Abstract
Background: Paroxysmal dyskinesias (PDs) are rare, episodic movement disorders characterized by sudden and involuntary hyperkinetic motor events. In paediatric populations, their diagnosis is often complicated by clinical overlap with epilepsy and other neurological conditions. Genetic underpinnings have increasingly been recognized as key to understanding phenotypic heterogeneity and guiding treatment. Objectives: This systematic review aims to provide a comprehensive overview of paediatric PD, with a focus on genetic aetiologies, clinical features, subtype classification, and therapeutic approaches, including genotype–treatment correlations. Methods: We systematically reviewed the literature from 2014 to 2025 using PubMed. Inclusion criteria targeted paediatric patients (aged 0–18 years) with documented paroxysmal hyperkinetic movements and genetically confirmed or clinically suggestive PD. Data were extracted regarding demographics, dyskinesia subtypes, age at onset, genetic findings, and treatment efficacy. Gene categories were classified as PD-specific or pleiotropic based on functional and clinical features. Results: We included 112 studies encompassing 605 paediatric patients. The most common subtype was Paroxistic Kinesigenic Dyskinesia (PKD). Male sex was more frequently reported. The mean onset age was 5.99 years. A genetic diagnosis was confirmed in 505 patients (83.5%), involving 38 different genes. Among these, PRRT2 was the most frequently implicated gene, followed by SLC2A1 and ADCY5. Chromosomal abnormalities affecting the 16p11.2 region were identified in ten patients, including deletions and duplications. Among the 504 patients with confirmed monogenic variants, 390 (77.4%) had mutations in PD-specific genes, while 122 (24.2%) carried pleiotropic variants. Antiseizure drugs—particularly sodium channel blockers such as carbamazepine and oxcarbazepine—were the most frequently reported treatment, with complete efficacy documented in 59.7% of the studies describing their use. Conclusions: Paediatric PDs exhibit significant clinical and genetic heterogeneity. While PRRT2 remains the most common genetic aetiology, emerging pleiotropic genes highlight the need for comprehensive diagnostic strategies. Sodium channel blockers are effective in a subset of genetically defined PD, particularly PRRT2-positive cases. Patients with pathogenic variants in other genes, such as ADCY5 and SLC2A1, may benefit from specific therapies that can potentially change their clinical course and prognosis. These findings support genotype-driven management approaches and underscore the importance of genetic testing in paediatric movement disorders.
1. Introduction
Paroxysmal dyskinesias (PDs) are rare hyperkinetic movement disorders characterized by sudden, brief and recurrent episodes of involuntary movements, such as dystonia, chorea or athetosis, without loss of consciousness. These episodes are self-limited and may occur spontaneously or in response to specific triggers, distinguishing PD from other movement disorders and epileptic syndromes [1,2,3].
PDs are classically categorized into three main types based on their triggering factors: paroxysmal kinesigenic dyskinesia (PKD), precipitated by sudden voluntary movements; paroxysmal non-kinesigenic dyskinesia (PNKD), triggered by factors such as alcohol, caffeine or fatigue; and paroxysmal exercise-induced dyskinesia (PED), associated with prolonged exertion. A fourth, less common type, paroxysmal hypnogenic dyskinesia (PhD), occurs during sleep [4,5,6].
In paediatric populations, PDs typically present with an average age of onset between 3.9 and 8.8 years and show a male predominance. Dystonia is the most frequently reported symptom, followed by choreoathetosis [6]. Familial forms usually begin in childhood, whereas acquired forms tend to have later onset [7]. Despite clinical classification, significant phenotypic and genetic overlap exists among subtypes [2,6].
From a genetic perspective, PDs exhibit considerable heterogeneity. Mutations in PRRT2, PNKD, SLC2A1 and KCNMA1 genes have been implicated across PD subtypes [5,6,8]. PRRT2 mutations are the most prevalent and account for approximately 35% of all cases. These mutations are associated with a spectrum of paroxysmal disorders including PKD, benign familial infantile seizures and migraine [9,10]. The most common variant, c.649dupC, has been identified in several families using exome sequencing and linkage analysis [11]. Functionally, PRRT2 encodes a protein that interacts with SNAP-25, regulating synaptic transmission and neuronal excitability [9].
Genotype–phenotype correlations are imperfect but clinically informative. For example, PRRT2-positive PKD is associated with earlier onset, bilateral symptomatology and higher attack frequency, as well as a more favourable response to carbamazepine compared to PRRT2-negative cases [12]. Similarly, SLC2A1 mutations underlie some PED cases and may respond to ketogenic dietary interventions [2,6].
The diagnosis of PD in children is challenging due to symptom overlap with epilepsy, psychogenic movement disorders, and metabolic conditions. Electroencephalography (EEG) and, more importantly, next-generation genetic testing are essential for accurate differential diagnosis [5]. A combined approach using detailed clinical assessment and genetic screening is currently recommended [2,6].
Therapeutic strategies for paediatric PD are subtype-specific. PKD generally responds well to low doses of antiepileptic drugs (AEDs), such as carbamazepine and oxcarbazepine, with complete symptom resolution reported in some series [13,14]. PNKD and PED management focuses on identifying and avoiding known triggers [5]. Additional therapies such as acetazolamide, clonazepam, ketogenic diet and botulinum toxin have been employed in selected cases [3,6,15]. For refractory cases, surgical options may be considered [3].
Overall, the prognosis of paediatric PDs, particularly those associated with PRRT2 and PNKD mutations, is favourable, with many children experiencing remission in adolescence or adulthood [3]. However, the clinical and genetic complexity of these disorders necessitates ongoing research to optimize diagnostic accuracy and individualize therapy.
This review aims to provide a comprehensive overview of paroxysmal dyskinesias in the paediatric population, with a specific focus on their genetic underpinnings, clinical features and treatment options. We will explore and examine recent advances and emerging trends in the understanding of these conditions.
2. Materials and Methods
This systematic literature review was conducted and reported in accordance with the Preferred Reporting Items for Systematic Reviews and Meta-Analyses (PRISMA) guidelines [16]. The study protocol was prospectively registered on PROSPERO (CRD420251050698).
This scoping review, conducted following the Joanna Briggs Institute methodology, examined literature published between 2014 and 2025 on paediatric paroxysmal dyskinesias. A systematic search was performed in PubMed in April 2025 using the following combination of keywords: (‘paroxysmal dyskinesia’ OR ‘paroxysmal movement disorder’ OR ‘episodic dystonia’ OR ‘paroxysmal chorea’ OR ‘transient dystonia’ OR ‘paroxysmal hyperkinetic’ OR ‘intermittent dyskinesia’ OR ‘paroxysmal motor event’) AND ‘paediatric’. No automated filters (e.g., age, language) were applied in the database. Studies were screened manually according to predefined inclusion and exclusion criteria.
The quality of the included studies was assessed using the Newcastle–Ottawa Quality Assessment Scale. Studies were categorized as having low (≥7 stars), moderate (5–6 stars), or high (≤4 stars) risk of bias, with a maximum score of 9 stars. Two independent reviewers (MG and GP) conducted the quality assessments, and any discrepancies were resolved through discussion and consensus.
Titles and abstracts were independently screened by two reviewers (GP and MG). Full-text articles were then assessed for eligibility using predefined inclusion and exclusion criteria. Disagreements were resolved through discussion and consensus. No automation tools were used.
2.1. Inclusion Criteria
We included studies meeting the following criteria:
- Population: paediatric patients aged 0 to 18 years.
- Phenotype: presence of hyperkinetic involuntary movements (including chorea, dystonia, ballism, myoclonus, or combinations) with a paroxysmal course, defined by:
- ○
- Sudden onset and limited duration of episodes (ranging from seconds to hours);
- ○
- Intermittent or recurrent occurrence over time;
- ○
- Return to baseline or relatively stable neurological status between episodes.
- Diagnosis: a recognized clinical or genetic diagnosis associated with paroxysmal dyskinesia (e.g., PRRT2, PNKD, SLC2A1, GNAO1, ADCY5).
- Phenotypic description: clear documentation or inference of a paroxysmal pattern, even if the term “paroxysmal” is not explicitly used.
- Publication language: studies published in English or other languages with an English abstract available.
- Study type: we considered case reports, case series, cohort studies reporting relevant clinical data.
- Multiple patients or family descriptions: in cases describing multiple patients (either distinct or within the same family), only individuals with childhood-onset were included. In cases where families or groups were reported, paediatric individuals were included if they were individually described with adequate clinical detail, ensuring a clear distinction from other family members or cases.
2.2. Exclusion Criteria
We excluded studies with the following characteristics:
- Descriptions of continuous or non-paroxysmal hyperkinetic movements (e.g., progressive dystonias, persistent dyskinesias).
- Neurological conditions without a paroxysmal course of movement disorders (e.g., dyskinetic cerebral palsy, static or neurodegenerative encephalopathies).
- Studies focusing exclusively on adult patients (>18 years)
- Articles lacking sufficient clinical detail to assess the presence or absence of a paroxysmal movement pattern.
For the “age of onset” column, the following approximations were used: early infancy = 0.25 years; infancy = 0.5 years; adolescence = 14.5 years.
For the genetic analysis, we included only patients for whom a specific gene mutation was explicitly reported with a patient count. Cases with chromosomal abnormalities were considered separately unless associated with a confirmed monogenic variant.
The following variables were systematically extracted: age at onset, sex, dyskinesia subtype (PKD, PNKD, PED, PHD), gene or chromosomal anomaly involved, treatment type and response. When only qualitative age descriptors were available (e.g., ‘infancy’), we applied standardized numeric conversions. No data were extracted on funding sources from individual studies.
3. Results
3.1. Flow Chart of Included Studies
Search results are summarized in the Prisma Flow Chart in Figure 1 (PRISMA 2020 checklist in Supplementary Figure S1). Initially, 2968 studies were identified through the search strategy from the databases. After removing duplicates, 2522 studies remained. Following the title and abstract screening, 132 studies were assessed for eligibility.
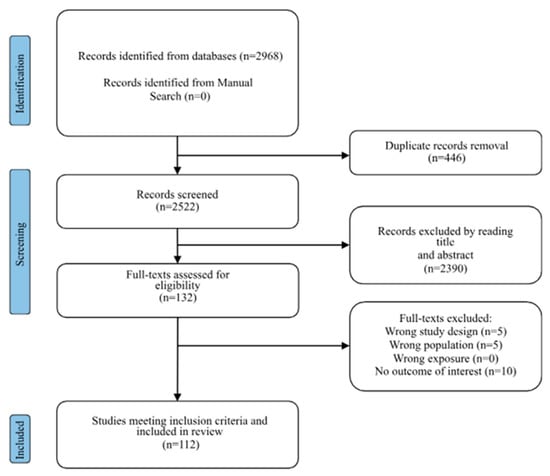
Figure 1.
Prisma flow-chart describing the study selection process. Here are references of included articles [2,6,10,17,18,19,20,21,22,23,24,25,26,27,28,29,30,31,32,33,34,35,36,37,38,39,40,41,42,43,44,45,46,47,48,49,50,51,52,53,54,55,56,57,58,59,60,61,62,63,64,65,66,67,68,69,70,71,72,73,74,75,76,77,78,79,80,81,82,83,84,85,86,87,88,89,90,91,92,93,94,95,96,97,98,99,100,101,102,103,104,105,106,107,108,109,110,111,112,113,114,115,116,117,118,119,120,121,122,123,124].
Finally, we included 112 studies in the systematic review (see Supplementary Table S1).
3.2. Ratings of Study Quality and Risk of Bias
According to the study’s quality ratings, 97 studies were rated as good quality, 9 as moderate quality and 6 as poor quality. Since most of the studies included in this review were of moderate or good quality, the risk of bias from them was low. Three researchers independently extracted data on the variables from the studies.
3.3. Population Characteristics
The 112 studies encompassed a total of 605 patients.
3.3.1. Gender Data
Gender information was available for 476 out of 605 patients, as reported in the included studies. Among these, 302 were male (63.4%) and 174 were female (36.6%). Gender data were missing for the remaining 129 patients. Table 1 summarizes the numerical and percentage distribution by gender.

Table 1.
Gender distribution of patients with paediatric dyskinesias from studies with available gender data.
3.3.2. Age at Onset
Data on the mean age at onset were available in 108 studies (601 patients). After standardizing all reported values to years, the mean age at onset across studies was 5.99 years, with a median of 5.00 years. The age at diagnosis does not take into account the diagnostic delay that often occurs for individuals with these movement disorders. The youngest reported mean age was 0.027 years (approximately 10 days), while the oldest was 17 years. Age values originally expressed in days or months were converted to years to allow consistent statistical analysis (see Table 2). In addition, qualitative descriptors were standardized as follows: “early infancy” was coded as 0.25 years, “infancy” as 0.5 years, and “adolescence” as 14.5 years.

Table 2.
Age at onset of paediatric dyskinesias across studies. The table summarizes the descriptive statistics for the reported mean age at onset across studies. Values were standardized to years. Entries reported in days or months were converted accordingly. Studies without usable age data were excluded from the calculation.
3.4. Distribution of Dyskinesia Subtypes
Among the paediatric patients reported in the included studies, three major subtypes of paroxysmal dyskinesia were identified: Paroxysmal Kinesigenic Dyskinesia (PKD), Paroxysmal Non-Kinesigenic Dyskinesia (PNKD) and Paroxysmal Exercise-induced Dyskinesia (PED). A total of 343 cases of PKD (56.8%), 142 cases of PNKD (23.5%) and 119 cases of PED (19.7%) were documented. The subtype was not mutually exclusive in all studies, and some reports included patients with multiple overlapping features. Data on subtype classification were available for the majority of patients; entries with missing information were excluded from percentage calculations. Cases originally reported with non-standard nomenclature were classified post hoc according to the most consistent clinical features described by the authors. Studies reporting mixed or ambiguous classifications were carefully reviewed and patients reassigned to the most appropriate subtype whenever possible. These findings are summarized in Table 3.

Table 3.
Distribution of dyskinesia subtypes among paediatric patients. The table summarizes the total number and percentage of patients diagnosed with different subtypes of paroxysmal dyskinesias across included studies. Subtypes include Paroxysmal Kinesigenic Dyskinesia (PKD), Paroxysmal Non-Kinesigenic Dyskinesia (PNKD), and Paroxysmal Exercise-induced Dyskinesia (PED). All values are based on reported data; missing entries were excluded from percentage calculations.
3.5. Paroxysmal Hypnogenic Dyskinesia (PHD) and Nocturnal Trigger in PNKD
In our cohort, Paroxysmal Hypnogenic Dyskinesia (PHD) was explicitly identified as a distinct clinical entity in only two studies, encompassing a total of three patients [52,79]. Notably, the case described by Almeida et al. [52] was associated with brachytelephalangic chondrodysplasia punctata. In the video available in the article [52], we note how it is particularly difficult to distinguish a paroxysmal nocturnal dyskinesia from a nocturnal frontal lobe seizure; an electroencephalographic recording of the episode is essential in order to resolve diagnostic doubts.
These cases lacked consistent genetic characterization.
Conversely, a subset of 25 patients originally classified under Paroxysmal Non-Kinesigenic Dyskinesia (PNKD) exhibited a prominent nocturnal trigger, such as onset during sleep, awakening, or falling asleep. For the purpose of this analysis, these cases were reclassified as PHD based on their clinical features [36,39,45,52,60,63,76,79,98,100,109,117]. Among this reclassified group, genetic variants were identified in 22 patients, including 13 with ADCY5 mutations (across five studies), 4 with NACC1, 2 with SLC16A2, and one each with PRRT2, ATP1A3, and DNML1. The remaining three patients had no identifiable genetic cause.
Details are summarised in Table 4.

Table 4.
Genetic and syndromic associations in Paroxysmal Hypnogenic Dyskinesia (PHD).
3.6. Genetic Findings
Among the 605 paediatric patients identified, 505 (83.5%) had a genetically confirmed diagnosis, while for 100 patients (16.5%) genetic data were incomplete, inconclusive or unavailable.
Among patients with a genetically confirmed diagnosis, a total of 504 monogenic variants were identified, corresponding to 38 distinct genes. These reflect the cases for which specific molecular findings were available and extractable from the included studies, accounting for 82.0% of the overall cohort. The most frequently reported gene mutation involved PRRT2 (46.29%), followed by SLC2A1 (16.21%) and ADCY5 (5.66%). The full distribution is summarized in Table 5.

Table 5.
Frequency of genes associated with paediatric dyskinesias. Percentages refer to patients who have genetically determined paroxysmal dyskinesia. For the “gene” column, if a numeric value preceded a gene (e.g., ‘5 PRRT2′), only that number of patients was attributed to the gene. Entries marked as ‘NA’ (not applicable) or “0” were excluded from the genetic analysis. Among the genes causing paroxysmal dyskinesia, the GCH1 gene is also described, although the number of affected individuals cannot be determined. The raw data and gene count script are available in the Supplementary Material (Supplementary Table S1).
Chromosomal abnormalities were reported in 10 patients, all involving the 16p11.2 region and including both deletions and duplications. Notably, one of these patients [97] also carried a PRRT2 mutation. The full distribution is summarized in Table 6.

Table 6.
Chromosomal abnormalities associated with paediatric dyskinesias.
One patient was reported with brachytelephalangic chondrodysplasia punctata (CDPX1), a rare X-linked skeletal dysplasia, presenting with a paroxysmal non-kinesigenic dyskinesia (PNKD) phenotype.
3.7. Gene Categories
To explore the genetic heterogeneity of paediatric paroxysmal dyskinesias (PDs), all genes identified in the included studies were categorized into two main functional groups: PD-specific genes and pleiotropic genes, in accordance with previous classifications [2,125]. PD-specific genes were defined as those predominantly associated with isolated paroxysmal movement disorders, typically without major comorbidities such as epilepsy, intellectual disability or neurodevelopmental delay. These genes are characteristically linked to well-defined PD subtypes (e.g., PKD, PED), with relatively consistent clinical features and often favourable outcomes. In contrast, pleiotropic genes were defined as those associated with broader neurodevelopmental or epileptic syndromes, where paroxysmal dyskinesia may be one of multiple neurological manifestations. These genes are commonly implicated in developmental and epileptic encephalopathies (DEEs), congenital syndromes or complex movement disorders with continuous or combined hyperkinetic signs. Representative examples include GNAO1, SCN8A, FOXG1 and SYNGAP1.
Based on this classification, 390 variants (76.2%) were mapped to PD-specific genes (e.g., PRRT2, SLC2A1, ADCY5, KCNA1, KCNMA1, TMEM151A), while 122 variants (23.8%) involved pleiotropic genes (e.g., GNAO1, SCN8A, FOXG1, SYNGAP1). These proportions reflect the distribution of 512 gene-level diagnoses identified among the 504 patients with confirmed monogenic variants. The complete distribution is illustrated in Figure 2.
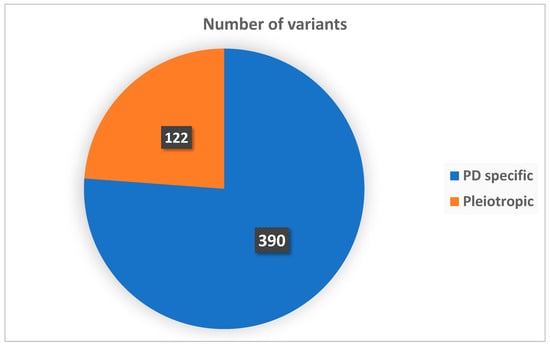
Figure 2.
Distribution of genes by functional category.
3.8. Temporal Trends in Genetic Complexity
An analysis of the literature over time reveals a shift in the genetic understanding of paediatric paroxysmal dyskinesias. In earlier reports, most patients carried mutations in paroxysmal dyskinesia-specific genes such as PRRT2, PNKD and SLC2A1, typically associated with isolated phenotypes and favourable treatment responses. However, in more recent years, the advent of next-generation sequencing (NGS) technologies has led to the increasing identification of pleiotropic genes such as GNAO1, SCN8A, FOXG1, and SYNGAP1, known to cause developmental and epileptic encephalopathies (DEEs) or complex neurodevelopmental syndromes. Figure 3 illustrates the proportional increase in pleiotropic gene-associated cases over the past decade.
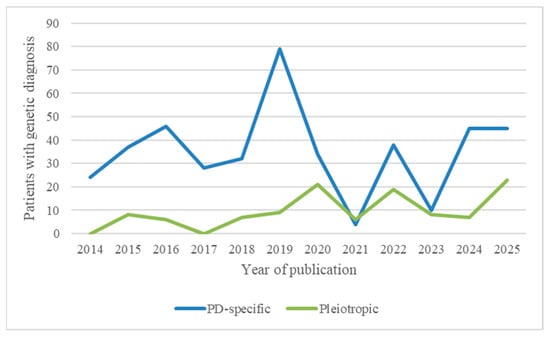
Figure 3.
Temporal distribution of genetically confirmed paediatric paroxysmal dyskinesia cases by gene category.
3.9. Pharmacological Treatment Summary
Due to the heterogeneity in treatment reporting and the frequent lack of patient-level therapeutic data, the analysis was conducted at the study level, considering each publication as a single observational unit.
Among the 112 studies included in the review, 97 (86.6%) reported at least one pharmacological intervention. Of these, 78 studies (80.4%) described the use of antiseizure medications (AEDs).
Beyond AEDs, other pharmacological strategies were documented: the ketogenic diet (KD) in 16 studies (16.5%), dopaminergic therapy (L-dopa/carbidopa) in five (5.2%), baclofen and trihexyphenidyl in four each (4.1%), acetazolamide in three (3.1%), caffeine in three (3.1%), deep brain stimulation (DBS) in three (3.1%) and botulinum toxin in two (2.1%). Other treatments—including thiamine, diazepam, benzodiazepines, flunarizine, tetrabenazine, lisdexamfetamine, gabapentin, clonidine, clonazepam, antioxidants, lomerizine, mitochondrial support, and low-valine dietary therapy—has been reported (1.0%).
Most commonly AEDs used were sodium channel blockers such as carbamazepine (CBZ) or oxcarbazepine (OXC), mainly used in patients with a mutation in the PRRT2 gene. CBZ/OXC treatment was specifically reported in 67 studies (69.1%). Among these, 40 studies (41.2%) described complete symptom resolution, while three (3.1%) reported partial benefit and three (3.1%) no clinical effect. In 21 studies (21.6%), the response to CBZ/OXC was not clearly documented. Genes associated with suboptimal or variable response included DNML1, ADCY5, ANO3, SLC2A1, CACNA1A, KCNA1, SLC26A4, SCN2A, RHOBTB2, GLDC, MECP2, PRRT2, KCNJ10, KCNMA1, TBC1D24, TMEM151A, ATP1A3, TMEM151A, RHOBTB2, ADCY5 and GNAO1.
Caffeine was mainly used in patients with a mutation in the ADCY5 gene; not all patients showed remission of symptoms, especially patients with static ADCY5-related cervical dystonia.
All percentages refer to the 97 studies that reported pharmacological treatments. Because multiple therapies were often described within a single publication, the percentages are not mutually exclusive. Non-pharmacological strategies such as trigger avoidance or physical/behavioural therapies were not systematically assessed and are thus excluded from this analysis.
4. Discussion
In our systematic review of the literature, it appears that there are 605 paediatric patients described in the literature with paroxysmal dyskinesia. There is a clear prevalence of male patients, a finding that is confirmed in the literature; for example, a recently published study by Huang et colleagues in 2020 [126] confirms the trend of having a clear prevalence in the male sex. Most of the patients described in this systematic review of the literature have paroxysmal kinesigenic dyskinesia. Notably, Kim and colleagues in 2018 [6] describe the highest number of individuals with PKD (paediatric age), with 40 cases. This finding coincides with the literature, according to which [127] PKD is the most common paroxysmal movement disorder. Among the genetic causes that cause PKD, the main one is the PRRT2 gene, as already described by Chen and colleagues in 2011 [128]. The PRRT2 gene, in our systematic review, appears to be the gene most involved in the development of paroxysmal dyskinesias that have an underlying genetic cause, contributing to the genesis especially of paroxysmal kinesigenic dyskinesias; we would like to specify that, as for example in the case of the Vaia et al. article from 2023 [26], it is pointed out that episodes of kinesigenic dyskinesia can originate as early as the age of 3 months of life. The most commonly used therapy in paroxysmal dyskinesias is carbamazepine. This finding is confirmed in the literature, where carbamazepine is the most widely used drug especially in paroxysmal dyskinesias kinesigenic from PRRT2 gene mutation [118,129]. The effectiveness of therapy dramatically affects patients’ quality of life. Although it is not always a data point that is not easily statistically quantifiable, and therefore not integrated into this systematic review, we would therefore like to emphasize that individuals with PKD also present with nonmotor symptoms, which greatly affect quality of life, as well described in this recent article by Asya Ekmen et colleagues in 2023 [130]. Carbamazepine, in general, works well on PKD, although the best results are obtained when the PRRT2 gene is involved. To understand the reasons for this mechanism, we have to remember how sodium blockers act; CBZ/OXC block and reduce neuronal excitability, which underlies neurological manifestations, including PKD [131]. The PRRT2 gene encodes for a protein located at the pre-synaptic level, which interacts with the SNARE complex, regulating neuronal excitability [132].
About the frequency of the types of PD found, after PKD we find PNKDs. The article containing the largest number of PNKDs is that of Masnada et colleagues [110] where 11 individuals with mutation on the SLC16A2 gene are described who have paroxysmal motor dyskinesias following external stimuli (e.g., a startle) or during a meal. Other genes are implicated in the genesis of PNKDs, including ADCY5. One of the genes most implicated in the development of PNKD is the ADCY5 gene. The early diagnosis of paroxysmal dyskinesias related to this gene appears particularly important, as caffeine therapy [133] significantly reduces dyskinetic symptoms (both in cases of PNKD and in the development of other types of paroxysmal dyskinesias). ADCY5 encodes for a type 5 adenylate cyclase, expressed mainly in the striatum. A2A receptors determine its activation, while D2 dopamine receptors inhibit it. Caffeine has A2A receptors as its main target [134,135]. The cases that are less responsive to therapy among those described in our systematic review involving the ADCY5 gene are, for example, those described by Quazza and colleagues [45], who describe movement disorders associated with the onset of static cervical dystonia; they seem to benefit most from methylphenidate therapy (0.6 mg/kg/day) in one case (PKD, PNKD and nocturnal episodes) and in one case with spontaneous resolution once they reach adulthood (PHD).
Regarding PEDs, of interest is François-Heude et al., 2022 [74] where movement disorders in valine metabolism, caused by HIBCH and ECHS1 deficiencies, are described. However, it is evident from both the literature and our systematic review that one of the genes mainly implicated in PEDs, as well as in other types of PD, is SLC2A1. The SLC2A1 gene encodes for GLUT1. The GLUT1 transporter allows glucose to pass through the blood–brain barrier. Its deficiency can therefore cause neurological manifestations such as epilepsy, neurodevelopmental disorders and movement disorders (including PD). The GLUT1 transporter allows the passage of glucose across the blood–brain barrier. Its deficiency can therefore cause neurological manifestations such as epilepsy, neurodevelopmental disorders and movement disorders (including PD) [136]. The ketogenic diet is an excellent solution in patients with this disease, as the brain uses ketones to obtain the energy it needs, instead of glucose, which is prevented from crossing the blood–brain barrier [137]. In the included studies, one of the most suggestive is that of Takahashi and colleagues, from 2020 [34]. Here, patients with the SLC2A1 mutation who have movement disorders and epilepsy are described. Patients on a ketogenic diet showed an improvement in movement disorder and, specifically, PD.
Another gene mentioned in the literature is PNKD. This gene, whose name is evocative for the dyskinesia it refers to, is located on chromosome 9. As described by Harvey and colleagues in 2025 [81], the main triggers in this case are stress and fatigue (but activation by alcohol and coffee is also possible) and transmission is autosomal dominant [138].
PHD deserve a special mention. This group, which constitutes a separate category in paroxysmal dyskinesias, is certainly the rarest and sometimes associated with peculiar genes; the gene most involved in our sample was ADCY5. Law and colleagues [100] describe carbamazepine therapy as effective in 1 patient with PHD; however, the efficacy of therapy appears to be more related to the gene involved in PHD.
Our systematic review has several limitations. In particular, the inclusion criteria for enrolling patients were rather stringent. Some articles of scientific interest may have been excluded; however, we believe this review gives a valid impression and is true to current scientific knowledge regarding paroxysmal dyskinesias in paediatric age.
5. Conclusions
The case history of the literature, in the time frame we have taken into consideration, has allowed us to obtain useful information. The first thing to perform is the anamnesis. Here, we will have to pay attention to the movements that are described by the patient and caregivers and any familiarity to movement disorder, and ask the parents if it is possible to make a video of the episodes [139]. Only later, when we have real suspicion of a movement disorder, can we propose genetic analyses. In our sample, as many as 16.5% of patients did not have a definite genetic diagnosis. This could be the starting point for carrying out extended genetic investigations, even beyond the genetic panels for movement disorders, in order to not miss variants that may not have been associated with similar phenotypes up to now.
It is also true, however, as in the case of PRRT2 paroxysmal kinesigenic dyskinesias, that having positive genetics allows us to go more safely towards a therapy such as carbamazepine or other sodium blockers, to strengthen the clinical suspicion of the referring physician. The same discussion about therapy is valid for other genes, such as SLC2A1 (ketogenic diet) and ADCY5 (caffeine). Further genetic and physiopathological studies of paroxysmal dyskinesias will be essential in the future to better understand which therapies can help us interrupt the disabling motor phenomenology and improve the quality of life of these patients.
Supplementary Materials
The following supporting information can be downloaded at: https://www.mdpi.com/article/10.3390/jcm14175925/s1, Supplementary Table S1: patients described in this systematic review, with clinical and genetic characteristics. Figure S1: PRISMA 2020 checklist.
Author Contributions
Conceptualization: C.A.C. and C.F.; methodology: G.P., M.G., G.S., C.A.C., A.P., S.R., A.C., D.F. and C.F.; data curation: G.P., M.G. and G.S.; writing—original draft preparation: G.P., M.G. and G.S.; writing—review and editing: C.A.C. and C.F.; supervision: C.F. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This research received no external funding.
Institutional Review Board Statement
Ethical review was not required for this study as it is a scoping review that analyses previously published data.
Informed Consent Statement
Informed consent was not required for this study as it is a scoping review that analyses previously published data.
Data Availability Statement
No new data were created or analysed in this study.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
References
- Demirkiran, M.; Jankovic, J. Paroxysmal Dyskinesias: Clinical Features and Classification. Ann. Neurol. 1995, 38, 571–579. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Erro, R.; Sheerin, U.; Bhatia, K.P. Paroxysmal Dyskinesias Revisited: A Review of 500 Genetically Proven Cases and a New Classification. Mov. Disord. 2014, 29, 1108–1116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Latorre, A.; Bhatia, K.P. Treatment of Paroxysmal Dyskinesia. Neurol. Clin. 2020, 38, 433–447. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Van Rootselaar, A.-F.; Van Westrum, S.S.; Tijssen, M.A.J.; Velis, D.N. The Paroxysmal Dyskinesias. Pract. Neurol. 2009, 9, 102–109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McGuire, S.; Chanchani, S.; Khurana, D.S. Paroxysmal Dyskinesias. Semin. Pediatr. Neurol. 2018, 25, 75–81. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, S.Y.; Lee, J.S.; Kim, W.J.; Kim, H.; Choi, S.A.; Lim, B.C.; Kim, K.J.; Chae, J.-H. Paroxysmal Dyskinesia in Children: From Genes to the Clinic. J. Clin. Neurol. 2018, 14, 492. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Goodenough, D.J. Familial and Acquired Paroxysmal Dyskinesias: A Proposed Classification With Delineation of Clinical Features. Arch. Neurol. 1978, 35, 827. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gardiner, A.R.; Jaffer, F.; Dale, R.C.; Labrum, R.; Erro, R.; Meyer, E.; Xiromerisiou, G.; Stamelou, M.; Walker, M.; Kullmann, D.; et al. The Clinical and Genetic Heterogeneity of Paroxysmal Dyskinesias. Brain 2015, 138, 3567–3580. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Méneret, A.; Gaudebout, C.; Riant, F.; Vidailhet, M.; Depienne, C.; Roze, E. PRRT2 Mutations and Paroxysmal Disorders. Eur. J. Neurol. 2013, 20, 872–878. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ebrahimi-Fakhari, D.; Saffari, A.; Westenberger, A.; Klein, C. The Evolving Spectrum of PRRT2-Associated Paroxysmal Diseases. Brain 2015, 138, 3476–3495. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.-L.; Cao, L.; Li, X.-H.; Hu, Z.-M.; Li, J.-D.; Zhang, J.-G.; Liang, Y.; San-A; Li, N.; Chen, S.-Q.; et al. Identification of PRRT2 as the Causative Gene of Paroxysmal Kinesigenic Dyskinesias. Brain 2011, 134, 3493–3501. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mao, C.; Shi, C.; Song, B.; Wu, J.; Ji, Y.; Qin, J.; Li, Y.; Wang, J.; Shang, D.; Sun, S.; et al. Genotype–Phenotype Correlation in a Cohort of Paroxysmal Kinesigenic Dyskinesia Cases. J. Neurol. Sci. 2014, 340, 91–93. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sohn, Y.H.; Lee, P.H. Paroxysmal Choreodystonic Disorders. In Handbook of Clinical Neurology; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2011; Volume 100, pp. 367–373. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chillag, K.L.; DeRoos, S.T. Oxcarbazepine Use in Paroxysmal Kinesigenic Dyskinesia: Report on Four Patients. Pediatr. Neurol. 2009, 40, 295–297. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Strzelczyk, A.; Bürk, K.; Oertel, W.H. Treatment of Paroxysmal Dyskinesias. Expert Opin. Pharmacother. 2011, 12, 63–72. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Page, M.J.; McKenzie, J.E.; Bossuyt, P.M.; Boutron, I.; Hoffmann, T.C.; Mulrow, C.D.; Shamseer, L.; Tetzlaff, J.M.; Akl, E.A.; Brennan, S.E.; et al. The PRISMA 2020 Statement: An Updated Guideline for Reporting Systematic Reviews. PLoS Med. 2021, 18, e1003583. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Z.-B.; Tian, M.-Q.; Gao, K.; Jiang, Y.-W.; Wu, Y. De Novo KCNMA1 Mutations in Children with Early-Onset Paroxysmal Dyskinesia and Developmental Delay: Letters: New observations. Mov. Disord. 2015, 30, 1290–1292. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, X.; Yu, T. Beyond Seizures: SCN8A Heterozygous Mutation Presenting with Epilepsy and Paroxysmal Dyskinesia. Ann. Med. Surg. 2025, 87, 438–440. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zagaglia, S.; Steel, D.; Krithika, S.; Hernandez-Hernandez, L.; Custodio, H.M.; Gorman, K.M.; Vezyroglou, A.; Møller, R.S.; King, M.D.; Hammer, T.B.; et al. RHOBTB2 Mutations Expand the Phenotypic Spectrum of Alternating Hemiplegia of Childhood. Neurology 2021, 96, e1539–e1550. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Youn, J.; Kim, J.S.; Lee, M.; Lee, J.; Roh, H.; Ki, C.-S.; Choa, J.W. Clinical Manifestations in Paroxysmal Kinesigenic Dyskinesia Patients with Proline-Rich Transmembrane Protein 2 Gene Mutation. J. Clin. Neurol. 2014, 10, 50. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- You, D.; Huang, Y.; Wang, X.; Li, W.; Li, F. Long-Term Low-Dose Lamotrigine for Paroxysmal Kinesigenic Dyskinesia: A Two-Year Investigation of Cognitive Function in Children. Front. Psychiatry 2024, 15, 1368289. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yin, X.-M.; Lin, J.-H.; Cao, L.; Zhang, T.-M.; Zeng, S.; Tian, W.-T.; Hu, Z.-M.; Li, N.; Wang, J.-L.; Guo, J.-F.; et al. Familial Paroxysmal Kinesigenic Dyskinesia Is Associated with Mutations in the KCNA1 Gene. Hum. Mol. Genet. 2018, 27, 625–637. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xu, Y.; Zhang, J.; Yu, K.; Feng, F.; Sun, X.; Li, C.; Li, H.; Cui, L. A Therapeutic Regimen for 3-Hydroxyisobutyryl-CoA Hydrolase Deficiency with Exercise-Induced Dystonia. Eur. J. Paediatr. Neurol. 2019, 23, 755–759. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wen, M.; Huang, H.; Huang, F.; Xu, R.; Zhang, J.; Fan, J.; Zeng, J.; Jiang, K.; Liu, D.; Huang, H.; et al. A New Genetic Diagnosis Strategy for Paroxysmal Kinesigenic Dyskinesia: Targeted High-throughput Detection of PRRT2 Gene c.649 Locus. Mol. Genet. Genomic Med. 2024, 12, e2469. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Waak, M.; Mohammad, S.S.; Coman, D.; Sinclair, K.; Copeland, L.; Silburn, P.; Coyne, T.; McGill, J.; O’Regan, M.; Selway, R.; et al. GNAO1-Related Movement Disorder with Life-Threatening Exacerbations: Movement Phenomenology and Response to DBS. J. Neurol. Neurosurg. Psychiatry 2018, 89, 221–222. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vaia, Y.; Previtali, R.; Malgesini, S.; Patanè, A.; Masnada, S.; Lodi, M.A.M.; Veggiotti, P.; Tonduti, D. Early Onset Paroxysmal Dyskinesia in PRRT2-Related Disorders. Mov. Disord. Clin. Pract. 2023, 10, 701–703. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ueda, K.; Shinawi, M.; Pearson, T.S. Paroxysmal Kinesigenic Dyskinesia in Twins With Chromosome 16p11.2 Duplication Syndrome. Neurol. Genet. 2021, 7, e549. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Türkdoğan, D.; Smolina, N.; Tekgül, Ş.; Gül, T.; Yeşilyurt, A.; Houlden, H.; Zuchner, S.; Brais, B.; Pellerin, D.; Başak, A.N. The First Case of Autosomal Recessive Cerebellar Ataxia with Prominent Paroxysmal Non-kinesigenic Dyskinesia Caused by a Truncating FGF14 Variant in a Turkish Patient. Mov. Disord. 2025, 40, 370–375. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tsai, M.; Nian, F.; Hsu, M.; Liu, W.; Liu, Y.; Liu, C.; Lin, P.; Hwang, D.; Chuang, Y.; Tsai, J. PRRT2 Missense Mutations Cluster near C-terminus and Frequently Lead to Protein Mislocalization. Epilepsia 2019, 60, 807–817. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Torisu, H.; Watanabe, K.; Shimojima, K.; Sugawara, M.; Sanefuji, M.; Ishizaki, Y.; Sakai, Y.; Yamashita, H.; Yamamoto, T.; Hara, T. Girl with a PRRT2 Mutation and Infantile Focal Epilepsy with Bilateral Spikes. Brain Dev. 2014, 36, 342–345. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tian, M.; Chen, J.; Li, J.; Pan, H.; Lei, W.; Shu, X. Damaging Novel Mutations in PIGN Cause Developmental Epileptic-Dyskinetic Encephalopathy: A Case Report. BMC Pediatr. 2022, 22, 222. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thouin, A.; Crompton, D.E. Glut1 Deficiency Syndrome: Absence Epilepsy and La Soupe Du Jour. Pract. Neurol. 2016, 16, 50–52. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tanabe, Y.; Taira, T.; Shimotake, A.; Inoue, T.; Awaya, T.; Kato, T.; Kuzuya, A.; Ikeda, A.; Takahashi, R. An adult female with proline-rich transmembrane protein 2 related paroxysmal disorders manifesting paroxysmal kinesigenic choreoathetosis and epileptic seizures. Rinsho Shinkeigaku 2019, 59, 144–148. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Takahashi, S.; Tanaka, R.; Takeguchi, R.; Kuroda, M.; Akaba, Y.; Ito, Y. The Role of Molecular Analysis of SLC2A1 in the Diagnostic Workup of Glucose Transporter 1 Deficiency Syndrome. J. Neurol. Sci. 2020, 416, 117041. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Seo, S.Y.; You, S.J. Paroxysmal Kinesigenic Dyskinesia in a Patient with a PRRT2 Mutation and Centrotemporal Spike Discharges on Electroencephalogram: Case Report of a 10-Year-Old Girl. Korean J. Pediatr. 2016, 59 (Suppl. 1), S157. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Stretavská, P.; Necpál, J.; Trúsiková, E.; Okáľová, K.; Latka, S.; Jech, R.; Zech, M. Paroxysmal Nocturnal Dystonia in DNM1L-Related Syndrome. Parkinsonism Relat. Disord. 2025, 133, 107351. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Steel, D.; Heim, J.; Kruer, M.C.; Sanchis-Juan, A.; Raymond, L.F.; Eunson, P.; Kurian, M.A. Biallelic Mutations of TBC1D24 in Exercise-Induced Paroxysmal Dystonia. Mov. Disord. 2020, 35, 372–373. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Soliani, L.; Martorell, L.; Yubero, D.; Verges, C.; Petit, V.; Ortigoza-Escobar, J.D. Paroxysmal Non-Kinesigenic Dyskinesia: Utility of the Quantification of GLUT1 in Red Blood Cells. Mov. Disord. Clin. Pract. 2022, 9, 252–254. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Solazzi, R.; Nanni, G.; Esposito, S.; Estienne, M.; Freri, E.; Zibordi, F.; Canafoglia, L.; Castellotti, B.; Granata, T. Repetitive Sleep Starts in Allan-Herndon-Dudley Syndrome. Pediatr. Neurol. 2023, 147, 24–27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Set, K.K.; Ghosh, D.; Huq, A.H.M.; Luat, A.F. Episodic Ataxia Type 1 (K-channelopathy) Manifesting as Paroxysmal Nonkinesogenic Dyskinesia: Expanding the Phenotype. Mov. Disord. Clin. Pract. 2017, 4, 784–786. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Senthilkumar, V.; Sivaraj, K. Paroxysmal Exercise-Induced Dyskinesia in Siblings Due to ECHS1 Gene Mutation—First Indian Case Report. Ann. Indian Acad. Neurol. 2020, 23, 837. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Satolli, S.; Invernizzi, F.; Danti, F.R.; Reale, C.; Panteghini, C.; Nardocci, N.; Garavaglia, B.; Zorzi, G. Two Cases of TMEM151A-Associated Paroxysmal Dyskinesia in a Single-Center Series of PRRT2-Negative Patients. Mov. Disord. Clin. Pract. 2023, 10, 842–844. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sanpera, J.; Gupta, R.; Singh, R.; Byrne, S. PRRT2—Associated Paroxysmal Kinesigenic Dyskinesia Only Evident with High-Speed Cricket Bowling. Mov. Disord. Clin. Pract. 2022, 9, 259–260. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ryan, C.S.; Fine, A.L.; Cohen, A.L.; Schiltz, B.M.; Renaud, D.L.; Wirrell, E.C.; Patterson, M.C.; Boczek, N.J.; Liu, R.; Babovic-Vuksanovic, D.; et al. De Novo DNM1L Variant in a Teenager With Progressive Paroxysmal Dystonia and Lethal Super-Refractory Myoclonic Status Epilepticus. J. Child Neurol. 2018, 33, 651–658. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Quazza, F.; Riant, F.; Patera, M.; Suppa, A.; Satolli, S.; Burglen, L.; Zech, M.; Boesch, S.; Indelicato, E.; Hainque, E.; et al. Atypical ADCY5-Related Movement Disorders: Highlighting Adolescent/Adult-Onset Cervical Dystonia. Parkinsonism Relat. Disord. 2025, 132, 107274. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pan, G.; Zhang, L.; Zhou, S. Clinical Features of Patients with Paroxysmal Kinesigenic Dyskinesia, Mutation Screening of PRRT2 and the Effects of Morning Draughts of Oxcarbazepine. BMC Pediatr. 2019, 19, 439. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ousingsawat, J.; Talbi, K.; Gómez-Martín, H.; Koy, A.; Fernández-Jaén, A.; Tekgül, H.; Serdaroğlu, E.; Schreiber, R.; Ortigoza-Escobar, J.D.; Kunzelmann, K. Broadening the Clinical Spectrum: Molecular Mechanisms and New Phenotypes of ANO3-Dystonia. Brain 2024, 147, 1982–1995. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Olivotto, S.; Duse, A.; Bova, S.M.; Leonardi, V.; Biganzoli, E.; Milanese, A.; Cereda, C.; Bertoli, S.; Previtali, R.; Veggiotti, P. Glut1 Deficiency Syndrome throughout Life: Clinical Phenotypes, Intelligence, Life Achievements and Quality of Life in Familial Cases. Orphanet J. Rare Dis. 2022, 17, 365. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Okumura, A.; Shimojima, K.; Kurahashi, H.; Numoto, S.; Shimada, S.; Ishii, A.; Ohmori, I.; Takahashi, S.; Awaya, T.; Kubota, T.; et al. PRRT2 Mutations in Japanese Patients with Benign Infantile Epilepsy and Paroxysmal Kinesigenic Dyskinesia. Seizure 2019, 71, 1–5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Okazaki, T.; Saito, Y.; Ueda, R.; Sugihara, S.; Tamasaki, A.; Nishimura, Y.; Ohno, K.; Togawa, M.; Ohno, T.; Horie, A.; et al. Effect of Intrathecal Baclofen on Delayed-Onset Paroxysmal Dystonia Due to Compression Injury Resulting From Congenital and Progressive Spinal Bone Deformities in Chondrodysplasia Punctata. Pediatr. Neurol. 2016, 56, 80–85.e2. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Agrawal, M.; Chaurasia, R.N.; Kumar, A.; Pathak, A.; Singh, V.K. A Curious Case of a Child With Recurrent Twisting Movements of Limbs. Cureus 2023, 15, e42037. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Almeida, L.; Dure, L.S. Paroxysmal Hypnogenic Dyskinesia. Neurology 2014, 82, 1935. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ananth, A.L.; Robichaux-Viehoever, A.; Kim, Y.-M.; Hanson-Kahn, A.; Cox, R.; Enns, G.M.; Strober, J.; Willing, M.; Schlaggar, B.L.; Wu, Y.W.; et al. Clinical Course of Six Children With GNAO1 Mutations Causing a Severe and Distinctive Movement Disorder. Pediatr. Neurol. 2016, 59, 81–84. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ancora, C.; Ortigoza-Escobar, J.D.; Valletti, M.A.; Furia, F.; Nielsen, J.E.K.; Møller, R.S.; Gardella, E. Emergence of Lingual Dystonia and Strabismus in Early-Onset SCN8A Self-Limiting Familial Infantile Epilepsy. Epileptic. Disord. 2024, 26, 219–224. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baglioni, V.; Esposito, D.; Bernardi, K.; Novelli, M.; Zaccaria, V.; Galosi, S.; Pisani, F. Misdiagnosis of Functional Neurological Symptom Disorders in Paediatrics: Narrative Review and Relevant Case Report. Clin. Child Psychol. Psychiatry 2024, 29, 1026–1042. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Balagura, G.; Riva, A.; Marchese, F.; Iacomino, M.; Madia, F.; Giacomini, T.; Mancardi, M.M.; Amadori, E.; Vari, M.S.; Salpietro, V.; et al. Clinical Spectrum and Genotype-Phenotype Correlations in PRRT2 Italian Patients. Eur. J. Paediatr. Neurol. 2020, 28, 193–197. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Baldi, S.; Zhu, J.-L.; Hu, Q.-Y.; Wang, J.-L.; Zhang, J.-B.; Zhang, S.-H. A Novel PRRT2 Variant in Chinese Patients Suffering from Paroxysmal Kinesigenic Dyskinesia with Infantile Convulsion. Behav. Neurol. 2020, 2020, 2097059. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bech, S.; Løkkegaard, A.; Nielsen, T.T.; Nørremølle, A.; Grønborg, S.; Hasholt, L.; Steffensen, G.K.; Graehn, G.; Olesen, J.H.; Tommerup, N.; et al. Paroxysmal Cranial Dyskinesia and Nail-Patella Syndrome Caused by a Novel Variant in the LMX1B Gene. Mov. Disord. 2020, 35, 2343–2347. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bernardi, K.; Thiel, M.; Koy, A. Positive Effects of Caffeine Therapy in a Girl with PDE2A-Related Paroxysmal Dyskinesia. Mov. Disord. Clin. Pract. 2025, 12, 1014–1016. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carecchio, M.; Mencacci, N.E.; Iodice, A.; Pons, R.; Panteghini, C.; Zorzi, G.; Zibordi, F.; Bonakis, A.; Dinopoulos, A.; Jankovic, J.; et al. ADCY5-Related Movement Disorders: Frequency, Disease Course and Phenotypic Variability in a Cohort of Paediatric Patients. Parkinsonism Relat. Disord. 2017, 41, 37–43. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Castellotti, B.; Ragona, F.; Freri, E.; Solazzi, R.; Ciardullo, S.; Tricomi, G.; Venerando, A.; Salis, B.; Canafoglia, L.; Villani, F.; et al. Screening of SLC2A1 in a Large Cohort of Patients Suspected for Glut1 Deficiency Syndrome: Identification of Novel Variants and Associated Phenotypes. J. Neurol. 2019, 266, 1439–1448. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Castiglioni, C.; Verrigni, D.; Okuma, C.; Diaz, A.; Alvarez, K.; Rizza, T.; Carrozzo, R.; Bertini, E.; Miranda, M. Pyruvate Dehydrogenase Deficiency Presenting as Isolated Paroxysmal Exercise Induced Dystonia Successfully Reversed with Thiamine Supplementation. Case Report and Mini-Review. Eur. J. Paediatr. Neurol. 2015, 19, 497–503. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chang, F.C.F.; Westenberger, A.; Dale, R.C.; Smith, M.; Pall, H.S.; Perez-Dueñas, B.; Grattan-Smith, P.; Ouvrier, R.A.; Mahant, N.; Hanna, B.C.; et al. Phenotypic Insights into ADCY5-associated Disease. Mov. Disord. 2016, 31, 1033–1040. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cottrill, N.; McCully, B.; Payne, M. Paroxysmal Kinesigenic Dyskinesia Presented Following Concussion. J. Mov. Disord. 2019, 12, 52–53. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dayasiri, K.; Weerapperuma, N.; Wright, J.; Anand, G. Paroxysmal Kinesigenic Dyskinesia: A Diagnostic Challenge. BMJ Case Rep. 2021, 14, e235112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Giorgis, V.; Teutonico, F.; Cereda, C.; Balottin, U.; Bianchi, M.; Giordano, L.; Olivotto, S.; Ragona, F.; Tagliabue, A.; Zorzi, G.; et al. Sporadic and Familial Glut1ds Italian Patients: A Wide Clinical Variability. Seizure 2015, 24, 28–32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Pedro Baena, S.; Sariego Jamardo, A.; Castro, P.; López González, F.J.; Sánchez Carpintero, R.; Cerisola, A.; Troncoso, M.; Witting, S.; Barrios, A.; Fons, C.; et al. Exploring the Spectrum of RHOBTB2 Variants Associated with Developmental Encephalopathy 64: A Case Series and Literature Review. Mov. Disord. Clin. Pract. 2023, 10, 1671–1679. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dekker, M.C.J.; Chengo, R.; Kumburu, H.H.; Kamsteeg, E.-J.; Hamel, B.C. Paroxysmal Kinesigenic Dyskinesia: First Molecularly Confirmed Case from Africa. Tremor Hyperkinetic Mov. 2020, 10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deng, Y.; Xu, J.; Yao, C.; Wang, L.; Dong, X.; Zhao, C. Characteristics of Infantile Convulsions and Choreoathetosis Syndrome Caused by PRRT2 Mutation. Pediatr. Investig. 2022, 6, 11–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dhakar, M.B.; Bamford, N.S. Pearls & Oy-Sters: Alternating Hemiplegia of Childhood Mimics Focal Epilepsy and Paroxysmal Dyskinesia in Infancy. Neurology 2018, 91, 47–49. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dhamija, R.; Goodkin, H.P.; Bailey, R.; Chambers, C.; Brenton, J.N. A Case of KCNQ2-Associated Movement Disorder Triggered by Fever. J. Child Neurol. 2017, 32, 1123–1124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dzinovic, I.; Škorvánek, M.; Necpál, J.; Boesch, S.; Švantnerová, J.; Wagner, M.; Havránková, P.; Pavelekova, P.; Haň, V.; Janzarik, W.G.; et al. Dystonia as a Prominent Presenting Feature in Developmental and Epileptic Encephalopathies: A Case Series. Parkinsonism Relat. Disord. 2021, 90, 73–78. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dzinovic, I.; Graf, E.; Brugger, M.; Berutti, R.; Příhodová, I.; Blaschek, A.; Winkelmann, J.; Jech, R.; Vill, K.; Zech, M. Challenges in Establishing the Diagnosis of PRRT2-Related Dystonia: Recurrent Pathogenic Variants in a Homopolymeric Stretch. Mov. Disord. Clin. Pract. 2023, 10, 1159–1161. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- François-Heude, M.; Lebigot, E.; Roze, E.; Warde, M.T.A.; Cances, C.; Damaj, L.; Espil, C.; Fluss, J.; De Lonlay, P.; Kern, I.; et al. Movement Disorders in Valine Métabolism Diseases Caused by HIBCH and ECHS1 Deficiencies. Eur. J. Neurol. 2022, 29, 3229–3242. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Freri, E.; Canafoglia, L.; Ciaccio, C.; Rossi Sebastiano, D.; Caputo, D.; Solazzi, R.; Sciacca, F.L.; Iascone, M.; Panzica, F.; Granata, T.; et al. Cortical Myoclonus and Complex Paroxysmal Dyskinesias in a Patient with NAA15 Variant. Mov. Disord. 2024, 39, 1238–1240. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Friedman, J.R.; Méneret, A.; Chen, D.; Trouillard, O.; Vidailhet, M.; Raskind, W.H.; Roze, E. ADCY5 Mutation Carriers Display Pleiotropic Paroxysmal Day and Nighttime Dyskinesias. Mov. Disord. 2016, 31, 147–148. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Furukawa, G.; Negishi, Y.; Takeuchi, T.; Ishihara, N.; Okumura, A. Lacosamide for Children with Paroxysmal Kinesigenic Dyskinesia. Brain Dev. 2020, 42, 617–620. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ganos, C.; Mencacci, N.; Gardiner, A.; Erro, R.; Batla, A.; Houlden, H.; Bhatia, K.P. Paroxysmal Kinesigenic Dyskinesia May Be Misdiagnosed in Co-Occurring Gilles de La Tourette Syndrome. Mov. Disord. Clin. Pract. 2014, 1, 84–86. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Guo, Q.; Yang, Y.; Lin, Y.; Li, L.; Zhan, S.; Liu, A.; Gao, L.; Lin, H.; Wang, Y. Paroxysmal Dyskinesia on Waking: Two Case Reports. Sleep Med. 2016, 25, 63–66. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hara, M.; Matsuishi, T.; Takahashi, S.; Yamashita, Y. Sertraline Treatment for Paroxysmal Nonkinesigenic Dyskinesia Comorbid with Anxiety and Depression. eNeurologicalSci 2024, 36, 100520. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Harvey, S.; Allen, N.M.; Byrne, S.; Lynch, B.; McSweeney, N.; Neville, S.; O’Mahony, O.; O’Regan, M.; O’Rourke, D.; Reade, E.; et al. Pediatric Paroxysmal Movement Disorders—A Clinical Epidemiological Study in an Irish Cohort. Eur. J. Paediatr. Neurol. 2025, 55, 70–78. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hosseinpour, S.; Tavasoli, A.R.; Rohani, M.; Emamikhah, M. Rolandic Epilepsy with Paroxysmal Exercise-Induced Dystonia and Writer’s Cramp: A Case Report. Neurol. Sci. 2023, 44, 381–384. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, Y.; Liang, L.; Xu, X.; Liu, Y.; Gao, F.; He, X.; Wang, Q.K. Identification of a New Gain-of-function Variant p.N536Y of KCNMA1 Associated with PNKD3 in the Chinese Population. Acta Physiol. 2025, 241, e70039. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hully, M.; Vuillaumier-Barrot, S.; Le Bizec, C.; Boddaert, N.; Kaminska, A.; Lascelles, K.; De Lonlay, P.; Cances, C.; Des Portes, V.; Roubertie, A.; et al. From Splitting GLUT1 Deficiency Syndromes to Overlapping Phenotypes. Eur. J. Med. Genet. 2015, 58, 443–454. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Illsinger, S.; Korenke, G.C.; Boesch, S.; Nocker, M.; Karall, D.; Nuoffer, J.M.; Laugwitz, L.; Mayr, J.A.; Scholl-Bürgi, S.; Freisinger, P.; et al. Paroxysmal and Non-Paroxysmal Dystonia in 3 Patients with Biallelic ECHS1 Variants: Expanding the Neurological Spectrum and Therapeutic Approaches. Eur. J. Med. Genet. 2020, 63, 104046. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Innes, E.A.; Marne, F.A.L.; Macintosh, R.; Nevin, S.M.; Briggs, N.E.; Vivekanandarajah, S.; Webster, R.I.; Sachdev, R.K.; Bye, A.M.E. Neurodevelopmental Outcomes in a Cohort of Australian Families with Self-Limited Familial Epilepsy of Neonatal/Infantile Onset. Seizure 2024, 115, 1–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ito, Y.; Takahashi, S.; Kagitani-Shimono, K.; Natsume, J.; Yanagihara, K.; Fujii, T.; Oguni, H. Nationwide Survey of Glucose Transporter-1 Deficiency Syndrome (GLUT-1DS) in Japan. Brain Dev. 2015, 37, 780–789. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jain, P.; Sharma, S.; Breedveld, G.; Bonifati, V.; Aneja, S. Proline-Rich Transmembrane Protein 2 Gene Mutation in a Sporadic Paroxysmal Kinesigenic Dyskinesia. J. Pediatr. Neurosci. 2017, 12, 112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jiang, Y.; Yuan, F.; Yang, Y.; Sun, X.; Song, L.; Jiang, W. CHRNA4 Variant Causes Paroxysmal Kinesigenic Dyskinesia and Genetic Epilepsy with Febrile Seizures Plus? Seizure 2018, 56, 88–91. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiménez Legido, M.; Cortés Ledesma, C.; Bernardino Cuesta, B.; López Marín, L.; Cantarín Extremera, V.; Pérez-Cerdá, C.; Pérez González, B.; López Martín, E.; González Gutiérrez-Solana, L. Estudio de pacientes pediátricos con fenotipo clínico y bioquímico de síndrome de déficit de transportador de glucosa cerebral (GLUT-1). Neurología 2022, 37, 91–100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kelly, M.; Park, M.; Mihalek, I.; Rochtus, A.; Gramm, M.; Pérez-Palma, E.; Axeen, E.T.; Hung, C.Y.; Olson, H.; Swanson, L.; et al. Spectrum of Neurodevelopmental Disease Associated with the GNAO1 Guanosine Triphosphate–Binding Region. Epilepsia 2019, 60, 406–418. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Keros, S.; Heim, J.; Hakami, W.; Zohar-Dayan, E.; Ben-Zeev, B.; Grinspan, Z.; Kruer, M.C.; Meredith, A.L. Lisdexamfetamine Therapy in Paroxysmal Non-kinesigenic Dyskinesia Associated with the KCNMA1-N999S Variant. Mov. Disord. Clin. Pract. 2022, 9, 229–235. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, H.; Lee, J.S.; Lee, Y.; Kim, S.Y.; Lim, B.C.; Kim, K.J.; Choi, M.; Chae, J.-H. Diagnostic Challenges Associated with GLUT1 Deficiency: Phenotypic Variabilities and Evolving Clinical Features. Yonsei Med. J. 2019, 60, 1209. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kita, M.; Kuwata, Y.; Murase, N.; Akiyama, Y.; Usui, T. A Novel Truncation Mutation of the PRRT2 Gene Resulting in a 16-Amino-Acid Protein Causes Self-inducible Paroxysmal Kinesigenic Dyskinesia. Mov. Disord. Clin. Pract. 2017, 4, 625–628. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Klepper, J.; Leiendecker, B.; Eltze, C.; Heussinger, N. Paroxysmal Nonepileptic Events in Glut1 Deficiency. Mov. Disord. Clin. Pract. 2016, 3, 607–610. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kollia, E.; Kokkinou, E.; Outsika, C.; Koltsida, G.; Zouvelou, V.; Vontzalidis, A.; Dalivigka, Z.; Veltra, D.; Sofocleous, C.; Marinakis, N.M.; et al. Motor Phenotyping in a Greek Cohort of Patients with Neonatal and Infantile Onset Developmental and Epileptic Encephalopathy. Eur. J. Paediatr. Neurol. 2025, 55, 1–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Komatsu, K.; Fukumura, S.; Minagawa, K.; Nakashima, M.; Saitsu, H. A New Case of Concurrent Existence of PRRT2-Associated Paroxysmal Movement Disorders with c.649dup Variant and 16p11.2 Microdeletion Syndrome. Brain Dev. 2022, 44, 474–479. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Komulainen-Ebrahim, J.; Kangas, S.M.; López-Martín, E.; Feyma, T.; Scaglia, F.; Martínez-Delgado, B.; Kuismin, O.; Suo-Palosaari, M.; Carr, L.; Hinttala, R.; et al. Hyperkinetic Movement Disorder Caused by the Recurrent c. 892C >T NACC1 Variant. Mov. Disord. Clin. Pract. 2024, 11, 708–715. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kurahashi, H.; Azuma, Y.; Takeuchi, T.; Shimada, M.; Numoto, S.; Nishida, M.; Ito, Y.; Ogi, T.; Okumura, A. Paroxysmal Kinesigenic Dyskinesia in Two Siblings With Novel Heterozygous TMEM151A Frameshift Variant: The First Case Report in Japan. Am. J. Med. Genet. A 2025, 197, e64079. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Law, C.; Yeung, W.; Cheung, Y.; Chan, H.; Fung, E.; Hui, J.; Yung, I.O.; Yuen, Y.; Chan, A.O.; Lam, C.W.; et al. A Common PRRT2 Mutation in Familial Paroxysmal Kinesigenic Dyskinesia in Hong Kong: A Case Series of 16 Patients. Hong Kong Med. J. 2016, 22, 619–622. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Laxmi, V.; Gunasekaran, P.K.; Manjunathan, S.; Gupta, R.; Kumar, A.; Saini, L. Associated Movement Disorder as a Clue for the Diagnosis of Paroxysmal Kinesigenic Dyskinesia in a Child with Focal Epilepsy. J. Neurosci. Rural Pract. 2023, 14, 558–559. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lebon, S.; Suarez, P.; Alija, S.; Korff, C.M.; Fluss, J.; Mercati, D.; Datta, A.N.; Poloni, C.; Marcoz, J.-P.; Campos-Xavier, A.B.; et al. When Should Clinicians Search for GLUT1 Deficiency Syndrome in Childhood Generalized Epilepsies? Eur. J. Paediatr. Neurol. 2015, 19, 170–175. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lipari Pinto, P.; Machado, C.; Janeiro, P.; Dupont, J.; Quintas, S.; Sousa, A.B.; Gaspar, A. NGLY1 Deficiency—A Rare Congenital Disorder of Deglycosylation. JIMD Rep. 2020, 53, 2–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, D.-T.; Tang, X.-Q.; Wan, R.-P.; Luo, S.; Guan, B.-Z.; Li, B.; Liu, L.-H.; Li, B.-M.; Liu, Z.-G.; Xie, L.-S.; et al. PRRT2 Gene Mutations Associated with Infantile Convulsions Induced by Sucking and the Genotype-Phenotype Correlation. Front. Neurol. 2022, 13, 836048. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Luo, H.; Xie, L.; Hong, S.; Li, X.; Li, M.; Hu, Y.; Ma, J.; Wu, P.; Zhong, M.; Cheng, M.; et al. The Genotype and Phenotype of Proline-Rich Transmembrane Protein 2 Associated Disorders in Chinese Children. Front. Pediatr. 2021, 9, 676616. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lüthy, K.; Mei, D.; Fischer, B.; De Fusco, M.; Swerts, J.; Paesmans, J.; Parrini, E.; Lubarr, N.; Meijer, I.A.; Mackenzie, K.M.; et al. TBC1D24-TLDc-Related Epilepsy Exercise-Induced Dystonia: Rescue by Antioxidants in a Disease Model. Brain 2019, 142, 2319–2335. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, L.-Y.; Han, L.; Niu, M.; Chen, L.; Yu, Y.-Z.; Feng, T. Screening of the TMEM151A Gene in Patients With Paroxysmal Kinesigenic Dyskinesia and Other Movement Disorders. Front. Neurol. 2022, 13, 865690. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martorell, L.; Macaya, A.; Pérez-Dueñas, B.; Ortigoza-Escobar, J.D. Acetazolamide Improves Episodic Ataxia in a Patient with Non-Verbal Autism and Paroxysmal Dyskinesia Due To PRRT2 Biallelic Variants. Mov. Disord. Clin. Pract. 2022, 9, 979–982. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marzin, P.; Mignot, C.; Dorison, N.; Dufour, L.; Ville, D.; Kaminska, A.; Panagiotakaki, E.; Dienpendaele, A.-S.; Penniello, M.-J.; Nougues, M.-C.; et al. Early-Onset Encephalopathy with Paroxysmal Movement Disorders and Epileptic Seizures without Hemiplegic Attacks: About Three Children with Novel ATP1A3 Mutations. Brain Dev. 2018, 40, 768–774. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Masnada, S.; Sarret, C.; Antonello, C.E.; Fadilah, A.; Krude, H.; Mura, E.; Mordekar, S.; Nicita, F.; Olivotto, S.; Orcesi, S.; et al. Movement Disorders in MCT8 Deficiency/Allan-Herndon-Dudley Syndrome. Mol. Genet. Metab. 2022, 135, 109–113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Matsumoto, N.; Takahashi, S.; Okayama, A.; Araki, A.; Azuma, H. Benign Infantile Convulsion as a Diagnostic Clue of Paroxysmal Kinesigenic Dyskinesia: A Case Series. J. Med. Case Reports 2014, 8, 174. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Matsuura, R.; Hamano, S.; Hiwatari, E.; Ikemoto, S.; Hirata, Y.; Koichihara, R.; Kikuchi, K. Zonisamide Therapy for Patients With Paroxysmal Kinesigenic Dyskinesia. Pediatr. Neurol. 2020, 111, 23–26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nakayama-Kamada, C.; Enatsu, R.; Fukumura, S.; Kuribara, T.; Ochi, S.; Mikuni, N. A Case of Paroxysmal Kinesigenic Dyskinesia Suspected to Be Reflex Epilepsy. Nagoya J. Med. Sci. 2021, 83, 361–365. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Narváez, C.; Lacaux, P.; Cortés, C.; Manterola, C.; Carrasco, X. Variabilidad Fenotípica Del Déficit de GLUT1: ¿cuándo Es Necesario Sospechar? Rev. Chil. Pediatría 2020, 91, 260. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Necpál, J.; Zech, M.; Valachová, A.; Sedláček, Z.; Bendová, Š.; Hančárová, M.; Okáľová, K.; Winkelmann, J.; Jech, R. Severe Paroxysmal Dyskinesias without Epilepsy in a RHOBTB2 Mutation Carrier. Parkinsonism Relat. Disord. 2020, 77, 87–88. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nomura, S.; Kashiwagi, M.; Tanabe, T.; Oba, C.; Yanagi, K.; Kaname, T.; Okamoto, N.; Ashida, A. Rapid-Onset Dystonia-Parkinsonism with ATP1A3 Mutation and Left Lower Limb Paroxysmal Dystonia. Brain Dev. 2021, 43, 566–570. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pérez-Dueñas, B.; Gorman, K.; Marcé-Grau, A.; Ortigoza-Escobar, J.D.; Macaya, A.; Danti, F.R.; Barwick, K.; Papandreou, A.; Ng, J.; Meyer, E.; et al. The Genetic Landscape of Complex Childhood-Onset Hyperkinetic Movement Disorders. Mov. Disord. 2022, 37, 2197–2209. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chou, I.-C.; Lin, S.-S.; Lin, W.-D.; Wang, C.-H.; Chang, Y.-T.; Tsai, F.-J.; Tsai, C.-H. Successful Control with Carbamazepine of Family with Paroxysmal Kinesigenic Dyskinesia of PRRT2 Mutation. BioMedicine 2014, 4, 15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Döring, J.H.; Saffari, A.; Bast, T.; Brockmann, K.; Ehrhardt, L.; Fazeli, W.; Janzarik, W.G.; Kluger, G.; Muhle, H.; Møller, R.S.; et al. The Phenotypic Spectrum of PRRT2-Associated Paroxysmal Neurologic Disorders in Childhood. Biomedicines 2020, 8, 456. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hashemi, B.; Huntsman, R.J.; Li, H.; Zhang, D.; Xi, Y. New Presentation of CLIFAHDD Syndrome with a Novel Variant in NALCN Gene: A Report of a Rare Case. Clin. Case Rep. 2023, 11, e7647. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, X.M.; Gong, Y.H.; Lu, S.; Cheng, S.C.; Yao, B.Z. Clinical manifestations and genetic diagnosis of paroxysmal kinesigenic dyskinesia. Zhongguo Dang Dai Er Ke Za Zhi 2017, 19, 1169–1173. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Chen, D.H.; Méneret, A.; Friedman, J.R.; Korvatska, O.; Gad, A.; Bonkowski, E.S.; Stessman, H.A.; Doummar, D.; Mignot, C.; Anheim, M.; et al. ADCY5-related dyskinesia: Broader spectrum and genotype-phenotype correlations. Neurology 2015, 85, 2026–2035. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Ji, X.N.; Xu, C.J.; Gao, Z.J.; Chen, S.H.; Xu, K.M.; Chen, Q. Glucose transporter 1 deficiency syndrome: Features of movement disorders, diagnosis and treatment. Zhongguo Dang Dai Er Ke Za Zhi 2018, 20, 209–213. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Kaushik, J.S.; Bala, K.; Dubey, R. Paroxysmal Kinesigenic Dyskinesia. Indian Pediatr. 2018, 55, 74. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kegele, J.; Krüger, J.; Koko, M.; Lange, L.; Marco Hernandez, A.V.; Martinez, F.; Münchau, A.; Lerche, H.; Lauxmann, S. Genetics of Paroxysmal Dyskinesia: Novel Variants Corroborate the Role of KCNA1 in Paroxysmal Dyskinesia and Highlight the Diverse Phenotypic Spectrum of KCNA1- and SLC2A1-Related Disorders. Front. Neurol. 2021, 12, 701351. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, X.; Wang, S.; Guo, X.; Tian, W.; Zhan, F.; Zhu, Z.; Yin, X.; Liu, Q.; Yin, K.; Liu, X.; et al. The Phenotypic and Genetic Spectrum of Paroxysmal Kinesigenic Dyskinesia in China. Mov. Disord. 2020, 35, 1428–1437. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, J.-J.; Li, H.-F.; Wu, Z.-Y. Paroxysmal Kinesigenic Dyskinesia: Genetics and Pathophysiological Mechanisms. Neurosci. Bull. 2024, 40, 952–962. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, W.-J.; Lin, Y.; Xiong, Z.-Q.; Wei, W.; Ni, W.; Tan, G.-H.; Guo, S.-L.; He, J.; Chen, Y.-F.; Zhang, Q.-J.; et al. Exome Sequencing Identifies Truncating Mutations in PRRT2 That Cause Paroxysmal Kinesigenic Dyskinesia. Nat. Genet. 2011, 43, 1252–1255. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cao, L.; Huang, X.; Wang, N.; Wu, Z.; Zhang, C.; Gu, W.; Cong, S.; Ma, J.; Wei, L.; Deng, Y.; et al. Recommendations for the Diagnosis and Treatment of Paroxysmal Kinesigenic Dyskinesia: An Expert Consensus in China. Transl. Neurodegener. 2021, 10, 7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ekmen, A.; Doulazmi, M.; Méneret, A.; Jegatheesan, P.; Hervé, A.; Damier, P.; Gras, D.; Roubertie, A.; Piard, J.; Mutez, E.; et al. Non-Motor Symptoms and Quality of Life in Patients with PRRT2-Related Paroxysmal Kinesigenic Dyskinesia. Mov. Disord. Clin. Pract. 2023, 10, 1082–1089. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mantegazza, M.; Curia, G.; Biagini, G.; Ragsdale, D.S.; Avoli, M. Voltage-gated sodium channels as therapeutic targets in epilepsy and other neurological disorders. Lancet Neurol. 2010, 9, 413–424. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tan, G.H.; Liu, Y.Y.; Wang, L.; Li, K.; Zhang, Z.Q.; Li, H.F.; Yang, Z.F.; Li, Y.; Li, D.; Wu, M.Y.; et al. PRRT2 deficiency induces paroxysmal kinesigenic dyskinesia by regulating synaptic transmission in cerebellum. Cell Res. 2018, 28, 90–110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Méneret, A.; Gras, D.; McGovern, E.; Roze, E. Caffeine and the Dyskinesia Related to Mutations in the ADCY5 Gene. Ann. Intern. Med. 2019, 171, 439. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xie, X.; Ramkumar, V.; Toth, L.A. Adenosine and dopamine receptor interac-tions in striatum and caffeine-induced behavioral activation. Comp. Med. 2007, 57, 538–545. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Huang, Z.L.; Qu, W.M.; Eguchi, N.; Chen, J.F.; Schwarzschild, M.A.; Fredholm, B.B.; Urade, Y.; Hayaishi, O. Adenosine A2A, but not A1, receptorsmediate the arousal effect of caffeine. Nat. Neurosci. 2005, 8, 858–859. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Klepper, J. Glut1 Deficiency Syndrome: Novel Pathomechanisms, Current Concepts, and Challenges. J. Inherit. Metab. Dis. 2025, 48, e70044. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Auvin, S. Targeted therapies in epilepsies. Rev. Neurol. 2025, 181, 450–455. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Garg, D.; Mohammad, S.; Shukla, A.; Sharma, S. Genetic Links to Episodic Movement Disorders: Current Insights. Appl. Clin. Genet. 2023, 16, 11–30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Delorme, C.; Giron, C.; Bendetowicz, D.; Méneret, A.; Mariani, L.L.; Roze, E. Current challenges in the pathophysiology, diagnosis, and treatment of paroxysmal movement disorders. Expert. Rev. Neurother. 2021, 21, 81–97. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).