Abstract
Data on the clinical characteristics, severity and management of COVID-19 from the Middle East region, especially the United Arab Emirates (UAE), is very limited. We studied the clinical characteristics, laboratory biomarkers, risk factors for severity and pharmacotherapy of hospitalized COVID-19 patients in this single-center, analytical cross-sectional study conducted in a secondary care hospital of the UAE. A total of 585 patients were included in the study (median age, 49 years (IQR, 39–59); 66% male). Age > 45 years (OR = 2.07, 95% CI: 1.04–4.14, p = 0.040), male gender (OR = 3.15, 95% CI: 1.52–6.51, p = 0.002), presentation symptoms such as fever (OR = 3.68, 95% CI:1.34–10.11, p = 0.011) and shortness of breath/dyspnea (OR = 5.36, 95% CI: 2.69–10.67, p < 0.001), Hb < 13 g/dL (OR = 3.17, 95% CI: 1.51–6.65, p = 0.002), neutrophils > 7 × 103/mcL (OR = 4.89, 95% CI: 1.66–14.37, p=0.004), lymphocytes < 1 × 103/mcL (OR = 7.78, 95% CI: 1.01–60.19, p = 0.049), sodium < 135 mmol/L (OR = 5.42, 95% CI: 1.05–27.95, p = 0.044), potassium < 3.6 mmol/L (OR = 3.36, 95% CI: 1.03–11.01, p = 0.045), urea > 6.5 mmol/L (OR = 3.37, 95% CI: 1.69–6.73, p = 0.001) and LDH > 227 IU/L (OR = 6.26, 95% CI: 1.61–24.32, p = 0.008) were independent predictors of the severity of COVID-19. Antivirals (524, 89.6%) and corticosteroids (358, 61.2%) were prescribed for the management of COVID-19. In conclusion, older age, male gender, presentation symptoms such as fever and dyspnea, low hemoglobin, neutrophilia, lymphopenia, hyponatremia, hypokalemia, elevated levels of urea and lactate dehydrogenase were found to be independent risk factors for severe COVID-19. The pharmacotherapy of COVID-19 patients in our study was diverse, and the medications were prescribed based on the clinical condition of the patients.
1. Introduction
Coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19), caused by severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus 2 (SARS-CoV-2), has exponentially spread to almost all the countries in the world [1] and has posed unprecedented challenges to the healthcare system. Globally, as of 14 March 2022, more than 458 million cases of COVID-19 have been reported, including more than 6 million deaths [2]. In the United Arab Emirates (UAE), around 885 thousand COVID-19 cases and 2302 deaths have been reported as of 14 March 2022 [3].
People of all ages are at risk of contracting the disease. However, older-aged people and those with chronic medical conditions have a higher probability of developing severe disease [4]. The clinical presentation of the disease is heterogeneous and can range from asymptomatic to severe disease with pneumonia, acute respiratory distress syndrome and even death [4,5,6]. Studies have shown that COVID-19 can also lead to neurologic, cardiovascular, hematologic, gastrointestinal, dermatologic, musculoskeletal, renal and hepatic complications. Thromboembolic complications have also been reported in patients with COVID-19 [7,8].
A number of vaccines such as BNT162b2 (Pfizer-BioNTech), mRNA-1273 (Moderna), Ad26.COV2.S (Johnson & Johnson/Janssen), AZD1222 (Oxford/AstraZeneca), etc. have been given approvals and emergency use authorizations in different countries around the world [9]. The Ministry of Health and Prevention, UAE has also approved four vaccines for use in eligible individuals against the COVID-19 infection, vaccines by Sinopharm, Pfizer-BioNTech, Sputnik V, Oxford-AstraZeneca and Moderna [10].
The spectrum of pharmacotherapy for COVID-19 management is rapidly changing and evolving. A range of drugs used for other indications and many investigational agents is still being evaluated in clinical trials for their roles in the management of COVID-19 [11,12,13]. Currently, the mainstay of management includes prevention and control of infection and supportive care, with supplemental oxygen and mechanical ventilation [11,13].
Country-specific guidelines, varying from country to country, have been published all over the world with recommendations for COVID-19 management [13,14,15]. In the UAE also, the National Clinical Committee for COVID-19 Management, Ministry of Health and Prevention has published guidance on the clinical management of COVID-19 [14].
Presently, the number of COVID-19 cases and deaths has dropped significantly, globally [16] as well as in the UAE [17]. In the UAE, this drop is attributed to high COVID-19 vaccination rates. In addition to this, compliance with precautionary measures and strengthened medical facilities have resulted in enhanced recovery and reduced mortality rates. However, given the emerging new variants of SARS-CoV-2 and the rapidity with which the COVID-19 landscape is evolving, this pandemic is far from over. It is very important to make well-timed diagnoses and initiate the effective management of patients based on the severity of the disease. Therefore, the present study investigated the clinical characteristics, risk factors for severity and pharmacotherapy of COVID-19 patients admitted in a secondary care hospital in the UAE.
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Study Population and Setting
This single-center, analytical cross-sectional study was conducted at Ibrahim Bin Hamad Obaidallah Hospital, which is a COVID-19 dedicated hospital in the emirate of Ras Al Khaimah, UAE. It is a secondary care multispecialty center with internal medicine, nephrology, neurology, cardiology, gastroenterology, geriatrics, psychiatry and emergency medicine departments. Patients with positive real-time, reverse transcriptase–polymerase chain reaction (RT-PCR) tests for SARS-CoV2 and admitted to the study site between 1 April 2020 and 31 April 2021 were included in the study. The minimum sample size, considering the proportion of patients with severe illness 14% [18], with a 95% confidence level and a 3% margin of error, was 514.
2.2. Severity of COVID-19
The study population was stratified into four groups as per the severity of illness at the time of admission in accordance with the National Guidelines for the Clinical Management and Treatment of COVID-19, Ministry of Health and Prevention, UAE [14]: asymptomatic, mild, moderate, severe and critical. The first three groups, asymptomatic, mild and moderate, were further grouped together as a non-severe group, and the latter two, severe and critical, as the severe group.
2.3. Data Collection
Patient data were collected from the electronic medical records and included epidemiological information, clinical characteristics, laboratory investigations and treatment regiments. All the collected data were reviewed by the study investigators to ensure completeness. All measures were taken to preserve the integrity and confidentiality of the patient data.
2.4. Statistical Analysis
Study data was analyzed using Statistical Package for the Social Sciences (SPSS) version 27.0. Skewness and kurtosis were checked before the analysis. The normality of the data distribution was tested using Shapiro–Wilk test. Frequency and percentages with 95% confidence intervals (CIs) were used to describe categorical variables. The median and interquartile range (IQR) with 95% CIs were used for continuous variables. A chi square test or Fisher’s exact test was used for comparing categorical variables, whereas a two-sample median test was used to compare continuous variables. Patients were stratified as per the severity of COVID-19 into two groups: severe and non-severe. The multiple imputation technique was used for handling missing data. Logistic regression models, univariable and multivariable, were used to identify the risk factors associated with COVID-19 severity. The odds ratios (OR) along with the 95% CIs were reported. All statistical tests were 2-tailed, and p < 0.05 was considered statistically significant.
2.5. Ethics
The study was approved by the Ras Al Khaimah Medical and Health Sciences University Research and Ethics Committee (Number: RAKMHSU-REC-012-2020/21-F-P) and the Ministry of Health and Prevention Research Ethics Committee/RAK Subcommittee (MOHAP/REC/2020/56-2020-F-P). Additionally, the study received approvals from the Medical Director of Ibrahim Bin Hamad Obaidallah Hospital and Undersecretary of Hospital Sector, Ministry of Health and Prevention, UAE.
3. Results
3.1. Socio-Demographic and Clinical Characteristics
A total of 585 patients with COVID-19 who were hospitalized at the study site during the study period were included in the study. Out of these patients, 386 (66%) were males and 394 (67%) were non-Arabs. The median age of the study population was 49 years (IQR, 39–59) with a majority of patients in the age group of 41–60 years (282, 48.2%). The median body mass index (BMI) of the study patients was 28.0 kg/m2 (IQR, 25–33). One hundred and forty-four (25%) patients had a history of contact with a known COVID-19 case whereas 441 patients had no clear history of direct contact. Only a fraction of patients in our study were alcoholics (26, 4.4%) and smokers (38, 6.5%). Majority of the patients had one to two comorbidities (267, 45.6%), with diabetes being the most common comorbid condition (234, 40.0%), followed by hypertension (214, 36.6%) and cardiovascular disease (119, 20.3%). The median length of hospital stay in our study was 9 days (IQR, 6–14) with a maximum of 60 days and a minimum of 1 day.
Regarding the severity of the disease, the majority of the COVID-19 patients in our study had moderate disease (229, 39.1%), followed by mild (165, 28.2%), severe (116, 19.8%) and critical (38, 6.5%) disease. One hundred and seventy-three patients (30%) were admitted to intensive care unit for the management of their condition, and only 116 (19.8%) patients were intubated and received mechanical ventilation. The most common symptoms on presentation to the hospital were fever (465, 79.5%) and dry cough (417, 71.3%), followed by shortness of breath (316, 54 %), myalgia (126, 21.5 %) and nausea or vomiting (80, 13.7%).
A significantly higher proportion of patients over the age of 45 years was in the severe group as compared to the non-severe group (67.5% vs. 57.3%, p = 0.026). In addition to this, the severe group had a significantly higher proportion of males than the non-severe group (76.6% vs. 62.2%, p = 0.001). Furthermore, patients with a higher number of underlying diseases were more likely to develop severe symptoms. The severe group had a significantly higher proportion of patients with more than two comorbidities than the non-severe group (26.6 % vs. 17.9%, p = 0.035). The proportions of patients having diabetes as a comorbid condition was significantly higher in the severe group than the non-severe group (48.7% vs. 36.9%, p = 0.010). The length of hospital stay was significantly higher in severe patients as compared to non-severe patients (14.0 days (IQR 10.0–20.0) vs. 8.0 days (IQR 5.0–11.0), p < 0.001).
In terms of clinical presentation, our results revealed that significantly higher proportions of patients had a fever (93.5% vs. 74.5%, p < 0.001) and frequent onsets of dyspnea (30.5% vs. 13.9%, p < 0.001) in the severe group compared to the non-severe group. Mild symptoms such as fatigue (12.3% vs. 5.8%, p = 0.026), sore throat (10.2% vs. 3.9%, p = 0.016), headache (11.4% vs. 4.5%, p = 0.013) and abdominal pain (8.8% vs. 2.6%, p = 0.010) were significantly more common in the non-severe group than in the severe group. The detailed patient characteristics are presented in Table 1

Table 1.
Demographic and clinical characteristics of COVID-19 patients stratified by severity of disease.
3.2. Vitals and Laboratory Characteristics
Our results showed that temperature, heart rate and blood pressure did not significantly differ between severe and non-severe patients. However, the difference in respiratory rates between the two groups was statistically significant, with the respiratory rate being higher in the severe patients (24 breaths/min (IQR, 20–30) vs. 18 breaths/min (IQR, 18–22), p < 0.001) than in the non-severe patients. The vital signs and laboratory characteristics of COVID-19 patients stratified by severity of the disease are depicted in Table 2 and Figure 1.

Table 2.
Vital signs and laboratory characteristics of study population stratified by severity of disease.
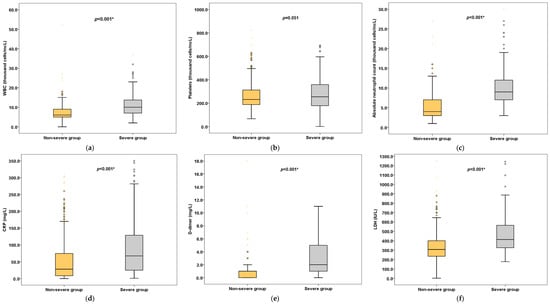
Figure 1.
Laboratory results (selected) stratified by severity of disease. Box plots represent (a) WBC, (b) Platelets, (c) Neutrophils, (d) CRP, (e) D-dimer, (f) LDH. * Statistically significant.
As for the hematology investigations, hemoglobin (Hb) (11.9 g/dL (IQR, 10–13.1) vs. 14.0 g/dL (IQR, 12–15), p < 0.001) and red blood cell count (RBC) (4 × 106/mcL (IQR, 4–5) vs. 5 × 106/mcL (IQR, 4–5), p < 0.001) were significantly lower in severe patients than in non-severe patients. Severe patients had significantly higher neutrophil counts (9 × 103/mcL (IQR, 7–12) vs. 4 × 103/mcL (IQR, 3–7), p < 0.001) compared to non-severe patients. Additionally, in terms of biochemistry tests, severe patients had significantly higher levels of urea (9 mmol/L (IQR, 5–14) vs. 4.1 mmol/L (IQR, 3–7), p < 0.001), aspartate aminotransferase (AST) (50 IU/L (IQR, 30–86) vs. 39 IU/L (IQR, 26–54), p = 0.001), alanine aminotransferase (ALT) (54.5 IU/L (IQR, 35–96.5) vs. 44 IU/L (IQR, 44–75.2), p < 0.001) and blood glucose (8 mmol/L (IQR, 6–11) vs. 7 mmol/L (IQR, 6–10), p = 0.002).
Regarding the inflammatory markers, the levels of C-reactive protein (CRP) (67.5 mg/L (IQR, 25.0–130.8) vs. 28.0 mg/L (IQR, 8.5–74.7), p < 0.001), ferritin (673.5 ng/mL (IQR, 389.8–1489.5) vs. 439.5 ng/mL (IQR, 179.0–869.0), p < 0.001) and procalcitonin (2.0 ug/L (IQR, 1.0–5.0) vs. 0.0 ug/L (IQR, 0.0–0.02), p < 0.001) were significantly elevated in severe patients compared to in non-severe patients. Additionally, higher levels of coagulation indicators, prothrombin time (PT) (13 secs (IQR, 12–14) vs. 12 secs (11.0–13.0), p < 0.001) and D-dimer (2.0 mg/L (IQR, 1.0–5.0) vs. 1.0 mg/L (IQR, 0.0–1.0), p < 0.001) were reported in severe patients. Furthermore, the cardiac biomarkers, such as troponin, creatine kinase (CK) and creatine kinase-MB (CK-MB), were significantly higher in the severe group but within the normal limits. However, lactate dehydrogenase (LDH) (414 IU/L (IQR, 324–565) vs. 308 IU/L (IQR, 235.2–401), p < 0.001) and pro brain natriuretic peptide (proBNP) (204.5 ng/L (IQR, 60–892.8) vs. 71.0 ng/L (IQR, 27–195), p < 0.001) were significantly increased in patients with severe disease.
3.3. Risk Factors for Severity of Disease
To identify the risk factors associated with the severity of COVID-19, a univariable logistic regression analysis, including 50 key characteristics as independent variables, was performed. Laboratory variables were converted into categorical variables as per their reference ranges before including them in the model. Non-severe disease was the reference category in the univariable model. Thirty-six variables were found to be associated with severity of COVID-19 in the univariable model, as depicted in Table 3.

Table 3.
Univariable logistic regression model of risk factors for severity of COVID-19.
Age greater than 45 years (OR = 1.549, 95% CI: 1.052–2.283, p = 0.027); higher BMI (OR = 1.032, 95% CI: 1.004–1.061, p = 0.023); male gender (OR = 1.994, 95% CI: 1.309–3.037; p = 0.001); comorbidities greater than two (OR = 1.668, 95% CI: 1.081–2.575, p = 0.021); presentation symptoms such as fever (OR = 4.935, 95% CI: 2.509–9.707, p < 0.001), shortness of breath (OR = 9.814, 95% CI: 5.852–16.457, p < 0.001) and dyspnea (OR = 2.716, 95% CI: 1.752–4.210, p < 0.001); RBC less than 4.5 × 106/mcL (OR = 4.807, 95% CI: 3.244–7.122, p < 0.001); Hb less than 13 g/dL (OR = 4.124, 95% CI: 2.789–6.097, p < 0.001); white blood count (WBC) greater than 11 × 103/mcL (OR = 4.303, 95% CI: 2.042–9.068, p < 0.001); neutrophils greater than 7 × 103/mcL (OR = 10.085, 95% CI: 4.205–24.188, p < 0.001); lymphocytes less than 1 × 103/mcL (OR = 1.351, 95% CI: 1.114–13.382, p = 0.033); platelets less than 150 × 103/mcL (OR = 4.883, 95% CI: 2.646–9.011, p < 0.001); sodium less than 135 mmol/L (OR = 23.011, 95% CI: 6.715–78.847, p < 0.001); potassium less than 3.6 mmol/L (OR = 7.717, 95% CI: 3.782–15.748, p < 0.001); urea greater than 6.5 mmol/L (OR = 5.222, 95% CI: 3.517–7.754, p < 0.001); serum creatinine greater than 115 umol/L (OR = 2.452, 95% CI: 1.592–3.777, p < 0.001); AST greater than 37 IU/L (OR = 1.592, 95% CI: 1.082–2.342, p = 0.018); ALT greater than 63 (OR = 1.602, 95% CI: 1.096–2.342, p = 0.015); PT greater than 12.3 s (OR = 3.602, 95% CI: 2.442–5.312, p < 0.001); CK greater than 308 IU/L (OR = 2.144, 95% CI: 1.318–3.488, p = 0.002); CK-MB greater than 3.6 IU/L (OR = 2.945, 95% CI: 2.001–4.334, p < 0.001); troponin greater than 60 ng/L (OR = 2.313, 95% CI: 1.549–3.454, p < 0.001); proBNP greater than 126 ng/L (OR = 2.250, 95% CI: 1.528–3.314, p < 0.001); procalcitonin greater than 0.10 ug/L (OR = 3.981, 95% CI: 2.663–5.951, p < 0.001); D-dimer greater than 0.55 mg/L (OR = 1.763, 95% CI: 3.476–9.768, p < 0.001); ferritin greater than 388 ng/mL (OR = 2.636, 95% CI: 1.733–4.007, p < 0.001); CRP greater than 3 mg/L (OR = 5.067, 95% CI: 1.999–12.849, p < 0.001) and LDH greater than 227 IU/L (OR = 10.249, 95% CI: 3.699–28.401, p < 0.001) were associated with increased risks of COVID-19 severity in univariate logistic regression model. However, presentation symptoms such as fatigue, sore throat and headache were associated with decreased risks of COVID-19 severity.
Our results of multivariable logistic regression analysis showed that the risks of having severe disease were 2.070 (95% CI: 1.035–4.141, p = 0.040) times higher among patients belonging to the age group of greater than 45 years, when compared with patients of less than 45 years. Male patients had a 3.151 (95% CI: 1.524–6.515, p = 0.002)-times greater risk of having severe disease compared to female patients.
Patients with presentation symptoms such as fever (OR = 3.681, 95% CI: 1.340–10.112, p = 0.011) and shortness of breath/dyspnea (OR = 5.360, 95% CI: 2.691–10.677, p < 0.001) had a significantly higher risk of contracting severe COVID-19 than did patients with no such symptoms. However, patients with mild presentation symptoms such as fatigue (OR = 0.256, 95% CI: 0.077–0.853, p = 0.027), nausea or vomiting (OR = 0.313, 95% CI: 0.099–0.992, p = 0.048) were less likely to develop severe disease.
Laboratory parameters including an Hb less than 13 g/dL (OR=3.170, 95% CI: 1.511–6.650, p = 0.002), neutrophils greater than 7 × 103/mcL (OR = 4.894, 95% CI: 1.666–14.373, p = 0.004), lymphocytes less than 1 × 103/mcL (OR = 7.783, 95% CI: 1.006–60.198, p = 0.049), sodium less than 135 mmol/L (OR = 5.417, 95% CI: 1.050–27.953, p = 0.044), potassium less than 3.6 mmol/L (OR = 3.364, 95% CI: 1.028–11.012, p=0.045), urea greater than 6.5 mmol/L (OR = 3.368, 95% CI: 1.687–6.726, p = 0.001) and LDH greater than 227 IU/L (OR = 6.257, 95% CI: 1.609–24.325, p = 0.008) were found to be independent risk factors associated with severe COVID-19 (Table 4).

Table 4.
Multivariable logistic regression model of the risk factors for severity of COVID-19.
3.4. Pharmacotherapy for COVID-19 Patients
Different drugs were used for COVID-19 management depending on the clinical condition of the patients and the guideline recommendations during the study period. Antivirals, interferons, corticosteroids, antimalarials, antibiotics, antiparasitics, interleukin-6 inhibitors and cell-based therapy were used for COVID-19 management in the study. Among 585 of the study participants, the majority of the patients were on antiviral drugs (524, 89.6%) including remdesivir, favipiravir, lopinavir/ritonavir, oseltamivir and camostat mesylate followed by antibiotics (377, 64.4%) including doxycycline and azithromycin; corticosteroids (358, 61.2%) including dexamethasone, methylprednisolone, hydrocortisone and prednisone; antimalarial drugs (246, 42.1%) such as hydroxychloroquine, chloroquine; interferons (183, 31.3%) such as interferon alfa-2b, interferon-beta-b1 and peginterferon alfa-2a; antiparasitic drugs (61, 10.4%) such as ivermectin; cell-based therapy (21, 3.6%); and interlukin-6 inhibitors (8, 1.4%) such as tocilizumab.
Our results revealed that a significantly higher proportion of patients received antiviral drugs (96.8 % vs. 87.0 %, p = 0.001) in the severe group compared to the non-severe group. In addition to this, a significantly higher number of severe patients received corticosteroids (91.6% vs. 50.3%, p < 0.001) compared to non-severe patients. Regarding individual drugs, remdesivir and favipiravir were more likely to be prescribed to severe patients than to non-severe patients (15.6% vs. 6.0%, p < 0.001). Moreover, a significantly higher proportion of patients received dexamethasone (52.6% vs. 28.3%, p < 0.001) and methylprednisolone (56.5% vs. 21.8%, p < 0.001) in the severe group than in the non-severe group. Table 5 details the drug utilization pattern in the study population stratified by the severity of the disease.

Table 5.
Pharmacotherapy of COVID-19 patients stratified by severity of the disease.
4. Discussion
Currently, the number of COVID-19 cases and associated deaths have dropped significantly, globally [16] as well as in the UAE [17]. In the UAE, this is drop is attributed to high COVID-19 vaccination rates. The UAE has one of the world’s highest vaccination rates, with around 96% of the population having received one dose of vaccine and around 86% of the population fully vaccinated [19]. In addition to this, compliance with precautionary measures and strengthened medical facilities have resulted in improved circumstances, enhanced recovery rate and reduced mortality rate. However, the pandemic is far from over, and it is very important to make well-timed diagnoses and initiate effective treatment for COVID-19 patients based on the severity of the disease. Therefore, the present study investigated the clinical characteristics, risk factors for severity and pharmacotherapy of COVID-19 in the UAE population.
Out of the total 585 COVID-19 patients, the proportion of male patients was higher than female patients. This study finding is in accordance with other studies on COVID-19, which reported a similar gender distribution [20,21,22]. In terms of the severity of the disease, a significantly higher proportion of males was in the severe group than of females. Additionally, multivariable logistic regression analyses revealed that male patients had a significantly greater risk of having severe disease compared to female patients. This finding is supported by a global COVID-19 meta-analysis that identified the male gender as a risk factor for the development of severe disease [23]. This finding can be attributed to gender differences in the innate and adaptive immune systems, angiotensin-converting enzyme 2 (ACE2) receptors expression, comorbidities and socio-cultural and behavioral aspects, which may account for the female advantage in COVID-19 [23].
Furthermore, we report that that the median age of severe patients was significantly higher compared to of non-severe patients, and the multivariable logistic regression model also showed that older age was an independent risk factor for disease severity. These findings are in line with previous studies, which reported older age as a critical independent predictor of severity and mortality in COVID-19 [24,25,26]. This could be because of many reasons, such as an increased number of comorbidities with age, an ageing immune system and the prevalence of polypharmacy in older adults.
Our results revealed that nearly half of the study population had had at least one comorbidity, with diabetes mellitus being the most common followed by hypertension and cardiovascular diseases. A number of previous studies [20,25,27] have reported similar comorbidity distribution, wherein hypertension, diabetes and cardiovascular diseases were the most common comorbidities among COVID-19 patients. We also report that a significantly higher proportion of patients with comorbid diabetes were in the severe group. Moreover, univariable logistic regression analysis revealed that diabetic patients had a significantly higher risk of contracting severe COVID-19. Similar observations have been reported by a number of previous studies analyzing the association between severity of COVID-19 and diabetes [28,29]. The reason for this association is the syndromic nature of diabetes, wherein accompanying comorbidities such as obesity, hypertension and cardiovascular diseases, older age and hyperglycemia all contribute towards increasing the risk of severe COVID-19.
Fever was the most common symptom is our study population, followed by dry cough and shortness of breath. These clinical features of COVID-19 patients in our study were consistent with several previous reports [20,22,30] that reported fever as the predominant symptom. However, a recent study conducted in the UAE by Harbi et al. reported cough as the most common symptom in hospitalized COVID-19 patients. Furthermore, Wang et al. and Zayet et al. reported other symptoms such as diarrhea, nausea, smell and taste disorders [22,31]. These symptoms were less common in our study population. Symptoms such as fever and shortness of breath were present in a significantly higher proportion of patients in the severe group as compared to in the non-severe group. Similar clinical presentations were reported by a meta-analysis, where fever was associated with severe or critical disease [32] and by Sun et al., wherein severe subgroup of COVID-19 patients had more frequent dyspnea or shortness of breath compared to the non-severe subgroup [26]. Furthermore, our multivariable logistic regression model revealed that patients with presentation symptoms such as fever and shortness of breath/dyspnea had a significantly higher risk of severe COVID-19 as compared to patients with no such symptoms. Our results are in accordance with the studies that have identified fever as a risk factor of severe disease and poor patient outcomes [33,34], likewise with studies that reported dyspnea as an indicator for progression to severe disease [35,36]. However, we also report that patients with mild presentation symptoms such as fatigue, nausea or vomiting were less likely to develop severe disease. Our results showed that temperature, heart rate and blood pressure did not significantly differ between severe and non-severe patients. However, the difference in respiratory rates between the two groups was statistically significant, with respiratory rates being higher in the severe patients than in the non-severe patients. These results are in line with the findings of previous reports [37].
Regarding the hematological characteristics of the study population, we report that in severe patients, Hb and RBC were significantly lower, whereas WBC and neutrophil counts were significantly higher as compared to non-severe patients. A univariable model revealed that an Hb less than 13 g/dL, WBC greater than 11 × 103/mcL, neutrophils greater than 7 × 103/mcL, lymphocytes less than 1 × 103/mcL and platelets less than 150 × 103/mcL were associated with severe COVID-19. However, a multivariable model identified only an Hb less than 13 g/dL, neutrophils greater than 7 × 103/mcL and lymphocytes less than 1 × 103/mcL. Our results are consistent with the findings of previous studies that reported anemia [38], neutrophilia [39], lymphopenia [39] and thrombocytopenia [40] to be linked with severe COVID-19.
The association of anemia with severe disease can be attributed to the fact that, in the COVID-19 setting, there is respiratory compromise and an increase in oxygen demand; in such a situation, anemia can further reduce the oxygen supply to the tissues, leading to further complications and adverse outcomes. Neutrophilia is reported to predict adverse outcomes in COVID-19 patients, and the neutrophil–to–lymphocyte ratio has been recognized as a predictor for severe disease [41]. Dysregulated neutrophil activity might be the reason for the immune-mediated increased COVID-19 severity [42]. Lymphopenia has been reported to be a prevalent manifestation in patients with severe COVID-19 as the virus directly attacks the lymphocytes coupled with disordered inflammatory cytokine milieu, leading to increased lymphocyte apoptosis [43]. The association of thrombocytopenia with COVID-19 severity can be explained by irreversible platelet consumption during the hyper-inflammation and hyper-coagulable states of severe COVID-19. In addition to this, viral infection can decrease maturation and increase the apoptosis of platelets [44].
Many studies have reported that COVID-19 has a significant impact on liver related biomarkers [45,46]. Higher serum AST and ALT levels and lower serum albumin levels have been associated with COVID-19 severity [47]. Our univariable model also revealed that patients with AST levels greater than 37 IU/L and ALT levels greater than 63 IU/L had a significantly higher risk of severe disease as compared to patients with normal levels of these enzymes. Since elevated liver enzymes are associated with disease severity, liver functions should be monitored for COVID-19 patients.
Electrolyte abnormalities are common in COVID-19 patients. These electrolyte disturbances are known to have an impact on the prognosis of the disease. Our multivariable logistic regression analysis identified sodium levels less than 135 mmol/L and potassium levels less than 3.6 mmol/L as independent risk factors associated with severe COVID-19. These results are consistent with the findings of studies conducted by Tezcan et al. and Moreno-P et al. [48,49]. Tezcan et al. reported that hyponatremia was associated with unfavorable outcomes and was an independent factor related to mortality in COVID-19 patients [48]. Moreno-P et al. identified hypokalemia as a sensitive biomarker for severe COVID-19 and as an independent predictor of invasive mechanical ventilation [49]. Hachim et al. identified urea as one of the predictors of developing critical COVID-19 [50]. In our study also, a urea level greater than 6.5 mmol/L at presentation was independently associated with severe disease. A baseline assessment of electrolytes and urea can play a crucial role in evaluating the risk of severe COVID-19.
A number of studies reported associations of inflammatory markers with COVID-19 severity [51,52]. Similarly, in our study also, a CRP greater than 3 mg/L, ferritin greater than 388 ng/mL and procalcitonin greater than 0.10 ug/L were found to be associated with severe COVID-19 in the univariable model. Coagulation disorders are frequently reported in patients with severe COVID-19 [53]. Many studies have reported that D-dimer dynamics can gauge the severity of COVID-19 with elevated levels linked to poor outcomes in patients [54]. In our study, severe patients had significantly higher levels of coagulation indicators, PT and D-dimer. The elevated D-dimer level indicates hypercoagulability and may accentuate thrombosis in COVID-19. Furthermore, we report that the cardiac biomarker, an LDH greater than 227 IU/L, was found to be an independent risk factor of severe COVID-19. Our results are consistent with a pooled analysis of nine studies involving 1532 patients which reported that elevated LDH levels were linked with increased odds of developing severe disease in patients with COVID-19 [55].
In our study, the management of COVID-19 patients was conducted in accordance with the National Guidelines for Clinical Management and Treatment of COVID-19 [14] published by the National Clinical Committee for COVID-19 Management, Ministry of Health and Prevention, UAE. Our results revealed that different types of drugs were prescribed for the management of COVID-19 and its associated complications in the study, namely: antiviral drugs, interferons, corticosteroids, antimalarial drugs, antibiotics, antiparasitic drugs, interleukin-6 inhibitors and cell-based therapy. A recent study conducted in the UAE reported similar pharmacotherapy pattern in hospitalized COVID-19 patients [56]. The majority of the patients in our study were on antivirals and corticosteroids. These results are similar to the drug-utilizing study conducted by Sun et al. in which majority of the COVID-19 patients were prescribed antivirals and glucocorticoids [26].
The most frequently prescribed antiviral in our study was favipiravir, followed by lopinavir/ritonavir. Favipiravir is a novel RNA-dependent RNA polymerase inhibitor with reported antiviral properties against a broad array of RNA viruses. Cai et al. and Chen et al. studied the effects of favipiravir against other antivirals in COVID-19 [57,58]. Cai et al. reported that favipiravir treated COVID-19 patients had better radiological improvement and quicker viral clearance as compared to lopinavir/ritonavir treated patients [57]. Furthermore, Chen et al. concluded that favipiravir was associated with a significantly shortened time to fever and cough reduction compared to umifenovir in COVID-19 [58]. Remdesivir, the only US-FDA-approved antiviral drug for the treatment of hospitalized COVID-19 patients on supplemental oxygen, was found to be effective in shortening the recovery time in hospitalized COVID-19 patients [59]. In our study, 50 patients fulfilling the treatment criteria as per the national guidelines were prescribed with remdesivir.
Severe COVID-19 patients can develop lung injury and multi-organ dysfunction because of systemic inflammatory response. Corticosteroids owing to their potent anti-inflammatory effects can play a key role in preventing and mitigating these effects. The RECOVERY trial reported that dexamethasone improved survival in ventilated and oxygen-receiving COVID-19 patients [60]. In our study also, a significantly higher proportion of severe patients received low dose dexamethasone compared to non-severe patients. Additionally, overall, out of the total 154 severe patients, 141 received corticosteroids for the management of COVID-19. These results are consistent with the findings of Lin et al. [61].
Interferons, a family of cytokines, with in vitro and in vivo antiviral properties, are proposed as a potential treatment for COVID-19. Studies have reported the clinical benefit of interferons IFN-β1b, IFN-α-2b and PEG IFN-α2b in severe COVID-19 [62,63,64]. In our study, nearly one-third of the patients received interferon therapy with IFN-β1b, IFN-α-2b and PEG IFN-α2b. A significantly higher proportion of severe patients received interferon therapy as compared to non-severe patients. This finding is attributed to the fact that interferon therapy has been shown to improve clinical outcomes in severely ill COVID-19 patients.
Tocilizumab, an interleukin-6 inhibitor, has been reported to minimize the risk of death in hospitalized severe-COVID-19 patients [65]. It has been approved in combination with dexamethasone by the US-FDA for use in certain severe hospitalized patients showing rapid respiratory decompensation. Likewise, in our study also, nine patients in the severe group received this drug for the management for their severe condition.
Several studies have suggested increased risks of thromboembolic manifestations associated with COVID-19. Guidelines recommend that hospitalized COVID-19 patients should receive prophylactic-dose anticoagulation [13,14]. In line with these guidelines, most of the patients in our study were given prophylactic-dose anticoagulant. Enoxaparin, the preferred low-molecular weight heparin for anticoagulation, was the most frequently prescribed medication in our study.
Early in the pandemic, the COVID-19 disease process was not clearly understood, and symptomatic and supportive care were the only available management options. During that time, there was an increased use of hydroxychloroquine and chloroquine in COVID-19 patients despite no rigorous evidence for efficacy. Since then, chloroquine and hydroxychloroquine, with or without azithromycin, have been examined for the treatment of COVID-19 in a number of clinical trials. Many RCTs and observational studies reported a lack of benefit and potential for toxicity with hydroxychloroquine or chloroquine in the management of COVID-19 [66,67,68]. Likewise, initially in our study, hydroxychloroquine and chloroquine with or without azithromycin were prescribed to the non-severe group of patients.
We found that the pharmacotherapy of COVID-19 patients in our study was diverse, and most of the medications were prescribed considering the clinical condition of the patients, including patients’ characteristics, disease severity, age and comorbidities. This drug utilization pattern of our study is consistent with previous studies that evaluated treatment patterns in COVID-19 patients [26,61]. The varied prescription pattern reported by different studies including ours is attributed to the following factors; firstly, the spectrum of pharmacotherapies for the management of COVID-19 is rapidly growing and evolving, and secondly, with time there are evolution and revisions to the treatment guidelines depending on the best available data at the given time point.
Our study had some limitations. First, the causal inference of the identified relationships is limited due to the cross-sectional study design. Second, data for some of the laboratory parameters of patients were missing. Although the missing data was replaced by an imputation technique, their role might not be estimated aptly in determining the severity of the disease. Thirdly, being a single-center study, the findings cannot be generalized and need to be validated in a larger patient population.
5. Conclusions
In our study, older age, male gender, presentation symptoms such as fever and dyspnea, low Hb, neutrophilia, lymphopenia, hyponatremia, hypokalemia, elevated levels of urea and LDH were found to be independent risk factors for developing severe disease among COVID-19 patients. The pharmacotherapy of COVID-19 patients in our study was diverse, and the medications were prescribed based on the clinical condition of the patients in accordance with the national guidelines. Data from this study will contribute towards the early detection of patients at a high risk of developing critical illness and the optimization of treatments in this rapidly evolving pandemic.
Author Contributions
Conceptualization, A.M.J.A., S.A.R., M.T.K. and A.C.; Methodology, A.M.J.A., S.A.R., M.T.K. and A.C.; Software; A.M.J.A. and S.A.R.; Formal Analysis, A.M.J.A. and S.A.R.; Investigation, A.M.J.A., S.A.R., M.T.K. and A.C.; Resources, S.A.R., A.M.J.A., M.T.K. and A.C.; Data Curation, A.M.J.A., Writing—Original Draft Preparation, A.M.J.A., S.A.R., M.T.K. and A.C.; Writing—Review and Editing, S.A.R., M.T.K. and A.C.; Supervision, S.A.R., M.T.K. and A.C. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This research received no external funding.
Institutional Review Board Statement
The study was approved by the Ras Al Khaimah Medical and Health Sciences University Research and Ethics Committee (Number: RAKMHSU-REC-012-2020/21-F-P) and the Ministry of Health and Prevention Research Ethics Committee/RAK Subcommittee (MOHAP/REC/2020/56-2020-F-P). Additionally, the study received approvals from the Medical Director of Ibrahim Bin Hamad Obaidallah Hospital and the Undersecretary of Hospital Sector, Ministry of Health and Prevention, UAE.
Informed Consent Statement
Formal consent was not required for this type of study as it was an observational, non-interventional study without any direct involvement of the patients. All patient data were de-identified prior to analysis, and authors had all necessary administrative permissions to access and publish the data.
Data Availability Statement
Data will be available from the corresponding author upon reasonable request.
Acknowledgments
The authors thank the Ministry of Health and Prevention, UAE, administration of Ibrahim Bin Hamad Obaidallah Hospital, Ras Al Khaimah, UAE. The authors acknowledge Emirates Health Services, UAE for their inputs and providing the approval for publishing the manuscript. The authors also thank S Gurumadhva Rao, President; Padma GM Rao, Dean; Sathvik B Sridhar, Chairperson, RAK Medical and Health Sciences University for their support and encouragement.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
References
- Zhu, N.; Zhang, D.; Wang, W.; Li, X.; Yang, B.; Song, J.; Zhao, X.; Huang, B.; Shi, W.; Lu, R.; et al. A Novel Coronavirus from Patients with Pneumonia in China. N. Engl. J. Med. 2020, 382, 727–733. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Johns Hopkins University and Medicine Coronavirus Resource Center–Global. Available online: https://coronavirus.jhu.edu/ (accessed on 24 October 2021).
- Johns Hopkins University and Medicine Coronavirus Resource Center–United Arab Emirates. Available online: https://coronavirus.jhu.edu/region/united-arab-emirates (accessed on 24 October 2021).
- Wiersinga, W.J.; Rhodes, A.; Cheng, A.C.; Peacock, S.J.; Prescott, H.C. Pathophysiology, Transmission, Diagnosis, and Treatment of Coronavirus Disease 2019 (COVID-19): A Review. JAMA J. Am. Med. Assoc. 2020, 324, 782–793. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Guan, W.J.; Ni, Z.Y.; Hu, Y.; Liang, W.H.; Ou, C.Q.; He, J.X.; Liu, L.; Shan, H.; Lei, C.L.; Hui, D.S.C.; et al. Clinical Characteristics of Coronavirus Disease 2019 in China. N. Engl. J. Med. 2020, 382, 1708–1720. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, Q.; Guan, X.; Wu, P.; Wang, X.; Zhou, L.; Tong, Y.; Ren, R.; Leung, K.S.M.; Lau, E.H.Y.; Wong, J.Y.; et al. Early Transmission Dynamics in Wuhan, China, of Novel Coronavirus-Infected Pneumonia. N. Engl. J. Med. 2020, 382, 1199–1207. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xie, Y.; Wang, Z.; Liao, H.; Marley, G.; Wu, D.; Tang, W. Epidemiologic, Clinical, and Laboratory Findings of the COVID-19 in the Current Pandemic: Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. BMC Infect. Dis. 2020, 20, 640. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- da Rosa Mesquita, R.; Francelino Silva, L.C.; Santos Santana, F.M.; Farias de Oliveira, T.; Campos Alcântara, R.; Monteiro Arnozo, G.; Rodrigues da Silva Filho, E.; Galdino dos Santos, A.G.; Oliveira da Cunha, E.J.; Salgueiro de Aquino, S.H.; et al. Clinical Manifestations of COVID-19 in the General Population: Systematic Review. Wien Klin. Wochenschr. 2021, 133, 377–382. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Different COVID-19 Vaccines|CDC. Available online: https://www.cdc.gov/coronavirus/2019-ncov/vaccines/different-vaccines.html (accessed on 25 October 2021).
- Vaccines against COVID-19 in the UAE–The Official Portal of the UAE Government. Available online: https://u.ae/en/information-and-services/justice-safety-and-the-law/handling-the-covid-19-outbreak/vaccines-against-covid-19-in-the-uae (accessed on 25 October 2021).
- Sanders, J.M.; Monogue, M.L.; Jodlowski, T.Z.; Cutrell, J.B. Pharmacologic Treatments for Coronavirus Disease 2019 (COVID-19): A Review. JAMA J. Am. Med. Assoc. 2020, 323, 1824–1836. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC) Therapeutic Options for COVID-19 Patients|CDC. Available online: https://www.cdc.gov/coronavirus/2019-ncov/hcp/therapeutic-options.html (accessed on 25 October 2021).
- National Institutes of Health Therapeutic Management of Hospitalized Adults with COVID-19. Available online: https://www.covid19treatmentguidelines.nih.gov/management/clinical-management/hospitalized-adults--therapeutic-management/ (accessed on 29 September 2020).
- National Clinical Committee for COVID-19 Management. National Guidelines for Clinical Management and Treatment of COVID-19; Version 4; United Arab Emirates Ministry of Health: Dubai, United Arab Emirates, 2020; Volume 19, pp. 1–61. Available online: https://www.dha.gov.ae/en/HealthRegulation/Documents/National_Guidelines_of_COVID_19_1st_June_2020.pdf (accessed on 29 September 2020).
- Overview COVID-19 Rapid Guideline: Managing COVID-19. Available online: https://www.nice.org.uk/guidance/ng191 (accessed on 25 October 2021).
- World Health Organization Weekly Epidemiological Update on COVID-19. 5 October 2021. Available online: https://www.who.int/publications/m/item/weekly-epidemiological-update-on-covid-19---5-october-2021 (accessed on 15 October 2021).
- Reuters UAE’s Daily COVID-19 Cases Fall below 100. Available online: https://www.reuters.com/world/middle-east/uaes-daily-covid-19-cases-fall-below-100–2021–10–17/ (accessed on 20 October 2021).
- Wu, Z.; McGoogan, J.M. Characteristics of and Important Lessons from the Coronavirus Disease 2019 (COVID-19) Outbreak in China. JAMA 2020, 323, 1239. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Emirates News Agency UAE Continues to Lead in Global Rankings for COVID-19 Vaccination Rates: UAE Government Media Briefing. Available online: https://wam.ae/en/details/1395302980184 (accessed on 20 October 2021).
- Richardson, S.; Hirsch, J.S.; Narasimhan, M.; Crawford, J.M.; McGinn, T.; Davidson, K.W.; Barnaby, D.P.; Becker, L.B.; Chelico, J.D.; Cohen, S.L.; et al. Presenting Characteristics, Comorbidities, and Outcomes among 5700 Patients Hospitalized with COVID-19 in the New York City Area. JAMA J. Am. Med. Assoc. 2020, 323, 2052–2059. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pijls, B.G.; Jolani, S.; Atherley, A.; Derckx, R.T.; Dijkstra, J.I.R.; Franssen, G.H.L.; Hendriks, S.; Richters, A.; Venemans-Jellema, A.; Zalpuri, S.; et al. Demographic Risk Factors for COVID-19 Infection, Severity, ICU Admission and Death: A Meta-Analysis of 59 Studies. BMJ Open 2021, 11, e044640. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, D.; Hu, B.; Hu, C.; Zhu, F.; Liu, X.; Zhang, J.; Wang, B.; Xiang, H.; Cheng, Z.; Xiong, Y.; et al. Clinical Characteristics of 138 Hospitalized Patients With 2019 Novel Coronavirus–Infected Pneumonia in Wuhan, China. JAMA 2020, 323, 1061. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Peckham, H.; de Gruijter, N.M.; Raine, C.; Radziszewska, A.; Ciurtin, C.; Wedderburn, L.R.; Rosser, E.C.; Webb, K.; Deakin, C.T. Male Sex Identified by Global COVID-19 Meta-Analysis as a Risk Factor for Death and ITU Admission. Nat. Commun. 2020, 11, 6317. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, X.; Yu, Y.; Xu, J.; Shu, H.; Xia, J.; Liu, H.; Wu, Y.; Zhang, L.; Yu, Z.; Fang, M.; et al. Clinical Course and Outcomes of Critically Ill Patients with SARS-CoV-2 Pneumonia in Wuhan, China: A Single-Centered, Retrospective, Observational Study. Lancet Respir. Med. 2020, 8, 475–481. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Xu, K.; Zhou, M.; Yang, D.; Ling, Y.; Liu, K.; Bai, T.; Cheng, Z.; Li, J. Application of Ordinal Logistic Regression Analysis to Identify the Determinants of Illness Severity of COVID-19 in China. Epidemiol. Infect. 2020, 148, e146. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sun, F.; Kou, H.; Wang, S.; Lu, Y.; Zhao, H.; Li, W.; Zhou, Q.; Jiang, Q.; Cheng, Y.; Yang, K.; et al. An Analytical Study of Drug Utilization, Disease Progression, and Adverse Events among 165 COVID-19 Patients. Annu. Transl. Med. 2021, 9, 306. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grasselli, G.; Zangrillo, A.; Zanella, A.; Antonelli, M.; Cabrini, L.; Castelli, A.; Cereda, D.; Coluccello, A.; Foti, G.; Fumagalli, R.; et al. Baseline Characteristics and Outcomes of 1591 Patients Infected with SARS-CoV-2 Admitted to ICUs of the Lombardy Region, Italy. JAMA J. Am. Med. Assoc. 2020, 323, 1574–1581. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Rawshani, A.; Kjölhede, E.A.; Rawshani, A.; Sattar, N.; Eeg-Olofsson, K.; Adiels, M.; Ludvigsson, J.; Lindh, M.; Gisslén, M.; Hagberg, E.; et al. Severe COVID-19 in People with Type 1 and Type 2 Diabetes in Sweden: A Nationwide Retrospective Cohort Study. Lancet Reg. Health Eur. 2021, 4, 100105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gregory, J.M.; Slaughter, J.C.; Duffus, S.H.; Smith, T.J.; LeStourgeon, L.M.; Jaser, S.S.; McCoy, A.B.; Luther, J.M.; Giovannetti, E.R.; Boeder, S.; et al. COVID-19 Severity Is Tripled in the Diabetes Community: A Prospective Analysis of the Pandemic’s Impact in Type 1 and Type 2 Diabetes. Diabetes Care 2021, 44, 526–532. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, C.; Chen, X.; Cai, Y.; Xia, J.; Zhou, X.; Xu, S.; Huang, H.; Zhang, L.; Zhou, X.; Du, C.; et al. Risk Factors Associated with Acute Respiratory Distress Syndrome and Death in Patients with Coronavirus Disease 2019 Pneumonia in Wuhan, China. JAMA Intern. Med. 2020, 180, 934. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Zayet, S.; Kadiane-Oussou, N.J.; Lepiller, Q.; Zahra, H.; Royer, P.-Y.; Toko, L.; Gendrin, V.; Klopfenstein, T. Clinical Features of COVID-19 and Influenza: A Comparative Study on Nord Franche-Comte Cluster. Microbes Infect. 2020, 22, 481–488. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Islam, M.A.; Kundu, S.; Alam, S.S.; Hossan, T.; Kamal, M.A.; Hassan, R. Prevalence and Characteristics of Fever in Adult and Paediatric Patients with Coronavirus Disease 2019 (COVID-19): A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis of 17515 Patients. PLoS ONE 2021, 16, e0249788. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chew, N.W.; Ngiam, J.N.; Tham, S.M.; Lim, Z.Y.; Li, T.Y.W.; Cen, S.; Yap, E.S.; Tambyah, P.A.; Santosa, A.; Cross, G.B.; et al. Fever as a Predictor of Adverse Outcomes in COVID. QJM Int. J. Med. 2021, 114, 706–714. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, C.; Wang, H.; Liang, Z.; Peng, L.; Zhao, F.; Yang, L.; Cao, M.; Wu, W.; Jiang, X.; Zhang, P.; et al. Predicting Illness Severity and Short-Term Outcomes of COVID-19: A Retrospective Cohort Study in China. Innovation 2020, 1, 100007. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zheng, Z.; Peng, F.; Xu, B.; Zhao, J.; Liu, H.; Peng, J.; Li, Q.; Jiang, C.; Zhou, Y.; Liu, S.; et al. Risk Factors of Critical & Mortal COVID-19 Cases: A Systematic Literature Review and Meta-Analysis. J. Infect. 2020, 81, e16–e25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, S.R.; Nam, S.H.; Kim, Y.R. Risk Factors on the Progression to Clinical Outcomes of COVID-19 Patients in South Korea: Using National Data. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2020, 17, 8847. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, D.; Cui, P.; Zeng, S.; Wang, S.; Feng, X.; Xu, S.; Li, R.; Gao, Y.; Yu, R.; Wang, Y.; et al. Risk Factors for Developing into Critical COVID-19 Patients in Wuhan, China: A Multicenter, Retrospective, Cohort Study. EClinicalMedicine 2020, 25, 100471. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hariyanto, T.I.; Kurniawan, A. Anemia Is Associated with Severe Coronavirus Disease 2019 (COVID-19) Infection. Transfus. Apher. Sci. 2020, 59, 102926. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Henry, B.; Cheruiyot, I.; Vikse, J.; Mutua, V.; Kipkorir, V.; Benoit, J.; Plebani, M.; Bragazzi, N.; Lippi, G. Lymphopenia and Neutrophilia at Admission Predicts Severity and Mortality in Patients with COVID-19: A Meta-Analysis. Acta Biomed. 2020, 91, e2020008. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zong, X.; Gu, Y.; Yu, H.; Li, Z.; Wang, Y. Thrombocytopenia Is Associated with COVID-19 Severity and Outcome: An Updated Meta-Analysis of 5637 Patients with Multiple Outcomes. Lab. Med. 2021, 52, 10–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Simadibrata, D.M.; Calvin, J.; Wijaya, A.D.; Ibrahim, N.A.A. Neutrophil-to-Lymphocyte Ratio on Admission to Predict the Severity and Mortality of COVID-19 Patients: A Meta-Analysis. Am. J. Emerg. Med. 2021, 42, 60–69. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cavalcante-Silva, L.H.A.; Carvalho, D.C.M.; Lima, É.A.; Galvão, J.G.F.M.; da Silva, J.S.F.; Sales-Neto, J.M.; Rodrigues-Mascarenhas, S. Neutrophils and COVID-19: The Road so Far. Int. Immunopharmacol. 2021, 90, 107233. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tan, L.; Wang, Q.; Zhang, D.; Ding, J.; Huang, Q.; Tang, Y.Q.; Wang, Q.; Miao, H. Lymphopenia Predicts Disease Severity of COVID-19: A Descriptive and Predictive Study. Signal. Transduct. Target. Therapy 2020, 5, 33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Terpos, E.; Ntanasis-Stathopoulos, I.; Elalamy, I.; Kastritis, E.; Sergentanis, T.N.; Politou, M.; Psaltopoulou, T.; Gerotziafas, G.; Dimopoulos, M.A. Hematological Findings and Complications of COVID. Am. J. Hematol. 2020, 95, 834–847. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Zhang, Y.; Zheng, L.; Liu, L.; Zhao, M.; Xiao, J.; Zhao, Q. Liver Impairment in COVID-19 Patients: A Retrospective Analysis of 115 Cases from a Single Centre in Wuhan City, China. Liver Int. 2020, 40, 2095–2103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Lei, F.; Liu, Y.; Zhou, F.; Qin, J.; Zhang, P.; Zhu, L.; Zhang, X.; Cai, J.; Lin, L.; Ouyang, S.; et al. Longitudinal Association Between Markers of Liver Injury and Mortality in COVID-19 in China. Hepatology 2020, 72, 389–398. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Parohan, M.; Yaghoubi, S.; Seraji, A. Liver Injury Is Associated with Severe Coronavirus Disease 2019 (COVID-19) Infection: A Systematic Review and Meta-analysis of Retrospective Studies. Hepatol. Res. 2020, 50, 924–935. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tezcan, M.E.; Dogan Gokce, G.; Sen, N.; Zorlutuna Kaymak, N.; Ozer, R.S. Baseline Electrolyte Abnormalities Would Be Related to Poor Prognosis in Hospitalized Coronavirus Disease 2019 Patients. New Microbes New Infect. 2020, 37, 100753. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moreno-Pérez, O.; Leon-Ramirez, J.M.; Fuertes-Kenneally, L.; Perdiguero, M.; Andres, M.; Garcia-Navarro, M.; Ruiz-Torregrosa, P.; Boix, V.; Gil, J.; Merino, E.; et al. Hypokalemia as a Sensitive Biomarker of Disease Severity and the Requirement for Invasive Mechanical Ventilation Requirement in COVID-19 Pneumonia: A Case Series of 306 Mediterranean Patients. Int. J. Infect. Dis. 2020, 100, 449–454. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hachim, M.Y.; Hachim, I.Y.; Naeem, K.B.; Hannawi, H.; Salmi, I.A.; Hannawi, S. D-Dimer, Troponin, and Urea Level at Presentation With COVID-19 Can Predict ICU Admission: A Single Centered Study. Front. Med. 2020, 7, 585003. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zeng, F.; Huang, Y.; Guo, Y.; Yin, M.; Chen, X.; Xiao, L.; Deng, G. Association of Inflammatory Markers with the Severity of COVID-19: A Meta-Analysis. Int. J. Infect. Dis. 2020, 96, 467–474. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mahat, R.K.; Panda, S.; Rathore, V.; Swain, S.; Yadav, L.; Sah, S.P. The Dynamics of Inflammatory Markers in Coronavirus Disease-2019 (COVID-19) Patients: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. Clin. Epidemiol. Glob. Health 2021, 11, 100727. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Deng, Y.; Liu, W.; Liu, K.; Fang, Y.Y.; Shang, J.; Zhou, L.; Wang, K.; Leng, F.; Wei, S.; Chen, L.; et al. Clinical Characteristics of Fatal and Recovered Cases of Coronavirus Disease 2019 in Wuhan, China: A Retrospective Study. Chin. Med. J. 2020, 133, 1261–1267. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shi, L.; Wang, Y.; Wang, Y.; Duan, G.; Yang, H. An Updated Meta-analysis on the Relationship between D-dimer Levels and Severity of Coronavirus Disease. Int. J. Lab. Hematol. 2020, 42, e207–e210. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Henry, B.M.; Aggarwal, G.; Wong, J.; Benoit, S.; Vikse, J.; Plebani, M.; Lippi, G. Lactate Dehydrogenase Levels Predict Coronavirus Disease 2019 (COVID-19) Severity and Mortality: A Pooled Analysis. Am. J. Emerg. Med. 2020, 38, 1722–1726. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Al Harbi, M.; Al Kaabi, N.; Al Nuaimi, A.; Abdalla, J.; Khan, T.; Gasmelseed, H.; Khan, A.; Hamdoun, O.; Weber, S. Clinical and Laboratory Characteristics of Patients Hospitalised with COVID-19: Clinical Outcomes in Abu Dhabi, United Arab Emirates. BMC Infect. Dis. 2022, 22, 136. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cai, Q.; Yang, M.; Liu, D.; Chen, J.; Shu, D.; Xia, J.; Liao, X.; Gu, Y.; Cai, Q.; Yang, Y.; et al. Experimental Treatment with Favipiravir for COVID-19: An Open-Label Control Study. Engineering 2020, 6, 1192–1198. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, C.; Zhang, Y.; Huang, J.; Yin, P.; Cheng, Z.; Wu, J.; Chen, S.; Zhang, Y.; Chen, B.; Lu, M.; et al. Favipiravir Versus Arbidol for Clinical Recovery Rate in Moderate and Severe Adult COVID-19 Patients: A Prospective, Multicenter, Open-Label, Randomized Controlled Clinical Trial. Front. Pharmacol. 2021, 12, 683296. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Beigel, J.H.; Tomashek, K.M.; Dodd, L.E.; Mehta, A.K.; Zingman, B.S.; Kalil, A.C.; Hohmann, E.; Chu, H.Y.; Luetkemeyer, A.; Kline, S.; et al. Remdesivir for the Treatment of Covid-19–Final Report. N. Engl. J. Med. 2020, 383, 1813–1826. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- RECOVERY Collaborative Group; Horby, P.; Lim, W.S.; Emberson, J.R.; Mafham, M.; Bell, J.L.; Linsell, L.; Staplin, N.; Brightling, C.; Ustianowski, A.; et al. Dexamethasone in Hospitalized Patients with Covid. N. Engl. J. Med. 2021, 384, 693–704. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, K.J.; Schneeweiss, S.; Tesfaye, H.; D’Andrea, E.; Liu, J.; Lii, J.; Murphy, S.N.; Gagne, J.J. Pharmacotherapy for Hospitalized Patients with COVID-19: Treatment Patterns by Disease Severity. Drugs 2020, 80, 1961–1972. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alavi Darazam, I.; Shokouhi, S.; Pourhoseingholi, M.A.; Naghibi Irvani, S.S.; Mokhtari, M.; Shabani, M.; Amirdosara, M.; Torabinavid, P.; Golmohammadi, M.; Hashemi, S.; et al. Role of Interferon Therapy in Severe COVID-19: The COVIFERON Randomized Controlled Trial. Sci. Rep. 2021, 11, 8059. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yu, J.; Lu, X.; Tong, L.; Shi, X.; Ma, J.; Lv, F.; Wu, J.; Pan, Q.; Yang, J.; Cao, H.; et al. Interferon-α-2b Aerosol Inhalation Is Associated with Improved Clinical Outcomes in Patients with Coronavirus Disease. Br. J. Clin. Pharmacol. 2021, 87, 4737–4746. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pandit, A.; Bhalani, N.; Bhushan, B.L.S.; Koradia, P.; Gargiya, S.; Bhomia, V.; Kansagra, K. Efficacy and Safety of Pegylated Interferon Alfa-2b in Moderate COVID-19: A Phase II, Randomized, Controlled, Open-Label Study. Int. J. Infect. Dis. 2021, 105, 516–521. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xu, X.; Han, M.; Li, T.; Sun, W.; Wang, D.; Fu, B.; Zhou, Y.; Zheng, X.; Yang, Y.; Li, X.; et al. Effective Treatment of Severe COVID-19 Patients with Tocilizumab. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2020, 117, 10970–10975. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- RECOVERY Collaborative Group; Horby, P.; Mafham, M.; Linsell, L.; Bell, J.L.; Staplin, N.; Emberson, J.R.; Wiselka, M.; Ustianowski, A.; Elmahi, E.; et al. Effect of Hydroxychloroquine in Hospitalized Patients with Covid. N. Engl. J. Med. 2020, 383, 2030–2040. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cavalcanti, A.B.; Zampieri, F.G.; Rosa, R.G.; Azevedo, L.C.P.; Veiga, V.C.; Avezum, A.; Damiani, L.P.; Marcadenti, A.; Kawano-Dourado, L.; Lisboa, T.; et al. Hydroxychloroquine with or without Azithromycin in Mild-to-Moderate Covid. N. Engl. J. Med. 2020, 383, 2041–2052. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Geleris, J.; Sun, Y.; Platt, J.; Zucker, J.; Baldwin, M.; Hripcsak, G.; Labella, A.; Manson, D.K.; Kubin, C.; Barr, R.G.; et al. Observational Study of Hydroxychloroquine in Hospitalized Patients with Covid. N. Engl. J. Med. 2020, 382, 2411–2418. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).