Cost–Benefit Analysis of WDM-PON Traffic Protection Schemes
Featured Application
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
3. Presumptive WDM-PON Architectures
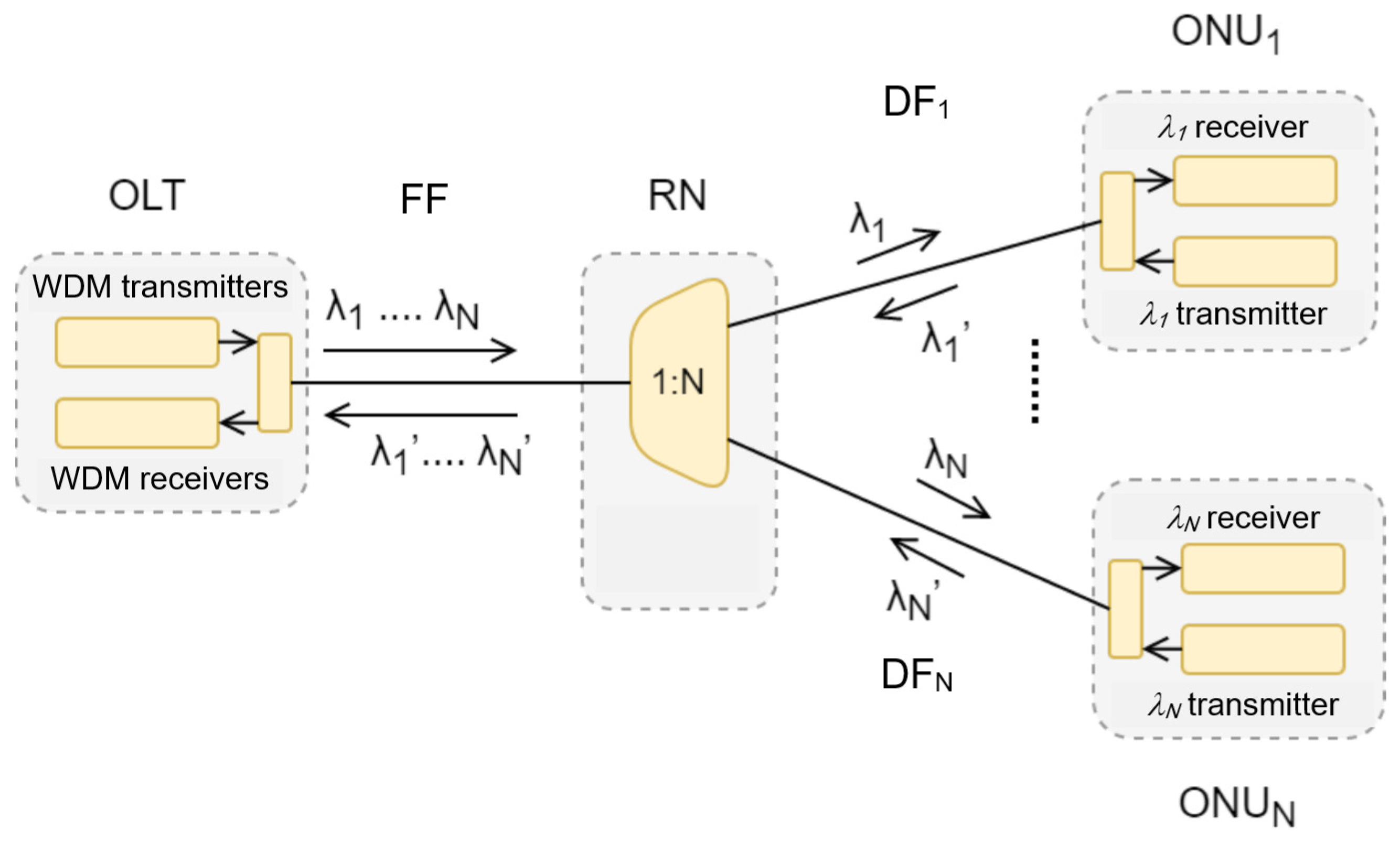
3.1. The P2MP Architecture of the WDM-PON Access Network
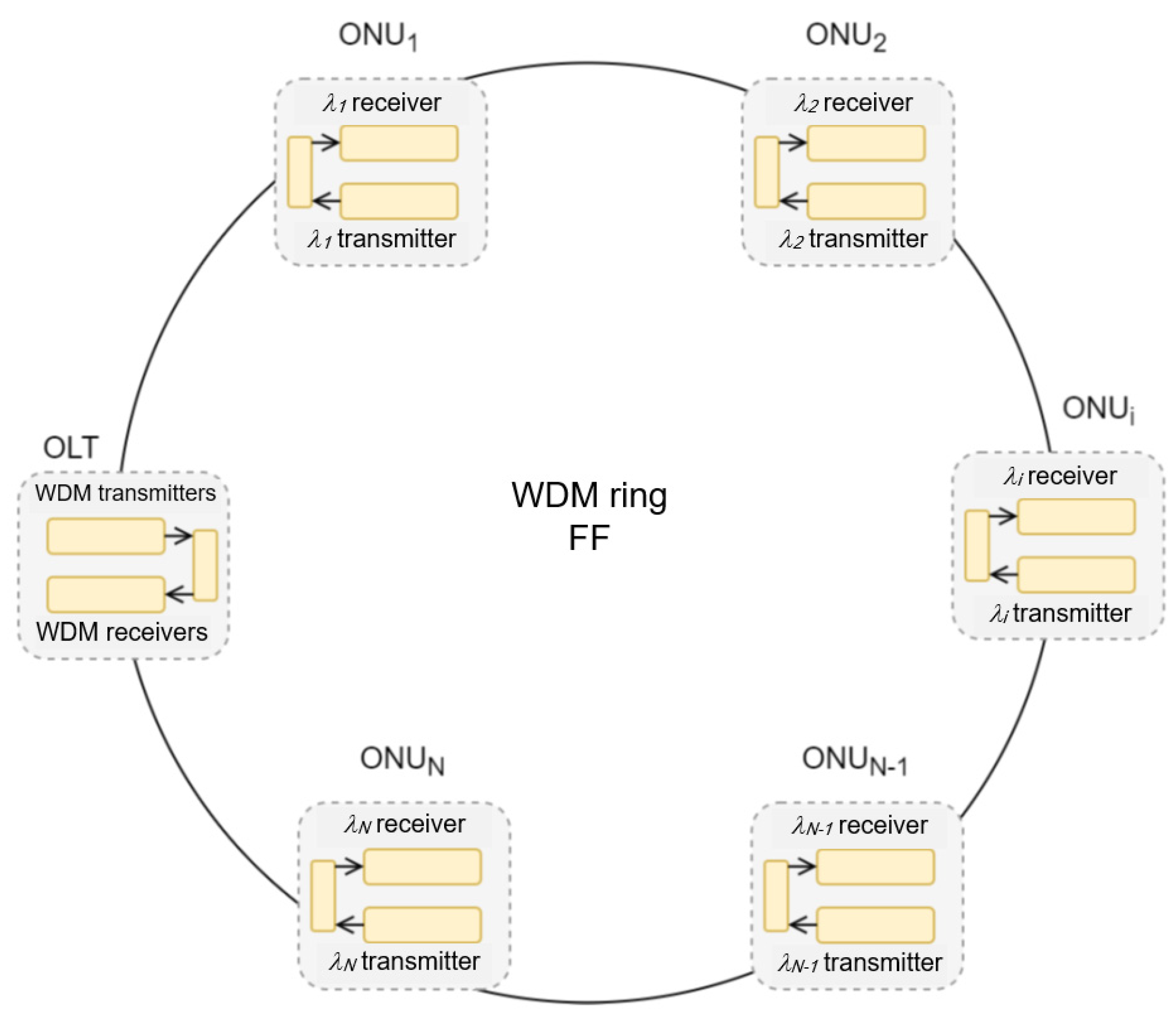
3.2. The Ring Architecture of the WDM-PON Access Network
3.3. The Combined Architecture of the WDM-PON Metropolitan-Access Network
3.4. Traffic Protection Schemes in WDM-PONs
3.5. Considered Presumptive Scenarios for Traffic Protection in P2MP WDM-PON Architectures
- Type B protected P2MP access network is characterized by the protection of the Feeder Fiber (FF). Since the FF is shared by all connected subscribers, its failure results in the interruption of service delivery that affects a large number of users. Due to its simplicity and low implementation costs, this protection is particularly attractive to operators with small- to medium-scale traffic loads [23].
- Dual-parented Type B protected P2MP access network extends previous protection by duplicating both the OLT equipment and the FF. In WDM-PONs compared to TDM-PONs, a significantly larger number of subscribers are connected to a single OLT through the FF. Consequently, failures of either the OLT or the FF affect overall network reliability and disrupt service provisioning for a large number of users. Therefore, their protection has a critical importance [23].
- Type C protected P2MP access networks represent a dedicated path protection mechanism achieved by duplicating all network components (FF, RN, DF, and ONU) except the OLT. Additional components (EDFA) may be included in this protection scheme for a network reach extension when it is applied in rural areas. Because this protection provides a high level of network availability, it also requires substantial capital expenditures [23].
3.6. Considered Presumptive Scenarios for Traffic Protection in Ring WDM-PON Architectures
- A protected ring access network is designed to provide traffic protection in case of fiber failure and to suppress Rayleigh backscattering noise. This scheme allows improvements in the network scalability and increases the available channel capacity per ONU. It employs two optical paths—a working path and a protection path. In the event of a fiber failure, optical modules are capable of protecting and restoring communication channels using appropriate optical switches to ensure immediate traffic protection [15].
- A protected ring metro-access network combines multiple network topologies and employs duplicated feeder fibers arranged in a ring infrastructure. Two synchronous optical switches are used to select either working or protecting optical fibers. This protection scheme does not extend to the distribution part of the passive optical network. It is capable of handling extremely high data traffic loads of up to 1 Tbit/s, supporting a large number of users, and covering wide geographical areas. Because any physical-layer failure causes significant losses of end-user data, an effective monitoring and traffic protection system must be implemented. This protection scheme provides high network availability and maintains lower costs compared to other protection schemes considered for ring topologies [25].
3.7. Reliability Representations for WDM-PON Traffic Protection Schemes
4. Cost–Benefit Analysis Considerations for WDM-PON Traffic Protection Schemes
4.1. Capital Expenditures Considerations
4.2. Operational Expenditures Considerations
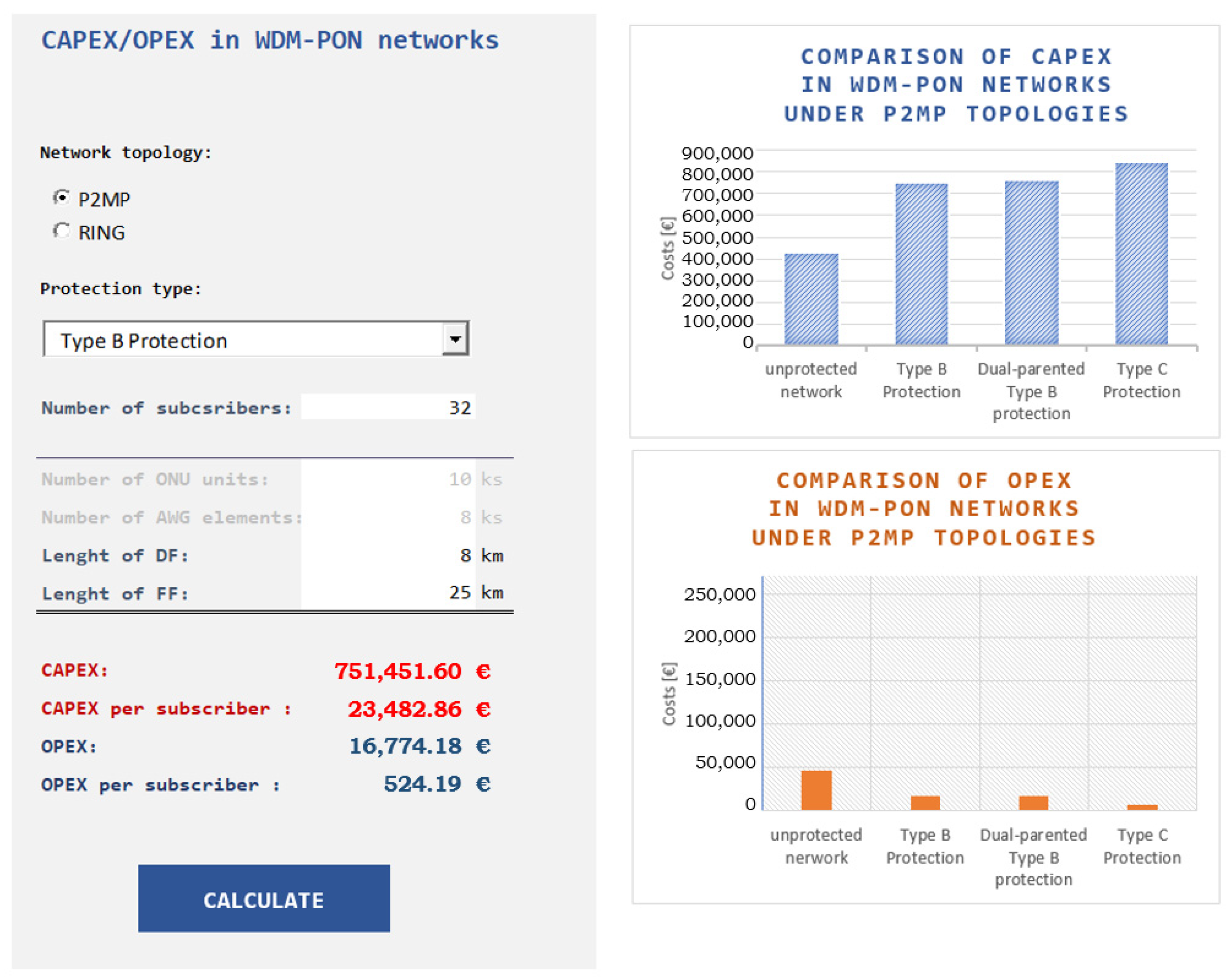
5. The WDM-PON Cost Evaluator
The Simulation Interface of the WDM-PON Network Cost Evaluator Tool
6. Evaluation of WDM-PON Traffic Protection Schemes
6.1. Cost–Benefit Comparison of Protection Scenarios in P2MP WDM-PON Architectures
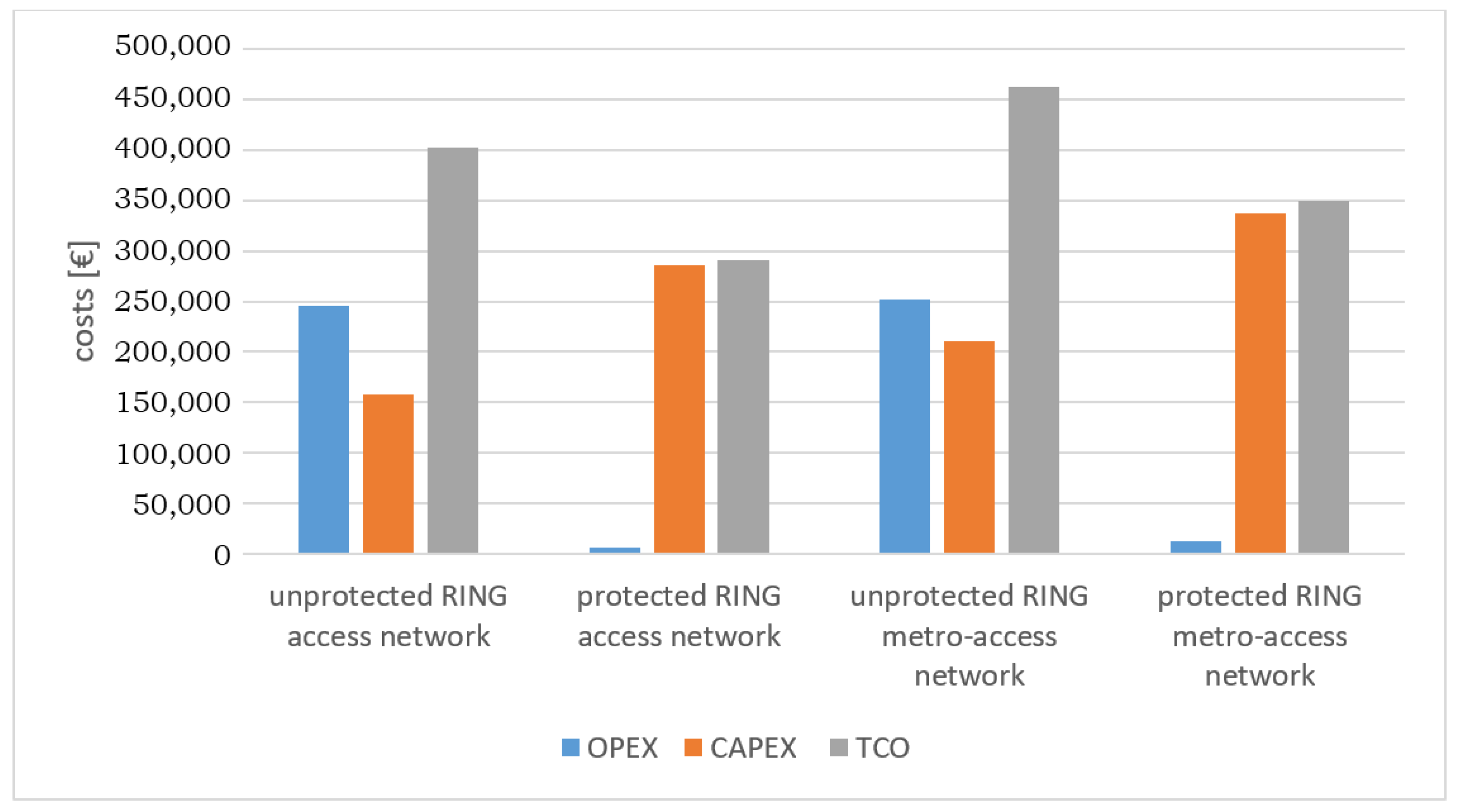
6.2. Cost–Benefit Comparison of Protection Scenarios in Ring WDM-PON Architectures
7. Discussion
8. Conclusions
Research Directions and Future Challenges
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| AI | Artificial Intelligence |
| AWG | Arrayed Waveguide Grating |
| BER | Bit Error Rate |
| CAPEX | Capital Expenditures |
| C-RAN | Cloud Radio Access Network |
| DF | Distribution Fiber |
| DDF | Drop Distribution Fiber |
| EDFA | Erbium-Doped Fiber Amplifier |
| F5G | Fifth Generation Fixed Network |
| FF | Feeder Fiber |
| FSO | Free Space Optics |
| FTTH | Fiber To The Home |
| GenAI | Generative Artificial Intelligence |
| HPON | Hybrid Passive Optical Network |
| ILP | Integer Linear Programming |
| ITU-T | International Telecommunication Union-Telecommunication Standardization Sector |
| LDPC | Low-Density Parity-Check |
| MILP | Mixed-Integer Linear Programming |
| ML | Machine Learning |
| NG-PON | Next-Generation Passive Optical Network |
| OPEX | Operational Expenditures |
| OLT | Optical Line Terminal |
| ONU | Optical Network Unit |
| ONT | Optical Network Terminal |
| OS | Optical Splitter |
| P2MP | Point-to-MultiPoint |
| PON | Passive Optical Network |
| PON-FSO | Passive Optical Network-Free Space Optics |
| RBD | Reliability Block Diagram |
| RN | Remote Node |
| SLA | Service Level Agreement |
| SMF | Single-Mode Fiber |
| TCO | Total Cost of Ownership |
| TDM | Time Division Multiplexing |
| TDM-PON | Time Division Multiplexing Passive Optical Network |
| TWDM-PON | Time- and Wavelength-Division Multiplexing Passive Optical Network |
| UDWDM-PON | Ultra Dense Wavelength Division Multiplexing Passive Optical Network |
| UP | Underlay Plane |
| VBA | Visual Basic for Applications |
| WDM | Wavelength Division Multiplexing |
| WDM-PON | Wavelength Division Multiplexing Passive Optical Network |
References
- Jaffer, S.S.; Hussain, A.; Qureshi, M.A.; Khan, Y.; Mirza, J.; Qureshi, K.K.; Ali, M.M. Reliable and Cost-Efficient Protection Scheme for 5G Fronthaul/Backhaul Network. Heliyon 2023, 9, e14215. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Guo, Y.; Gan, C.; Fang, Y.; Zhu, Y. Low-Cost WDM-PON Supporting Flexible Point-to-point Communication Between Any Two ONUs for Data Centers. Opt. Fiber Technol. 2023, 75, 103153. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fayad, A. Optimization of 5G and Beyond Networks for Cost-and Energy-Efficiency. Ph.D. Thesis, Budapest University of Technology and Economics (Hungary), Budapest, Hungary, 2024. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mohammed, A.; Alrabeiah, M.; Alouini, M.-S.; Al-Naffouri, T.Y. Traffic-Aware Cost Optimization for Hybrid Fiber/mmWave 5G Fronthaul. IEEE Access 2024, 12, 56123–56135. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, T.-H.; Liao, C.-Y.; Yeh, C.-H.; Chen, Y.-W.; Kao, Y.-H.; Lin, S.-Y.; Lin, Y.-H.; Liaw, S.-K. A Self-Healing WDM Access Network with Protected Fiber and FSO Link Paths Effective Against Fiber Breaks. Photonics 2025, 12, 323. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- AlQahtani, D.; El-Nahal, F. WDM-PON Free Space Optical (FSO) System Utilizing LDPC Decoding for Enhanced Cellular C-RAN Fronthaul Networks. Photonics 2025, 12, 391. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ullah, R.; Ullah, S.; Almadhor, A.; Alwageed, H.S.; Al-Atawi, A.A.; Ren, J.; Chen, S. A High-Capacity Optical Metro Access Network: Efficiently Recovering Fiber Failures with Robust Switching and Centralized Optical Line Terminal. Sensors 2024, 24, 1074. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ahmad, J.; Latif, S.; Khan, I.U.; Alshehri, M.S.; Khan, M.S.; Alasbali, N.; Jiang, W. An Interpretable Deep Learning Framework for Intrusion Detection in Industrial Internet of Things. Internet Things 2025, 33, 101681. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Klinkowski, M. Dedicated Path Protection with Flexible Switching Selection in Passive Optical 5G Xhaul Access Networks. Photonics 2024, 11, 908. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mazzei, C.; Crescitelli, M.; Fioramanti, D.; Quagliarini, A.; Reale, A.; Brunetti, F. Technical-Economic Analysis to Identify the Acceptable Maximum Attenuation on PON FTTH Lines for Wholesale Network Operators. Sci. Rep. 2023, 13, 12372. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fernandez, A.; Stol, N. CAPEX and OPEX Simulation Study of Cost-Efficient Protection Mechanisms in Passive Optical Networks. Opt. Switch. Netw. 2015, 17, 14–24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Akhtar, M.S.; Biswas, P.; Adhya, A. An ILP-based CapEx and OpEx efficient multi-stage TDM/TWDM PON design methodology. Opt. Fiber Technol. 2018, 46, 205–214. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Haddaji, N.; Bayati, A.; Nguyen, K.K.; Cheriet, M. BackHauling-as-a-Service (BHaaS) for 5G Optical Sliced Networks: An Optimized TCO Approach. J. Light. Technol. 2018, 36, 4006–4017. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Róka, R. Performance Analysis of Wavelength Division Multiplexing-Based Passive Optical Network Protection Schemes by Means of the Network Availability Evaluator. Appl. Sci. 2022, 12, 7911. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Róka, R. Performance Analysis of TDM-PON Protection Schemes by Means of the PON Network Availability Evaluator. In Proceedings of the Seventh International Congress on Information and Communication Technology ICICT, London, UK, 26 July 2022; pp. 21–24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, J.; Wosinska, L.; Mas, M.C.; Jaeger, M. Cost vs. Reliability Performance Study of Fiber Access Network Architectures. IEEE Commun. Mag. 2010, 48, 56–65. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- ITU-T. Recommendation G.694.1: Spectral Grids for WDM Applications: DWDM Frequency Grid; International Telecommunication Union: Geneva, Switzerland, 2012. [Google Scholar]
- Ramantas, K.; Vlachos, K.; Ellinas, G.; Hadjiantonis, A. Efficient Resource Management via Dynamic Bandwidth Sharing in a WDM-PON ring-based architecture. In Proceedings of the 14th International Conference on Transparent Optical Networks (ICTON), Coventry, UK, 2–5 July 2012; pp. 1–4. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yeh, C.; Chow, C.; Huang, S.; Sung, J.; Liu, Y.; Pan, C. Ring-based WDM Access Network Providing both Rayleigh Backscattering Noise Mitigation and Fiber-Fault Protection. J. Light. Technol. 2012, 30, 3211–3218. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Róka, R. Hybrid PON Networks-Features, Architectures and Configuration; LAP Lambert Academic Publishing: Saarbrücken, Germany, 2015; ISBN 978-3-659-43686-4. [Google Scholar][Green Version]
- ITU-T. Series G-Supplement 51: Passive Optical Network Protection Considerations; International Telecommunication Union: Geneva, Switzerland, 2016. [Google Scholar][Green Version]
- Fan, P.; Chen, H.; Chen, M.; Xie, S. Self-Protected Scheme for Wavelength Reusable WDM Passive Optical Networks. In Proceedings of the National Fiber Optic Engineers Conference, Los Angeles, CA, USA, 6–10 March 2011; pp. 1–3. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Larsen, C.P.; Gavler, A.; Wang, K. Comparison of Active and Passive Optical Access Networks. In Proceedings of the 9th Conference on Telecommunication, Media and Internet, Ghent, Belgium, 7–9 June 2010; pp. 1–5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Machuca, C.M.; Wosinska, L.; Chen, J. Assessment Methodology of Protection Schemes for Next Generation Optical Access Networks. Opt. Fiber Technol. 2015, 26, 82–93. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Esmail, M.; Fathallah, H. Optical Coding for Next-Generation Survivable Long-Reach Passive Optical Networks. J. Opt. Commun. Netw. 2012, 4, 1062–1074. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Imtiaz, W.; Iqbal, J.; Qamar, A.; Ali, H.; Idrus, S. Impact of Fiber Duplication on Protection Architectures Feasibility for Passive Optical Networks. In Optical Fiber and Wireless Communications; InTech: Rijeka, Croatia, 2017. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Davim, J.P.; Ziaie, S.; Pinto, A.P. CAPEX Model for PON Technology Using Single and Cascaded Splitter Schemes. In Proceedings of the IEEE International Conference on Computer as a Tool EUROCON, Lisbon, Portugal, 27–29 April 2011; pp. 192–196. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- FS EUROPE. © 2009–2025 Neufahrn, Germany. Available online: https://www.fs.com/de-en (accessed on 18 October 2025).





| P2MP Architectures | Ring Architectures |
|---|---|
| Unprotected P2MP access network | Unprotected ring access network |
| Type B protected P2MP access network | Protected ring access network |
| Dual-parented Type B protected P2MP access network | Unprotected ring metro-access network |
| Type C protected P2MP access network | Protected ring metro-access network |
| Components | Item | Value | Unit of Measure | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| OC | Electricity consumption | OLT | 0.235 | kWh |
| ONU | 0.01 | kWh | ||
| Electricity price | 0.142 | €/kWh | ||
| OR | Repair cost | 1000 | €/h | |
| OP | Penalties for service failures | P2MP | - | €/h |
| ring | 100 | €/h | ||
| Y | Number of years | 10 | year |
| Component | Item | Ports | Cost (€) | Unit of Measure |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| COLT | OLT base | 792 | pcs | |
| OLT fiber switch | 509 | pcs | ||
| OLT module 10G | 829 | pcs | ||
| OLT module 40/100G | 2001 | pcs/port | ||
| OLT receiver | 319 | pcs | ||
| RACK set | 800 | pcs | ||
| CFF | FF | 1400 | €/km | |
| CDF | DF | 300 | €/km | |
| CAWG | AWG | 4 | 262.80 | pcs |
| 8 | 657.60 | pcs | ||
| 16 | 802.60 | pcs | ||
| 32 | 2037.60 | pcs | ||
| 64 | 2700.00 | pcs | ||
| 96 | 12,471.40 | pcs | ||
| CONU | ONU | 47 | pcs | |
| COS | OS | 2059 | pcs | |
| CL | Excavation works | 10,000 | €/km | |
| Fiber optic duct | 400 | €/km | ||
| Cable inflation | 1000 | €/km |
| Input Parameter | Default Values |
|---|---|
| P2MP Architecture | |
| Number of subscribers | 32 |
| Distribution Fiber (DF) length | 8 km |
| Feeder Fiber (FF) length | 25 km |
| Ring Architecture | |
| Number of ONUs | 10 |
| Distribution Fiber (DF) length | 8 km |
| Feeder Fiber (FF) length | 3 km |
| P2MP Architectures | OPEX [€] | CAPEX [€] | TCO [€] |
|---|---|---|---|
| Unprotected P2MP access network | 46,723.13 | 430,942.60 | 477,665.73 |
| Type B protected P2MP access network | 16,774.18 | 751,451.60 | 768,225.78 |
| Dual-parented Type B protected P2MP access network | 16,729.33 | 765,252.60 | 781,981.93 |
| Type C protected P2MP access network | 6948.61 | 848,593.20 | 855,541.81 |
| Ring Architectures | OPEX [€] | CAPEX [€] | TCO [€] |
| Unprotected ring access network | 245,344.96 | 157,350.00 | 402,694.96 |
| Protected ring access network | 5736.95 | 285,350.00 | 291,086.95 |
| Unprotected ring metro-access network | 252,322.54 | 210,809.80 | 463,132.34 |
| Protected ring metro-access network | 12,714.52 | 336,750.80 | 349,465.32 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Fuňák, F.; Róka, R. Cost–Benefit Analysis of WDM-PON Traffic Protection Schemes. Appl. Sci. 2025, 15, 12120. https://doi.org/10.3390/app152212120
Fuňák F, Róka R. Cost–Benefit Analysis of WDM-PON Traffic Protection Schemes. Applied Sciences. 2025; 15(22):12120. https://doi.org/10.3390/app152212120
Chicago/Turabian StyleFuňák, Filip, and Rastislav Róka. 2025. "Cost–Benefit Analysis of WDM-PON Traffic Protection Schemes" Applied Sciences 15, no. 22: 12120. https://doi.org/10.3390/app152212120
APA StyleFuňák, F., & Róka, R. (2025). Cost–Benefit Analysis of WDM-PON Traffic Protection Schemes. Applied Sciences, 15(22), 12120. https://doi.org/10.3390/app152212120







