions on the language of publication.
2.2. Information Sources
The literature search was conducted in the following databases: Scopus, PubMed, CINAHL, SciELO, and Cochrane Library. A manual search was also performed by examining the reference lists of identified studies to find other relevant articles.
The structured language used for the search was derived from MeSH terms and Health Sciences Descriptors (DeCS). The English descriptors used were: “ultrasound,” “ultrasound-guided,” “refill,” “refill port,” “pocket fill,” “pump refill,” “intrathecal,” “intrathecal pump,” and “intrathecal pumps.” The Boolean operators employed were “OR” and “AND.”
2.3. Search Strategy
Table 1 Below details the search strategy used for this work, along with the date the search was conducted.

Table 1.
Search string.
2.4. Data Extraction Process
After executing the search strategy, the identified articles were transferred to the Mendeley web application using the Mendeley Web Importer tool. They were then organized into folders according to the database from which they were obtained, and all duplicates were removed.
The included studies consisted of Randomized Controlled Trials (RCTs) and case reports whose objectives were to evaluate the use of ultrasound for refilling intrathecal infusion pumps, and which were published between 2004 and 2024. Two reviewers (JCM and BLC) independently screened the title, abstract, and keywords of each identified study from the search and applied the inclusion and exclusion criteria. For potentially eligible studies, the same procedure was applied to the full-text articles. Discrepancies between the reviewers were resolved through discussion or by a third reviewer (RGM).
Data regarding quality, patient characteristics, interventions, and relevant outcomes were extracted independently by two reviewers (JCM and BLC).
2.5. Data Collection Process and Collected Data
Two reviewers (JCM and BLC) extracted the notable data from each included article. They also assessed the strengths and weaknesses of each RCT and case report.
The article selection process is explained in more detail in the Section 3.
2.6. Risk of Bias in Individual Studies
To perform the methodological evaluation of the selected articles for this study, we analyzed the design, methodology, and study type of each work, aiming to select the most specific methodological evaluation scale for each case.
Of the 13 articles, 9 were case studies and 4 were RCTs.
To evaluate the methodological quality and risk of bias of the included case reports, the JBI Critical Appraisal Checklist for Case Reports was used. This tool, developed by the Joanna Briggs Institute, allows for a systematic and qualitative assessment of each study, ensuring a rigorous and transparent evaluation of the evidence. The results of this appraisal are presented in the following table.
Table 2 below shows the results obtained after the methodological evaluation using the JBI scale.

Table 2.
Methodological Evaluation According to JBI.
For articles whose methodology corresponded to Randomized Clinical Trials (RCTs), the scientific quality was assessed using the PEDro scale. This scale provides information on clinical scientific evidence and scores it based on indicators, adding 1 point for each present indicator and 0 points if absent, allowing for a total score of 10 points. If a clinical trial obtains a score between 9 and 10, it indicates very good quality; between 6 and 8 indicates good quality; between 4 and 5 indicates fair quality; and a score below 4 indicates poor quality. In the case of the articles selected for this systematic review, the values ranged from 5 to 9, consequently receiving an average score of 6.5, which indicates that the average scientific quality is considered “good quality.” The quality evaluations for each of the RCTs can be observed in Table 1.
The results obtained after the methodological evaluation using the PEDro scale are shown in the following table (Table 3).

Table 3.
Methodological Evaluation According to PEDro.
In addition, to evaluate the risk of bias of the included randomized clinical trials (RCTs), the RoB 2 (Risk of Bias 2.0) tool was used. This instrument, developed by the Cochrane group, assesses methodological quality across five key domains: randomization, deviations from intended interventions, missing data, measurement of the outcome, and selection of the reported result. The risk of bias judgments (low, some concerns, or high) for each domain are detailed in the following table (Table 4).

Table 4.
Methodological Evaluation According to Rob 2.
Based on the information provided by this review, a series of premises are derived that will serve to standardize concepts regarding the use of ultrasound for refilling intrathecal infusion pumps. The scarcity of studies on this type of technique is confirmed.
3. Results
The flowchart of this systematic review is presented below (Figure 1).
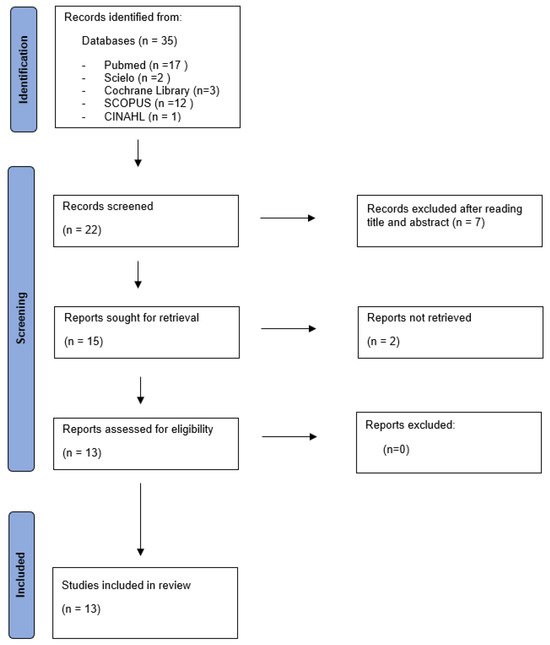
Figure 1.
Flow diagram.
The following table (Table 5) presents a summary of the main results.

Table 5.
Results table.
In Figure 2, a refill port visualized by ultrasound can be observed. The first case found was published in 2007 by Hurdle et al. [7], highlighting the potential relevance of using ultrasound to locate the refill port for intrathecal infusion pumps in difficult cases. They emphasize that the technique is simple and effective, although they could not provide reliable data on a reduction in procedure time. Similarly, Shankar et al. [8] discussed the use of ultrasound in a challenging case, noting its effectiveness and its role in helping to prevent complications. Peccora et al. [10] described a case where ultrasound was used to detect fluid extravasation into the subcutaneous pocket during refilling, underscoring its importance for detecting such issues and preventing potential complications.
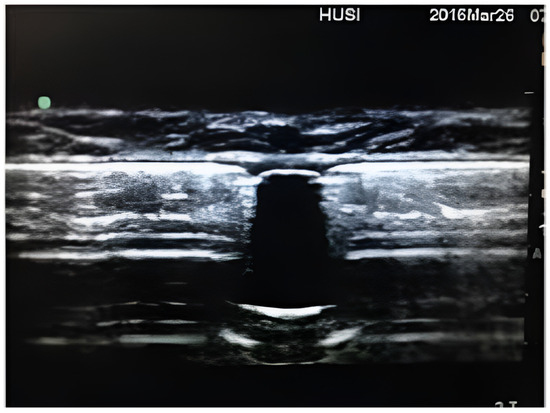
Figure 2.
Refill port as seen with the ultrasound device.
Furthermore, Maneyapanda et al. [12] also emphasized the use of ultrasound in difficult cases, presenting three clinical examples with challenging access and observing that ultrasound could prevent complications. In their work, Caruso et al. [13] reported two clinical cases with patients who had difficult access to the refill port, suggesting that ultrasound could be useful in these situations but that more in-depth study is needed. Consistent with this, García Eslava et al. [14] presented another case where ultrasound was used to locate the refill port, emphasizing that it minimizes risks and the number of punctures. They also highlighted the short training time—approximately 30 min—required for inexperienced personnel to learn the technique. Finally, Pinho et al. [15] also studied a case of difficult access, highlighting the use of the indirect method by marking the area on the patient’s abdomen with the aid of ultrasound. They noted that ultrasound is a simple and safe method that can prevent complications.
Other research has focused on preclinical studies. Gofeld et al. [9] conducted a study with cadavers, determining a 100% predictive value for needle placement. Consistent with García Eslava et al. [14], they emphasized the ease with which inexperienced professionals can learn the technique. They also provided a differentiated sonographic description of intrathecal infusion pumps. Delving deeper into this topic, Saulino et al.’s [11] descriptive study examined intrathecal infusion pumps ex vivo using ultrasound. They highlighted a rapid learning curve for the technique and noted that these devices possess unique sonographic characteristics.
Lastly, Maino et al. [16] conducted a 24-month study comparing intrathecal infusion pump refilling using ultrasound versus the traditional method. Their results suggest that the traditional method requires fewer punctures for refilling. In a separate study with 22 patients, Matthys et al. [17] found that the use of ultrasound prevents complications and is more effective in patients where the distance from the pump to the abdominal surface is greater than 10 mm. However, they found no difference in patients where the distance is less than 10 mm. Similarly, Singa et al. [18] conducted a study with 107 patients to assess their preferences for refilling (ultrasound vs. traditional method). On average, patients preferred ultrasound-guided refills because they found them to be less painful. However, they did not believe these refills were faster than the traditional method. To conclude, the most recent study by Stone et al. [19] used a sample of 17 patients to determine satisfaction with the technique, assessing pain, patient satisfaction, and procedure duration. Their conclusions showed that needle-in-body time was reduced, although not significantly. They also found no improvements in terms of pain perception, patient satisfaction, or professional-perceived difficulty.
4. Discussion
This systematic review aimed to update the existing knowledge on the use of ultrasound for locating the refill port of intrathecal infusion pumps. The topic has a limited number of publications, highlighting its specificity and the pioneering nature of this report.
Regarding the technique’s efficacy, there is a broad consensus favoring the use of ultrasound over the traditional method, which uses a template or is performed “blindly,” as presented in the study by Matthys et al. [17]. However, some articles suggest no significant difference between the two techniques, noting that ultrasound is often reserved for more complex situations. These include cases of seroma accumulation around the pump or when pump access is difficult due to patient-specific factors, as described by Peccora et al. [10]. Matthys et al. [17] also mention that ultrasound is more effective in patients where the distance from the skin to the pump surface is greater than 10 mm.
Most of the reviewed articles provide limited information on the technique’s safety. While some indirectly mention that complications can be reduced, no measurable data are presented in this regard, according to Narváez Sarmiento et al. [3].
In articles analyzing patient pain during the procedure, a significant decrease or absence of pain is established with the use of ultrasound compared to the traditional method, according to Singa et al. [18]. However, some reports, such as that by Stone et al. [19], note no difference in pain reduction.
Concerning the procedure duration, no significant differences are observed between the two techniques. Some reports suggest that ultrasound may increase procedure time, while others state that it decreases the time, though not significantly (Caruso et al. [13]). This discrepancy suggests that procedure time would be an interesting topic for future investigation to ascertain if it is genuinely shortened with either technique.
Generally, most articles reviewed use ultrasound for cases with difficult refill port access, and the majority are case reports with only one to three patients, as stated by Hurdle et al. [7]. Studies with larger patient samples do not mention cases where refill port access was more complex.
There is little emphasis on the professional role of those performing the technique, with the assumption that they are all physicians. The performance of this technique by nursing professionals is not mentioned. However, García Eslava et al. [14] mention that the average learning time for ultrasound-guided intrathecal pump refilling is no more than 30 min.
The main limitation of this review was the scarcity of publications on the topic. Furthermore, most cases are case reports with few patients and lack validated assessment scales.
Future research directions derived from this study should focus on using validated scales and measuring relevant data such as pain during the technique, patient satisfaction, time spent on refilling, and the learning curve for professionals. Similarly, it would be beneficial to explore the professional roles that carry out the technique, as nurses perform this procedure in many pain units, and their approach warrants investigation.
5. Conclusions
Patients with intrathecal infusion pumps require frequent pump refills. This technique has traditionally been performed using a plastic template or “blindly.” However, in some cases, the use of ultrasound has been shown to potentially facilitate the technique, especially in cases of greater access complexity.
It has been observed that using an ultrasound device can be accessible to professionals without extensive training in its operation, which makes the technique easier and more approachable for both professionals and patients. The learning curve for this technique could be short, which would facilitate the training of the professionals involved.
No conclusive data are presented regarding the technique’s effect on pain reduction, patient satisfaction, reduction in time spent refilling the pump, or the prior experience level of the professional performing it. This area could be interesting for future studies, including validated scales and questionnaires to shed light on these types of data.
Finally, the role of nursing professionals as potential individuals responsible for refills should be highlighted.
Author Contributions
Conceptualization, R.R.-B., J.C.-M., B.L.C. and J.C.S.-G.; data curation, J.C.-M., N.C.T. and J.C.S.-G.; formal analysis, R.R.-B., J.C.-M. and J.C.S.-G.; investigation, R.R.-B., N.C.T., B.L.C. and J.C.S.-G.; methodology, R.R.-B. and N.C.T.; project administration, A.R.-C., R.R.-B., J.C.-M. and J.C.S.-G.; resources, B.L.C., J.C.S.-G., R.R.-B. and N.C.T.; supervision, A.R.-C., R.G.M. and R.R.-B.; validation, R.R.-B., J.C.-M. and B.L.C.; visualization, A.R.-C., R.R.-B., J.C.-M. and B.L.C.; writing—original draft, J.C.-M., R.R.-B. and J.C.S.-G.; writing—review and editing, R.R.-B., J.C.-M., R.G.M. and J.C.S.-G. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This research received no external funding.
Institutional Review Board Statement
This systematic review was conducted following a protocol available on the website: [http://www.crd.york.ac.uk/PROSPERO/] (accessed on 20 July 2025), with registration number CRD 42024595671.
Informed Consent Statement
Not applicable.
Data Availability Statement
Data regarding this study is available upon request to the corresponding author.
Acknowledgments
This study was carried out within the framework of the research project: Importance of Ultrasound for Nursing in Detecting the Refill Port of Intrathecal Analgesic Infusion Pumps, as part of the Doctoral Programme in Clinical Medicine and Public Health at the University of Granada. We are grateful to the Official College of Nursing of Granada (CODEGRA) for their help in the research support program, and to the Chair of Research in Nursing Care of the University of Granada and the Official College of Nursing of Granada.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
References
- Puebla Díaz, F. Types of pain and the WHO therapeutic ladder: Iatrogenic pain. Oncology 2005, 28, 33–37. [Google Scholar]
- Rey-Ares, L.; Bardach, A.; Pichon-Riviere, A.; Augustovski, F.; García Martí, S.; Alcaraz, A.; Ciapponi, A.; López, A. Intrathecal Opioid Infusion Pumps for Chronic Oncological and Non-Oncological Pain; Institute for Clinical Effectiveness and Health Policy (IECS): Buenos Aires, Argentina, 2017; Available online: https://pesquisa.bvsalud.org/portal/resource/pt/biblio-948312 (accessed on 26 March 2022).
- Narváez Sarmiento, I.M.; Hernández Santos, J.R.; Tenopala Villegas, S.; Jiménez Ramos, A.; Cardona Hurtado, G.; Torres Huerta, J.C. Implantable intrathecal infusion pump in patients with chronic pain: Evaluation of disability and quality of life. Rev. Soc. Esp. Dolor 2010, 17, 268–273. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Karri, J.; Singh, M.; Modi, D.J.; Orhurhu, V.; Seale, C.; Saulino, M.; Marathe, A.; Vydra, D.; Hagedorn, J.M.; Bruel, B.; et al. Combination intrathecal drug therapy strategies for pain management. Pain Physician 2021, 24, 549. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Deer, T.R.; Pope, J.E.; Hanes, M.C.; McDowell, G.C. Intrathecal Therapy for Chronic Pain: A Review of Morphine and Ziconotide as Firstline Options. Pain Med. 2019, 20, 784–798. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Grape, S.; El-Boghdadly, K.; Albrecht, E. Management of adverse effects of intrathecal opioids in acute pain. Best Pract. Res. Clin. Anaesthesiol. 2023, 37, 199–207. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hurdle, M.-F.B.; Locketz, A.J.; Smith, J. A technique for ultrasound-guided intrathecal drug-delivery system refills. Am. J. Phys. Med. Rehabil. 2007, 86, 250–251. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shankar, H. Ultrasound-guided localization of difficult-to-access refill port of the intrathecal pump reservoir. Neuromodulation 2009, 12, 215–218. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gofeld, M.; McQueen, C.K. Ultrasound-guided intrathecal pump access and prevention of the pocket fill. Pain Med. 2011, 12, 607–611. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Peccora, C.D.; Ross, E.L.; Hanna, G.M. Aberrant intrathecal pump refill: Ultrasound-guided aspiration of a substantial quantity of subcutaneous hydromorphone. Reg. Anesth. Pain Med. 2013, 38, 544–546. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Saulino, M.; Gofeld, M. “Sonology” of programmable intrathecal pumps. Neuromodulation 2014, 17, 696–698. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Maneyapanda, M.B.; Chang Chien, G.C.; Mattie, R.; Amorapanth, P.; Reger, C.; McCormick, Z.L. Ultrasound guidance for technically challenging intrathecal baclofen pump refill: Three cases and procedure description. Am. J. Phys. Med. Rehabil. 2016, 95, 692–697. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Caruso, P.; Mazzon, G.; Sarra, V.M.; Tacconi, L.; Manganotti, P. The use ultrasound guided for refilling intrathecal baclofene pump in complicated clinical cases: A practical approach. J. Clin. Neurosci. 2018, 57, 194–197. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- García-Eslava, J.S.; Barahona-Correa, J.E.; Moreno, D.A.; Bonilla, A. Usefulness of ultrasound: Intrathecal pump refill in the management of chronic pain. A case report. Colomb. J. Anesthesiol. 2018, 46, 68–71. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pinho, S.; Ferreira, A.; Calado, D.; Hatia, M.; Faria, F. Ultrasound-guided intrathecal baclofen pump refilling method for management of spasticity in a complex clinical case. Cureus 2022, 14, e31537. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Maino, P.; van Kuijk, S.M.J.; Perez, R.S.G.M.; Koetsier, E. Refill procedures of intrathecal drug delivery systems with a recessed fill port on the pump surface: A prospective comparison study of ultrasound-guided vs. Blind refill technique. Neuromodulation 2019, 22, 799–804. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Matthys, C.; Jacobs, M.; Rossat, J.; Perruchoud, C. Accuracy of template versus ultrasound identification of the reservoir access port of intrathecal drug delivery system. Neuromodulation 2020, 23, 944–948. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Singa, R.M.; Buvanendran, A.; McCarthy, R.J. A comparison of refill procedures and patient outcomes following ultrasound-guided and template-guided intrathecal drug delivery systems with recessed ports. Neuromodulation 2020, 23, 938–943. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Stone, S.N.; Wei, D.; Reger, C. Ultrasound guidance versus landmark guidance for intrathecal baclofen pump refill: A randomized pilot study. PM&R 2023, 15, 1425–1430. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).