Abstract
Traditional villages face many difficulties in the era of globalization, especially in light of fast industrialization and urbanization. The breakdown of settlement patterns and the erosion of local characteristics and cultural identities pose critical issues for the sustainable development of these communities. While research on traditional villages and dwellings in core cultural areas is relatively advanced, there remains a significant gap in studies focusing on traditional villages and dwellings in multicultural intermingling regions. By clarifying the characteristics of traditional villages and the cultural landscapes of dwellings under the influence of multiple cultures, as well as their differentiation and underlying mechanisms, this research aims to provide theoretical support for the protective planning of world cultural heritage, which is increasingly characterized by clustering and regionalization. Taking the traditional villages and dwellings in the Jiangxi and Anhui junction area as a case study, we developed a cultural landscape factor system for traditional villages and dwellings across four dimensions: natural environment, spatial configuration, dwelling typology, and historical and cultural context. Using geographic information systems (GIS) zoning methods and statistical spatial analysis, we divided the area into three distinct cultural landscape zones. The findings indicate that the cultural landscapes within each zone exhibit unique regional characteristics at both the village and dwelling levels, particularly in site selection, settlement patterns, and architectural aesthetics. Differentiation across zones is shaped by natural factors, such as topography and water systems, as well as by regional culture, historical migration, the chronological sequence of regional development, commerce and trade growth, and the evolution of administrative systems, alongside broader cultural, economic, and social factors, showing consistent patterns. This study demonstrates that utilizing a scientific and objective zoning approach to accurately identify the cultural landscape characteristics and differentiation patterns across various cultural zones, while clarifying the historical evolution of villages and the transformation of dwelling forms, provides practical insights for cultural landscape zoning in other multicultural regions. Furthermore, it provides scientific guidance to advance China’s rural revitalization strategy and supports the regional protection and sustainable development of world cultural heritage.
1. Introduction
The term “cultural landscape” was first introduced by the World Heritage Council in 1992, defined as “an exceptionally rich tapestry of natural and human interactions”, representing a shared masterpiece where humanity and nature are intricately intertwined [1]. Traditional settlements are meticulously crafted material living spaces designed by humans to meet socio-economic needs, serving as tangible cultural landscapes inseparable from residential architecture. Together, they form one of the significant cultural landscapes formed throughout human history [2]. In the 19th century, countries such as England and France pioneered research on traditional village cultural landscapes, which laid the foundation for theoretical frameworks guiding their protection practices. By the mid-20th century, European nations like France, the UK, and the USA enacted a series of landscape protection laws to preserve ancient villages, scenic areas, and rural landscapes. These laws primarily emphasize the perception and transformation of traditional village cultural landscapes [3,4], research on cultural landscape heritage [5], cultural landscape protection and management [6], and the digitization of cultural landscapes [7]. In the 1990s, influenced by postmodernist thought and the concept of rural multifunctionality, the study of traditional village cultural landscapes gradually became mainstream within the social sciences [8]. In China, research in this field began in the late 1980s to early 1990s, initially focusing on “settlement landscapes”, emphasizing the unique characteristics of residential architecture and regional settlements. Since then, the research scope has expanded from single-element studies to cultural landscape zoning encompassing multiple cultural elements. The identification of cultural landscape elements is mainly carried out through the landscape genetics method [9], which classifies the material elements and socio-cultural elements of villages. The material elements include natural ecology, traditional architecture, historical environment elements, etc.; the intangible cultural elements include religious beliefs, village culture, traditional handicrafts, operas and dances, motifs and metaphors, dialects, etc. With the growing interest from both domestic and international scholars, research on traditional villages has transitioned from a singular, static foundational study to a multidisciplinary and multi-faceted dynamic inquiry, yielding significant outcomes.
In recent years, the swift advancements in technology, culture, and economy within Western European and North American nations have posed significant environmental challenges, impacting both the natural landscape and rural communities [10]. In China, the rapid pace of industrialization and urbanization has led traditional villages to confront issues such as rampant commercialization, population out-migration, fragmentation in the protection of cultural heritage, and inadequate efforts in the preservation of traditional culture [11,12,13,14]. This has resulted in the homogenization of village cultural landscapes and a gradual erosion of their unique identities [15,16]. Furthermore, a lack of in-depth research on the distinctive characteristics of cultural landscapes in villages has worsened their loss, posing challenges to the preservation of village history and culture. Consequently, the safeguarding of traditional village characteristics and the pursuit of sustainable development have emerged as significant topics of interest within the academic community [17,18]. In this context, traditional villages with well-preserved landscapes and regional characteristics, traditional architecture reflecting local regional culture, and rich intangible cultural heritage are selected for the study of their cultural landscape characteristics and cultural zoning of villages and dwellings. Cultural zoning of these areas and the delineation of regions with similar cultural landscapes enable a deeper understanding of the diversity of cultural landscapes from a regional perspective. This, in turn, will provide scientific guidance for the protection of various types of traditional villages. Therefore, elucidating the characteristics of different cultural landscapes in villages and further investigating the patterns of cultural landscape differentiation across zones can offer valuable scientific insights and references for regionalized cultural heritage protection and sustainable development on a global scale.
In light of the aforementioned points, both Chinese and international scholars have conducted extensive research and achieved significant findings in the domain of cultural landscapes and cultural landscape zoning. In terms of research scale, international researchers primarily adopt a macro-level perspective [19], utilizing the comprehensive attributes of cultural landscapes as criteria for broad zoning, but they often overlook studies at smaller scales such as the provincial and regional levels. In contrast, research on the cultural landscape zoning of villages in China predominantly emphasizes these smaller scales [20,21], focusing on typical cultural core areas, while cultural intermingling zones have received limited attention. Cultural intermingling regions are defined as transitional areas where multiple cultural circles converge, characterized by intricate natural geography and notable cultural diversity. This rich and varied nature renders the traditional villages and residential cultural landscapes in these intermingled areas exceptionally complex, making the analysis of their landscape characteristics and differentiation patterns more challenging compared to cultural core areas. In terms of research methodology, most studies remain qualitative and gradually integrate quantitative approaches. Qualitative research is mainly based on the descriptive method, the dominant factor method [22], and the landscape gene mapping method [23]. Among these, the landscape gene mapping method involves scholars introducing the biological concept of genes into traditional villages, thereby proposing the theory of village cultural landscape genes [24]. This method, along with geographical methods such as 3S (Geographic Information Systems, Remote Sensing, and Global Positioning Systems), spatial syntax [25], and complex adaptive systems (CAS) [26], as well as the gene chain method [27], is used to analyze traditional villages and propose research methods for identifying and mapping the cultural landscape genes of traditional villages. The quantitative and qualitative combined method mainly adopts the hierarchical analysis method and the geographic information systems combined method [20], as well as clustering methods to calculate village similarity [28].
Throughout the current research, the content has gradually expanded, but the research scale and research methodology have certain deficiencies.
Firstly, the predominant focus of traditional village landscape research in China is on cultural core areas, the marginalized cultural integration areas in academic discourse. Recognizing the interdependent and complementary relationship between cultural core areas and integration zones; neglecting the latter results in a fragmented research framework for traditional villages. Therefore, it is imperative to broaden the research scope to encompass multicultural integration areas to enhance the overall research framework concerning villages and residential environments. Consequently, there is an urgent need to expand the research system for villages and dwellings to include areas of multicultural intermingling. Secondly, although quantitative research has been conducted on the selection of “dominant factors”, methods such as the “Delphi Method” and “Hierarchical Analysis Method” are used to determine the superimposed weights. However, reliance on human-determined weights introduces subjectivity, resulting in a lack of objectivity in the zoning process.
This article examines the characterization of cultural landscapes and the principles of differentiation from the perspectives of genealogy and cultural zoning, using the traditional villages and residential structures in the Jiangxi-Anhui junction area as a case study. This region is geographically defined as the intersection of northeastern Jiangxi and southern Anhui, representing a quintessential area of cultural fusion between Jiangxi and Anhui. Historically, the robust cultures of Gan and Hui have engaged in continuous interaction through trade, migration, and cultural exchange, leading to the evolution of village and residential forms through cultural amalgamation, resulting in rich cultural landscapes.
The objective of this study is to clarify the distinctive features of these village and residential cultural landscapes, as well as the geographic variations across different regions, and to uncover the underlying mechanisms driving this differentiation. This research not only enhances the overall framework of village and residential studies but also offers new theoretical insights and practical examples for the differentiated preservation of traditional villages in multicultural contexts and the region’s sustainable development. Additionally, it aims to provide scientific guidance and reference for advancing China’s rural revitalization strategy and promoting effective regional protection and sustainable development of global cultural heritage.
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Delineation of the Study Area
The border region between Jiangxi Province and Anhui Province, located at the junction of Gan Culture and Hui Culture, serves as a significant area for the exchange and integration of these two cultural heritages. The administrative divisions in this area have experienced numerous adjustments through differentiation and consolidation over time. The parameters of this study were defined by considering various factors, including cultural transmission, dialects, geographic environment, administrative boundaries, and the relative balance of research resources. The study area is illustrated in Figure 1. In terms of administrative divisions, the area includes all of Jingdezhen City in Jiangxi Province, Poyang County and Wuyuan County in Shangrao City, Jiangxi Province, and Duchang County in Jiujiang City, Jiangxi Province. It also includes Qimen County, She County, and Xiuning County in Huangshan City, Anhui Province. In total, this region comprises two municipal districts (Zhushan District and Changjiang District), one county-level city (Leping City), and seven counties (Fuliang County, Wuyuan County, Duchang County, Qimen County, She County, Xiuning County, and Poyang County), covering a total area of 21,700 square kilometers.
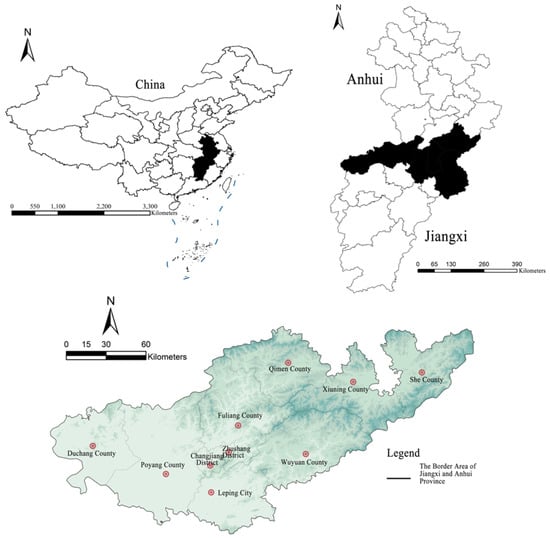
Figure 1.
Location map and research scope of the border area between Jiangxi and Anhui Provinces, Source: Drawn by authors based on the satellite base map of Map World GS (2024) No. 0650 Data Sources.
2.2. Characterization of the Study Area
2.2.1. Physical Geography: Mountain Ranges and River Connections
The border region between Jiangxi and Anhui features extensive mountain ranges and interconnected rivers, with the Xin’an River and the Chang River serving as vital links within the area. The topography is diverse, dominated by mountains and hills interspersed with river valley plains. The mountain ranges primarily extend in a northeast-southwest orientation, with a concentration in the northeast, resulting in a topographical gradient characterized by elevated terrain in the northeast and descending elevations in the southwest, thereby forming a distinctive and complex geomorphological landscape. This area is encircled by mountains to the north, east, and south, with mountain ranges of varying elevations flanking the Xin River, forming an “inverted mountain” configuration. Notable peaks include Zhanggong Mountain, Huaiyu Mountain, and Wuyi Mountain, situated from north to south, with the Xin River Basin at the center. In the Jiangxi-Anhui border area, the hydrological network is well-developed, featuring numerous rivers, the majority of which are part of the Poyang Lake and Qiantang River systems. The Xin River and Rao River are the two principal rivers in northeast Jiangxi, traversing the region from north to south before flowing into Poyang Lake and ultimately flowing into the Yangtze River through the lake’s outlet. The Xin’an River, a significant waterway in Huizhou, originates from Wugujian Mountain in the Huaiyu Mountain Range and flows into the Qiantang River via Qiandao Lake. Consequently, mountains serve as boundary elements influencing cultural distinctions between the two regions, while the water systems serve as connective elements that foster the development of a commodity economy and sustain cultural similarities, thereby contributing to the creation of vibrant villages and rich dwellings’ cultural landscapes.
2.2.2. Cultural District Location: Gan Cultural and Hui Cultural Intermingling Area
The Jiangxi-Anhui junction area lies at the intersection of two dominant cultures, Gan Culture and Hui Culture, making it a quintessential area of cultural fusion. Geographically, Jiangxi Province is surrounded by mountains to the east, west, and south, with the Yangtze River to the north, and is flanked by Fujian and Zhejiang to the east, two lakes to the west, and Guangdong to the south, while Anhui lies to the north. This unique geographic environment is characterized by its independence without isolation. It has been historically recognized as the “three rivers enfold it like the front part of a garment, and the five lakes encircle it like a girdle. It controls the savage Jing area and connects Ou and Yue”, which has allowed it to maintain a dominant position in transportation since ancient times. During the Spring and Autumn Period, Jiangxi fell under the jurisdiction of the states of Wu, Chu, and Yue, leading to the emergence of distinct regional cultures in eastern, northern, and southern Jiangxi. These cultures gradually unified after the Han Dynasty, further shaped by various population migrations throughout subsequent dynasties, which contributed to the development of contemporary Gan culture. As noted by Mo Minghao and Ying Ye, “The essence of ’Gan culture’ is a subculture that emerged from the integration of foreign cultures into Jiangxi, with the traditional culture of the Central Plains serving as the foundation. This subculture evolved through convergence, fusion, modification, and innovation, influenced by Jiangxi’s unique geographic context [29]. “The Raozhou region, located in the northeast of Jiangxi, falls within the cultural sphere of Gan, centered around Hongzhou (present-day Nanchang).
Historically, the Huizhou region encompassed “six counties”, including She County, Xiuning County, Qimen County, Wuyuan County, Yi County, and Jixi County. Presently, it is located in southern Anhui Province, at the intersection of Anhui, Zhejiang, and Jiangxi provinces. Surrounded by five major mountain ranges and their tributaries—Huangshan; Tianmu Mountain; Baiji Mountain; Wulong Mountain; and Jiuhua Mountain—Huizhou forms a relatively isolated geographic unit. However, ancient water systems such as the Qingge River, Xin’an River, and Shuiyang River traversed these mountains, serving as vital transportation routes that facilitated cultural dissemination and exchange. Before the Qin and Han dynasties, the Huizhou area was inhabited by the Shan-Yue people, who were part of the nomadic farming culture of South Vietnam. Following the Eastern Han Dynasty, the migration of prominent families and individuals led to the gradual infiltration of Central Plains culture into the region. Over the ensuing millennia, “the culture of the Central Plains significantly influenced Shan-Yue culture, fostering its refinement and elegance; while Shan-Yue culture also deeply permeated Central Plains culture, imparting a more robust character”, ultimately leading to the evolution of Hui culture into a distinct new cultural identity [30]. The culture of Anhui subsequently developed, forming a cultural circle that radiates from western Zhejiang, southern Anhui, and northeastern Jiangxi. The Jiangxi-Anhui border region serves as a significant confluence of the Gan Culture and Hui Culture, in addition to its geographical boundaries. The Hui Rao ancient road and waterways functioned as critical conduits for cultural exchange, facilitating interactions through trade, migration, and education. Traditional villages and dwellings act as vessels for this cultural interchange, reflecting the unique cultural landscape of the region.
2.3. Study Object
The selection of traditional villages and dwellings located in the Jiangxi-Anhui border area was derived from four primary sources: (1) the Jiangxi-Anhui Junction area included in the six batches of “Chinese traditional villages” officially recognized and announced; (2) the Jiangxi-Anhui Junction area in the provincial traditional villages that have been announced; (3) villages designated as provincial-level famous historical and cultural villages or hosting provincial-level and county-level cultural relics protection units; (4) to ensure comprehensive coverage of the Jiangxi-Anhui junction area and avoid “substituting points for surfaces”, one to three villages with typical geographic environments and representative cultural traits were selected from each township based on on-site census data. The sources were thoroughly screened and organized to remove duplicates and exclude highly urbanized villages, resulting in a total of 260 traditional villages being identified as samples (Figure 2).
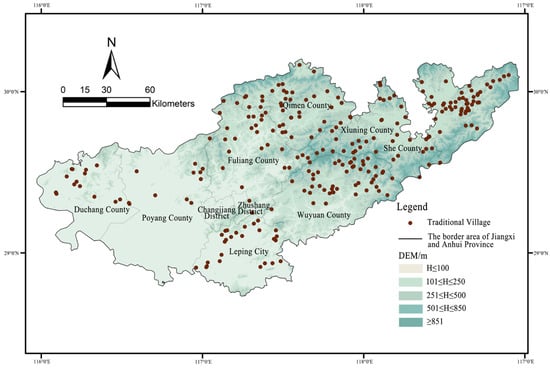
Figure 2.
Spatial distribution Map of traditional villages in the border area of Jiangxi and Anhui Provinces, Source: Drawn by authors based on the satellite base map of Map World GS (2024) No. 0650 Data Sources.
2.4. Data Source
The research data primarily originates from three sources: (1) Geographic Information Systems. Traditional villages were represented as “points” on the geospatial data on the macro spatial scale, and the geographic coordinates of the traditional villages were extracted using Google Earth and imported into ArcGIS 10.8 software to build a geospatial database of the traditional villages and dwellings in the Jiangxi-Anhui junction area. The basic geographic information data mainly comes from the geospatial data cloud. (https://www.gscloud.cn, accessed on 1 December 2024). (2) Literature and Historical Materials. Literature and historical data were collected from multiple sources: the Digital Museum of Traditional Villages in China (https://www.dmctv.cn, accessed on 1 December 2024), county records, gazetteers, and ethnographies of Xin’an and Xiuning, as well as research findings pertaining to traditional villages and dwellings in the Jiangxi-Anhui junction area. Dialect data were extracted from the Chinese dialect map of the southeastern region found in the 1987 Atlas of Chinese Language. (3) Field Research. Attribute information, including village names, spatial configurations, street layouts, and dwelling types, was gathered through interviews, aerial photography, conventional photography, and mapping techniques.
2.5. Research Methodology
2.5.1. Deconstruction of Cultural Landscape
The formation of the cultural landscape of traditional villages is mainly influenced by multiple factors, including geographic environment, regional culture, and socio-economic conditions. Its characteristics and differences can be identified through the analysis of cultural landscape factors. Due to the different perspectives, types of selected factors, sample sizes, and delineation methods, the results of the delineation may vary. In order to improve the accuracy of the delineation results, it is necessary to select different levels of cultural landscape factors that can intuitively reflect the cultural characteristics of the region and analyze them with sufficient sample data.
2.5.2. ArcGIS Spatial Analysis Method
In the data platform to obtain the DEM, water system, and other data in the Jiangxi-Anhui junction area, and imported into the ArcGIS software for vectorization processing, to generate maps of different cultural landscape factors, so that the distribution of landscape elements can be visualized, and accurately delineate the traditional villages and dwellings in the Jiangxi-Anhui junction area, to reveal the spatial differentiation law of the traditional villages and dwellings in the Jiangxi-Anhui junction area cultural landscapes.
2.5.3. Principal Component Analysis
Principal component analysis (PCA) is a kind of analysis method to simplify the structure of data sets through the idea of dimensionality reduction, which plays an important role in the evaluation system of multiple indicators. Using PCA, the correlated cultural landscape factors of multiple villages and dwellings are transformed into a small number of uncorrelated ’principal component factors’, which reflect the information contained in the original multiple factors, not only from the multi-indicator factor by reducing the dimensionality of the data, eliminating the differences in the scale [31], to increase the amount of information carried by cultural factors. In order to fully reflect the characteristics of the cultural landscape, the principal component factor is only based on the mathematical and scientific data. The principal component factors are only combined according to the weight relationship determined by mathematical statistics, which reduces the subjectivity of the traditional “expert scoring method” to determine the weight value. The extraction steps are as follows:
Calculate the correlation coefficient matrix R for the normalized array Z:
- (1)
- Calculate the eigenvalues of the correlation coefficient matrix R:
Solve for P eigenvalues λ1 ≥ λ2 ≥ … ≥ λP ≥ 0.
- (2)
- Determine the number of principal components, m so that the extraction rate of principal component factor information reaches more than 80%:
2.5.4. Systematic Cluster Analysis
Systematic cluster analysis, also known as hierarchical cluster analysis, is one of the most widely used clustering methods, which can significantly overcome the drawbacks of subjectivity and arbitrariness in traditional classification methods. The principle is that each sample (or variable) is regarded as a class, and according to the distance between the samples (or variables), it will be clustered step by step until it is clustered into a class of a clustering method [31].
Before clustering analysis, the principal component factors extracted through principal component analysis are used as the variables for subsequent clustering analysis, which can effectively help to identify the similarities and differences between the samples, improve the clustering efficiency and accuracy, and at the same time enhance the interpretability of the clustering results, align better with practical needs, and provide a more scientific and objective reference for zoning traditional villages and residential cultural landscapes. In cluster analysis, villages are treated as independent data points, and their attributes are defined by principal component factors. The first level of clustering measures similarity or difference in cultural landscapes based on the “distance between villages” (similarity), and the nearest villages are merged into new categories based on the “distance between categories”. In the second level of clustering, the new categories in the previous level are regarded as new data points, and the similarity calculation and category merging are repeated until all the villages are aggregated into one large category, forming a cluster analysis tree diagram, which provides references and bases for the zoning of traditional villages and residential cultural landscapes. The number of clusters can be specified in advance according to the actual needs or judged reasonable by professional knowledge according to the belonging of the samples of each category [32].
2.6. Overview of Research Methodology
Through field research and relevant data analysis, representative traditional villages and residential cultural landscape factors were selected to construct a cultural landscape factor system. The cultural landscape factors were vectorized using ArcGIS software to create a data-driven geographic information database, enabling the visualization of their spatial distribution characteristics. With the help of SPSS 22.0 statistical software, using the quantitative analysis means of principal component analysis, objectively determining the principal component factors, and using the principal component factors as the variable data to carry out systematic clustering, the traditional villages with the closest cultural landscape characteristics are divided into the same cluster; based on the results of the systematic clustering of data line indicators, according to the commonality of cultural landscape, the proximity of the level of cultural development, the similarity of the process of cultural development, the continuity of the cultural region, the cultural center with regional cultural characteristics and other principles, the cultural center with regional cultural characteristics. Cultural characteristics of the cultural center and other principles [2], combined with other descriptive indicator factor information, precise cultural zoning of traditional villages and residential houses in the Jiangxi-Anhui junction area, to summarize the typical characteristics of the different zones and the differentiation patterns. From the perspective of historical geography, the formation mechanism of the geographical differentiation of different cultural landscape zones is explored by combining the factors of natural geography, social culture, and establishment history.
3. Traditional Villages and Dwellings Cultural Landscape Zoning Analysis
3.1. Selection of Cultural Landscape Factors and System Construction
Cultural factors serve as the essential components of cultural landscape elements, playing a crucial role in identifying and interpreting the distinctive traits of a cultural landscape. They also account for the significant variations that differentiate one cultural landscape from another [33]. According to the existing research results, synthesize the generalization of cultural landscape elements, combined with the information base of the field research of traditional villages in the Jiangxi-Anhui junction area, analyze the connotative qualities of the cultural landscape of the traditional villages in the region with material attributes and immaterial attributes of the cultural landscape, and select the most recognizable and representative factors of the cultural landscape from them. First of all, the natural geographic environment is the basis for shaping the village landscape, which is an intrinsic element that cannot be ignored [34]. The topography, elevation, and river flow not only determine the location and layout of the village but also deeply influence the architectural style and structure of residential buildings, including their appearance, number of floors, decorations, and roof forms. The study of these factors helps to understand the cultural landscape. Studying these factors helps to understand the interaction between cultural landscape and natural environment. Secondly, as the most intuitive and recognizable cultural landscape factors, the spatial form of traditional villages and the shape of traditional houses are the external characteristics of the geographic environment of villages and houses, which contain rich cultural elements [35]. The intertwined effects of natural geography and social and cultural environments have jointly shaped the unique appearance of traditional villages and traditional houses. The spatial layout of traditional villages not only reflects the social structure and cultural concepts of villages but also shows the adaptive relationship between villages and the natural environment. The form of the settlement, the pattern of streets and lanes, the scale and size, and the choice of orientation together constitute the spatial macro-organization of the village landscape. In addition, village site selection and village environment elements contain cultural connotations such as feng shui concepts [36], which have different forms of expression in different regions. As an important part of the village landscape, the diversity of residential buildings stems from the influence of topography, climate, regional culture, and other factors, which makes the residential buildings in different regions show significant regional differences in terms of architectural appearance, number of floors, architectural decorations, roof forms, and other aspects. Finally, the social and cultural environment has a far-reaching impact on village landscapes, as cultural landscapes are not static and should also take into account the factor of time, reflecting historical influences in the division of cultural zones. Therefore, factors such as language, the age of village establishment, the origin of migration, and the dominant culture reflect the formation and development of the cultural landscape, which shapes the historical memory and cultural identity of villages and influences their development and construction.
Consequently, based on the recent scholarly research in this domain [15,16,22,37], as well as referring to the principles for identifying cultural landscape factors: (1) intrinsic uniqueness; (2) extrinsic uniqueness; (3) local uniqueness; (4) overall dominance [38]. 21 cultural landscape factors were selected to reflect the characteristics and cultural attributes of the Jiangxi-Anhui junction region. These factors were drawn from aspects such as the natural geographic environment, traditional settlements, traditional dwellings, and historical culture. These factors are organized into four levels “natural environment”, “spatial configuration”, “dwelling typology”, and “historical and cultural elements”, which collectively construct the cultural landscape factor system of traditional villages and dwelling structures in the Jiangxi-Anhui junction area (Table 1). Based on the characteristics of the factor information, the identified factors are categorized into data types and descriptive indicators. The data-based indicators, totaling 14, are derived from DEM maps and other specialized maps for attribute extraction and vectorized analysis, employing typology and morphology for classification. The descriptive indicators, totaling 7, are gathered through field surveys, questionnaire interviews, and other qualitative data collection methods.

Table 1.
Attribute table of cultural landscape factors for traditional villages and dwellings in the border area of Jiangxi and Anhui Provinces.
3.2. Characteristics of Spatial Distribution of Data-Driven Cultural Landscape Factors
Construct the aforementioned cultural landscape factor system using the selected 260 research samples. Use Google Earth to accurately locate their geographical coordinates, link the 14 data-type indicators to the target information in ArcGIS software, and treat traditional villages as “point” elements in the geographical space on a macro spatial scale. Perform vectorization to create the corresponding spatial distribution geographical atlas, which visually expresses the spatial distribution characteristics of the data-type cultural landscape factors (Figure 3).
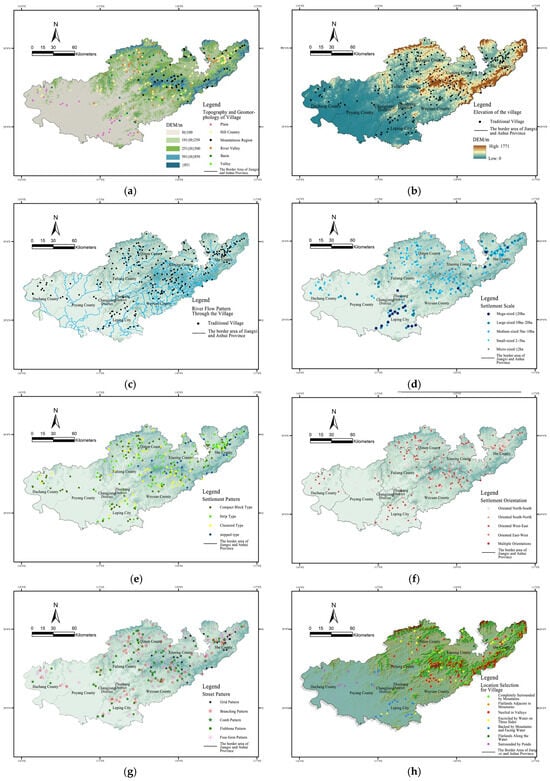
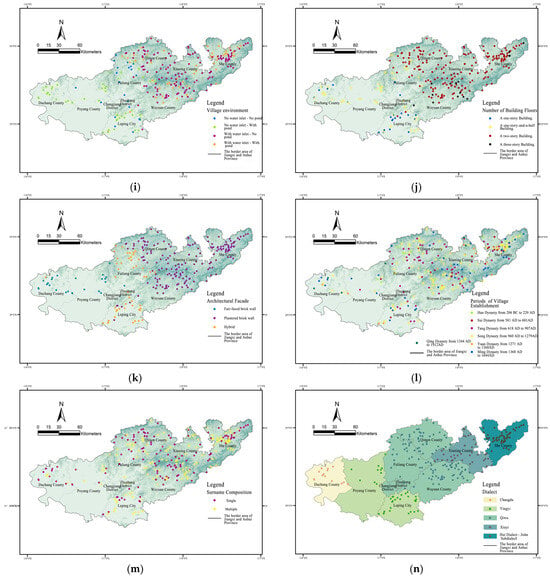
Figure 3.
Spatial distribution characteristics of data-based cultural landscape factor types in traditional villages at the Jiangxi-Anhui border region: (a) topography and geomorphology, (b) elevation, (c) river flow pattern through the villages, (d) settlement size, (e) settlements pattern, (f) orientation of the settlements, (g) street pattern, (h) location selection for villages, (i) villages environment, (j) stories of dwellings, (k) appearance of dwellings, (l) periods of villages establishment, (m) clan structure of villages, (n) dialect. Source: Drawn by authors based on the satellite base map of Map World GS (2024) No. 0650 Data Sources.
3.3. Principal Component Analysis of Data-Driven Cultural Landscape Factors
3.3.1. Model Testing
In this study, the original 14 data-driven cultural landscape factors were standardized using the Z-score method via SPSS 22.0 software to generate a new set of standardized data. The applicability of factor analysis was then evaluated through the Kaiser-Meyer-Olkin test and Bartlett’s test of sphericity. As indicated in Table 2, the KMO value is 0.717, suggesting a moderate correlation among the data variables [39]. Additionally, the result of Bartlett’s test yielded a value of 462.989 with a significance level of 0.000 [39], further confirming the intercorrelation among the variables. Both tests indicate that the data are correlated and satisfy the statistical prerequisites for conducting factor analysis and principal component analysis.

Table 2.
KMO and Bartlett correlation test.
3.3.2. Determination of Principal Components
The extraction of the number of principal components is based on the criterion that principal components correspond to the first m components with eigenvalues exceeding 1. This criterion is typically employed as the basis for determining the number of principal components [40,41]. As illustrated in Table 3, following the eigenvalue criterion, four principal components can be extracted through principal component analysis, i.e., m = 4. The cumulative variance contribution rate is 83.139%, which exceeds the threshold of 80%, indicating that these four principal components provide a robust explanation of the variables and can effectively replace the original 14 data-driven cultural landscape factors. Subsequently, the method of maximum variance rotation was applied to derive Table 4, where the factor loading vector reflects the contribution level of each factor to each principal component; a higher absolute value signifies a greater degree of contribution from the factor [42]. From Table 4, it can be seen that the first principal component basically reflects the information of the four factors: dialect, stories of traditional dwellings, village elevation, and village environment; the second principal component basically reflects the information pertaining to both the period of village establishment and the choice of village location; the third principal component basically reflects the information of individual indicators of architectural appearance at the level of dwellings form; and the fourth principal component basically reflects the information of the two factors of settlements orientation and clan structure.

Table 3.
Variance decomposition and principal component extraction analysis table.

Table 4.
Principal component loading factor matrix.
3.4. Cluster Analysis of Data-Driven Cultural Landscape Factor Systems
In this analysis, each of the 260 villages was treated as an independent class, utilizing the four primary component factors identified earlier as variables for the cluster analysis. The intergroup linkage method was employed for clustering, while the squared Euclidean distance was used as the interval distance metric. Initially, no specific range for the number of clusters was established, and a cluster analysis spectrum was generated (refer to Figure 4 and Table 5). As illustrated in Figure 4, when the distance coefficient d = 5, the villages are categorized into 34 groups; at d = 10, this number decreases to 12; at d = 15, it further consolidates into 6 categories; at d = 20, it reduces to 3 categories; and at d = 25, all villages are aggregated into a single category. For further analysis, the number of clusters was restricted to a range of 1 to 5 categories, and the cluster analysis was repeated. The results revealed the corresponding genus area codes for the villages within each cluster. These codes were imported into ArcGIS software, aligned with the villages’ attribute lists, and visualized in a spatial geographic atlas of clusters ranging from 1 to 5 classes. Through comparative analysis, it was determined that when the number of clusters is limited to 1 or 2 characteristic areas, the spatial distribution of traditional villages becomes overly complex, making it challenging to distinguish the unique cultural landscape features of each area system, while the differences in the cultural landscapes of traditional villages remain minimal. However, when the number of clusters is set to 3 or 4, certain villages located on the county peripheries form distinct clusters, providing a more suitable basis for micro-zoning sub-districts. To comprehensively assess the impact of natural environmental factors, such as topography and hydrology, alongside human environmental factors, including dialect, population migration, and multiculturalism, on the cultural landscape characteristics of villages in the Jiangxi-Anhui junction area [43,44], the study concludes that the village culture remains unaffected when the distance threshold is established. Specifically, it is determined that a distance threshold of d = 20 provides a more rational classification of the 260 villages into 3 categories.
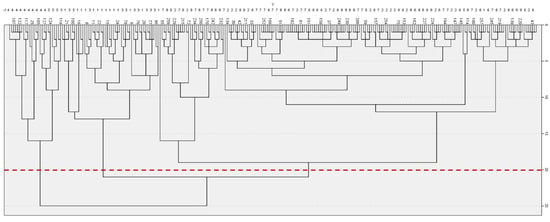
Figure 4.
Dendrogram of hierarchical cluster analysis based on principal component factors.

Table 5.
Table of clustering results.
4. Results
The clustering outcomes of the data-driven cultural landscape factors were integrated with descriptive cultural landscape elements, such as the planar configuration of dwellings, predominant cultural influences in villages, and migration origins. This integration aims to identify common characteristics, followed by spatial overlay and meticulous adjustments of boundaries to ensure the precision of the zoning results. Building upon this foundation and in consideration of the actual requirements for the subsequent protection, development, and management of traditional villages and dwellings, while also accounting for the administrative boundaries of districts and counties, the traditional villages in the Jiangxi-Anhui junction area are ultimately categorized into three sub-districts characterized by their cultural landscapes. Utilizing the “four-segment” naming convention [45], the three zones in the Jiangxi-Anhui Junction District are designated in the format of “geographic location—topographic features—dominant culture—common name.” The three primary traditional village cultural landscape areas in the Jiangxi-Anhui junction region are the western plains water culture-dominated traditional village cultural landscape area, the central hilly plains multi-cultural symbiosis traditional village cultural landscape area, and the eastern hilly mountains clan culture-dominated traditional village cultural landscape area (Figure 5).
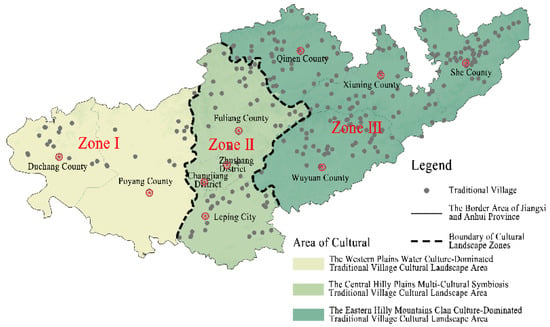
Figure 5.
Division map of traditional villages and dwellings cultural landscapes in the border region of Jiangxi and Anhui Provinces. Source: Drawn by authors based on the satellite base map of Map World GS (2024) No. 0650 Data Sources.
4.1. Typical Characteristics of Traditional Villages and Residential Cultural Landscape Areas in the Border Region of Jiangxi and Anhui Provinces
4.1.1. Characteristics of Water Culture-Dominated Traditional Village Cultural Landscape Area in the Western Plains
The western cultural landscape area of the Jiangxi-Anhui Junction Zone encompasses Duchang County and Poyang County, which are part of the Gan Dialect region. Situated adjacent to Poyang Lake, this area is characterized by a plain topography with an average elevation of 40 m.
At the village landscape level, the cultural landscape area is characterized by a layout primarily consisting of surrounding ponds and a flat waterfront, with a typical village pattern featuring a well-organized grid of intersecting streets. Villages in plains or river valley areas often develop around ancestral halls, forming compact, clustered layouts. The unrestricted topography of these areas allows them to easily develop into large villages, while flooding has led to multiple relocations, making it challenging to maintain their original patterns and styles. Some villages have experienced multiple relocations due to flooding, resulting in the establishment of small-scale communities that struggle to retain their original patterns and styles. In terms of the clan structure of villages, most of the villages are primarily dominated by single-surname communities. Concerning the village environment, there are no water inlets present, but numerous ponds exist, reflecting the enduring traditions of fishery culture and feng shui beliefs, which dictate the placement of ponds at the forefront and within the villages.
At the dwelling landscape level: This cultural landscape area exemplifies typical Gan-style architecture, encompassing a building area of approximately 170 square meters. The structure features clear water brick walls, open halls, and openings along the central axis, with some buildings showcasing straw frame construction in the two bays of the halls. The rooms flanking the central area include attics primarily designated for storage. The building’s exterior, featuring a wooden hooded or monogrammed entrance, is in poor condition.
4.1.2. Characteristics of Multi-Cultural Symbiosis Traditional Village Cultural Landscape Area in the Central Hilly Plains
The Central Cultural Landscape Area at the Jiangxi-Anhui Junction encompasses Jingdezhen City, including Fuliang County, Zhujiang District, Changjiang District, and Leping City, spanning both the Hui Dialect and Gan Dialect regions. This area is situated in a combination of plain and hilly terrains, with an average elevation of 78 m.
At the village landscape level: The cultural landscape area is characterized by diverse topographical features and varying natural environments, which significantly influence village siting, layout, and architectural forms. Villages on the plains are typically located on the shoreline, dispersed in a block shape, unrestricted by topography, and have regular interlocking street patterns. Village sizes range from super-large to medium-sized. In contrast, hilly areas adopt a feng shui-inspired layout, utilizing mountain springs and forming scenic backdrops of mountains and water. Street patterns here are more varied, including interlocking, comb-like, and free-form arrangements. Due to topographical limitations, the majority of the villages are small to medium-sized, with a more varied street layout. The local theater and clan cultures have a big impact on the settlements’ general layout, and they typically congregate and grow around theaters or clan temples as the center. Numerous immigrants from nearby provinces and towns were drawn to the area by the growth of the pottery and tea industries, as well as other commodity economies. As a result, vast villages with multiple surnames coexisting peacefully were formed. Village environments emphasize feng shui-inspired water features, including bridges, trees, pavilions, and memorial arches. These elements form rich, water-focused landscapes, reflecting deep cultural traditions.
At the dwelling landscape level: The cultural landscape in this region is significantly shaped by two dominant influences: Gan Culture and Hui Culture. This interplay has resulted in the emergence of distinct architectural styles, characterized by a blend of Gan-style and Hui-style elements. The dwelling structures exhibit both clear water brick walls and stucco brick walls, reflecting a multicultural synthesis. Building diversity includes single-story, one-and-a-half-story, and two-story designs. In the northern part of Fuliang County, Huizhou-style architecture is particularly prominent, with some buildings featuring two stories and a dwelling footprint of approximately 160 square meters. In the Leping area, traditional architecture vividly showcases the fusion of Gan-style and Hui-style. The entrances of these buildings resemble the door covers typical of the Gan-style, while their overall outline adheres to the straight “Wo Hu Duo” style, highlighting the unique characteristics of Gan-style architecture, with a building area of around 175 square meters. Structurally, Huizhou architecture is known for its “fat beams and thin pillars”, which is similar to the architectural structure of the Leping area.
4.1.3. Characteristics of Clan Culture-Dominant Traditional Village Cultural Landscape Area in the Eastern Hilly Mountainous
The eastern cultural landscape area at the Jiangxi-Anhui junction encompasses Wuyuan County, Qimen County, Xiuning County, and She County, all of which fall within the Hui Dialect region. This area is characterized by hilly and mountainous terrain, with an average elevation of 204 m.
At the village landscape level: The cultural landscape is situated in an environment that is surrounded by mountains and water, which influences the planning and architectural forms of the villages. Guided by the feng shui principles derived from the Zhouyi [36], the village layouts typically feature a configuration that places the back against the mountains and faces the water. The presence of hills, mountains, basins, and other topographical characteristics results in a variety of street patterns and settlement layouts, including cluster-type, belt-type, and ladder-type, which follow the variations in the terrain for a hierarchical distribution. Under the influence of Huizhou clan culture and the patriarchal system, villages with a single form of settlement and a hierarchical street structure were formed. Regarding the village environment, the influence of geomantic culture has resulted in a significant emphasis on the development of water outlets, primarily through the construction of bridges, trees, pavilions, and pagodas, thereby creating a diverse and rich landscape of water features. Village environments emphasize water-related feng shui features, including ponds, bridges, and memorial arches.
At the dwelling landscape level: The dwelling’s landscape is emblematic of Hui-style architecture, with distinctive features such as whitewashed walls and fire-sealing horse-head walls that define the exterior of the buildings. This is significantly different from the Gan-style architecture, which is characterized by the clear-water brick wall. The building typically has two or three floors and occupies an area of roughly 150 square meters because it is narrow and dense, making it easier to develop at high altitudes. The spatial layout reflects a cultural emphasis on etiquette and order, often featuring a main entrance axis that includes both the main door and a ceremonial door, positioned merely one meter apart. This design facilitates the exclusive movement of servants and the designated embroidery space for women, illustrating the Huizhou people’s cultural values regarding social hierarchy.
4.2. Traditional Villages and Dwellings Cultural Landscapes in the Jiangxi-Anhui Junction Region
When examining the landscape variations across these zones, it is evident that cultural landscape factors distinctly differentiate the regions in terms of village siting, settlement forms, and architectural styles.
4.2.1. Zonal Differentiation of Village Sites
The selection of village sites, informed by empirical research findings and the geographical characteristics of mountains and water bodies, can be classified into seven distinct patterns. As depicted in Figure 6a, there are notable geographical distribution variations across the three zones. Zone I is characterized by flat terrain adjacent to Poyang Lake, reflecting the influence of long-standing fishing culture and feng shui principles. Villages here commonly favor locations surrounded by ponds or situated on lakeside flatlands, where access to water supports daily life and production while facilitating effective drainage. Zone II, situated in plains and hilly regions, predominantly features traditional villages in the plains located on lakeside flatlands, while certain areas in the hilly region of Fuliang County, previously part of Qimen County, have been shaped by the dissemination of Huizhou culture through trade and migration. As a result, site selection in this zone is often guided by Huizhou cultural feng shui concepts, leading to a preference for locations that are backed by mountains and face water. Zone III emphasizes the impact of feng shui culture on site selection, with settlements consistently choosing sites backed by mountains and facing water. Furthermore, in order to escape from the war, the immigrants from the northern central plains mostly settled in the valley crevice, surrounded by mountains on all sides.
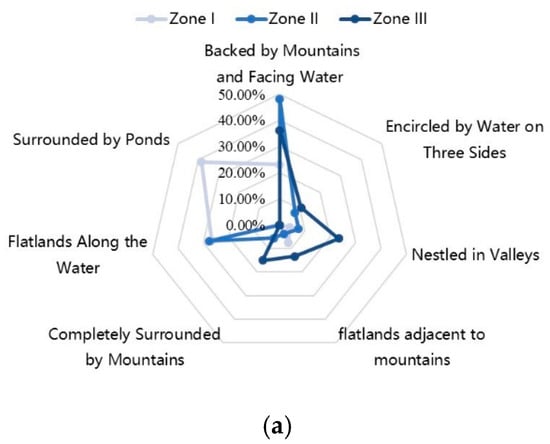
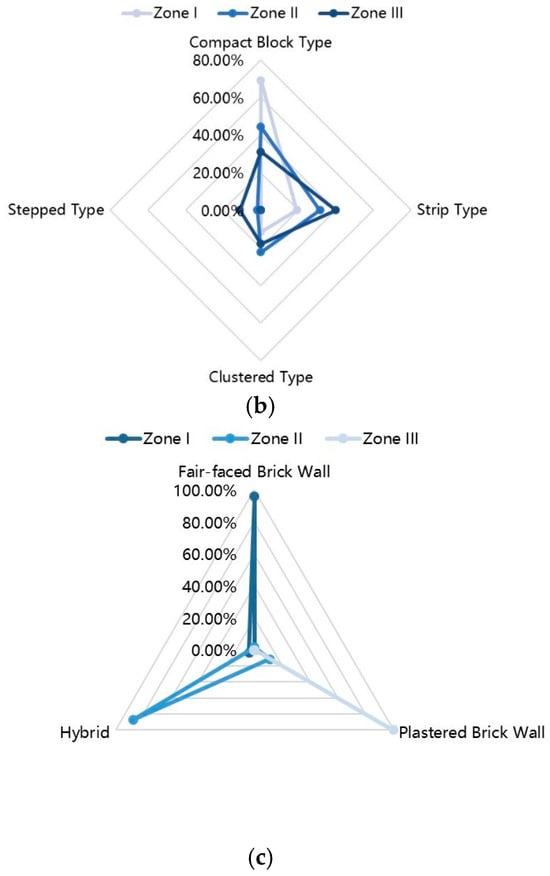
Figure 6.
Distribution Ratio of Cultural Landscape Factors of Traditional Villages and Dwellings in the Border Region between Jiangxi and Anhui Provinces: (a) Location selection for villages; (b) Settlement pattern; (c) Appearance of dwellings.
4.2.2. Zonal Differentiation of Settlement Patterns
Integrating findings from both current and previous research, traditional settlement patterns in the Jiangxi-Anhui junction area are categorized into four types: cluster, belt, group, and ladder-shaped. Figure 3e illustrates the geospatial distribution of these traditional settlement patterns within the Jiangxi-Anhui junction area. The four settlement types exhibit a gradual increase from west to east across the three sub-areas, highlighting distinct trends across the three sub-regions. From Area I to Area III, the proportion of cluster-type settlements gradually decreases, while belt-type and terrace-type settlements dominate (see Figure 6b). In summary, the western region is predominantly characterized by cluster-type settlements, the central region is primarily defined by group-type settlements with multi-clan aggregation, the belt type aligns with the foothills and water systems, and the eastern region is mainly characterized by both belt and terrace types following the mountain contours. This distribution underscores the significant role of topography and geomorphology in shaping traditional settlement patterns, which outweigh the influence of social and human factors.
4.2.3. Zonal Differentiation of Architectural Aesthetics
As “homologous” cultures, Gan Culture and Hui Culture exhibit certain parallels in their architectural expressions, particularly regarding compositional elements and spatial organization. However, a detailed examination reveals significant regional disparities in their architectural representations, including the appearance of traditional dwellings, entrance designs, patio configurations, eave spaces, and roof styles. Figure 3k illustrates the spatial distribution of architectural aesthetics in traditional dwelling structures within the Jiangxi-Anhui junction area. The architectural styles can be categorized into three distinct zones (Figure 6c): Zone I features clear water brick walls, indicative of advanced brick firing techniques in the region. Zone III is characterized by stuccoed brick walls, which create dwellings with an aesthetic of whitewashed surfaces and tiled roofs. Zone II serves as a transitional area between Zones I and III, where the eaves of the brick walls are ornamented, while the remainder of the wall showcases the material of the freshwater brick.
Combined with the above analysis of the typical characteristics of villages and dwellings in each cultural landscape area and the geographical differences of the main cultural landscape factors, the traditional villages and dwellings in each cultural area are summarized in Table 6 and Table 7.

Table 6.
Comparison of Cultural Landscape Regional Differentiation of Traditional Villages and Dwelling Houses in the Border Area Between Jiangxi and Anhui Provinces.

Table 7.
Comparison of cultural landscape regional differentiation of traditional villages and dwelling houses in the border area between Jiangxi and Anhui provinces.
4.3. Mechanisms of Formation for Traditional Villages and Distinctions in Dwellings and Cultural Landscapes
The traditional villages and dwellings located at the junction of Jiangxi and Anhui are not only significant aspects of folk culture studies within architectural history but also represent a critical dimension in the historical and social analysis of a region characterized by multicultural interactions. Therefore, an understanding of the landscape zoning characteristics, informed by the spatial attributes of these villages and dwellings, should be incorporated into the examination of the “history of social change in the region.” Consequently, the exploration of landscape zoning features, grounded in the spatial characteristics of villages and dwellings, must also align with the research trajectory of “regional social change history.” Furthermore, the attributes of multicultural integration should be contextualized within a specific regional social history, and the mechanisms underlying the differentiation of traditional villages and dwellings should be investigated in relation to the natural geographic and historical context of the cultural convergence between Jiangxi and Anhui.
4.3.1. Endogenous Dynamics: Natural Geographic Environment
The natural geographic environment factors will affect the production and operation activities in the village and the construction of the village for a long time, which is the endogenous driving force for the geographical differentiation of the villages and residential cultural landscapes of the three cultural districts and shapes the spatial forms and residential architectural styles of the villages at the macro- and micro-levels together.
At the macro level, the Jiangxi-Anhui junction region exhibits a diverse topography and geomorphology, characterized by intersecting mountain ranges and a dense network of water systems [46]. When overlaying the traditional village and dwellings cultural landscape zoning of the Jiangxi-Anhui junction region with the mountain ranges, as illustrated in Figure 7a, it becomes evident that the remnants of the Huangshan Mountain, Placebo Mountain, and Lotus Mountain Range delineate the primary boundaries between the three major sub-districts. This geographical configuration has, to some extent, impeded cultural exchanges between the areas. Notably, the Zhanggong Mountain Range and Wuhuashan Mountain Range, situated between Wuyuan County and Xiuning County, act as a substantial barrier that obstructs the connection between Northeast Jiangxi and South Anhui, thereby contributing to the differentiation of cultural landscape zoning. Furthermore, when the cultural landscape zoning of the villages is superimposed onto the water system map (Figure 7b), a correlation between the water systems and the cultural landscape patterns emerges. For instance, Zone I aligns with the Poyang Lake basin, Zone II corresponds to the Changjiang River basin and Le’an River basin, while Zone III is associated with the Xin’an River basin. These three principal cultural landscape areas are primarily structured around major river axes, reflecting the extent of the water network and forming a northeast-southwest-oriented strip area. The distribution patterns of each cultural landscape area exhibit distinct variations along the east-west transition. The meandering water systems within the valleys serve as vital channels and arteries, facilitating connections among people, trade, and cultural dissemination within the region.
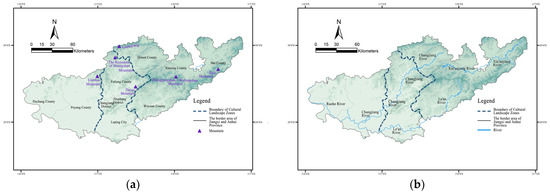
Figure 7.
The relationship between the cultural landscape zoning of traditional villages and dwellings and the mountain ranges and water systems in the border region of Jiangxi and Anhui provinces: (a) The relationship between the cultural zoning and mountain ranges in the border region of Jiangxi and Anhui provinces; (b) The relationship between the cultural zoning and water systems in the border region of Jiangxi and Anhui provinces. Source: Drawn by authors based on the satellite base map of Map World GS (2024) No. 0650 Data Sources.
At the micro level, the landscape pattern has a significant impact on the location of the village, the settlement pattern, the street pattern, and the architectural form of the dwellings. In Zone I, villages are mostly located in flat and open areas, forming compact and large-scale clustered villages; while in Zone III, villages are mostly located in hilly areas, and villages usually follow the topography of the mountains and are located in the valleys and hilly flat hinterlands to form small and medium-sized clustered or belt-type settlements. In Zone I and Zone II, due to the flat and open terrain, the street pattern is more regular and orderly, less restricted by the terrain, and the residential buildings cover a larger area and have a lower number of floors; whereas in Zone III, due to the mountainous terrain and the densely populated land being limited, different variants of the street form are generated, and the residential buildings need to develop to the upper floors to adapt to the environmental needs, so the number of floors of the buildings is mostly two or three.
4.3.2. Exogenous Dynamics: The Social and Human Environment
During the construction and development of traditional villages, external influences significantly impact the cultural landscape of the Jiangxi-Anhui junction area, resulting in characteristics that are both diverse and differentiated. Factors such as population migration, the dissemination of foreign cultures, economic trade development, and changes in historical establishment contribute indirectly to the evolution and development of village and dwelling cultural landscape patterns.
- Regional Culture as a Spiritual Guiding Mechanism
The formation of traditional villages and cultural landscapes in Area III is due to the influence of Huizhou culture, which has led to the formation of unique village forms and architectural styles. Huizhou culture originated from the exchange and fusion of the Central Plains culture and the local Shan-Yue culture, which gave birth to the Huizhou culture with an immigrant nature [47]. The influence of Huizhou clan culture on the spatial pattern is evident in Area III, where great importance is attached to bloodline and clan relationships, encouraging clans to live together to form villages with a single surname. Additionally, it emphasizes axes, creating a settlement pattern centered on ancestral halls or with entrance layouts, and the streets and lanes are clearly graded. Meanwhile, under the influence of Xin’an Science, feng shui is highly emphasized, and the concept of feng shui runs through the site selection, layout, and environment of the village. Among them, the water outlet in the village environment is a unique product of Huizhou culture and the beginning of the village space sequence, and the combination of the water outlet and the artificial buildings, such as pavilions, terraces, and buildings, constitutes the distinctive characteristics of Huizhou ancient villages. The residential buildings in Area III are typical representatives of Huizhou cultural characteristics, with green tiles and white walls, large-scale zigzag patios, richly stacked horse-head walls, brick-carved and plaque-type door covers, and exquisite Huizhou wood, brick, and stone carvings as the most important features of Huizhou architecture.
The I area is deeply influenced by Gan culture and traditional culture of the Central Plains, adopting the mode of gathering clans to live together and forming the layout pattern centered on ancestral halls. In the plain area, instead of deliberately seeking to live by the water, water ponds are dug to satisfy the water for production and living, meet the basic drainage needs, and often have ponds in front of the ancestral halls to enhance the importance of the clan system. The residential houses in Area I represent the Gan School of Architecture, which is characterized by green bricks and gray tiles, earth-shaped patios, richly stacked horse-head walls, and wooden door covers with decorations focusing on the beams and frames. From this, it can be seen that there are commonalities and differences between Gan School architecture and Huizhou School architecture. The uniqueness of the geographical location of Area II makes it influenced by two strong cultures, Gan culture and Hui culture, thus giving birth to the transitional characteristics of the intermingling of these two cultures. In terms of village pattern: due to the close interaction between Fuliang County and Qimen and the influence of its clan system, Fuliang County formed villages with ancestral hall buildings as the center or entrance layout, focusing on the location of villages and the construction of water outlets; the Leping area formed a unique theater culture under the influence of multiculturalism, with the theater and the ancestral hall buildings becoming the core of the layout of the villages. In terms of architectural style, the two styles of architecture coexist, and innovations in architectural appearance form a transitional phenomenon of mixing the two; the form of the patio evolved from the local cultural traditions and climatic factors of precipitation into a water-shaped patio.
- 2.
- Historical Migration and the Sequence of Regional Development as Mutation Mechanisms
The construction and development of villages in the border area of Gan and Anhui were closely tied to three significant periods of southward migration by Chinese scholarly clans throughout history. These migrations brought cultural, technological, and demographic changes to the region, forming distinct cultural landscapes. During the Eastern Han and Jin dynasties, due to wars and natural disasters, the Han people in the Central Plains moved southward, and most of them moved eastward to the Jiangsu and Anhui areas [48], while a few of them moved into the central and northern part of Jiangxi and Poyang Lake Basin, which contributed to the development and construction of the villages in Area I, Area II, and Area III and the outward movement of architectural culture. After the Anshi Rebellion in the Tang Dynasty, the population of northern China moved southward again and entered Anhui and Jiangxi through the eastern line, and most of them built their foundation in the She County in Anhui and Jiangxi Raozhou (Jingdezhen) and Ji’an [49]. To the end of the Northern Song Dynasty, after the Jingkang disaster, Huizhou attracted a large number of people from the northern central plains because of its stable political environment, abundant products, and stable life, and the villages in Area III were rapidly developed and constructed [50]. However, due to the rapid increase in the population, the relationship between people and land is tense, leading to the II area and other neighboring areas of migration, so the II area of the northern dialect formed the Huizhou dialect, and the Huizhou-like architecture region appeared, and the Hui-like architectural style emerged. In order to fill the vacancies caused by the war in the two lakes area in the Ming Dynasty, a large-scale immigration movement was carried out—“Jiangxi filling in Hubei and Guangdong”; and the population of Jiangxi kept migrating to Hubei and Guangdong; so there were relatively few new villages in Area I and Area II. As for Area III, due to the rapid rise of Huizhou merchants, people tended to choose new locations for construction after accumulating enough capital, which led to the further construction and development of these settlements.
- 3.
- Commercial trade development as a promotion mechanism
The development of villages is closely tied to the growth of industries, particularly the driving force of commercial trade. Relying on the geographic advantages, convenient land and water transportation, and abundant materials, the border area of Jiangxi and Anhui Province has formed a commercial chain of production and trafficking, selling Jingdezhen porcelain, Fuliang tea, and Shezhou inkstone to all parts of the country. At the same time, in the frequent commercial links, the two places of culture are also in the subtle mutual infiltration.
During the period from the Sui and Tang dynasties to the early Ming Dynasty, the superior natural environment and sufficient labor force made it possible for Area I and Area II to have abundant products, which laid a solid foundation for the development of commerce. With the opening of the golden land and water transportation route of Dayu Ridge-Ganjiang River-Poyang Lake-Yangtze River-Great Canal, developed industrial and commercial towns arose along the river, featuring buildings with storefronts in front and residential spaces in the back [51], which was especially obvious in Area II. In addition, Area II relied on the river transportation and the ancient road to develop the porcelain trade business, which attracted people from all over the world to settle down, forming a cluster-type village with multiple surnames. Economic conditions were an important basis for the construction of traditional settlements, and economically developed families had the ability to feed their hometowns by constructing dozens of neatly laid out and grandly styled buildings. On the contrary, in the II district, in the Ming and Qing Dynasties, under the influence of Huizhou merchants, Huizhou culture rose to become a high-potential culture. After the rise of the local government officials and gentry families, they purchased a lot of land and built houses, which made the villages larger in scale, with complete facilities, a high architectural construction level, and exquisite and rich decorative details.
- 4.
- Changes in Institutional History
In ancient times, when transportation and information dissemination were limited, administrative divisions significantly influenced the development of cultural landscapes. Typically, administrative boundaries also delineated cultural regions, and these divisions played a formative role in shaping cultural landscapes. Historically, the administrative status of the Jiangxi-Anhui junction district has remained relatively stable overall, although there have been adjustments to some county affiliations, as illustrated in Figure 8.
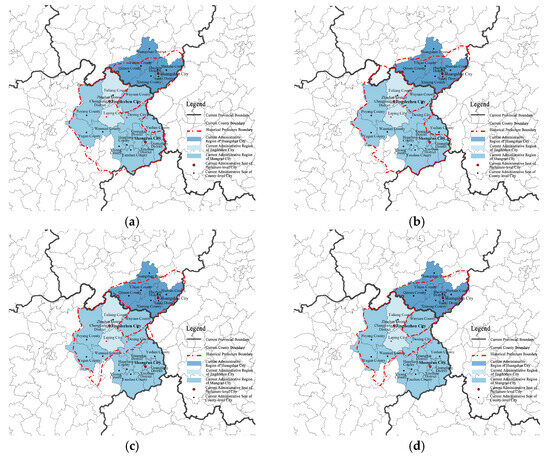
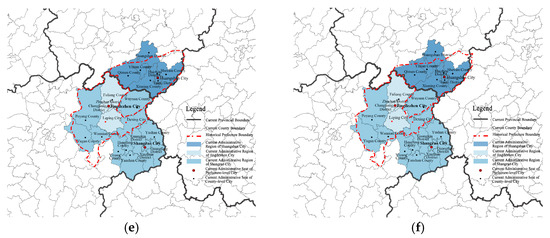
Figure 8.
Historical administrative division in the border region of Jiangxi and Anhui Provinces. (a) Administrative divisions of Sui dynasties; (b) Administrative divisions of Tang dynasties; (c) Administrative divisions of Song dynasties; (d) Administrative divisions of Yuan dynasties; (e) Administrative divisions of Ming dynasties; (f) Administrative divisions of Qing dynasties. Source: Adapted and drawn by the author, based on “A Comprehensive History of Administrative Divisions in China” and the satellite base map from Map World GS (2024) No. 0650 Data Sources.
The counties of She, Xiuining, Qimen, and Wuyuan in Area III have been part of Shezhou since the Tang Dynasty, with She County serving as the state capital during the Song Dynasty. This shared governance over an extended period resulted in similarities in cultural heritage and landscape development. Wuyuan County has been under the jurisdiction of Anhui Province since its establishment in the Tang Dynasty, undergoing several administrative changes: in 1934, it was incorporated into the fifth administrative district of Jiangxi Province; in 1947, it was reverted to the seventh administrative district of Anhui Province; and on May 1, 1949, it was ultimately transferred from Anhui Province back to Jiangxi Province [52]. Although it currently falls under Jiangxi Province, Wuyuan has been profoundly influenced by Hui culture since ancient times; the landscape patterns of these villages and the architectural styles of the homes reflect the characteristics of southern Anhui. Poyang County in Area I was governed by Rao Prefecture during the Tang Dynasty, while Duchang County was also under the jurisdiction of Rao Prefecture of Jiankang Army during the same period [53]. This historical context fostered frequent social, economic, and trade interactions between the two regions, resulting in strong cultural connections and a similar cultural landscape. In Zone II, Fuliang County was historically part of Poyang County of Yuzhang County, and a portion of its northern area was previously under the jurisdiction of Qimen County. Consequently, this has created a cultural transition zone influenced by both Gan-Po Culture and Hui Culture.
5. Discussion
5.1. Methodological Validation and Application as a Reference for Other Multicultural Regions
Current research on cultural integration zones primarily focuses on areas such as the Shaanxi-Gansu-Sichuan region, the Jiangxi-Fujian-Guangdong region, and the northwestern Yunnan cultural integration area. However, delineation remains ambiguous for regions like the Liaoning-Hebei border and the Jiangxi-Hunan border, which require further exploration. By selecting the representative Jiangxi-Anhui cultural intermingling area for the study of traditional villages and their residential cultural landscapes, this research contributes to enhancing the understanding of multicultural intermixing zones. Methodologically, the current study predominantly employs qualitative approaches, resulting in a lack of objectivity in both the processes and outcomes of cultural zoning. The integration of quantitative and qualitative methods, specifically through “principal component analysis and cluster analysis”, represents a significant advancement in the exploration and validation of the methodology for cultural landscape zoning in traditional villages and residential areas within the Jiangxi-Anhui junction. This approach not only serves as a methodological validation but also offers a more objective and comprehensive zoning framework, which will encourage and facilitate the in-depth study of traditional village cultural landscape zoning in other culturally intermingling regions.
5.2. Scientific Guidance for China’s Rural Revitalization Strategy
Through the in-depth analysis of the cultural landscape characteristics of traditional villages and residential houses in the border area of Jiangxi-Anhui, scientific guidance is provided for the promotion of China’s rural revitalization strategy, which includes the formulation of differentiated cultural landscape protection strategies: ① The water culture-led villages in the western plains focus on protecting the waterfront layout and the village form, maintaining their unique water and fishery cultures. Efforts should include developing waterfront cultural experience projects, such as fishery culture exhibitions and water village folk activities; ② The central hilly plains multi-cultural symbiosis type village focuses on the protection of the village pattern and cultural heritage, restoration and protection of historical ancestral halls, theaters, and other public buildings, maintenance of the community structure of the multi-caste harmonious cohabitation, and through the development of ceramic production workshops, tea performances, and other experience programs, to promote the cultural inheritance and economic development; ③ The eastern hilly and mountainous clan culture-led villages prioritize the preservation of village layouts backed by mountains and facing water, as well as the Huizhou architectural style. Restoration efforts focus on public buildings of historical value, such as clan temples, pagodas, and ancient bridges. At the same time, the rich cultural heritage of the Huizhou area will be utilized to develop cultural tourism projects. In addition, all districts need to develop cultural landscape tourism products, upgrade the level of public service facilities, develop special agriculture and cultural and creative industries, encourage community participation and capacity building, and provide policy support and financial guarantees, with a view to promoting the implementation of the strategy of rural revitalization.
5.3. Providing Scientific Guidance for the Conservation and Sustainable Development of the World’s Cultural Heritage
The scientific zoning methodology and multidisciplinary research tools adopted in the study provide new ideas and methods for the conservation and sustainable development of World Cultural Heritage. Through quantitative analysis and field research, the study demonstrates how to identify and protect heritage sites with unique cultural values in complex areas of cultural intermingling, providing a scientific basis for cross-regional heritage protection and management. In addition, the findings emphasize the importance of public participation and multidisciplinary cooperation, offering concrete data and recommendations for the formulation and implementation of global cultural heritage protection policies. These results not only help to enhance China’s influence in the field of international cultural heritage protection but also provide a new example of global cooperation in heritage conservation for international organizations such as UNESCO.
5.4. Limitations and Future Prospects
This paper has achieved some research results on the characteristics of traditional villages and residential cultural landscapes in multicultural intermingling areas and regional differentiation; however, there are still many uncertainties in the research process and results.
First of all, the village sample data mainly come from the national and provincial traditional village lists, and may not fully represent those villages that are not listed but also have cultural value. In addition, the sample may lack some small, marginalized villages, whose cultural landscapes may be more unique but have not been given sufficient attention. Secondly, the characteristics of these landscapes and their differentiation patterns are often regionally specific, making it challenging to generalize findings to other multicultural areas.
Despite the above limitations, future research needs to expand the sample, enhance the diversity and reliability of data sources, and select distinctive cultural landscape factors in order to explore more precise zoning methods. This will help to identify the characteristics of traditional villages in multicultural areas and improve the representativeness of the research results. At the same time, we should deepen the research on the formation mechanism of zonal differentiation and promote the application of quantitative methods so as to provide guidance for the conservation and sustainable development of traditional villages and cultural landscapes.
6. Conclusions
As a typical case of a multicultural intermingling area, the Jiangxi-Anhui Junction Area features a distinctive traditional village cultural landscape. Research and exploration of such areas are essential for enhancing the traditional village research framework. Using the division method of “constructing a cultural factor index system—data collection and processing—principal component analysis—cluster analysis—cultural zoning”; the traditional villages and residential cultural landscapes in the Jiangxi-Anhui junction area were divided into cultural landscape zones. The cultural landscape characteristics of each zone were summarized, and the differences among the zones were analyzed. Based on the natural geographic environment, traditional settlements, dwellings, and history and culture, we extracted 21 data-based cultural landscape factors and constructed a cultural landscape factor system covering four levels: natural environment, spatial form, dwelling form, and history and humanity. Using ArcGIS software, a data-driven geographic information database was created, visualizing the spatial distribution of cultural landscape factors. This provides a strong reference for cultural landscape zoning. Through principal component analysis and systematic clustering analysis, the traditional villages and residential cultural landscape in the Jiangxi-Anhui junction area were divided into three major subzones with the help of ArcGIS software: water culture dominant in the western plains, multi-cultural symbiosis in the central hilly plains, and clan culture dominant in the eastern hilly and mountainous areas. The results show that there are significant regional differences in the three subregions in terms of village site selection, settlement pattern, and architectural appearance. Based on the typical characteristics of different cultural landscapes and regional differences, this study investigates the formation mechanisms behind these variations. The analysis combines the endogenous dynamics of the natural geographic environment in the Jiangxi-Anhui cultural fusion area with the exogenous dynamics of regional culture, historical migration, and the area’s development sequence. Additional factors include the development of commerce and trade, as well as changes in administrative structures. These insights aim to provide a theoretical basis and scientific guidance for protecting and developing the cultural heritage of traditional villages and residential landscapes in multicultural fusion areas.
Author Contributions
Conceptualization, Y.D.; methodology, M.C.; software, M.C. and Y.L.; validation, Y.W. and L.Z.; investigation, M.C., Y.L. and L.Z.; resources, Y.D.; data curation, L.Z.; writing—original draft preparation, Y.D. and M.C.; writing—review and editing, Y.D.; visualization, Y.W. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This research was supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China: Research on the Morphological Evolution of Traditional Residences in the Border Area of Jiangxi and Anhui Provinces Based on Quantitative Models (Grant number 52068034); Jiangxi Provincial Education Department Postgraduate Innovation Fund Project: Research on the Informatization of Cultural Landscapes of Traditional Villages and dwellings in the Border Area of Jiangxi and Anhui Provinces (Grant number YC2023-S214).
Institutional Review Board Statement
Not applicable.
Informed Consent Statement
Not applicable.
Data Availability Statement
Some of the research materials and data used in this paper are available on the internet and through numerous public channels. Additionally, for more detailed information and data, please contact the author at yapengduan@whu.edu.cn.
Acknowledgments
The authors would like to thank Liping Peng from the Polytechnic University of Milan for her invaluable assistance and guidance throughout this research.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
References
- De Blij, H.J. Human Geography: Culture, Society, and Space, 4th ed.; Wiley: New York, NY, USA, 1993; p. 225. [Google Scholar]
- Situ, S. Cultural Geography of Guangdong, 3rd ed.; Guangdong People’s Publishing House: Guangzhou, China, 2013; p. 114. [Google Scholar]
- Antrop, M. Landscape change and the urbanization process in Europe. Landsc. Urban Plan. 2004, 67, 9–26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Iwata, Y.; Fukamachi, K.; Morimoto, Y. Public perception of the cultural value of Satoyama landscape types in Japan. Landsc. Ecol. Eng. 2011, 7, 173–184. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Taylor, K. New Lives, New Landscapes. Landscape, Heritage and Rural Revitalisation: Whose Cultural Values? Built. Herit. 2019, 3, 50–63. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fagerholm, N.; Eilola, S.; Kisanga, D.; Arki, V.; Käyhkö, N. Place-based landscape services and potential of participatory spatial planning in multifunctional rural landscapes in Southern highlands, Tanzania. Landsc. Ecol. 2019, 34, 1769–1787. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, X. Artificial intelligence in the protection and inheritance of cultural landscape heritage in traditional village. Sci. Program. 2022, 2022, 9117981. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cloke, P. Country backwater to virtual village? Rural studies and ‘the cultural turn. J. Rural Stud. 1997, 13, 367–375. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, P.; Liu, C.; Deng, Y.; Shen, X.; Li, B. Research on the Zoning of Traditional Settlement Landscapes and Identification of Landscape Gene Elements in China. Acta Geogr. Sin. 2010, 65, 1496–1506. [Google Scholar]
- Antrop, M. Sustainable landscapes: Contradiction, fiction or utopia? Landsc. Urban Plan. 2006, 75, 187–197. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.; Sun, Q.; Zou, L. Spatial-temporal evolution and driving mechanism of rural production-living-ecological space in Pingtan islands, China. Habitat Int. 2023, 137, 102833. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.; Zhang, X.; Xu, M.; Zhang, X.; Shan, B.; Wang, A. Spatial patterns and driving factors of rural population loss under urban–rural integration development: A micro-scale study on the village level in a hilly region. Land 2022, 11, 99. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, X.; Xue, P.; Wang, F.; Qin, Y.; Duan, X.; Yang, Z. How to become one? The modern bond of traditional villages in centralized contiguous protection and utilization areas in China. Habitat Int. 2024, 145, 103018. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, W.; Shi, Q.; Wang, G. Analysis of Performance and Genetic Characteristics of Cultural Landscapes in Traditional Villages along the Jinzhong Section of the Wanli Tea Road from a Landscape Gene Information Chain Perspective: A Case Study of Xiamen Village. Sustainability 2024, 16, 8131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, F.; Yu, F.; Zhu, X.; Pan, X.; Sun, R.; Cai, H. Disappearing gradually and unconsciously in rural China: Research on the sunken courtyard and the reasons for change in Shanxian County, Henan Province. J. Rural Stud. 2016, 47, 630–649. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fang, Y.; Liu, J. Cultural landscape evolution of traditional agricultural villages in North China—Case of Qianzhai Village in Shandong Province. Chin. Geogr. Sci. 2008, 18, 308–315. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, Y.; Ahmad, Y. Heritage Protection Perspective of Sustainable Development of Traditional Villages in Guangxi, China. Sustainability 2023, 15, 3387. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, H.; Tong, Y. Spatial differentiation of traditional villages using ArcGIS and GeoDa: A case study of Southwest China. Ecol. Inform. 2022, 68, 101416. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aono, H. Shin Chiri B; Ninomiya Shoten: Tokyo, Japan, 1979; pp. 48–51. [Google Scholar]
- Sun, Y.; Ou, Q. Research on the traditional zoning, evolution, and integrated conservation of village cultural landscapes based on “production-living-ecology spaces” – A case study of villages in Meicheng, Guangdong, China. Open Geosci. 2021, 13, 1303–1317. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, L.; Sun, C.; Wang, M.; Xiao, X. Construction and Characterization of Traditional Village Landscape Cultural Genome Atlases: A Case Study in Xupu County, Hunan, China. Sustainability 2024, 16, 9524. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhuo, X.; Xiao, D. A Study on the Regional Differences in the Landscape of Hakka Traditional Villages on the Borders of Jiangxi, Fujian, and Guangdong. Urban Plan. 2023, 47, 110–122+132. [Google Scholar]
- Cao, K.; Liu, Y.; Cao, Y.; Wang, J.; Tian, Y. Construction and characteristic analysis of landscape gene maps of traditional villages along ancient Qin-Shu roads, Western China. Heritage Sci. 2024, 12, 37. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, P. Research on the Construction and Application of Landscape Genomic Atlas of Traditional Settlements in China. Ph.D. Thesis, Peking University, Beijing, China, 2011. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, X.; Li, S.; Li, L.; Guo, Y.; Liu, J. The representation of regional cultural gene and the concept of spatial control of transgene based on human perspective. Hum. Geogr. 2014, 29, 1–9. [Google Scholar]
- Xiang, H.; Qin, Y.; Xie, M.; Zhou, B. Study on the “space gene” diversity of traditional dong villages in the Southwest Hunan Province of China. Sustainability 2022, 14, 14306. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, B.; Zeng, R.; Liu, P.; Liu, Y.; Dou, Y. Study on the evolution of human settlements in traditional villages based on CAS theory: A case study of Zhang Guying Village. Geogr. Res. 2018, 37, 1982–1996. [Google Scholar]
- Zheng, W.; Deng, Y.; Luo, L.; Liu, P.; Liu, X. Quantitative Evaluation and Zoning of Traditional Settlement Cultural Landscapes in Western Hunan. Hum. Geogr. 2016, 31, 55–60. [Google Scholar]
- Mo, M.; Ye, Y. Characteristics of Jiangxi Regional Culture and Geographical Factors of Its Formation. J. Jiangxi Norm. Univ. (Nat. Sci.) 2004, 29, 555–558. [Google Scholar]
- Luan, C. The Formation and Evolution Process of Huizhou Culture. Anhui Hist. 2014, 58, 109–113+121. [Google Scholar]
- Hou, W. Discussing to comprehensive evaluation by principal component. Appl. Stat. Manag. 2006, 25, 211–214. [Google Scholar]
- Yang, W.; Zhang, T. SPSS Statistical Analysis and Industry Application Case Studies, 4th ed.; Tsinghua University Press: Beijing, China, 2011; p. 158. [Google Scholar]
- Zhou, S.; Kong, X.; Zhu, H. Cultural Geography, 1st ed.; Higher Education Press: Beijing, China, 2004; pp. 226–227. [Google Scholar]
- Shen, X.; Liu, P.; Deng, Y. Landscape Regionalization and Utilization Value of Traditional Settlements in Southern China. Geogr. Res. 2006, 25, 485–494. [Google Scholar]
- Li, J.; Yang, D.; Xiao, D. Regional Differentiation and Formation Mechanism of Cultural Landscapes of Traditional Settlements and Vernacular Dwellings on Hainan Island. Urban Dev. Stud. 2020, 27, 1–8. [Google Scholar]
- Sun, L. Analysis on the Site Selection Pattern of Traditional Villages Influenced by Traditional Feng Shui Culture. Shanxi Archit. 2021, 47, 18–21. [Google Scholar]
- Li, J.; Wang, J.; Li, X. Heritage Value Assessment and Landscape Preservation of Traditional Chinese Villages Based on the Daily Lives of Local Residents: A Study of Tangfang Village in China and the UNESCO HUL Approach. Land 2024, 13, 1535. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, P. Genetic Expression of Ancient Village Cultural Landscape and Landscape Identification. J. Hengyang Norm. Univ. (Soc. Sci. Ed.) 2003, 24, 1–8. [Google Scholar]
- Han, X.; Zhang, Y.; Sun, F. Method for determining index weight based on principal component analysis. J. Sichuan Ordnance 2012, 33, 124–126. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, R.X.; Kuang, J.; Gong, Q.; Hou, X.L. Principal component regression analysis with SPSS. Comput. Methods Programs Biomed. 2003, 71, 141–147. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maitra, S.; Yan, J. Principle component analysis and partial least squares: Two dimension reduction techniques for regression. Appl. Multivar. Statist. Models 2008, 79, 79–90. [Google Scholar]
- Li, F. Principle and Application of Factor Analysis. Ind. Technol. Forum 2014, 13, 76–77. [Google Scholar]
- Duan, Y.; Ni, S.; Liu, J. Comparative Study on the Morphology of Traditional Residences at the Border of Jiangxi and Anhui from the Perspective of Cultural Geography: A Case Study of Ancient Huizhou Wuyuan County and Ancient Raozhou Fugan County. Urban Archit. 2019, 16, 74–76+126. [Google Scholar]
- Shan, W. Research on Village Landscape Design at the Interprovincial Border of Jiangxi and Anhui from the Perspective of Sharing Concept. Master’s Thesis, Jingdezhen Ceramic Institute, Jingdezhen, China, 2022. [Google Scholar]
- Long, H.; Zou, J.; Li, T.; Liu, Y. Evaluation and Regional Typology of Rural Transformation Development: A Case Study of the “Southern Jiangsu-Northern Shaanxi” Belt. Geogr. Res. 2012, 31, 495–506. [Google Scholar]
- Duan, Y.; Guo, Y. A Preliminary Exploration of Quantitative Methods for Studying Traditional Dwelling Morphology: A Case Study of the Border Region Between Jiangxi and Anhui. Archit. Cult. 2020, 17, 77–78. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, B. Basic Concepts and Historical Status of Huizhou Culture. J. Anhui Univ. (Nat. Sci.) 2002, 27, 28–33. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, X. Northern Immigrants and Economic Development in Huizhou During the Late Tang and Five Dynasties Periods. J. Anhui Norm. Univ. (Humanit. Soc. Sci.) 2006, 51, 687–691. [Google Scholar]
- Xu, Y. A Study on the Landscape of Traditional Villages in Jiangxi Province Influenced by Immigrant Culture. Ph.D. Thesis, Beijing Forestry University, Beijing, China, 2021. [Google Scholar]
- Li, J.; Chu, J.; Ye, J. Spatial Evolution Characteristics and Driving Mechanisms of Ancient Huizhou Traditional Villages. Econ. Geogr. 2018, 38, 153–165. [Google Scholar]
- Zhong, Y.; Tang, L. The Symbiotic Integration of Traditional Dwelling Architectural Forms and Regional Culture: A Case Study of Ming Dynasty Dwellings in Jingdezhen. Sino-Foreign Archit. 2017, 23, 36–38. [Google Scholar]
- Wuyuan County Committee Office. Gazetteer of Placenames in Wuyuan County, Jiangxi Province; Wuyuan County Committee: Shangrao, China, 1985; pp. 1–2. [Google Scholar]
- Boyang County Office. Gazetteer of Placenames in Boyang County, Jiangxi Province; Boyang County Committee: Shangrao, China, 1983; pp. 1–2. [Google Scholar]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).