1. Introduction
One major area of scientific research today is climate change and climate variability, which is clearly in response to the incontestable phenomenon of global warming that has been widely addressed in IPCC publications [
1]. Although records show that air temperatures have been increasing since the end of the Little Ice Age, this pattern became considerably more pronounced at the end of the 20th century. While during the 1880–2019 period as a whole the air temperatures rose by approximately 0.7 °C/100 years, in the final 30 years of this timeframe (1990–2019), the increase in temperature has actually been in the region of 2.0 °C/100 years [
2]. Trenberth [
3] demonstrated that this warming trend has actually been characterized by distinct spatial variations: it has been more significant in land than over the oceans. In Europe, warming has accelerated at a faster rate than in other continents [
4,
5], and this has manifested itself in a higher incidence of heat waves of greater intensity, in which temperatures significantly surpassed the long-term average of whole months, or even seasons, in which temperatures significantly surpassed the long-term average [
6,
7]. According to agreed-upon prognoses, rapid warming will continue in the future [
8].
On the other hand, data from different sources and years show quite clearly that rising air temperatures in Europe and its nearby surrounding areas vary significantly in terms of both time and place [
9,
10,
11]. This means that the warming trend of recent years is actually a complex and spatially diversified phenomenon [
12,
13,
14]. Accurate evaluation of its potential social and economic impacts requires sustained monitoring that relies on a consistent dataset.
According to the latest research [
11], the current upward trend in air temperatures in Europe began in the second half of the 1980s. Previously, temperatures had remained more or less stable. Conclusions were drawn from a classic statistical analysis of an area-average series of air temperature values over a period of 70 years, between 1951 and 2020, using the linear regression goodness of fit method as the basis for their calculations. This is because the slope of the linear regression of average annual temperatures and seasonal temperatures in the 1986–2020 timeframe turned out to be approximately twice as great as for the entire 70-year period as a whole. The results of this analysis provided the stimulus for further research based on data with a greater temporal resolution, i.e., average monthly air temperature values in tandem with objective and more advanced techniques based on artificial intelligence (AI), i.e., machine learning. Such new approaches are finding increasing applications in many scientific areas and are also being applied in a variety of ways in climate studies [
15,
16,
17,
18].
Previous studies have examined the time periods of significant air temperature changes across Europe [
19]. These findings provided a direct impetus for the present study, which offers a detailed analysis of changes in mean monthly air temperatures in Poland using a neural network model. According to an analysis of mean monthly air temperatures [
19] over a 70-year period, the annual temperature record can be divided into two distinct phases: an earlier period of relative stability and a subsequent phase marked by a clear increase in temperature. The present study focuses on this latter period of warming, aiming to (i) develop a time series model for monthly mean temperatures recorded after 1999 and (ii) generate forecasts of monthly average temperature values for Poland.
Time series forecasting has traditionally been dominated by linear models, such as the autoregressive integrated moving average (ARIMA) model [
20]. With recent advances in artificial intelligence, hybrid approaches combining conventional statistical methods with artificial neural networks have been increasingly applied to time series analysis [
21,
22]. Such methodologies enable the identification of both linear and nonlinear dependencies within time series data, thereby improving predictive accuracy and model robustness. In the present study, a pure deep learning approach, the Neural Basis Expansion Analysis for Interpretable Time Series (N-BEATS) model [
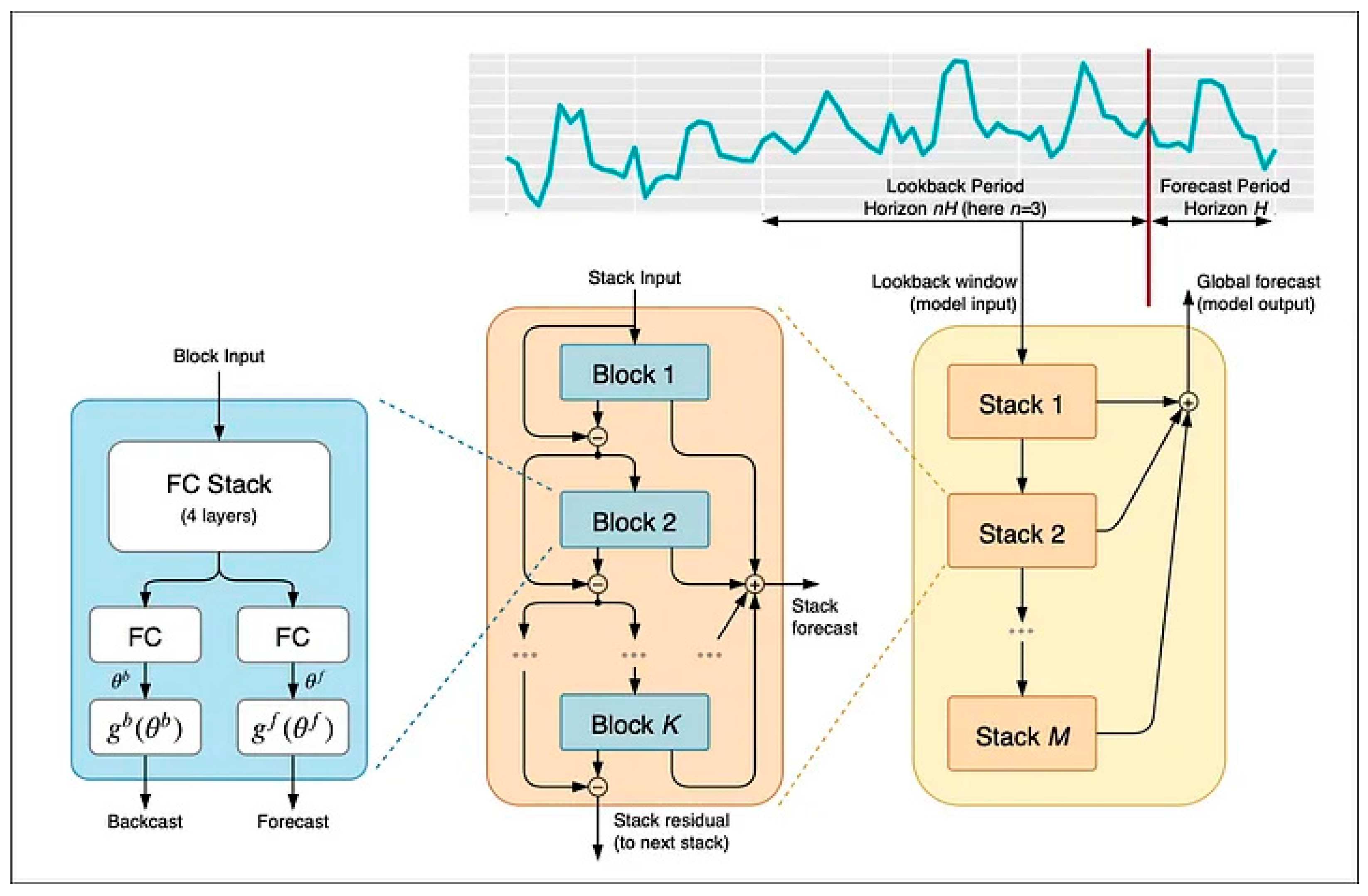
23], was employed. The N-BEATS model was benchmarked against state-of-the-art forecasting frameworks, including a Transformer-based architecture and an XGBoost variant, in order to assess its methodological advantages in modeling air temperature variability. Model parameters were optimized through a grid search procedure, ensuring that the resulting forecasts reflect the most accurate configuration for the analyzed dataset.
The article first provides an exploratory overview of the data, followed by a methodological framework combining clustering of annual temperature cycles with time series modeling based on machine learning. The subsequent analysis presents and evaluates the forecasting results.
3. Results
The annual variability plots presented in
Figure 5, calculated using five-year moving windows for all eight meteorological stations, consistently reveal an overall increase in temperature throughout the study period.
A steady rise in temperature, illustrated as a sequence of colors ranging from blue to purple, has been especially pronounced since the final decades of the previous century (the 1980s and the 1990s). No distinct rise on this scale can be observed between the 1950s and the 1970s. However, the rate of temperature change varied across individual months, which is reflected in the differing thickness of the plotted trajectories. In particular, the winter months (January–March) exhibit greater variability and a more complex structure compared to the smoother and more consistent trends observed for the remaining months of the year. This pattern suggests that the warming process in Poland has not been uniform throughout the annual cycle but rather exhibits distinct seasonal differences in both magnitude and temporal dynamics.
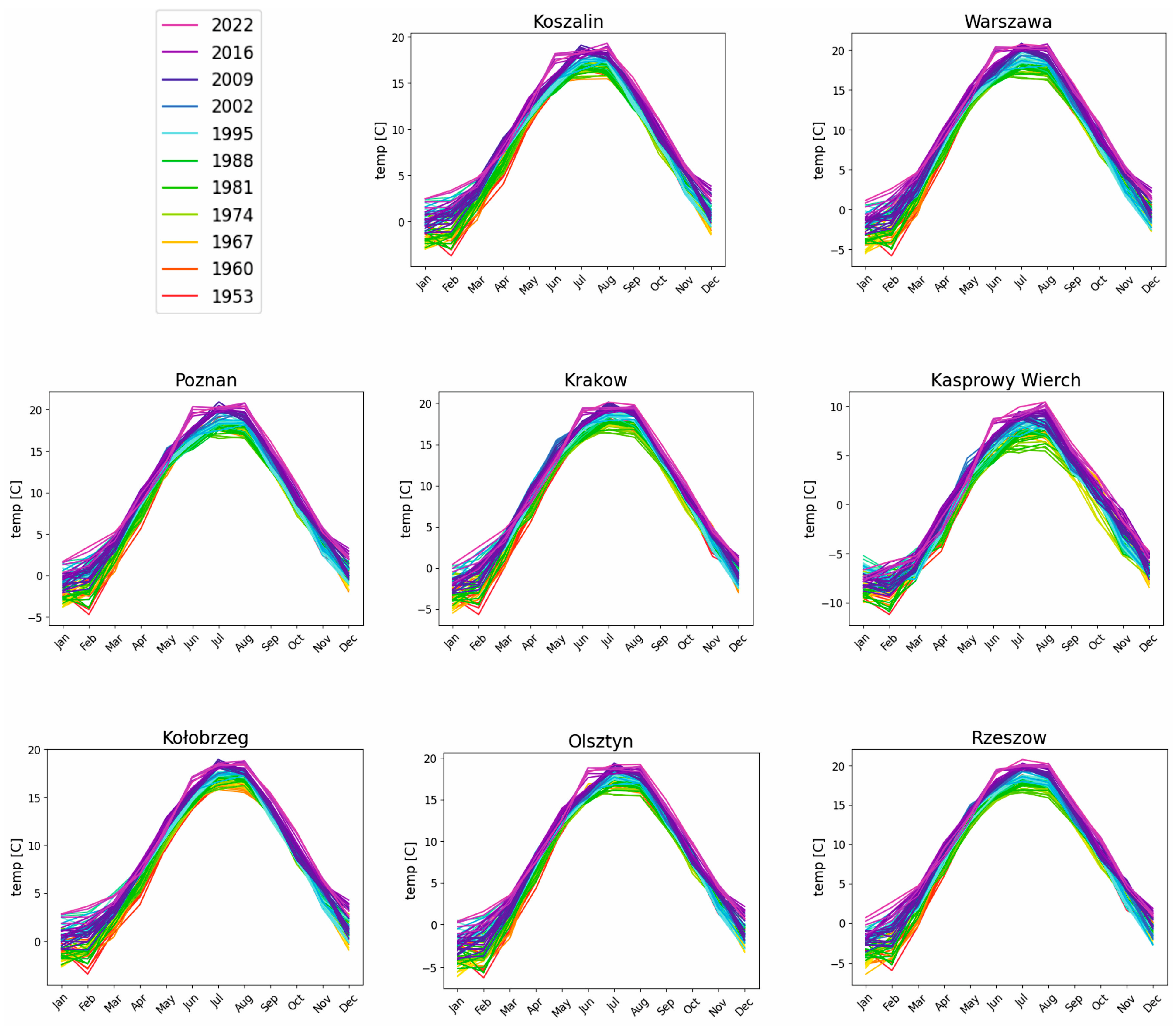
Figure 6 presents the course of mean monthly temperature values for stations located in Poland (surface mean temperature values) between 1951 and 2024. The mean temperature values were prepared individually for particular months in a calendar year.
The temperature values shown in
Figure 6 align with the average temperature values calculated for the entire European dataset [
19]. The patterns in mean temperature values for particular months indicate variability. After an initial period of fluctuations around the mean temperature value each month a consistent upward trend is noticeable in mean monthly temperature values. This change is especially evident in mean temperatures in the spring and summer months (March–July). Mean temperature curves calculated for the autumn and winter months (August–February) also indicate an increase in the mean temperature; however, such a rise does not point to such a strong linear trend as was noted in the summer months. Moreover, in recent years, a distinct downward tendency in mean temperatures has been noted for the period from August to November, suggesting a localized cooling effect during the early autumn season.
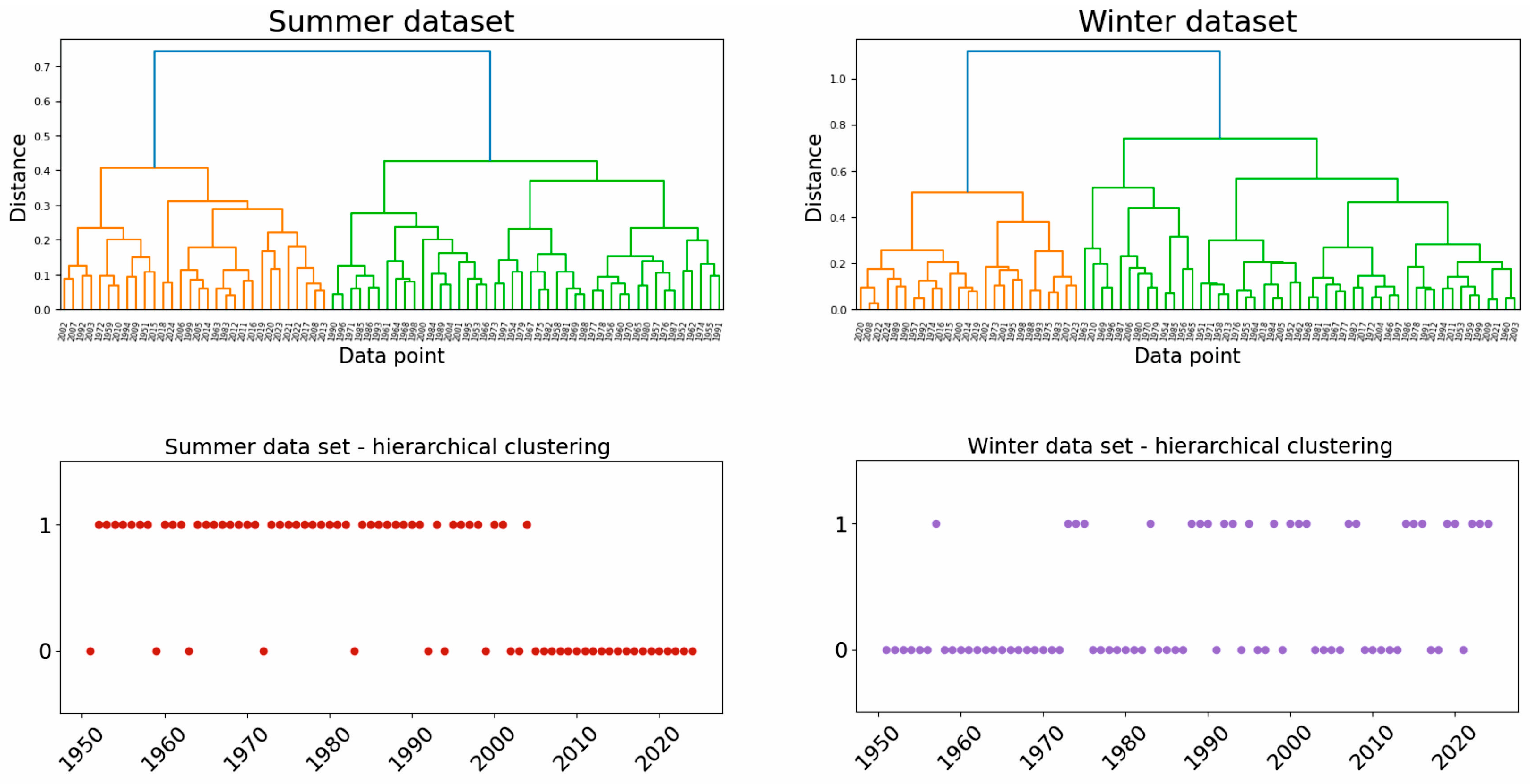
The results obtained from the clustering of mean annual cycles, performed for data recorded for stations located in Poland, are presented in
Figure 7. Similarly to the clustering of mean annual cycles of temperature values conducted for the whole of Europe [
19], a distinct separation was observed in the distribution of annual temperature profiles. Furthermore, the analysis confirmed that these differences are primarily driven by variations in temperatures recorded during the summer months, which exert the greatest influence on the overall structure of the annual thermal cycle.
The post-1999 period, corresponding to the phase of intensified warming, was subsequently utilized to develop forecasts of monthly mean air temperature values for Poland using the N-BEATS deep learning model. All computations were performed with the Darts open-source Python library (v3.11.9), which provides a unified framework for time series analysis and forecasting. The dataset, comprising monthly mean air temperature records from meteorological stations distributed across Poland, was normalized and subsequently partitioned into training and validation subsets according to an 80:20 ratio. The training set was used to train an interpretable version of the model. The
input_chunk_length parameter, which specifies the number of past time steps provided to the model as input, and the
output_chunk_length parameter, defining the forecasting horizon, were determined through a grid search procedure. The hyperparameter ranges explored in this procedure were:
input_chunk_length = [12, 24, 36, 48] and
output_chunk_length = [6, 12, 18]. The number of training epochs was set to 100, as no further improvement in the loss function was observed beyond this point. Forecast performance for each combination of these parameters was assessed using MAPE, RMSE, and R
2, with the results presented in
Table 2.
The combination of input_chunk_length = 24 and output_chunk_length = 12 was selected for the final model. Although the performance metrics were very similar to the shorter forecasting horizon (output_chunk_length = 6), the choice of 12 months naturally aligns with predicting the entire annual cycle.
For the selected hyperparameter configuration of the N-BEATS model (
input_chunk_length = 24,
output_chunk_length = 12), its predictive performance was benchmarked against two state-of-the-art alternatives: a Transformer-based model and an XGBoost variant. The results of this comparison are presented in
Table 3.
The results clearly indicate that N-BEATS outperformed both benchmark models across all evaluation metrics. In particular, it achieved the lowest MAPE (12.2%), reflecting superior accuracy in relative terms, as well as the lowest RMSE, confirming a reduced magnitude of absolute forecast errors. Moreover, the coefficient of determination (R2 = 0.90) demonstrates that N-BEATS explained a higher proportion of variance in the observed data compared to XGBoost (R2 = 0.88) and the Transformer model (R2 = 0.86).
Given these results, the N-BEATS model was selected for generating the final forecasts. A global model for Poland was trained using 80% of the combined dataset from all eight meteorological stations, comprising a total of 1996 data points. The use of N-BEATS made it possible to simultaneously analyze multiple time series, which was particularly advantageous given the relatively limited number of observations available for each individual station. By adopting a modeling approach capable of jointly utilizing several series during the training phase, the effective size of the training dataset was increased approximately eightfold, thereby enhancing the model’s ability to generalize and capture shared temporal dynamics across different locations. The values of RMSE, MAPE, and R
2 obtained for the validation sets of all eight stations are presented in
Table 4.
The forecast evaluation results are relatively consistent across most of the meteorological stations. For the majority of locations, MAPE values remain close to 14%, with RMSE values ranging between 0.08 and 0.09 °C and R2 values around 0.85–0.87, indicating a stable level of accuracy and good model fit. The lowest error values were obtained for Rzeszów (MAPE = 13.37%, RMSE = 0.08, R2 = 0.87), suggesting that forecasts for this location are particularly reliable. In contrast, the mountain station at Kasprowy Wierch exhibits a noticeably higher MAPE of 21.58% and a lower R2 of 0.83, which may be attributed to the greater variability and complexity of temperature dynamics in high-altitude environments. Slightly elevated errors are also observed for the coastal station in Kołobrzeg (MAPE = 16.30%), reflecting the influence of maritime climatic factors. Overall, the results confirm the robustness of the forecasting framework, while also highlighting that prediction accuracy may vary depending on local climatic and topographical conditions.
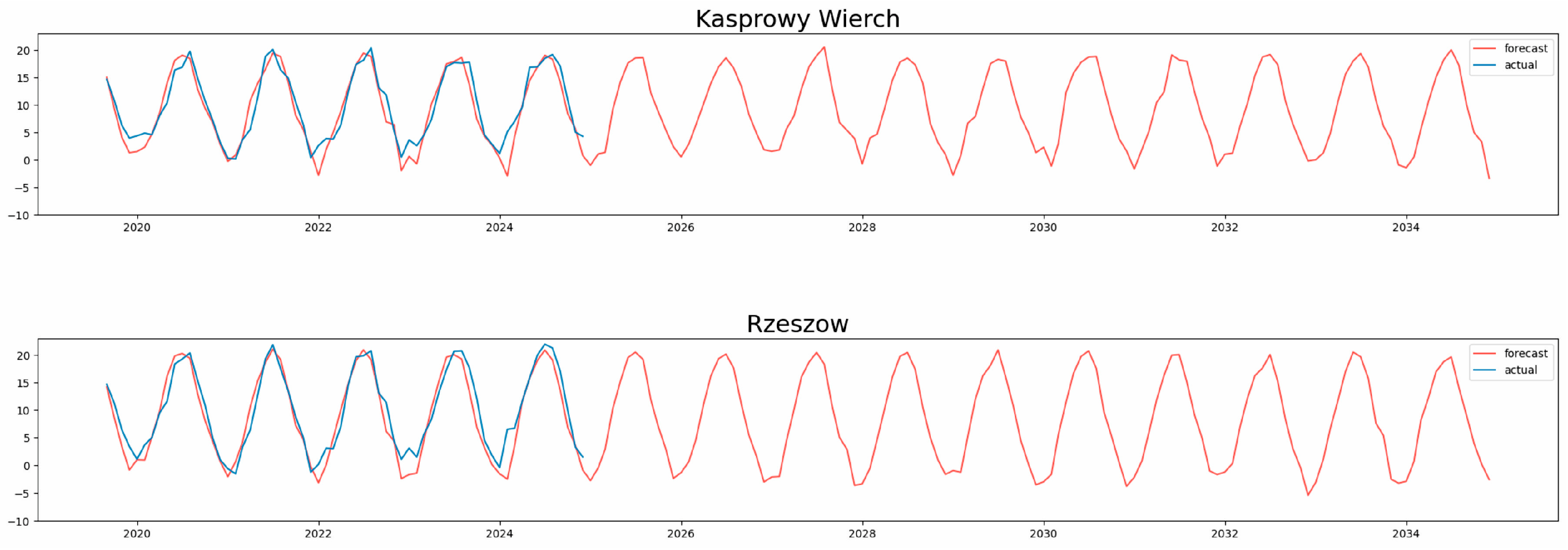
The predicted results for two meteorological stations—Rzeszów and Kasprowy Wierch—together with the actual values from the validation sets (rescaled to their original real-world units) are presented in
Figure 8. These two stations were selected as they represent the best and worst forecast performance, respectively, within the group of analyzed locations in terms of MAPE, RMSE, and R
2. The monthly average temperatures were forecast for a future time span of ten years, covering the period from January 2025 to December 2034.
The predicted results differ not only in terms of local variations (predictions for urban areas) but also within the range of forecasted temperatures (e.g., the difference between the predicted value for the meteorological station at Kasprowy Wierch and the predicted values for the other seven stations located in different cities in Poland). The forecasts presented in the previous figure, which cover the period corresponding with the validation set (from September 2019 to December 2024), are to a considerable extent in harmony with the actual validation data.
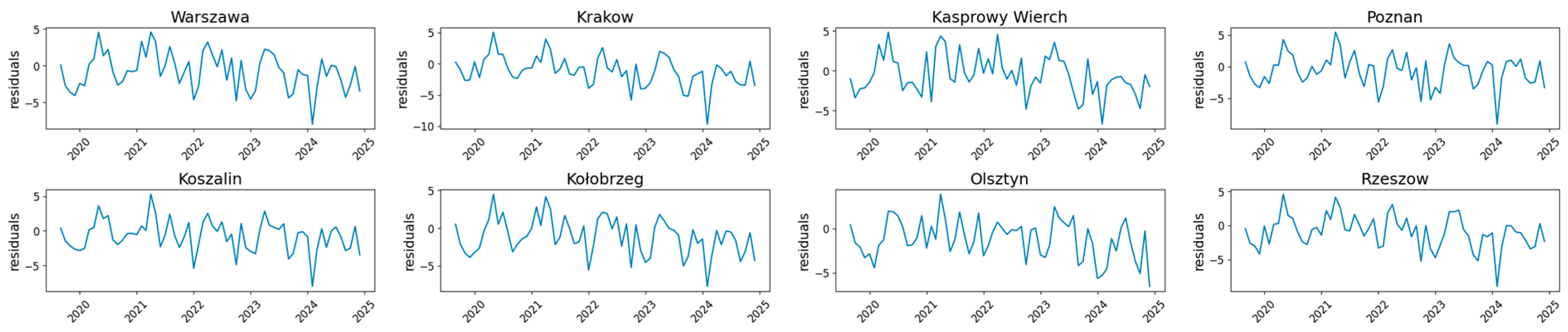
Figure 9 shows the residuals between the predictions and the validation set for all five meteorological stations.
Residual diagnostics confirmed that the residuals obtained from N-BEATS forecasts were, in most cases, normally distributed, uncorrelated, and homoscedastic. The Shapiro–Wilk test indicated no significant deviations from normality for any of the eight stations, confirming that the model captured the main patterns of thermal variability without systematic bias. The Ljung–Box test results suggested that residuals were free from serial correlation at most stations, with the exception of Warszawa and Kasprowy Wierch, where weak autocorrelation was detected (p < 0.05). However, this effect was marginal and did not materially affect overall forecast performance. Furthermore, the ARCH test showed no evidence of heteroscedasticity across all analyzed stations (p > 0.05), implying a stable variance of forecast errors over time.
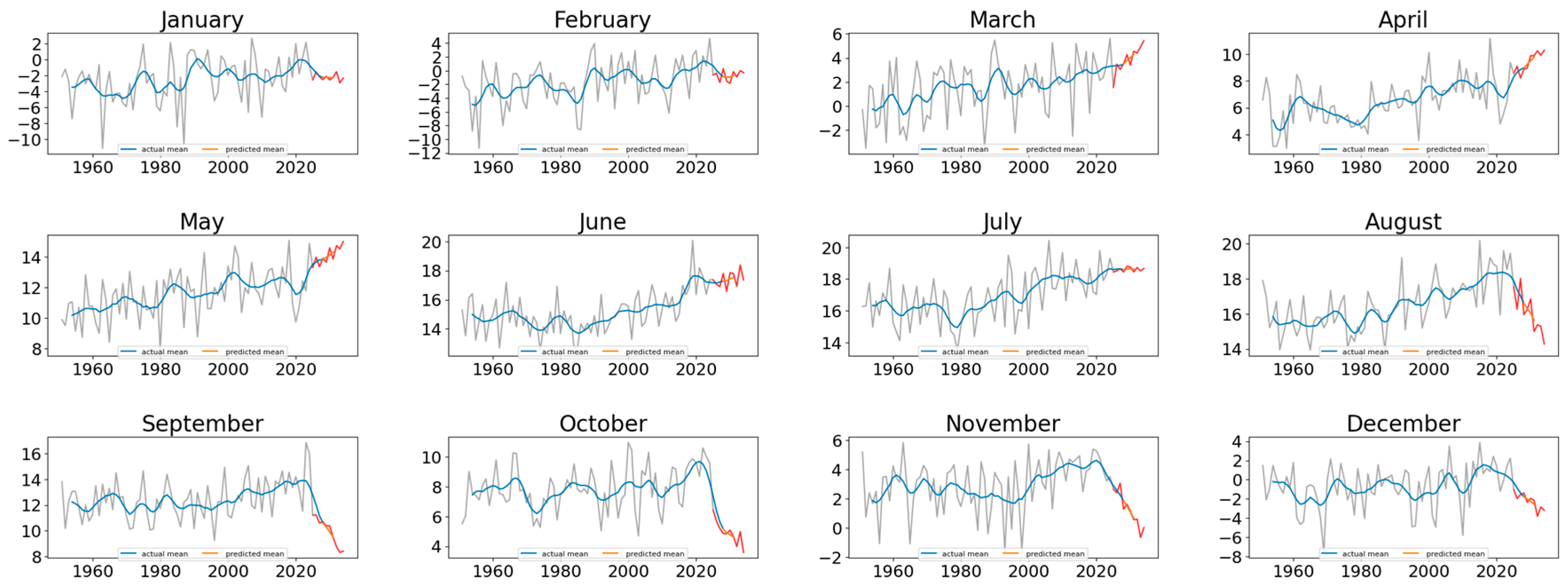
In the case of the predicted values for the period between January 2025 and December 2034, it should be emphasized that, based on this type of graphical representation, no distinct global trend or noticeable local shifts can be identified in the projected monthly mean temperatures (
Figure 10). The forecasts presented for Poland in
Figure 9 clearly illustrate the differing dynamics that characterize the winter and summer months. Furthermore, the rate of change, expressed as a linear trend fitted to the data, is summarized in
Table 5 which presents the estimated slopes (°C decade
−1) for each month, together with their 95% confidence intervals. The results presented in
Table 5 indicate pronounced seasonal variability in the projected temperature trends across the forecast period. Statistically significant positive trends were identified for March, April, and May, suggesting a potential warming tendency during the spring months. In contrast, late summer and autumn months (August–November) display statistically significant negative trends, implying a possible cooling pattern during this part of the year.
The magnitude of these trends ranges from approximately –3.6 °C decade−1 in November to +3.3 °C decade−1 in March, reflecting substantial inter-monthly differences in the forecasted temperature evolution. For the winter months (December–February), the estimated slopes are small and statistically insignificant (p > 0.05), which may indicate that temperature variations during this period are driven by more complex, potentially nonlinear processes rather than by a consistent linear trend.
4. Discussion
The results obtained in this study confirm the occurrence of long-term warming trends in Poland, consistent with broader European and global climate patterns. Analysis of 74 years of temperature observations from five meteorological stations revealed a marked shift around 1999, when a stable climatic phase gave way to accelerated warming. This transition is particularly visible in the summer months, which have shown stronger linear increases in mean temperatures compared with the winter season. Such a pattern mirrors findings for other European regions, suggesting that Poland’s climate dynamics are part of a wider continental-scale process.
The clustering analysis further demonstrated that the key driver of the observed changes lies in summer temperature values. This seasonal asymmetry is of particular importance for environmental and socio-economic systems: rising summer temperatures are associated with an increased frequency of heatwaves, water shortages, and higher energy demand for cooling, while warmer winters may influence agricultural cycles, biodiversity, and the hydrological balance.
From a methodological perspective, the use of the N-BEATS deep learning model proved effective for forecasting monthly average temperatures. The model achieved relatively low error rates (MAPE values between 14.0% and 21.6%), which are comparable to results reported in previous climate-focused time series studies using hybrid statistical–neural approaches. The highest forecasting error was recorded for the Kasprowy Wierch station, which can be attributed to its mountainous location. At higher altitudes, temperature patterns are strongly influenced by orographic effects, atmospheric circulation, and local variability, making predictions more challenging compared with urban lowland stations.
The forecasts for the decade 2025–2034 suggest a continuation of the observed warming, though with pronounced seasonal variability. The increase in spring and early summer temperatures (March–July) aligns with projections of intensified continental warming under climate change scenarios.