Abstract
The bioactive components present in onion peel powder are a promising factor in preventing/treating obesity. Overweight/obesity causes metabolic changes, which can lead to leptin resistance in the central nervous system (CNS) and, thus, to structural and functional changes in the brain. Objectives: The presented study focused on evaluating the influence of a diet supplemented with onion peel powder on the immunoexpression of leptin receptors (LepRs) in the hippocampus in obese rats and the potential anti-obesity role of the onion in the brain. Methods: To induce obesity, the animals were given a high-energy chow containing lard and sucrose. Onion skin powder was used to modify the standard and high-energy diets (10.5 g per rat/week) of Wistar rats in a 14-week experiment followed by a brain IHC study. Results: The effect of the onion diet on the expression of neuronal LepRs and astrocytes in the hippocampus was analyzed. Obese animals receiving onion in the diet showed significant growth in the average number of immunoreactive LepR (LepR-IR) neurons (p = 0.00108) and their average size (p = 0.00168) in the CA1 field of the hippocampus. Meanwhile, in obese rats not given onion peel powder, a significant increase in the average density of astrocytes was observed (p < 0.0001). Conclusions: The increased density of astrocytes in the hippocampus of obese animals can probably have a beneficial effect on brain changes in overweight individuals. The inclusion of onion in the diet of overweight/obese individuals may lead to increased hippocampal neuroplasticity, manifested by changes in the immunoexpression of LepRs. It can be speculated that the observed changes have a protective effect on the CNS structures during obesity, but this undoubtedly requires further research.
1. Introduction
Onion (Allium cepa L.) is a widely available plant that is a source of many natural phytochemicals and bioactive compounds that benefit human health. It contains flavonoids, phytosterols, and saponins, as well as sulfur amino acids and many vitamins and minerals [1]. Over the years, numerous studies have shown many health-promoting properties of onions, including antioxidant [2], anti-inflammatory [3], antimicrobial [4] and anticancer properties [5]. It has been shown that consuming onion extract can lower blood glucose levels, thereby helping to reduce the risk factors associated with diabetes [6] and [7], and onion may also lower blood cholesterol levels [8]. Flavonoids in onions, including the most active one, quercetin, have a neuroprotective effect, preventing brain aging by inhibiting apoptosis, which induces brain degeneration [9]. It has also been shown that onion can be effective in the prevention and treatment of obesity and have beneficial effects on related comorbidities [10].
In particular, the properties of dry onion skin, which can be used as a source of valuable nutrients, are of interest. Numerous studies have confirmed that it contains insoluble dietary fiber, minerals (especially calcium and potassium), and highly bio-accessible and in vitro bioavailable flavonoids with well-documented antioxidant and anti-inflammatory properties [11,12]. Our previous studies indicated that dry onion skin can be a good source of quercetin in pasta. Such an addition gives the pasta antioxidant and potentially anti-inflammatory properties, which are enhanced during the cooking process [13].
Under physiological conditions, adipose tissue adipocytes secrete adipokines, including leptin (Lep), which, through food centers located in the hypothalamus, inhibits the release of neuropeptide Y, thereby suppressing appetite while promoting energy expenditure by increasing thermogenesis, activating lipolysis, and inhibiting lipogenesis [14]. However, in obesity, blood leptin levels rise, suggesting that individuals with obesity exhibit leptin resistance manifested by a decrease in the number of receptors for leptin or a decline in their sensitivity to the hormone. It was observed that the administration of onion peel extract (at the dose of 0.2 g/100 g diet) in a model of obese rats associated with a high-energy diet reduced body fat (mainly mesenteric) by increasing adiponectin levels while decreasing leptin levels [15].
Leptin crosses the blood–brain barrier (BBB) and activates leptin receptors (LepRs) that are widely distributed throughout the central nervous system (CNS), including the hippocampus [16,17]. The hippocampus is a limbic system structure located in the temporal lobe. It controls the transfer of information from short-term to long-term memory, learning, and spatial orientation. The hippocampus is divided into a dorsal part, more involved in cognitive and spatial functions, and a ventral part responsible for emotions [18]. Leptin has the ability to modify the activity of potassium channels in the hippocampus, thereby regulating neuronal excitability. LepRs have been suggested to be involved in the enhancement of synaptic plasticity in the hippocampus and, consequently, in the improvement in hippocampus-dependent behaviors such as spatial learning and memory [19].
The long-term consumption of a high-fat diet can cause pathological changes in the cellular integrity of the BBB, contributing to leptin resistance in the CNS and, consequently, to structural changes in the brain and cognitive deficits [20]. One of the brain areas adversely affected by leptin resistance is the hippocampus [21]. Among other effects, obesity alters the structure of dendrites in this region, which may indicate that the hippocampus is highly susceptible to metabolic disorders [22]. Therefore, the present study aimed to investigate the effect of dietary supplementation with onion peel powder on hippocampal leptin receptor immunoreactivity and astrocyte density in obese rats fed a high-fat diet for three months.
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Onion
Onion was obtained from the Polanowska cultivar (Czesławice Experimental Farm, Czesławice, Poland (51°18′23″ N, 22°16′02″ E). Onion skin powder was prepared as described in our previous articles [13,23]. The onion was manually peeled to obtain dry skin, which was washed twice with deionized water and dried in a convection dryer (Zelmer, Warsaw, Poland) at 50 °C for 12 h. The dried material was powdered using a laboratory mill (Proficook, Opole, Poland) and sieved to pass through the appropriate 0.5 mm mesh screen.
2.2. Animals
This experiment was approved by the 2nd Local Ethical Committee for Animal Experiments at the University of Life Sciences in Lublin, Poland (Permit No. 53/2016, released on 28 September 2016). The experiment was carried out in compliance with the ARRIVE guidelines.
Male 8-week-old Wistar SPF rats with a body weight of approx. 200–250 g (n = 32) were housed in individual cages (the vivarium of the University of Life Sciences in Lublin) under a 12 h light/12 h dark cycle (the light was turned on at 06:00 am) at a room temperature of 21 ± 1 °C with a relative humidity of 55 ± 10%. The cages were ventilated every 4 min.
All animals were subjected to 7 days of acclimatization and then randomly divided into 4 groups (n = 8): the first was the control group (Control), which received a standard commercial rodent chow in the amount of 210 g per rat/week; the second was the control+onion group, which (Control+O) received a standard rodent chow (210 g per rat/week) with 5% onion peel powder (10.5 g per rat/week). The remaining two groups received a high-energy chow, in an amount of 210 g per rat/week, in order to induce obesity throughout the experiment: the third group was the obese group (Obese), which received a high-energy chow; the fourth group was the obese+onion group (Obese+O), which received a high-energy chow with 5% onion peel powder (10.5 g per rat/week). The compositions of both feeds are presented in Table 1.

Table 1.
The percentages of ingredients in the standard and high-energy chows.
The dose of onion peel powder was estimated based on data from the literature [9,24]. A full characterization of the onion skin powder used as a dietary supplement is shown in Table 2.

Table 2.
Chemical composition and antioxidant properties of onion skin powder [13,23].
At the beginning of the experiment (after 7 days of acclimatization), animals were weighed, and subsequent body weight measurements were taken every 7 days during the experiment. Food was also weighed in each cage to monitor and calculate the amount of chow consumed by each rat. Animals received water ad libitum throughout the experiment. The duration of the experiment was 14 weeks.
2.3. Immunohistochemistry and Antibodies
After euthanasia (decapitation), the brains were immediately stored in a 10% solution of buffered formalin (at pH = 7). After 12 h of storage at 4 °C, the brains were dehydrated in increasing concentrations of ethyl alcohol. As described previously [25], the brains were finally embedded in paraffin blocks and cut with a microtome into 5 µm thick sections (Microm HM 360, Microm, Walldorf, Germany). The regions of Bregma ranging from −2.5 mm to −3.8 mm of the rat brain were analyzed. The brain sections were placed on adhesive glass slides (Superfrost Plus, Thermo Scientific, Braunschweig, Germany) and used for further immunohistochemical staining using the peroxidase anti-peroxidase method (PAP) according to the following protocol: First, to remove paraffin, the sections were washed in xylene three times for 15 min each. Then, the slides were hydrated via sequential incubation with a graded series of ethyl alcohol, and in the end, they were washed in distilled water. In the following step, the slides were put in a container containing citrate buffer (at pH = 6) and heated three times for 7 min to 97 °C using a microwave (800 W) to retrieve antigens. Then, the selected brain sections were outlined with a hydrophobic marker (ImmEdgeTM Hydrophobic Barrier Pen, Vector Laboratories, Burlingame, CA, USA). In order to block the endogenous peroxidase activity, the sections were chilled and washed in 3% hydrogen peroxidase for the following 20 min.
The brain slides were then flushed twice with PBS solution at pH = 7.4 (each time for 15 min) and subjected to incubation in 2.5% normal goat serum (ImPRESSTM, MP-7451, Vector Labs, Burlingame, CA, USA) at room temperature (RT) for the next 20 min. Then, one part of the sections was incubated for 24 h at 4 °C with primary polyclonal rabbit antibodies raised against leptin receptor LepR (1:200, DF7139, Biorbyt, BIOKOM, Falenty, Poland), while the second part was incubated with primary rabbit anti-glial fibrillary acidic protein (GFAP) antibody (G9269, 1:80, Sigma Aldrich, St. Louis, MO, USA) overnight at 4 °C. After this procedure, the slides were washed two times for 15 min using a washing buffer and covered for 1 h with the anti-rabbit Ig (ImPRESSTM, MP-7451 Vector Labs, Burlingame, CA, USA). The 3.3′-diaminobenzidine chromogen was used to visualize primary antisera (ImmPACTTM DAB, SK-4105, Vector Labs, Burlingame, CA, USA). For the following 20 min, counterstaining with Mayer’s hematoxylin was performed. After this procedure, the brain slides were rinsed with distilled water, and the sections were again dehydrated in increasing concentrations of ethyl alcohol. Later, the samples were cleared using xylene, mounted in DPX (Sigma-Aldrich, St. Louis, MO, USA), and cover-slipped.
A “negative control” procedure was used to test the specificity of the antibodies. Sections not exposed to primary antibodies (omission or replacement with non-immunoreactive sera) were stained as a negative control. In the negative control procedure, no positive immunoreactions could be detected.
2.4. The Hippocampus Structure and Topography
The hippocampus, also known as Ammon’s horn (CA), is a small brain structure located in the posterior part of the temporal lobe, which forms part of the limbic system. The hippocampus is divided into three segments called fields (CA1–CA3) and the dentate gyrus (DG). The present study focuses on the CA1 field, recognized as being well developed, with a high neuronal density, and it is the most sensitive to disease factors among the hippocampal field [26,27]. Functionally, the hippocampus consists of a dorsal section, which primarily performs cognitive and spatial functions, and a ventral section, which is involved in emotional processes and stress [28]. The focus of this study was conducting an examination of the dorsal hippocampus using a light microscope (Axiolab, Zeiss, Jena, Germany).
2.5. Determination of Leptin Receptor Immunoreactive (LepR-IR) Neuron Number and Size in CA1 Field of Hippocampus
The slides were viewed under a light microscope (Axiolab, Zeiss, Jena, Germany). Images were acquired using a digital camera (C11440-36U, Hamamatsu Photonics, Shizuoka, Japan) connected to a standard PC with CellˆM 2.3 image analysis software ver. 13.1 (Olympus cellSens Standard) under a 20× objective. The resolution was 1024 × 1024 pixels. During the study, approximately 25–30 immunostained sections for LepR neurons were taken from each animal in each group. Explanation: In this study, the term “neuron” refers to the body of the neuron, the perikaryon. Therefore, the average number of perikaryons and their sizes were determined.
The average number of LepR-IRs neurons in the present study was determined by analysis and counting of no less than one hundred neurons with and without an immunohistochemical reaction in the CA1 field of the hippocampus in each of the groups. Moreover, measurements of the LepR-IR neurons in the hippocampal CA1 field were performed in 3 cross-sections, vertical, horizontal, and diagonal, to precisely calculate the average size of the LepR neurons. CellˆM 2.3 software (Olympus cellSens standard) was used for a morphometric analysis of LepR-IR neurons, their number, and sizes. To increase the accuracy of the performed experiments, at least two independent observers participated in the quantification analyses and averaged the results.
2.6. The Determination of the Density of GFAP-Immunoreactive (GFAP-IR) Astrocytes in the CA1 Field of the Hippocampus
Astrocyte density in the CA1 hippocampal field was assessed using systematic random sampling as outlined by West [29]. This unbiased method counts cells within a defined tissue volume and accounts for tissue shrinkage (shrinkage factor of 0.75 for 4% formalin at pH 7.4) [30]. An Olympus BX53 microscope was used with a numerical aperture of NA = 1.4, a 60× oil immersion objective, a Marzhauser automated stage, and Cell M 2.3 image analysis software (version 13.1, Olympus cell sens standard, Olympus Corporation, Tokyo, Japan). Structure boundaries were mapped at a low magnification (2.5×), after which a counting frame was automatically set, ensuring at least two cells could fit within its dimensions. Cell profiles were classified by glial cell type based on morphology, and astrocyte density was calculated per unit area. Section thickness was measured at three random sites to maintain consistency, and all areas had an equal probability of inclusion in the analysis [29].
2.7. Statistical Analysis
Statistica software ver. 13.1 (StatSoft, Kraków, Poland) was used for the analysis. Normality was assessed using the Kolmogorov–Smirnov test, and Levene’s homogeneity of variance test was applied to examine the equality of variances. One-way ANOVA was used to compare the effects of onion supplementation on the body weights of animals in particular weeks of observations as well as on the LepR-IR neuronal number, mean neuron size, and mean astrocyte density. Tukey’s post hoc analysis was performed at a significance level of p ≤ 0.01 and p ≤ 0.001 to estimate the differences between the experimental groups. The data on the figures are expressed as the means ± SEM (standard error of the mean; box) and standard deviation (whiskers).
3. Results
3.1. Body Weight
The animals were weighed weekly, and the average body weight gains (g) are shown in Figure 1. In the sixth week of the experiment, a significant increase in the average body weight of rats receiving high-energy food was observed compared to the control groups. The results of the statistical analysis indicated that there were no statistically significant distinctions between the obese rats’ groups (Obese vs. Obese+O). However, starting from the 12th week of the experiment, obese animals receiving high-energy food with onion peel powder began to show a gradually lower mean body weight gain (g) compared to the obese animals (Obese group) that did not receive onion supplementation. Taking into account the animals from the control groups receiving standard rodent food, their average body weight from the fourth week of the experiment was significantly lower compared to that of the obese rats (Figure 1).
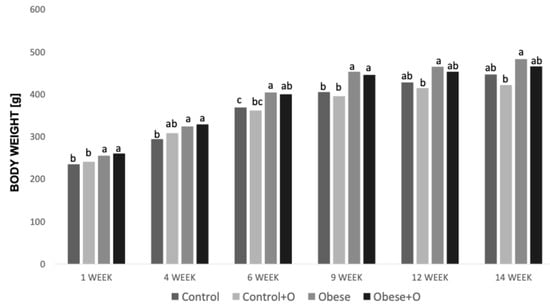
Figure 1.
Changes in body weight (g) of rats in experimental groups: Control—rats receiving standard feed; Control+O—rats receiving 5% onion peel powder; Obese—rats receiving high-energy chow; Obese+O—rats receiving high-energy chow with 5% onion peel powder in 1, 4, 6, 9, 12, and 14 weeks of trial. Data were analyzed using one-way analysis of variance followed by Tukey’s analysis test. Statistically significant differences between experimental groups in each presented week are indicated by letters a–c at p < 0.01; n = 8.
3.2. Immunohistochemistry
The observation of multiform (round, oval, fusiform, and triangular) LepR-IR neurons in all study groups revealed an uneven distribution in the marginal, pyramidal, and multiform layers of the CA1 field of the rat hippocampus. The neurons were distinguished by cytoplasmic and nuclear reactions, although the cytoplasm exhibited more intense staining (Figure 2).
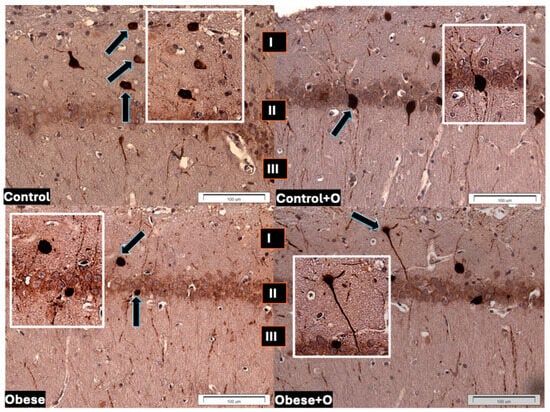
Figure 2.
LepR neuronal immunoreactivity in hippocampal CA1 field of experimental rats’ brains in respective groups: Control—rats receiving standard feed; Control+O—rats receiving 5% onion peel powder; Obese—rats receiving high-energy chow; Obese+O—rats receiving high-energy chow with 5% onion peel powder. Layers of CA1 field: I. marginal; II. pyramidal; III. multiform. Arrows indicate LepR-IR neurons; boxes illustrate magnified appearance of LepR neurons. Scale bar: 100 μm.
Furthermore, all examined groups showed GFAP-IR astrocytes located in the hippocampal CA1 field. The cytoplasm of astrocyte bodies and processes localized GFAP. Numerous branched processes were characteristic of the astrocyte. Primary processes branched from the glial cell bodies. Many astrocytes had short secondary processes branching from the primary processes (Figure 3).
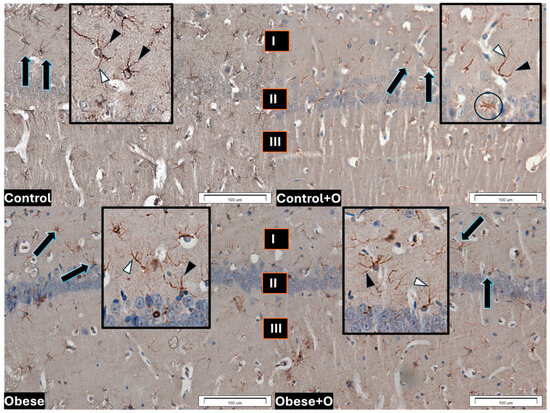
Figure 3.
GFAP astrocyte immunoreactivity in the hippocampal CA1 field of the experimental rats’ brains in the respective groups: Control—rats receiving standard feed; Control+O— rats receiving 5% onion peel powder; Obese—rats receiving high-energy chow; Obese+O—rats receiving high-energy chow with 5% onion peel powder. The layers of the CA1 field: I. marginal; II. pyramidal; and III. multiform. The number of immunopositive astrocytes in the Obese group with short and long astrocytic processes is elevated. The arrows indicate GFAP-IR astrocytes; the boxes illustrate the magnified appearance of GFAP astrocytes. The black arrowheads show short secondary processes branching from the primary processes, while the white arrowheads indicate primary processes branching from the astrocyte body. The image primarily shows fibrous astrocytes, while the black circle highlights a protoplasmic astrocyte, which is in the clear minority. The scale bar is 100 μm.
3.3. Leptin Receptor Immunoreactive (LepR-IR) Neurons
3.3.1. The Mean Number of LepR-IR Neurons
Statistically significant decreases in the mean LepR-IR neuronal counts were observed in the hippocampal CA1 in the obese rats (obesity group) compared to those in the Obese+O group and the control groups receiving standard food (p = 0.00108) (Figure 4). In the group of obese rats additionally receiving onion peel powder, a significant growth in the average number of LepR-IR neurons was noted compared to those in the Obese group, but there were no statistically significant differences between the Obese+O group and the control group. Feeding non-obese rats (Control+O group) with onion had no significant effect on the immunodetection of LepRs in the neurons of the CA1 field of the rat hippocampus (Figure 4).
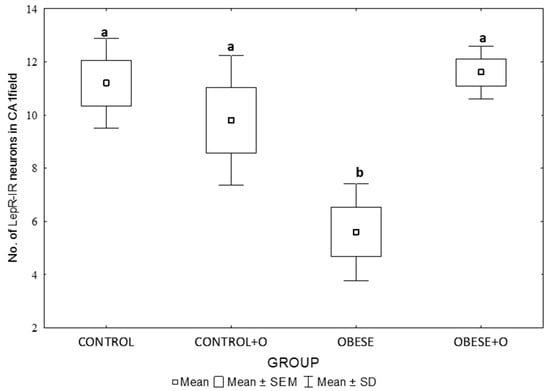
Figure 4.
The differences in the average number of LepR-IR neurons in the CA1 field of the rats’ hippocampus between the experimental groups: Control—rats receiving standard feed; Control+O—rats receiving 5% onion peel powder; Obese—rats receiving high-energy chow; Obese+O—rats receiving high-energy chow with 5% onion peel powder. The data were analyzed using a one-way analysis of variance followed by Tukey’s analysis test. The data are expressed as the means ± SEM (standard error of the mean; box) and standard deviation (whiskers). The statistically significant differences are marked by the letters a and b at p = 0.00108; n = 8.
3.3.2. The Mean Size of LepR-IR Neurons
Looking at the CA1 area of the hippocampus, onion supplementation caused a significant increase in the mean size of LepR-IR neurons in the animals in the obese group (Obese+O) compared to those in the obese group that were not fed onion skin powder (p = 0.00168). There were no significant differences in the mean neuron size between the control groups (Control vs. Control+O) or between the two control groups and the Obese+O group. On the other hand, the LepR-IR neurons were statistically significantly smaller in the obese rats (Obese group) than in the controls (Control group) (p = 0.00168) (Figure 5).
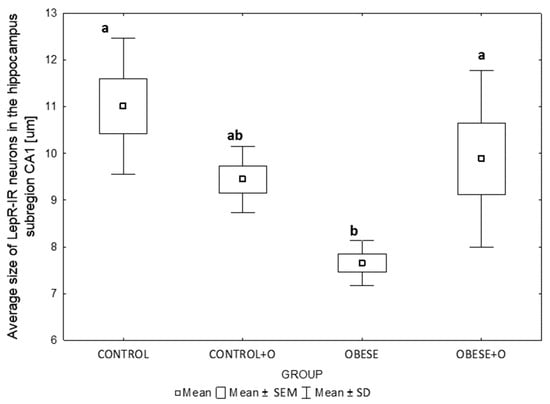
Figure 5.
The differences in the average size of LepR-IR neurons in the hippocampus subregion CA1 of rats in the following experimental groups: Control—rats receiving standard feed; Control+O—rats receiving 5% onion peel powder; Obese—rats receiving high-energy chow; Obese+O—rats receiving high-energy chow with 5% onion peel powder. The data were analyzed using a one-way analysis of variance followed by Tukey’s analysis test. The data are expressed as the means ± SEM (standard error of the mean; box) and standard deviation (whiskers). The statistically significant differences between the experimental groups are marked by the letters a and b at p = 0.00168; n = 8.
3.4. The GFAP-Immunoreactive (GFAP-IR) Astrocytes
A morphometric analysis allowed us to determine the number of GFAP astrocytes in the examined field of the rat hippocampus. The graph (Figure 6) presents data on the averages of 10 measurements of the GFAP astrocyte density from the CA1 field of the hippocampus. The result is given as the number of GFAP-IR astrocytes per mm3.
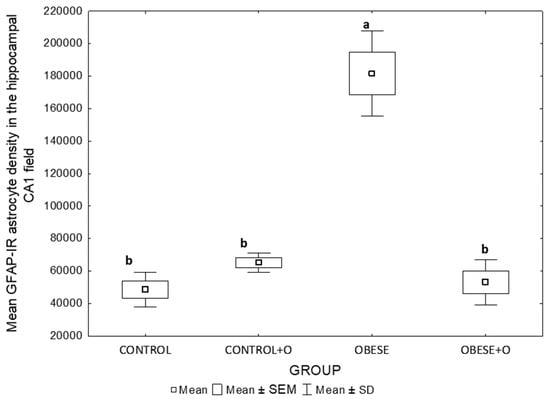
Figure 6.
The mean GFAP-IR astrocyte density in the hippocampal CA1 field of the rat groups studied (Control, Control+O, Obesity, and Obesity+O groups). The data show the mean density of GFAP-immunostained cells in an area of 2.5 × 10−3 mm2 of the CA1 field. The data were analyzed using a one-way analysis of variance followed by Tukey’s analysis test. The data are expressed as the means ± SEM (standard error of the mean; box) and standard deviation (whiskers). The statistically significant differences (p < 0.0001) between the experimental groups are marked by the letters a and b and n = 8.
A statistical analysis of the examined area of the rat hippocampus did not show significant differences between the control groups (Control and Control+O) and the group of obese animals supplemented with onion peel powder (Obese+O), assuming a significance of p < 0.0001 (Figure 6). The only group of animals for which statistically significant differences were found was the Obese group (significance at the level of p < 0.0001) (Figure 6).
4. Discussion
Obesity is a chronic condition resulting from an imbalance between consumed and expended calories. Overweight/obesity is also linked to functional and structural changes in the brain. The “obese” brain shrinks. Numerous original scientific papers indicate that a high-energy diet over a long period reduces synaptogenesis or brain volume [31,32,33] while simultaneously increasing neuronal apoptosis [34,35]. Furthermore, it is an essential risk factor for the development of neurodegenerative disorders. According to Flores-Dorantes et al. [36], Alzheimer’s disease or Parkinson’s disease are most likely initiated by various metabolic changes associated with obesity-induced CNS damage [37]. Obesity has been shown to cause significant changes in areas of the brain with so-called “high metabolic demand,” such as the hippocampus [17,38]. Mitochondria are responsible for maintaining a constant supply of energy to nerve cells. They are impaired in obesity, leading to neuronal damage, dysfunction, and, ultimately, neurotoxicity [39]. Reduced hippocampal neurogenesis has been observed in leptin-resistant rodents, along with changes in synaptic architecture and dendritic structure [40,41]. Due to obesity, the number of LepRs decreases, or their sensitivity to this hormone diminishes [19]. Likewise, the current study’s findings showed a decline in the number of LepR-IR neurons in the CA1 field of the rat hippocampus in the group that received high-energy food compared to the control group. Moreover, we observed that LepR-IR neurons in the obese brain are significantly smaller than those in the control group. The size of LepR-IR neurons, which express leptin receptors (LepR), may influence their sensitivity to leptin through biophysical and molecular factors. Larger neurons, with an increased surface area and potentially a higher density of receptors, can enhance leptin signaling if the distribution of receptors scales proportionally. However, a larger neuronal size may also hinder signal propagation and increase energy demands. In the context of obesity, the size of LepR-IR neurons alone is unlikely to mitigate obesity unless accompanied by functional enhancements in leptin signaling [14,42,43]. Equally important is the fact that morphological changes in the rodent hippocampus do not only concern neurons but also astrocytes, which help brain homeostasis by controlling the ion concentration and increasing neuronal survival due to the high activity of enzymes neutralizing free radicals [44]. Based on the findings of the latest research, it can be argued that a high-energy diet increases astrocyte density and hippocampal gliosis [45]. The present study revealed a significant increase in the average GFAP-IR astrocyte density in the CA1 hippocampal field of obese rats compared to the other study groups. Similarly, Hsuchou et al. [46] also found astrocyte density growth in obese adult mice. Tsai et al. [47] also showed that the level of GFAP-IR astrocytes increases in the mice’s hippocampus (including the CA1 field) following the administration of a high-fat diet for 3 months. However, there is a discrepancy in the data regarding astrogliosis in brain regions associated with cognition and memory. Raider et al. [48] did not observe an increase in GFAP-IR astrocyte density in the rat hippocampus in response to a high-fat diet. The increase in the number of astrocytes in the hippocampus in obesity is linked to similar mechanisms of inflammation and cellular stress seen in other brain regions, such as the hypothalamus, but with unique implications for cognitive functions like learning, memory, and mood regulation. The increase in astrocytes in the hippocampus in obesity is a response to metabolic, inflammatory, and oxidative stress. While initially protective, this response becomes maladaptive when inflammation is persistent. As a result, the overactivity and proliferation of astrocytes can impair hippocampal function, potentially contributing to the cognitive and emotional challenges often seen in individuals with obesity. Understanding these mechanisms highlights the potential for therapeutic strategies targeting inflammation and astrocyte reactivity to protect hippocampal function and improve cognitive outcomes in individuals with obesity [49,50,51].
Obesity is a social, health, and therapeutic problem. The World Health Organization (WHO) classified obesity as an epidemic of our time, with over 50% of adults struggling with overweight and/or obesity. Flavonoids, present in onions, among other substances, are increasingly used in the prevention and treatment of obesity. One of the most active is quercetin, which controls the adipose tissue mass by inducing adipocyte apoptosis or inhibiting their formation [52]. The reduction in body weight observed after taking onion peel powder may be related to its bioactive compounds (quercetin), which affect metabolic and hormonal pathways. Quercetin can activate AMP-activated protein kinase (AMPK), promoting fatty acid oxidation and glucose uptake while inhibiting fat storage, which additionally helps in weight reduction [53]. Furthermore, onion peel might influence gut microbiota, which can improve metabolism and leptin signaling [54]. Quercetin has also been demonstrated to exert neuroprotective effects due to its anti-inflammatory properties, and furthermore, it improves cognitive functions [55,56]. In addition, quercetin reduces the production of pro-inflammatory cytokines, suppresses pro-inflammatory pathways such as NF-κB, and enhances anti-inflammatory mediators like IL-10, potentially restoring the balance of adipose tissue. This may indicate significant benefits in limiting cellular changes associated with inflammation [10,57]. However, there is a lack of information on how bioactive compounds affect the structure and functioning of the brain after exposure to a high-energy diet. It is known that obesity is associated with an increase in the presence of inflammatory cytokines in the hippocampus, which in turn impairs its neuroplasticity, resulting in damaged hippocampus-dependent memory [58,59]. The presented study revealed that bioactive components in onion peel powder resulted in a significant increase in the mean number of LepR-IR neurons in obese animals. Conversely, no significant changes were noted in the average number of LepR-IR neurons in the groups of “non-obese” rats. Furthermore, our findings reveal that the mean size of LepR-IR neurons was markedly larger in the group of obese rats that were administered onion peel powder with food in comparison to the obese group. It can be reasonably inferred that the bioactive compounds in onion peel powder probably exert an anti-inflammatory effect by reducing the cellular changes that manifest in the hippocampus as a consequence of obesity.
The present study is limited because it does not include additional analyses, which some may consider a key element in the scientific process. The study aimed to determine the immunoexpression of leptin receptors in the rat hippocampus using the IHC method based on data from the existing global literature, indicating that the leptin receptor is widely distributed in the hippocampus, particularly in rodents [14,19]. Additionally, antibody specificity was assessed using a negative control in which the primary antibodies were replaced with the antibody diluent, and the specificity of the LepR antibody has also been characterized previously [46]. This allows us to acknowledge this limitation and consider the potential for further research in this area. Secondly, the authors of this project focused on the CNS; therefore, this project does not consider changes in adipose tissue following supplementation with high-energy food alongside the simultaneous application of onion peel powder. Nevertheless, we believe these limitations do not completely undermine the novelty and significance of our study.
5. Conclusions
In the present study, the immunohistochemical method (IHC) was employed to determine the immunoexpression of leptin receptors and astrocyte density in the hippocampus of obese rats fed a diet containing onion peel powder. The powder was created by drying onion peels in a convection dryer at 50 °C for 12 h. The prepared material was ground into a powder and incorporated into the feed at a concentration of 5% for three months. Based on the results obtained, it can be concluded that onion peel supplementation significantly influenced the number of LepR neurons in obese animals, whereas it had no significant effect on the non-obese groups. The findings suggest that changes in the brain may be accelerated by chronic metabolic disorders, such as overweight and obesity—specifically, a significant decrease in the number of LepR neurons in the hippocampus. Additionally, the bioactive compounds present in onion peel may aid in further prevention and therapy for obesity. The beneficial effects of onion peel can mitigate obesity due to the bioactive compounds it contains, known for their anti-inflammatory, antioxidant, and metabolism-regulating properties. However, most of the evidence stems from in vitro and animal studies. Consequently, further research, particularly clinical studies, is essential to enhance the understanding of the impact of bioactive compounds found in plants on the proper functioning of the central nervous system, confirm their efficacy, comprehend their bioavailability, and establish the appropriate dosage in humans.
Author Contributions
Conceptualization, M.K.; methodology, M.K., R.S. and M.M.-M.; software, R.S. and W.R; validation, R.S., M.M.-M. and A.W.; formal analysis, R.S., A.W. and W.R.; investigation, M.K. and R.S.; resources, M.M.-M., W.G., M.B.A. and A.W.; data curation, M.K. and R.S.; writing—original draft preparation, M.K. and M.M.-M.; writing—review and editing, M.K. and M.M.-M.; visualization, M.K.; supervision, W.G., A.W. and M.B.A.; project administration, M.K.; funding acquisition, M.M.-M. and W.G. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This research received no external funding.
Institutional Review Board Statement
This experiment was approved by the 2nd Local Ethical Committee for Animal Experiments at the University of Life Sciences in Lublin, Poland (Permit No. 53/2016, released on 28 September 2016). The experiment was carried out in compliance with the ARRIVE guidelines.
Informed Consent Statement
Not applicable.
Data Availability Statement
The data that support the findings of this study are available from the corresponding author upon reasonable request.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
References
- Marrelli, M.; Amodeo, V.; Statti, G.; Conforti, F. Biological Properties and Bioactive Components of Allium cepa L.: Focus on Potential Benefits in the Treatment of Obesity and Related Comorbidities. Molecules 2018, 24, 119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ouyang, H.; Hou, K.; Peng, W.; Liu, Z.; Deng, H. Antioxidant and Xanthine Oxidase Inhibitory Activities of Total Polyphenols from Onion. Saudi J. Biol. Sci. 2018, 25, 1509–1513. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jakaria, M.; Azam, S.; Cho, D.-Y.; Haque, M.E.; Kim, I.-S.; Choi, D.-K. The Methanol Extract of Allium cepa L. Protects Inflammatory Markers in LPS-Induced BV-2 Microglial Cells and Upregulates the Antiapoptotic Gene and Antioxidant Enzymes in N27-A Cells. Antioxidants 2019, 8, 348. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Loredana, L.; Giuseppina, A.; Filomena, N.; Florinda, F.; Marisa, D.M.; Donatella, A. Biochemical, Antioxidant Properties and Antimicrobial Activity of Different Onion Varieties in the Mediterranean Area. J. Food Meas. Charact. 2019, 13, 1232–1241. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tsuboki, J.; Fujiwara, Y.; Horlad, H.; Shiraishi, D.; Nohara, T.; Tayama, S.; Motohara, T.; Saito, Y.; Ikeda, T.; Takaishi, K.; et al. Onionin A Inhibits Ovarian Cancer Progression by Suppressing Cancer Cell Proliferation and the Protumour Function of Macrophages. Sci. Rep. 2016, 6, 29588. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Akash, M.S.H.; Rehman, K.; Chen, S. Spice Plant Allium cepa: Dietary Supplement for Treatment of Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus. Nutrition 2014, 30, 1128–1137. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jini, D.; Sharmila, S. Green Synthesis of Silver Nanoparticles from Allium cepa and Its in Vitro Antidiabetic Activity. Mater. Today Proc. 2020, 22, 432–438. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Helen, A.; Krishnakumar, K.; Vijayammal, P.L.; Augusti, K.T. Antioxidant Effect of Onion Oil (Allium cepa Linn) on the Damages Induced by Nicotine in Rats as Compared to Alpha-Tocopherol. Toxicol. Lett. 2000, 116, 61–68. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hegazy, E.; Sabry, A.; Khalil, W.K.B. Neuroprotective Effects of Onion and Garlic Root Extractsagainst Alzheimer’s Disease in Rats: Antimicrobial, Histopathological, and Molecular Studies. BioTechnologia 2022, 103, 153–167. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lee, J.-S.; Cha, Y.-J.; Lee, K.-H.; Yim, J.-E. Onion Peel Extract Reduces the Percentage of Body Fat in Overweight and Obese Subjects: A 12-Week, Randomized, Double-Blind, Placebo-Controlled Study. Nutr. Res. Pract. 2016, 10, 175. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gawlik-Dziki, U.; Kaszuba, K.; Piwowarczyk, K.; Świeca, M.; Dziki, D.; Czyż, J. Onion Skin—Raw Material for the Production of Supplement That Enhances the Health-Beneficial Properties of Wheat Bread. Food Res. Int. 2015, 73, 97–106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Benítez, V.; Mollá, E.; Martín-Cabrejas, M.A.; Aguilera, Y.; López-Andréu, F.J.; Cools, K.; Terry, L.A.; Esteban, R.M. Characterization of Industrial Onion Wastes (Allium cepa L.): Dietary Fibre and Bioactive Compounds. Plant Foods Hum. Nutr. 2011, 66, 48–57. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Michalak-Majewska, M.; Złotek, U.; Szymanowska, U.; Szwajgier, D.; Stanikowski, P.; Matysek, M.; Sobota, A. Antioxidant and Potentially Anti-Inflammatory Properties in Pasta Fortified with Onion Skin. Appl. Sci. 2020, 10, 8164. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Obradovic, M.; Sudar-Milovanovic, E.; Soskic, S.; Essack, M.; Arya, S.; Stewart, A.J.; Gojobori, T.; Isenovic, E.R. Leptin and Obesity: Role and Clinical Implication. Front. Endocrinol. 2021, 12, 585887. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, O.Y.; Lee, S.; Do, H.; Moon, J.; Lee, K.; Cha, Y.; Shin, M. Influence of Quercetin-rich Onion Peel Extracts on Adipokine Expression in the Visceral Adipose Tissue of Rats. Phytother. Res. 2012, 26, 432–437. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Banks, W.A. Peptides and the Blood–Brain Barrier. Peptides 2015, 72, 16–19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, D.W.; Glendining, K.A.; Grattan, D.R.; Jasoni, C.L. Maternal Obesity in the Mouse Compromises the Blood-Brain Barrier in the Arcuate Nucleus of Offspring. Endocrinology 2016, 157, 2229–2242. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fanselow, M.S.; Dong, H.-W. Are the Dorsal and Ventral Hippocampus Functionally Distinct Structures? Neuron 2010, 65, 7–19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Van Doorn, C.; Macht, V.A.; Grillo, C.A.; Reagan, L.P. Leptin Resistance and Hippocampal Behavioral Deficits. Physiol. Behav. 2017, 176, 207–213. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Izquierdo, A.G.; Crujeiras, A.B.; Casanueva, F.F.; Carreira, M.C. Leptin, Obesity, and Leptin Resistance: Where Are We 25 Years Later? Nutrients 2019, 11, 2704. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Boitard, C.; Etchamendy, N.; Sauvant, J.; Aubert, A.; Tronel, S.; Marighetto, A.; Layé, S.; Ferreira, G. Juvenile, but Not Adult Exposure to High-fat Diet Impairs Relational Memory and Hippocampal Neurogenesis in Mice. Hippocampus 2012, 22, 2095–2100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- De Paula, G.C.; Brunetta, H.S.; Engel, D.F.; Gaspar, J.M.; Velloso, L.A.; Engblom, D.; De Oliveira, J.; De Bem, A.F. Hippocampal Function Is Impaired by a Short-Term High-Fat Diet in Mice: Increased Blood–Brain Barrier Permeability and Neuroinflammation as Triggering Events. Front. Neurosci. 2021, 15, 734158. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Michalak-Majewska, M.; Teterycz, D.; Muszyński, S.; Radzki, W.; Sykut-Domańska, E. Influence of Onion Skin Powder on Nutritional and Quality Attributes of Wheat Pasta. PLoS ONE 2020, 15, e0227942. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sung, Y.-Y.; Kim, S.-H.; Kim, D.-S.; Park, S.H.; Yoo, B.W.; Kim, H.K. Nutritional Composition and Anti-Obesity Effects of Cereal Bar Containing Allium Fistulosum (Welsh Onion) Extract. J. Funct. Foods 2014, 6, 428–437. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Matysek, M.; Kowalczuk-Vasilev, E.; Szalak, R.; Baranowska-Wójcik, E.; Arciszewski, M.B.; Szwajgier, D. Can Bioactive Compounds in Beetroot/Carrot Juice Have a Neuroprotective Effect? Morphological Studies of Neurons Immunoreactive to Calretinin of the Rat Hippocampus after Exposure to Cadmium. Foods 2022, 11, 2794. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Derakhshan, F.; Toth, C. Insulin and the Brain. Curr. Diabetes Rev. 2013, 9, 102–116. [Google Scholar]
- Infante-Garcia, C.; Ramos-Rodriguez, J.J.; Galindo-Gonzalez, L.; Garcia-Alloza, M. Long-Term Central Pathology and Cognitive Impairment Are Exacerbated in a Mixed Model of Alzheimer’s Disease and Type 2 Diabetes. Psychoneuroendocrinology 2016, 65, 15–25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- The Hippocampus Book; Andersen, P., Morris, R., Amaral, D., Bliss, T., O’Keefe, J., Eds.; Oxford University Press: Oxford, UK, 2006; ISBN 978-0-19-510027-3. [Google Scholar]
- West, M.J. Stereological Methods for Estimating the Total Number of Neurons and Synapses: Issues of Precision and Bias. Trends Neurosci. 1999, 22, 51–61. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baak, J.P.; Noteboom, E.; Koevoets, J.J. The Influence of Fixatives and Other Variations in Tissue Processing on Nuclear Morphometric Features. Anal. Quant. Cytol. Histol. 1989, 11, 219–224. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Raji, C.A.; Ho, A.J.; Parikshak, N.N.; Becker, J.T.; Lopez, O.L.; Kuller, L.H.; Hua, X.; Leow, A.D.; Toga, A.W.; Thompson, P.M. Brain Structure and Obesity. Hum. Brain Mapp. 2010, 31, 353–364. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cherbuin, N.; Sargent-Cox, K.; Fraser, M.; Sachdev, P.; Anstey, K.J. Being Overweight Is Associated with Hippocampal Atrophy: The PATH Through Life Study. Int. J. Obes. 2015, 39, 1509–1514. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gómez-Apo, E.; Mondragón-Maya, A.; Ferrari-Díaz, M.; Silva-Pereyra, J. Structural Brain Changes Associated with Overweight and Obesity. J. Obes. 2021, 2021, 1–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Horvath, T.L.; Sarman, B.; García-Cáceres, C.; Enriori, P.J.; Sotonyi, P.; Shanabrough, M.; Borok, E.; Argente, J.; Chowen, J.A.; Perez-Tilve, D.; et al. Synaptic Input Organization of the Melanocortin System Predicts Diet-Induced Hypothalamic Reactive Gliosis and Obesity. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2010, 107, 14875–14880. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lizarbe, B.; Soares, A.F.; Larsson, S.; Duarte, J.M.N. Neurochemical Modifications in the Hippocampus, Cortex and Hypothalamus of Mice Exposed to Long-Term High-Fat Diet. Front. Neurosci. 2019, 12, 985. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Flores-Dorantes, M.T.; Díaz-López, Y.E.; Gutiérrez-Aguilar, R. Environment and Gene Association with Obesity and Their Impact on Neurodegenerative and Neurodevelopmental Diseases. Front. Neurosci. 2020, 14, 863. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bhat, Z.F.; Morton, J.D.; Mason, S.; Bekhit, A.E.-D.A.; Bhat, H.F. Obesity and Neurological Disorders: Dietary Perspective of a Global Menace. Crit. Rev. Food Sci. Nutr. 2019, 59, 1294–1310. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moraes, J.C.; Coope, A.; Morari, J.; Cintra, D.E.; Roman, E.A.; Pauli, J.R.; Romanatto, T.; Carvalheira, J.B.; Oliveira, A.L.R.; Saad, M.J.; et al. High-Fat Diet Induces Apoptosis of Hypothalamic Neurons. PLoS ONE 2009, 4, e5045. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schmitt, L.O.; Gaspar, J.M. Obesity-Induced Brain Neuroinflammatory and Mitochondrial Changes. Metabolites 2023, 13, 86. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grillo, C.A.; Piroli, G.G.; Junor, L.; Wilson, S.P.; Mott, D.D.; Wilson, M.A.; Reagan, L.P. Obesity/Hyperleptinemic Phenotype Impairs Structural and Functional Plasticity in the Rat Hippocampus. Physiol. Behav. 2011, 105, 138–144. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Arnold, S.E.; Lucki, I.; Brookshire, B.R.; Carlson, G.C.; Browne, C.A.; Kazi, H.; Bang, S.; Choi, B.-R.; Chen, Y.; McMullen, M.F.; et al. High Fat Diet Produces Brain Insulin Resistance, Synaptodendritic Abnormalities and Altered Behavior in Mice. Neurobiol. Dis. 2014, 67, 79–87. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lindqvist, A.; Mohapel, P.; Bouter, B.; Frielingsdorf, H.; Pizzo, D.; Brundin, P.; Erlanson-Albertsson, C. High-fat Diet Impairs Hippocampal Neurogenesis in Male Rats. Eur. J. Neurol. 2006, 13, 1385–1388. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Freeman, L.R.; Haley-Zitlin, V.; Stevens, C.; Granholm, A.-C. Diet-Induced Effects on Neuronal and Glial Elements in the Middle-Aged Rat Hippocampus. Nutr. Neurosci. 2011, 14, 32–44. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Verkhratsky, A.; Nedergaard, M. Physiology of Astroglia. Physiol. Rev. 2018, 98, 239–389. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hao, S.; Dey, A.; Yu, X.; Stranahan, A.M. Dietary Obesity Reversibly Induces Synaptic Stripping by Microglia and Impairs Hippocampal Plasticity. Brain Behav. Immun. 2016, 51, 230–239. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hsuchou, H.; Pan, W.; Barnes, M.J.; Kastin, A.J. Leptin Receptor mRNA in Rat Brain Astrocytes. Peptides 2009, 30, 2275–2280. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tsai, S.-F.; Wu, H.-T.; Chen, P.-C.; Chen, Y.-W.; Yu, M.; Wang, T.-F.; Wu, S.-Y.; Tzeng, S.-F.; Kuo, Y.-M. High-Fat Diet Suppresses the Astrocytic Process Arborization and Downregulates the Glial Glutamate Transporters in the Hippocampus of Mice. Brain Res. 2018, 1700, 66–77. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Raider, K.; Ma, D.; Harris, J.L.; Fuentes, I.; Rogers, R.S.; Wheatley, J.L.; Geiger, P.C.; Yeh, H.-W.; Choi, I.-Y.; Brooks, W.M.; et al. A High Fat Diet Alters Metabolic and Bioenergetic Function in the Brain: A Magnetic Resonance Spectroscopy Study. Neurochem. Int. 2016, 97, 172–180. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Yang, Y. Astrocytes: Targets in Obesity. Oncotarget 2015, 6, 12835–12836. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cardoso, C.V.; Martins, M.M.; Otton, R.; Bondan, E.F. Abstract # 2059 Hippocampal Astrogliosis in Obese Animals. Brain Behav. Immun. 2019, 76, e5–e6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Obara-Michlewska, M. The Contribution of Astrocytes to Obesity-Associated Metabolic Disturbances. J. Biomed. Res. 2022, 36, 299. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kobylińska, A.; Janas, K.M. Health—Promoting Effect of Quercetin in Human Diet. Postępy Hig. Med. Dośw. 2015, 69, 51–62. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, J.; Yoshitomi, H.; Liu, T.; Zhou, B.; Sun, W.; Qin, L.; Guo, X.; Huang, L.; Wu, L.; Gao, M. Isoquercitrin Activates the AMP–Activated Protein Kinase (AMPK) Signal Pathway in Rat H4IIE Cells. BMC Complement. Altern. Med. 2014, 14, 42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hejazi, N.; Ghalandari, H.; Nouri, M.; Askarpour, M. Onion Supplementation and Health Metabolic Parameters: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis of Randomized Controlled Trials. Clin. Nutr. ESPEN 2023, 58, 1–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, X.-W.; Chen, J.-Y.; Ouyang, D.; Lu, J.-H. Quercetin in Animal Models of Alzheimer’s Disease: A Systematic Review of Preclinical Studies. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2020, 21, 493. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumar, M.; Barbhai, M.D.; Hasan, M.; Punia, S.; Dhumal, S.; Radha; Rais, N.; Chandran, D.; Pandiselvam, R.; Kothakota, A.; et al. Onion (Allium Cepa L.) Peels: A Review on Bioactive Compounds and Biomedical Activities. Biomed. Pharmacother. 2022, 146, 112498. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wróbel-Biedrawa, D.; Grabowska, K.; Galanty, A.; Sobolewska, D.; Podolak, I. A Flavonoid on the Brain: Quercetin as a Potential Therapeutic Agent in Central Nervous System Disorders. Life 2022, 12, 591. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Erion, J.R.; Wosiski-Kuhn, M.; Dey, A.; Hao, S.; Davis, C.L.; Pollock, N.K.; Stranahan, A.M. Obesity Elicits Interleukin 1-Mediated Deficits in Hippocampal Synaptic Plasticity. J. Neurosci. 2014, 34, 2618–2631. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, D.-H.; Yamamoto, M.; Hernandez, C.M.; Khodadadi, H.; Baban, B.; Stranahan, A.M. Visceral Adipose NLRP3 Impairs Cognition in Obesity via IL-1R1 on CX3CR1+ Cells. J. Clin. Investig. 2020, 130, 1961–1976. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).