New Trends, Advantages and Disadvantages in Anticoagulation and Coating Methods Used in Extracorporeal Life Support Devices
Abstract
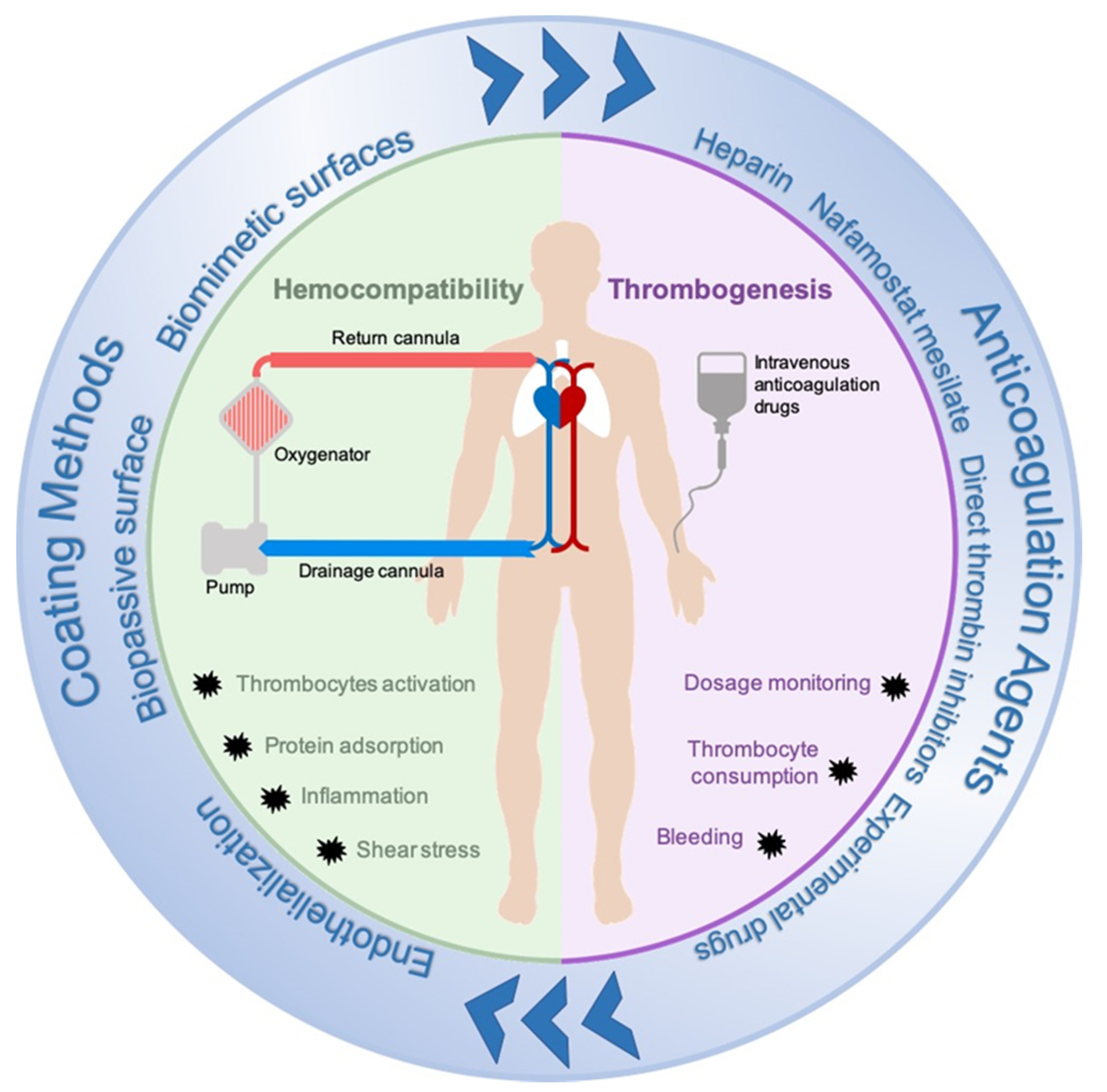
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
3. Results
3.1. Anticoagulation Agents
3.1.1. Clinically Used Anticoagulation Agents
Unfractionated Heparin
Nafamostat Mesilate
Direct Thrombin Inhibitors
3.1.2. Anticoagulation under Investigation
Low Molecular Weight Heparin
Recombinant Forms of Hirudin
Direct Oral Anticoagulants
3.2. Circuit Modifications: Coating Methods
3.2.1. Bioactive Surfaces
3.2.2. Biopassive Surfaces
3.2.3. Endothelialization
4. Future Perspective and Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Extracorporeal Life Support Organization. ELSO Registry International Summary. 2020. Available online: https://www.elso.org/Registry/Statistics/InternationalSummary.aspx (accessed on 22 December 2020).
- Millar, J.E.; Fanning, J.P.; McDonald, C.I.; McAuley, D.F.; Fraser, J.F. The inflammatory response to extracorporeal membrane oxygenation (ECMO): A review of the pathophysiology. Crit. Care 2016, 20, 1–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chung, M.; Cabezas, F.R.; Nunez, J.I.; Kennedy, K.F.; Rick, K.; Rycus, P.; Mehra, M.R.; Garan, A.R.; Kociol, R.D.; Grandin, E.W. Hemocompatibility-Related Adverse Events and Survival on Venoarterial Extracorporeal Life Support: An ELSO Registry Analysis. JACC Heart Fail. 2020, 8, 892–902. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thiagarajan, R.R.; Barbaro, R.; Rycus, P.T.; McMullan, D.M.; Conrad, S.A.; Fortenberry, J.D.; Paden, M.L. Extracorporeal Life Support Organization Registry International Report 2016. ASAIO J. 2017, 63, 60–67. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lequier, L.; Annick, G.; Al-Ibrahim, O.; Bembea, M.; Brodie, D.; Brogan, T.; Buckvold, S.; Chicoine, L.; Conrad, S.; Cooper, D.; et al. ELSO Anticoagulation Guidelines; The Extracorporeal Life Support Organization: Ann Arbor, MI, USA, 2014; pp. 1–17. [Google Scholar]
- Thomas, J.; Kostousov, V.; Teruya, J. Bleeding and Thrombotic Complications in the Use of Extracorporeal Membrane Oxygenation. Semin. Thromb. Hemost. 2018, 44, 020–029. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mulder, M.M.G.; Fawzy, I.; Lancé, M.D. ECMO and anticoagulation: A comprehensive review. Neth. J. Crit. Care 2018, 26, 6–13. [Google Scholar]
- Hou, X. Anticoagulation monitoring in extracorporeal membrane oxygenation. Perfusion 2021, 36, 438–439. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Giani, M.; Russotto, V.; Pozzi, M.; Forlini, C.; Fornasari, C.; Villa, S.; Avalli, L.; Rona, R.; Foti, G. Thromboelastometry, Thromboelastography, and Conventional Tests to Assess Anticoagulation During Extracorporeal Support: A Prospective Observational Study. ASAIO J. 2021, 67, 196–200. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Drop, J.G.; Erdem, Ö.; Wildschut, E.D.; Rosmalen, J.; Maat, M.P.M.; Kuiper, J.; Houmes, R.J.M.; Ommen, C.H. Use of rotational thromboelastometry to predict hemostatic complications in pediatric patients undergoing extracorporeal membrane oxygenation: A retrospective cohort study. Res. Pr. Thromb. Haemost. 2021, 5, 12553. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cuker, A. Clinical and Laboratory Diagnosis of Heparin-Induced Thrombocytopenia: An Integrated Approach. Semin. Thromb. Hemost. 2013, 40, 106–114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pollak, U. Heparin-induced thrombocytopenia complicating extracorporeal membrane oxygenation support: Review of the literature and alternative anticoagulants. J. Thromb. Haemost. 2019, 17, 1608–1622. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pabst, D.; Boone, J.B.; Soleimani, B.; Brehm, C.E. Heparin-induced thrombocytopenia in patients on extracorporeal membrane oxygenation and the role of a heparin-bonded circuit. Perfusion 2019, 34, 584–589. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Silvetti, S.; Koster, A.; Pappalardo, F. Do We Need Heparin Coating for Extracorporeal Membrane Oxygenation? New Concepts and Controversial Positions About Coating Surfaces of Extracorporeal Circuits. Artif. Organs 2014, 39, 176–179. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Murphy, D.A.; Hockings, L.E.; Andrews, R.K.; Aubron, C.; Gardiner, E.; Pellegrino, V.A.; Davis, A.K. Extracorporeal Membrane Oxygenation—Hemostatic Complications. Transfus. Med. Rev. 2015, 29, 90–101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Seeliger, B.; Döbler, M.; Friedrich, R.; Stahl, K.; Kühn, C.; Bauersachs, J.; Steinhagen, F.; Ehrentraut, S.F.; Schewe, J.-C.; Putensen, C.; et al. Comparison of anticoagulation strategies for veno-venous ECMO support in acute respiratory failure. Crit. Care 2020, 24, 1–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Baek, N.N.; Jang, H.R.; Huh, W.; Kim, Y.G.; Kim, D.J.; Oh, H.Y.; Lee, J.E. The role of nafamostat mesylate in continuous renal replacement therapy among patients at high risk of bleeding. Ren. Fail. 2012, 34, 279–285. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Han, S.J.; Han, W.; Song, H.-J.; Kim, C.-S.; Jeong, S.-M.; Kang, M.W. Validation of Nafamostat Mesilate as an Anticoagulant in Extracorporeal Membrane Oxygenation: A Large-Animal Experiment. Korean J. Thorac. Cardiovasc. Surg. 2018, 51, 114–121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, S.J.; Kim, H.S.; Kim, K.I.; Whang, S.M.; Hong, K.S.; Lee, W.K.; Lee, S.H. Use of Nafamostat Mesilate as an Anticoagulant during Extracorporeal Membrane Oxygenation. J. Korean Med Sci. 2011, 26, 945–950. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Han, W.; Bok, J.S.; Cho, H.J.; Yu, J.H.; Na, M.H.; Kang, S.; Kang, M.-W. Single-center experience of extracorporeal membrane oxygenation mainly anticoagulated with nafamostat mesilate. J. Thorac. Dis. 2019, 11, 2861–2867. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lim, J.Y.; Kim, J.B.; Choo, S.J.; Chung, C.H.; Lee, J.W.; Jung, S.H. Anticoagulation During Extracorporeal Membrane Oxygenation; Nafamostat Mesilate Versus Heparin. Ann. Thorac. Surg. 2016, 102, 534–539. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Di Nisio, M.; Middeldorp, S.; Büller, H.R. Direct Thrombin Inhibitors. N. Engl. J. Med. 2005, 353, 1028–1040. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, T.; He, J.; Wang, Z.; Cui, Z. Modification strategies to improve the membrane hemocompatibility in extracorporeal membrane oxygenator (ECMO). Adv. Compos. Hybrid Mater. 2021, 1–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Burstein, B.; Wieruszewski, P.M.; Zhao, Y.-J.; Smischney, N. Anticoagulation with direct thrombin inhibitors during extracorporeal membrane oxygenation. World J. Crit. Care Med. 2019, 8, 87–98. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Teruya, J.; Hensch, L.; Bruzdoski, K.; Adachi, I.; Hui, S.-K.R.; Kostousov, V. Monitoring bivalirudin therapy in children on extracorporeal circulatory support devices: Thromboelastometry versus routine coagulation testing. Thromb. Res. 2020, 186, 54–57. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ranucci, M.; Ballotta, A.; Kandil, H.; Isgrò, G.; Carlucci, C.; Baryshnikova, E.; Pistuddi, V.; The Surgical and Clinical Outcome Research Group. Bivalirudin-based versus conventional heparin anticoagulation for postcardiotomy extracorporeal membrane oxygenation. Crit. Care 2011, 15, R275. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pieri, M.; Agracheva, N.; Bonaveglio, E.; Greco, T.; De Bonis, M.; Covello, R.D.; Zangrillo, A.; Pappalardo, F. Bivalirudin Versus Heparin as an Anticoagulant During Extracorporeal Membrane Oxygenation: A Case-Control Study. J. Cardiothorac. Vasc. Anesth. 2013, 27, 30–34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Berei, T.J.; Lillyblad, M.P.; Wilson, K.J.; Garberich, R.F.; Hryniewicz, K.M. Evaluation of Systemic Heparin Versus Bivalirudin in Adult Patients Supported by Extracorporeal Membrane Oxygenation. ASAIO J. 2018, 64, 623–629. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kaseer, H.; Soto-Arenall, M.; Sanghavi, D.; Moss, J.; Ratzlaff, R.; Pham, S.; Guru, P. Heparin vs bivalirudin anticoagulation for extracorporeal membrane oxygenation. J. Card. Surg. 2020, 35, 779–786. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sanfilippo, F.; Asmussen, S.; Maybauer, D.M.; Santonocito, C.; Fraser, J.F.; Erdoes, G.; Maybauer, M. Bivalirudin for Alternative Anticoagulation in Extracorporeal Membrane Oxygenation: A Systematic Review. J. Intensiv. Care Med. 2017, 32, 312–319. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Netley, J.; Roy, J.; Greenlee, J.; Hart, S.; Todt, M.; Statz, B. Bivalirudin Anticoagulation Dosing Protocol for Extracorporeal Membrane Oxygenation: A Retrospective Review. J. Extra Corpor. Technol. 2018, 50, 161–166. [Google Scholar]
- Coughlin, M.A.; Bartlett, R.H. Anticoagulation for Extracorporeal Life Support: Direct Thrombin Inhibitors and Heparin. Asaio J. 2015, 61, 652–655. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Beiderlinden, M.; Treschan, T.; Görlinger, K.; Peters, J. Argatroban in Extracorporeal Membrane Oxygenation. Artif. Organs 2007, 31, 461–465. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sakai, M.; Ohteki, H.; Narita, Y.; Naitoh, K.; Natsuaki, M.; Itoh, T. Argatroban as a potential anticoagulant in cardiopulmonary bypass-studies in a dog model. Cardiovasc. Surg. 1999, 7, 187–194. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Young, G.; Yonekawa, K.E.; Nakagawa, P.; Nugent, D.J. Argatroban as an alternative to heparin in extracorporeal membrane oxygenation circuits. Perfusion 2004, 19, 283–288. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Menk, M.; Briem, P.; Weiss, B.; Gassner, M.; Schwaiberger, D.; Goldmann, A.; Pille, C.; Weber-Carstens, S. Efficacy and safety of argatroban in patients with acute respiratory distress syndrome and extracorporeal lung support. Ann. Intensiv. Care 2017, 7, 1–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dingman, J.S.; Smith, Z.R.; Coba, V.E.; Peters, M.A.; To, L. Argatroban dosing requirements in extracorporeal life support and other critically ill populations. Thromb. Res. 2020, 189, 69–76. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Traylor, K.L.; Witt, D.M.; Babin, J.L. Laboratory Monitoring of Low-Molecular-Weight Heparin and Fondaparinux. Semin. Thromb. Hemost. 2016, 43, 261–269. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Klein, S.M.; Slaughter, T.F.; Vail, P.T.; Ginsberg, B.; El-Moalem, H.E.; Alexander, R.; D’Ercole, F.; Greengrass, R.A.; Perumal, T.T.; Welsby, I.; et al. Thromboelastography as a perioperative measure of anticoagulation resulting from low molecular weight heparin: A comparison with anti-Xa concentrations. Anesth. Analg. 2000, 91, 1091–1095. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gratz, J.; Pausch, A.; Schaden, E.; Baierl, A.; Jaksch, P.; Erhart, F.; Hoetzenecker, K.; Wiegele, M. Low molecular weight heparin versus unfractioned heparin for anticoagulation during perioperative extracorporeal membrane oxygenation: A single center experience in 102 lung transplant patients. Artif. Organs 2020, 44, 638–646. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Krueger, K.; Schmutz, A.; Zieger, B.; Kalbhenn, J. Venovenous Extracorporeal Membrane Oxygenation With Prophylactic Subcutaneous Anticoagulation Only: An Observational Study in More Than 60 Patients. Artif. Organs 2017, 41, 186–192. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martel, N.; Lee, J.; Wells, P.S. Risk for heparin-induced thrombocytopenia with unfractionated and low-molecular-weight heparin thromboprophylaxis: A meta-analysis. Blood 2005, 106, 2710–2715. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Petros, S. Lepirudin in the management of patients with heparin-induced thrombocytopenia. Biol. Targets Ther. 2008, 2, 481–490. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deitcher, S.R.; Topoulos, A.P.; Bartholomew, J.R.; Kichuk-Chrisant, M.R. Lepirudin anticoagulation for heparin-induced thrombocytopenia. J. Pediatr. 2002, 140, 264–266. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Balasubramanian, S.K.; Tiruvoipati, R.; Chatterjee, S.; Sosnowski, A.; Firmin, R.K. Extracorporeal Membrane Oxygenation with Lepirudin Anticoagulation for Wegener’s Granulomatosis with Heparin-Induced Thrombocytopenia. ASAIO J. 2005, 51, 477–479. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dager, W.E.; Gosselin, R.C.; Yoshikawa, R.; Owings, J.T. Lepirudin in Heparin-Induced Thrombocytopenia and Extracorporeal Membranous Oxygenation. Ann. Pharmacother. 2004, 38, 598–601. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Frame, J.N.; Rice, L.; Bartholomew, J.R.; Whelton, A. Rationale and design of the PREVENT-HIT study: A randomized, open-label pilot study to compare desirudin and argatroban in patients with suspected heparin-induced thrombocytopenia with or without thrombosis. Clin. Ther. 2010, 32, 626–636. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boyce, S.W.; Bandyk, D.F.; Bartholomew, J.R.; Frame, J.N.; Rice, L. A Randomized, Open-Label Pilot Study Comparing Desirudin and Argatroban in Patients With Suspected Heparin-Induced Thrombocytopenia With or Without Thrombosis: PREVENT-HIT Study. Am. J. Ther. 2011, 18, 14–22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Phan, X.T.; Nguyen, T.H.; Tran, T.T.; Huynh, T.-H.T.; Hoang, T.-H.T.; Nguyen, V.-C.V.; Pham, T.N.T. Suspected heparin-induced thrombocytopenia in a COVID-19 patient on extracorporeal membrane oxygenation support: A case report. Thromb. J. 2020, 18, 1–5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ryerson, L.M.; Lequier, L.L. Anticoagulation Management and Monitoring during Pediatric Extracorporeal Life Support: A Review of Current Issues. Front. Pediatr. 2016, 4, 67. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pflaum, M.; Kühn-Kauffeldt, M.; Schmeckebier, S.; Dipresa, D.; Chauhan, K.; Wiegmann, B.; Haug, R.; Schein, J.; Haverich, A.; Korossis, S. Endothelialization and characterization of titanium dioxide-coated gas-exchange membranes for application in the bioartificial lung. Acta Biomater. 2017, 50, 510–521. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arens, J.; Grottke, O.; Haverich, A.; Maier, L.S.; Schmitz-Rode, T.; Steinseifer, U.; Wendel, H.; Rossaint, R. Toward a Long-Term Artificial Lung. ASAIO J. 2020, 66, 847–854. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gerling, K.; Ölschläger, S.; Avci-Adali, M.; Neumann, B.; Schweizer, E.; Schlensak, C.; Wendel, H.-P.; Stoppelkamp, S. A Novel C1-Esterase Inhibitor Oxygenator Coating Prevents FXII Activation in Human Blood. Biomolecules 2020, 10, 1042. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lequier, L.; Horton, S.B.; McMullan, D.M.; Bartlett, R.H. Extracorporeal Membrane Oxygenation Circuitry. Pediatr. Crit. Care Med. 2013, 14, S7–S12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Borchardt, R.; Schlanstein, P.; Arens, J.; Graefe, R.; Schreiber, F.; Schmitz-Rode, T.; Steinseifer, U. Description of a Flow Optimized Oxygenator With Integrated Pulsatile Pump. Artif. Organs 2010, 34, 904–910. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hesselmann, F.; Focke, J.M.; Schlanstein, P.C.; Steuer, N.B.; Kaesler, A.; Reinartz, S.D.; Schmitz-Rode, T.; Steinseifer, U.; Jansen, S.V.; Arens, J. Introducing 3D-potting: A novel production process for artificial membrane lungs with superior blood flow design. Bio-Design Manuf. 2021, 1–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thompson, A.J.; Buchan, S.; Carr, B.; Poling, C.; Hayes, M.; Fernando, U.P.; Kaesler, A.; Schlanstein, P.; Hesselmann, F.; Arens, J.; et al. Low-Resistance, Concentric-Gated Pediatric Artificial Lung for End-Stage Lung Failure. ASAIO J. 2020, 66, 423–432. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arens, J.; Schnoering, H.; Pfennig, M.; Mager, I.; Vázquez-Jiménez, J.F.; Schmitz-Rode, T.; Steinseifer, U. The Aachen MiniHLM—A miniaturized heart-lung machine for neonates with an integrated rotary blood pump. Artif. Organs. 2010, 34, 707–713. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schiel, S.B.S.; Nogawa, A.; Rice, R.; Anzai, T.; Tanaka, M. X Coating: A new biopassive polymer coating. Can. Perfus. Can. 2001, 11, 8–17. [Google Scholar]
- Jaffer, I.H.; Fredenburgh, J.C.; Hirsh, J.; Weitz, J.I. Medical device-induced thrombosis: What causes it and how can we prevent it? J. Thromb. Haemost. 2015, 13, S72–S81. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ontaneda, A.; Annich, G.M. Novel Surfaces in Extracorporeal Membrane Oxygenation Circuits. Front. Med. 2018, 5, 321. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gerlach, M.; Föhre, B.; Keh, D.; Riess, H.; Falke, K. Global and Extended Coagulation Monitoring during Extracorporeal Lung Assist with Heparin-Coated Systems in ARDS Patients. Int. J. Artif. Organs 1997, 20, 29–36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ao, H.; Tajiri, A.; Yanagi, F.; Okamoto, T.; Tashiro, M.; Sakanashi, Y.; Tanimoto, H.; Moon, J.; Terasaki, H. Heparin Bonding of the Extracorporeal Circuit Reduces Thrombosis During Prolonged Lung Assist in Goats. ASAIO J. 2000, 46, 723–729. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ichinose, K.; Okamoto, T.; Tanimoto, H.; Yoshitake, A.; Tashiro, M.; Sakanashi, Y.; Kuwana, K.; Tahara, K.; Kamiya, M.; Terasaki, H. Comparison of a New Heparin-coated Dense Membrane Lung with Nonheparin-coated Dense Membrane Lung for Prolonged Extracorporeal Lung Assist in Goats. Artif. Organs 2004, 28, 993–1001. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tashiro, M.; Okamoto, T.; Sakanashi, Y.; Ao, H.; Imaizumi, T.; Tanimoto, H.; Yanagi, F.; Sugita, M.; Mimura, R.; Terasaki, H. Experimental evaluation of the V-point heparin-bonding system applied to a dense-membrane artificial lung during 24-hour extracorporeal circulation in beagles. Artif. Organs 2001, 25, 655–663. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Larm, O.; Larsson, R.; Olsson, P. A New Non-Thrombogenic Surface Prepared by Selective Covalent Binding of Heparin Via a Modified Reducing Terminal Residue. Biomater. Med Devices, Artif. Organs 1983, 11, 161–173. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tanzi, M.C. Bioactive technologies for hemocompatibility. Expert Rev. Med Devices 2005, 2, 473–492. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ashcraft, M.; Douglass, M.; Chen, Y.; Handa, H. Combination strategies for antithrombotic biomaterials: An emerging trend towards hemocompatibility. Biomater. Sci. 2021, 9, 2413–2423. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Videm, V.; Svennevig, J.L.; Fosse, E.; Semb, G.; Osterud, A.; Mollnes, T.E. Reduced complement activation with heparin-coated oxygenator and tubings in coronary bypass operations. J. Thorac. Cardiovasc. Surg. 1992, 103, 806–813. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wendel, H.; Ziemer, G. Coating-techniques to improve the hemocompatibility of artificial devices used for extracorporeal circulation. Eur. J. Cardio Thorac. Surg. 1999, 16, 342–350. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maul, T.M.; Massicotte, M.P.; Wearden, P.D. ECMO Biocompatibility: Surface Coatings, Anticoagulation, and Coagulation Monitoring. In Extracorporeal Membrane Oxygenation: Advances in Therapy; IntechOpen: London, UK, 2016. [Google Scholar]
- Doymaz, S. Anticoagulation during ECMO: The Past, Present and Future. J. Intensiv. Crit. Care 2018, 4, 1–6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Yang, Z.; Yang, Y.; Xiong, K.; Li, X.; Qi, P.; Tu, Q.; Jing, F.; Weng, Y.; Wang, J.; Huang, N. Nitric oxide producing coating mimicking endothelium function for multifunctional vascular stents. Biomaterials 2015, 63, 80–92. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chiletti, R.; Horton, S.; Bednarz, A.; Bartlett, R.; Butt, W. Safety of nitric oxide added to the ECMO circuit: A pilot study in children. Perfusion 2018, 33, 74–76. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roberts, T.R.; Garren, M.R.; Handa, H.; Batchinsky, A.I. Toward an artificial endothelium: Development of blood-compatible surfaces for extracorporeal life support. J. Trauma Acute Care Surg. 2020, 89, S59–S68. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- De Somer, F.; François, K.; Van Oeveren, W.; Poelaert, J.; De Wolf, D.; Ebels, T.; Van Nooten, G. Phosphorylcholine coating of extracorporeal circuits provides natural protection against blood activation by the material surface. Eur. J. Cardio-Thoracic Surg. 2000, 18, 602–606. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Thiara, A.S.; Andersen, V.Y.; Videm, V.; Mollnes, T.E.; Svennevig, K.; Hoel, T.N.; Fiane, A.E. Comparable biocompatibility of Phisio- and Bioline-coated cardiopulmonary bypass circuits indicated by the inflammatory response. Perfusion 2010, 25, 9–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gunaydin, S.; Farsak, B.; Kocakulak, M.; Sari, T.; Yorgancioglu, C.; Zorlutuna, Y. Clinical performance and biocompatibility of poly(2-methoxyethylacrylate)—coated extracorporeal circuits. Ann. Thorac. Surg. 2002, 74, 819–824. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Murakami, D.; Mawatari, N.; Sonoda, T.; Kashiwazaki, A.; Tanaka, M. Effect of the Molecular Weight of Poly(2-methoxyethyl acrylate) on Interfacial Structure and Blood Compatibility. Langmuir 2018, 35, 2808–2813. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Teligui, L.; Dalmayrac, E.; Mabilleau, G.; Macchi, L.; Godon, A.; Corbeau, J.J.; Denommé, A.S.; Bouquet, E.; Boer, C.; Baufreton, C. An ex vivo evaluation of blood coagulation and thromboresistance of two extracorporeal circuit coatings with reduced and full heparin dose. Interact. Cardiovasc. Thorac. Surg. 2014, 18, 763–769. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Blackman, L.D.; Gunatillake, P.A.; Cass, P.; Locock, K.E.S. An introduction to zwitterionic polymer behavior and applications in solution and at surfaces. Chem. Soc. Rev. 2019, 48, 757–770. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, Y.-B.; Shi, K.-H.; Jiang, H.-L.; Gong, Y.-K. Significantly reduced adsorption and activation of blood components in a membrane oxygenator system coated with crosslinkable zwitterionic copolymer. Acta Biomater. 2016, 40, 153–161. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Preston, T.J.; Ratliff, T.M.; Gomez, D.; Olshove, V.F.; Nicol, K.K.; Sargel, C.L.; Chicoine, L.G. Modified Surface Coatings and their Effect on Drug Adsorption within the Extracorporeal Life Support Circuit. J. Extra Corpor. Technol. 2010, 42, 199–202. [Google Scholar]
- Zwirner, U.; Höffler, K.; Pflaum, M.; Korossis, S.; Haverich, A.; Wiegmann, B. Identifying an optimal seeding protocol and endothelial cell substrate for biohybrid lung development. J. Tissue Eng. Regen. Med. 2018, 12, 2319–2330. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cornelissen, C.G.; Dietrich, M.; Gromann, K.; Frese, J.; Krueger, S.; Sachweh, J.S.; Jockenhoevel, S. Fibronectin coating of oxygenator membranes enhances endothelial cell attachment. Biomed. Eng. Online 2013, 12, 7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pflaum, M.; Merhej, H.; Peredo, A.; De, A.; Dipresa, D.; Wiegmann, B.; Wolkers, W.; Haverich, A.; Korossis, S. Hypothermic preservation of endothelialized gas-exchange membranes. Artif. Organs 2020, 44, e552–e565. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wiegmann, B.; Figueiredo, C.; Gras, C.; Pflaum, M.; Schmeckebier, S.; Korossis, S.; Haverich, A.; Blasczyk, R. Prevention of rejection of allogeneic endothelial cells in a biohybrid lung by silencing HLA-class I expression. Biomaterials 2014, 35, 8123–8133. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Moore, C.A.; Shah, N.N.; Smith, C.P.; Rameshwar, P. 3D Bioprinting and Stem Cells. Methods Mol. Biol. 2018, 1842, 93–103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
| Anticoagulation Agent | Inhibition Site | Monitoring | Half-Time | Antidote | Advantages | Disadvantages | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Clinically Used Anticoagualtion Agents | Unfractionated Heparin | Factor Xa and thrombin inhibition | Anti-factor Xa, ACT, aPTT | 1–3 h | Protamine-sulfate | Saturable clearance mechanism and renal clearance, widely used most experience | Risk of HITT, variable effects on APTT, no linear effect |
| Nafamostat mesilate | Serine protease inhibitor | ACT, aPTT | 8–10 min | No antidote | Short half time anti-inflammatory effect | No large prospective trials available, short half time, higher costs than UFH | |
| Bivalirudin | Direct thrombin inhibitor | ACT, aPPT, PTT | 25 min | No antidote | Renal clearance no risk for HITT easy titration | May interfere with APTT, less effective inhibition in areas of stasis | |
| Argatroban | Direct thrombin inhibitor | ACT, aPTT | 45–50 min | No antidote | Hepatic clearance No risk for HITT Good dose response | Can interfere with INR, lesser coagulation inhibition in areas of stasis | |
| Anticoagulant Agents Under Investigation | Low-molecular-weight-heparin | Factor IIa and Xa inhibition | Anti-factor Xa, aPTT | 3–6 h | Protamine-sulfate | lower risk of HITT partially effective | AntiXa levels, accumulation in renal impairment |
| Lepirudin | Direct thrombin inhibitor | ACT, aPTT, ECT | 1–2 h | No antidote | Renal clearance No risk for HITT | Limited evidence in ECLS, risk for anaphylaxis, no longer available | |
| Rivaroxaban | Direct-Xa inhibitor | Anti-factor Xa | 5–9 h | Andexanet alfa | Rapid onset of action, few drug interactions | No clear laboratory monitoring available, only oral administration possible |
| Main Coating Compount(s) | Commercial Name of Coating | Company | |
|---|---|---|---|
| Bioactive | Heparin | Cortiva Bioactive surface | Medtronic |
| Heparin | Rheoparin | Xenios/Fresenius | |
| Albumin + Heparin | Bioline | Maquet/Getinge | |
| Albumin + Heparin | X.ellence | Xenios/Fresenius | |
| Biopassive | Albumin | Rheopak | Chalice Medical |
| Albumin | Recombinant Albumin Coating | Hemovent | |
| Albumin | Safeline (discontinued) | Maquet/Getinge | |
| Albumin | X.eed | Xenios/Fresenius | |
| Phosphorylcholine | PC phosphorylcholine | Eurosets | |
| Phosphorylcholine | PH.I.S.I.O Coating | Liva Nova | |
| poly(2-methoxyethylacrylate) (PMEA) | Xcoating | Terumo | |
| Sulphate and sulphonate groups and polyethylene oxide (PEO) | Balance Biosurface | Medtronic | |
| Sulphonate groups, polyethylene oxide (PEO) and heparin | Trillium Biosurface | Medtronic | |
| Amphyphilic polymer | Softline | Maquet/Getinge |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Willers, A.; Arens, J.; Mariani, S.; Pels, H.; Maessen, J.G.; Hackeng, T.M.; Lorusso, R.; Swol, J. New Trends, Advantages and Disadvantages in Anticoagulation and Coating Methods Used in Extracorporeal Life Support Devices. Membranes 2021, 11, 617. https://doi.org/10.3390/membranes11080617
Willers A, Arens J, Mariani S, Pels H, Maessen JG, Hackeng TM, Lorusso R, Swol J. New Trends, Advantages and Disadvantages in Anticoagulation and Coating Methods Used in Extracorporeal Life Support Devices. Membranes. 2021; 11(8):617. https://doi.org/10.3390/membranes11080617
Chicago/Turabian StyleWillers, Anne, Jutta Arens, Silvia Mariani, Helena Pels, Jos G. Maessen, Tilman M. Hackeng, Roberto Lorusso, and Justyna Swol. 2021. "New Trends, Advantages and Disadvantages in Anticoagulation and Coating Methods Used in Extracorporeal Life Support Devices" Membranes 11, no. 8: 617. https://doi.org/10.3390/membranes11080617
APA StyleWillers, A., Arens, J., Mariani, S., Pels, H., Maessen, J. G., Hackeng, T. M., Lorusso, R., & Swol, J. (2021). New Trends, Advantages and Disadvantages in Anticoagulation and Coating Methods Used in Extracorporeal Life Support Devices. Membranes, 11(8), 617. https://doi.org/10.3390/membranes11080617







