Abstract
Earthquakes are unpreventable natural disasters that result in many casualties and economic losses in the regions where they occur. Earthquake prediction and seismic risk assessments are essential in minimising these losses. Due to the complex nature of seismic events, it is necessary to use a cutting-edge methodology to predict earthquake occurrence effectively. Machine learning methods have been among the most efficient and current methods for solving complex nonlinear problems and analysing big datasets. Because of this feature, they are widely used for predicting earthquakes and earthquake parameters. This study focuses on applying machine learning methods to analyse seismic events in Western Turkey from 1975 to 2024. The aim is to compare the effectiveness of five machine learning approaches for predicting earthquake magnitudes: Long Short-Term Memory (LSTM), Adaptive Neuro-Fuzzy Inference Systems (ANFIS), Decision Tree (DT), Random Forest (RF), and Convolutional Neural Network (CNN). The outcomes of these applied methods are encouraging in terms of the prediction of magnitude. Among all the results, the LSTM method is slightly more successful than the other methods, with a Root Mean Square Error (RMSE) of 0.1391, Mean Square Error (MSE) of 0.0193, Mean Absolute Error (MAE) of 0.1046 and Mean Absolute Percentage Error (MAPE) of 3.0631%, respectively.
1. Introduction
Earthquakes are among the most devastating natural disasters. These seismic events have the potential to inflict severe destruction over a very short time, often resulting in significant casualties and property losses. For over a century, the scientific community has endeavoured to develop effective and reliable methods for earthquake prediction [,,,,,]. However, it is important to note that earthquakes exhibit chaotic and stochastic behaviour, making the precise prediction of damaging earthquakes difficult [].
In recent years, machine learning (ML) methods have been applied in various fields for geophysical studies, yielding significant results [,,,,,,,]. It has also been widely used in seismological studies [,,,,,,,], specifically in predicting earthquakes. Machine learning has the potential to deliver superior performance compared to traditional methods in earthquake prediction. Preliminary studies concentrated on investigating the prospective capabilities of artificial neural networks (ANNs) in this domain. Refs. [,] were pioneers in demonstrating the applicability of artificial neural networks in predicting earthquakes. Ref. [] utilised artificial neural networks to predict seismic events in Chile, which is one of the countries with high seismic activity. By the end of the 2010s, increasing computational power and successful applications of big datasets led to deep learning methods gaining interest in earthquake prediction. The review by Al Banna et al. [] summarises the current challenges and future directions in earthquake prediction using machine learning, serving as an essential reference point. Ref. [] applied novel machine learning algorithms to predict seismic activity in Northern Pakistan. The prediction of earthquakes using the random forest algorithm was investigated through an analysis of seismic activity in Indonesia by Budiman and Ifriza []. This was demonstrated recently by Berhich et al. [], who employed recurrent neural networks for location-dependent earthquake prediction. Ref. [] investigated the role and applicability of AI-based methods in overcoming the current challenges in real-time earthquake prediction. A recent study by Ommi and Hashemi [] examined the performance of machine learning techniques in one of the most seismically active regions, Northern Zagros, and presented valuable findings regarding their applications. Deep learning has yielded better results when treating earthquake prediction as a global spatio-temporal forecasting problem, but this process has given rise to the issue of spatial distortion. Ref. [] proposed a new model based on the spherical convolutional LSTM and U-Net framework. Their findings demonstrate the model’s potential, along with standard spherical CNNs, to reduce spatial distortions in global earthquake prediction. Recently, ref. [] presented a novel approach that utilises earthquake catalogues to investigate earthquake activity in Taiwan. They developed three attention-based bidirectional long short-term memory (Bi-LSTM) models to predict future earthquakes’ time, magnitude, and location based on previous events from earthquake catalogue data from 2002 to 2022. Time predictions were made through regression, while magnitude and location predictions were made through classification.
The objective of earthquake prediction is to predict the time, location and magnitude of the next destructive earthquake. Predicting the magnitude of a future earthquake is one of the important issues in earthquake prediction studies, as it significantly affects possible damage. Panakkat and Adeli [] were among the first authors to propose multiple seismicity indicators for predicting the next month’s largest earthquake using neural networks. Similarly, Adeli and Panakkat [] presented a probabilistic neural network (PNN) to predict the magnitude of the largest earthquake in the Southern California region. In 2011, Moustra et al. [] applied an Artificial Neural Network (ANN) to predict earthquake occurrence in Greece using two different input datasets. In the initial phase, an attempt was made to predict the next day’s earthquake magnitude. In the subsequent phase of the study, the researchers sought to forecast the magnitude of the impending earthquake after detecting pre-seismic signals, known as Seismic Electric Signals (SESs). Asim et al. [] applied a range of machine learning techniques, including pattern recognition, neural networks, recurrent neural networks, random forests and linear programming boost ensemble classifiers, with the aim of predicting earthquakes of 5.5 ≤ M in the Hindukush region. Pandit and Biswal [] developed a model using ANFIS with two algorithms to predict earthquake magnitudes. The model was trained using data from forty-five real earthquakes of 5 ≤ M, recorded between 1933 and 1985, from different regions. Asim et al. [] developed seismic analysis and machine learning models for the purpose of predicting short-term low-magnitude seismic activity in Cyprus. In recent studies, ML methods, including the long short-term memory (LSTM), bidirectional long short-term memory (BILSTM), bidirectional long short-term memory with attention (BILSTM-AT), and transformer models, were used to predict future earthquake magnitudes in the Horn of Africa by Abebe et al. []. Wang et al. [] applied a deep learning model (EEWNet) based on CNN (Convolutional Neural Network) to estimate magnitude using an initial P-wave for less than 3 s from a single station. Berhich et al. [] employed an attention-based LSTM network to predict the time, magnitude and location of future large-scale seismic events in Japan. The monthly average magnitudes of earthquakes between 1970 and 2000 in the Gediz graben system were analysed using autoregressive integrated moving average (ARIMA), singular spectrum analysis (SSA), and deep learning methods, including convolutional neural network (CNN) and long short-term memory (LSTM) by Öncel Çekim []. They reported that LSTM achieved the best and most accurate results among the applied methods.
This study analysed earthquakes in Western Turkey with a magnitude of 3 ≤ M between 1975 and 2024. The weekly average magnitude of these earthquakes was calculated, and five different ML methods—LSTM, ANFIS, DT, RF, and CNN—were applied to predict the average magnitude of earthquakes expected in the region the following week. The primary aim of this study is to compare the performance of five different machine learning methods, each with unique structures, commonly used in fields such as earthquake prediction, magnitude prediction, and location prediction. This research seeks to identify which method delivers the most effective performance using the same dataset, thereby highlighting advancements in this important area.
2. Data and Data Pre-Processing
Due to its tectonic structure, Western Turkey is one of the seismically active regions. Numerous destructive earthquakes have been recorded in the region throughout both historical and instrumental periods. This study focuses on earthquakes with magnitudes 3 ≤ M that took place between 1975 and 2024 in Western Turkey, within the latitudes of 36° N to 42° N and longitudes of 26° E to 32° E.
In the initial phase of the study, the magnitude data was analysed using daily, weekly, and monthly averages. The daily average data were deemed unsuitable for evaluation due to numerous consecutive days with missing data. In the monthly average data, the effect of large earthquakes was diminished, and the data appeared smoothed. Weekly average values were ultimately used for this study, as these effects were relatively less pronounced. The study is based on catalogue data from the Kandilli Observatory and Earthquake Research Institute (KOREI). The events have also been verified against the catalogues of the Disaster and Emergency Management Presidency of the Republic of Turkey (AFAD) (T.C. İçişleri Bakanlığı Afet ve Acil Durum Yönetimi Başkanlığı) and the United States Geological Survey (USGS) (Search Earthquake Catalog|U.S. Geological Survey). Nevertheless, in the earlier part of the study period, data for only 15 non-consecutive weeks are missing, believed to be due to instrumental issues. To complete the dataset for these missing weeks, a linear interpolation method was applied.
During the study period, 34,488 events with 3 ≤ M were recorded. As demonstrated in Figure 1, GMT 6.5 [] (The Generic Mapping Tools, GitHub—GenericMappingTools/gmt: The Generic Mapping Tools) was used to visualise fault lines (red lines), earthquakes (red dots), and topographic data.
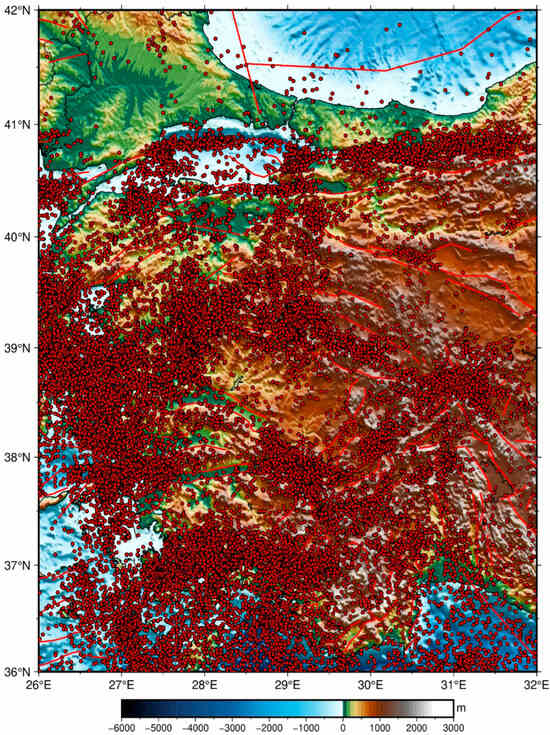
Figure 1.
Study area and earthquakes with M ≥ 3 between 1975 and 2024.
The average magnitudes were calculated for 2608 weeks in the study area from 1975 to 2024 (Figure 2). Upon examination of the dataset prepared for ML applications, the maximum weekly mean magnitude value was determined to be 4.8.
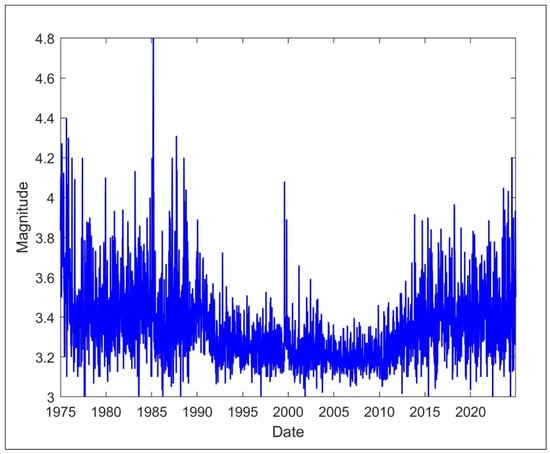
Figure 2.
Weekly average magnitude data used in ML applications from 1975 to 2024.
3. Methods
The earthquake catalogue data from Western Turkey was analysed, focusing on events with a magnitude of 3 ≤ M. The objective of this study was to predict the weekly average magnitude using five different machine learning methods: Long Short-Term Memory (LSTM), Adaptive Neuro-Fuzzy Inference System (ANFIS), Random Forest (RF), Convolutional Neural Network (CNN), and Decision Tree (DT). The performance of each method was evaluated using several metrics, including Root Mean Square Error (RMSE), Mean Square Error (MSE), Mean Absolute Error (MAE), and Mean Absolute Percentage Error (MAPE).
3.1. Long Short-Term Memory (LSTM)
Long-short-term memory (LSTM) networks represent an advanced Recurrent Neural Network (RNN) category that demonstrates learning and predicting long-term requirements within the sequential dataset. In contrast to traditional RNN, which often encounters difficulty capturing the intricate relationships that unfold over extended periods, LSTM is specifically designed to overcome this limitation. They achieve this through the innovative use of “memory cells” and sophisticated gate mechanisms introduced by Hochreiter and Schmidhuber []. At the core of an LSTM network are three essential gates: the input gate, the forget gate, and the output gate. The input gate decides which new information should be added to the memory cell, allowing the network to incorporate relevant data effectively. The forget gate regulates which information should be discarded, ensuring that only pertinent historical data is retained. Finally, the output gate manages the information from the memory cell, controlling what the network ultimately learns and predicts. This structured approach enables LSTM to maintain contextual awareness over long sequences, making it highly effective for various time series and sequential data tasks [].
3.2. Adaptive Neuro-Fuzzy Inference System (ANFIS)
Different computational methods integrate the capabilities of fuzzy systems with artificial neural networks, collectively known as neuro-fuzzy systems. One of the most well-known types of neuro-fuzzy systems is the Adaptive Network-based Fuzzy Inference System (ANFIS), proposed by Jang []. ANFIS effectively merges neural networks’ learning capabilities with fuzzy logic’s reasoning power, significantly improving prediction accuracy. ANFIS can generate a set of fuzzy if–then rules and suitable membership functions to produce the desired input–output pairs. It employs a hybrid learning algorithm to determine the parameters of fuzzy inference systems. During the training process, a specific dataset optimises the membership function parameters of the fuzzy inference system by combining the least squares method with the backpropagation gradient descent method.
3.3. Decision Trees (DT)
Decision trees (DT) are supervised machine-learning techniques for classification and regression tasks Breiman et al. []. Their structure is inspired by hierarchical tree models, which consist of a root node, internal nodes, branches, and leaf nodes. Ensemble learning methodologies have been demonstrated to enhance their performance. A decision tree is usually drawn from left to right, starting from the root and extending downwards. The initial node of the tree is called the root node, and the end node is called the leaf node. Each internal node has two or more branches extending from it. The nodes represent a particular characteristic, while the branches symbolise the range of values associated with that characteristic. The fundamental principle of forming a decision tree involves sequentially asking questions about the data and utilising the features from the training data to ensure the most effective classification or prediction based on the responses to these questions. The decision tree constructs prediction rules by analysing the answers to these questions. The process begins at the root node, where it makes sequential splits to partition the data into specific intervals, continuing until it reaches terminal (leaf) nodes. These leaf nodes represent the predicted continuous value of the target variable. The model’s generalisation performance on new data is evaluated using a test dataset, typically measured with metrics such as RMSE and MSE.
3.4. Random Forests (RF)
Random forests (RF), introduced by Breiman [], are a powerful and highly effective predictive tool and one of the most popular techniques in machine learning. This algorithm uses the strengths of multiple decision trees and skilfully combines them through a process known as “bootstrap aggregation” or “bagging.” The effectiveness of random forests in improving accuracy and managing complexity has led to their widespread adoption in many applications, making them a leading predictive tool in machine learning. A decision tree-based method combines several decision trees to build a robust and accurate model. Each decision tree makes a prediction based on a subset of data, and the forecasts from all trees are combined to form the final prediction. Creating multiple trees and combining their predictions makes the model more robust and accurate.
3.5. Convolutional Neural Network (CNN)
A convolutional neural network (CNN) is a feedforward network that is applied for prediction or classification using a supervised learning approach. A CNN consists of three fundamental stages: an input layer, a series of convolutional layers, and an output layer. Data is efficiently organised and formatted in the input layer to ensure optimal use in the subsequent stages. Convolutional or hidden layers generate feature maps essential for learning and classification. In addition, the CNN architecture consists of pooling and fully connected layers. Pooling layers are typically placed after each convolutional layer to reduce the amount of collected data. Fully connected layers are usually located at the end of the network, where input data is categorised based on features extracted from the sequences of convolutional and pooling layers. Two-dimensional convolutional algorithms (2D-CNN) are commonly used for image classification. Additionally, one-dimensional networks (1D-CNN) can be employed for signal classification, with the primary difference being the lower dimensionality of the elements used in 1D networks. 1D-CNN is extensively utilised for analysing time-series data because it can extract local patterns and temporal dependencies [].
4. Applications
The present study utilised five machine learning algorithms, namely LSTM, CNN, ANFIS, RF and DT, to accurately predict the weekly average magnitude within the study area. The dataset, organised for machine learning applications, is divided into training and test sets. The training set is used to train the model, while the test set is used to make predictions and evaluate the model’s performance. This study allocated 80% of the dataset for the training set, and 20% was designated as the test set. The performance metrics of the applied ML methods are evaluated with root mean squared error (RMSE), mean squared error (MSE), mean absolute error (MAE), and mean absolute percentage error (MAPE). The corresponding formulas are given in Equations (1)–(4):
where n denotes the total number of observations, y indicates the actual values, and ŷ represents the predicted values. The processes were carried out using MATLAB version 2024b.
As shown in Figure 3, the training set contains an average weekly magnitude of 2087 weeks from 1975 to 2014. Similarly, the test set has an average weekly magnitude of 521 weeks from 2015 to 2024. The maximum average magnitude in the training set was 4.8, which was calculated at 4.2 in the test set.
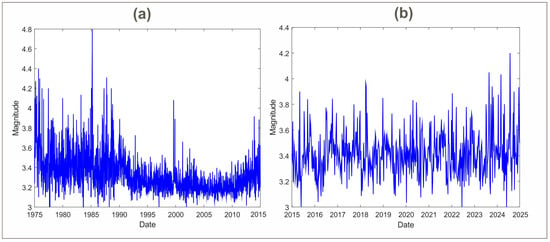
Figure 3.
(a) Training dataset; (b) test dataset.
4.1. Long Short-Term Memory (LSTM) Application
LSTM is an effective tool for analysing time series and sequential data. For this reason, it is one of the preferred methods for predicting the weekly average earthquake magnitudes. In this stage, the weekly average magnitudes generated in the previous step were utilised for training over 2087 weeks and testing over 521 weeks. After experimenting with various model configurations, the most successful performance was achieved with an architecture that included a sequence input layer, an LSTM layer, a fully connected layer, and a regression output layer (Figure 4).
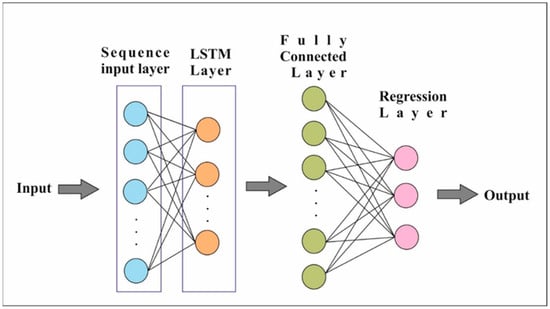
Figure 4.
LSTM architecture.
The output of the LSTM layer, which contains 100 neurons and uses tanh as the activation function, is transmitted to the fully connected layer. The training options were set with a batch size of 64, an initial learning rate of 0.05, and an Adam optimizer for 100 epochs. The regression layer generates outputs from the network for making predictions. The performance criteria obtained for the best LSTM model were 0.1391%, 0.0193%, 0.1046% and 3.0631% for RMSE, MSE, MAE and MAPE, respectively. The predicted weekly average magnitude results for the LSTM are shown as the red line in Figure 5.
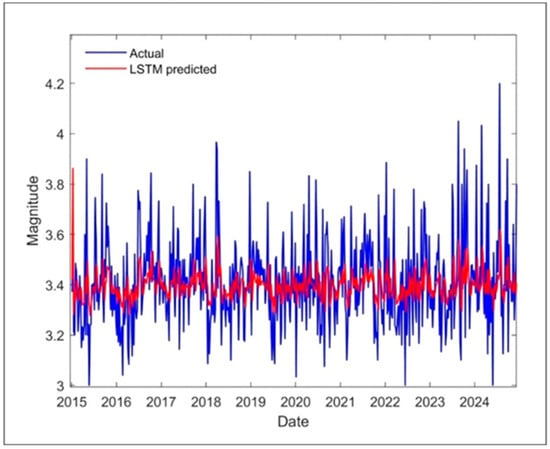
Figure 5.
Actual and predicted LSTM weekly average magnitude results.
4.2. Adaptive Neuro-Fuzzy Inference Systems (ANFIS) Application
ANFIS offers accuracy and reliability in time series forecasting using the advantageous aspects of fuzzy logic and artificial neural networks. Within this framework, the performance of ANFIS was analysed by comparing it with other ML methods. The weekly average magnitude data were evaluated using various membership functions in the implementation phase. The evaluation process involved the testing of different rules and membership functions, and it was found that the most optimal results were achieved with a Gaussian membership function and two fuzzy rules following 13 epochs.
Figure 6 illustrates the architecture of a Sugeno-type fuzzy inference system with two rules, as implemented in this study. The system consists of five layers: the fuzzy layer, product layer, normalised layer, defuzzification layer, and output layer.
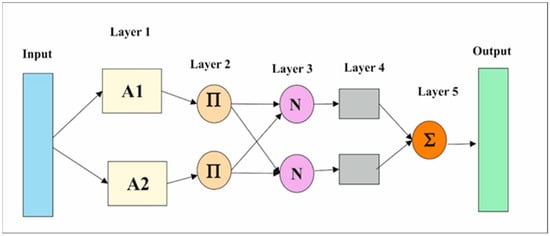
Figure 6.
ANFIS architecture.
The performance metrics for the predicted weekly magnitude results were 0.1998, 0.0399, 0.1530, and 4.4062% for RMSE, MSE, MAE, and MAPE, respectively. Figure 7 shows the actual and predicted weekly average magnitudes.
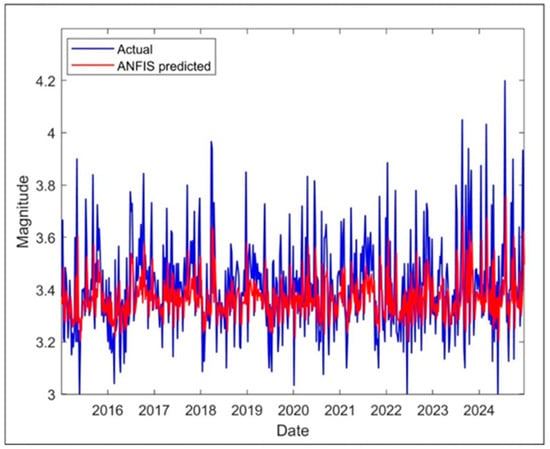
Figure 7.
Actual and predicted ANFIS weekly average magnitude results.
4.3. Decision Tree (DT) Application
Decision Tree, a practical and efficient time series prediction tool, was implemented to analyse its efficacy in earthquake magnitude prediction. This section aims to methodically examine the viability and practicality of employing the decision tree approach for earthquake magnitude prediction. An ensemble of bagged regression decision trees was applied to the dataset to predict the average magnitude for the following week. After a series of experiments, it was determined that the most efficacious regression decision tree yielded 15 minimum leaf nodes (Figure 8).
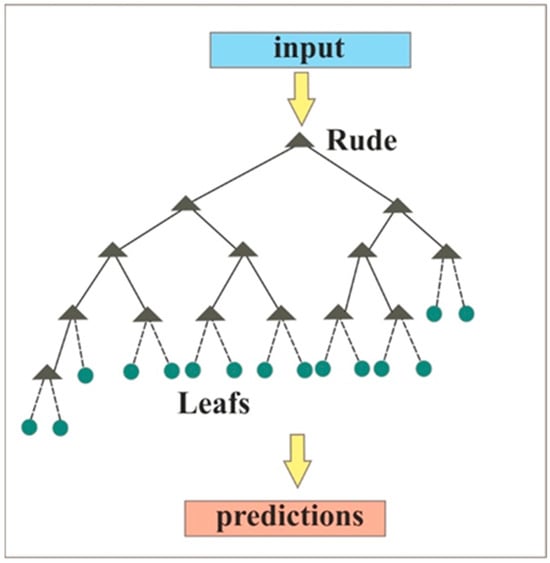
Figure 8.
Decision Tree architecture.
After establishing the regression decision tree, RMSE 0.1991, MSE 0.0396, MAE 0.1541, and MAPE 4.4562 were calculated, respectively. The predicted weekly average magnitude values are shown in Figure 9 as a red line.
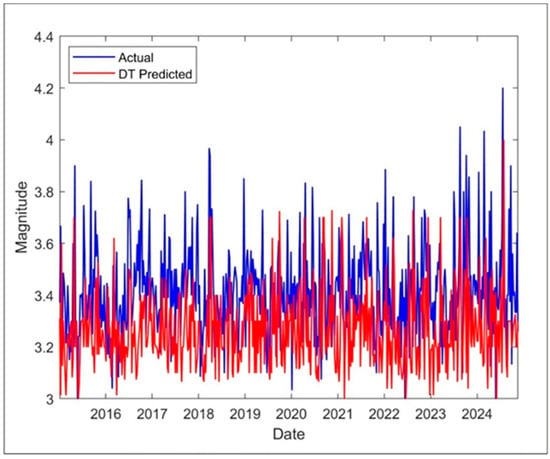
Figure 9.
Actual and predicted DT weekly average magnitude results.
4.4. Random Forest (RF) Application
A single decision tree often overfits the training data by memorising noise and specific details. In contrast, a random forest, an ensemble method that combines multiple decision trees, reduces the risk of overfitting through collective decision-making. By aggregating predictions from many trees, random forests generate more robust and generalisable results. This ensemble approach effectively balances the variances of individual trees, leading to better predictive performance than a standalone decision tree. Thus, the RF and DT performance in earthquake magnitude prediction was analysed. Furthermore, the results of both methods were compared with other applied ML methods. In the random forest application stage, different numbers of trees were utilised to predict the weekly average magnitude, and the best result was obtained using the ensemble of 70 trees (Figure 10).
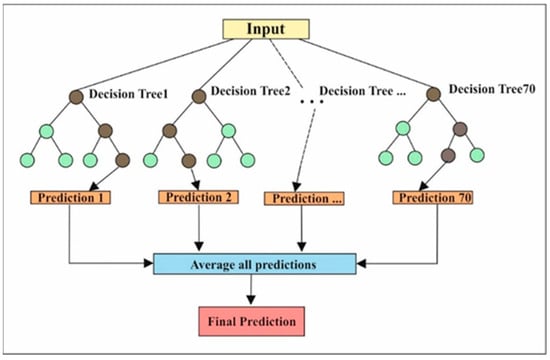
Figure 10.
Random Forest architecture.
As a result of the RF application, the errors calculated to evaluate the method’s effectiveness were as follows: RMSE was 0.1999, MSE was 0.04, MAE was 0.1557, and MAPE was 4.6044%. The result obtained is illustrated by the red line in Figure 11.
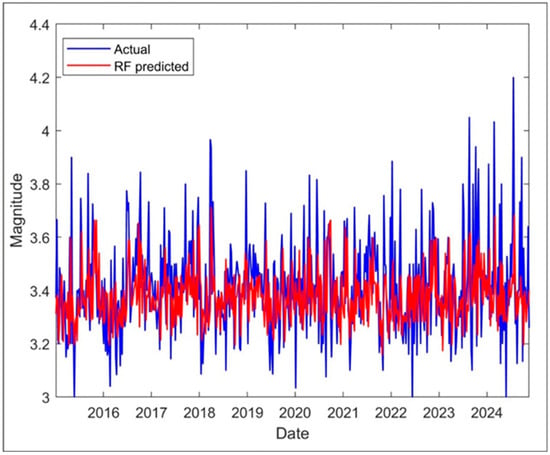
Figure 11.
Actual and predicted RF weekly average magnitude results.
4.5. One-Dimensional Convolutional Neural Network (1D-CNN) Application
1D-CNN is an ML architecture optimised for time series, signal processing and sequential data. Unlike traditional 2D-CNN, it automatically learns temporal or sequential patterns using one-dimensional (1D) filters. Given these characteristics, this study uses this method to predict earthquake magnitudes. After various experiments, the best result obtained from the 1D-CNN architecture was determined as a sequence input layer, two convolutional layers, two pooling layers, a fully connected layer, and one regression layer (Figure 12). The rectified linear unit (Relu) activation function is used to ensure nonlinearity. In both convolutional layers, the filter size was set to 1, the number of kernels to 128, the padding type to ‘same’, and the stride to 1. The max pooling method is employed in the pooling layers, with a stride of 1.
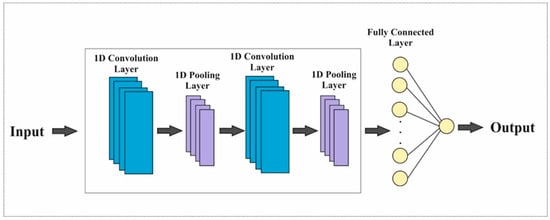
Figure 12.
One-Dimensional CNN architecture.
The training parameters were configured with a mini-batch size of 32 and an initial learning rate of 0.05, running for 100 epochs. The performance metrics obtained for the 1D-CNN method used to predict the weekly average magnitude were as follows: RMSE of 0.1609, MSE of 0.0259, MAE of 0.1277, and a MAPE of 3.6695%. The actual and predicted magnitudes are shown in Figure 13.
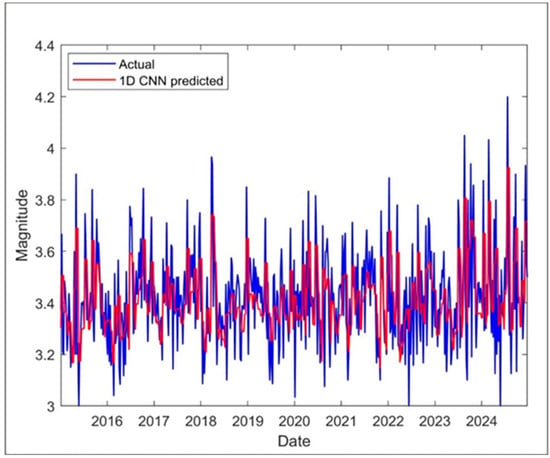
Figure 13.
Actual and predicted 1D-CNN weekly average magnitude results.
5. Results and Discussions
This study aims to predict the weekly average magnitudes of earthquakes occurring in Western Turkey using five different ML methods. To achieve this objective, 2087 weeks of average magnitude data were used for the training, and 521 weeks of average magnitude data were used for the testing. The predicted magnitude values were compared with the actual values using the performance metrics defined in Section 4. Applications’. As demonstrated in Table 1, the performance of the applied ML methods has been evaluated according to the specified performance metrics.

Table 1.
Comparison of five ML methods for predicting weekly average magnitude in terms of performance metrics.
In the present study, the best result for predicting the weekly average magnitude was achieved using the LSTM method, yielding values of 0.1391, 0.0193, 0.1046, and 3.0631% for RMSE, MSE, MAE, and MAPE performance metrics (Table 1 and Figure 14), respectively. Similarly, 1D-CNN performed very closely to LSTM results with RMSE, MSE, MAE and MAPE values of 0.1609, 0.0259, 0.1277 and 3.6695%, respectively. The results obtained from ANFIS and RF are also promising in terms of magnitude prediction.
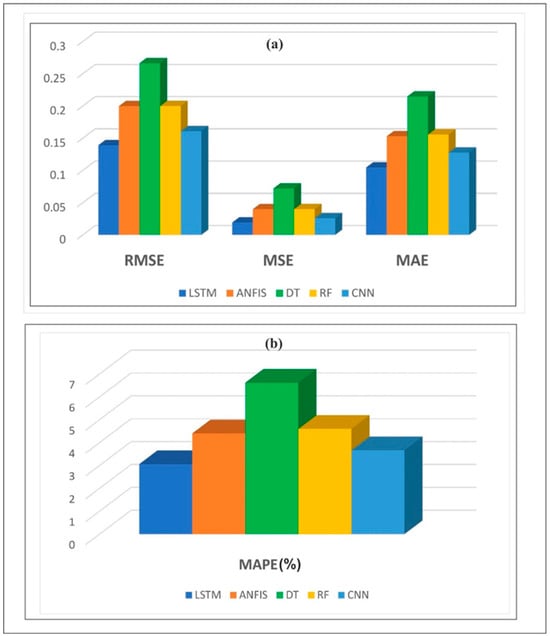
Figure 14.
Performance metrics of the applied five ML methods. (a) RMSE, MSE and MAE; (b) MAPE.
The maximum error values for RMSE, MSE, MAE and MAPE were obtained as 0.2683, 0.0720, 0.2147 and 6.6231%, respectively, due to the DT method in Western Turkey. However, it is essential to note that these results were found to be at an acceptable level compared with the results of other studies [,] in the literature that made earthquake magnitude predictions. Studies in the literature that predict magnitude have generally focused on either a single ML method [,,,,,] or two to three ML methods [,,,]. This study examines the performance of five different ML methods commonly used in earthquake prediction applications, using the same dataset for comparison. Öncel Çekim et al. [] utilised earthquakes of magnitude M > 3 that occurred in the Aegean region in their studies. They calculated the monthly average magnitudes of earthquakes in the region and analysed them using two time series methods, ARIMA and singular spectrum analysis (SSA), and two deep learning methods, convolutional neural networks (CNN) and long short-term memory (LSTM). Upon examining their results, the MAE and MSE values achieved were as follows: 0.1264 and 0.0324 for ARIMA, 0.1074 and 0.0229 for SSA, 0.1283 and 0.0300 for CNN, and 0.0618 and 0.0100 for LSTM. They obtained the best result with the LSTM method. Benrich et al. [] implement LSTM, Gated Recurrent Network (GRU), and their hybrid model (LSTM-GRU) to predict earthquakes that occurred in three different regions: Morocco, Japan, and Turkey. Their magnitude prediction results for six different clusters from Turkey revealed the following performance metrics: for LSTM: MSE values ranged from 0.01 to 0.06, RMSE values ranged from 0.11 to 0.25, and MAE values ranged from 0.08 to 0.18. For GRU: MSE values varied between 0.01 and 0.08, RMSE values ranged from 0.11 to 0.28, and MAE values ranged from 0.08 to 0.19. For the hybrid model (LSTM-GRU), MSE values ranged from 0.01 to 0.07, RMSE values varied between 0.11 and 0.26, and MAE values ranged from 0.08 to 0.19. Considering these results, since the current article’s study area covers only Western Turkey, the performance measures obtained for the relevant study’s western clusters and the values given in Table 1 are compatible. Similarly, Abebe et al. [] applied DL-based methods, such as the transformer algorithm, LSTM, bidirectional long short-term memory (BILSTM), and bidirectional long short-term memory with attention (BILSTM-AT), for magnitude prediction in the Horn of Africa. They achieved performances of 0.539, 0.453, 0.673, and 48.516% using LSTM; 0.518, 0.425, 0.652, and 43.542% using BI-LSTM; 0.368, 0.228, 0.477, and 36.287% using BI-LSTM-AT; and 0.276, 0.147, 0.383, and 28.868% using the Transformer model for the MAE, MSE, RMSE, and MAPE performance metrics, respectively, on the 3-month average magnitude values. When the results of the methods were examined, they obtained the best results were obtained from the Transformer model. In conclusion, a comparative analysis with existing literature indicates that the performance metrics obtained in this study are consistent with those reported in other studies, despite variations in the temporal resolution of the input data (i.e., using monthly and 3-month averages compared to the weekly average values utilised here). Notably, the present study findings align with the study of Öncel Çekim et al. [], who also identified the LSTM model as the most effective forecasting method. This study reinforces that conclusion, as the LSTM approach demonstrated slightly better performance across all evaluated metrics compared to the other four methods. Moreover, the performance of the CNN model in this study was closely aligned with the results reported by Öncel Çekim et al. [], demonstrating good reproducibility and consistency across different datasets and experimental setups. Consequently, as shown in Table 1, the findings of the present study, which employs five ML methods with different structures, are promising for predicting earthquake magnitudes.
6. Conclusions
Magnitude, one of the three critical parameters in earthquake prediction studies, was predicted by applying five different machine learning methods within the scope of this study. The study area was Western Turkey, one of the seismically active regions with many destructive earthquakes. Earthquake Catalogue data in the region between 1975 and 2024 were organised, and weekly average magnitude values were calculated. LSTM, ANFIS, DT, RF and 1D-CNN machine learning methods were applied to the dataset to predict the average magnitude for the following week. The LSTM method obtained the best results for RMSE, MSE, MAE, and MAPE performance metrics of 0.1391, 0.0193, 0.1046, and 3.0631%, respectively. Upon examination of the results, it was observed that the 1D-CNN method, following the LSTM method, yielded slightly better and more satisfactory outcomes compared to the other three ML methods: ANFIS, RF, and DT. The values obtained were as follows: an RMSE of 0.1609, MSE of 0.0259, MAE of 0.1277, and MAPE of 3.6695%. The ANFIS model demonstrated performance metrics with RMSE, MSE, MAE, and MAPE values of 0.1998, 0.0399, 0.1530, and 4.4062%, respectively. These results were very close to those of the RF model, which had RMSE, MSE, MAE, and MAPE values of 0.1999, 0.0400, 0.1557, and 4.6044%. While DT results tend to be relatively higher than those obtained with other methods, the performance metrics RMSE, MSE, MAE, and MAPE were 0.2683, 0.0720, 0.2147 and 6.6231%, respectively, all of which are within acceptable limits considering other studies in the literature.
Funding
This research received no external funding.
Data Availability Statement
The earthquake catalogue data used in this study were compiled by the following institutions: Republic of Turkey Prime Ministry Disaster and Emergency Management Presidency (AFAD) (T.C. İçişleri Bakanlığı Afet ve Acil Durum Yönetimi Başkanlığı), Kandilli Observatory and Earthquake Research Institute (KOREI) (Kandilli Observatory and Earthquake Research Institute) and United States Geological Survey (USGS) (Search Earthquake Catalogue|U.S. Geological Survey.
Acknowledgments
I would like to express my gratitude to the esteemed editor and the anonymous reviewers for their constructive contributions.
Conflicts of Interest
The author declares that they have no financial or personal conflicts of interest that could influence this article.
References
- Geller, R.J. Earthquake prediction: A critical review. Geophys. J. Int. 1997, 131, 425–450. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kossobokov, V.G.; Romashkova, L.L.; Keilis-Borok, V.I.; Healy, J.H. Testing earthquake prediction algorithms: Statistically significant advance prediction of the largest earthquakes in the Circum-Pacific, 1992–1997. Phys. Earth Planet. Inter. 1999, 111, 187–196. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Keilis-Borok, V.I. Earthquake Prediction: State-of-the-Art and Emerging Possibilities. Annu. Rev. Earth Planet. Sci. 2002, 30, 1–33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gorshkov, A.; Kossobokov, V.; Soloviev, A. Recognition of earthquake-prone areas. In Nonlinear Dynamics of the Lithosphere and Earthquake Prediction; Keilis-Borok, V., Soloviev, A., Eds.; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2003; pp. 239–310. [Google Scholar]
- Kossobokov, V.G. Earthquake prediction: 20 years of global experiment. Nat. Hazards 2013, 69, 1155–1177. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gorshkov, A.; Soloviev, A. Chapter 7—Morphostructural zoning for identifying earthquake-prone areas. In Earthquakes and Sustainable Infrastructure; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2022. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lomnitz, C. Fundamentals of Earthquake Prediction; Wiley: New York, NY, USA, 1994. [Google Scholar]
- Kaftan, I.; Şalk, M.; Şenol, Y. Evaluation of gravity data by using artificial neural networks case study: Seferihisar geothermal area (Western Turkey). J. Appl. Geophys. 2011, 75, 711–718. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kaftan, I.; Sındırgı, P.; Akdemir, O. Inversion of self potential anomalies with Multilayer Perceptron Neural Networks. Pure Appl. Geophys. 2014, 171, 1939–1949. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Crocker, J.; Kumar, K.; Cox, B. Using explainability to design physics-aware CNNS for solving subsurface inverse problems. Comput. Geotech. 2023, 159, 105452. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cho, S.; Pyun, S.; Choi, B.; Lee, G.; Jang, S.; Choi, Y. Prediction of S-wave velocity models from surface waves using deep learning. Near Surf. Geophys. 2023, 22, 281–297. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Santos, O.S.D.L.; Lemos, B.J.; Souza, D.V.A.P.; Cerqueira, G.A. Automatic Zero-Phase Wavelet Estimation from Seismic Trace Using a Multilayer Perceptron Neural Network: An Application in a Seismic Well-Tie. J. Appl. Geophys. 2024, 222, 105305. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, C.; Liu, G.; Liao, S. Probing fractured reservoir of enhanced geothermal systems with fuzzy-genetic inversion model: Impacts of geothermal reservoir environment. Energy 2024, 290, 130320. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roy, A.; Ekinci, Y.L.; Balkaya, Ç.; Ai, H. Deep learning-based inversion with discrete cosine transform discretization for two-dimensional basement relief imaging of sedimentary basins from observed gravity anomalies. Geophys. Prospect. 2025, 73, 113–129. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Toushmalani, R.; Essa, K.S.; Ibraheem, I.M. A Well-Structured Metaheuristic Optimization Technique for Magnetic Data Inversion of 2D Dipping Dyke-like Geological Structures Using the Cuckoo Optimization Algorithm. Arab. J. Sci. Eng. 2025, 50, 6663–6672. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kaftan, I.; Şalk, M.; Şenol, Y. Processing of earthquake catalog data of Western Turkey with artificial neural networks and adaptive neuro-fuzzy inference system. Arab. J. Geosci. 2017, 10, 243. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiao, P.; Alavi, A.H. Artificial intelligence in seismology: Advent, performance and future trends. Geosci. Front. 2020, 11, 739–744. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gök, E.; Kaftan, I. Prediction of Peak Ground Acceleration by Artificial Neural Network and Adaptive Neuro fuzzy Inference System. Ann. Geophys. 2022, 65, SE106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sedaghati, F.; Pezeshk, S. Ensemble Region-Specific GMMs for Subduction Earthquakes. Seismol. Res. Lett. 2023, 95, 1735–1758. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kubo, H.; Naoi, M.; Kano, M. Recent advances in earthquake seismology using machine learning. Earth Planets Space 2024, 76, 36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tan, A.; Horasan, G.; Kalafat, D.; Gülbaği, A. Comparison of a linear discrimination function and artificial neural networks approach to discriminate the seismic events in Ankara (Turkey). Ann. Geophys. 2024, 67, SE321. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kolivand, P.; Saberian, P.; Tanhapour, M.; Karimi, F.; Kalhori, S.R.N.; Javanmard, Z.; Heydari, S.; Talari, S.S.H.; Mousavi, S.M.L.; Alidadi, M.; et al. A systematic review of Earthquake Early Warning (EEW) systems based on Artificial Intelligence. Earth Sci. Inform. 2024, 17, 957–984. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, P.; Ren, T.; Shen, R.; Chen, H.; Liu, X.; Meng, F. Determination of earthquake focal mechanism via multi-task learning. Comput. Geosci. 2024, 184, 105513. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bodri, B. A neural network model for earthquake occurrence. J. Geodyn. 2001, 32, 289–310. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alves, E.I. Earthquake forecasting using neural networks: Results and future work. Nonlinear Dyn. 2006, 44, 341–349. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reyes, J.; Morales-Esteban, A.; Martínez-Álvarez, F. Neural networks to predict earthquakes in Chile. Appl. Soft Comput. 2013, 13, 1314–1328. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Al Banna, M.H.; Taher, K.A.; Kaiser, M.S.; Mahmud, M.; Rahman, M.S.; Hosen, A.S.; Cho, G.H. Application of artificial intelligence in predicting earthquakes: State-of-the-art and future challenges. IEEE Access 2020, 8, 192880–192923. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aslam, B.; Zafar, A.; Khalil, U.; Azam, U. Seismic activity prediction of the northern part of Pakistan from novel machine learning technique. J. Seismol. 2021, 25, 639–652. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Budiman, K.; Ifriza, Y.N. Analysis of earthquake forecasting using random forest. J. Soft Comput. Explor. 2021, 2, 153–162. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Berhich, A.; Belouadha, F.Z.; Kabbaj, M.I. A location-dependent earthquake prediction using recurrent neural network algorithms. Soil Dyn. Earthq. Eng. 2022, 161, 107389. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bhatia, M.; Ahanger, T.A.; Manocha, A. Artificial intelligence based real-time earthquake prediction. Eng. Appl. Artif. Intell. 2023, 120, 105856. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ommi, S.; Hashemi, M. Machine learning technique in the north Zagros earthquake prediction. Appl. Comput. Geosci. 2024, 22, 100163. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Z.; Wang, Y. A Global Earthquake Prediction Model Based on Spherical Convolutional LSTM. IEEE Trans. Geoscıence Remote Sens. 2024, 62, 1–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, P.; Fang, Y. Development of Attention-Based Bidirectional Long Short-Term Memory Networks for Earthquake Prediction in Taiwan. Nat. Hazards Rev. 2025, 26, 04025026. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Panakkat, A.; Adeli, H. Neural network models for earthquake magnitude prediction using multiple seismicity indicators. Int. J. Neural Syst. 2007, 17, 13–33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Adeli, H.; Panakkat, A. A probabilistic neural network for earthquake magnitude prediction. Neural Netw. 2009, 22, 1018–1024. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moustra, M.; Avraamides, M.; Christodoulou, C. Artificial neural networks for earthquake prediction using time series magnitude data or seismic electric signals. Expert Syst. Appl. 2011, 38, 15032–15039. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Asim, K.M.; Martinez-Alvarez, F.; Basit, A.; Iqbal, T. Earthquake magnitude prediction in Hindukush region using machine learning techniques. Nat. Hazards 2017, 85, 471–486. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pandit, A.; Biswal, K.C. Prediction of earthquake magnitude using adaptive neuro fuzzy inference system. Earth Sci. Inform. 2019, 12, 513–524. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Asim, K.M.; Moustafa, S.S.R.; Niaz, I.A.; Elawadi, E.A.; Iqbal, T.; Martínez-Alvarez, F. Seismicity analysis and machine learning models for short-term low magnitude seismic activity predictions in Cyprus. Soil Dyn. Earthq. Eng. 2020, 130, 105932. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abebe, E.; Kebede, H.; Kevin, M.; Demissie, Z. Earthquakes magnitude prediction using deep learning for the Horn of Africa. Soil Dyn. Earthq. Eng. 2023, 170, 107913. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Li, X.; Wang, Z.; Liu, J. Deep learning for magnitude prediction in earthquake early warning. Gondwana Res. 2023, 123, 164–173. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Berhich, A.; Belouadha, F.Z.; Kabbaj, M.I. An attention-based LSTM network for large earthquake prediction. Soil Dyn. Earthq. Eng. 2023, 165, 107663. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Öncel Çekim, H.; Karakavak, H.N.; Özel, G.; Tekin, S. Earthquake magnitude prediction in Turkey: A comparative study of deep learning methods, ARIMA and singular spectrum analysis. Environ. Earth Sci. 2023, 82, 387. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wessel, P.; Luis, J.F.; Uieda, L.; Scharroo, R.; Wobbe, F.; Smith, W.H.F.; Tian, D. The Generic Mapping Tools version 6. Geochem. Geophys. Geosyst. 2019, 20, 5556–5564. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hochreiter, S.; Schmidhuber, J. Long short-term memory. Neural Comput. 1997, 9, 1735–1780. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gers, F.A.; Schmidhuber, J.; Cummins, F. Learning to Forget: Continual Prediction with LSTM. Neural Comput. 2000, 12, 2451–2471. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jang, J.S.R. ANFIS: Adaptive-network-based fuzzy inference system. IEEE Trans. Syst. Man Cybern. 1993, 23, 665–685. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Breiman, L.; Friedman, J.H.; Olshen, R.A.; Stone, C.J. Classification and Regression Trees; Wadsworth: Monterey, CA, USA, 1984; 368p. [Google Scholar]
- Breiman, L. Random forests. Mach. Learn. 2001, 45, 5–32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- LeCun, Y.; Bengio, Y. Convolutional networks for images, speech, and time series. In The Handbook of Brain Theory and Neural Networks; Hal Open Science: Lyon, France, 1998. [Google Scholar]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the author. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).