Short-Term Outcomes of Post-Mastectomy Immediate Pre-Pectoral Reconstruction with Implant and Acellular Dermal Matrix
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
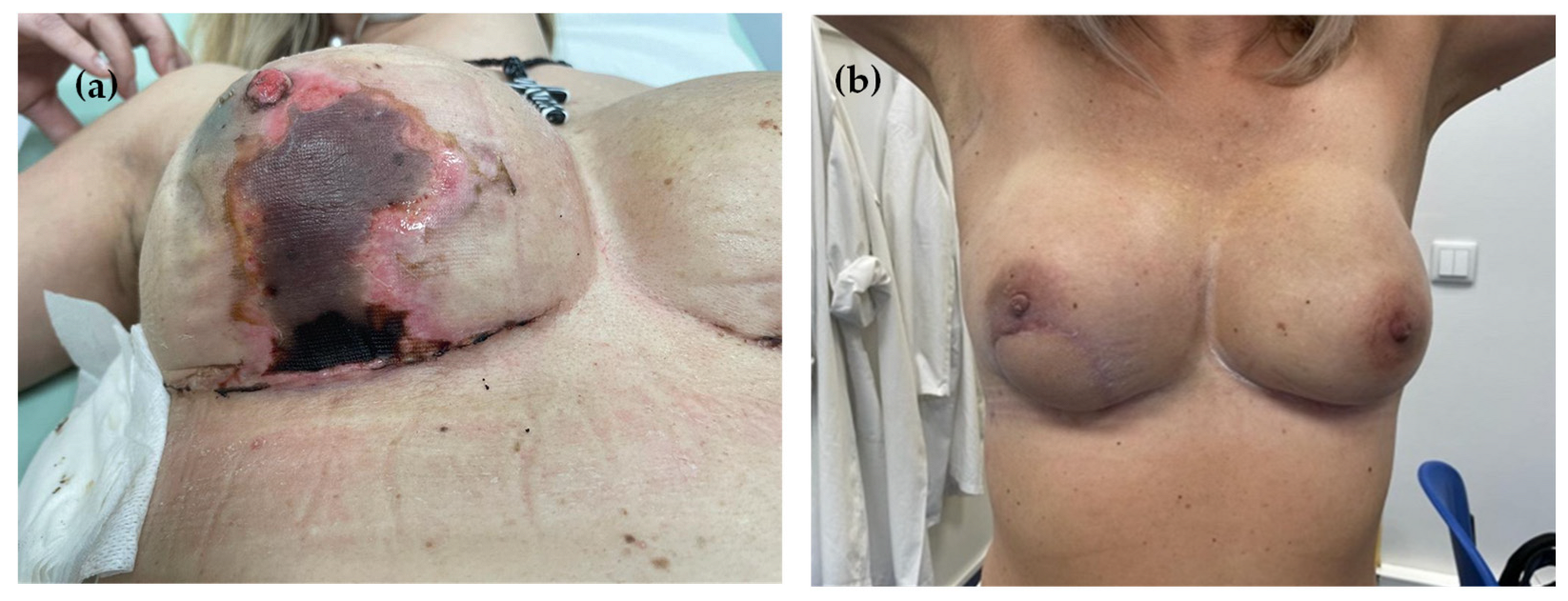
3. Results
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| ADM | Acellular Dermal Matrix |
| BCS | Breast Conservative Surgery |
| BMI | Body Mass Index |
| DTI | Direct-to-Implant |
| IBR | Implant-based Reconstruction |
| IQR | Inter-quartile Range |
| MRI | Magnetic Resonance Imaging |
| NAC | Nipple-areolar Complex |
| NSM | Nipple-sparing Mastectomy |
| NST | Non-special Type |
| SSM | Skin-sparing Mastectomy |
References
- Bray, F.; Laversanne, M.; Sung, H.; Ferlay, J.; Siegel, R.L.; Soerjomataram, I.; Jemal, A. Global cancer statistics 2022: GLOBOCAN estimates of incidence and mortality worldwide for 36 cancers in 185 countries. CA Cancer J. Clin. 2024, 74, 229–263. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Malata, C.M.; Mcintosh, S.A.; Purushotham, A.D.; Purushotham, M.A.D. Immediate Breast Reconstruction after Mastectomy for Cancer. Br. J. Surg. 2000, 87, 1455–1472. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kummerow, K.L.; Du, L.; Penson, D.F.; Shyr, Y.; Hooks, M.A. Nationwide trends in mastectomy for early-stage breast cancer. JAMA Surg. 2015, 150, 9–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mahmood, U.; Hanlon, A.L.; Koshy, M.; Buras, R.; Chumsri, S.; Tkaczuk, K.H.; Cheston, S.B.; Regine, W.F.; Feigenberg, S.J. Increasing National Mastectomy Rates for the Treatment of Early Stage Breast Cancer. Ann. Surg. Oncol. 2013, 20, 1436–1443. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- De La Cruz, L.; Moody, A.M.; Tappy, E.E.; Blankenship, S.A.; Hecht, E.M. Overall Survival, Disease-Free Survival, Local Recurrence, and Nipple–Areolar Recurrence in the Setting of Nipple-Sparing Mastectomy: A Meta-Analysis and Systematic Review. Ann. Surg. Oncol. 2015, 22, 3241–3249. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Costeira, B.; da Silva, F.B.; Oom, R.; Costa, C.; Moniz, J.V.; Abecasis, N.; Santos, C.R. Locoregional recurrence in skin-sparing and nipple-sparing mastectomies. J. Surg. Oncol. 2022, 125, 352–360. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shin, D.S.; Bang, Y.J.; Choi, J.Y.; Jang, S.Y.; Lee, H.; Kwak, Y.; Chae, B.J.; Yu, J.; Lee, J.E.; Kim, S.W.; et al. Oncologic Outcomes of Immediate Breast Reconstruction in the Setting of Neoadjuvant Chemotherapy: A Long-term Follow-up Study of a Matched Cohort. J. Breast Cancer 2024, 27, 14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- van Bommel, A.C.M.; de Ligt, K.M.; Schreuder, K.; Maduro, J.; Van Dalen, T.; Peeters, M.V.; Mureau, M.; Siesling, S. The added value of immediate breast reconstruction to health-related quality of life of breast cancer patients. Eur. J. Surg. Oncol. 2020, 46, 1848–1853. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bailey, C.R.; Ogbuagu, O.; Baltodano, P.A.; Simjee, U.F.; Manahan, M.A.; Cooney, D.S.; Jacobs, L.K.; Tsangaris, T.N.; Cooney, C.M.; Rosson, G.D. Quality-of-Life Outcomes Improve with Nipple-Sparing Mastectomy and Breast Reconstruction. Plast. Reconstr. Surg. 2017, 140, 219–226. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marks, J.M.; Farmer, R.L.; Afifi, A.M. Current Trends in Prepectoral Breast Reconstruction: A Survey of American Society of Plastic Surgeons Members. Plast. Reconstr. Surg.–Glob. Open 2020, 8, e3060. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Graziano, F.D.; Plotsker, E.L.; Rubenstein, R.N.; Haglich, K.; Stern, C.S.; Matros, E.M.; Nelson, J.A. National Trends in Acellular Dermal Matrix Utilization in Immediate Breast Reconstruction. Plast. Reconstr. Surg. 2023, 153, 25e–36e. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jafferbhoy, S.; Chandarana, M.; Houlihan, M.; Parmeshwar, R.; Narayanan, S.; Soumian, S.; Harries, S.; Jones, L.; Clarke, D. Early multicentre experience of pre-pectoral implant based immediate breast reconstruction using Braxon®. Gland. Surg. 2017, 6, 682–688. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, J.; Hou, J.; Li, Z.; Wang, B.; Sun, J. Efficacy of Acellular Dermal Matrix in Capsular Contracture of Implant-Based Breast Reconstruction: A Single-Arm Meta-analysis. Aesthetic Plast. Surg. 2020, 44, 735–742. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nolan, I.T.; Farajzadeh, M.M.; Boyd, C.J.; Bekisz, J.M.; Gibson, E.G.; Salibian, A.A. Do we need acellular dermal matrix in prepectoral breast reconstruction? A systematic review and meta-analysis. J. Plast. Reconstr. Aesthetic Surg. 2023, 86, 251–260. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sbitany, H.; Piper, M.; Lentz, R. Prepectoral Breast Reconstruction: A Safe Alternative to Submuscular Prosthetic Reconstruction following Nipple-Sparing Mastectomy. Plast. Reconstr. Surg. 2017, 140, 432–443. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bernini, M.; Calabrese, C.; Cecconi, L.; Santi, C.; Gjondedaj, U.; Roselli, J.; Nori, J.; Fausto, A.; Orzalesi, L.; Casella, D. Subcutaneous Direct-to-Implant Breast Reconstruction. Plast. Reconstr. Surg. Glob. Open 2015, 3, e574. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ostapenko, E.; Nixdorf, L.; Devyatko, Y.; Exner, R.; Wimmer, K.; Fitzal, F. Prepectoral Versus Subpectoral Implant-Based Breast Reconstruction: A Systemic Review and Meta-analysis. Ann. Surg. Oncol. 2023, 30, 126–136. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hölmich, L.R.; Sayegh, F.; Salzberg, C.A. Immediate or delayed breast reconstruction: The aspects of timing, a narrative review. Ann. Breast Surg. 2023, 7, 6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tellarini, A.; Garutti, L.; Corno, M.; Tamborini, F.; Paganini, F.; Fasoli, V.; Di Giovanna, D.; Valdatta, L. Immediate post-mastectomy prepectoral breast reconstruction with animal derived acellular dermal matrices: A systematic review. J. Plast. Reconstr. Aesthetic Surg. 2023, 86, 94–108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Albornoz, C.R.; Cordeiro, P.G.; Pusic, A.L.; McCarthy, C.M.; Mehrara, B.J.; Disa, J.J.; Matros, E. Diminishing Relative Contraindications for Immediate Breast Reconstruction: A Multicenter Study. J. Am. Coll. Surg. 2014, 219, 788–795. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Amin, M.B.; Greene, F.L.; Edge, S.B.; Compton, C.C.; Gershenwald, J.E.; Brookland, R.K.; Meyer, L.; Gress, D.M.; Byrd, D.R.; Winchester, D.P. The Eighth Edition AJCC Cancer Staging Manual: Continuing to build a bridge from a population-based to a more “personalized” approach to cancer staging. CA Cancer J. Clin. 2017, 67, 93–99. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Regnault, P. Breast ptosis. Definition and treatment. Clin. Plast. Surg. 1976, 3, 193–203. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kalstrup, J.; Balslev Willert, C.; Brinch-Møller Weitemeyer, M.; Hougaard Chakera, A.; Hölmich, L.R. Immediate direct-to-implant breast reconstruction with acellular dermal matrix: Evaluation of complications and safety. Breast 2021, 60, 192–198. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lohmander, F.; Lagergren, J.; Roy, P.G.; Johansson, H.; Brandberg, Y.; Eriksen, C.; Frisell, J. Implant Based Breast Reconstruction with Acellular Dermal Matrix. Ann. Surg. 2019, 269, 836–841. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kilmer, L.H.; Challa, S.; Stranix, J.T.; Campbell, C.A. Case-matched Comparison of Implant-based Breast Reconstruction with and without Acellular Dermal Matrix. Plast. Reconstr. Surg. Glob. Open 2024, 12, e5660. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kouwenberg, C.A.E.; de Ligt, K.M.; Kranenburg, L.W.; Rakhorst, H.M.; de Leeuw, D.M.; Siesling, S.; Busschbach, J.J.; Mureau, M.A.M.M. Long-Term Health-Related Quality of Life after Four Common Surgical Treatment Options for Breast Cancer and the Effect of Complications: A Retrospective Patient-Reported Survey among 1871 Patients. Plast. Reconstr. Surg. 2020, 146, 1–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Plotsker, E.L.; Graziano, F.D.; Rubenstein, R.N.; Haglich, K.; Allen, R.J., Jr.; Coriddi, M.R.; Dayan, J.H.; Poulton, R.; McKernan, C.; Mehrara, B.J.; et al. Early Complications in Prepectoral Breast Reconstructions with and without Acellular Dermal Matrix: A Preliminary Analysis of Outcomes. Plast. Reconstr. Surg. 2024, 153, 786–793. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Negenborn, V.L.; Dikmans, R.E.G.; Bouman, M.B.; Winters, H.A.H.; Twisk, J.W.R.; Ruhé, P.Q.; Mureau, M.A.M.; Smit, J.M.; Tuinder, S.; Hommes, J.; et al. Predictors of complications after direct-to-implant breast reconstruction with an acellular dermal matrix from a multicentre randomized clinical trial. Br. J. Surg. 2018, 105, 1305–1312. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chatterjee, A.; Nahabedian, M.Y.; Gabriel, A.; Macarios, D.; Parekh, M.; Wang, F.; Griffin, L.; Sigalove, S. Early assessment of post-surgical outcomes with pre-pectoral breast reconstruction: A literature review and meta-analysis. J. Surg. Oncol. 2018, 117, 1119–1130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dueñas-Rodríguez, B.; Navarro-Cecilia, J.; Luque-López, C.; Sánchez-Andujar, B.; Garcelán-Trigo, J.A.; Ramírez-Expósito, M.J.; Martínez-Martos, J.M. Single-Stage Immediate Breast Reconstruction with Acellular Dermal Matrix after Breast Cancer: Comparative Study and Evaluation of Breast Reconstruction Outcomes. Cancers 2023, 15, 5349. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Glynou, S.P.; Sousi, S.; Cook, H.; Zargaran, A.; Zargaran, D.; Mosahebi, A. A comparison of acellular dermal matrices (ADM) efficacy and complication profile in women undergoing implant-based breast reconstruction: A systematic review and network meta-analysis. BMC Cancer 2024, 24, 1598. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hinson, C.; Sink, M.; Sammer, D.; Zhang, A.Y.; Odobescu, A. Extended Antibiotic Prophylaxis in Implant-based Breast Reconstruction: A Systematic Review and Meta-analysis. Aesthet. Surg. J. 2025, 21, sjaf144. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- ASBRS Preoperative Antibiotics and Surgical Site Infection. Available online: https://www.breastsurgeons.org/docs/statements/asbrs-ccs-preoperative-antibiotics-and-surgical-site-infection.pdf (accessed on 18 August 2025).
- Blok, Y.L.; van Lierop, E.; Plat, V.D.; Corion, L.U.M.; Verduijn, P.S.; Krekel, N.M.A. Implant Loss and Associated Risk Factors following Implant-based Breast Reconstructions. Plast. Reconstr. Surg. Glob. Open 2021, 9, e3708. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Panayi, A.; Agha, R.; Sieber, B.; Orgill, D. Impact of Obesity on Outcomes in Breast Reconstruction: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. J. Reconstr. Microsurg. 2018, 34, 363–375. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pires, G.; Marquez, J.L.; Memmott, S.; Sudduth, J.D.; Moss, W.; Eddington, D.; Hobson, G.D.; Tuncer, F.; Agarwal, J.P.; Kwok, A.C. Early Complications after Prepectoral Tissue Expander Placement in Breast Reconstruction with and without Acellular Dermal Matrix. Plast. Reconstr. Surg. 2024, 153, 1221–1229. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hwang, K.; Son, J.S.; Ryu, W.K. Smoking and Flap Survival. Plast. Surg. 2018, 26, 280–285. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gabriel, A.; Storm-Dickerson, T.L.; Chan, V.; Lord, R.; O’Rorke, E.; Maxwell, G.P. Prepectoral Breast Reconstruction in Morbidly Obese Patients. Plast. Reconstr. Surg. Glob. Open 2022, 10, e4261. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Doyle, B.; Shaari, E.; Hamed, H.; Kothari, A. Outcomes after skin-reducing mastectomy and immediate hybrid breast reconstruction using combination of acellular dermal matrix and de-epithelialized dermal flap in large and/or ptotic breasts. Ann. Breast Surg. 2022, 6, 12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bae, J.; Mun, G.H.; Lee, K.T.; Pyon, J.K. Nomogram-Based Approach for Predicting Complication Risks following Prepectoral Direct-to-Implant Breast Reconstruction. Plast. Reconstr. Surg. 2025, 156, 19–27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Escandón, J.M.; Butterfield, J.A.; Christiano, J.G.; Gooch, J.C.; Olzinski, A.T.; Prieto, P.A.; Skinner, K.A.; Langstein, H.N.; Manrique, O.J.M. Wise Pattern versus Transverse Pattern Mastectomy in Two-Stage Implant-Based Breast Reconstruction: A Propensity Score–Matched Analysis. Plast. Reconstr. Surg. 2023, 152, 69S–80S. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Antoniazzi, E.; De Grazia, A.; Dell’Antonia, F.; Pasquali, S.; Burelli, P.; Rizzetto, C.; Berna, G. Immediate prepectoral breast reconstruction in nipple-sparing mastectomy with Wise-pattern incision in large and ptotic breasts: Our experience and short-term results. J. Plast. Reconstr. Aesthet. Surg. 2024, 91, 154–163. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]

| N = 200 | |
|---|---|
| Age in years, median [IQR] | 49 (43;56) |
| BMI | |
| Median [IQR], kg/m2 | 26 (23;29) |
| Overweight (BMI 25–29.9 kg/m2), n (%) | 113 (56.5) |
| Obese (BMI > 30 kg/m2), n (%) | 31(15.5) |
| Active smoker, n (%) | 53 (26.5) |
| Comorbidities, n (%) | |
| Diabetes mellitus | 7 (3.5) |
| Dyslipidemia | 15 (7.5) |
| Hypertension | 7 (3.5) |
| Genetic risk, n (%) | 42 (21.0) |
| BRCA1 | 11 (5.5) |
| BRCA2 | 22 (11.0) |
| CHEK2 | 5 (2.5) |
| PALB2 | 3 (1.5) |
| TP53 | 1 (0.5) |
| Bilateral surgery, n (%) | 181 (90.5) |
| Bilateral mastectomy | 47 (23.5) |
| Contralateral BCS | 5 (2.5) |
| Contralateral symmetrization | 129 (64.5) |
| Mastectomy indication, n (%)—n = 247 | |
| Invasive carcinoma | 175 (70.9) |
| In situ carcinoma | 26 (10.5) |
| Risk-reducing | 46 (18.6) |
| Neoadjuvant chemotherapy, n (%) | 80 (45.7) |
| cT staging, n (%)—n = 175 | |
| 1 | 65 (37.1) |
| 2 | 89 (50.9) |
| 3 | 21 (12.0) |
| cN staging, n (%)—n = 175 | |
| 0 | 113 (64.6) |
| 1 | 57 (32.6) |
| 2 | 5 (2.8) |
| Histologic subtypes, n (%)—n = 175 | |
| NST | 144 (82.3) |
| Lobular | 26 (14.9) |
| Metaplastic | 2 (1.1) |
| Mucinous | 2 (1.1) |
| Neuroendocrine | 1 (0.6) |
| Molecular subtypes, n (%)—n = 175 | |
| Luminal A | 70 (40.0) |
| Luminal B Her2− | 65 (37.1) |
| Luminal B Her2+ | 10 (5.7) |
| Her2 type | 12 (6.9) |
| Triple negative | 17 (9.7) |
| Missing | 1 (0.6) |
| N = 247 | |
|---|---|
| Mastectomy type, n (%) | |
| Nipple-sparing mastectomy (NSM) | 206 (83.4) |
| Skin-sparing mastectomy (SSM) | 41 (16.6) |
| Mastectomy incision, n (%) | |
| NSM—n = 206 | |
| Wise-pattern | 151 (73.3) |
| Inframammary | 40 (19.4) |
| Periareolar | 8 (3.9) |
| Lateral | 7 (3.4) |
| SSM—n = 41 | |
| Wise-pattern | 34 (83.0) |
| Periareolar (elliptical) | 4 (9.7) |
| Inframammary (secondary NAC excision) | 3 (7.3) |
| NAC preservation in NSM, n (%)—n = 206 | |
| Superior pedicle | 123 (59.7) |
| Free grafting | 83 (40.3) |
| Implant size (cc), median [IQR] | 375 (330;475) |
| Length of stay (days), median [IQR] | 2 (2;2) |
| N = 247 | |
|---|---|
| 90-day complication, n (%) | 36 (14.6) |
| Type of complication, n (%) | |
| Skin ischemia/necrosis (including NAC) | 31 (12.6) |
| Primary implant infection | 5 (2.0) |
| Hemorrhage | 2 (0.8) |
| NAC necrosis, n (%)—n = 206 | 14 (6.8) |
| 90-day re-operation, n (%) | 23 (8.4) |
| Re-operation procedure, n (%)—n = 23 | |
| Latissimus dorsi flap | 14 (60.9) |
| Tissue expander replacement | 3 (13.1) |
| Implant replacement | 2 (8.7) |
| Hemostasis revision | 2 (8.7) |
| Scar revision | 1 (4.3) |
| Skin graft | 1 (4.3) |
| Reconstructive failure, n (%) | 19 (7.7) |
| Complete loss of reconstruction, n (%) | 1 (0.4) |
| Variables | Any Complication | Skin Ischemia | Reoperation | NAC Loss (Subgroup NSM) | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| OR | p-Value | OR | p-Value | OR | p-Value | OR | p-Value | |
| Age, years | 1.01 (0.98–1.04) | 0.616 | 1.01 (0.97–1.05) | 0.639 | 0.99 (0.96–1.04) | 0.925 | 0.98 (0.94–1.03) | 0.407 |
| Obesity (BMI ≥ 30) | 1.09 (0.39–3.07) | 0.872 | 0.7 (0.20–2.53) | 0.601 | 0.80 (0.22–2.86) | 0.729 | 0.67 (0.15–3.05) | 0.599 |
| Overweight (BMI 25–29.9) | 1.04 (0.47–2.32) | 0.924 | 1.06 (0.44–2.54) | 0.895 | 0.90 (0.37–2.22) | 0.826 | 0.90 (0.33–2.47) | 0.842 |
| Active smoker | 0.75 (0.31–1.85) | 0.536 | 1.16 (0.46–2.97) | 0.754 | 0.59 (0.19–1.83) | 0.355 | 1.81 (0.62–5.30) | 0.275 |
| Diagnosis (oncologic vs. prophylactic) | 0.50 (0.23–1.24) | 0.139 | 0.58 (0.23–1.50) | 0.250 | 0.48 (0.19–1.25) | 0.127 | 0.79 (0.24–2.52) | 0.690 |
| Neoadjuvant chemotherapy | 0.51 (0.22–1.14) | 0.095 | 0.38 (0.15–0.99) | 0.042 | 0.46 (0.18–1.22) | 0.111 | 0.52 (0.18–1.51) | 0.221 |
| Bilateral breast surgery | 3.39 (0.43–6.57) | 0.218 | 1.13 (1.13–1.08) | 0.143 | 1.11 (1.06–1.16) | 0.171 | 1.09 (1.05–1.13) | 0.230 |
| NSM (vs. SSM) | 1.65 (0.55–4.96) | 0.369 | 1.80 (0.52–6.27) | 0.351 | 1.53 (0.44–5.42) | 0.500 | -- | -- |
| Wise-pattern incision | 1.30 (0.58–2.94) | 0.524 | 1.49 (0.54–4.15) | 0.438 | 0.48 (0.19–1.25) | 0.127 | 0.831 (0.28–2.51) | 0.743 |
| Implant volume | 1.00 (0.99–1.01) | 0.785 | 1.00 (0.99–1.01) | 0.661 | 1.00 (0.99–1.01) | 0.796 | 1.00 (0.99–1.01) | 0.507 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Costeira, B.; Gonçalves, B.; Soares, A.; Oom, R.; Costa, C.S.; Vargas Moniz, J.; Abecasis, N.; Rodrigues dos Santos, C. Short-Term Outcomes of Post-Mastectomy Immediate Pre-Pectoral Reconstruction with Implant and Acellular Dermal Matrix. J. Clin. Med. 2025, 14, 7181. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm14207181
Costeira B, Gonçalves B, Soares A, Oom R, Costa CS, Vargas Moniz J, Abecasis N, Rodrigues dos Santos C. Short-Term Outcomes of Post-Mastectomy Immediate Pre-Pectoral Reconstruction with Implant and Acellular Dermal Matrix. Journal of Clinical Medicine. 2025; 14(20):7181. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm14207181
Chicago/Turabian StyleCosteira, Beatriz, Beatriz Gonçalves, António Soares, Rodrigo Oom, Cristina Sousa Costa, João Vargas Moniz, Nuno Abecasis, and Catarina Rodrigues dos Santos. 2025. "Short-Term Outcomes of Post-Mastectomy Immediate Pre-Pectoral Reconstruction with Implant and Acellular Dermal Matrix" Journal of Clinical Medicine 14, no. 20: 7181. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm14207181
APA StyleCosteira, B., Gonçalves, B., Soares, A., Oom, R., Costa, C. S., Vargas Moniz, J., Abecasis, N., & Rodrigues dos Santos, C. (2025). Short-Term Outcomes of Post-Mastectomy Immediate Pre-Pectoral Reconstruction with Implant and Acellular Dermal Matrix. Journal of Clinical Medicine, 14(20), 7181. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm14207181






