Abstract
In recent years, it has become increasingly important to study the beneficial properties of derivatives of grapes and grapevine. The objective of this study was to determine the antioxidant activity of Vitis labrusca leaf extracts, comparing conventional and organic grapevines, in different brain areas of rats. We used male Wistar rats treated with grapevine leaf extracts for a period of 14 days, and on the 15th day, we administered in half of the rats, mineral oil and the other half, carbon tetrachloride (CCl4). The animals were euthanized by decapitation and the cerebral cortex, hippocampus and cerebellum were removed to assess oxidative stress parameters and the activity of antioxidant enzymes. Lipid peroxidation levels (TBARS) were unchanged. However, CCl4 induced oxidative damage to proteins in all tissues studied, and this injury was prevented by both extracts. Superoxide dismutase (SOD) activity was increased by CCl4 in the cerebral cortex and decreased in other tissues. However, CCl4 increased catalase (CAT) activity in the cerebellum and decreased it in the cerebral cortex. The SOD/CAT ratio was restored in the cerebellum by both extracts and only in the cerebral cortex by the organic extract.
1. Introduction
Vitis labrusca is the main species used in the manufacture of juices and wines in South America [1]. There are various ways to grow grapes, which include conventional and organic cultivation. In organic cultivation, chemicals that interfere with productivity are not employed, unlike in conventional cultivation, where pesticides are used to control pests [2]. Currently, it is known that grape juices produced from organic cultivation contain higher amounts of polyphenols when compared to grapes from conventional cultivation [1].
Polyphenols are present in grapes and their derivatives [1,3,4]. These bioactive compounds are synthesized by plants and stored in the skin in response to fungal attack, mechanical damage and ultraviolet rays. Some human health benefits have been attributed to polyphenols in recent years, including their antioxidant action on reactive species [5,6]. These phenolic compounds, e.g., catechin, resveratrol, flavonoids, quercetin, rutin, kaempherol and naringin, were found in the leaves of V. labrusca grapevines in previous studies [7,8].
Reactive species are molecules derived from various biological processes capable of causing DNA, protein and lipid damage [9]. This damage generated by reactive species is combated by antioxidant defenses, enzymatic and non-enzymatic. Antioxidant enzymes include superoxide dismutase (SOD) and catalase (CAT), while α-tocopherol (vitamin E), β-carotene (pro-vitamin A) and ascorbic acid (vitamin C) are some of the non-enzymatic antioxidants [10]. In normal situations, the human body produces antioxidants or procures them from the diet, and either way, they are capable of reducing the concentration of reactive species [11]. The imbalance between the production of reactive species and amount of antioxidants characterizes oxidative stress [12]. Damage caused by oxidative stress to the central nervous system has been associated with the development of neurodegenerative diseases such as Parkinson’s disease and Alzheimer’s disease [9,13].
Some studies, in vivo and in vitro, have shown that products derived from grapes or grape leaves, seeds or juices are able to inhibit the damage caused by oxidative stress in the central nervous system [8,14]. Two studies demonstrated the beneficial properties of these derivatives (flavan-3-ol compounds and grape juice) on oxidative damage, in this case induced by pentylenetetrazol (PTZ) [15,16]. An in vitro study showed that extracts of leaves from organic and conventional grapevines were able to exert protective effects against the oxidative damage (lipid peroxidation and protein oxidation) and enzymatic (SOD and CAT) changes in liver, kidney and heart caused by hydrogen peroxide (H2O2) treatment [7]. There are numerous substances capable of inducing damage by oxidative stress, such as carbon tetrachloride (CCl4) [17,18]. CCl4 is toxic partly because of its liposolubility, and when bound to proteins and lipids, it induces tissue degeneration, which may lead to hepatic steatosis, tubular necrosis and hepatic encephalopathy [17,18,19].
Only in vitro studies have demonstrated the neuroprotective activity of V. labrusca leaf extract, and no in vivo investigations have been reported confirming this activity. The present study aimed to evaluate the reduction of oxidative stress parameters in cerebral cortex, hippocampus and cerebellum of male Wistar rats after chronic treatment with the V. labrusca leaf extracts, comparing organic and conventional grapevines.
2. Experimental Section
2.1. Reagents
Thiobarbituric acid was purchased from Merck (Darmstadt, Germany), and 2,4-dinitrophenylhydrazine (DNPH) was obtained from Sigma (St. Louis, MO, USA). All other chemicals were of analytical grade and purchased from local suppliers.
2.2. Grapevine Leaf Extracts
V. labrusca leaves, variety Bordo, from both conventional and organic grapevines, were collected in November 2011. The plants were identified by the Herbarium of the Centro Universitario Metodista do IPA. The organic grapevines received the ECOVIDA certification. The leaves were weighed and digested using Xpress digestion tubes (CEM Corporation, Matthews, NC, USA). Afterwards, Milli-Q (Millipore Corporation, Billerica, MA, USA) water was added and to the tubes containing the leaves, and the mixture was subjected to microwave digestion. The samples were then transferred to a flask with Sarstedt focuser (Sarstedt Inc., Newton, NC, USA) with more Milli-Q water added. The samples were centrifuged and the supernatant obtained was used in all experiments.
2.3. Phenolic Compounds
The concentration of phenolic compounds was determined using the method described by Singleton and Rossi (1999), a modification of the Folin-Ciocalteau colorimetric method [20]. The results were expressed as mg/100 g leaves.
The extracts were analyzed by high performance liquid chromatography (HPLC) using an 1100 HPLC system (Agilent Technologies, Santa Clara, CA, USA) and the test standards chlorogenic acid, taxifolin, ferrulic acid, naringin, rutin, quercetin, luteolin, kaempferol, apigenin, catechin, epicatechin and resveratrol. The 1100 HPLC system consisted of a quaternary pump system, LiChrospher RP-18 (5 μm) column and UV detector. An injection volume of 50 μL and a flow rate of 1.0 mL/min were used. The quantification of catechin was performed as described by Saucier et al. (2001) [21]. Solvent A was water with 5% acetic acid; solvent B was methanol with 5% acetic acid; the elution was isocratic at 90% A and 10% solvent B, with a total analysis time of 45 min and detection at 280 nm. For flavonoid standards, solvent A was methanol with 2% acetic acid and solvent B was Milli-Q water with 2% acetic acid, with a total analysis time of 50 min and detection at 350 nm [22]. For quantification of resveratrol, solvent A was water with pH 2.5 and solvent B, methanol; a gradient of 90% solvent A and 10% solvent B to 100% solvent B was used, a total analysis time of 45 min and detection at 313 nm [23]. All standards were purchased from Fluka Analytical (St. Gallen, Switzerland) or Sigma-Aldrich (St. Louis, MO, USA).
2.4. Animals
Thirty male Wistar rats, 90 days old and weighing approximately 300 g, were obtained from the animal facility of the Centro Universitário Metodista IPA. The animals had free access to water and commercial diet containing 20.5% protein (predominantly soybean), 54% carbohydrate, 4% fat, 4.5% fiber, 7% ash and 10% moisture. The animals were maintained on a 12 h light/12 h dark cycle at a temperature of 22 °C ± 1 °C. All experimental procedures were performed with the approval of the Ethics Commission for Animal Use (CEUA) of the Centro Universitário Metodista IPA, No. 01/2012.
2.5. Treatment
All animals received once a day a single intraperitoneal injection for 14 days. On the basis of a previous study [24], the animals were divided into three experimental groups (n = 10 each). Group 1 (control) received saline (0.9% NaCl); Group 2 received conventional grapevine leaf extract (30 mg/kg); and group 3 received organic extract (30 mg/kg). On the 15th day, half of the animals in each group received a single intraperitoneal dose of CCl4 (3 mL/kg) and the other half, a single dose, also intraperitoneally, of mineral oil (control). After 4 h, the animals were euthanized by decapitation. The cerebellum, hippocampus and cerebral cortex were dissected, homogenized in 1.5% KCl with a manual homogenizer, and stored in a freezer (−80 °C) until analysis.
2.6. Parameters of Oxidative Stress
As an index of lipid peroxidation, we used thiobarbituric acid reactive species (TBARS) production during an acid-heating reaction, which is widely adopted as a sensitive method for measuring lipid peroxidation, as previously described by Wills (1996) [25]. Briefly, the samples were mixed with 10% trichloroacetic acid (TCA) and 0.67% thiobarbituric acid (TBA) and then heated in a boiling water bath for 15 min in closed tubes. TBARS were determined by absorbance at 535 nm. Results were expressed as nmol/mg protein. Oxidative damage to proteins was assessed by determining carbonyl groups on the basis of the reaction with dinitrophenylhydrazine (DNPH), as previously described by Levine et al. (1990) [26]. DNPH reacts with protein carbonyls to form hydrazones that can be measured spectrophotometrically. Briefly, 500 μL 10 mM DNPH in 2 M HCl were added at room temperature for 1 h, with vortexing every 10–15 min. Next, 500 μL 20% TCA were added, and tubes were mixed and centrifuged for 3 min. The supernatant was then discarded, and the pellets were washed three times with 1 mL of ethanol-ethyl acetate (1:1) to remove free reagent. After centrifugation, the precipitated protein was redissolved in 0.6 mL guanidine solution. Proteins were dissolved within 15 min at 37 °C. The insoluble material was removed by centrifugation in a microcentrifuge for 3 min. The absorbance was read at 370 nm. Equal amounts of protein samples without DNPH were used as controls. The results were expressed in nmol/mg protein.
2.7. Determination of Antioxidant Enzymes
SOD activity was determined by a spectrophotometric method, measuring the inhibition of the rate of adrenochrome formation at 480 nm (SP-2200 Spectrophotometer, Bioespectro, Curitiba, Brazil) in medium containing 1 mM adrenalin and 50 mM glycine [27]. The results were expressed in U SOD/mg protein. The method used to determine CAT activity has been described by Aebi (1984) [28] and determines the rate of H2O2 degradation measuring absorbance at 240 nm (Spectrophotometer SP-2200, Bioespectro). The results were expressed as UCAT/mg protein.
2.8. Protein Determination
Protein concentration was determined according to the method described by Lowry et al. (1951) [29].
2.9. Statistical Analysis
The results were expressed as the mean and standard deviation. The data were evaluated for normality using the Kolmogorov-Smirnov test. We observed a normal distribution of the data. The differences between all the groups were analyzed by three-way analysis of variance (ANOVA), followed by Tukey’s post-test. Student’s t-test was used for comparison between two means. P < 0.05 was considered significant. All analyses were performed using the statistical program Statistical Package for the Social Sciences (SPSS) version 17.0 (International Business Machines Corporation, New York, NY, USA).
3. Results and Discussion
Our study evaluated the effect of chronic treatment with V. labrusca leaf extracts prepared from organic and conventional grapevines, on oxidative stress parameters in cerebral cortex, hippocampus and cerebellum of male Wistar rats. Products from grapevines are known to be some of the most important sources of polyphenols. We found that both extracts are sources of these compounds, including resveratrol and catechin (Table 1). The organic extract was richer in total polyphenols and resveratrol when compared with the conventional extract. However, conventional cultivation favored increased levels of catechin. Our findings are corroborated by several previous studies that have demonstrated that the way grapes are grown influences the amount of total polyphenols [8,24] and concentration of catechin, as shown by Dani et al. (2010) [8]. In organic cultivation, pesticides are not used, resulting in a larger amount of polyphenols synthesized by the plant under these conditions [30]. However, another related work comparing organic and conventional grape juice found that organic grape juice was richer in all the phenolic compounds found in our study, in other words, organic grape juice had higher concentrations of total polyphenols, catechin and resveratrol [15]. In our study, the polyphenols chlorogenic acid, taxifolin, ferrulic acid, naringin, rutin, quercetin, luteolin, kaempferol, apigenin and epicatechin were not identified in either extract. However, Dani et al. (2010) [8] detected the presence of the polyphenols rutin, naringin, quercetin and kaempferol as well. This can be explained by differences in extraction methods used in the current and previous studies [8]. This was also evident in a study conducted by Orhan et al. (2007) [31] with leaves of Vitis vinifera, which found that the amounts of phenolic compounds at end of the process depended on the solvent used in the extraction. For example, extraction with chloroform yielded lower amounts of total polyphenols compared to extraction with ethanol [31].

Table 1.
Content of total polyphenols, catechin and resveratrol in V. labrusca leaf extracts using organic and conventional grapevines.
| EXTRACT | Total Polyphenols (mg/100 g) | Catechin (mg/100 g) | Resveratrol (mg/100 g) |
|---|---|---|---|
| CONVENTIONAL | 19.83 ± 0.76 | 211.82 ± 5.05 | 0.01 ± 0.003 |
| ORGANIC | 81.79 ± 2.68* | 161.10 ± 0.97 * | 0.04 ± 0.004 * |
* Statistical difference, p < 0.05.
In the last years, these compounds have been the subject of much research because they generate many benefits to human health [32]. The benefits of these bioactive compounds include reducing the risk of liver, cardiovascular and neurodegenerative diseases, as well as exerting antioxidant and anticarcinogenic actions [33]. Along this line, the human brain is often in contact with reactive molecules produced by the normal metabolism of oxygen or derived from exogenous sources, which are known as reactive oxygen species [34]. Thus, the central nervous system has been considered to be predisposed to oxidative damage [35], mainly by possessing a high concentration of lipids and requiring a high consumption of oxygen, so it is a potential damage target for oxidative stress [9,35,36]. To assess the biological activity of these extracts, we evaluated their neuroprotective effect through their ability to inhibit lipid peroxidation and protein oxidation as well as by modulation of antioxidant enzyme activity. In our study, there was no statistical difference between the treatments evaluated with regard to lipid peroxidation, demonstrating that CCl4 was not able to induce damage to lipids in any of the tissues evaluated (Figure 1A). However, in another study, lipid damage induced by CCl4 in the striatum and substantia nigra brain of Wistar rats was reduced with the administration of organic and conventional grape juice [24]. Lipid peroxidation was also reduced in an in vivo experiment performed with Vitis vinifera grapevine leaf extract in rat liver, where levels of lipid peroxidation decreased significantly after treatment of animals with the extract in question [31]. The same was demonstrated in in vitro studies conducted with grapevine leaf extracts (Vitis labrusca), conventional and organic. It was observed that levels of lipid peroxidation damage generated by the damage inducer also decreased after treatment with the extracts in the cerebral cortex, hippocampus, cerebellum, kidney, heart and liver [7,8].
The protein carbonyl assay showed that CCl4 increased protein damage in all tissues, and both extracts were able to reduce these levels. In the hippocampus and cerebellum, both extracts reduced damage to proteins in the same proportion, though in the cerebral cortex, the organic extract produced a more significant reduction in protein oxidation as compared to conventional extract (Figure 1B). Our data corroborated the results of another study conducted with similar V. labrusca leaf extract but that study was conducted with tissue in vitro [7]. In a study carried out with grape juice, protein oxidation was also decreased in the group receiving the juice [24].
Cells possess antioxidant defenses, including the enzymes SOD and CAT [11]. We observed that the treatment with CCl4 increased SOD activity in cerebral cortex, while reducing activity in other tissues (Figure 2A). In the cerebral cortex, only the organic extract was able to restore enzyme activity altered by CCl4, to similar levels as the control group. The organic extract was also shown to be effective against damage caused by CCl4 in the hippocampus. This decrease caused by the organic extract was not observed in the cerebellum. In this tissue, the damage induced did not cause an increase in SOD activity. Nevertheless, in the cerebellum, the conventional extract was able to increase SOD activity, and when only extracts were administered, both reduced the activity of this enzyme, as did CCl4. However, in the groups that received the extracts and damage inducer, there was an increase in SOD level, but it remained below the control value. Another study showed that organic grapevine leaf extract increased SOD activity in kidney and liver and increased CAT activity in heart [7]. Increased SOD levels have also been observed in rat plasma with an extract of Vitis coignetiae Pulliat [37] and in rat liver and kidney with an extract of Vitis vinifera [11].
With regard to CAT activity, we observed that the CCl4 reduced enzyme activity in the cerebral cortex, which was not reversed by treatment with extracts (Figure 2B).
Similarly, in another study, grapevine leaf extract also reduced CAT activity in cerebral cortex exposed to H2O2 in vitro [8]. The groups treated only with extracts behaved similarly to the control group. In the cerebellum, CCl4 caused an increase in CAT activity, while enzyme activity levels in the other groups were the same as the control. In the hippocampus, no difference was observed between the treatments. Conventional and organic grape juice was found to inhibit the decrease in SOD and CAT activity induced by pentylenetetrazol, a potent convulsant drug [15].
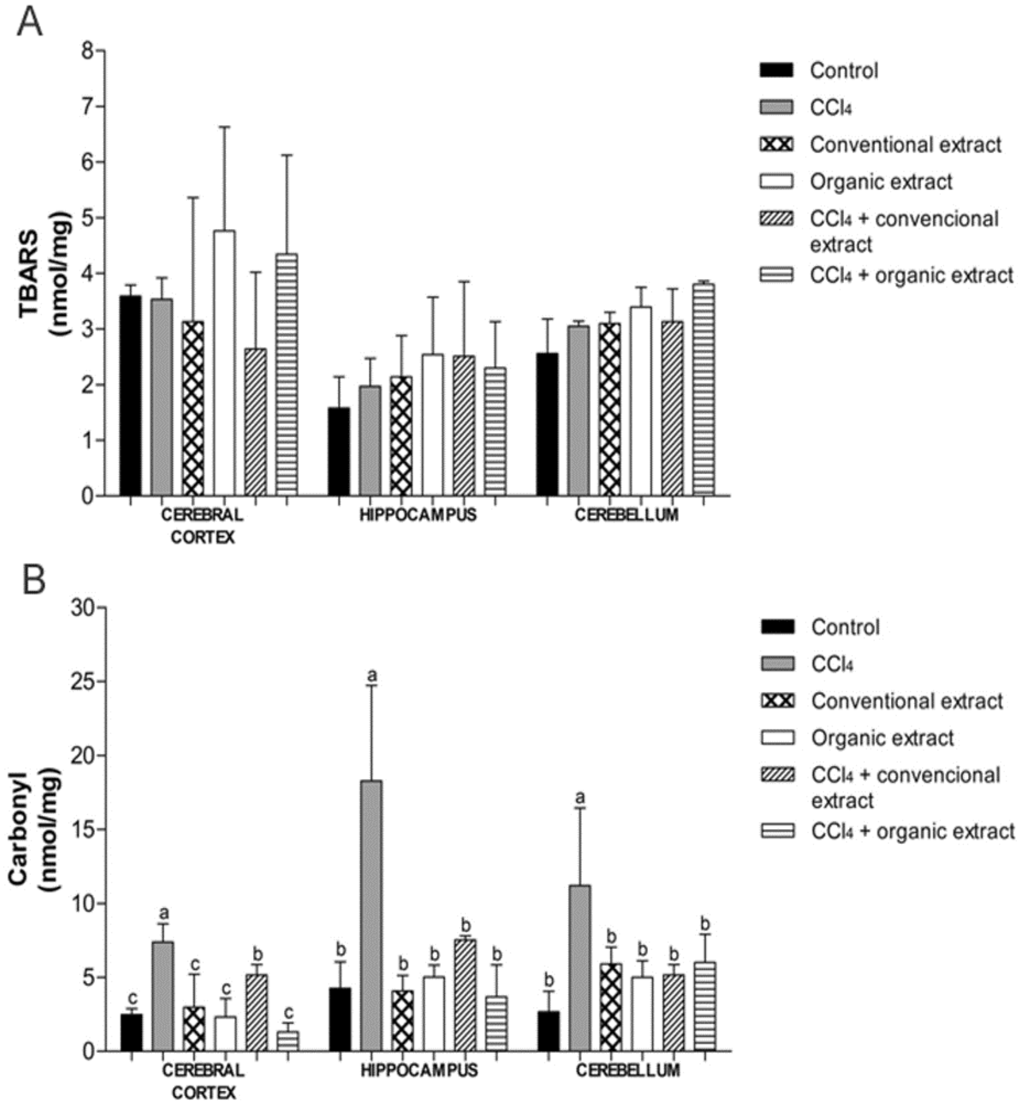
Figure 1.
(A) Levels of thiobarbituric acid reactive species (TBARS) (nmol/mg) and (B) Carbonyl (nmol/mg protein) in brain tissues of rats treated with different extracts (organic and conventional) and carbon tetrachloride (3 mL/kg). Data are expressed as mean ± SD. Different letters indicate statistical difference according to ANOVA and Tukey’s post-test (p < 0.05) for each tissue evaluated.
Figure 1.
(A) Levels of thiobarbituric acid reactive species (TBARS) (nmol/mg) and (B) Carbonyl (nmol/mg protein) in brain tissues of rats treated with different extracts (organic and conventional) and carbon tetrachloride (3 mL/kg). Data are expressed as mean ± SD. Different letters indicate statistical difference according to ANOVA and Tukey’s post-test (p < 0.05) for each tissue evaluated.
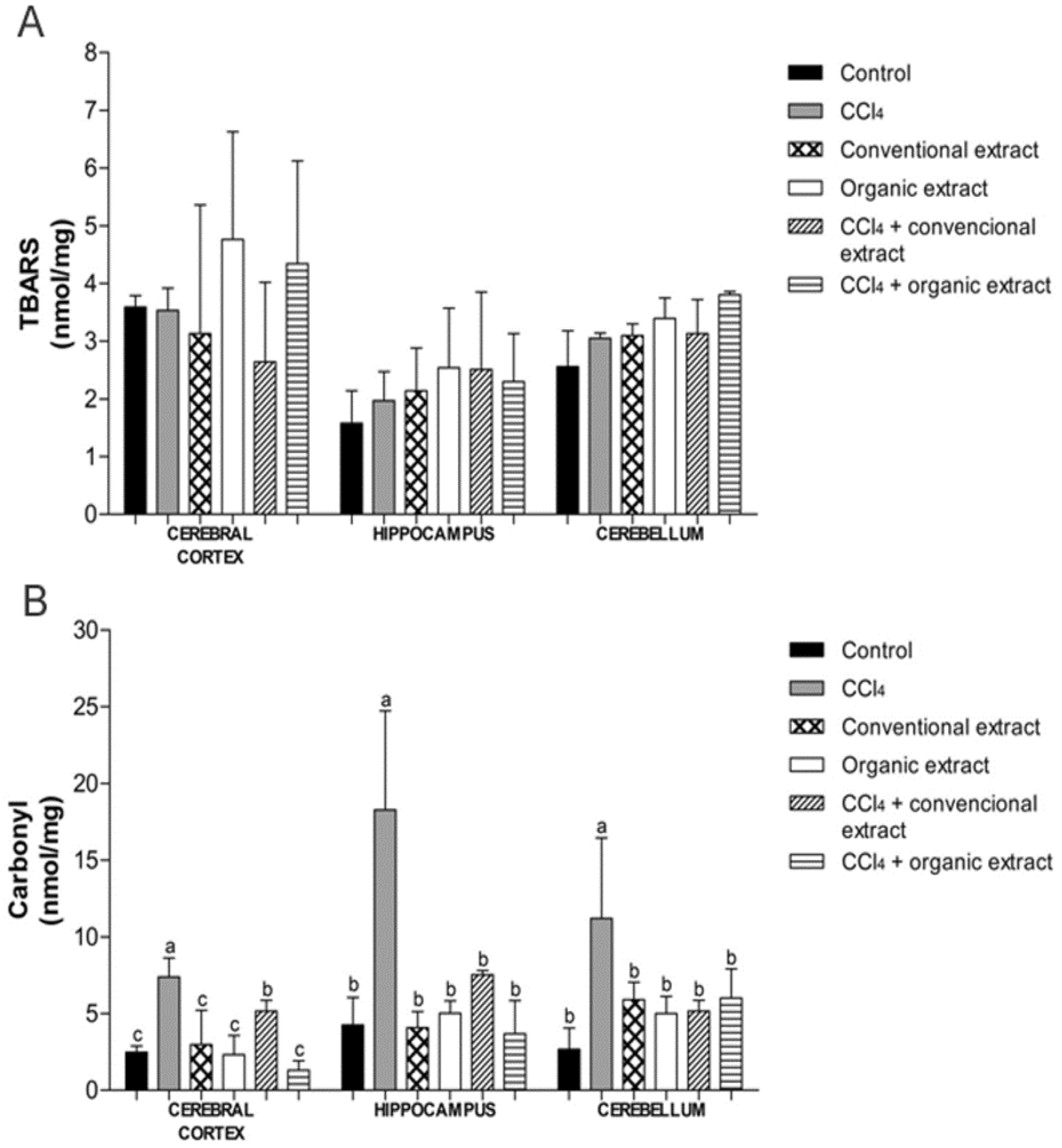
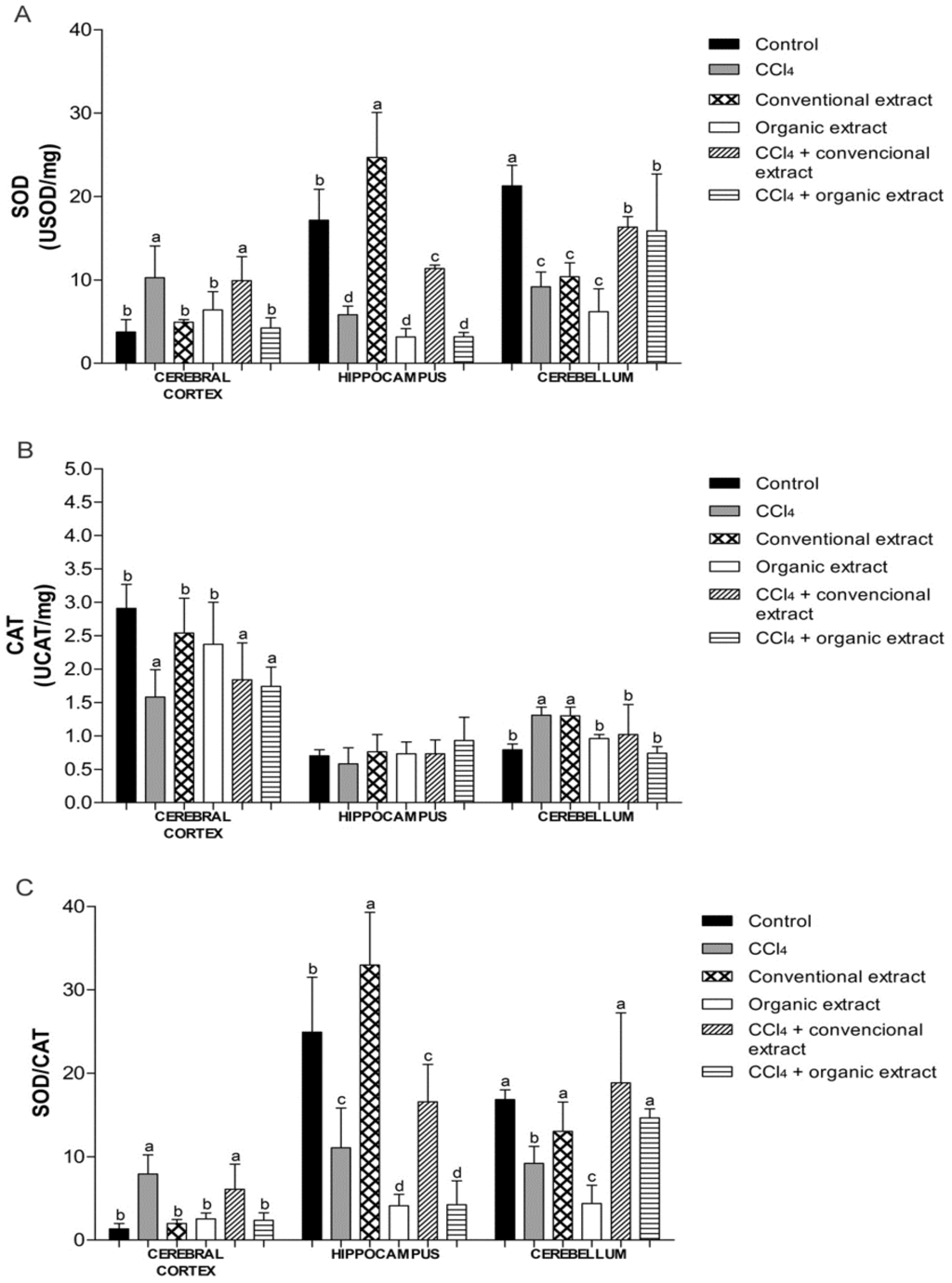
Figure 2.
(A) Superoxide dismutase (SOD) activity (USOD/mg protein) (B) Catalase (CAT) activity (UCAT/mg protein) and (C) SOD/CAT ratio in brain tissues of rats treated with different extracts (organic and conventional) and carbon tetrachloride (3 mL/kg). Data are expressed as mean ± SD. Different letters indicate statistical difference according to ANOVA and Tukey’s post-test (p < 0.05) for each tissue evaluated.
Figure 2.
(A) Superoxide dismutase (SOD) activity (USOD/mg protein) (B) Catalase (CAT) activity (UCAT/mg protein) and (C) SOD/CAT ratio in brain tissues of rats treated with different extracts (organic and conventional) and carbon tetrachloride (3 mL/kg). Data are expressed as mean ± SD. Different letters indicate statistical difference according to ANOVA and Tukey’s post-test (p < 0.05) for each tissue evaluated.
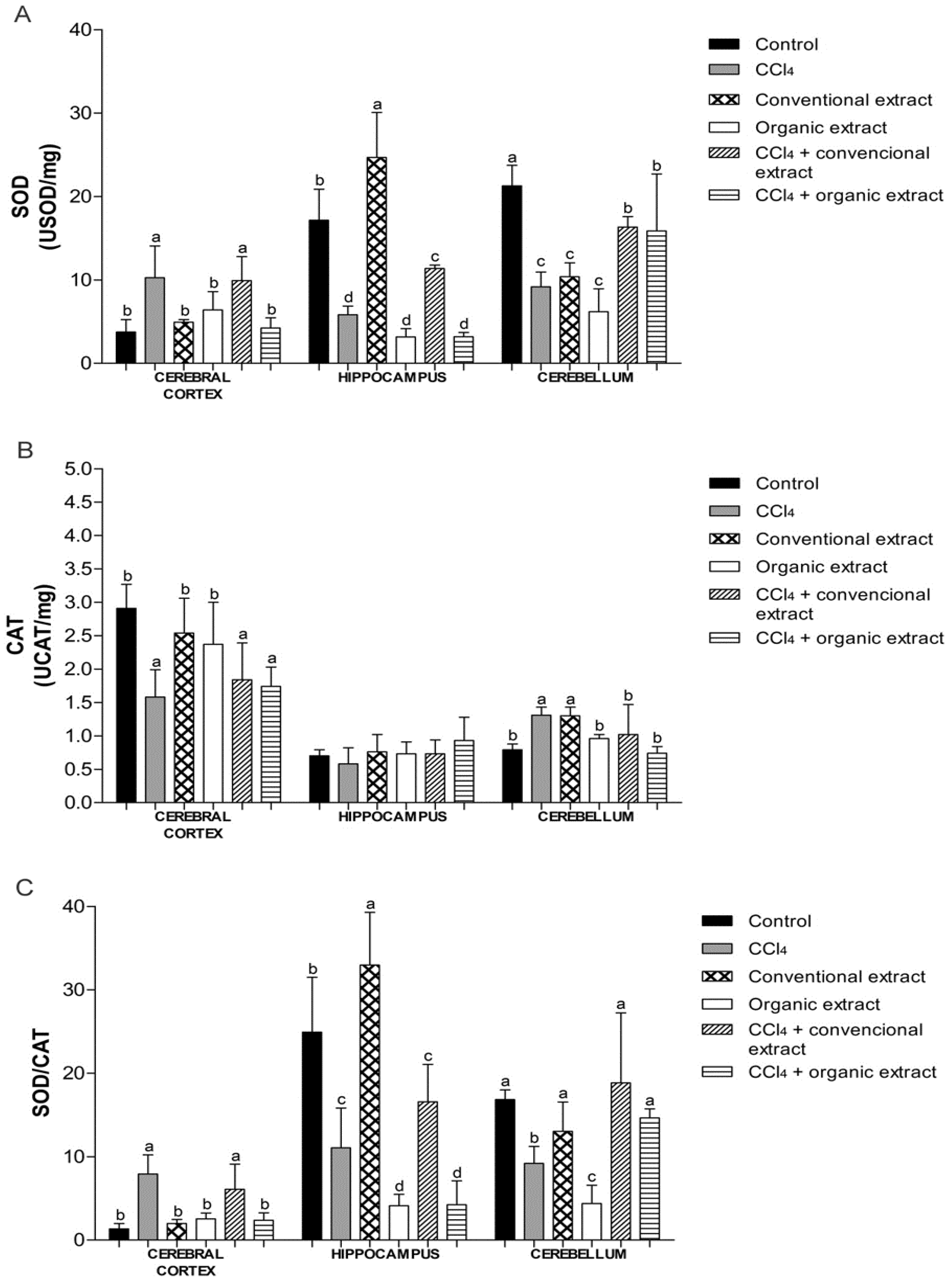
Besides SOD and CAT activities, we also evaluated the relationship between these enzymes. The SOD/CAT ratio is an essential parameter to check if there is an imbalance between these two enzymes (Figure 2C). An imbalance between antioxidant defenses may generate increased oxidative stress and thus cause various diseases [38]. In the cerebellum, both extracts restored SOD/CAT, whereas in the cerebral cortex, only the organic extract maintained this ratio at a similar level as the control group. This finding could be attributed to the higher polyphenol content of the organic extract. Still, in the cerebral cortex, we observed an increase in this ratio in the CCl4 group, as well as with the inducing agent combined with conventional extract. We also noted that this ratio in this tissue in the other experimental groups was lower, which was also observed in a study of the effect of grape juice on the striatum and substantia nigra of rats [24]. This behavior was not observed in the hippocampus. This difference in antioxidant enzyme activity, lipid damage and oxidative protein damage, according to the brain structure evaluated, as previously mentioned in other studies [39,40]. This difference can be attributed, for example, to the differences in blood supply in each of the different brain regions [41]. However, further studies are needed for better understanding of the sensitivity of each of the structures evaluated.
4. Conclusions
Thus, the results of this study suggest that the treatment of rats with grapevine leaf extract could be effective against protein oxidative damage and in reestablishing the SOD/CAT ratio in central nervous system tissues, which when excessive or unbalanced, respectively, can contribute to neurodegenerative disorders.
Acknowledgments
This work was supported by Centro Universitário Metodista do IPA, CAPES, FAPERGS and CNPq. A. Leyva (USA) helped with English editing of the manuscript.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
References
- Dani, C.; Oliboni, L.S.; Bonatto, D.; Vanderlinde, R.; Salvador, M.; Henriques, J.A. Phenolic content and antioxidant activities of white and purple juices manufactured with organically-produced grapes. Food Chem. Toxicol. 2007, 45, 2574–2580. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Asami, D.K.; Hong, Y.; Barrett, D.M.; Mitchell, A. Comparison of the total phenolic and ascorbic acid content of freeze-dried and air-dried marionberry, strawberry, and corn grown using conventional, organic, and sustainable agricultural practices. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2003, 51, 1237–1247. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rockenbach, I.I.; Gonzaga, L.V.; Rizelio, V.M.; Gonçalves, A.E.; Genovese, M.I.; Fett, R. Phenolic compounds and antioxidant activity of seed and skin extracts of red grape (Vitis vinifera and Vitis labrusca) pomace from Brazilian winemaking. Food Res. Int. 2011, 44, 897–901. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xia, E.; Deng, G.; Guo, Y.; Li, H. Biological activities of polyphenols from grapes. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2010, 11, 622–646. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Belguendouz, F.L.; Gozzelino, M.T. Interaction of transresveratrol with plasma lipoproteins. Biochem. Pharmacol. 1998, 15, 811–816. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Frémont, L.; Belquendouz, L.; Depal, S. Antioxidant activity of resveratrol and alcohol-free wine polyphenols related to LDL oxidation and polysaturated fatty acids. Life Sci. 1999, 64, 2511–2521. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Oliboni, L.; Dani, C.; Funchal, C.; Henriques, J.A.; Salvador, M. Hepatoprotective, cardioprotective, and renal-protective effects of organic and conventional grapevine leaf extracts (Vitis labrusca var. Bordo) on rats tissues. An. Acad. Bras. Ciênc. 2011, 83, 1403–1411. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dani, C.; Oliboni, L.S.; Agostini, F.; Funchal, C.; Serafini, L.; Henriques, J.A.; Salvador, M. Phenolic content of grapevine leaves (Vitis labrusca var. Bordo) and its neuroprotective effect against peroxide damage. Toxicol. In Vitro 2010, 24, 148–153. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Markesberry, W.R. The role of oxidative stress in Alzheimer disease. Arch. Neurol. 1999, 56, 1449–1452. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pietta, P. Flavonoids as antioxidants. J. Nat. Prod. 2000, 63, 1035–1042. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pari, L.; Suresh, A. Effect of grape (Vitis vinifera L.) leaf extract on alcohol induced oxidative stress in rats. Food Chem. Toxicol. 2008, 46, 1627–1634. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Haliwell, B. Role of free radicals in the neurodegenerative diseases: Therapeutic implications for antioxidant treatment. Drug Aging 2001, 18, 685–716. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singh, R.P.; Sharad, S.; Kapur, S. Free radicals and oxidative stress in neurodegenerative diseases: Relevance of dietary antioxidants. J. Indian Acad. Clin. Med. 2004, 5, 218–225. [Google Scholar]
- Devi, S.A.; Chandrasekar, B.K.; Manjula, K.R.; Ishi, N. Grape seed proanthocyanidin lowers brain oxidative stress in adult and middle-aged rats. Exp. Gerontol. 2011, 46, 958–964. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rodrigues, A.D.; Scheffel, T.B.; Scola, G.; Santos, M.T.; Fank, B.; de Freitas, S.C.V.; Dani, C.; Vanderlinde, R.; Henriques, J.A.P.; Coitinho, A.S.; et al. Neuroprotective and anticonvulsant effects of organic and conventional purple grape juices on seizures in Wistar rats induced by pentylenetetrazole. Neurochem. Int. 2012, 60, 799–805. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Scola, G.; Scheffel, T.; Gambato, G.; Freitas, S.; Dani, C.; Funchal, C.; Gomez, R.; Coitinho, A.; Salvador, M. Flavan-3-ol compounds prevent pentylenetetrazol-induced oxidative damage in rats without producing mutations and genotoxicity. Neurosci. Lett. 2013, 534, 145–149. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jayakumar, T.; Sakthivel, M.; Thomas, P.A.; Geraldine, P. Pleutorus ostreatus, an oyester mushroom, decreases the oxidative stress induced by carbon tetrachloride in rat kidneys, heart and brain. Chem. Biol. Interact. 2008, 176, 108–120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ozturk, F.; Ucar, M.; Ozturk, I.C.; Vardi, N.; Batcioglu, K. Carbon tetrachloride induced nephotoxicity and protective effect of betaine in Sprague-Dawley rats. Urology 2003, 62, 353–356. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Simile, M.M.; Banni, S.; Angioni, E.; Carta, G.; de Miglio, M.R.; Muroni, M.R.; Calvisi, D.F.; Carru, A.; Pascale, R.M.; Feo, F. 5-Methyl thioadenosine administration prevents lipid peroxidation and fibrogenesis induced in rat liver by carbon tetrachloride intoxication. J. Hepatol. 2001, 34, 386–394. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singleton, V.L.; Orthofer, R.; Lamuela-Raventós, R.M. Analysis of Total Phenols and Other Oxidation Substrates and Antioxidants by Means of Folin–Ciocalteau Reagent. In Methods in Enzymology; Packer, L., Ed.; Academic Press: San Diego, CA, USA, 1999; pp. 159–178. [Google Scholar]
- Saucier, C.; Mirabel, M.; Daviud, F.; Longieras, A.; Glories, T. Rapid fractionation of grape seeds proanthocyanidins. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2001, 49, 5732–5735. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fillip, R.; López, P.; Gilberti, J.; Coussio, J.; Ferraro, G. Phenolic compounds in seven South American Ilex species. Fitoterapia 2001, 72, 774–778. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ector, B.J.; Magee, J.B.; Hegwood, C.P.; Coign, M.J. Resveratrol concentration in muscadine berries, juice, pomace, purees, seeds, and wines. Am. J. Enol. Vitic. 1996, 47, 57–62. [Google Scholar]
- Dani, C.; Pasquali, M.A.; Oliveira, M.R.; Umezu, F.M.; Salvador, M.; Henriques, J.A.; Moreira, J.C.F. Protective effects of purple grape juice on carbon tetrachloride-induced oxidative stress in brains of adult wistar rats. J. Med. Food 2008, 11, 55–61. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wills, E.D. Mechanism of lipid peroxide formation in animal tissues. Biochem. J. 1996, 99, 667–676. [Google Scholar]
- Levine, R.L.; Garland, D.; Oliver, C.N.; Amici, A.; Climent, I.; Ahn, B.W. Determination of carbonyl content in oxidatively modified proteins. Methods Enzymol. 1990, 186, 464–478. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bannister, J.V.; Calabrese, L. Assays for SOD. Method Biochem. Anal. 1987, 32, 279–312. [Google Scholar]
- Aebi, H. Catalase in vitro. Methods Enzymol. 1984, 105, 121–126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lowry, O.H.; Rosebrouh, N.J.; Lewis-Farr, A.L.; Randall, R.J. Protein measurement with the Folin phenol reagent. J. Biol. Chem. 1951, 193, 265–275. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- IFOAM—International Foundation for Organic Agriculture. Norms for Organic Production and Processing; IFOAM: Bonn, Germany, 2005. [Google Scholar]
- Orhan, D.D.; Orhan, N.; Ergun, E.; Ergun, F. Hepatoprotective effect of Vitis vinifera L. leaves on carbon tetrachloride-induced acute liver damage in rats. J. Ethnopharmacol. 2007, 112, 145–151. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wollgast, J.; Anklam, E. Polyphenols in chocolate: Is there a contribution to human health? Food Res. Int. 2000, 22, 449–459. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Altas, S.; Kızıl, G.; Kızıl, M.; Ketani, A.; Haris, P.I. Protective effect of Diyarbakır watermelon juice on carbon tetrachloride-induced toxicity in rats. Food Chem. Toxicol. 2011, 49, 2433–2438. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Groot, H. Reactive oxygen species in tissue injury. Hepatogastroenterology 1994, 41, 328–332. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Halliwell, B. Oxidative stress and neurodegeneration: Where are we now? J. Neurochem. 2006, 97, 1634–1658. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gama, C.S.; Berk, M.; Andreazza, A.C.; Kapczinski, F.; Belmonte-de-Abreu, P. Serum levels of brain-derived neurotrophic factor and thiobarbituric acid reative substances in chronically medicated schizophrenic patients: A positive correlation. Rev. Bras. Psiquiatr. 2008, 30, 337–340. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Takayama, F.; Nakamoto, K.; Kawasaki, H.; Mankura, M.; Egashira, T.; Ueki, K.; Hasegawa, A.; Okada, S.; Mori, A. Beneficial effects of Vitis coignetiae Pulliat leaves on nonalcoholic steatohepatitis in a rat model. Acta Med. 2009, 63, 105–111. [Google Scholar]
- Dal-Pizzol, F.; Klamt, F.; Benfato, M.S.; Bernard, E.A.; Moreira, J.C. Retinol supplementation induces oxidative stress and modulates antioxidant enzyme activities in rat Sertoli cells. Free Radic. Res. 2001, 34, 395–404. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hota, S.K.; Barhwal, K.; Singh, S.B.; Ilavazhagan, G. Differential temporal response of hippocampus, cortex and cerebellum to hypobaric hypoxia: A biochemical approach. Neurochem. Int. 2007, 51, 384–390. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zupan, G.; Pilipović, K.; Hrelja, A.; Peternel, S. Oxidative stress parameters in different rat brain structures after electroconvulsive shock-induced seizures. Prog. Neuro Psychopharmacol. Biol. Psychiatry 2008, 32, 771–777. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Erecinska, M.; Silver, I.A. Calcium Handling by hippocampal Neurons under Physiologic and Pathologic Condition. In Advances in Neurology: Cellular and Molecular Mechanism of Ischemic Brain Damage; Seisjo, B.K., Wieloch, T., Eds.; Lippincott Raven Publishers: Philadelphia, PA, USA, 1996; pp. 119–131. [Google Scholar]
© 2014 by the authors; licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/3.0/).
