Abstract
Background: The mucosal high-risk (HR) human papillomavirus (HPV) is associated with oropharyngeal carcinogenesis. Aims of this study were to evaluate the prevalence of HR-HPV infection in laryngeal squamous cell carcinoma (LSCC) from different subsites, and the clinico-biological meaning of p16 overexpression. Methods: Ninety-seven LSCCs submitted to primary surgery (n = 75) or to post-irradiation salvage laryngectomy (n = 22) were evaluated for HR-HPV DNA and RNA using Luminex-based assays. p16 immunohistochemistry was performed. Results: HR-HPV DNA from HPV16 was detected in seven cases (8.75%), without significant differences between supraglottic and glottic lesions. HPV RNA was never detected. p16 overexpression correlated with HR-HPV DNA, but the kappa agreement score was poor. HPV DNA showed no impact on prognosis. p16 overexpression was associated with a better survival (OS, RFS) in primarily operated cases, while an inverse association with OS was observed in the salvage surgery group. Conclusions: HR-HPV infection appears to have a marginal role in LSCC independent of the anatomical subsite. p16 expression is deregulated in LSCC independent of HPV but displays a prognostic role in patients submitted to primary surgery. The negative predictive role of p16 overexpression in patients undergoing salvage surgery deserves more investigations for validation and elucidation of its clinical relevance.
1. Introduction
Human papillomaviruses (HPVs) are known to infect cutaneous and mucosal epithelia. Some types of HPV from genus alpha, in particular HPV16, have been associated with many human cancers, i.e., cervical, oropharyngeal, anal, vulvar, and penile [1,2] and are collectively called high-risk human papillomavirus (HR HPV) genotypes. The role of HPV in the carcinogenic process in humans is mainly mediated by two oncoproteins, E6 and E7 [3]. A total of 31.1% of cancers attributable to infectious agents, amounting to more than 690,000 cancers diagnosed each year (500,000 of which are cervical cancers) are attributed to HR HPV [4].
The role of HPV in laryngeal carcinogenesis, postulated back in the 1980s [5], is less prominent than in other sites and is not currently considered clinically relevant [6,7]. In IARC’s Monograph 100B, the evidence for a role of HPV16 and 18 in LSCC is defined as “non-conclusive” [1]. All the available guidelines and protocols dealing with HPV-driven carcinogenesis in head and neck, such as those from the National Comprehensive Cancer Network, the College of American Pathologists, the Royal College of Pathologists, and Cancer Care Ontario (currently under review), only recommend HPV detection in OPSCC [8]. Rates of HPV infection in LSCCs reported in the literature are extremely variable. IARC’s Monograph 90 [9], which included only PCR-based studies, found a positivity rate ranging from 7% to 59% and prominence of HPV16 (74%). Reported detection rates are influenced by the population tested, the methodology used, and possibly the site of origin of the lesion. In fact, a higher prevalence of HPV in LSCCs of the supraglottic and in particular of the marginal area has been reported [10].
However, the mere detection of HPV DNA is not indicative of a cancerogenic role of HPV in a certain malignancy. Only detection methods able to demonstrate transcription of E6 and E7 viral oncogenes, such as mRNA detection essays, can give some evidence of an active role of the virus [11]. Studies using such methods are much less common but are of paramount importance in defining the role of HPV in LSCCs [10,12,13,14,15,16,17,18,19] and indicate a prevalence of HPV-driven carcinogenesis outside the oropharynx probably not exceeding 5% of the SCCs, if not lower.
p16 is an onco-suppressor that negatively regulates cell cycle progression by inhibiting cyclin-dependent kinases, frequently inactivated in many human malignancies [20,21,22,23,24]. Being a well-known epiphenomenon of the E7 mediated unlocking of the G1-S restriction point through the inhibition and degradation of pRb, the overexpression of the p16 protein has been widely used as a surrogate marker of HPV-driven carcinogenesis in a subset neoplasms known to be HPV-related [1]. The clinical reliability of such a role in head and neck cancer, and oropharyngeal squamous cell carcinoma in particular, is currently a relevant matter of debate [10,25,26], yet p16 overexpression is considered a reliable surrogate marker of HPV-driven carcinogenesis in the new American Joint Committee on Cancer (AJCC) staging system for oropharyngeal squamous cell carcinoma (OPSCC) [27,28].
The role of p16 as a standalone prognostic marker, disentangled by its relevance as a surrogate marker for HPV, has been investigated in breast cancer, where its expression seems related to a worse prognosis [29], and in oesophageal squamous cell carcinoma, where among conflicting reports some suggest that it may predict a better overall survival [30]. In laryngeal squamous cell carcinoma (LSCC), the expression pattern of p16 has been investigated, but available data regarding its role as a standalone marker are conflicting. Some reports in the literature connect the expression of p16 with a lack of progression to cancer from precancerous lesions [31], a trend toward better survival in RT-treated patients [17], a longer relapse-free survival (RFS) [14,32], and in a recent paper a significant impact both on disease-specific survival and overall survival in surgically treated patients [33]. However, other studies failed to confirm these findings [26,34,35,36].
The main aim of the present study was to investigate the presence of HPV oncogenes in laryngeal cancers through DNA and mRNA detection assays in the same samples, as well as to investigate the role of p16 as a surrogate marker of HPV infection and/or prognostic marker in LSCC. A secondary aim was to verify the hypothesis of a specific HPV carcinogenic role in the supraglottic/marginal larynx.
2. Materials and Methods
Ninety-seven LSCC patients submitted to primary and salvage surgery at Policlinico Gemelli Hospital (Catholic University of the Sacred Heart), Rome, between 1998 and 2013 were included. Data about smoking and alcohol consumption had been collected. All patients had undergone a careful work up, as described elsewhere [37,38,39], all cases had been discussed and followed up by the tumour board and the clinical data archived prospectively in a digital archive (SpiderNet/Speed). Upon retrieval from the archive, all cases were restaged with the VIIth version of the AJCC staging system. All patients provided their informed consent. Exclusion criteria were non-squamous histology, denial of informed consent, or scarcity of stored FFPE material in the histopathology archive. The last criterion led to the exclusion of primary early glottic cancers, most often diagnosed through very small samples (often less than 2 mm3).
The present study was approved by the local ethical committee of Fondazione Policlinico Universitario A. Gemelli (Prot Mol.HN sf33976/16 rif. A. 20363/13 id. 204).
2.1. Preparation of Paraffin Sections and DNA Extraction
Slides, prepared at the Institute of Microbiology of Policlinico Gemelli according to the HPV-AHEAD protocol, were sent to the laboratories of the IARC Infections and Cancer Biology group at Lyon, France, for HPV DNA analysis. DNA was extracted after an overnight incubation of the paraffin tissue sections in a digestion buffer (10 mM Tris/HCl pH 7.4, 0.5 mg/mL proteinase K, and 0.4% Tween 20).
2.2. HPV Type-Specific E7 PCR Bead-Based Multiplex Genotyping
HPV DNA positivity was determined by a type-specific multiplex genotyping (TS-MPG) assay combining multiplex PCR and bead-based Luminex technology (Luminex Corporation, Austin, TX, USA). The test uses type-specific primers targeting the E7 region of 19 different hr-HPV (HPV 16, 18, 26, 31, 33, 35, 39, 45, 51, 52, 53, 56, 58, 59, 66, 68a and b, 70, 73, and 82) and 2 low risk HPV (HPV 6 and 11) genotypes.
Two primers for the amplification of β-globin were included as a positive control for template DNA quality. After PCR amplification, 10 μL of each reaction mixture was analysed by multiplex HPV genotyping (MPG) using Luminex technology (Luminex Corporation, Austin, TX, USA) as described previously [40]. All HPV DNA-positive FFPE specimens and a randomly selected subgroup of approximately 10% of HPV DNA-negative specimens were further analysed for the presence of HPV E6*I mRNA.
2.3. HPV RNA Analysis
Total RNA was purified from three pooled sections of the same tissue block using the Pure Link FFPE Total RNA Isolation Kit (Invitrogen, Carlsbad, CA) as described previously [41]. RT-PCR was carried out using the QuantiTect Virus Kit (Qiagen, Hilden, Germany) in a total volume of 25 μL containing 5 μL of 5xQuantiTect Virus Mastermix, 0.25 μL of 100xQuantiTect Virus RT Mix, 0.4 μM of each oligonucleotide, and 1 μL RNA as described previously [42]. The HPV type-specific E6*I mRNA assay developed for 20 HR- or pHR-HPV types was applied for the detection of viral transcripts. The assay amplifies a 65–75 base pair amplicon of HPV and an 81 base pair amplicon of ubiquitin C (ubC) cDNA.
The HPV RNA analysis was performed at the German Cancer Research Center laboratories in Heidelberg, Germany.
2.4. p16 Immunohistochemistry
P16 expression was evaluated by IHC through a monoclonal antibody (clone E6H4, CINtec p16 Histology Kit, Mtm-laboratories, Heidelberg, Germany). FFPE sections were deparaffinized with xylene and rehydrated with alcohol. Antigens were retrieved with a 10 min cycle in epitope retrieval solution (pH 9.0, 95–99 °C). The material was then cooled down at room temperature for 20 min. Endogenous peroxidase was blocked with 5 min immersion in 3% hydrogen peroxide solution. Then a 30 min incubation with the p16 antibody at room temperature was performed, followed by an incubation with a secondary goat anti-mouse for p16. Finally, the sample has been developed with a chromogen substrate solution for 10 min (AEC; Dako, Copenhagen, Denmark) and then stained with haematoxylin (Dako), dehydrated, mounted on slides with a permanent mounting medium and covered. Immunoreactivity was evaluated under microscopic vision. Scoring was performed by an expert pathologist, and the semiquantitative method used included only nuclear staining using the German immunoreactive score of Remmele and Stegner (IRS). An intensity score (absent: 0, weak: 1, moderate: 2, strong: 3) and an extension score (0% = 0, 1–10% = 1, 11–50% = 2, 51– 80% = 3, 81–100% = 4) were attributed to each case. A composite IRS score accounting for both was then calculated by multiplying the sheer numbers (0–12). IHC procedures were performed at the Institute of Histopathology, Policlinico Gemelli, Rome, Italy.
2.5. Statistics
Two IRS cut-offs (4 and 6, respectively) were tested with regard to prediction of HPV infection and/or prognosis. The first one was already described in the literature for the evaluation of p16 expression [43]; we also evaluated a higher cut-off, closer to the one most used in the literature [44], to reduce false-positive cases, which are the most undesirable from the perspective of treatment deintensification [27].
Statistical analysis was performed using JMP software, release 7.0.1, from the SAS Institute. The correlation between p16 IHC and HPV status was verified using a χ2 test. To assess the reliability of p16 IHC as a diagnostic test for HPV-driven carcinogenesis we computed the Kappa value as previously described [10,25]. Survival curves were always calculated from the time of the first diagnosis. For the univariate analysis, Kaplan–Meyer curves were calculated, and significance was evaluated with the Log-Rank tests.
3. Results
3.1. Clinicopathological Data
The study includes 97 LSCC patients. For every patient, we analysed just one tumour sample coming from the main surgery, which in 75 cases (77.3%) was the primary treatment (with or without adjuvant therapy), and in 22 cases (22.7%) was performed for salvage after recurrence. Table 1 lists the patients’ characteristics and the clinicopathological features. As expected, alcohol consumption correlated with supraglottic site; no other correlation was detected among behavioural risk factors, staging data, HPV DNA, p16 IHC. No correlation between behavioural risk factors and prognosis was detected. At the last follow-up, 2 patients were alive with disease (2.1%), 11 were dead from other diseases (11.3%), 24 were dead from disease (24.7%), and 60 were alive with no evident disease (61.9%). Along their clinical history, 55 patients had a relapse (56.7%) (39 [40.2%] local, 1 [1%] local and distant, 8 [8.2%] locoregional, 3 [3.1%] regional, and 4 [4.1%] distant).

Table 1.
Personal and clinicopathological data of the patients, stratified in primary and salvage surgeries. Groups were compared by means of Mann-Whitney U test and chi-square test.
Seventeen samples resulted negative for ß-globin and were excluded for viral DNA/RNA analyses (Figure 1).
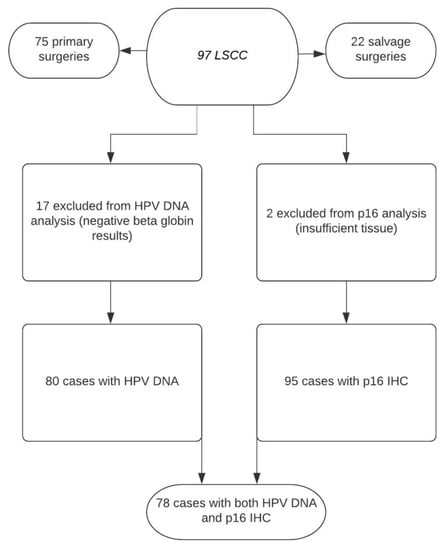
Figure 1.
Flowchart describing the availability of data for different patient groups.
3.2. HPV DNA, RNA and p16 Testing Results
Among the 80 cases tested for HPV DNA, 7 (8.75%) tested positive for HR-HPV16 DNA. No correlation was found between the subsite and HPV DNA positivity (p = 0.505). All the HPV DNA-positive cases were further tested for viral RNA but found none of them was positive for HPV RNA, although all seven samples resulted positive for the RNA quality control marker, ubiquitin C (ubC). In 2 out of 97 cases, p16 IHC could not be evaluated for insufficient FFPE tissue. Of the remaining 95 samples, 48.42% were positive for p16 overexpression with an IRS cut-off ≥4 (moderate intensity in at least 11–50% of cells), while only 31.57% were positive with a cut-off ≥6 (moderate intensity in 51–80% of cells or strong intensity in 11–50% of cells).
We evaluated the correlation between p16 IHC and HPV DNA status in the 78 cases where both were available, detecting a significant correlation only when considering as cut-off the composite IRS score ≥ 4 (p = 0.007 at Likelihood Ratio test) but not when considering the composite IRS score ≥ 6 (p = 0.0733 at Likelihood Ratio test). We then checked the reliability of p16 IHC as a surrogate marker for HPV DNA detection, obtaining a poor agreement (Kappa = 0.14 with IRS score ≥ 4 and Kappa = 0.133 with IRS score ≥ 6), deriving from the high number of false-positive cases (Figure 2).
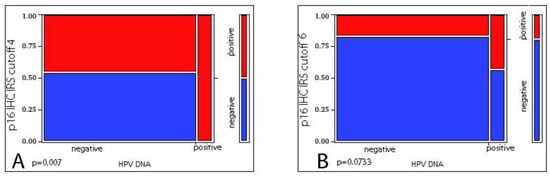
Figure 2.
Correlation between p16 IHC and HPV DNA ((A) IRS score ≥ 4 p = 0.007 at Likelihood Ratio test; (B) IRS score ≥ 6 p = 0.0733 at Likelihood Ratio test).
3.3. HPV DNA, RNA, and p16 Impact on Prognosis
Next, we evaluated the impact of HPV DNA detection on prognosis, even if transcriptionally active HPV was demonstrated through mRNA testing in none of the cases. HPV DNA detection was not associated with differences in overall survival (OS) (p = 0.64 at Log-Rank) (Figure 3A), relapse-free survival (RFS) (p = 0.86 at Log-Rank) (Figure 3D), or disease-specific survival (DSS) (p = 0.93 at Log-Rank).
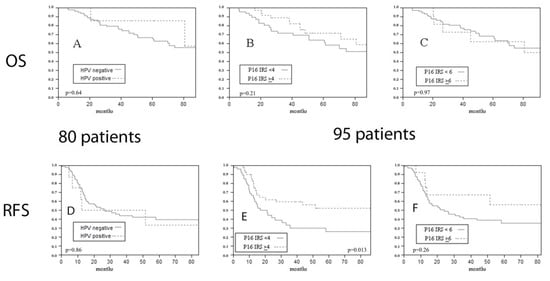
Figure 3.
Impact of HPV DNA ((A) p = 0.64 at Log-Rank) and of p16 expression ((B) IRS ≥ 4 cut-off p = 0.21 at Log-Rank; (C) IRS ≥ 6 cut-off p = 0.97 at Log-Rank) on overall survival. Impact of HPV DNA ((D) p = 0.86 at Log-Rank) and of p16 expression ((E) IRS ≥ 4 cut-off p = 0.013 at Log-Rank; (F) IRS ≥ 6 cut-off p = 0.26 at Log-Rank) on relapse free survival of the overall series.
p16 overexpression did not show any predictive value for OS (IRS ≥ 4 cut-off p = 0.21 at Log-Rank; IRS ≥ 6 cut-off p = 0.97 at Log-Rank) (Figure 3B,C) or DSS (IRS ≥ 4 cut-off p = 0.85 at Log-Rank; IRS ≥ 6 cut-off p = 0.96 at Log-Rank), but higher p16 expression with the IRS ≥ 4 cut-off was associated with a significantly better RFS (IRS ≥ 4 cut-off p = 0.013 at Log-Rank; IRS ≥ 6 cut-off p = 0.26 at Log-Rank) (Figure 3E,F).
When primary cases (n = 75) and post-irradiation recurrences (n = 22) were analysed separately, p16 positivity at IHC, with IRS > 4 as cut-off, was associated with a better OS in primarily operated cases (IRS ≥ 4 cut-off p = 0.015 at Log-Rank; IRS ≥ 6 cut-off p = 0.5 at Log-Rank), and, surprisingly, with worse overall survival in salvage surgeries after irradiation (IRS ≥ 4 cut-off p = 0,038 at Log-Rank test; IRS ≥ 6 cut-off p = 0.07 at Log-Rank) (Figure 4).

Figure 4.
Impact of HPV DNA ((A) p = 0.48 at Log-Rank; D p = 0.62 at Log-Rank) and of p16 expression ((B) IRS ≥ 4 cut-off p = 0.015 at Log-Rank; (C) IRS ≥ 6 cut-off p = 0.5 at Log-Rank; (E) IRS ≥ 4 cut-off p = 0.038 at Log-Rank test; (F) IRS ≥ 6 cut-off p = 0.07 at Log-Rank), when available, on OS in primarily operated cases (A–C) and in salvage surgeries (D–F). p16 overexpression with a IRS score>4 is associated with better survival in primaries (B) and to a worse survival in recurrences (E).
We calculated RFS from the time of first treatment; so, in the salvage surgery group, where the time of surgery and of sample collection coincided with time to recurrence, this oncological endpoint was not considered. When evaluating RFS in primarily operated cases, p16 overexpression, considering a composite score ≥ 4, showed an association with a better RFS (IRS ≥ 4 cut-off p = 0.049 at Log-Rank; IRS ≥ 6 cut-off p = 0.26 at Log-Rank) (Figure 5).
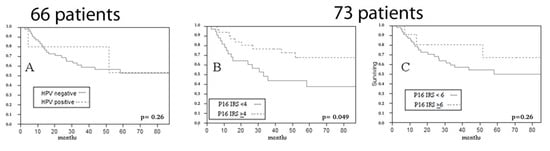
Figure 5.
Impact of HPV DNA ((A) p = 0.26 at Log-Rank) and of p16 expression ((B) IRS ≥ 4 cut-off p = 0.049 at Log-Rank; (C) IRS ≥ 6 cut-off p = 0.26 at Log-Rank) on relapse free survival of primarily operated patients (HPV DNA was available in 66 cases, p16 IHC in 73).
4. Discussion
LSCC is the only head and neck site with decreasing survival rates in recent decades [43,45]. Such a trend has been linked to the push towards surgical and non-surgical function/organ preservation [38], in the absence of reliable predictive biomarkers to help in treatment selection. With these premises and considering the well-known prognostic role in OPSCC [14,25,46], it is clear why a potential role of HPV in LSCCs has raised great interest. In the present series, conducted with patients mostly coming from Central and Southern Italy, HPV DNA was detected in about 9% of LSCC, well within the wide range (5.7–25%) reported in the most recent literature [10,12,13,14,18,19,41,47,48,49]. Our data do not lend support to the hypothesis of a prevalent role of HPV in supraglottic SCC [10].
Regardless, in the larynx more than in the oropharynx, where the role of HPV infection is proven, the transcriptional activity and in particular the expression of HPV oncogenes E6 and E7 appears fundamental to hypothesize a carcinogenic role. Data from the literature indicate without doubt that the prevalence of HPV-driven carcinogenesis in the larynx estimated with an mRNA-based approach is much lower [10], ranging from 1.5%, to 7%, with figures well consistent with the present results (0%).
Despite the absence of HR-HPV mRNA in the present series, suggesting that the HPV in the DNA positive cases may have not been transcriptionally active, we tested HPV-DNA in relation to oncological outcomes anyway, finding no statistically significant impact on OS, RFS, and DSS. In the literature, whichever is the method used for HPV testing in LSCC, evidence about a prognostic/predictive role outside the oropharynx is lacking as well [12,14,49,50].
The absence of demonstrated predictive relevance of HPV infection in laryngeal oncology, makes the issue concerning the reliability and standardization of HPV detection methods in LSCC less critical than in OPSCC [27]. However, our data confirm that in LSCC, and in general outside the oropharynx, p16 overexpression is substantially independent of HPV infection [10,14,19,34,49,51] and cannot be used to confirm transcriptional activity of HPV in LSCCs, as seen in some studies [18].
Apart from its potential role as a surrogate marker of HPV infection, p16, encoded by the antioncogene Ink4a, is an important cyclin-dependent kinase inhibitor. Loss of p16 expression, mostly an epigenetic suppression mediated by methylation, has been described, well before the demonstration of HPV-driven carcinogenesis, to be a frequent molecular abnormality in HNSCC [18,52,53] with a negative prognostic impact in LSCC [31]. Other studies looking for an impact of p16 on prognosis failed to demonstrate a statistical significance for any of the prognostic indexes analysed, even if often describing a consistent trend [14,36]. In the present work, when considering the whole series, p16 overexpression, determined on the lower cut-off, was significantly associated with a longer RFS, without an impact on the other oncological endpoints.
The present series is not homogeneous as for primary treatment, and not either for time of cancer sample collection, including primary surgery specimens, and previously irradiated cancers, with specimens from salvage surgeries, collected after recurrence. This can be considered a bias, but also an advantage, as we could analyse the two groups separately. In primarily operated cases, p16 expression was strongly associated with longer RFS and OS, and appeared as a prognostic marker, substantially independent of HPV status. On the contrary, in the salvage surgery group, recurrent cancers with p16 overexpression seemed to show a significantly worse survival. The last finding is surprising and, taken together with the first one, potentially extremely interesting from the perspective of a molecular prediction of the response to different treatment modalities and ultimately in guiding treatment selection. Nevertheless, it needs further evaluation, as the salvage surgery group was small (22 patients). Furthermore, in this group, the question of whether p16 expression was the same as at diagnosis or changed between the diagnosis and the recurrence, maybe because of irradiation, remains unanswered.
5. Conclusions
Our data, along with those reported by other researchers, do not support a strong role of HPV in supraglottic SCC, evidence further consolidated by the extremely low prevalence in cases studied with an mRNA-based approach. However, when considered as a standalone biomarker, we found p16 overexpression to be significantly associated with a longer RFS. The different impact of p16 on primarily operated and salvaged patients is extremely interesting for its potential role in treatment selection, but it needs further evaluation.
Author Contributions
Conceptualization: R.G. and F.B. Funding acquisition: T.G., G.C.M., G.C., G.D., V.V., M.T. and F.B. Methodology: F.M. and F.B. Project administration: G.C.M., G.C., G.D., V.V., M.T. and F.B. Visualization: F.B. Validation: G.C.M., G.C., G.D., V.V., M.T. and F.B. Formal analysis: R.G. and F.B. Investigation: R.G., T.G., D.H., D.R., G.C., F.M., M.P., D.A., G.P., M.T. and F.B. Data curation: R.G., T.G., D.H., D.R., G.C., M.P., D.A. and F.B. Writing—original draft: R.G., T.G., D.R., G.C., F.M., M.T. and F.B. Writing—review and editing: R.G., D.H., D.R., G.C.M., M.P., D.A., G.C., G.D., V.V., M.T. and F.B. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This research received no external funding.
Institutional Review Board Statement
The study was conducted in accordance with the Declaration of Helsinki, and approved by the Institutional Review Board (or Ethics Committee) of Fondazione Policlinico Universitario A. Gemelli (protocol code Prot Mol.HN sf33976/16 rif. A. 20363/13 id. 204 date of approval: 15 September 2016).
Informed Consent Statement
Written informed consent was obtained from the patients to publish this paper.
Data Availability Statement
The data presented in this study are available on request from the corresponding author.
Acknowledgments
We thank Michael Pawlita for RNA analysis.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
References
- IARC Working Group on the Evaluation of Carcinogenic Risks to Humans Biological Agents. Volume 100 B. A Review of Human Carcinogens. IARC Monogr. Eval. Carcinog. Risks Hum. 2012, 100, 1–441. [Google Scholar]
- Nauta, I.H.; Heideman, D.A.M.; Brink, A.; van der Steen, B.; Bloemena, E.; Koljenović, S.; de Jong, R.J.B.; Leemans, C.R.; Brakenhoff, R.H. The Unveiled Reality of Human Papillomavirus as Risk Factor for Oral Cavity Squamous Cell Carcinoma. Int. J. Cancer 2021, 149, 420–430. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Viarisio, D.; Gissmann, L.; Tommasino, M. Human Papillomaviruses and Carcinogenesis: Well-Established and Novel Models. Curr. Opin. Virol. 2017, 26, 56–62. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lancet, T. The Lancet GLOBOCAN 2018: Counting the Toll of Cancer. Lancet 2018, 392, 985. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Syrjänen, K.J.; Surjänen, S.M. Histological Evidence for the Presence of Condylomatous Epithelial Lesions in Association with Laryngeal Squamous Cell Carcinoma. ORL J. Otorhinolaryngol. Relat. Spec. 1981, 43, 181–194. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Colevas, A.D.; Yom, S.S.; Pfister, D.G.; Spencer, S.; Adelstein, D.; Adkins, D.; Brizel, D.M.; Burtness, B.; Busse, P.M.; Caudell, J.J.; et al. NCCN Guidelines Insights: Head and Neck Cancers, Version 1.2018. J. Natl. Compr. Cancer Netw. 2018, 16, 479–490. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, D.; Shi, Y.; Tang, Y.; Yin, H.; Guo, Y.; Wen, S.; Wang, B.; An, C.; Wu, Y.; Gao, W. Effect of HPV Infection on the Occurrence and Development of Laryngeal Cancer: A Review. J. Cancer 2019, 10, 4455–4462. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pfister, D.G.; Spencer, S.; Adelstein, D.; Adkins, D.; Anzai, Y.; Brizel, D.M.; Bruce, J.Y.; Busse, P.M.; Caudell, J.J.; Cmelak, A.J.; et al. Head and Neck Cancers, Version 2.2020, NCCN Clinical Practice Guidelines in Oncology. J. Natl. Compr. Cancer Netw. 2020, 18, 873–898. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- IARC Working Group on the Evaluation of Carcinogenic Risks to Humans; World Health Organization; International Agency for Research on Cancer Human Papillomaviruses. Human Papillomaviruses. 2007. Available online: https://monographs.iarc.who.int/wp-content/uploads/2018/06/mono100B-11.pdf (accessed on 22 January 2022).
- Bussu, F.; Sali, M.; Gallus, R.; Vellone, V.G.; Zannoni, G.F.; Autorino, R.; Dinapoli, N.; Santangelo, R.; Martucci, R.; Graziani, C.; et al. HPV Infection in Squamous Cell Carcinomas Arising from Different Mucosal Sites of the Head and Neck Region. Is p16 Immunohistochemistry a Reliable Surrogate Marker? Br. J. Cancer 2013, 108, 1157–1162. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Venuti, A.; Paolini, F. HPV Detection Methods in Head and Neck Cancer. Head Neck Pathol. 2012, 6 (Suppl. 1), S63–S74. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Isayeva, T.; Li, Y.; Maswahu, D.; Brandwein-Gensler, M. Human Papillomavirus in Non-Oropharyngeal Head and Neck Cancers: A Systematic Literature Review. Head Neck Pathol. 2012, 6 (Suppl. 1), S104–S120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Upile, N.S.; Shaw, R.J.; Jones, T.M.; Goodyear, P.; Liloglou, T.; Risk, J.M.; Boyd, M.T.; Sheard, J.; Sloan, P.; Robinson, M.; et al. Squamous Cell Carcinoma of the Head and Neck Outside the Oropharynx Is Rarely Human Papillomavirus Related. Laryngoscope 2014, 124, 2739–2744. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Young, R.J.; Urban, D.; Angel, C.; Corry, J.; Lyons, B.; Vallance, N.; Kleid, S.; Iseli, T.A.; Solomon, B.; Rischin, D. Frequency and Prognostic Significance of p16(INK4A) Protein Overexpression and Transcriptionally Active Human Papillomavirus Infection in Laryngeal Squamous Cell Carcinoma. Br. J. Cancer 2015, 112, 1098–1104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bishop, J.A.; Ma, X.-J.; Wang, H.; Luo, Y.; Illei, P.B.; Begum, S.; Taube, J.M.; Koch, W.M.; Westra, W.H. Detection of Transcriptionally Active High-Risk HPV in Patients with Head and Neck Squamous Cell Carcinoma as Visualized by a Novel E6/E7 mRNA in Situ Hybridization Method. Am. J. Surg. Pathol. 2012, 36, 1874–1882. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lewis, J.S., Jr.; Ukpo, O.C.; Ma, X.-J.; Flanagan, J.J.; Luo, Y.; Thorstad, W.L.; Chernock, R.D. Transcriptionally-Active High-Risk Human Papillomavirus Is Rare in Oral Cavity and Laryngeal/hypopharyngeal Squamous Cell Carcinomas--a Tissue Microarray Study Utilizing E6/E7 mRNA in Situ Hybridization. Histopathology 2012, 60, 982–991. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chernock, R.D.; Wang, X.; Gao, G.; Lewis, J.S., Jr.; Zhang, Q.; Thorstad, W.L.; El-Mofty, S.K. Detection and Significance of Human Papillomavirus, CDKN2A(p16) and CDKN1A(p21) Expression in Squamous Cell Carcinoma of the Larynx. Mod. Pathol. 2013, 26, 223–231. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Castellsagué, X.; Alemany, L.; Quer, M.; Halec, G.; Quirós, B.; Tous, S.; Clavero, O.; Alòs, L.; Biegner, T.; Szafarowski, T.; et al. HPV Involvement in Head and Neck Cancers: Comprehensive Assessment of Biomarkers in 3680 Patients. J. Natl. Cancer Inst. 2016, 108, djv403. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Taberna, M.; Resteghini, C.; Swanson, B.; Pickard, R.K.L.; Jiang, B.; Xiao, W.; Mena, M.; Kreinbrink, P.; Chio, E.; Gillison, M.L. Low Etiologic Fraction for Human Papillomavirus in Larynx Squamous Cell Carcinoma. Oral Oncol. 2016, 61, 55–61. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Serrano, M. The Tumor Suppressor Protein p16INK4a. Exp. Cell Res. 1997, 237, 7–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gonzalez, S.; Serrano, M. A New Mechanism of Inactivation of the INK4/ARF Locus. Cell Cycle 2006, 5, 1382–1384. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ueki, K.; Ono, Y.; Henson, J.W.; Efird, J.T.; von Deimling, A.; Louis, D.N. CDKN2/p16 or RB Alterations Occur in the Majority of Glioblastomas and Are Inversely Correlated. Cancer Res. 1996, 56, 150–153. [Google Scholar]
- Di Vinci, A.; Perdelli, L.; Banelli, B.; Salvi, S.; Casciano, I.; Gelvi, I.; Allemanni, G.; Margallo, E.; Gatteschi, B.; Romani, M. p16(INK4a) Promoter Methylation and Protein Expression in Breast Fibroadenoma and Carcinoma. Int. J. Cancer 2005, 114, 414–421. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fukushima, N.; Sato, N.; Ueki, T.; Rosty, C.; Walter, K.M.; Wilentz, R.E.; Yeo, C.J.; Hruban, R.H.; Goggins, M. Aberrant Methylation of Preproenkephalin and p16 Genes in Pancreatic Intraepithelial Neoplasia and Pancreatic Ductal Adenocarcinoma. Am. J. Pathol. 2002, 160, 1573–1581. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bussu, F.; Sali, M.; Gallus, R.; Petrone, G.; Zannoni, G.F.; Autorino, R.; Dinapoli, N.; Santangelo, R.; Vellone, V.G.; Graziani, C.; et al. Human Papillomavirus (HPV) Infection in Squamous Cell Carcinomas Arising from the Oropharynx: Detection of HPV DNA and p16 Immunohistochemistry as Diagnostic and Prognostic Indicators—A Pilot Study. Int. J. Radiat. Oncol. Biol. Phys. 2014, 89, 1115–1120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hernandez, B.Y.; Rahman, M.; Lynch, C.F.; Cozen, W.; Unger, E.R.; Steinau, M.; Thompson, T.; Saber, M.S.; Altekruse, S.F.; Goodman, M.T.; et al. p16(INK4A) Expression in Invasive Laryngeal Cancer. Papillomavirus Res. 2016, 2, 52–55. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bussu, F.; Ragin, C.; Boscolo-Rizzo, P.; Rizzo, D.; Gallus, R.; Delogu, G.; Morbini, P.; Tommasino, M. HPV as a Marker for Molecular Characterization in Head and Neck Oncology: Looking for a Standardization of Clinical Use and of Detection Method(s) in Clinical Practice. Head Neck 2019, 41, 1104–1111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Amin, M.B.; Greene, F.L.; Edge, S.B.; Compton, C.C.; Gershenwald, J.E.; Brookland, R.K.; Meyer, L.; Gress, D.M.; Byrd, D.R.; Winchester, D.P. The Eighth Edition AJCC Cancer Staging Manual: Continuing to Build a Bridge from a Population-Based to a More “Personalized” Approach to Cancer Staging. CA Cancer J. Clin. 2017, 67, 93–99. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Salih, M.M.; Higgo, A.A.; Eed, E.M. Prognostic Significance of p16 Protein Expression in Breast Cancer. Vivo 2022, 36, 336–340. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, C.; Wang, J.; Chen, Z.; Gao, Y.; He, J. Immunohistochemical Prognostic Markers of Esophageal Squamous Cell Carcinoma: A Systematic Review. Chin. J. Cancer 2017, 36, 65. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gallo, O.; Santucci, M.; Franchi, A. Cumulative Prognostic Value of p16/CDKN2 and p53 Oncoprotein Expression in Premalignant Laryngeal Lesions. J. Natl. Cancer Inst. 1997, 89, 1161–1163. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Barrueco, A.S.; Galán, F.G.; Aubá, J.M.V.; Tapia, G.D.; Hernández, S.F.; Arroba, C.M.-A.; Español, C.C.; Álvarez, C.A. p16 Influence on Laryngeal Squamous Cell Carcinoma Relapse and Survival. Otolaryngol. Head Neck Surg. 2019, 160, 1042–1047. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Allegra, E.; Bianco, M.R.; Mignogna, C.; Caltabiano, R.; Grasso, M.; Puzzo, L. Role of P16 Expression in the Prognosis of Patients with Laryngeal Cancer: A Single Retrospective Analysis. Cancer Control. 2021, 28, 10732748211033544. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chung, C.H.; Zhang, Q.; Kong, C.S.; Harris, J.; Fertig, E.J.; Harari, P.M.; Wang, D.; Redmond, K.P.; Shenouda, G.; Trotti, A.; et al. p16 Protein Expression and Human Papillomavirus Status as Prognostic Biomarkers of Nonoropharyngeal Head and Neck Squamous Cell Carcinoma. J. Clin. Oncol. 2014, 32, 3930–3938. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Deng, Z.; Hasegawa, M.; Aoki, K.; Matayoshi, S.; Kiyuna, A.; Yamashita, Y.; Uehara, T.; Agena, S.; Maeda, H.; Xie, M.; et al. A Comprehensive Evaluation of Human Papillomavirus Positive Status and p16INK4a Overexpression as a Prognostic Biomarker in Head and Neck Squamous Cell Carcinoma. Int. J. Oncol. 2014, 45, 67–76. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meshman, J.; Wang, P.-C.; Chin, R.; John, M.S.; Abemayor, E.; Bhuta, S.; Chen, A.M. Prognostic Significance of p16 in Squamous Cell Carcinoma of the Larynx and Hypopharynx. Am. J. Otolaryngol. 2017, 38, 31–37. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- de Vincentiis, M.; De Virgilio, A.; Bussu, F.; Gallus, R.; Gallo, A.; Bastanza, G.; Parrilla, C.; Greco, A.; Galli, J.; Turchetta, R.; et al. Oncologic Results of the Surgical Salvage of Recurrent Laryngeal Squamous Cell Carcinoma in a Multicentric Retrospective Series: Emerging Role of Supracricoid Partial Laryngectomy. Head Neck 2015, 37, 84–91. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bussu, F.; Paludetti, G.; Almadori, G.; De Virgilio, A.; Galli, J.; Miccichè, F.; Tombolini, M.; Rizzo, D.; Gallo, A.; Giglia, V.; et al. Comparison of Total Laryngectomy with Surgical (cricohyoidopexy) and Nonsurgical Organ-Preservation Modalities in Advanced Laryngeal Squamous Cell Carcinomas: A Multicenter Retrospective Analysis. Head Neck 2013, 35, 554–561. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bussu, F.; Tagliaferri, L.; Mattiucci, G.; Parrilla, C.; Rizzo, D.; Gambacorta, M.A.; Lancellotta, V.; Autorino, R.; Fonnesu, C.; Kihlgren, C.; et al. HDR Interventional Radiotherapy (brachytherapy) in the Treatment of Primary and Recurrent Head and Neck Malignancies. Head Neck 2019, 41, 1667–1675. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gheit, T.; Abedi-Ardekani, B.; Carreira, C.; Missad, C.G.; Tommasino, M.; Torrente, M.C. Comprehensive Analysis of HPV Expression in Laryngeal Squamous Cell Carcinoma. J. Med. Virol. 2014, 86, 642–646. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Halec, G.; Holzinger, D.; Schmitt, M.; Flechtenmacher, C.; Dyckhoff, G.; Lloveras, B.; Höfler, D.; Bosch, F.X.; Pawlita, M. Biological Evidence for a Causal Role of HPV16 in a Small Fraction of Laryngeal Squamous Cell Carcinoma. Br. J. Cancer 2013, 109, 172–183. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Halec, G.; Schmitt, M.; Dondog, B.; Sharkhuu, E.; Wentzensen, N.; Gheit, T.; Tommasino, M.; Kommoss, F.; Bosch, F.X.; Franceschi, S.; et al. Biological Activity of Probable/possible High-Risk Human Papillomavirus Types in Cervical Cancer. Int. J. Cancer 2013, 132, 63–71. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Koo, C.-L.; Kok, L.-F.; Lee, M.-Y.; Wu, T.S.; Cheng, Y.-W.; Hsu, J.-D.; Ruan, A.; Chao, K.-C.; Han, C.-P. Scoring Mechanisms of p16INK4a Immunohistochemistry Based on Either Independent Nucleic Stain or Mixed Cytoplasmic with Nucleic Expression Can Significantly Signal to Distinguish between Endocervical and Endometrial Adenocarcinomas in a Tissue Microarray Study. J. Transl. Med. 2009, 7, 25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Begum, S.; Gillison, M.L.; Ansari-Lari, M.A.; Shah, K.; Westra, W.H. Detection of Human Papillomavirus in Cervical Lymph Nodes: A Highly Effective Strategy for Localizing Site of Tumor Origin. Clin. Cancer Res. 2003, 9, 6469–6475. [Google Scholar]
- Miller, K.D.; Siegel, R.L.; Lin, C.C.; Mariotto, A.B.; Kramer, J.L.; Rowland, J.H.; Stein, K.D.; Alteri, R.; Jemal, A. Cancer Treatment and Survivorship Statistics, 2016. CA Cancer J. Clin. 2016, 66, 271–289. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fakhry, C.; Westra, W.H.; Li, S.; Cmelak, A.; Ridge, J.A.; Pinto, H.; Forastiere, A.; Gillison, M.L. Improved Survival of Patients with Human Papillomavirus-Positive Head and Neck Squamous Cell Carcinoma in a Prospective Clinical Trial. J. Natl. Cancer Inst. 2008, 100, 261–269. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ndiaye, C.; Mena, M.; Alemany, L. Correction to Lancet Oncol 2014; 15: 1324. HPV DNA, E6/E7 mRNA, and p16INK4a Detection in Head and Neck Cancers: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. Lancet Oncol. 2015, 16, e262. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gama, R.R.; Carvalho, A.L.; Longatto Filho, A.; Scorsato, A.P.; López, R.V.M.; Rautava, J.; Syrjänen, S.; Syrjänen, K. Detection of Human Papillomavirus in Laryngeal Squamous Cell Carcinoma: Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. Laryngoscope 2016, 126, 885–893. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- D’Souza, G.; Westra, W.H.; Wang, S.J.; van Zante, A.; Wentz, A.; Kluz, N.; Rettig, E.; Ryan, W.R.; Ha, P.K.; Kang, H.; et al. Differences in the Prevalence of Human Papillomavirus (HPV) in Head and Neck Squamous Cell Cancers by Sex, Race, Anatomic Tumor Site, and HPV Detection Method. JAMA Oncol 2017, 3, 169–177. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Akarslan, Z. Diagnosis and Management of Head and Neck Cancer; InTech: Rijeka, Croatia, 2017; ISBN 9789535134954. [Google Scholar]
- Rizzo, D.; Graziani, C.; Gallus, R.; Zannoni, G.F.; Lucchetti, D.; Parrilla, C.; Boninsegna, A.; Galli, J.; Paludetti, G.; Bussu, F.; et al. Stem Cell Markers in Oral and Oropharyngeal Squamous Cell Carcinomas in Relation to the Site of Origin and HPV Infection: Clinical Implications. Acta Otorhinolaryngol. Ital. 2020, 40, 90–98. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reed, A.L.; Califano, J.; Cairns, P.; Westra, W.H.; Jones, R.M.; Koch, W.; Ahrendt, S.; Eby, Y.; Sewell, D.; Nawroz, H.; et al. High Frequency of p16 (CDKN2/MTS-1/INK4A) Inactivation in Head and Neck Squamous Cell Carcinoma. Cancer Res. 1996, 56, 3630–3633. [Google Scholar]
- Olshan, A.F.; Weissler, M.C.; Pei, H.; Conway, K.; Anderson, S.; Fried, D.B.; Yarbrough, W.G. Alterations of the p16 Gene in Head and Neck Cancer: Frequency and Association with p53, PRAD-1 and HPV. Oncogene 1997, 14, 811–818. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).