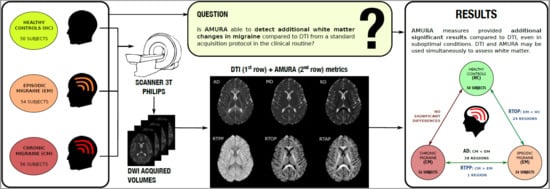
Alternative Microstructural Measures to Complement Diffusion Tensor Imaging in Migraine Studies with Standard MRI Acquisition
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Participants
2.2. MRI Acquisition
2.3. MRI Processing
2.3.1. Diffusion MRI Preprocessing
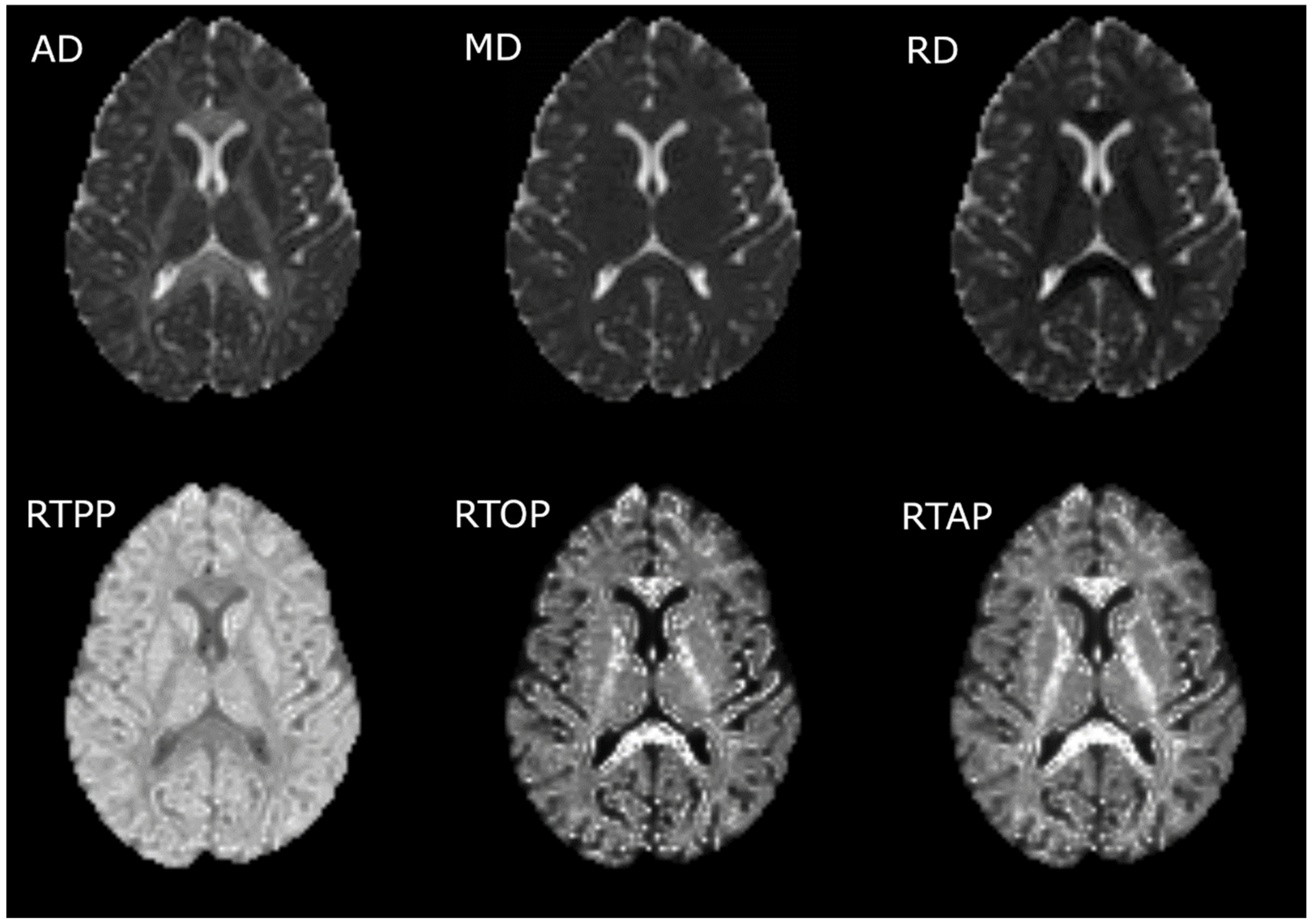
2.3.2. Calculation of the Diffusion Measures
2.3.3. Tract-Based Spatial Statistics (TBSS)
2.4. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
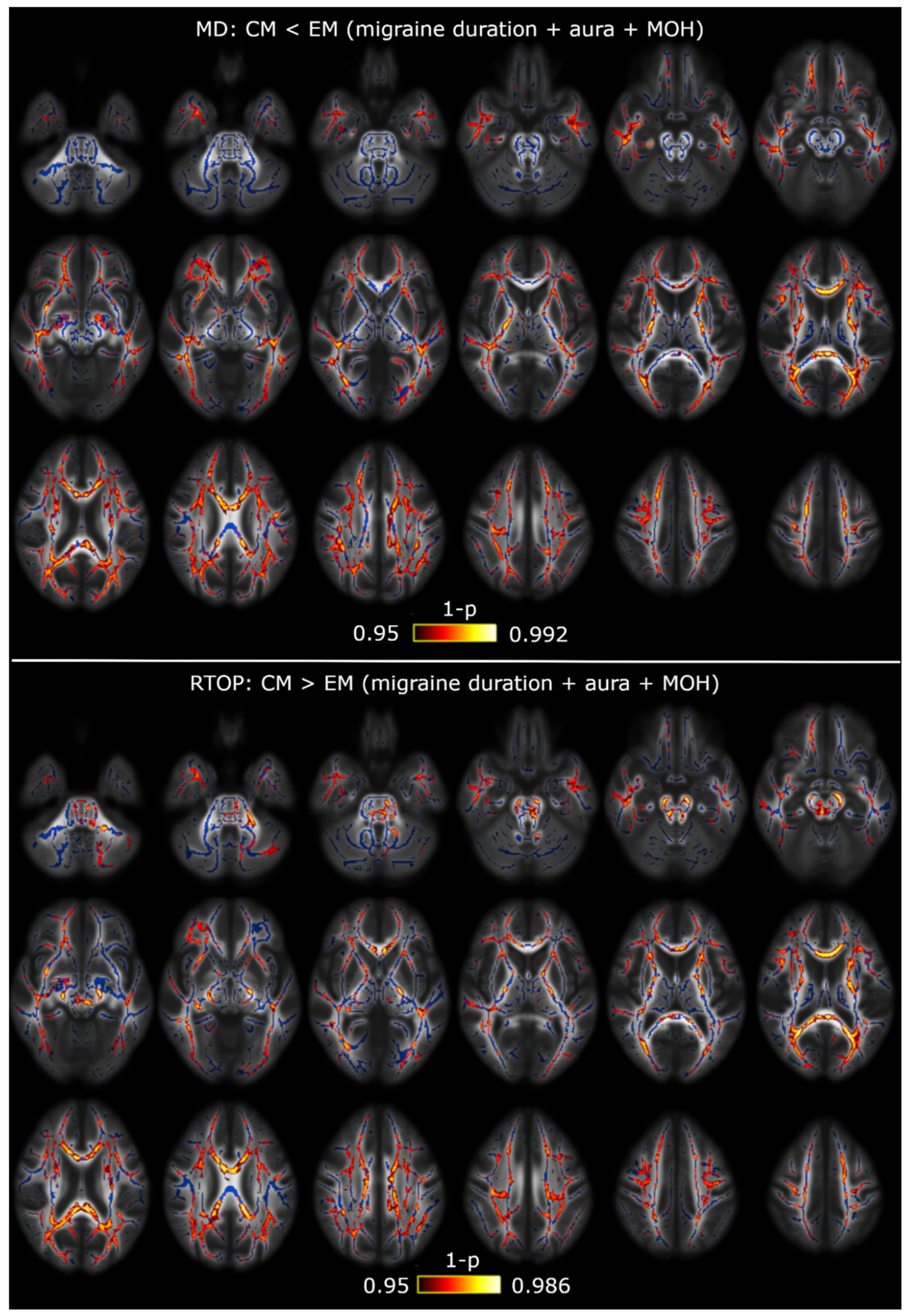
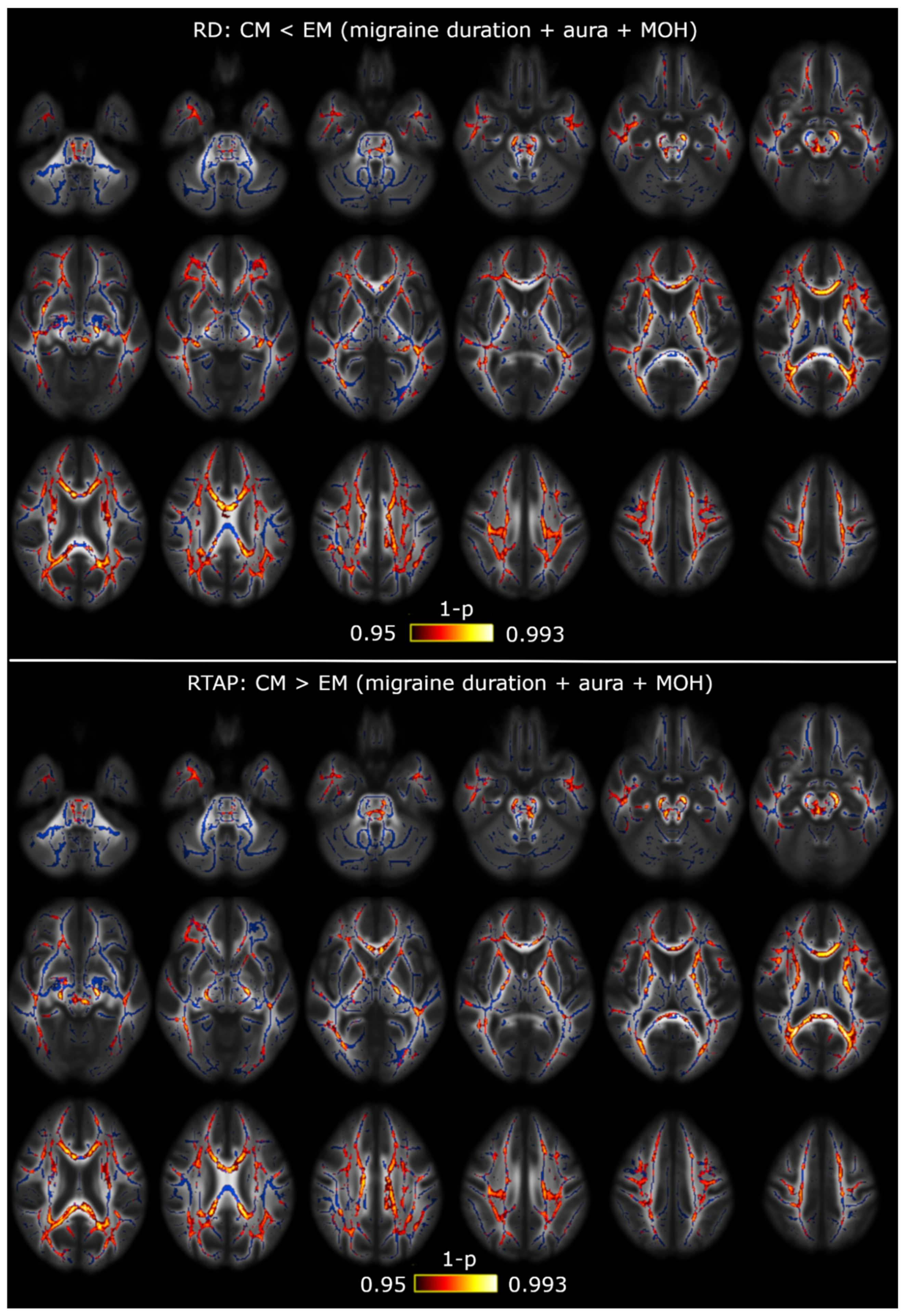
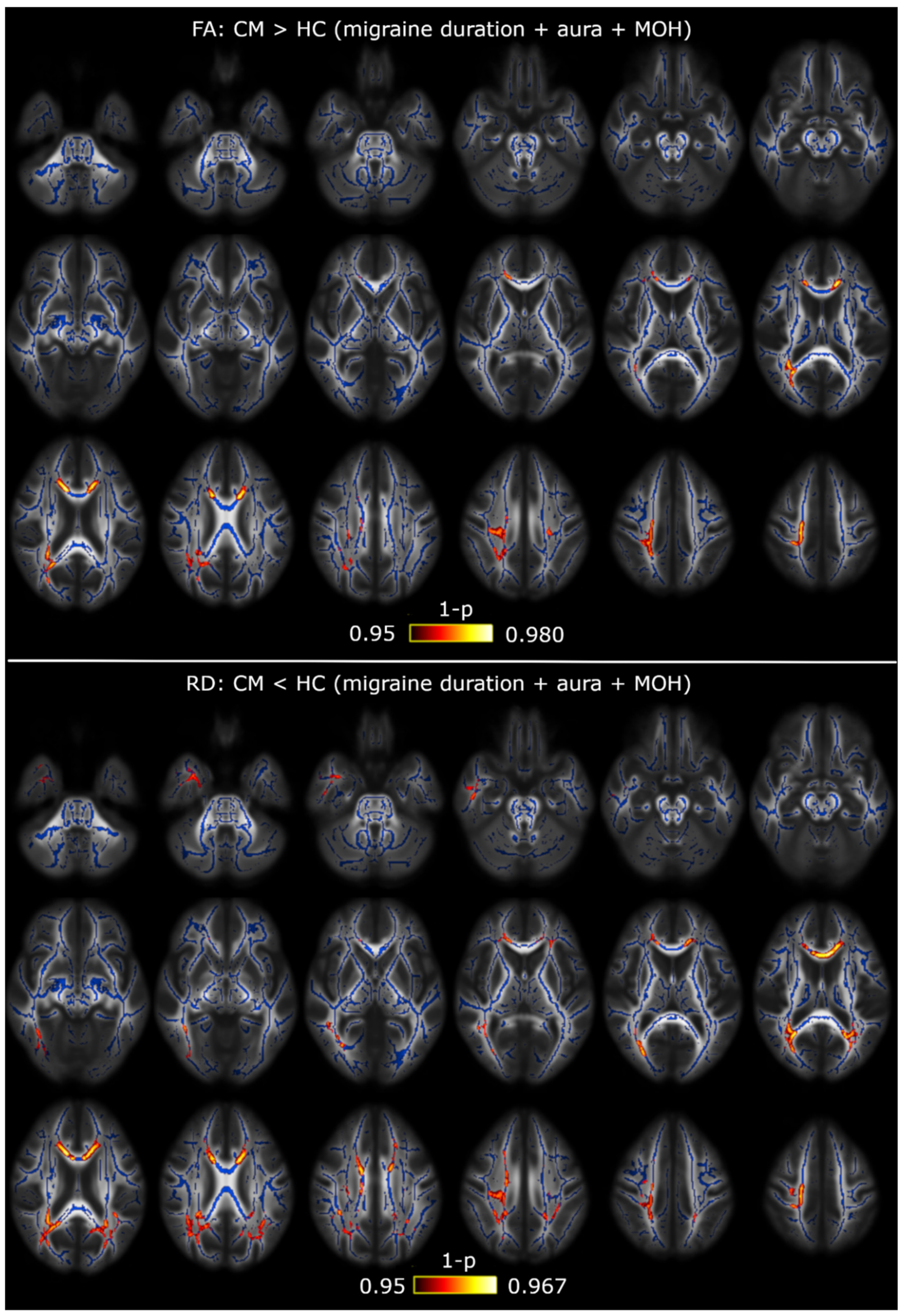
3.1. TBSS
3.2. TBSS with Covariates
3.3. Correlation Analysis
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Appendix A
Appendix B
| White Matter Region | Minimum p-Value (FWE-Corrected) | Volume (mm3) | MNI Peak Coordinate (mm), (x,y,z) |
|---|---|---|---|
| Middle cerebellar peduncle | 0.023 | 1295 | (−20,−50,−32) |
| Superior cerebellar peduncle R/L | 0.028/0.030 | 101/115 | (5,−28,−19)/(−4,−28,−19) |
| Inferior cerebellar peduncle L | 0.035 | 46 | (−10,−50,−25) |
| Superior longitudinal fasciculus R | 0.033 | 720 | (32,−4,20) |
| Splenium of corpus callosum | 0.042 | 32 | (18,−49,27) |
| Superior corona radiata R/L | 0.030/0.032 | 335/136 | (28,−15,19)/(−27,−11,20) |
| Posterior corona radiata R | 0.035 | 83 | (28,−34,19) |
| External capsule R/L | 0.033/0.031 | 127/171 | (30,−10,14)/(−28,−10,18) |
| Posterior limb of internal capsule R/L | 0.029/0.032 | 301/281 | (26,−17,13)/(−27,−17,17) |
| Retrolenticular part of internal capsule R/L | 0.031/0.032 | 473/59 | (30,−29,7)/(−25,−23,12) |
| Sagittal stratum R | 0.034 | 150 | (38,−28,−4) |
| Posterior thalamic radiation R | 0.034 | 51 | (30,−39,16) |
| Cerebral peduncle R/L | 0.028/0.031 | 207/258 | (10,−28,−16)/(−9,−20,−20) |
| Corticospinal tract R/L | 0.030/0.031 | 105/125 | (11,−22,−22)/(−7,−18,−22) |
| Pontine crossing tract | 0.030 | 56 | (4,−26,−24) |
| Fornix (cres) R | 0.037 | 46 | (35,−12,−14) |
| White Matter Region | Minimum p-Value (FWE-Corrected) | Volume (mm3) | MNI Peak Coordinate (mm), (x,y,z) |
|---|---|---|---|
| Superior corona radiata L | 0.026 | 116 | (−26,−11,20) |
| External capsule L | 0.022 | 303 | (−34,−15,−8) |
| Posterior limb of internal capsule L | 0.024 | 472 | (−15,10,0) |
| Retrolenticular part of internal capsule L | 0.025 | 347 | (−33,−34,6) |
| Sagittal stratum L | 0.023 | 133 | (−36,−17,−9) |
| Posterior thalamic radiation L | 0.025 | 38 | (−35,−39,7) |
| Cerebral peduncle L | 0.024 | 105 | (−15,−13,−5) |
| White Matter Region | Minimum p-Value (FWE-Corrected) | Volume (mm3) | MNI Peak Coordinate (mm), (x,y,z) |
|---|---|---|---|
| Superior longitudinal fasciculus R | 0.033 | 271 | (32,−4,19) |
| Body of corpus callosum | 0.042 | 47 | (19,−30,31) |
| Splenium of corpus callosum | 0.042 | 209 | (19,−31,31) |
| Anterior corona radiata R | 0.033 | 295 | (25,17,12) |
| Superior corona radiata R | 0.038 | 236 | (32,−6,20) |
| Posterior corona radiata R | 0.039 | 133 | (25,−23,22) |
| External capsule R | 0.031 | 661 | (30,1,13) |
| Posterior limb of internal capsule R | 0.039 | 217 | (24,−19,1) |
| Retrolenticular part of internal capsule R | 0.036 | 425 | (38,−29,0) |
| Anterior limb of internal capsule R | 0.035 | 83 | (23,17,11) |
| Sagittal stratum R | 0.036 | 132 | (33,−23,−4) |
| Fornix (cres) R | 0.035 | 36 | (33,−22,−6) |
| White Matter Region | Minimum p-Value (FWE-Corrected) | Volume (mm3) | MNI Peak Coordinate (mm), (x,y,z) |
|---|---|---|---|
| Superior corona radiata R/L | 0.046/0.040 | 50/87 | (20,−28,40)/(−26,−11,19) |
| External capsule L | 0.033 | 278 | (−33,−11,1) |
| Anterior limb of internal capsule L | 0.044 | 31 | (−18,2,12) |
| Posterior limb of internal capsule L | 0.034 | 377 | (−23,−22,3) |
| Retrolenticular part of internal capsule L | 0.034 | 315 | (−30,−23,2) |
| Sagittal stratum L | 0.034 | 114 | (−36,−17,−9) |
| Cerebral peduncle L | 0.036 | 37 | (−14,−12,−5) |
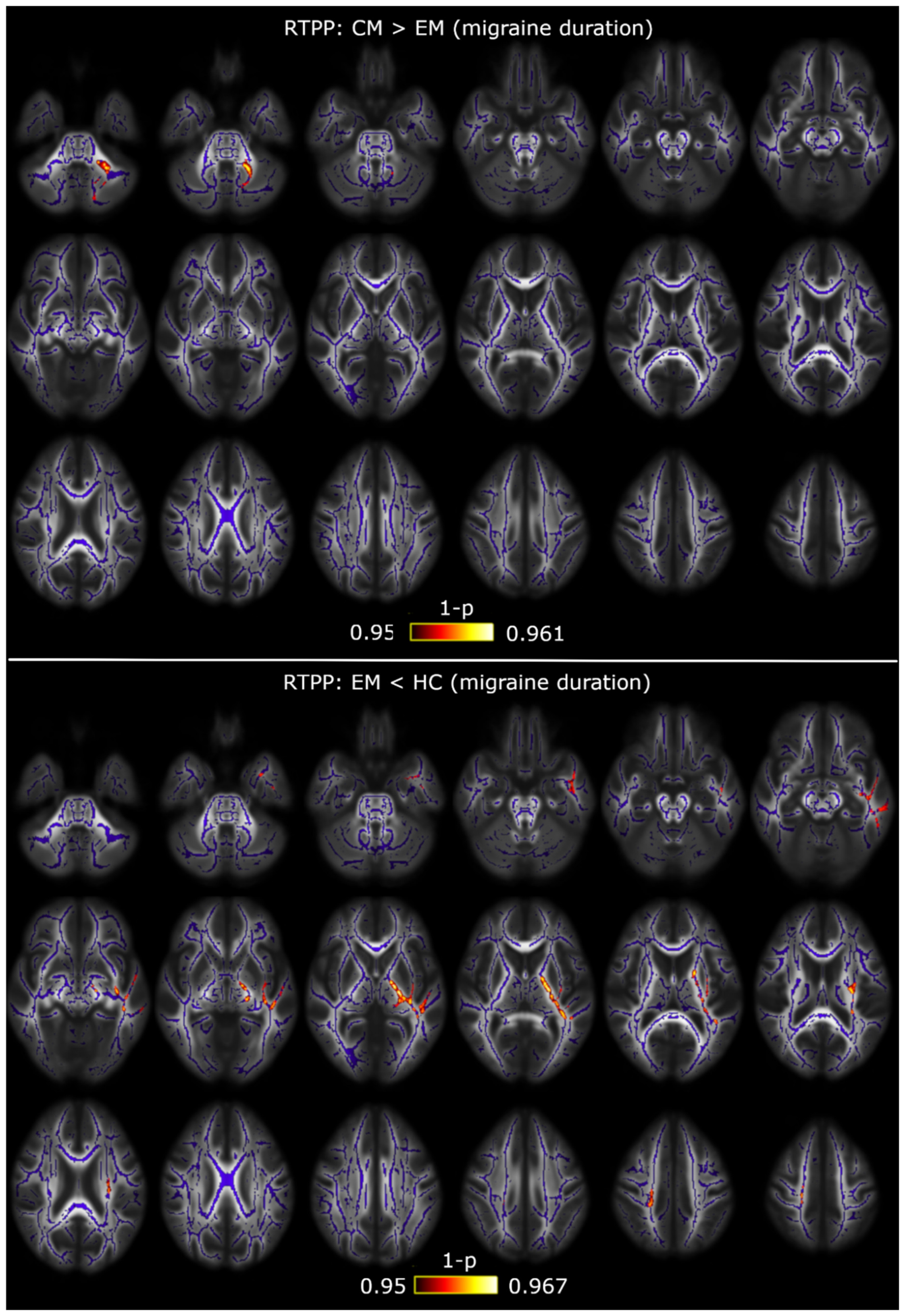
| White Matter Region | Minimum p-Value (FWE-Corrected) | Volume (mm3) | MNI Peak Coordinate (mm), (x,y,z) |
|---|---|---|---|
| Superior longitudinal fasciculus R | 0.046 | 179 | (39,−9,26) |
| External capsule R | 0.044 | 244 | (33,−14,−3) |
| Retrolenticular part of internal capsule R | 0.045 | 157 | (34,−21,−2) |
| Sagittal stratum R | 0.045 | 194 | (39,−18,−12) |
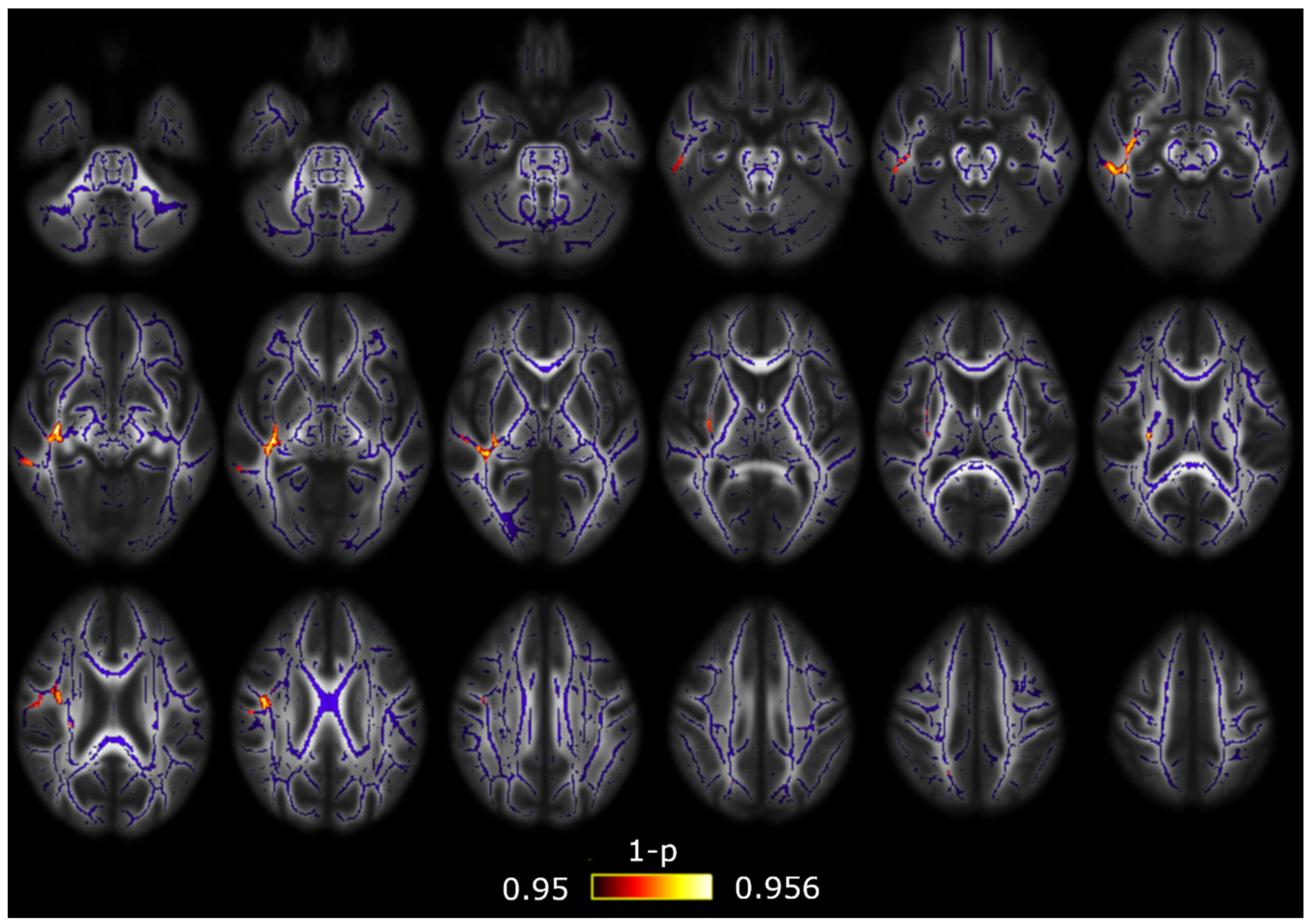
| White Matter Region | Minimum p-Value (FWE-Corrected) | Volume (mm3) | MNI Peak Coordinate (mm), (x,y,z) |
|---|---|---|---|
| Middle cerebellar peduncle | 0.047 | 31 | (−21,−65,−40) |
| White Matter Region | Minimum p-Value (FWE-Corrected) | Volume (mm3) | MNI Peak Coordinate (mm), (x,y,z) |
|---|---|---|---|
| Middle cerebellar peduncle | 0.026 | 439 | (−23,−55,−42) |
| Superior longitudinal fasciculus R/L | 0.045/0.039 | 52/464 | (33,1,27)/(−36,−4,−18) |
| Anterior corona radiata L | 0.042 | 66 | (−23,16,27) |
| Superior corona radiata L | 0.041 | 160 | (−26,4,26) |
| Posterior corona radiata L | 0.039 | 42 | (−29,−60,21) |
| External capsule R | 0.018 | 36 | (36,−16,−9) |
| Retrolenticular part of internal capsule R/L | 0.019/0.043 | 239/40 | (39,−38,−3)/(−39,−33,−1) |
| Sagittal stratum R/L | 0.012/0.036 | 387/194 | (44,−29,−14)/(−40,−33,−6) |
| Posterior thalamic radiation R/L | 0.015/0.039 | 188/176 | (39,−41,−2)/(−30,−65,17) |
| Fornix (cres) R | 0.017 | 75 | (35,−16,−12) |
| Cingulum (hippocampus) R | 0.017 | 68 | (29,−18,27) |
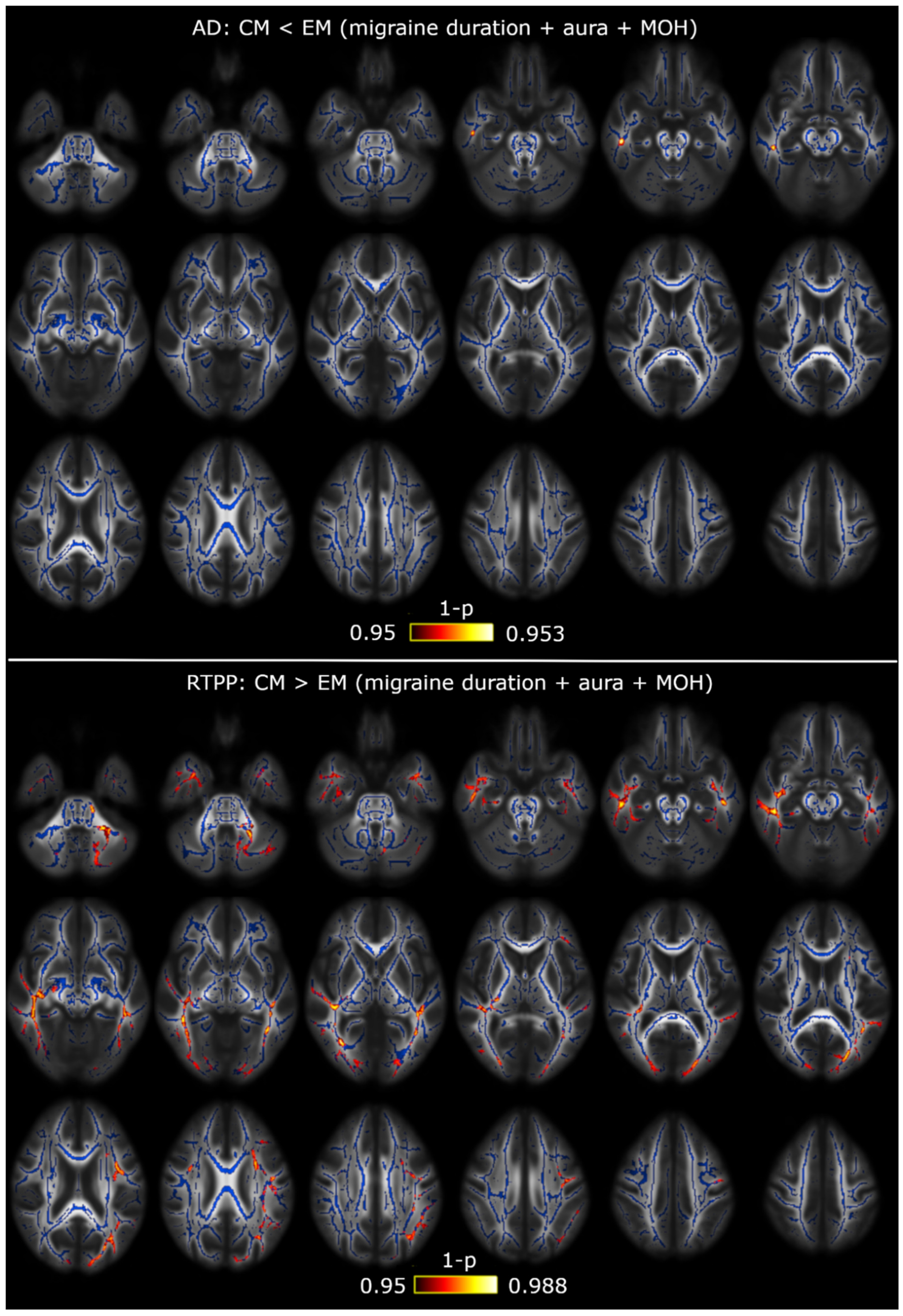
| White Matter Region | Minimum p-Value (FWE-Corrected) | Volume (mm3) | MNI Peak Coordinate (mm), (x,y,z) |
|---|---|---|---|
| Superior longitudinal fasciculus R/L | 0.012/0.012 | 950/1030 | (38,−35,31)/(−35,−35,27) |
| Genu of corpus callosum | 0.012 | 653 | (18,20,25) |
| Body of corpus callosum | 0.012 | 1440 | (16,16,29) |
| Splenium of corpus callosum | 0.009 | 1170 | (26,−58,12) |
| Anterior corona radiata R/L | 0.011/0.012 | 1147/980 | (26,16,25)/(−25,18,21) |
| Superior corona radiata R/L | 0.011/0.012 | 904/820 | (25,12,28)/(−25,6,28) |
| Posterior corona radiata R/L | 0.009/0.012 | 265/246 | (28,−63,19)/(−30,−60,21) |
| External capsule R/L | 0.012/0.012 | 549/576 | (30,11,−1)/(−25,10,14) |
| Posterior limb of internal capsule R/L | 0.012/0.016 | 390/261 | (23,−6,17)/(−22,−10,16) |
| Retrolenticular part of internal capsule R/L | 0.012/0.016 | 390/271 | (30,−38,17)/(−38,−33,0) |
| Anterior limb of internal capsule R/L | 0.012/0.012 | 229/416 | (22,8,13)/(−20,9,13) |
| Sagittal stratum R/L | 0.014/0.016 | 444/309 | (44,−30,−15)/(−40,−28,−7) |
| Posterior thalamic radiation R/L | 0.008/0.012 | 601/470 | (29,−61,13)/(−30,−66,−16) |
| Fornix (cres) R/L | 0.015/0.018 | 171/177 | (33,−7,−19)/(−35,−11,−17) |
| Cingulum R/L | 0.014/0.016 | 53/135 | (10,−46,22)/(−10,−40,28) |
| Cingulum (hippocampus) R/L | 0.018/0.019 | 84/67 | (24,−29,−15)/(−19,−38,−7) |
| Superior fronto-occipital fasciculus R/L | 0.012/0.012 | 59/46 | (22,−1,21)/(−21,1,20) |
| Uncinate fasciculus R | 0.025 | 35 | (34,0,−15) |
| Tapetum R/L | 0.009/0.016 | 82/75 | (31,−52,14)/(−28,−50,16) |
| White Matter Region | Minimum p-Value (FWE-Corrected) | Volume (mm3) | MNI Peak Coordinate (mm), (x,y,z) |
|---|---|---|---|
| Middle cerebellar peduncle | 0.033 | 694 | (−6,−19,−32) |
| Superior cerebellar peduncle R/L | 0.033/0.034 | 66/49 | (6,−29,−19)/(−7,−34,−23) |
| Inferior cerebellar peduncle L | 0.040 | 113 | (−11,−46,−29) |
| Superior longitudinal fasciculus R/L | 0.016/0.019 | 610/722 | (35,−44,26)/(−32,7,22) |
| Genu of corpus callosum | 0.018 | 905 | (−13,22,18) |
| Body of corpus callosum | 0.018 | 1783 | (−13,18,21) |
| Splenium of corpus callosum | 0.015 | 1680 | (25,−53,19) |
| Anterior corona radiata R/L | 0.018/0.019 | 972/555 | (25,15,28)/(−25,13,23) |
| Superior corona radiata R/L | 0.018/0.019 | 710/793 | (25,12,28)/(−24,5,20) |
| Posterior corona radiata R/L | 0.014/0.019 | 291/287 | (28,−63,19)/(−18,−40,36) |
| External capsule R/L | 0.019/0.019 | 408/250 | (26,17,7)/(−25,10,14) |
| Posterior limb of internal capsule R/L | 0.020/0.019 | 297/390 | (23,−6,17)/(−22,−10,16) |
| Retrolenticular part of internal capsule R/L | 0.030/0.038 | 223/131 | (29,−37,17)/(−38,−33,0) |
| Anterior limb of internal capsule R/L | 0.019/0.019 | 319/436 | (22,18,9)/(−21,14,13) |
| Sagittal stratum R/L | 0.020/0.039 | 252/204 | (38,−15,−12)/(−40,−28,−7) |
| Posterior thalamic radiation R/L | 0.014/0.022 | 529/364 | (28,−64,18)/(−30,−66,16) |
| Cerebral peduncle R/L | 0.033/0.032 | 233/323 | (10,−29,−16)/(−8,−18,−20) |
| Corticospinal tract R/L | 0.034/0.033 | 99/205 | (11,−25,−22)/(−7,−21,−27) |
| Medial lemniscus R/L | 0.034/0.034 | 36/68 | (6,−33,−30)/(−4,−33,−26) |
| Pontine crossing tract | 0.033 | 217 | (6,−30,−30) |
| Fornix (cres) R | 0.020 | 164 | (33,7,−19) |
| Cingulum R/L | 0.029/0.019 | 43/160 | (10,−46,22)/(−10,−40,28) |
| Superior fronto-occipital fasciculus R/L | 0.020/0.019 | 61/54 | (22,6,20)/(−21,1,20) |
| Uncinate fasciculus R | 0.039 | 43 | (34,0,−18) |
| Tapetum R/L | 0.015/0.021 | 78/100 | (31,−52,14)/(−26,−49,19) |
| White Matter Region | Minimum p-Value (FWE-Corrected) | Volume (mm3) | MNI Peak Coordinate (mm), (x,y,z) |
|---|---|---|---|
| Superior cerebellar peduncle R | 0.043 | 49 | (4,−29,−17) |
| Superior longitudinal fasciculus R/L | 0.009/0.007 | 667/711 | (33,−40,29)/(−28,−44,31) |
| Genu of corpus callosum | 0.010 | 1005 | (−14,23,19) |
| Body of corpus callosum | 0.007 | 1749 | (−17,−23,34) |
| Splenium of corpus callosum | 0.007 | 1192 | (−23,−52,19) |
| Anterior corona radiata R/L | 0.009/0.007 | 1145/728 | (27,12,23)/(−24,13,15) |
| Superior corona radiata R/L | 0.009/0.007 | 966/991 | (26,8,25)/(−26,−18,28) |
| Posterior corona radiata R/L | 0.007/0.007 | 350/392 | (28,−63,16)/(−26,−62,16) |
| External capsule R/L | 0.009/0.007 | 426/362 | (26,16,9)/(−24,15,10) |
| Posterior limb of internal capsule R/L | 0.011/0.008 | 363/277 | (20,−4,12)/(−22,−11,14) |
| Retrolenticular part of internal capsule R/L | 0.011/0.011 | 234/276 | (30,−38,17)/(−37,−34,2) |
| Anterior limb of internal capsule R/L | 0.009/0.007 | 337/440 | (22,7,15)/(−21,14,13) |
| Sagittal stratum R/L | 0.029/0.011 | 267/189 | (40,−14,−16)/(−41,−26,−8) |
| Posterior thalamic radiation R/L | 0.007/0.008 | 512/303 | (28,−63,16)/(−26,−62,16) |
| Pontine crossing tract | 0.044 | 182 | (−2,−31,−35) |
| Fornix (cres) R/L | 0.030/0.013 | 182/191 | (35,−8,−19)/(−35,−11,−17) |
| Cingulum R/L | 0.018/0.011 | 35/141 | (10,−34,35)/(−9,−39,29) |
| Superior fronto-occipital fasciculus R/L | 0.009/0.007 | 85/61 | (22,6,19)/(−21,1,20) |
| Uncinate fasciculus R | 0.020 | 43 | (34,1,−15) |
| Tapetum R/L | 0.008/0.008 | 82/75 | (31,−52,14)/(−28,−48,20) |
| White Matter Region | Minimum p-Value (FWE-Corrected) | Volume (mm3) | MNI Peak Coordinate (mm), (x,y,z) |
|---|---|---|---|
| Middle cerebellar peduncle | 0.032 | 85 | (9,−21,−39) |
| Superior cerebellar peduncle R/L | 0.043/0.043 | 59/42 | (4,−29,−17)/(−7,−34,−23) |
| Superior longitudinal fasciculus R/L | 0.032/0.021 | 60/54 | (34,−45,28)/(−28,−44,31) |
| Genu of corpus callosum | 0.033 | 890 | (−13,23,19) |
| Body of corpus callosum | 0.021 | 1633 | (−17,−24,34) |
| Splenium of corpus callosum | 0.021 | 1612 | (−23,−52,19) |
| Anterior corona radiata R/L | 0.031/0.021 | 919/498 | (27,12,23)/(−24,13,15) |
| Superior corona radiata R/L | 0.029/0.021 | 672/804 | (19,−23,36)/(−24,3,20) |
| Posterior corona radiata R/L | 0.021/0.021 | 299/327 | (28,−63,19)/(−23,−32,32) |
| External capsule R/L | 0.032/0.021 | 81/157 | (26,16,8)/(−26,10,14) |
| Posterior limb of internal capsule R/L | 0.011/0.008 | 300/420 | (19,−11,2)/(−22,−10,14) |
| Retrolenticular part of internal capsule L | 0.028 | 127 | (−36,−34,1) |
| Anterior limb of internal capsule R/L | 0.009/0.007 | 364/432 | (23,18,8)/(−22,6,18) |
| Sagittal stratum R/L | 0.032/0.029 | 207/165 | (40,−42,−5)/(−40,−28,−7) |
| Posterior thalamic radiation R/L | 0.021/0.023 | 510/245 | (28,−63,16)/(−27,−63,18) |
| Cerebral peduncle R/L | 0.032/0.031 | 227/319 | (10,−29,−15)/(−17,−16,−6) |
| Corticospinal tract R/L | 0.032/0.032 | 107/141 | (6,−28,−40)/(−7,−20,−24) |
| Medial lemniscus R/L | 0.032/0.032 | 34/61 | (6,−33,−30)/(−4,−33,−26) |
| Pontine crossing tract | 0.032 | 204 | (−2,−31,−35) |
| Cingulum L | 0.022 | 162 | (−9,−39,29) |
| Cingulum (hippocampus) R | 0.042 | 40 | (24,−29,−15) |
| Superior fronto-occipital fasciculus R/L | 0.032/0.021 | 60/54 | (22,5,19)/(−21,1,20) |
| Tapetum R/L | 0.023/0.021 | 82/104 | (31,−52,14)/(−25,−46,20) |
| White Matter Region | Minimum p-Value (FWE-Corrected) | Volume (mm3) | MNI Peak Coordinate (mm), (x,y,z) |
|---|---|---|---|
| Superior longitudinal fasciculus L | 0.042 | 135 | (−29,−25,37) |
| Superior corona radiata L | 0.040 | 244 | (−22,−23,41) |
| External capsule L | 0.033 | 281 | (−35,−16,−8) |
| Posterior limb of internal capsule L | 0.031 | 430 | (−16,−8,4) |
| Retrolenticular part of internal capsule L | 0.035 | 297 | (−33,−35,6) |
| Anterior limb of internal capsule L | 0.035 | 37 | (−11,0,2) |
| Sagittal stratum L | 0.034 | 153 | (−40,−29,−6) |
| Cerebral peduncle L | 0.033 | 98 | (−15,−13,−5) |
| White Matter Region | Minimum p-Value (FWE-Corrected) | Volume (mm3) | MNI Peak Coordinate (mm), (x,y,z) |
|---|---|---|---|
| Superior longitudinal fasciculus L | 0.046 | 32 | (−41,−38,4) |
| External capsule L | 0.046 | 127 | (−34,−14,−8) |
| Posterior limb of internal capsule L | 0.044 | 277 | (−16,−8,4) |
| Retrolenticular part of internal capsule L | 0.047 | 202 | (−30,−23,2) |
| Sagittal stratum L | 0.042 | 83 | (−40,−30,−5) |

| White Matter Region | Minimum p-Value (FWE-Corrected) | Volume (mm3) | MNI Peak Coordinate (mm), (x,y,z) |
|---|---|---|---|
| Superior longitudinal fasciculus R | 0.037 | 78 | (35,−44,26) |
| Genu of corpus callosum | 0.037 | 387 | (−14,21,21) |
| Body of corpus callosum | 0.037 | 463 | (−12,19,21) |
| Splenium of corpus callosum | 0.034 | 87 | (25,−53,19) |
| Anterior corona radiata R | 0.042 | 91 | (17,24,24) |
| Superior corona radiata R/L | 0.049/0.046 | 258/48 | (20,−30,41)/(−22,−20,36) |
| Posterior corona radiata R | 0.020 | 285 | (20,−30,39) |
| Posterior thalamic radiation R | 0.034 | 100 | (28,−56,17) |
| Tapetum R | 0.034 | 94 | (30,−46,17) |
| White Matter Region | Minimum p-Value (FWE-Corrected) | Volume (mm3) | MNI Peak Coordinate (mm), (x,y,z) |
|---|---|---|---|
| Superior longitudinal fasciculus R/L | 0.038/0.046 | 218/127 | (35,−48,25)/(−29,−45,31) |
| Genu of corpus callosum | 0.033 | 566 | (−14,21,21) |
| Body of corpus callosum | 0.033 | 985 | (−12,19,21) |
| Splenium of corpus callosum | 0.035 | 314 | (25,−52,22) |
| Anterior corona radiata R/L | 0.040/0.038 | 144/188 | (17,27,21)/(−15,16,30) |
| Superior corona radiata R | 0.037 | 337 | (20,−29,41) |
| Posterior corona radiata R/L | 0.035/0.046 | 311/120 | (28,−55,20)/(−29,−57,21) |
| Posterior thalamic radiation R/L | 0.035/0.046 | 389/38 | (28,−63,17)/(−31,−52,16) |
| Tapetum R/L | 0.038/0.044 | 95/69 | (30,−47,17)/(−26,−51,18) |
References
- Headache Classification Committee of the International Headache Society. The International Classification of Headache Disorders, 3rd edition. Cephalalgia 2018, 38, 1–211. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Szabó, N.; Kincses, Z.T.; Párdutz, A.; Tajti, J.; Szok, D.; Tuka, A.; Király, A.; Babos, M.; Vörös, E.; Bomboi, G.; et al. White matter microstructural alterations in migraine: A diffusion-weighted MRI study. Pain 2012, 153, 651–656. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yu, D.; Yuan, K.; Zhao, L.; Dong, M.; Liu, P.; Yang, X.; Liu, J.; Sun, J.; Zhou, G.; Xue, T.; et al. White matter integrity affected by depressive symptoms in migraine without aura: A tract-based spatial statistics study. NMR Biomed. 2013, 26, 1103–1112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gomez-Beldarrain, M.; Oroz, I.; Garcia Zapirain, B.; Fernandez Ruanova, B.; Garcia Fernandez, Y.; Cabrera, A.; Anton-Ladislao, A.; Aguirre-Larracoechea, U.; Garcia-Monco, J.C. Right fronto-insular white matter tracts link cognitive reserve and pain in migraine patients [erratum in J Headache Pain. 2016;17:22]. J. Headache Pain 2015, 17, 4. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shibata, Y.; Ishiyama, S.; Matsushita, A. White matter diffusion abnormalities in migraine and medication overuse headache: A 1.5-T tract-based spatial statistics study. Clin. Neurol. Neurosurg. 2018, 174, 167–173. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Messina, R.; Rocca, M.A.; Colombo, B.; Pagani, E.; Falini, A.; Comi, G.; Filippi, M. White matter microstructure abnormalities in pediatric migraine patients. Cephalalgia 2015, 35, 1278–1286. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Planchuelo-Gómez, Á.; García-Azorín, D.; Guerrero, Á.L.; Aja-Fernández, S.; Rodríguez, M.; de Luis-García, R. White matter changes in chronic and episodic migraine: A diffusion tensor imaging study. J. Headache Pain 2020, 21, 1. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Coppola, G.; Di Renzo, A.; Tinelli, E.; Petolicchio, B.; Di Lorenzo, C.; Parisi, V.; Serrao, M.; Calistri, V.; Tardioli, S.; Cartocci, G.; et al. Patients with chronic migraine without history of medication overuse are characterized by a peculiar white matter fiber bundle profile. J. Headache Pain 2020, 21, 92. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Neeb, L.; Bastian, K.; Villringer, K.; Gits, H.C.; Israel, H.; Reuter, U.; Fiebach, J.B. No microstructural White Matter Alterations in Chronic and Episodic Migraineurs: A Case-Control Diffusion Tensor Magnetic Resonance Imaging Study. Headache 2015, 55, 241–251. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tuch, D.S.; Reese, T.G.; Wiegell, M.R.; Wedeen, V.J. Diffusion MRI of Complex Neural Architecture. Neuron 2003, 40, 885–895. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tristán-Vega, A.; Westin, C.-F.; Aja-Fernández, S. Estimation of fiber orientation probability density functions in high angular resolution diffusion imaging. Neuroimage 2009, 47, 638–650. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jensen, J.H.; Helpern, J.A.; Ramani, A.; Lu, H.; Kaczynski, K. Diffusional kurtosis imaging: The quantification of non-gaussian water diffusion by means of magnetic resonance imaging. Magn. Reson. Med. 2005, 53, 1432–1440. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wedeen, V.J.; Hagmann, P.; Tseng, W.-Y.I.; Reese, T.G.; Weisskoff, R.M. Mapping complex tissue architecture with diffusion spectrum magnetic resonance imaging. Magn. Reson. Med. 2005, 54, 1377–1386. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Özarslan, E.; Koay, C.G.; Shepherd, T.M.; Komlosh, M.E.; İrfanoğlu, M.O.; Pierpaoli, C.; Basser, P.J. Mean Apparent Propagator (MAP) MRI: A novel diffusion imaging method for mapping tissue microstructure. Neuroimage 2013, 78, 16–32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ning, L.; Westin, C.-F.; Rathi, Y. Estimating diffusion propagator and its moments using directional radial basis functions. IEEE Trans. Med. Imaging 2015, 34, 2058–2078. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aja-Fernández, S.; de Luis-García, R.; Afzali, M.; Molendowska, M.; Pieciak, T.; Tristán-Vega, A. Micro-structure diffusion scalar measures from reduced MRI acquisitions. PLoS ONE 2020, 15, 1–25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Planchuelo-Gómez, Á.; García-Azorín, D.; Guerrero, Á.L.; Aja-Fernández, S.; Rodríguez, M.; de Luis-García, R. Structural connectivity alterations in chronic and episodic migraine: A diffusion magnetic resonance imaging connectomics study. Cephalalgia 2020, 40, 367–383. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Headache Classification Committee of the International Headache Society. The International Classification of Headache Disorders, 3rd edition (beta version). Cephalalgia 2013, 33, 629–808. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Serrano, D.; Lipton, R.B.; Scher, A.I.; Reed, M.L.; Stewart, W.F.; Manack Adams, A.; Buse, D.C. Fluctuations in episodic and chronic migraine status over the course of 1 year: Implications for diagnosis, treatment and clinical trial design. J. Headache Pain 2017, 18, 101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zigmond, A.S.; Snaith, R.P. The hospital anxiety and depression scale. Acta Psychiatr. Scand. 1983, 67, 361–370. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tournier, J.-D.; Smith, R.; Raffelt, D.; Tabbara, R.; Dhollander, T.; Pietsch, M.; Christiaens, D.; Jeurissen, B.; Yeh, C.-H.; Connelly, A. MRtrix3: A fast, flexible and open software framework for medical image processing and visualisation. Neuroimage 2019, 202, 116–137. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Veraart, J.; Novikov, D.S.; Christiaens, D.; Ades-Aron, B.; Sijbers, J.; Fieremans, E. Denoising of diffusion MRI using random matrix theory. Neuroimage 2016, 142, 394–406. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Andersson, J.L.; Sotiropoulos, S.N. An integrated approach to correction for off-resonance effects and subject movement in diffusion MR imaging. Neuroimage 2015, 125, 1063–1078. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Smith, S.M.; Jenkinson, M.; Woolrich, M.W.; Beckmann, C.F.; Behrens, T.E.; Johansen-Berg, H.; Bannister, P.R.; De Luca, M.; Drobnjak, I.; Flitney, D.E.; et al. Advances in functional and structural MR image analysis and implementation as FSL. Neuroimage 2004, 23, S208–S219. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Brady, M.; Smith, S. Segmentation of brain MR images through a hidden Markov random field model and the expectation-maximization algorithm. IEEE Trans. Med. Imaging 2001, 20, 45–57. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dhollander, T.; Raffelt, D.; Connelly, A. Unsupervised 3-tissue response function estimation from single-shell or multi-shell diffusion MR data without a co-registered T1 image. ISMRM Work. Break. Barriers Diffus. MRI 2016, 5. [Google Scholar]
- Jenkinson, M.; Beckmann, C.F.; Behrens, T.E.; Woolrich, M.W.; Smith, S.M. FSL. Neuroimage 2012, 62, 782–790. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pelletier, A.; Periot, O.; Dilharreguy, B.; Hiba, B.; Bordessoules, M.; Chanraud, S.; Pérès, K.; Amieva, H.; Dartigues, J.-F.; Allard, M.; et al. Age-Related Modifications of Diffusion Tensor Imaging Parameters and White Matter Hyperintensities as Inter-Dependent Processes. Front. Aging. Neurosci. 2015, 7, 255. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Avram, A.V.; Sarlls, J.E.; Barnett, A.S.; Özarslan, E.; Thomas, C.; Irfanoglu, M.O.; Hutchinson, E.; Pierpaoli, C.; Basser, P.J. Clinical feasibility of using mean apparent propagator (MAP) MRI to characterize brain tissue microstructure. Neuroimage 2016, 127, 422–434. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Smith, S.M.; Jenkinson, M.; Johansen-Berg, H.; Rueckert, D.; Nichols, T.E.; Mackay, C.E.; Winkins, K.E.; Ciccarelli, O.; Cader, M.Z.; Matthews, P.M.; et al. Tract-based Spatial Statistics: Voxelwise analysis of multi-subject diffusion data. Neuroimage 2006, 31, 1487–1505. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mori, S.; Wakana, S.; Nagae-Poetscher, L.M.; van Zijl, P.C. MRI Atlas of Human White Matter; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2005. [Google Scholar]
- Oishi, K.; Zilles, K.; Amunts, K.; Faria, A.; Jiang, H.; Li, X.; Akhter, K.; Hua, K.; Woods, R.; Toga, A.W.; et al. Human brain white matter atlas: Identification and assignment of common anatomical structures in superficial white matter. Neuroimage 2008, 43, 447–457. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hua, K.; Zhang, J.; Wakana, S.; Jiang, H.; Li, X.; Reich, D.S.; Calabresi, P.A.; Pekar, J.J.; van Zijl, P.C.M.; Mori, S. Tract Probability Maps in Stereotaxic Spaces: Analyses of White Matter Anatomy and Tract-Specific Quantification. Neuroimage 2008, 39, 336–347. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rueckert, D.; Sonoda, L.I.; Hayes, C.; Hill, D.L.; Leach, M.O.; Hawkes, D.J. Nonrigid registration using free-form deformations: Application to breast MR images. IEEE Trans. Med. Imaging 1999, 18, 712–721. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nichols, T.E.; Holmes, A.P. Nonparametric permutation tests for functional neuroimaging: A primer with examples. Hum. Brain Mapp 2002, 15, 1–25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Smith, S.M.; Nichols, T.E. Threshold-free cluster enhancement: Addressing problems of smoothing, threshold dependence and localisation in cluster inference. Neuroimage 2009, 44, 83–98. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Benjamini, Y.; Hochberg, Y. Controlling the false discovery rate: A practical and powerful approach to multiple testing. J. R. Stat. Soc. Ser. B 1995, 57, 289–300. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, D.; Yuan, K.; Qin, W.; Zhao, L.; Dong, M.; Liu, P.; Yang, X.; Liu, J.; Sun, J.; Zhou, G.; et al. Axonal loss of white matter in migraine without aura: A tract-based spatial statistics study. Cephalalgia 2013, 33, 34–42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alexander, A.L.; Lee, J.E.; Lazar, M.; Field, A.S. Diffusion Tensor Imaging of the Brain. Neurotherapeutics 2007, 4, 316–329. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, S.-W.; Liang, H.-F.; Cross, A.H.; Song, S.-K. Evolving Wallerian Degeneration after Transient Retinal Ischemia in Mice Characterized by Diffusion Tensor Imaging. Neuroimage 2008, 40, 1–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Winklewski, P.J.; Sabisz, A.; Naumczyk, P.; Jodzio, K.; Szurowska, E.; Szarmach, A. Understanding the Physiopathology Behind Axial and Radial Diffusivity Changes—What Do We Know? Front. Neurol 2018, 9, 92. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bilgiç, B.; Kocaman, G.; Arslan, A.B.; Noyan, H.; Sherifov, R.; Alkan, A.; Asil, T.; Parman, Y.; Baykan, B. Volumetric differences suggest involvement of cerebellum and brainstem in chronic migraine. Cephalalgia 2016, 36, 301–308. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vincent, M.; Hadjikhani, N. The cerebellum and migraine. Headache 2007, 47, 820–833. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Borsook, D.; Burstein, R. The enigma of the dorsolateral pons as a migraine generator. Cephalalgia 2012, 32, 803–812. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chong, C.D.; Plasencia, J.D.; Frakes, D.H.; Schwedt, T.J. Structural alterations of the brainstem in migraine. NeuroImage. Clin. 2016, 13, 223–227. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rocca, M.A.; Pagani, E.; Colombo, B.; Tortorella, P.; Falini, A.; Comi, G.; Filippi, M. Selective Diffusion Changes of The Visual Pathways in Patients with Migraine: A 3-T Tractography Study. Cephalalgia 2008, 28, 1061–1068. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chong, C.D.; Schwedt, T.J. Migraine affects white-matter tract integrity: A diffusion-tensor imaging study. Cephalalgia 2015, 35, 1162–1171. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marciszewski, K.K.; Meylakh, N.; Di Pietro, F.; Macefield, V.G.; Macey, P.M.; Henderson, L.A. Altered brainstem anatomy in migraine. Cephalalgia 2018, 38, 476–486. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kattem Husøy, A.; Eikenes, L.; Håberg, A.K.; Hagen, K.; Stovner, L.J. Diffusion tensor imaging in middle-aged headache sufferers in the general population: A cross-sectional population-based imaging study in the Nord-Trøndelag health study (HUNT-MRI). J. Headache Pain 2019, 20, 78. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qin, Z.; He, X.-W.; Zhang, J.; Xu, S.; Li, G.-F.; Su, J.; Shi, Y.-H.; Ban, S.; Hu, Y.; Liu, Y.-S.; et al. Structural changes of cerebellum and brainstem in migraine without aura. J. Headache Pain 2019, 20, 93. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chong, C.D.; Peplinski, J.; Berisha, V.; Ross, K.; Schwedt, T.J. Differences in fibertract profiles between patients with migraine and those with persistent post-traumatic headache. Cephalalgia 2019, 39, 1121–1133. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rocca, M.A.; Colombo, B.; Inglese, M.; Codella, M.; Comi, G.; Filippi, M. A diffusion tensor magnetic resonance imaging study of brain tissue from patients with migraine. J. Neurol. Neurosurg. Psychiatry 2003, 74, 501–503. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Burstein, R.; Jakubowski, M.; Garcia-Nicas, E.; Kainz, V.; Bajwa, Z.; Hargreaves, R.; Becerra, L.; Borsook, D. Thalamic sensitization transforms localized pain into widespread allodynia. Ann. Neurol. 2010, 68, 81–91. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Maleki, N.; Becerra, L.; Upadhyay, J.; Burstein, R.; Borsook, D. Direct optic nerve pulvinar connections defined by diffusion MR tractography in humans: Implications for photophobia. Hum. Brain Mapp. 2012, 33, 75–88. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Coppola, G.; Di Renzo, A.; Tinelli, E.; Lepre, C.; Di Lorenzo, C.; Di Lorenzo, G.A.; Scapeccia, M.; Parisi, V.; Serrao, M.; Colonnese, C.; et al. Thalamo-cortical network activity between migraine attacks: Insights from MRI-based microstructural and functional resting-state network correlation analysis. J. Headache Pain 2016, 17, 100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tracey, I.; Mantyh, P.W. The Cerebral Signature for Pain Perception and Its Modulation. Neuron 2007, 55, 377–391. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moulton, E.A.; Becerra, L.; Maleki, N.; Pendse, G.; Tully, S.; Hangreaves, R.; Burstein, R.; Borsook, D. Painful Heat Reveals Hyperexcitability of the Temporal Pole in Interictal and Ictal Migraine States. Cereb. Cortex 2011, 21, 435–448. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hadjikhani, N.; Ward, N.; Boshyan, J.; Napadow, V.; Maeda, Y.; Truini, A.; Caramia, F.; Tinelli, E.; Mainero, C. The missing link: Enhanced functional connectivity between amygdala and visceroceptive cortex in migraine. Cephalalgia 2013, 33, 1264–1268. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Coppola, G.; Di Renzo, A.; Tinelli, E.; Iacovelli, E.; Lepre, C.; Di Lorenzo, C.; Di Lorenzo, G.; Di Lenola, D.; Parisi, V.; Serrao, M.; et al. Evidence for brain morphometric changes during the migraine cycle: A magnetic resonance-based morphometry study. Cephalalgia 2015, 35, 783–791. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schwedt, T.J.; Berisha, V.; Chong, C.D. Temporal Lobe Cortical Thickness Correlations Differentiate the Migraine Brain from the Healthy Brain. PLoS ONE 2015, 10, e0116687. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yuan, K.; Qin, W.; Liu, P.; Zhao, L.; Yu, D.; Zhao, L.; Dong, M.; Liu, J.; Yang, X.; von Deneen, K.M.; et al. Reduced Fractional Anisotropy of Corpus Callosum Modulates Inter-Hemispheric Resting State Functional Connectivity in Migraine Patients without Aura. PLoS ONE 2012, 7, e45476. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Granziera, C.; DaSilva, A.F.M.; Snyder, J.; Tuch, D.S.; Hadjikhani, N. Anatomical Alterations of the Visual Motion Processing Network in Migraine with and without Aura. PLoS Med. 2006, 3, e402. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- DaSilva, A.F.M.; Granziera, C.; Tuch, D.S.; Snyder, J.; Vincent, M.; Hadjikhani, N. Interictal alterations of the trigeminal somatosensory pathway and PAG in migraine. Neuroreport 2007, 18, 301–305. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schmitz, N.; Admiraal-Behloul, F.; Arkink, E.B.; Kruit, M.C.; Schoonmann, G.G.; Ferrari, M.D.; Van Buchem, M.A. Attack frequency and disease duration as indicators for brain damage in migraine. Headache 2008, 48, 1044–1055. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, X.L.; Fang, Y.N.; Gao, Q.C.; Lin, E.J.; Hu, S.H.; Ren, L.; Ding, M.H.; Luo, B.N. A Diffusion Tensor Magnetic Resonance Image Study of Corpus Callosum From Adult Patients With Migraine Complicated With Depressive/Anxious Disorder. Headache 2011, 51, 237–245. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Coppola, G.; Tinelli, E.; Lepre, C.; Iacovelli, E.; Di Lorenzo, C.; Di Lorenzo, G.; Serrao, M.; Pauri, F.; Fiermonte, G.; Bianco, F.; et al. Dynamic changes in thalamic microstructure of migraine without aura patients: A diffusion tensor magnetic resonance imaging study. Eur J. Neurol 2014, 21, 287-e13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Szabó, N.; Faragó, P.; Király, A.; Veréb, A.; Csete, G.; Tóth, E.; Kocsis, K.; Kincses, B.; Tuka, B.; Párdutz, A.; et al. Evidence for Plastic Processes in Migraine with Aura: A Diffusion Weighted MRI Study. Front. Neuroanat 2017, 11, 138. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yalcin, A.; Ceylan, M.; Bayraktutan, O.F.; Akkurt, A. Episodic Migraine and White Matter Hyperintensities: Association of Pain Lateralization. Pain Med. 2018, 19, 2051–2057. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xie, H.; Zhang, Q.; Huo, K.; Liu, R.; Jian, Z.-J.; Bian, Y.-T.; Li, G.-L.; Zhu, D.; Zhang, L.-H.; Yang, J.; et al. Association of white matter hyperintensities with migraine features and prognosis. BMC Neurol 2018, 18, 93. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Porter, A.; Gladstone, J.P.; Dodick, D.W. Migraine and white matter hyperintensities. Curr. Pain Headache Rep. 2005, 9, 289–293. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- May, A. Understanding migraine as a cycling brain syndrome: Reviewing the evidence from functional imaging. Neurol Sci 2017, 38, 125–130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Karsan, N.; Goadsby, P.J. Biological insights from the premonitory symptoms of migraine. Nat. Rev. Neurol. 2018, 14, 699–710. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gudmundsson, L.S.; Scher, A.I.; Sigurdsson, S.; Geerlings, M.I.; Vidal, J.-S.; Eiriksdottir, G.; Garcia, M.I.; Harris, T.B.; Kjartansson, O.; Aspelund, T.; et al. Migraine, depression, and brain volume: The AGES-Reykjavik Study. Neurology 2013, 80, 2138–2144. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]

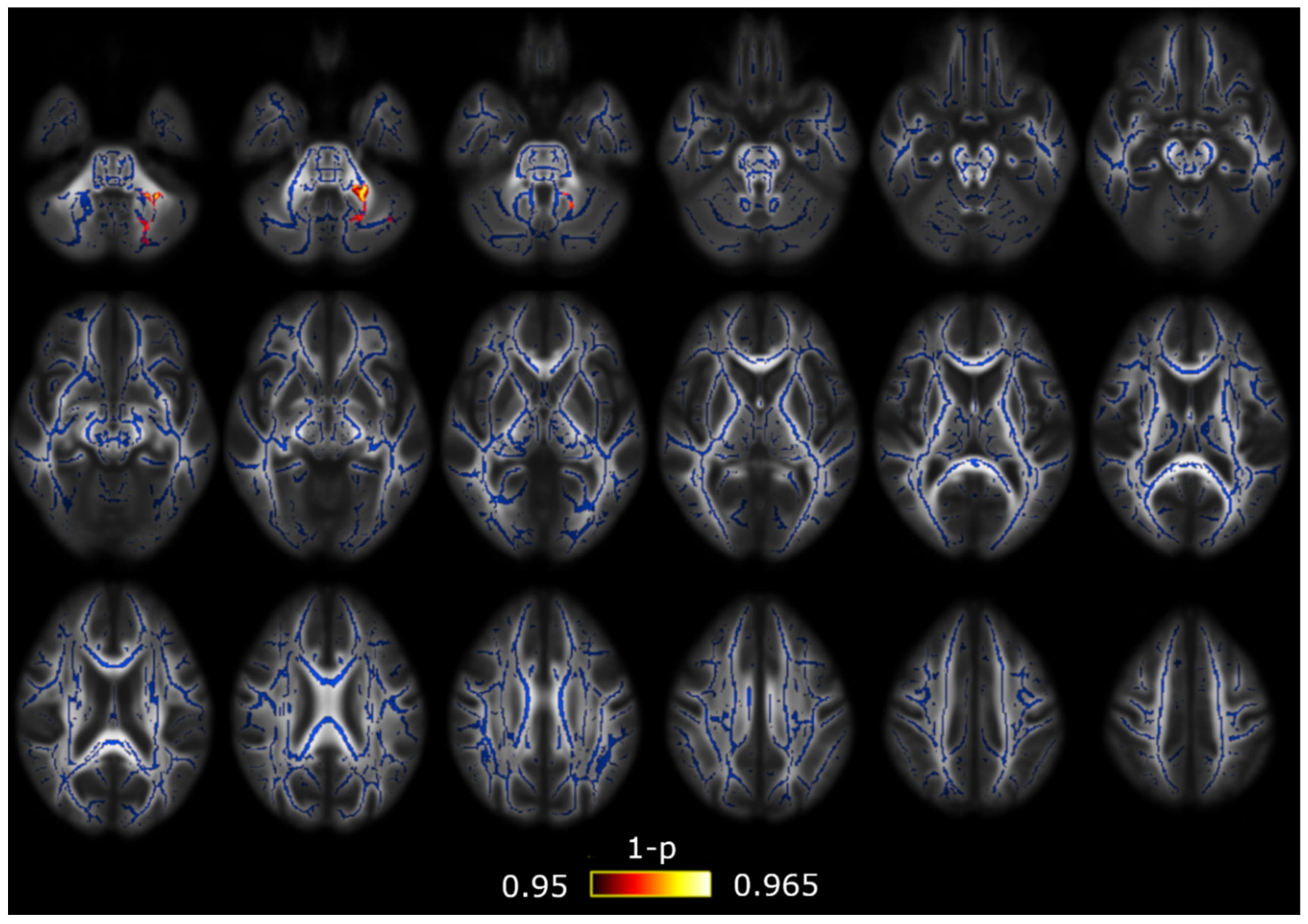

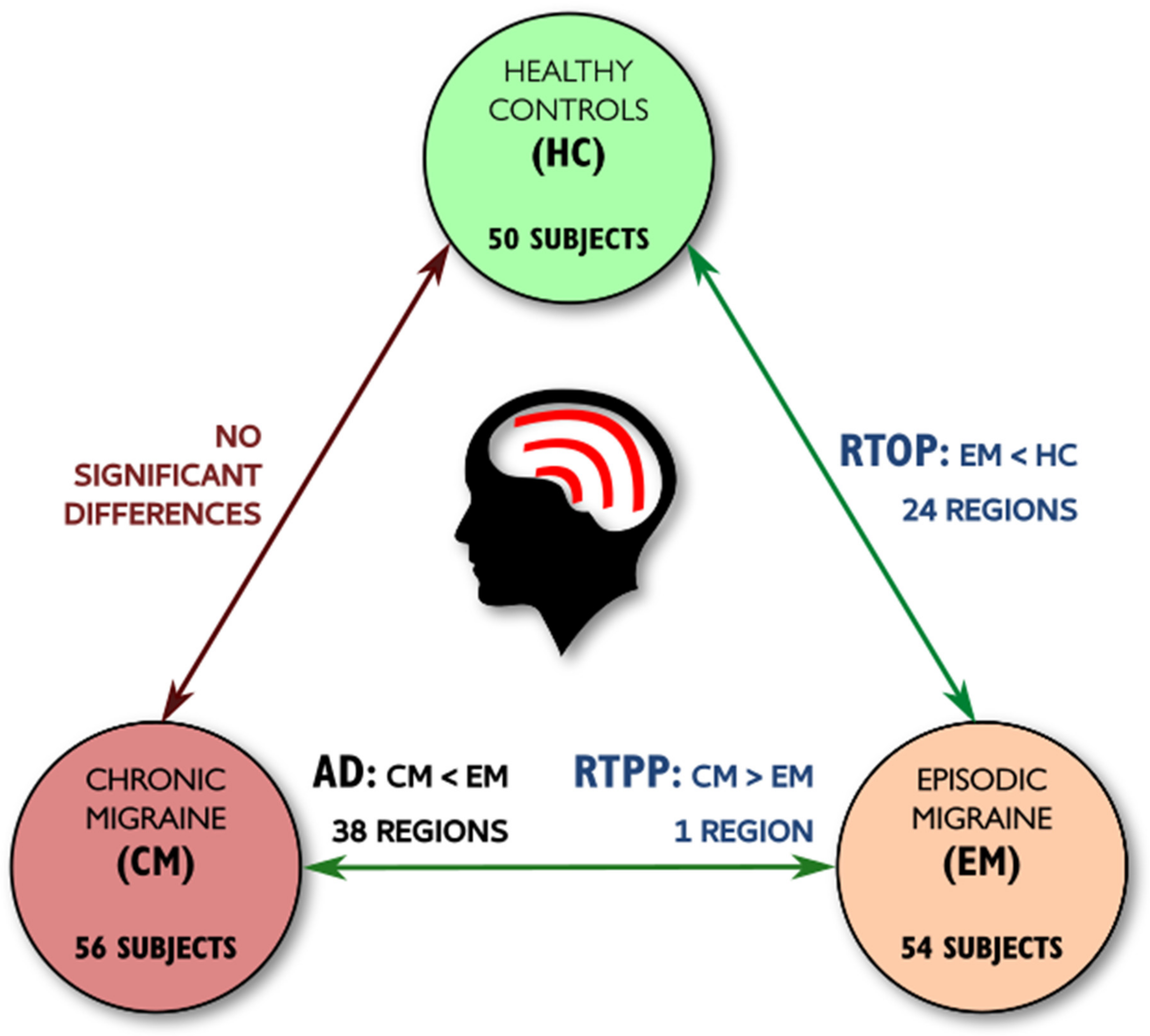
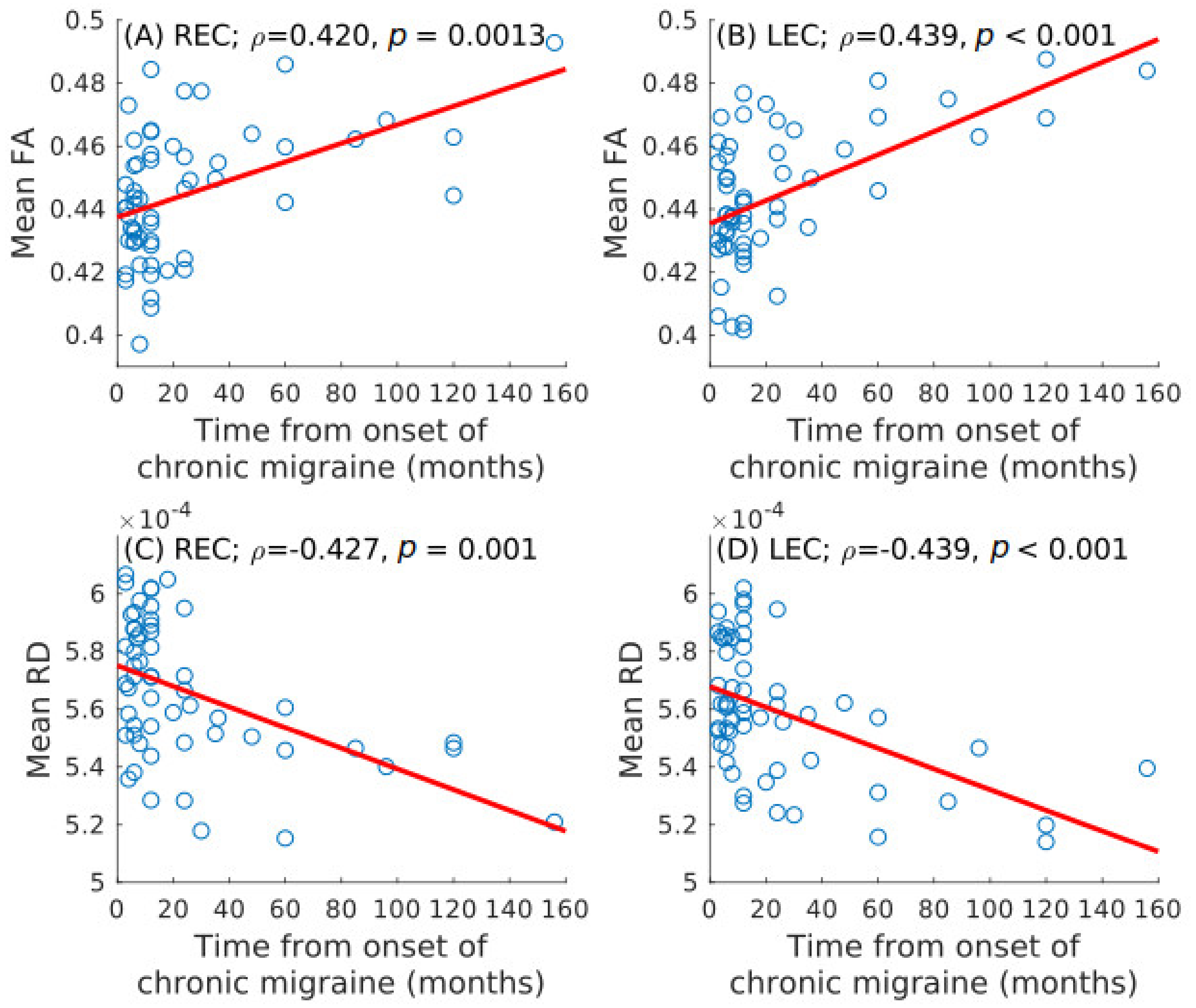
| HC (n = 50) | EM (n = 54) | CM (n = 56) | Statistical Test | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Gender, male/female | 11/39 (22/78%) | 9/45 (17/83%) | 6/50 (11/89%) | χ2(2, N = 160) = 2.48, p = 0.29 † |
| Age (years) | 36.1 ± 13.2 | 37.1 ± 8.2 | 38.1 ± 8.7 | χ2 (2) = 2.85, p = 0.24 ‡ |
| Duration of the migraine history (years) | 14.1 ± 11.1 | 19.6 ± 10.4 | t(108) = −2.7, p = 0.008 § | |
| Time from onset of CM (months) | 24.5 ± 32.9 | |||
| Headache frequency (days/month) | 3.6 ± 1.9 | 23.3 ± 6.3 | U = 44.0, p < 0.001 ⁋ | |
| Migraine frequency (days/month) | 3.6 ± 1.9 | 13.9 ± 6.9 | U = 108.5, p < 0.001 ⁋ | |
| Overusing medication | 0 (0%) | 42 (75%) | p < 0.001 ⁑ | |
| Aura | 9 (17%) | 1 (2%) | p = 0.007 ⁑ |
| White Matter Region | Minimum p-Value (FWE-Corrected) | Volume (mm3) | MNI Peak Coordinate (mm), (x,y,z) |
|---|---|---|---|
| Middle cerebellar peduncle | 0.007 | 2206 | (−20,−50,−32) |
| Superior cerebellar peduncle R/L | 0.020/0.020 | 142/126 | (5,−28,−19)/(−4,−28,−19) |
| Inferior cerebellar peduncle R/L | 0.019/0.009 | 75/89 | (12,−43,−35)/(−13,−45,−31) |
| Superior longitudinal fasciculus R/L | 0.021/0.021 | 971/874 | (33,−4,20)/(−36,−49,15) |
| Genu of corpus callosum | 0.019 | 455 | (10,−28,1) |
| Body of corpus callosum | 0.032 | 842 | (−4,30,23) |
| Splenium of corpus callosum | 0.025 | 873 | (22,−50,25) |
| Anterior corona radiata R/L | 0.024/0.018 | 556/805 | (18,21,−11)/(−18,38,−1) |
| Superior corona radiata R/L | 0.020/0.022 | 666/396 | (28,−16,21)/(−27,−11,20) |
| Posterior corona radiata R/L | 0.022/0.022 | 201/214 | (25,−24,24)/(−30,−52,22) |
| External capsule R/L | 0.020/0.018 | 459/695 | (30,−10,14)/(−22,16,−12) |
| Posterior limb of internal capsule R/L | 0.020/0.022 | 569/536 | (26,−17,13)/(−27,−17,17) |
| Retrolenticular part of internal capsule R/L | 0.023/0.023 | 457/344 | (31,−34,15)/(−25,−22,3) |
| Anterior limb of internal capsule R/L | 0.022/0.020 | 216/290 | (15,−1,7)/(−20,18,3) |
| Sagittal stratum R/L | 0.022/0.022 | 471/359 | (37,−49,−4)/(−41,−18,−13) |
| Posterior thalamic radiation R/L | 0.022/0.022 | 353/279 | (37,−50,−2)/(−35,−52,13) |
| Cerebral peduncle R/L | 0.020/0.022 | 234/265 | (11,−23,−21)/(−9,−19,−20) |
| Corticospinal tract R/L | 0.019/0.023 | 106/165 | (10,−27,−26)/(−7,−18,−22) |
| Medial lemniscus R/L | 0.020/0.015 | 82/103 | (8,−39,−40)/(−7,−37,−40) |
| Pontine crossing tract | 0.018 | 82 | (8,−31,−27) |
| Fornix (cres) R/L | 0.024/0.024 | 74/45 | (35,−12,−14)/(−34,−15,−13) |
| Cingulum (hippocampus) L | 0.036 | 56 | (−17,−42,−2) |
| White Matter Region | Minimum p-Value (FWE-Corrected) | Volume (mm3) | MNI Peak Coordinate (mm), (x,y,z) |
|---|---|---|---|
| Anterior thalamic radiation L/R | 0.020/0.021 | 316/232 | (−21,18,3)/(9,−29,−14) |
| Corticospinal tract L/R | 0.022/0.018 | 627/601 | (−24,−20,9)/(10,−28,−26) |
| Cingulum (hippocampus) L | 0.036 | 37 | (−17,−43,−2) |
| Forceps major | 0.024 | 375 | (−18,−85,8) |
| Forceps minor | 0.018 | 1601 | (−17,39,−2) |
| Inferior fronto-occipital fasciculus L/R | 0.018/0.022 | 994/973 | (−23,27,3)/(37,−49,−4) |
| Inferior longitudinal fasciculus L/R | 0.022/0.022 | 418/507 | (−35,−52,12)/(44,−33,−12) |
| Superior longitudinal fasciculus L/R | 0.021/0.021 | 1023/828 | (−36,−50,14)/(31,−6,17) |
| Superior longitudinal fasciculus (temporal part) R | 0.022 | 62 | (49,−33,−11) |
| Uncinate fasciculus L | 0.018 | 83 | (−18,21,−9) |
| White Matter Region | Minimum p-Value (FWE-Corrected) | Volume (mm3) | MNI Peak Coordinate (mm), (x,y,z) |
|---|---|---|---|
| Middle cerebellar peduncle | 0.042 | 908 | (13,−30,−26) |
| Superior cerebellar peduncle R/L | 0.042/0.042 | 65/65 | (7,−32,−19)/(−5,−31,−18) |
| Inferior cerebellar peduncle L | 0.045 | 96 | (−13,−45,−31) |
| Genu of corpus callosum | 0.047 | 44 | (18,31,15) |
| Anterior corona radiata R | 0.044 | 446 | (26,35,−1) |
| Superior corona radiata R | 0.048 | 84 | (23,−12,19) |
| External capsule R/L | 0.042/0.046 | 415/392 | (33,−19,−2)/(−33,−13,1) |
| Posterior limb of internal capsule R/L | 0.042/0.046 | 285/420 | (20,−20,−4)/(−22,−8,14) |
| Retrolenticular part of internal capsule R/L | 0.041/0.044 | 244/314 | (37,−26,−2)/(−37,−34,2) |
| Anterior limb of internal capsule L | 0.046 | 43 | (−17,−2,12) |
| Sagittal stratum R/L | 0.041/0.044 | 243/97 | (39,−29,−5)/(−40,−29,−6) |
| Cerebral peduncle R | 0.042 | 254 | (12,−25,−21) |
| Corticospinal tract R/L | 0.042/0.042 | 156/135 | (11,−25,−22)/(−7,−25,−26) |
| Medial lemniscus R/L | 0.045/0.046 | 83/87 | (9,−32,−25)/(−4,−37,−30) |
| Pontine crossing tract | 0.042 | 163 | (−4,−30,−28) |
| Fornix (cres) R | 0.041 | 148 | (32,−22,−6) |
| Uncinate fasciculus R | 0.043 | 32 | (35,−4,−14) |
| White Matter Region | Minimum p-Value (FWE-Corrected) | Volume (mm3) | MNI Peak Coordinate (mm), (x,y,z) |
|---|---|---|---|
| Anterior thalamic radiation L/R | 0.046/0.042 | 34/68 | (−7,−36,−27)/(9,−29,−14) |
| Corticospinal tract L/R | 0.042/0.042 | 284/374 | (−7,−25,−26)/(11,−25,−22) |
| Forceps minor | 0.046 | 342 | (19,38,16) |
| Inferior fronto-occipital fasciculus L/R | 0.044/0.044 | 240/676 | (−39,−30,−4)/(37,−27,−3) |
| Inferior longitudinal fasciculus L/R | 0.043/0.042 | 309/167 | (−41,−28,−4)/(42,−14,−14) |
| Uncinate fasciculus L/R | 0.048/0.044 | 62/71 | (−35,−2,−20)/(34,1,−16) |
© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Planchuelo-Gómez, Á.; García-Azorín, D.; Guerrero, Á.L.; de Luis-García, R.; Rodríguez, M.; Aja-Fernández, S. Alternative Microstructural Measures to Complement Diffusion Tensor Imaging in Migraine Studies with Standard MRI Acquisition. Brain Sci. 2020, 10, 711. https://doi.org/10.3390/brainsci10100711
Planchuelo-Gómez Á, García-Azorín D, Guerrero ÁL, de Luis-García R, Rodríguez M, Aja-Fernández S. Alternative Microstructural Measures to Complement Diffusion Tensor Imaging in Migraine Studies with Standard MRI Acquisition. Brain Sciences. 2020; 10(10):711. https://doi.org/10.3390/brainsci10100711
Chicago/Turabian StylePlanchuelo-Gómez, Álvaro, David García-Azorín, Ángel L. Guerrero, Rodrigo de Luis-García, Margarita Rodríguez, and Santiago Aja-Fernández. 2020. "Alternative Microstructural Measures to Complement Diffusion Tensor Imaging in Migraine Studies with Standard MRI Acquisition" Brain Sciences 10, no. 10: 711. https://doi.org/10.3390/brainsci10100711
APA StylePlanchuelo-Gómez, Á., García-Azorín, D., Guerrero, Á. L., de Luis-García, R., Rodríguez, M., & Aja-Fernández, S. (2020). Alternative Microstructural Measures to Complement Diffusion Tensor Imaging in Migraine Studies with Standard MRI Acquisition. Brain Sciences, 10(10), 711. https://doi.org/10.3390/brainsci10100711