Autoimmune Hepatitis and Drug-Induced Liver Injury in Japan
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. AIH
2.1. Epidemiology of AIH: Trends in Japan
2.2. Pathogenesis of AIH
2.3. Diagnosis of AIH
2.3.1. AIH, Autoantibodies, and Pathology
2.3.2. AIH and International Diagnostic Criteria
2.3.3. Acute AIH and IgG4-Related AIH
2.4. Treatment of AIH
2.4.1. Treatment for AIH and Prognosis
2.4.2. AIH, Azathioprine, and NUDT 15 Gene Polymorphism
2.4.3. AIH and Pregnancy and UDCA Therapy
2.4.4. When to End Treatment for AIH
2.4.5. AIH and Liver Transplantation
2.5. COVID-19 Vaccine and AIH
3. DILI
3.1. Clinical Features and Diagnosis for DILI
3.2. Assessment Method for DILI
3.3. ICIs and Liver Injury
3.4. Treatment for DILI
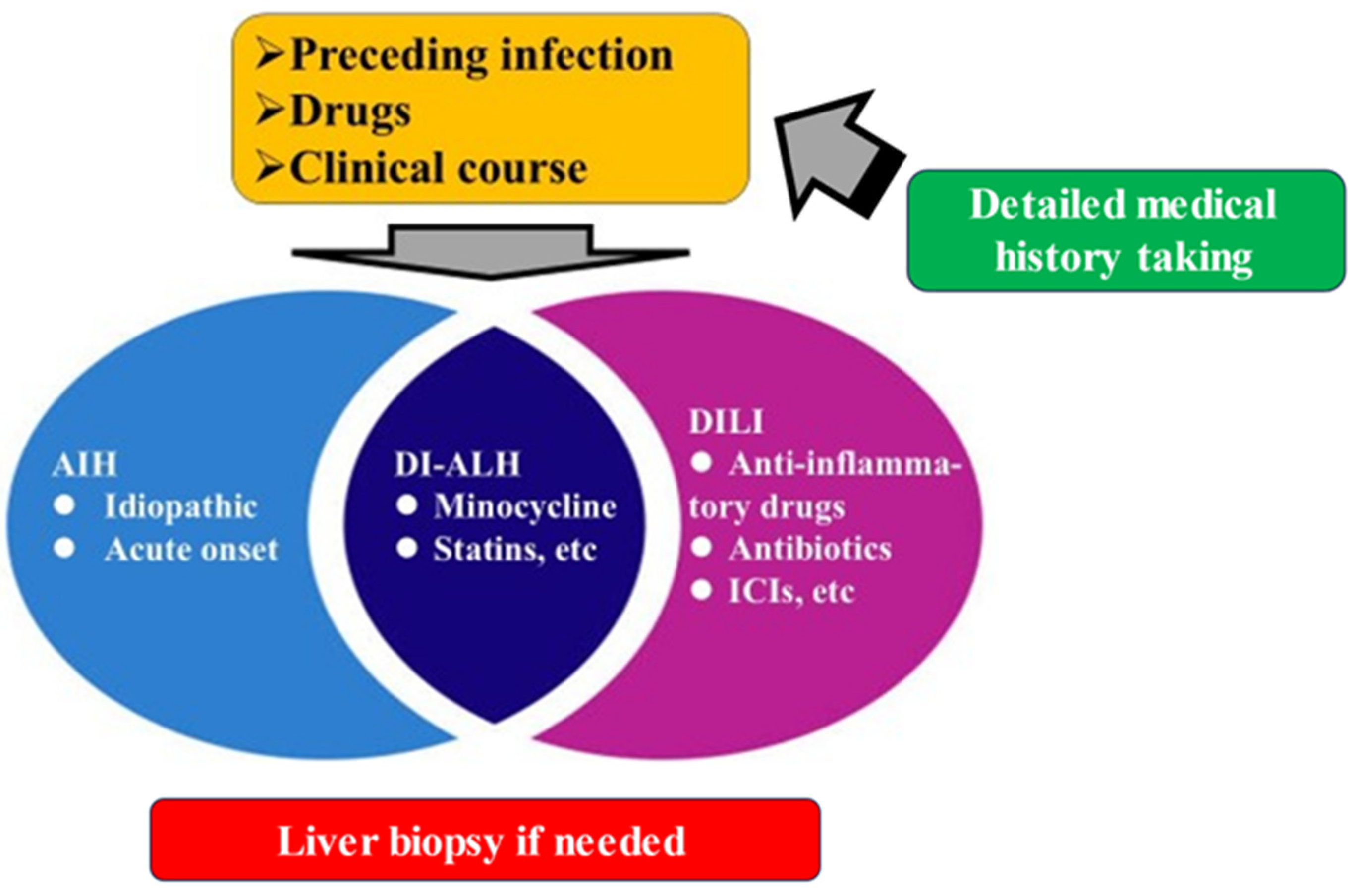
4. DI-ALH
5. Final Remarks
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
References
- Tanaka, A.; Mori, M.; Matsumoto, K.; Ohira, H.; Tazuma, S.; Takikawa, H. Increase trend in the prevalence and male-to-female ratio of primary biliary cholangitis, autoimmune hepatitis, and primary sclerosing cholangitis in Japan. Hepatol. Res. 2019, 49, 881–889. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sirbe, C.; Simu, G.; Szabo, I.; Grama, A.; Pop, T.L. Pathogenesis of Autoimmune Hepatitis-Cellular and Molecular Mechanisms. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2021, 22, 13578. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahmed, T.; Ahmad, J. Recent advances in the diagnosis of drug-induced liver injury. World J. Hepatol. 2024, 16, 186–192. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Andrade, R.J.; Aithal, G.P.; de Boer, Y.S.; Liberal, R.; Gerbes, A.; Regev, A.; Terziroli Beretta-Piccoli, B.; Schramm, C.; Kleiner, D.E.; De Martin, E.; et al. Nomenclature, diagnosis and management of drug-induced autoimmune-like hepatitis (DI-ALH): An expert opinion meeting report. J. Hepatol. 2023, 79, 853–866. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shiffman, M.L. Autoimmune Hepatitis: Epidemiology, Subtypes, and Presentation. Clin. Liver Dis. 2024, 28, 1–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Katsumi, T.; Ueno, Y. Epidemiology and surveillance of autoimmune hepatitis in Asia. Liver Int. 2022, 42, 2015–2022. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Takahashi, A.; Arinaga-Hino, T.; Ohira, H.; Torimura, T.; Zeniya, M.; Abe, M.; Yoshizawa, K.; Takaki, A.; Suzuki, Y.; Kang, J.H.; et al. Autoimmune hepatitis in Japan: Trends in a nationwide survey. J. Gastroenterol. 2017, 52, 631–640. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tanaka, A.; Harada, K. Acute presentation of autoimmune hepatitis—From acute hepatitis to ALF and ACLF. Hepatol. Int. 2024, 18, 1385–1395. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Takahashi, A.; Ohira, H.; Abe, K.; Zeniya, M.; Abe, M.; Arinaga-Hino, T.; Torimura, T.; Yoshizawa, K.; Takaki, A.; Kang, J.H.; et al. Increasing incidence of acute autoimmune hepatitis: A nationwide survey in Japan. Sci. Rep. 2020, 10, 14250. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tan, C.K.; Ho, D.; Wang, L.M.; Kumar, R. Drug-induced autoimmune hepatitis: A minireview. World J. Gastroenterol. 2022, 28, 2654–2666. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sucher, E.; Sucher, R.; Gradistanac, T.; Brandacher, G.; Schneeberger, S.; Berg, T. Autoimmune Hepatitis-Immunologically Triggered Liver Pathogenesis-Diagnostic and Therapeutic Strategies. J. Immunol. Res. 2019, 2019, 9437043. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lübbering, D.; Preti, M.; Schlott, L.; Schultheiß, C.; Weidemann, S.; Lohse, A.W.; Binder, M.; Carambia, A.; Herkel, J. Autoantigen-selected B cells are bystanders in spontaneous T cell-driven experimental autoimmune hepatitis. Immunology 2023, 170, 214–229. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Abe, K.; Takahashi, A.; Fujita, M.; Hayashi, M.; Okai, K.; Nozawa, Y.; Ohira, H. Interleukin-33/ST2-mediated inflammation plays a critical role in the pathogenesis and severity of type I autoimmune hepatitis. Hepatol. Commun. 2019, 3, 670–684. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nishikawa, H.; Enomoto, H.; Iwata, Y.; Kishino, K.; Shimono, Y.; Hasegawa, K.; Nakano, C.; Takata, R.; Nishimura, T.; Yoh, K.; et al. B-Cell Activating Factor Belonging to the Tumor Necrosis Factor Family and Interferon-γ-Inducible Protein-10 in Autoimmune Hepatitis. Medicine 2016, 95, e3194. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Terziroli Beretta-Piccoli, B.; Mieli-Vergani, G.; Vergani, D. Autoimmune Hepatitis: Serum Autoantibodies in Clinical Practice. Clin. Rev. Allergy Immunol. 2022, 63, 124–137. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yüksekyayla, O.; Kina, N.; Ulaba, A.; Emin, E.M.; Batibay, E.; Şimşek, C.; Yildiz, Z.F.; Wahlin, S.; Efe, C. The frequency and clinical significance of antibodies to soluble liver antigen/liver pancreas in autoimmune hepatitis: A prospective single-center study. Eur. J. Gastroenterol. Hepatol. 2024, 36, 652–656. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luo, L.; Ma, Q.; Lin, L.; Wang, H.; Ye, J.; Zhong, B. Prevalence and Significance of Antinuclear Antibodies in Biopsy-Proven Nonalcoholic Fatty Liver Disease: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. Dis. Markers 2022, 2022, 8446170. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Enomoto, H.; Nishiguchi, S. Similarities and Differences in Autoimmune Hepatitis Epidemiology between East and West: Autoimmune Hepatitis in East Asia, Southeast Asia, and South Asia. Inflamm. Intest. Dis. 2017, 1, 150–158. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Heneghan, M.A.; Lohse, A.W. Update in clinical science: Autoimmune hepatitis. J. Hepatol. 2025, 82, 926–937. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alvarez, F.; Berg, P.A.; Bianchi, F.B.; Bianchi, L.; Burroughs, A.K.; Cancado, E.L.; Chapman, R.W.; Cooksley, W.G.; Czaja, A.J.; Desmet, V.J.; et al. International Autoimmune Hepatitis Group Report: Review of criteria for diagnosis of autoimmune hepatitis. J. Hepatol. 1999, 31, 929–938. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hennes, E.M.; Zeniya, M.; Czaja, A.J.; Parés, A.; Dalekos, G.N.; Krawitt, E.L.; Bittencourt, P.L.; Porta, G.; Boberg, K.M.; Hofer, H.; et al. Simplified criteria for the diagnosis of autoimmune hepatitis. Hepatology 2008, 48, 169–176. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Muratori, P.; Granito, A.; Pappas, G.; Muratori, L. Validation of simplified diagnostic criteria for autoimmune hepatitis in Italian patients. Hepatology 2009, 49, 1782–1783. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Qiu, D.; Wang, Q.; Wang, H.; Xie, Q.; Zang, G.; Jiang, H.; Tu, C.; Guo, J.; Zhang, S.; Wang, J.; et al. Validation of the simplified criteria for diagnosis of autoimmune hepatitis in Chinese patients. J. Hepatol. 2011, 54, 340–347. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miyake, Y.; Iwasaki, Y.; Kobashi, H.; Yasunaka, T.; Ikeda, F.; Takaki, A.; Yamamoto, K. Clinical features of autoimmune hepatitis diagnosed based on simplified criteria of the International Autoimmune Hepatitis Group. Dig. Liver Dis. 2010, 42, 210–215. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Minaga, K.; Watanabe, T.; Chung, H.; Kudo, M. Autoimmune hepatitis and IgG4-related disease. World J. Gastroenterol. 2019, 25, 2308–2314. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Granito, A.; Muratori, P.; Muratori, L. Acute-on-chronic liver failure: A complex clinical entity in patients with autoimmune hepatitis. J. Hepatol. 2021, 75, 1503–1505. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mack, C.L.; Adams, D.; Assis, D.N.; Kerkar, N.; Manns, M.P.; Mayo, M.J.; Vierling, J.M.; Alsawas, M.; Murad, M.H.; Czaja, A.J. Diagnosis and Management of Autoimmune Hepatitis in Adults and Children: 2019 Practice Guidance and Guidelines From the American Association for the Study of Liver Diseases. Hepatology 2020, 72, 671–722. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ohira, H.; Takahashi, A.; Zeniya, M.; Abe, M.; Arinaga-Hino, T.; Joshita, S.; Takaki, A.; Nakamoto, N.; Kang, J.H.; Suzuki, Y.; et al. Clinical practice guidelines for autoimmune hepatitis. Hepatol. Res. 2022, 52, 571–585. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miao, Q.; Yan, L.; Zhou, Y.; Li, Y.; Zou, Y.; Wang, L.; Bai, Y.; Zhang, J. Association of genetic variants in TPMT, ITPA, and NUDT15 with azathioprine-induced myelosuppression in southwest china patients with autoimmune hepatitis. Sci. Rep. 2021, 11, 7984. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Snijders, R.J.; Milkiewicz, P.; Schramm, C.; Gevers, T.J. Health-related quality of life in autoimmune hepatitis. World J. Hepatol. 2021, 13, 1642–1652. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, R.; Zhou, L.; Zhang, J.; Wang, B. Abnormal intestinal permeability and microbiota in patients with autoimmune hepatitis. Int. J. Clin. Exp. Pathol. 2015, 8, 5153–5160. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, Q.; Tian, H.; Kang, Y.; Tian, Y.; Li, L.; Kang, X.; Yang, H.; Wang, Y.; Tian, J.; Zhang, F.; et al. Probiotics alleviate autoimmune hepatitis in mice through modulation of gut microbiota and intestinal permeability. J. Nutr. Biochem. 2021, 98, 108863. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kakuta, Y.; Kawai, Y.; Okamoto, D.; Takagawa, T.; Ikeya, K.; Sakuraba, H.; Nishida, A.; Nakagawa, S.; Miura, M.; Toyonaga, T.; et al. NUDT15 codon 139 is the best pharmacogenetic marker for predicting thiopurine-induced severe adverse events in Japanese patients with inflammatory bowel disease: A multicenter study. J. Gastroenterol. 2018, 53, 1065–1078. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- El Jamaly, H.; Eslick, G.D.; Weltman, M. Systematic review with meta-analysis: Autoimmune hepatitis in pregnancy. Scand. J. Gastroenterol. 2021, 56, 1194–1204. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chung, Y.Y.; Heneghan, M.A. Autoimmune hepatitis in pregnancy: Pearls and pitfalls. Hepatology 2022, 76, 502–517. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lammert, C.; Loy, V.M.; Oshima, K.; Gawrieh, S. Management of Difficult Cases of Autoimmune Hepatitis. Curr. Gastroenterol. Rep. 2016, 18, 9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Torisu, Y.; Nakano, M.; Takano, K.; Nakagawa, R.; Saeki, C.; Hokari, A.; Ishikawa, T.; Saruta, M.; Zeniya, M. Clinical usefulness of ursodeoxycholic acid for Japanese patients with autoimmune hepatitis. World J. Hepatol. 2017, 9, 57–63. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Koh, C.; Zhao, X.; Samala, N.; Sakiani, S.; Liang, T.J.; Talwalkar, J.A. AASLD clinical practice guidelines: A critical review of scientific evidence and evolving recommendations. Hepatology 2013, 58, 2142–2152. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- European Association for the Study of the Liver. EASL Clinical Practice Guidelines: Autoimmune hepatitis. J. Hepatol. 2015, 63, 971–1004. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- van Gerven, N.M.; Verwer, B.J.; Witte, B.I.; van Hoek, B.; Coenraad, M.J.; van Erpecum, K.J.; Beuers, U.; van Buuren, H.R.; de Man, R.A.; Drenth, J.P.; et al. Relapse is almost universal after withdrawal of immunosuppressive medication in patients with autoimmune hepatitis in remission. J. Hepatol. 2013, 58, 141–147. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Montano-Loza, A.J.; Carpenter, H.A.; Czaja, A.J. Improving the end point of corticosteroid therapy in type 1 autoimmune hepatitis to reduce the frequency of relapse. Am. J. Gastroenterol. 2007, 102, 1005–1012. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yoshiji, H.; Nagoshi, S.; Akahane, T.; Asaoka, Y.; Ueno, Y.; Ogawa, K.; Kawaguchi, T.; Kurosaki, M.; Sakaida, I.; Shimizu, M.; et al. Evidence-based clinical practice guidelines for Liver Cirrhosis 2020. J. Gastroenterol. 2021, 56, 593–619. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Montano-Loza, A.J.; Bhanji, R.A.; Wasilenko, S.; Mason, A.L. Systematic review: Recurrent autoimmune liver diseases after liver transplantation. Aliment. Pharmacol. Ther. 2017, 45, 485–500. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Montano-Loza, A.J.; Ronca, V.; Ebadi, M.; Hansen, B.E.; Hirschfield, G.; Elwir, S.; Alsaed, M.; Milkiewicz, P.; Janik, M.K.; Marschall, H.U.; et al. Risk factors and outcomes associated with recurrent autoimmune hepatitis following liver transplantation. J. Hepatol. 2022, 77, 84–97. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bartoli, A.; Gitto, S.; Sighinolfi, P.; Cursaro, C.; Andreone, P. Primary biliary cholangitis associated with SARS-CoV-2 infection. J. Hepatol. 2021, 74, 1245–1246. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lui, Y.; Sawalha, A.H.; Lu, Q. COVID-19 and autoimmune diseases. Curr. Opin. Rheumatol. 2021, 33, 155–162. [Google Scholar]
- Rocco, A.; Sgamato, C.; Compare, D.; Nardone, G. Autoimmune hepatitis following SARS-CoV-2 vaccine: May not be a casuality. J. Hepatol. 2021, 75, 728–729. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, E.J.; Cines, D.B.; Gernsheimer, T.; Kessler, C.; Michel, M.; Tarantino, M.D.; Semple, J.W.; Arnold, D.M.; Godeau, B.; Lambert, M.P.; et al. Thrombocytopenia following pfizer and moderna SARS-CoV-2 vaccination. Am. J. Hematol. 2021, 96, 534–537. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zheng, H.; Zhang, T.; Xu, Y.; Lu, X.; Sang, X. Autoimmune hepatitis after COVID-19 vaccination. Front. Immunol. 2022, 13, 1035073. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, R.; Wu, H.; Xu, Y.; Xu, X.; Xu, Y.; Huang, H.; Lv, X.; Liao, C.; Ye, J.; Li, H. Underlying mechanisms and treatment of acetaminophen-induced liver injury (Review). Mol. Med. Rep. 2025, 31, 106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Iorga, A.; Dara, L.; Kaplowitz, N. Drug-Induced Liver Injury: Cascade of Events Leading to Cell Death, Apoptosis or Necrosis. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2017, 18, 1018. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hama, N.; Abe, R.; Gibson, A.; Phillips, E.J. Drug-Induced Hypersensitivity Syndrome (DIHS)/Drug Reaction with Eosinophilia and Systemic Symptoms (DRESS): Clinical Features and Pathogenesis. J. Allergy Clin. Immunol. Pract. 2022, 10, 1155–1167.e5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hayashi, P.H.; Lucena, M.I.; Fontana, R.J.; Bjornsson, E.S.; Aithal, G.P.; Barnhart, H.; Gonzalez-Jimenez, A.; Yang, Q.; Gu, J.; Andrade, R.J.; et al. A revised electronic version of RUCAM for the diagnosis of DILI. Hepatology 2022, 76, 18–31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, X.; Wang, Y.; Lai, R.; Wang, X.; Yu, Y.; Li, M.; Zhao, H.; Ma, Z.; Li, M.; Guo, T.; et al. Validation of the revised electronic version of RUCAM for diagnosis of DILI in Chinese patients. Hepatol. Commun. 2024, 8, e0235. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McGill, M.R.; Jaeschke, H. Biomarkers of drug-induced liver injury. Adv. Pharmacol. 2019, 85, 221–239. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Kwon, D.; Choi, G.; Park, S.A.; Cho, S.; Cho, S.; Ko, S. Liver Acinus Dynamic Chip for Assessment of Drug-Induced Zonal Hepatotoxicity. Biosensors 2022, 12, 445. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Danan, G.; Benichou, C. Causality assessment of adverse reactions to drugs—I. A novel method based on the con clusions of international consensus meetings: Application to drug-induced liver injuries. J. Clin. Epidemiol. 1993, 46, 1323–1330. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tanaka, A.; Tsuji, K.; Komiyama, Y.; Tsuruya, K.; Kakisaka, K.; Tsutsui, A.; Ichimoto, K.; Ueno, M.; Okazaki, Y.; Kamimura, H.; et al. RECAM-J 2023-Validation and development of the Japanese version of RECAM for the diagnosis of drug-induced liver injury. Hepatol. Res. 2024, 54, 503–512. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kleiner, D.E.; Chalasani, N.P.; Lee, W.M.; Fontana, R.J.; Bonkovsky, H.L.; Watkins, P.B.; Hayashi, P.H.; Davern, T.J.; Navarro, V.; Reddy, R.; et al. Hepatic histological findings in suspected drug-induced liver injury: Systematic evaluation and clinical associations. Hepatology 2014, 59, 661–670. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- López-Pascual, E.; Rienda, I.; Perez-Rojas, J.; Rapisarda, A.; Garcia-Llorens, G.; Jover, R.; Castell, J.V. Drug-Induced Fatty Liver Disease (DIFLD): A Comprehensive Analysis of Clinical, Biochemical, and Histopathological Data for Mechanisms Identification and Consistency with Current Adverse Outcome Pathways. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2024, 25, 5203. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ghabril, M.; Vuppalanchi, R. Drug-induced nodular regenerative hyperplasia. Semin. Liver Dis. 2014, 34, 240–245. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, X.; Zhang, X. Hepatocellular adenoma: Where are we now? World J. Gastroenterol. 2022, 28, 1384–1393. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Aiso, M.; Takikawa, H.; Tsuji, K.; Kagawa, T.; Watanabe, M.; Tanaka, A.; Sato, K.; Sakisaka, S.; Hiasa, Y.; Takei, Y.; et al. Analysis of 307 cases with drug-induced liver injury between 2010 and 2018 in Japan. Hepatol. Res. 2019, 49, 105–110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Regev, A.; Avigan, M.I.; Kiazand, A.; Vierling, J.M.; Lewis, J.H.; Omokaro, S.O.; Di Bisceglie, A.M.; Fontana, R.J.; Bonkovsky, H.L.; Freston, J.W.; et al. Best practices for detection, assessment and management of suspected immune-mediated liver injury caused by immune checkpoint inhibitors during drug development. J. Autoimmun. 2020, 114, 102514. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bessone, F.; Björnsson, E.S. Drug-Induced Liver Injury due to Biologics and Immune Check Point Inhibitors. Med. Clin. N. Am. 2023, 107, 623–640. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tang, S.Q.; Tang, L.L.; Mao, Y.P.; Li, W.F.; Chen, L.; Zhang, Y.; Guo, Y.; Liu, Q.; Sun, Y.; Xu, C.; et al. The Pattern of Time to Onset and Resolution of Immune-Related Adverse Events Caused by Immune Checkpoint Inhibitors in Cancer: A Pooled Analysis of 23 Clinical Trials and 8436 Patients. Cancer Res. Treat. 2021, 53, 339–354. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Martins, F.; Sofiya, L.; Sykiotis, G.P.; Lamine, F.; Maillard, M.; Fraga, M.; Shabafrouz, K.; Ribi, C.; Cairoli, A.; Guex-Crosier, Y.; et al. Adverse effects of immune-checkpoint inhibitors: Epidemiology, management and surveillance. Nat. Rev. Clin. Oncol. 2019, 16, 563–580. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cunningham, M.; Gupta, R.; Butler, M. Checkpoint inhibitor hepatotoxicity: Pathogenesis and manage ment. Hepatology 2024, 79, 198–212. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kawakami, H.; Tanizaki, J.; Tanaka, K.; Haratani, K.; Hayashi, H.; Takeda, M.; Kamata, K.; Takenaka, M.; Kimura, M.; Chikugo, T.; et al. Imaging and clinicopathological features of nivolumab-related cholangitis in patients with non-small cell lung cancer. Investig. New Drugs 2017, 35, 529–536. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pi, B.; Wang, J.; Tong, Y.; Yang, Q.; Lv, F.; Yu, Y. Immune-related cholangitis induced by immune checkpoint inhibitors: A systematic review of clinical features and management. Eur. J. Gastroenterol. Hepatol. 2021, 33 (Suppl. S1), e858–e867. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- European Association for the Study of the Liver. EASL Clinical Practice Guidelines: Drug-induced liver injury. J. Hepatol. 2019, 70, 1222–1261. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Loeper, J.; Descatoire, V.; Maurice, M.; Beaune, P.; Belghiti, J.; Houssin, D.; Ballet, F.; Feldmann, G.; Guengerich, F.P.; Pessayre, D. Cytochromes P-450 in human hepatocyte plasma membrane; recognition by several autoantibodies. Gastroenterology 1993, 104, 203–216. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Robin, M.A.; Le, R.M.; Descatoire, V.; Pessayre, D. Plasma membrane cytochromes P450 as neoantigens and autoimmune targets in drug-induced hepatitis. J. Hepatol. 1997, 26 (Suppl. S1), 23–30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Björnsson, E.S.; Medina-Caliz, I.; Andrade, R.J.; Lucena, M.I. Setting up criteria for drug-induced autoimmune-like hepatitis through a systematic analysis of published reports. Hepatol. Commun. 2022, 6, 1895–1909. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]

Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Nishikawa, H.; Kim, S.K.; Asai, A. Autoimmune Hepatitis and Drug-Induced Liver Injury in Japan. J. Clin. Med. 2025, 14, 4514. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm14134514
Nishikawa H, Kim SK, Asai A. Autoimmune Hepatitis and Drug-Induced Liver Injury in Japan. Journal of Clinical Medicine. 2025; 14(13):4514. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm14134514
Chicago/Turabian StyleNishikawa, Hiroki, Soo Ki Kim, and Akira Asai. 2025. "Autoimmune Hepatitis and Drug-Induced Liver Injury in Japan" Journal of Clinical Medicine 14, no. 13: 4514. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm14134514
APA StyleNishikawa, H., Kim, S. K., & Asai, A. (2025). Autoimmune Hepatitis and Drug-Induced Liver Injury in Japan. Journal of Clinical Medicine, 14(13), 4514. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm14134514






