Abstract
A learning management system (LMS) plays a crucial role in supporting students’ educational activities by centralized platforms for course delivery, communication, and student support. Recently, many universities have integrated chatbots into their LMS to assist students with various inquiries and tasks. However, existing chatbots often necessitate human interventions to manually respond to complex queries, resulting in limited scalability and efficiency. In this paper, we present a memory-augmented large language model (LLM) framework that enhances the reasoning and contextual continuity of LMS-based chatbots. The proposed framework first embeds user queries and retrieves semantically relevant entries from various LMS resources, including instructional documents and academic frequently asked questions. Retrieved entries are then filtered through a two-stage confidence filtering process that combines similarity thresholds and LLM-based semantic validation. Validated information, along with user queries, is processed by LLM for response generation. To maintain coherence in multi-turn interactions, the chatbot incorporates short-term, long-term, and temporal event memories, which track conversational flow and personalize responses based on user-specific information, such as recent activity history and individual preferences. To evaluate response quality, we employed a multi-layered evaluation strategy combining BERTScore-based quantitative measurement, an LLM-as-a-Judge approach for automated semantic assessment, and a user study under multi-turn scenarios. The evaluation results consistently confirm that the proposed framework improves the consistency, clarity, and usefulness of the responses. These findings highlight the potential of memory-augmented LLMs for scalable and intelligent learning support within university environments.
1. Introduction
A learning management system (LMS) is a digital platform that facilitates course delivery, resource sharing, assessment, and communication in higher education [1]. In the aftermath of the Coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19) pandemic, educational institutions have increasingly adopted both fully online formats and blended learning approaches that combine conventional classroom teaching with online components [2]. This shift has reinforced the role of the LMS as critical infrastructure for delivering accessible, scalable, and interactive learning experiences in universities. A modern LMS provides a wide range of functionalities, including lecture material distribution, assignment and assessment management, discussion forums, and communication tools that foster active engagement between students and instructors. These functionalities collectively promote learner engagement, support timely feedback, and have been shown to positively enhance academic outcomes. In addition to supporting learners, an LMS enables instructors to collect and respond to questions from the learners, thereby allowing for iterative refinement of course content. As a result, an LMS has become an indispensable component of the modern university curricula, with institutions leveraging its capabilities to enhance instructional effectiveness, learning accessibility, and student satisfaction [3].
To promote the effective use of an LMS in educational environments, learners must be sufficiently informed about how to navigate and operate the platform [4]. For example, learner proficiency in core features, such as posting and commenting in discussion forums, participating in polls, and attaching files, can facilitate active and meaningful peer interaction. In addition, essential LMS features, including the ability to resubmit assignments, to access online lecture links through the LMS interface, and to receive course announcements via email should be optimized to align with the learners’ environments and preferences. To address these challenges, an increasing number of universities have integrated chatbot systems that deliver real-time, context-aware support for LMS-related inquiries, thereby improving overall learning accessibility and user satisfaction [5,6,7].
The word “chatbot” is derived from “chat” and “robot”, representing an automated system for conversation [8]. In modern contexts, chatbots are defined as intelligent virtual assistants designed to assist users in navigating, operating, and interacting with software platforms [9]. In traditional chatbot systems, student inquiries are handled manually by university student assistants responding to each question [10]. However, this approach suffers from low efficiency, as it requires human assistants to interpret each query, to identify relevant information, such as specific sections of the LMS user manual, and to generate appropriate responses. Consequently, a reliance on manual processes imposes substantial constraints on the scalability and operational efficiency of chatbots in universities.
Recent advances in natural language processing (NLP) and large language models (LLMs) have drawn increasing attention to the growing interest in automating a chatbot system [11]. LLMs, which are pre-trained on large-scale textual corpora, exhibit strong capabilities in contextual comprehension and response generation [12]. By reducing reliance on human intervention, LLMs significantly improve the efficiency of chatbot deployment. In addition, the emergence of retrieval-augmented generation (RAG) has further accelerated the development of artificial intelligence (AI)-powered chatbots [13]. RAG enhances response accuracy by integrating language models with real time information retrieval. RAG retrieves relevant content from external knowledge bases in response to user queries and incorporates the retrieved information into the response generation process. By leveraging retrieved data into the generation process, RAG enables language models to overcome the static limitations of pre-training and to provide contextually relevant, up-to-date responses [14]. These advancements contribute to improved response quality, enhanced contextual understanding, and greater generalization capabilities in LLM-based chatbots.
In the context of higher education, a growing body of research has investigated the use of chatbots as student support tools, ranging from automated frequently asked question (FAQ) services to AI-driven academic advising systems [15,16,17]. These studies have consistently reported improvements in information accessibility, response speed, and learner engagement. Nevertheless, most existing implementations struggle to sustain coherent multi-turn dialogues or to adapt responses based on prior interactions. This limitation is particularly crucial in LMS environments, where students frequently ask follow-up questions that require the accurate recall of previous exchanges. Furthermore, only a few systems incorporate explicit mechanisms to filter out-of-scope or low-confidence responses, which is an essential capability for maintaining reliability and trust in institutional settings. These gaps highlight the need for an approach that combines robust memory capabilities with domain-relevance safeguards.
While recent LLM-based chatbots have demonstrated promising capabilities, more current implementations are limited to single-turn interactions [18]. However, in real-world educational environments, both learners and instructors frequently engage in multi-turn conversations, often characterized by follow-up questions and context-dependent inquiries. Relying solely on single-turn responses restricts the chatbot’s ability to maintain contextual continuity, often resulting in fragmented, ambiguous, or inaccurate answers. To generate coherent and contextually appropriate responses across multiple dialogue turns, it is essential for the chatbot to effectively retain and utilize conversational history. This necessitates the integration of a memory module that enables the chatbot to store and retrieve salient information from previous interactions. Therefore, a memory-augmented LLM-based chatbot can provide a promising solution for enhancing the continuity, relevance, and accuracy of responses in educational environments, including a university LMS.
In this paper, we propose a memory-augmented chatbot framework that integrates RAG with an LLM, specifically designed for development within a university LMS. The framework begins by preprocessing historical chat logs and FAQs into a question–answer format. A frozen pre-trained language model (PLM) is then used to generate embeddings and to construct the retrieval dataset. During inference, the chatbot retrieves the semantically most relevant entries based on the user query and assesses their relevance through a confidence check. If the retrieved information is considered sufficient, a re-ranking model and a memory module are employed to generate the final response. Otherwise, the chatbot returns a fallback message indicating that its inability provides a suitable answer. Following each interaction, both short-term and long-term memory are updated using retrieved information and integrated into the temporal event memory to preserve conventional context over time. This architecture enables the chatbot to maintain contextual continuity and to progressively improve response quality through memory-based refinement.
The main contributions of this paper are summarized as follows:
- We propose a memory-augmented chatbot framework that integrates RAG with an LLM to support context-aware multi-turn interactions within a university LMS.
- We design a memory module comprising short-term, long-term, and temporal event memories, which are continuously updated after each interaction to enhance dialogue continuity and contextual relevance.
- We develop structured prompt templates for key components of the proposed framework, including the confidence check, re-ranking model, and the memory module to guide the LLM in generating accurate responses and maintaining contextual consistency across multi-turn interactions.
- We validate the effectiveness of the proposed framework through BERTScore-based quantitative evaluation, an LLM-as-a-Judge approach, and a user study conducted within a real-world university LMS environment. The experimental results demonstrate that the proposed framework outperforms conventional chatbots in terms of contextual understanding, response relevance, and user satisfaction.
The remainder of this paper is organized as follows. Section 2 reviews the related works on chatbots. Section 3 describes the framework proposed in this study. Section 4 presents the dataset and the experimental settings. Section 5 reports the experimental results and provides an in-depth analysis. Section 6 discusses the study’s findings and proposes potential improvements. Finally, Section 7 concludes the paper and highlights avenues for future research.
2. Related Works
2.1. Chatbot Based on Conventional Natural Language Processing
Various studies have explored the development of chatbots capable of providing accurate responses using conventional NLP techniques. These chatbots typically rely on rule-based systems, pattern matching, or keyword extraction methods to interpret user input and to generate predefined responses.
Lalwani et al. [19] developed a college inquiry chatbot using traditional NLP and AI techniques to enhance user interaction on educational websites. The chatbot provided information related to admissions, examinations, academics, and student services through a conversational interface. This work demonstrated the use of rule-based and form-driven approaches to improve information accessibility in institutional contexts. Shiva et al. [20] proposed a modular framework for customer service chatbots that leverages NLP techniques, including intent classification, named entity recognition, and dialogue management. Their approach significantly improved user satisfaction and response accuracy compared to rule-based systems. Ortiz-Garces et al. [21] proposed an NLP-based chatbot that enhances response accuracy through advanced syntactic analysis. Their study highlighted the importance of grammatical structure and contextual keywords in understanding user intent and generating coherent answers.
However, these conventional NLP-based chatbots are inherently limited in handling complex, context-dependent queries and fail to maintain coherent multi-turn interactions. While they are effective for simple and repetitive inquiries, they lack robust mechanisms for dynamic context tracking, personalization, and domain adaptation, which are essential in modern LMS environments. This shows that, while conventional NLP approaches ensure a certain level of precision and control, they remain fundamentally inadequate for sustaining the complex, adaptive, and context-aware dialogue required in higher education settings.
2.2. Chatbot Based on Large Language Model
With the emergence of LLMs, chatbots have evolved to handle complex tasks with greater fluency and contextual awareness. These chatbots enable more natural interactions and can be customized for various purposes.
Yigci et al. [22] investigated the potential applications and implications of LLM-based chatbots in higher education. Their study highlighted both opportunities for personalized learning and risks related to academic integrity, misinformation, and ethical concerns. While acknowledging ongoing challenges, the study emphasized the transformative potential of LLMs in reshaping educational experiences. Smutny and Bojko [23] conducted a comparative study of LLM-based chatbots in the context of web development tasks. They evaluated LLM-based chatbots using criteria including accuracy, completeness, and security. The results showed that conversational chatbots outperformed programming assistants, particularly in managing open-ended tasks with minimal user guidance. Yang et al. [24] developed Quokka, an open-source LLM-based chatbot built on LLaMA-2. The chatbot was specialized for material science through continued pre-training on over one million domain-specific research articles. It was then instruction-tuned to provide accurate and contextually relevant responses for researchers, educators, and students in the field.
While LLM-based chatbots have demonstrated superior adaptability and contextual reasoning compared to conventional NLP-based chatbots, most existing implementations in the education domain either focus on a general question–answer format without explicit mechanisms for long-term context retention or lack safeguards for domain-relevance filtering. These shortcomings limit their reliability in specialized institutional environments, where both contextual continuity and response validity are critical. In contrast to conventional NLP chatbots, LLM-based systems achieve semantic depth but fall short in domain control and sustain coherence, indicating that adaptability alone does not ensure reliability in LMS applications.
2.3. Memory-Augmented Dialogue System
As dialogue systems, including chatbots, are increasingly required to manage multi-turn interactions and to maintain long-term context, memory-augmented architectures have emerged as a promising solution. These systems incorporate external or structured memory modules to enhance contextual consistency, to retain information across turns, and to improve the quality of generated responses.
Wu [25] explored the use of memory-augmented neural networks (MANNs) and neural copy mechanisms to improve task-oriented dialogue systems. The study introduced a transferable dialogue state generator for ontology-free state tracking and applied MANNs to enhance retrieval-based dialogue learning. It also proposed memory-to-sequence and global-to-local memory pointer networks to improve generation-based dialogue models. Wu and Yu [26] proposed a stateful memory-augmented transformer architecture designed to address the limitations of conventional encoder–decoder models in preserving long dialogue history. Their approach integrated an external memory module with pre-trained transformers to enable the efficient exchange of contextual information between past and current inputs. The experimental results on multiple dialogue and language modeling benchmarks demonstrated superior performance and efficiency compared to standard transformer baselines. He et al. [27] introduced MADial-Bench, a benchmark designed to evaluate memory-augmented dialogue systems through cognitively grounded memory-recall paradigms.
Although prior research has demonstrated the value of memory in enhancing dialogue coherence, most studies have focused on either generic conversational benchmarks or task-oriented domains outside the LMS context. Moreover, few studies have examined the combined impact of memory augmentation and domain-specific confidence checks to ensure both contextual accuracy and scope relevance. Thus, while memory-based systems improve coherence, their lack of LMS-specific adaptation and validation mechanisms means they cannot independently ensure trustworthy and contextually appropriate responses in educational settings.
2.4. Research Gap and Our Contribution
Across the three research streams reviewed above, namely conventional NLP-based chatbots, LLM-based chatbots, and memory-augmented dialogue systems, progress has been made along different dimensions: precision and structure, semantic adaptability, and contextual retention. However, these contributions remain fragmented and fail to meet the integrated requirements of modern LMS environments. Conventional NLP systems ensure structure but lack adaptability, LLM-based chatbots achieve semantic depth but overlook long-term coherence and domain control, and memory-augmented architectures enhance context retention but are rarely validated in LMS-specific scenarios.
This fragmented landscape reveals an unresolved gap: the absence of a unified framework that combines semantic adaptability, contextual continuity, and domain reliability. Our study addresses this gap by proposing an LLM-driven chatbot framework that integrates short-term, long-term, and temporal event memory modules with a confidence check mechanism for domain-specific filtering. By consolidating these complementary strands, the proposed framework ensures multi-turn coherence, improves contextual reasoning, and enhances response validity in LMS environments. Unlike prior studies that have examined these components in isolation, our work is the first to synthesize them within a single architecture tailored for educational applications, thereby providing both conceptual novelty and practical value. In doing so, our study advances beyond descriptive implementations to provide an analytically grounded synthesis of prior research streams, establishing a novel and robust approach tailored for educational applications.
3. Proposed Framework
This section describes the overall structure of the framework proposed in this study. Figure 1 illustrates the overall architecture of the proposed framework.
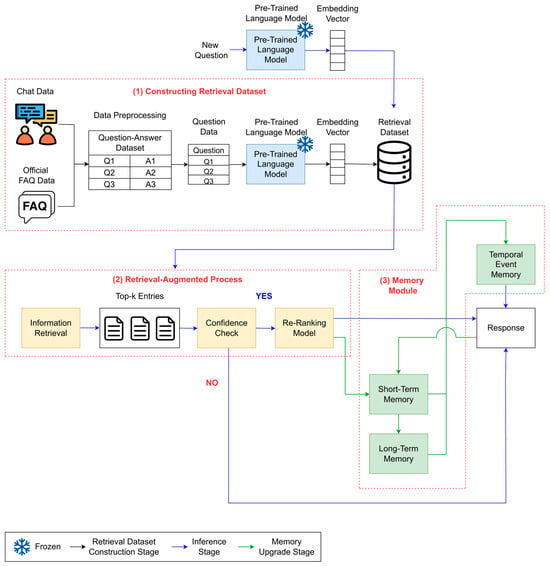
Figure 1.
Overall architecture of the proposed framework.
3.1. Constructing Retrieval Dataset
To enable retrieval-augmented response generation in LMS environments, it is essential to construct a dedicated dataset of semantically searchable content. Conventional LMS FAQ repositories and chatbot logs typically rely on keyword-based matching, which fails to capture semantic variations in user queries and results in irrelevant retrievals. To overcome this limitation, we design a two-stage pipeline for constructing a domain-specific retrieval dataset. In the first stage, raw chatbot logs and LMS FAQ data are preprocessed into a clean and structured question–answer format. In the second stage, the questions are converted into semantic embeddings using a Korean PLM. This resulting dataset serves as the foundation of the RAG pipeline, enabling the high-precision retrieval of relevant context. The details of each stage are described in Section 3.1.1 and Section 3.1.2.
3.1.1. Text Data Preprocessing
To construct a retrieval dataset for semantically relevant information selection, accumulated chatbot conversation logs from the university LMS and the official FAQ data are preprocessed into a structured question–answer format. Text preprocessing includes removing unnecessary characters and stopwords, and applying stemming and lemmatization to ensure consistency. These steps improve the model’s ability to interpret and process user input [28].
Previously, chatbot queries were addressed by student assistants through manual responses, and these interactions have been systematically archived. The accumulated records serve as valuable resources for constructing the retrieval dataset. To develop a general-purpose LMS chatbot for handling public inquiries, records containing personally identifiable information, such as instructor names and course titles, are excluded. Frequently, greeting and closing remarks are removed from both the question and the answer texts to enhance retrieval performance. Given that the chatbot targets a Korean university LMS, non-Korean dialogues are excluded to ensure linguistic consistency within the dataset. Through these preprocessing steps, a refined and standardized question–answer dataset is constructed as the foundation for the RAG system.
3.1.2. Generating Embedding Vector Using Pre-Trained Language Model
Semantic embedding vectors are generated from the preprocessed dataset, as described in Section 3.1.1. Since the chatbot receives user queries as input, embeddings are generated solely for question data exclusively using a PLM with frozen weights. The embedding generation process using the PLM is illustrated in Figure 2.
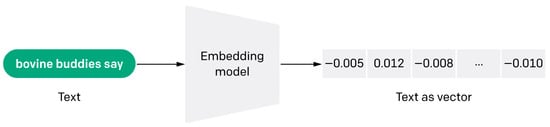
Figure 2.
Generating embedding vector using pre-trained language model as the embedding model.
As PLMs are trained on large-scale text corpora, they can capture contextual semantics from input text [29]. However, fine-tuning such large models on new data demands substantial computational resources [30]. Moreover, partial fine-tuning frequently leads to catastrophic forgetting, where previously acquired knowledge deteriorates [31]. To mitigate this issue, this study freezes the PLM’s weights to enable resource-efficient adaptation. This approach preserves the model’s generalization capacity while maintaining its ability to generate meaningful semantic representations [32].
Considering that user queries typically compose complete sentences, this study utilizes Sentence-BERT (SBERT) to extract sentence-level semantic embeddings [33]. SBERT modifies the bidirectional encoder representations from transformer (BERT) architecture [34] to produce fixed-size embeddings that effectively preserve contextual sentence meaning. As this study focuses on Korean language data, the ko-sbert-sts model is employed, which is a variant of SBERT fine-tuned on Korean sentence pairings [35]. The model leverages the KorNLU dataset, a resource specifically designed to enhance sentence-level semantic understanding in Korean [36]. It has been widely adopted for generating embeddings for Korean sentences.
3.2. Retrieval-Augmented Process
The retrieval-augmented process enhances both factual accuracy and contextual relevance by incorporating domain-specific knowledge into response generation. The process begins with semantic retrieval, where a user query is embedded and compared against the LMS dataset to identify the top-k most relevant entries, as detailed in Section 3.2.1. Unlike conventional RAG implementations, our framework introduces an additional two-stage confidence check and LLM-based re-ranking, ensuring that irrelevant or misleading content is filtered out before response generation. The entries are then passed through a two-stage confidence check to filter out irrelevant or misleading information, which is described in Section 3.2.2. Finally, the validated entries are re-ranked and contextually aligned using an LLM-driven model, as explained in Section 3.2.3, which further strengthens the reliability by prioritizing the most relevant knowledge. This structured pipeline ensures that only high-quality and contextually appropriate information informs the final response. It represents a novel integration of retrieval validation and ranking tailored for LMS environments.
3.2.1. Semantic Retrieval from LMS Dataset
The retrieval dataset constructed in Section 3.1 serves as the foundation for identifying semantically relevant entries in response to new user queries. When a new question is submitted to the chatbot, it is first converted into an embedding vector using the process illustrated in Figure 2. Based on the resulting embedding, the chatbot retrieves the top-k entries from the dataset that exhibits the highest semantic similarity.
To identify the most relevant results, cosine similarity is utilized to measure the semantic closeness between the user query and each dataset entry, as described in Equation (1) [37]. Here, A denotes the embedding vector of the user query, while B represents the embedding vector of a dataset entry, and n indicates the dimensionality of the vectors. Cosine similarity is calculated by dividing the dot product of the two vectors by the product of their magnitudes.
This method provides scalability for large datasets while maintaining computational efficiency, making it feasible for real-time deployment in institutional settings. Moreover, unlike keyword-based retrieval, semantic embedding retrieval allows the chatbot to handle diverse linguistic expressions of the same intent, which is crucial for LMS queries that vary across courses and users.
The top-k entries retrieved through this process are subsequently passed to downstream stages as reference materials for response generation. These retrieved entries serve as external knowledge sources that complement the LLM’s inherent knowledge, thereby enhancing both the contextual relevance and factual accuracy of the generated responses.
3.2.2. Confidence Check
To ensure response accuracy, the top-k entries retrieved in Section 3.2.1 should be assessed for their relevance to the user query. Incorporating low-relevance data as references risks propagating misleading information into the response, thereby reducing both factual accuracy and user trust [14]. Therefore, if the retrieved entries are not sufficiently relevant to the user query, no reference data is utilized for response generation.
To enhance the reliability of this retrieval validation process, we employ a two-stage confidence check module. Figure 3 illustrates the two-stage confidence check process for verifying the relevance of the retrieved content. In the first stage, the cosine similarity between the user query and each of the top-k retrieved entries is calculated. If the maximum similarity score exceeds a predefined threshold, a second-stage LLM-driven semantic evaluation is performed. The LLM evaluates the semantic relevance of each retrieved entry to the user query based on a structured prompt.
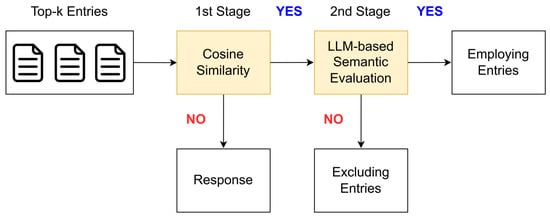
Figure 3.
Process of the two-stage confidence check.
Table 1 presents the structured prompt template utilized for the second-stage confidence check. Fields enclosed in curly brackets are dynamically populated based on the user’s input to the chatbot. The prompt consists of five components: role description, task specification, user query, retrieved entries, and output format. Role description defines the LLM’s role as a domain expert in retrieval systems and NLP. Task specification instructs the model to evaluate whether each retrieved entry is semantic relevant to the user query. The user query and the list of retrieved entries are provided in separate fields. The output format is a numbered list of binary decision, ‘Yes’ if the retrieved entry is relevant, or ‘No’ otherwise. This design minimizes hallucination risks and enforces domain-relevance filtering beyond what statistical similarity alone can achieve.

Table 1.
Template for prompt in confidence check.
Only the retrieved entries that successfully pass both stages of the confidence check are utilized for response generation. If none of the retrieved entries meet the similarity threshold or semantic relevance criteria, the chatbot refrains from generating an answer and instead returns a fallback response indicating that no sufficiently relevant information is available. This mechanism prevents the inclusion of misleading knowledge, increases user trust, and promotes transparency by explicitly acknowledging when the system lacks reliable references. Such an approach serves as an essential safeguard in LMS environments where inaccurate guidance can cause academic or administrative confusion.
3.2.3. Re-Ranking Model
To further enhance the relevance of the retrieved entries used for response generation, we incorporate a re-ranking model following the confidence check. Although the top-k entries are initially retrieved based on cosine similarity, this metric primarily captures general semantic similarity and may fail to accurately reflect contextual relevance to the user query.
The re-ranking model addresses this limitation by leveraging an LLM to evaluate the semantic alignment between each retrieved entry and the user query [38]. Specifically, the query and the set of confidence-validated entries are provided as input to the LLM, which computes a relevance score for each entry based on its contextual suitability. A listwise ranking approach is adopted, whereby the LLM evaluates all entries simultaneously and ranks them according to relevance. This evaluation enables the LLM to assign relative relevance scores, ensuring that the knowledge most aligned with the query’s intent is prioritized.
Table 2 presents the structured prompt template used to guide the LLM in re-ranking the confidence-validated entries. Consistent with Table 1, the prompt follows a five-component structure: role description, task specification, user query, retrieved entries, and output format. Elements enclosed in curly brackets represent variable fields dynamically populated based on the input. Role description defines the LLM’s domain expertise, while task specification instructs it to evaluate each entry based on semantic alignment and contextual relevance to the user query. The user query and the list of retrieved entries are provided in separate fields. The output format requests the LLM to return the entry numbers in descending order of relevance, thereby generating a ranked list that guides subsequent response generation.

Table 2.
Template for prompt in re-ranking model.
By refining the order of retrieved entries based on contextual relevance, the re-ranking model serves as a critical role that complements both statistical similarity and semantic filtering. Positioned between the confidence check and response generation, the re-ranking model ensures that the most contextually relevant information is prioritized. As a result, the framework not only improves factual accuracy but enhances coherence, instructional clarity, and user trust, thereby providing benefits over conventional retrieval-augmented methods that rely solely on similarity scores.
3.3. Memory Module
To support multi-turn interactions, the proposed framework incorporates a memory module comprising short-term, long-term, and temporal event memories. After each dialogue turn, these components are updated with the user query, retrieved content, and system response. While short-term and long-term memories capture recent context and cumulative user-specific data, respectively, the temporal event memory integrates both to provide a comprehensive dialogue history. This integrated history is then leveraged to generate coherent and context-aware responses. The structure and function of each memory type are detailed in Section 3.3.1, Section 3.3.2 and Section 3.3.3.
3.3.1. Short-Term Memory
Short-term memory captures key information from the most recent interaction to maintain immediate conversational context and to guide subsequent dialogue turns. This mechanism ensures that the chatbot remains contextually aware of ongoing conversations while minimizing unnecessary information retention.
Short-term memory extracts essential information from each dialogue to generate a structured summary of the current conversational state. Specifically, it identifies three key components: user intent, entities mentioned, and relevant facts. This concise representation facilitates efficient dialogue tracking and supports downstream modules, including long-term memory updating and temporal event memory synchronization.
The extraction process is performed by prompting an LLM with a structured instructional template, as presented in Table 3. The prompt follows a six-component structure: role description, task specification, user query, retrieved entries, generated answer, and output format. The role description defines the LLM’s role as a short-term memory agent for the chatbot, and the task specification instructs it to extract only essential information from the provided input. The user query, retrieved entries, and generated answers are supplied as separate input fields. The output format requires the LLM to produce a structured summary containing intent, entities, and facts.

Table 3.
Template for prompt in short-term memory.
Unlike conventional approaches that simply store raw dialogue history, this module introduces a selective and structured summarization process. This novelty allows the framework to reduce noise, to maintain coherent context, and to deliver more reliable responses in LMS environments.
3.3.2. Long-Term Memory
Long-term memory maintains a structured user profile that accumulates personalized information over extended interactions. Its primary role is to capture stable user-specific knowledge, including interests, preferences, entities, and known facts, thereby enabling the chatbot to generate progressively personalized and contextually relevant responses in future interactions.
To perform this function, long-term memory analyzes recent conversational data stored in short-term memory and selectively integrates meaningful updates into the long-term memory. As short-term memory may include both redundant and new information, long-term memory uses an LLM-based process to evaluate and filter updates before applying changes.
The process is guided by a structured prompt to ensure selective and consistent updates, as presented in Table 4. The prompt follows a five-component structure: role description, task specification, current long-term profile, recent short-term memory, and output format. The role description assigns the LLM as a long-term memory agent, while the task specification directs it to analyze incoming information, to update relevant fields as needed, and to maintain memory consistency. Current long-term memory and recent short-term memory are provided as input fields. The output format requires the LLM to generate a structured and concise update of long-term memory, categorized into interests, preferences, entities, and facts.

Table 4.
Template for prompt in long-term memory.
Following this prompt template, long-term memory systematically maintains an up-to-date user memory that accurately reflects evolving user behaviors, preferences, and knowledge. This incremental update mechanism enables scalable personalization while preserving the stability of accumulated user information. In contrast to conventional methods that rely on static user profiles, this dynamic update process provides clear benefits by continuously adapting to changing contexts, thereby improving both personalization and response reliability.
3.3.3. Temporal Event Memory
Temporal event memory functions as a consistency management that synchronizes short-term and long-term memories to maintain a unified user context. While short-term memory captures recent conversational details and long-term memory retains accumulated user knowledge, discrepancies may arise between the two sources as user interactions evolve. Temporal event memory systematically reconciles these differences, enabling the chatbot to sustain coherent, contextually informed, multi-turn dialogues.
Temporal event memory operates by receiving updated information from both short-term and long-term memory. It first compares this memory to detect any new facts, entities, interests, and preferences present in short-term memory but not yet reflected in long-term memory. If conflicts or inconsistencies are found, predefined resolution rules are applied to preserve consistency and to prevent contradictions. After resolving conflicts, temporal event memory maintains an event timeline that records significant updates or adjustments during the synchronization process. This timeline ensures traceability and auditability of the chatbot’s memory update history.
The process is guided by a structured LLM prompt designed to perform memory synchronization, as presented in Table 5. The prompt follows a five-component structure: role description, task specification, short-term memory, long-term memory, and output format. The role description defines the LLM’s role as a temporal event memory agent, while the task specification instructs the model to compare both short-term and long-term memory, to resolve inconsistencies, and to maintain a coherent update record. Short-term and long-term memory are provided as distinct input fields. The output format specifies the structure for both the updated long-term memory and the event timeline.

Table 5.
Template for prompt in temporal event memory.
Following this structured prompting framework, temporal event memory maintains a unified, up-to-date representation of user context, which serves as input for final response generation. Unlike conventional frameworks that treat memory modules independently, this integration provides practical gains by ensuring cross-memory consistency, enhancing contextual continuity, and enabling more reliable personalization in multi-turn dialogues.
3.4. Large Language Model-Based Response Generation
Response Generation
Response generation generates the chatbot’s final answers. It synthesizes multiple information sources to produce contextually appropriate, accurate, and personalized responses for the user. To achieve robust and reliable generation, two distinct pathways are implemented based on the availability of sufficient information in the retrieved entries.
When sufficient relevant information is available, as illustrated in Table 6, the response generation module integrates three primary inputs: the user query, the retrieved entries, and the updated user profile produced by the temporal event memory module. The retrieved entries provide external knowledge sources, while the user profile supplies accumulated personalization data, including interests, preferences, entities, and known facts. Guided by this structured prompt, the LLM analyzes the query, incorporates both the retrieved information and the user profile data, and generates a factually accurate, personalized response tailored to the user’s inquiry.

Table 6.
Template for prompt in response generation—Case (1) references to the given queries can provide meaningful information.
Conversely, when the retrieved entries lack sufficient information, the chatbot activates a fallback message, as shown in Table 7. In this scenario, the LLM is prompted to recognize the lack of information and to generate a polite and informative message indicating that no reliable answer can be provided under the current circumstances. This process prevents the generation of inaccurate or speculative responses.

Table 7.
Template for prompt in response generation—Case (2) references to the given queries cannot provide meaningful information.
This dual-path framework not only safeguards factual accuracy but highlights a clear improvement over conventional response generation approaches that rely on a single retrieval-dependent pipeline. By explicitly incorporating a fallback mechanism and personalization-aware integration, the proposed framework ensures higher transparency, reliability, and user trust in LMS-specific contexts.
4. Experimental Design
4.1. Dataset
This study utilized chatbot conversation data collected from the operation of a university LMS chatbot between 1 January 2022 and 30 June 2023, along with official FAQ data published on the LMS. Table 8 summarizes the dataset used in the experiments. Example entries are presented in Table 9 in English, while the original Korean texts are provided in Appendix A for reference. Through preprocessing, a total of 2435 question–answer pairs were extracted from 44,763 chatbot conversation logs and 183 FAQ records.

Table 8.
Summary of dataset.

Table 9.
Example of dataset.
4.2. Experimental Settings
To validate the effectiveness of the proposed framework, we evaluated chatbot’s ability to generate contextually appropriate responses under controlled conditions. Specifically, we compared its response behavior with and without the proposed memory module, which constitutes a core component of our framework. Here, the ‘without memory module’ setting corresponds to a strong RAG baseline, where RAG is fully implemented but conversational context is not retained across turns. By contrast, the ‘with memory module’ setting represents an enhanced configuration, where the memory module is integrated on strong RAG baseline to enable more coherent and context-aware multi-turn interactions.
Additionally, we evaluated the confidence check module to verify its ability to reliably filter irrelevant queries. Importantly, this evaluation was conducted in the combination of RAG baseline and memory-augmented setting, where both retrieval and dialogue continuity were already ensured. The confidence check was thus assessed for its capacity to constrain responses strictly within the predefined knowledge scope, preventing the chatbot from generating inaccurate or out-of-domain outputs during multi-turn conversations.
Regarding the confidence check, experiments were conducted using the following three query categories: (1) queries directly related to the LMS, (2) queries related to university topics but not specific to the LMS, and (3) queries unrelated to both the university and the LMS. As described in Section 3.2.1, the number of top-ranked entries retrieved for each query was set to five. The similarity threshold for the confidence check, as detailed in Section 3.2.2, was fixed at 0.7.
Both the memory module and the confidence check module were evaluated using 30 queries per category, and the chatbot’s responses were subsequently analyzed for appropriateness and consistency. Figure 4 illustrates the deployed service interface of the proposed framework, which was implemented as a web-based application using Streamlit [39]. This deployment enabled seamless interaction with the chatbot through a user-friendly interface, facilitating both controlled experimental testing and potential real-world use within the LMS environment. For privacy and security purposes, the actual service uniform resource locator (URL) displayed in the figure has been masked with a black box.
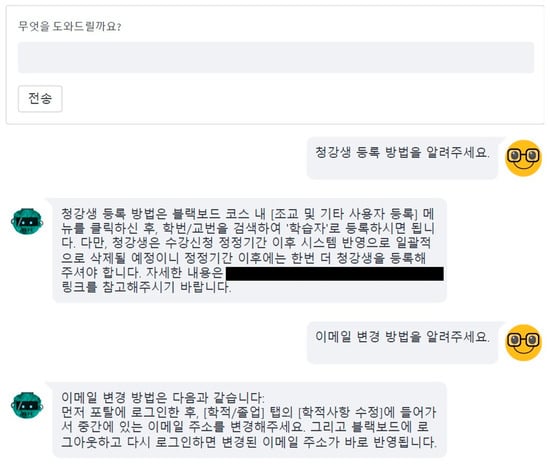
Figure 4.
Service image for the proposed framework. The example queries shown in Korean include “청강생 등록 방법” (Auditing student registration) and “이메일 변경 방법” (Email modification). The chatbot responses provide step-by-step instructions in Korean to reflect the actual LMS environment.
4.3. Evaluation Metrics
To evaluate the performance of the proposed framework, we adopted a three-tiered evaluation strategy that combines automated semantic similarity scoring, automated model-based assessment, and human-centered user evaluation. This layered approach enables both scalable performance benchmarking and practical usability validation, thereby offering a comprehensive view of the system’s capabilities. The evaluation was conducted separately for the two key components of the framework: the memory module and the confidence check module. Specifically, Section 4.3.1 describes a semantic similarity evaluation using BERTScore to assess the accuracy of the chatbot responses, and Section 4.3.2 presents an evaluation using the LLM-as-a-Judge approach. Section 4.3.3 describes a user study designed to assess the perceived effectiveness and satisfaction in real-world usage.
4.3.1. BERTScore-Based Evaluation
To establish a quantitative baseline for response accuracy, we first employed BERTScore as an automated evaluation metric. BERTScore is a widely adopted semantic similarity measure that computes the alignment between system-generated responses and ground-truth reference answers using contextual embeddings derived from pre-trained transformer models [40]. Unlike surface-level lexical overlap metrics, such as bilingual evaluation understudy (BLEU) [41] or recall-oriented understudy for gisting evaluation (ROUGE) [42], BERTScore captures deeper semantic correspondence, thereby providing a more reliable indicator of the factual correctness and linguistic adequacy of responses.
Formally, given a candidate response and a reference response , token embeddings are extracted from a pre-trained transformer model. The similarity between token embeddings is computed as cosine similarity, as shown in Equation (2). Here, indexes the embedding dimensions. Based on these similarities, BERTScore precision is defined as the average maximum similarity of each candidate token with the reference tokens, as shown in Equation (3). BERTScore recall is computed conversely as the average maximum similarity of each reference token with the candidate tokens, as shown in Equation (4). Finally, the BERTScore F1 score integrates both aspects using the harmonic mean, as given in Equation (5).
In our evaluation, we constructed a reference set of standard responses for both the memory module and the confidence check module test cases. Each system output was compared against the corresponding reference, and the BERTScore was calculated along three dimensions: precision, recall, and F1 score. Since our dataset consists of Korean dialogue, we utilized a Korean pre-trained BERT model (KoBERT) [43] to compute token embeddings for the BERTScore. This adaptation allows the metric to more faithfully capture semantic similarity in the Korean language. Precision reflects the extent to which the generated response content is semantically consistent with the reference, while recall measures the degree to which relevant content from the reference is preserved. The F1 score provides a balanced summary by integrating both aspects.
Nevertheless, we acknowledge that BERTScore, while highly effective for measuring semantic similarity, does not fully capture aspects such as contextual coherence, response helpfulness, or appropriateness of fallback strategies. To address these dimensions, we complemented the BERTScore-based evaluation with LLM-as-a-Judge scoring, described in Section 4.3.2, and a human-centered user study, described in Section 4.3.3. This layered evaluation framework ensures a balanced and comprehensive assessment of both factual accuracy and practical usability.
4.3.2. LLM-As-a-Judge Evaluation
In this study, we employed an LLM-as-a-Judge approach to automatically assess response quality across various conversation scenarios. LLM-as-a-Judge is an automated evaluation method in which an LLM scores system outputs based on predefined criteria [44]. By leveraging its reasoning and contextual understanding capabilities, this approach offers a scalable and consistent alternative to traditional human annotation. When guided by clear instructions and scoring definitions, the LLM-as-a-Judge can approximate expert-level judgments, making it a reliable proxy for human evaluation. We used OpenAI GPT-4o as the evaluation model and applied a 5-point Likert scale [45] to assess the chatbot output based on criteria specific to each module and test case. In this scale, a score a 1 indicates very poor performance, while a score of 5 indicates excellent performance. A complete list of all evaluation criteria is provided in Table 10.

Table 10.
Evaluation criteria used in the LLM-as-a-Judge, based on a 5-point Likert Scale.
For the memory module, multi-turn dialogues were evaluated along five criteria: contextual consistency, memory utilization, response relevance, overall coherence, and helpfulness. These criteria measure the chatbot’s ability to retain conversational flow, to leverage previous context, and to generate informative and coherent responses. For the confidence check module, evaluations were conducted for the three query categories defined in Section 4.2. Each case was assessed using five tailored criteria reflecting the objectives of safe and context-aware response generation. For example, Case 1 emphasized response clarity, factuality, helpfulness, and strategic appropriateness. Case 2 and Case 3 prioritized graceful fallback behavior, including politeness, redirection quality, and rejection appropriateness.
This automated procedure enabled consistent and scalable quality assessment without requiring manual annotation, providing a robust surrogate for expert judgment across diverse evaluation scenarios.
4.3.3. User Study Evaluation
In parallel, a user study was conducted with 30 university students to gather direct feedback on the chatbot’s usability and perceived quality. The participants were recruited specifically for the study through a university-wide call, independent of any specific course module. Each participant completed the evaluation individually and without mutual discussion, thereby ensuring the independence of ratings. Moreover, all participants had prior experience using the university’s actual LMS platform in real academic settings. This ensured that their assessments reflected authentic usage expectations and practical relevance.
The participants interacted with the chatbot and rated their experiences using a 5-point Likert scale, where 1 indicates “very dissatisfied” and 5 indicates “very satisfied”. For the memory module, user feedback focused on five criteria: usefulness, reliability, clarity, consistency, and overall satisfaction, as shown in Table 11. These criteria reflect the chatbot’s ability to maintain multi-turn coherence and to deliver trustworthy and understandable responses. For the confidence check module, the evaluation focused on the chatbot’s capacity to deliver accurate and contextually appropriate responses, as well as its ability to gracefully handle uncertainty by issuing polite and informative refusals when applicable. The assessment employed five criteria: appropriateness, accuracy, clarity, avoidance of irrelevant or made-up information, and overall satisfaction.

Table 11.
Evaluation criteria used in the user study, based on a 5-point Likert Scale.
In addition to the Likert-scale ratings, the participants were asked to answer two open-ended questions regarding their experience: (1) What aspects of the chatbot did you find particularly helpful? (2) What aspects could be improved? These qualitative responses were collected to identify recurring themes in user perception, to reveal areas of practical strength, and to uncover specific limitations not captured by the fixed-scale evaluation.
We acknowledge that the sample size of 30 participants, while consistent with prior exploratory user studies in human–computer interaction and educational chatbot research, represents a relatively small cohort. As such, the findings should be interpreted as indicative rather than fully generalizable. Nevertheless, this sample was sufficient to capture recurring themes, to identify usability strengths and weaknesses, and to validate the feasibility of the proposed framework in a realistic setting. Future studies will extend this evaluation by incorporating larger and more diverse participant groups across different courses, institutions, and demographic backgrounds to strengthen the statistical robustness and generalizability of the results.
This human-centered evaluation complements the automated LLM scoring by capturing subjective impressions, expectations, and levels of trust, which are critical in real-world educational applications. By applying this dual evaluation framework across both modules, we ensure a balanced and comprehensive analysis of system performance. The integration of model-based and human-centered perspectives provides a robust foundation for evaluating the effectiveness, reliability, and usability of memory-augmented conversational AI in LMS environments.
5. Experimental Results
5.1. Evaluation of Memory Module
To evaluate the effectiveness of the memory module, we conducted a multi-turn interaction experiment representing a realistic LMS helpdesk scenario. The test session consisted of ten consecutive dialogue turns, in which the user inquired about various topics related to assignment submission, modification, technical issues, plagiarism checks, instructor feedback, and error handling. The detailed experimental results are presented in Table 12, which contains English-translated dialogue excerpts for clarity. The original Korean interactions are included in Appendix A for reference. The experiment was performed under two settings: (1) without the memory module, where each query was treated independently without any conversational context, and (2) with the memory module, where the memory module was utilized to maintain dialogue continuity.

Table 12.
Evaluation of memory module—with and without memory module.
The results demonstrated that incorporating the memory module significantly improved the chatbot’s ability to handle context-dependent queries and to sustain coherent multi-turn conversations. In the memory-augmented setting, the chatbot referenced prior interactions, avoided redundant explanations, and generated responses that reflected accumulated user context. For example, when the user asked about resubmitting an assignment, the chatbot correctly acknowledged the prior submission and provided more personalized guidance regarding resubmission options. Similarly, when follow-up questions involved previously discussed deadlines, submission errors, or instructor permissions, the memory module enabled the chatbot to generate responses that were more adaptive and relevant. By contrast, without the memory module, the chatbot frequently repeated generic instructions without awareness of prior exchanges. This led to less efficient dialogues, with redundant information being presented repeatedly across turns. The lack of accumulated user context also limited the chatbot’s ability to provide nuanced responses to follow-up queries.
To complement this qualitative analysis, we computed the BERTScore on the original Korean dialogues using KoBERT [43]. The results, including the mean and standard deviation (SD) for each criterion, are summarized in Table 13. The memory-augmented setting yields a consistently higher precision, recall, and F1 score than the none of memory module baseline, with all three metrics exceeding 0.8 in both conditions. This indicates high semantic alignment between system outputs and references, and suggests that the memory module improves the answer accuracy and stability across multi-turn contexts without relying on exact lexical overlap. Building on these reference-based results, we next assessed conversation-level qualities that are not captured by lexical or embedding overlap alone.

Table 13.
BERTScore-based evaluation results for the memory module.
Beyond reference-based scoring, we conducted a quantitative evaluation using the LLM-as-a-Judge approach. In this setting, an LLM evaluated each dialogue turn on five predefined criteria. As shown in Table 14, the memory-augmented setting achieved substantial improvements across all metrics, with the largest gains observed in contextual consistency and memory utilization. The reported p-values were computed using two-tailed paired t-tests, comparing the paired scores from the same dialogue turns under the two conditions [46]. The results showed that differences in contextual consistency, memory utilization, and overall coherence were statistically significant (p < 0.01), indicating a probability of less than 1% that such improvements could occur by random chance.

Table 14.
LLM-as-a-Judge evaluation results for the memory module based on 5-point Likert scale.
While the increase in response relevance and helpfulness was relatively modest and did not reach statistical significance, it is important to note that both settings were built on a strong RAG pipeline that already ensured high-quality retrieval. The baseline condition incorporated a well-tuned retrieval mechanism with confidence validation, which helped maintain strong alignment between user queries and retrieved content. As such, the memory module was not expected to dramatically improve local relevance but rather to enhance higher-level dialogue qualities, such as contextual continuity, personalized recall, and coherence across multiple turns. This design choice explains the observed ceiling effect in relevance scores while still showing meaningful gains in context-sensitive dimensions. These findings suggest that incorporating a memory module beyond merely generating locally relevant responses enhances the chatbot’s ability to deliver more context-aware support in educational settings.
Further validation was obtained through a user study involving 30 university students, with the findings presented in Table 15. Each participant interacted with both versions of the chatbot and rated the experience on five criteria. The memory-augmented chatbot consistently received higher ratings across all metrics, with particularly notable gains in usefulness and reliability. Here as well, the p-values were derived from paired t-tests on the participant-level ratings, confirming that the observed improvements were statistically significant (p < 0.01) in all criteria.

Table 15.
User study evaluation results for the memory module based on 5-point Likert scale.
Taken together, the qualitative examples in Table 12, the BERTScore-based evaluation in Table 13, the LLM-based scoring in Table 14, and the user-reported evaluations in Table 15 provide converging evidence that the proposed memory module plays a critical role in enhancing multi-turn conversational capabilities. By systematically tracking both recent and historical interaction contexts, the memory-augmented framework enables the chatbot to deliver more coherent, personalized, and efficient support for LMS users.
5.2. Evaluation of Confidence Check Module
To assess the effectiveness of the proposed confidence check module, we conducted experiments using user queries categorized into three cases: (1) LMS-relevant queries, (2) university-related but LMS-irrelevant queries, and (3) queries unrelated to both LMS and university domains. The evaluation results are summarized in Table 16, Table 17 and Table 18, which present English-translated examples of the representative queries and responses. The corresponding Korean originals are provided in Appendix A for reference.

Table 16.
Evaluation of confidence check module—Case (1) Asking a question suitable for the LMS.

Table 17.
Evaluation of confidence check module—Case (2) Asking a question related to the university, but not related to the LMS.

Table 18.
Evaluation of confidence check module—Case (3) Asking a question not related to both the LMS and the university.
In the first case of LMS-relevant queries, the confidence check module correctly identified them, enabling the chatbot to retrieve appropriate entries from the dataset and to generate accurate responses. The responses included procedural guidance and policy information for tasks such as email address modification, assignment resubmission, video lecture attendance verification, discussion board usage, and auditing student registration. These results confirm the chatbot’s ability to recognize in-domain queries and to generate precise, contextually appropriate responses.
By contrast, when presented with university-related but LMS-irrelevant queries, the confidence check module successfully filtered out queries beyond its knowledge scope. Rather than generating potentially inaccurate responses, the chatbot returned fallback responses advising users to consult the official university websites or to contact the relevant departments. This behavior highlights the module’s ability to reject marginally related but out-of-scope queries, thereby improving chatbot reliability.
Finally, for queries completely unrelated to both the LMS and university domains, the confidence check module consistently rejected them by returning fallback responses indicating the lack of sufficient information. This illustrates the module’s robustness in handling out-of-domain queries and its capacity to prevent hallucinated or irrelevant outputs.
To complement the qualitative analysis, we computed the BERTScore on the original Korean response using KoBERT [43]. As summarized in Table 19, the confidence check module attains consistently strong semantic similarity across all three cases, with precision, recall, and F1 score exceeding 0.8 or approaching that range. Recall is generally higher than precision, indicating that the module preserves reference-relevant content while remaining conservative in token selection. Variability is lowest in Case 2, reflecting the stability of standardized fallback responses for university-related but LMS-irrelevant queries, whereas Case 3 shows larger variance due to the heterogeneity of out-of-domain inputs. Overall, these results suggest that the module not only filters out-of-scope queries but does so in a manner that remains semantically aligned with the intended reference behavior.

Table 19.
BERTScore-based evaluation results for the confidence check module.
To capture aspects not reflected by lexical or embedding overlap, we additionally conducted an LLM-as-a-Judge approach, as summarized in Table 20. Each response was rated on a 5-point Likert scale according to criteria specific to each case. Case 1 achieved the highest performance in clarity of message and response strategy appropriateness, indicating that the chatbot delivered highly clear and contextually well-structured in-domain responses. Case 2 received strong ratings for politeness and clarity of message, demonstrating that fallback messages remained courteous and unambiguous. Case 3 scored well in rejection appropriateness and fallback consistency, showing the chatbot’s ability to decline irrelevant queries in a consistent and professional manner.

Table 20.
LLM-as-a-Judge evaluation results for the confidence check module based on 5-point Likert scale.
In addition, Table 21 presents the results of a user study involving 30 university students, in which the participants evaluated the overall performance of the confidence check module across five metrics. Overall, the participants responded positively, particularly highlighting the clarity and appropriateness of the chatbot’s responses. The module was generally perceived as effective in minimizing irrelevant information, thereby enhancing the reliability and trustworthiness of the chatbot in real-world educational settings.

Table 21.
User study evaluation results for the confidence check module based on 5-point Likert scale.
Overall, these results demonstrate that the proposed confidence check module effectively distinguishes between in-domain and out-of-domain queries. By selectively generating only when sufficient domain-relevant information is available, the chatbot maintained high response accuracy, minimized unreliable outputs, and ensured safe and trustworthy deployment within the LMS environment.
5.3. Qualitative Evaluation of User Feedback
Qualitative feedback was collected from 30 university students to gain deeper insights into user experiences and perceptions of the proposed framework. Table 22 summarizes the representative user opinions categorized into positive feedback and improvement suggestions.

Table 22.
Opinions of users on the proposed framework.
Positive feedback underscored several notable strengths of the framework. The participants highlighted the chatbot’s ability to maintain multi-turn conversational context, to accurately address LMS-related queries, to deliver consistent answers even to redundant questions, and to provide timely responses. Several students further noted that the chatbot resolved their questions more quickly and provided clearer explanations compared to searching the handbook or FAQ pages. These observations indicate that the integration of the memory module and the confidence check module substantially enhanced the system’s reliability, responsiveness, and user trust.
By contrast, suggestions for improvement revealed potential directions for extending the chatbot’s capabilities. Several participants emphasized the need to support broader university-related topics beyond the LMS functionalities. Additional recommendations included integrating academic calendars for automatic scheduling support, enhancing personalization based on individual course enrollment, and refining the language style for more natural and human-like interaction. Another suggestion was to enable the chatbot to classify queries by complexity so that simple questions can be answered more quickly, while complex ones receive deeper investigation.
Overall, these qualitative insights provide actionable guidance for future development, reinforcing the practical applicability of a memory-augmented chatbot in educational environments while identifying specific opportunities for enhancing its versatility and user experience.
5.4. Error Analysis and Robustness Check
To complement the quantitative and user-centered evaluations, we conducted an error analysis and a set of robustness checks to identify residual failure modes and to assess the stability of the proposed framework under realistic perturbations.
The error analysis identified occasional challenges in tracking conversational context during extended multi-turn interactions. In some cases, previously mentioned information, such as submission status or deadline constraints, was not fully reflected in follow-up responses, or outdated contextual details remained after new input had been provided. These issues, while relatively infrequent, tended to occur when user queries involved long-range dependencies or subtle shifts in intent across turns. Addressing such cases may require further refinement of memory scope and update strategies to better manage evolving dialogue context.
Another notable source of error stemmed from borderline university-related queries that fell near the edges of the defined LMS domain. Although the confidence check module generally performed well in filtering out irrelevant inputs, it occasionally misclassified near-domain queries as in-domain. For example, queries about university-wide administrative policies or general student services, which are not directly related to LMS operations, were sometimes interpreted as valid. This led to vague or partially inaccurate responses. While such instances were relatively infrequent, they highlight the challenge of clearly delineating domain boundaries in real-world deployments.
To further evaluate the resilience of the system, we conducted robustness checks under controlled perturbations that simulate realistic variations in user input. Specifically, we tested the framework against paraphrased queries with altered syntax and vocabulary, shifts in linguistic register (e.g., neutral versus honorific styles), typographical errors involving keyboard-adjacent characters, irregular punctuation and spacing, and code-mixed expressions combining Korean with English technical terms. The system maintained stable performance under most paraphrased and style-shifted inputs, consistently retrieving relevant content and producing semantically appropriate responses.
Under higher degrees of input noise, such as heavy typos, the confidence check module remained conservative, effectively suppressing unsafe completions and defaulting to fallback messages when input intent was ambiguous. This conservative behavior contributed to preserving reliability even under degraded input conditions.
Finally, we swept the operating thresholds of the two-stage confidence module and observed a smooth trade-off between precision and recall. Among the tested values, a threshold setting of 0.7 provided the best balance, effectively minimizing false acceptances of out-of-domain queries while avoiding excessive rejections of legitimate LMS-related requests. Accordingly, we adopted this 0.7 threshold configuration in our main experiments and system development. These results collectively support the framework’s stability and robustness under common linguistic variability and noisy real-world conditions.
6. Discussion
This section discusses the broader implications and practical considerations of the proposed framework in university LMS environments. It is organized into three themes: multilingual adaptability, discussed in Section 6.1; data security and privacy, discussed in Section 6.2; and practical integration guidelines for educators, discussed in Section 6.3. These discussions contextualize the findings and suggest directions for real-world deployment and future enhancements.
6.1. Multilingual Adaptability
While the proposed framework was implemented and evaluated primarily for Korean-language interactions using Ko-SBERT and Korean LMS datasets, its architecture is inherently language-agnostic. This design allows for adaptation to multilingual or English-language LMS environments by substituting the embedding model and training data with appropriate language resources, such as multilingual SBERT [47] or English-specific sentence transformers [48].
In the Korean context, the use of Ko-SBERT was advantageous in handling agglutinative morphology and honorific expressions, both of which are essential for generating polite and contextually appropriate responses. For example, the model learned to match question forms like “How do I do it?” and “Is there a way?” to similar intent despite surface-level differences, improving semantic matching accuracy.
In multilingual deployments, potential challenges may include cross-lingual vocabulary normalization (e.g., resolving inconsistencies between English and local LMS terminologies), adapting politeness strategies to culturally appropriate norms (e.g., formal vs. informal tone in German or Japanese), and ensuring embedding consistency across languages for cross-lingual retrieval scenarios [49].
Nevertheless, due to the modular nature of the framework, each component (e.g., retriever, embedder, re-ranker, generator) can be independently swapped or fine-tuned [50]. This modularity enables the efficient reconfiguration of the system for diverse linguistic settings. Such a language-flexible design indicates high scalability and potential for deployment across global educational institutions, including bilingual universities and international campuses with multilingual user bases.
6.2. Data Security and Privacy Consideration
Given that the proposed framework processes LMS data containing potentially sensitive academic and personal information, ensuring robust data security and privacy is critical for real-world deployment [51]. In particular, memory-augmented conversational systems must balance the need to retain contextual information with the obligation to protect user confidentiality [52].
To safeguard personal information, all user identifiers (IDs), such as student IDs, account names, or email addresses, are anonymized before being stored or referenced by the system [53]. This approach ensures that no personally identifiable information (PII) is retained within the memory module or exposed during any stage of operation. Anonymized representations are used solely for the purpose of maintaining conversational coherence and user-specific personalization across multiple dialogue turns.
This anonymization procedure not only mitigates privacy risks but supports compliance with institutional data governance policies and ethical research standards [54]. Furthermore, by decoupling user identity from memory traces, the framework allows for future scalability and system auditing without compromising individual privacy. Such a privacy-conscious design is essential for fostering student trust, securing administrative approval, and facilitating long-term integration of AI tools into educational environments.
6.3. Practical Integration Guidelines for Educators
To facilitate the effective deployment of the proposed framework in real university settings, several practical integration steps are recommended for educators and institutional stakeholders. These steps are designed to ensure technical feasibility, instructional alignment, and operational sustainability.
At the technical level, integration with the existing LMS should be carefully planned. This involves verifying application programming interface (API) compatibility [55], ensuring stable data exchange between the chatbot and the LMS backend, and confirming that system operations align with the institution’s information technology (IT) protocols [56]. It is advisable to work closely with campus IT departments to configure secure access tokens, to manage rate limits, and to test failover behaviors to minimize service disruptions during peak usage.
From an operational standpoint, training and readiness among support personnel are essential. Designated staff, such as instructional designers or IT helpdesk managers, should receive structured training sessions on how to monitor chatbot logs, how to handle unexpected user inputs, and how to update the memory module with new or revised academic resources (e.g., updated policies or new support documentation) [57]. To streamline this process, an administration interface or low-code dashboard can be developed, allowing non-technical staff to manage the chatbot’s content in real time [58].
For ongoing improvement, institutions should implement usage analytics and performance monitoring to track the system’s effectiveness and reliability over time [59]. Key metrics may include query volume, successful response rate, fallback frequency, and user satisfaction ratings. These analytics can be visualized through a lightweight dashboard to support data-driven decision making and iterative improvements. Additionally, regular review cycles (e.g., every semester) should be scheduled to refine the chatbot based on observed error patterns, emerging user needs, or curriculum changes.
On the communication front, building trust with students through transparency is essential. The chatbot’s functional boundaries should be clearly disclosed, such as the types of queries it can handle, its limitations in providing personalized academic advice, and what users should do when a question falls outside its scope [60]. This information can be shared via LMS announcements or onboarding tutorials at the start of each term. Transparency about chatbot limitations helps prevent misuse and manages expectations.
By following these implementation guidelines, educational institutions can enhance student support, reduce the burden on human help desks, and promote equitable access to academic information. Importantly, careful alignment between the chatbot’s capabilities and institutional workflows ensures that its integration contributes meaningfully to student success while maintaining long-term scalability and compliance.
7. Conclusions
In this study, we proposed a memory-augmented LLM-based chatbot to enhance response quality within university LMS environments. The proposed framework integrated a memory module and a two-stage confidence check. The memory module, comprising short-term, long-term, and temporal event memory, enables the chatbot to maintain both immediate conversational context and user-specific historical information. The confidence check ensures responses are generated only for LMS-relevant queries through similarity-based filtering and LLM-based semantic validation.
Experimental results demonstrated that both components significantly improved the chatbot’s ability to generate accurate, contextually relevant, and personalized responses. Specifically, the memory module enabled robust multi-turn interactions by tracking user-specific dialogue history and preferences. The confidence check module effectively filtered irrelevant or inappropriate queries, ensuring reliable answer generation. The user study results confirmed that the proposed framework achieved a high response quality in terms of accuracy, contextual coherence, and user satisfaction. These findings suggest that integrating memory and semantic filtering modules can play a vital role in enhancing the trustworthiness and usability of educational chatbots in real-world LMS environments.
Given the inherent limitations of AI-powered chatbots, it is essential to design a chatbot that can adaptively learn and improve over time. In real-world educational environments, user interactions are diverse and often ambiguous, making robustness and adaptability essential chatbot attributes. Accordingly, our framework emphasizes not only initial response quality but long-term scalability and personalization. By continuously analyzing user interaction patterns, such as FAQ usage, recurring misunderstandings, or changes in learner preferences, the chatbot can be incrementally fine-tuned to better accommodate evolving user needs. Additionally, both implicit signals (e.g., repeated queries) and explicit feedback (e.g., ratings, comments) can be leveraged to retrain the memory module and to update the retrieval dataset semi-automatically.
Future work will focus on enhancing response quality by expanding the retrieval dataset to incorporate a broader range of academic, administrative, and student support resources, including university regulations, course syllabi, and institutional service information. We also plan to refine the memory module using more advanced memory representation learning to better capture subtle patterns in user behavior and preferences across extended timeframes.
Furthermore, we aim to generalize the chatbot to support multi-domain interactions within the broader university ecosystem. This includes integration with course registration platforms, grading systems, campus event services, and counseling or career support portals. These extensions will improve information accessibility, streamline university processes, and contribute to developing a data-driven, intelligent, and user-centric smart campus infrastructure.
Author Contributions
Conceptualization, J.L. and J.R.; methodology, J.L.; software, J.L.; validation and formal analysis, J.R.; investigation, J.L.; resources, J.R.; data curation, J.L.; writing—original draft preparation, J.L.; writing—review and editing, J.R.; visualization, J.L.; supervision and project administration, J.R. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This work was supported by the National Research Foundation of Korea (NRF) grant funded by the Korea government (MSIT) (RS-2025-00516023).
Institutional Review Board Statement
This study utilized de-identified question-and-answer logs collected from the university’s official learning management system (LMS), without direct interaction with individuals. According to Article 33-2 of the Enforcement Rule of the Korean Bioethics and Safety Act, this type of study is exempt from Institutional Review Board (IRB) review, as it involves the use of existing public records without any personally identifiable information. Thus, ethical approval was not required.
Informed Consent Statement
Informed consent was obtained from all student participants involved in the user study, who voluntarily agreed to take part in the evaluation.
Data Availability Statement
The data presented in this study are available upon request from the corresponding author. The data are not publicly available due to privacy.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
Appendix A
For clarity and readability, the main body of this paper presented only English-translated versions of representative chatbot dialogues. This appendix provides the original Korean texts corresponding to the tables included in the main text. Specifically, Table A1, Table A2, Table A3, Table A4 and Table A5 present the original Korean versions of Table 9, Table 12, Table 16, Table 17 and Table 18, respectively. By including the original dialogues, we aim to preserve the linguistic fidelity and to ensure the transparency of the dataset, allowing readers to verify the source texts and to examine the interactions in their authentic form.

Table A1.
Original Korean version of Table 9 (Example of dataset).
Table A1.
Original Korean version of Table 9 (Example of dataset).
| Dataset | Type | Example |
|---|---|---|
| Chat data | Question | 과제 재제출하는 방법을 알고 싶습니다. |
| Answer | 교수님께서 제출 가능 횟수를 2 회 이상으로 설정해 놓으신 경우에 한해 재제출이 가능합니다. 새로 제출 버튼이 보이지 않는다면 교수님꼐서 과제 제출 횟수를 1 회로 설정해놓으신 것입니다. 과제 제출 횟수 설정 권한은 교수님께 있습니다. 불가피하게 과제를 다시 제출하셔야 하는 경우 교수님께 직접 연락드리셔야 할 것 같습니다. | |
| Official FAQ data | Question | 실시간 강의 안내를 받았는데 메뉴가 안보여요. |
| Answer | 공지사항이나 이메일을 통해서 실시간 수업 강의 안내를 받으셨음에도 Collaborate, Zoom 메뉴가 보이지 않으신가요? 교수님께서 아직 메뉴를 열지 않은 상태인 것 같습니다. 교수님께 ‘메뉴보이기’ 활성화를 요청해주세요. |

Table A2.
Original Korean version of Table 12 (Evaluation of memory module—with and without memory module).
Table A2.
Original Korean version of Table 12 (Evaluation of memory module—with and without memory module).
| No | Type | Content |
|---|---|---|
| 1 | Question | 블랙보드에서 과제 제출은 어떻게 하나요? |
| Answer (w/o memory module) | 블랙보드에서 과제를 제출하는 방법에 대해 안내드리겠습니다. 과제 제출은 보통 다음과 같은 단계로 진행됩니다:
| |
| Answer (w/memory module) | 블랙보드에서 과제를 제출하려면 다음 단계를 따라주세요:
| |
| 2 | Question | 과제 제출하고 나서 파일을 수정하고 싶은데 가능한가요? |
| Answer (w/o memory module) | 과제를 제출한 후에는 블랙보드에서 직접 파일을 수정하는 것이 불가능합니다. 다만, 교수님께서 제출 가능 횟수를 2 회 이상으로 설정해 놓으신 경우에 한해 재제출이 가능합니다. 과제 제출 횟수 설정 권한은 교수님께 있으므로, 불가피하게 과제를 다시 제출해야 하는 경우에는 교수님께 직접 연락드려야 할 것 같습니다. | |
| Answer (w/memory module) | 네, 이미 제출하신 상태이므로 블랙보드 상에서 직접 파일을 수정하는 것은 어렵습니다. 다만 교수님께서 해당 과제의 제출 횟수를 두 번 이상으로 설정해 놓으신 경우에는 재제출이 가능합니다. 설정 여부는 과제 정보 화면에서 확인할 수 있으며, 만약 재제출이 불가능한 경우라면 교수님께 추가 제출 기회를 요청해보시는 것도 한 방법입니다. | |
| 3 | Question | 마감시간이 지났는데 제출이 가능한가요? |
| Answer (w/o memory module) | 제출 기한이 지난 과제는 블랙보드에서 직접 제출할 수 없습니다. 과제 제출과 관련된 권한은 교수님께 있으므로, 해당 과목의 교수님께 직접 문의하셔서 제출 가능 여부를 확인하시는 것이 좋겠습니다. | |
| Answer (w/memory module) | 지금 말씀하신 상황을 보면 마감이 지난 상태입니다, 이 경우는 시스템 상으로는 제출이 불가능하고 교수님께 추가 제출 권한을 요청하셔야 합니다. 이전에 이미 제출했던 건은 그대로 유지되며, 추가 제출 여부만 별도로 조정됩니다. 교수님께 상황을 상세히 말씀드리고 협조를 구하시는 것이 좋겠습니다. | |
| 4 | Question | 제출한 파일이 잘못 올라갔어요. 다시 올릴 수 있나요? |
| Answer (w/o memory module) | 제출한 파일을 수정하는 것은 블랙보드 시스템상 불가능합니다. 다만, 교수님께서 제출 가능 횟수를 2회 이상으로 설정해두신 경우에 한해 재제출이 가능합니다. 현재 설정이 어떻게 되어 있는지 확인해보시고, 만약 한 번의 제출만 허용되어 있다면 교수님께 직접 연락드려 사정을 설명하고 도움을 요청하시는 것이 좋겠습니다. | |
| Answer (w/memory module) | 조금 전에 말씀하신 것처럼 이미 한 번 제출하셨으니, 교수님이 추가 제출 허용 여부를 결정하실 겁니다. 가능하다면 교수님께 기존 제출 취소나 재제출 기회를 요청해 보세요. | |
| 5 | Question | 제출할 때 파일 용량 제한이 있나요? |
| Answer (w/o memory module) | SafeAssign 을 통해 파일을 제출할 때는 10 MB 의 용량 제한이 있습니다. 이 제한을 지켜주시면 원활한 업로드가 가능합니다. 또한, 파일명이 너무 길 경우 업로드에 문제가 생길 수 있으니, 파일명은 20자 이내로 해주시는 것이 좋습니다. | |
| Answer (w/memory module) | 네, SafeAssign 기준으로 파일 용량 10 MB 제한이 있습니다. 또한 파일명이 20자를 넘거나 특수문자가 포함되면 업로드 오류가 발생할 수 있으니 참고해 주세요. | |
| 6 | Question | 제출한 후 교수님 피드백은 어디서 확인하나요? |
| Answer (w/o memory module) | 제출한 후 교수님의 피드백은 블랙보드에서 확인할 수 있습니다. [성적보기] 탭으로 들어가셔서 제출된 과제 우측의 말풍선 아이콘을 클릭하시면 피드백을 확인할 수 있습니다. 또한, 제출한 과제명을 클릭하셔도 피드백을 볼 수 있습니다. 모바일에서는 파일이 제대로 열리지 않을 수 있으니, PC에서 확인하시는 것을 권장드립니다. 만약 피드백이 보이지 않는다면, 교수님께서 성적관리센터에서 해당 과제의 점수 컬럼을 공개 설정으로 변경하셔야 합니다. | |
| Answer (w/memory module) | 제출 완료 이후 교수님의 피드백은 블랙보드의 ‘성적보기’ 메뉴에서 확인하실 수 있습니다. 해당 과제를 선택하신 뒤 과제명 옆의 말풍선 아이콘을 클릭하면 교수님의 평가 내용 및 코멘트를 확인할 수 있습니다. 단, 성적 및 피드백이 학생에게 공개되려면 교수님께서 채점 완료 후 해당 성적 컬럼을 공개 상태로 변경하셔야 합니다. 공개가 지연될 경우 교수님께 문의해 보시면 됩니다. | |
| 7 | Question | 표절 검사 결과는 어디서 확인할 수 있나요? |
| Answer (w/o memory module) | 표절 검사 결과는 교수님께서 과제를 생성하실 때 SafeAssign 또는 Turnitin 을 사용하여 설정하셨다면 블랙보드에서 확인할 수 있습니다. 블랙보드에서의 표절 검사 기능에 대한 자세한 안내는 [블랙보드 퀵가이드] (URL) 확인하실 수 있습니다. 만약 교수님이 개인적으로 Turnitin 을 사용하여 표절 검사를 하셨다면, A 대학 도서관 홈페이지에서 관련 정보를 확인할 수 있습니다. 추가적인 문의가 필요하시면 A 대학 도서관에 직접 문의하시는 것이 좋습니다. | |
| Answer (w/memory module) | 현재 제출하신 과제가 SafeAssign 또는 Turnitin 으로 설정되어 있다면 블랙보드 내 과제 페이지에서 표절률 결과 확인이 가능합니다. 다만 표절률 공개 여부는 교수님께서 설정하시는 부분이라 설정에 따라 학생 화면에 보이지 않을 수도 있습니다. 만약 결과가 확인되지 않는다면 교수님께 공개 여부를 문의하시는 것이 좋습니다. | |
| 8 | Question | 표절률이 높게 나오면 어떻게 하나요? |
| Answer (w/o memory module) | 표절률이 높게 나왔을 때는 다음과 같은 방법을 고려해볼 수 있습니다:
| |
| Answer (w/memory module) | 이전에 제출한 파일을 기반으로 표절률이 높게 나왔을 가능성이 있습니다. 특히 인용 표기 누락, 동일한 문장 구조 반복 등이 주요 원인일 수 있습니다. 문제된 부분을 수정하거나 직접적인 인용 대신 재서술하여 표절률을 낮출 수 있습니다. 이후 교수님께 재제출 가능 여부를 문의하시고, Turnitin 가이드라인을 참고하여 수정하시면 보다 안전한 제출이 가능합니다. | |
| 9 | Question | 제출할 때 오류코드 400 이 뜨는데 어떻게 하나요? |
| Answer (w/o memory module) | 오류 코드 400 이 발생하는 경우, 몇 가지 해결 방법을 시도해 보실 수 있습니다. 먼저, 컴퓨터에 AhnLab, V3 등의 보안 프로그램이 실행 중이라면 이를 종료하고 다시 시도해 보세요. 크롬의 보안 정책 업데이트로 인해 이러한 프로그램이 블랙보드 로그인을 간헐적으로 차단할 수 있습니다. 또한, 크롬에서 문제가 지속된다면 Firefox나 Microsoft Edge 브라우저를 사용해 보시는 것도 좋은 방법입니다. 만약 여전히 문제가 해결되지 않는다면, 크롬의 설정에서 인터넷 기록을 삭제한 후 다시 시도해 보세요. 크롬 우측 상단의 점 세 개 버튼을 눌러 설정 패널을 열고, 개인정보 및 보안 탭에서 인터넷 기록 삭제를 선택하시면 됩니다. 이러한 방법으로도 문제가 해결되지 않는다면, 추가적인 지원을 위해 담당자에게 연락하시는 것이 좋겠습니다. | |
| Answer (w/memory module) | 오류코드 400은 보통 시스템 간 통신 오류 혹은 보안 프로그램 간섭에 의해 발생합니다. 우선 V3, AhnLab 등 보안 프로그램이 실행 중이라면 종료 후 시도해 보시고, 크롬 대신 Firefox, Edge 등의 브라우저로 변경하는 것도 도움이 됩니다. 추가로 캐시 및 쿠키 삭제도 시도해보실 수 있으며, 지속 발생 시 IT지원센터에 문의하시면 상세 지원을 받으실 수 있습니다. | |
| 10 | Question | 과제 제출이 제대로 됐는지 확인하는 방법 알려주세요. |
| Answer (w/o memory module) | 과제 제출이 제대로 되었는지 확인하려면, 블랙보드에 로그인한 후 해당 코스에 접속하세요. 왼쪽 메뉴에서 ‘과제 및 시험’을 클릭하시면 제출한 과제를 확인할 수 있습니다. 만약 이 메뉴가 보이지 않는다면, 교수님께서 해당 메뉴를 생성하지 않으셨을 수 있으니 교수님께 문의해 보시기 바랍니다. 추가로, 과제 제출과 관련된 보다 구체적인 설명은 [관련 메뉴얼 사이트](URL)를 참고하시면 도움이 될 것입니다. | |
| Answer (w/memory module) | 현재 제출 내역은 블랙보드 ‘과제 및 시험’ 메뉴에서 해당 과제를 클릭하면 확인할 수 있습니다. 제출된 파일명, 제출 시간, SafeAssign 검사 여부 등이 표시됩니다. 또 성적보기에서도 제출된 기록을 확인할 수 있으므로 두 경로 모두 확인해 보시면 보다 확실하게 제출 상태를 점검하실 수 있습니다. |

Table A3.
Original Korean version of Table 16 (Evaluation of confidence check module—Case (1) Asking a question suitable for the LMS).
Table A3.
Original Korean version of Table 16 (Evaluation of confidence check module—Case (1) Asking a question suitable for the LMS).
| No | Type | Content |
|---|---|---|
| 1 | Question | 이메일을 변경하고 싶은데, 어떻게 변경할 수 있나요? |
| Answer | 이메일을 변경하시려면 다음 단계를 따라주세요:
| |
| 2 | Question | 과제를 이미 제출했는데, 새롭게 제출하는 방법이 있나요? |
| Answer | 과제를 이미 제출하셨다면, 블랙보드에서 직접 수정하는 것은 불가능합니다. 다만, 교수님께서 제출 가능 횟수를 2 회 이상으로 설정해 놓으신 경우에 한해 재제출이 가능합니다. 만약 새로 제출할 수 있는 옵션이 보이지 않는다면, 교수님께서 제출 횟수를 1 회로 설정해 놓으신 것입니다. 이 경우, 과제를 다시 제출해야 하는 불가피한 상황이라면 교수님께 직접 연락드려서 도움을 요청하시는 것이 좋겠습니다. | |
| 3 | Question | 학생들이 동영상 강의 출석을 실시간으로 확인할 수 있나요? |
| Answer | 학생들이 동영상 강의 출석을 실시간으로 확인할 수 있도록 하려면, ‘영상출석현황’ 메뉴를 생성해야 합니다. 이 메뉴가 생성되면 학생들은 실시간으로 출석 현황을 확인할 수 있습니다. 다만, 출석 정보가 시스템에 반영되는 데 일정 시간이 걸릴 수 있으므로, 반영되지 않은 경우 잠시 기다리시면 곧 반영될 것입니다. 또한, 출석 관리 방식은 교수님마다 다를 수 있으니, 자세한 사항은 조교님이나 교수님께 문의하시는 것이 좋습니다. | |
| 4 | Question | 토론실에는 수정이나 삭제 기능이 있나요? |
| Answer | 토론실에서 게시글을 수정하거나 삭제할 수 있는지 여부는 해당 토론실의 설정에 따라 다릅니다. 일반적으로 교수님이 설정을 통해 작성자가 자신의 게시글을 삭제할 수 있도록 허용할 수 있습니다. 만약 삭제 버튼이 보이지 않는다면, 이는 교수님께서 해당 기능을 비활성화해 두셨기 때문일 수 있습니다. 이 경우, 교수님이나 조교님께 설정 변경을 요청해 보시는 것이 좋습니다. 추가로, 게시물 수정은 본인의 게시물에 커서를 올리면 [수정] 버튼을 통해 가능할 수 있으니 확인해 보시기 바랍니다. | |
| 5 | Question | 청강생 등록 방법을 알려주세요. |
| Answer | 청강생 등록 방법은 다음과 같습니다. 먼저, 사용자 등록 메뉴를 찾아주세요. 여기에서 학번이나 교번을 검색하여 학생을 찾은 후, ‘학습자’로 등록하시면 됩니다. 주의할 점은, 청강생은 수강신청 정정기간 이후 시스템 반영으로 인해 일괄적으로 삭제될 예정이므로, 정정기간 이후에는 다시 한 번 청강생을 등록해주셔야 합니다. 더 자세한 정보는 [이 링크]를 참고하세요. |

Table A4.
Original Korean version of Table 17 (Evaluation of confidence check module—Case (2) Asking a question related to the university, but not related to the LMS).
Table A4.
Original Korean version of Table 17 (Evaluation of confidence check module—Case (2) Asking a question related to the university, but not related to the LMS).
| No | Type | Content |
|---|---|---|
| 1 | Question | 교내 셔틀버스 시간표를 알려주세요. |
| Answer | 죄송합니다. 현재 교내 셔틀버스 시간표에 대한 정보를 제공할 수 없습니다. 더 정확한 정보를 원하시면 학교의 공식 웹사이트나 관련 부서에 문의해 주시기 바랍니다. | |
| 2 | Question | 학기 중 중도 휴학 방법에 대해 알려주세요. |
| Answer | 죄송합니다. 현재 요청하신 학기 중 중도 휴학 방법에 대한 구체적인 정보를 제공할 수 없습니다. 더 정확한 정보를 원하신다면, A 대학의 공식 포털 웹사이트나 학사 담당 부서에 직접 문의해주시기 바랍니다. | |
| 3 | Question | A 대학에 있는 입학전형에 대해 알려주세요. |
| Answer | 죄송합니다. 현재 A 대학의 입학전형에 대한 충분한 정보가 제공되지 않아 정확한 답변을 드리기 어렵습니다. A 대학의 공식 웹사이트나 입학처에 직접 문의하시면 더 정확하고 상세한 정보를 얻으실 수 있습니다. | |
| 4 | Question | 중앙도서관은 평일에 몇시까지 운영되나요? |
| Answer | 죄송합니다. 현재 중앙도서관의 평일 운영 시간에 대한 정확한 정보를 제공할 수 없습니다. 도서관의 공식 웹사이트를 방문하거나 직접 문의하시면 더 정확한 정보를 얻으실 수 있습니다. | |
| 5 | Question | 교내 기숙사 입사 신청은 어떻게 하나요? |
| Answer | 죄송합니다. 현재 귀하의 질문에 대한 신뢰할 수 있는 정보를 제공할 수 없습니다. 교내 기숙사 입사 신청에 대한 자세한 정보는 학교의 공식 웹사이트나 학생 서비스 센터에 문의하시기 바랍니다. |

Table A5.
Original Korean version of Table 18 (Evaluation of confidence check module—Case (3) Asking a question not related to both the LMS and the university).
Table A5.
Original Korean version of Table 18 (Evaluation of confidence check module—Case (3) Asking a question not related to both the LMS and the university).
| No | Type | Content |
|---|---|---|
| 1 | Question | 거대언어모델이란 무엇인가요? |
| Answer | 죄송합니다. 귀하의 질문에 대한 충분한 정보가 제공되지 않아 정확한 답변을 드리기 어렵습니다. 다른 질문이 있으시면 언제든지 문의해주세요. | |
| 2 | Question | Formula (1) 의 DRS 시스템은 어떻게 작동하나요? |
| Answer | 죄송합니다. 현재 제공된 정보로는 Formula (1) 의 DRS 시스템 작동 방식에 대한 신뢰할 수 있는 답변을 드리기 어렵습니다. 추가적인 자료나 정보를 확인해 보시거나, 다른 질문이 있으시면 언제든지 문의해 주세요. | |
| 3 | Question | 피타고라스 정리 공식을 알려주세요. |
| Answer | 죄송합니다. 현재 요청하신 정보에 대한 충분한 자료가 없어 정확한 답변을 드리기 어렵습니다. 다른 질문이 있으시면 언제든지 말씀해 주세요. | |
| 4 | Question | 조선왕조실록에 기록된 세종대왕의 맥북 프로 던짐 사건에 대해 알려줘. |
| Answer | 죄송합니다. 현재 요청하신 정보에 대한 신뢰할 수 있는 답변을 제공할 수 없습니다. 다른 질문이 있으시면 언제든지 말씀해 주세요. | |
| 5 | Question | 비트코인 현재 시세는 얼마인가요? |
| Answer | 죄송합니다. 현재 비트코인의 시세에 대한 정보를 제공할 수 없습니다. 최신 시세를 확인하려면 금융 뉴스 웹사이트나 암호화폐 거래소를 참조하시기 바랍니다. 추가적인 도움이 필요하시면 언제든지 말씀해주세요. |
References
- Rosário, A.T.; Dias, J.C. Learning Management Systems in Education: Research and Challenges; IGI Global: Hershey, PA, USA, 2022. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alturki, U.; Aldraiweesh, A. Application of Learning Management System (Lms) during the Covid-19 Pandemic: A Sustainable Acceptance Model of the Expansion Technology Approach. Sustainability 2021, 13, 10991. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sanchez, L.; Penarreta, J.; Soria Poma, X. Learning Management Systems for Higher Education: A Brief Comparison. Discov. Educ. 2024, 3, 58. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Adzharuddin, N. Learning Management System (LMS) among University Students: Does It Work? Int. J. e-Educ. e-Bus. e-Manag. e-Learn. 2013, 3, 248–252. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chaskopoulos, D.; Hægdahl, J.E.; Sagvold, P.; Trinquet, C.; Edalati, M. Implementing a Chatbot Solution for Learning Management System. arXiv 2022, arXiv:2206.13187. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bezverhny, E.; Dadteev, K.; Barykin, L.; Nemeshaev, S.; Klimov, V. Use of Chat Bots in Learning Management Systems. Procedia Comput. Sci. 2020, 169, 652–655. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Snekha, S.; Ayyanathan, N. An Educational CRM Chatbot for Learning Management System. Shanlax Int. J. Educ. 2023, 11, 58–62. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Misischia, C.V.; Poecze, F.; Strauss, C. Chatbots in Customer Service: Their Relevance and Impact on Service Quality. Procedia Comput. Sci. 2022, 201, 421–428. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Adamopoulou, E.; Moussiades, L. Chatbots: History, Technology, and Applications. Mach. Learn. Appl. 2020, 2, 100006. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahn, S.-H.; Lee, S.-J. Improving University Homepage FAQ Using Semantic Network Analysis. J. Digit. Converg. 2018, 16, 11–20. [Google Scholar]
- Dam, S.K.; Hong, C.S.; Qiao, Y.; Zhang, C. A Complete Survey on LLM-Based AI Chatbots. arXiv 2024, arXiv:2406.16937. [Google Scholar]
- Minaee, S.; Mikolov, T.; Nikzad, N.; Chenaghlu, M.; Socher, R.; Amatriain, X.; Gao, J. Large Language Models: A Survey. arXiv 2024, arXiv:2406.06196. [Google Scholar]
- Lewis, P.; Perez, E.; Piktus, A.; Petroni, F.; Karpukhin, V.; Goyal, N.; Küttler, H.; Lewis, M.; Yih, W.T.; Rocktäschel, T.; et al. Retrieval-Augmented Generation for Knowledge-Intensive NLP Tasks. arXiv 2020, arXiv:2005.11401. [Google Scholar]
- Gao, Y.; Xiong, Y.; Gao, X.; Jia, K.; Pan, J.; Bi, Y.; Dai, Y.; Sun, J. Retrieval-Augmented Generation for Large Language Models: A Survey. arXiv 2023, arXiv:2312.10997. [Google Scholar]
- Ranoliya, B.R.; Raghuwanshi, N.; Singh, S. Chatbot for University Related FAQs. In Proceedings of the 2017 International Conference on Advances in Computing, Udupi, India, 13–16 September 2017; pp. 1525–1530. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Iatrellis, O.; Samaras, N.; Kokkinos, K.; Panagiotakopoulos, T. Leveraging Generative AI for Sustainable Academic Advising: Enhancing Educational Practices through AI-Driven Recommendations. Sustainability 2024, 16, 7829. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bilquise, G.; Shaalan, K. AI-Based Academic Advising Framework: A Knowledge Management Perspective. Int. J. Adv. Comput. Sci. Appl. 2022, 13, 193–203. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Labadze, L.; Grigolia, M.; Machaidze, L. Role of AI Chatbots in Education: Systematic Literature Review. Int. J. Educ. Technol. High. Educ. 2023, 20, 1–17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lalwani, T.; Bhalotia, S.; Pal, A.; Bisen, S.; Rathod, V. Implementation of a Chat Bot System Using AI and NLP. Int. J. Innov. Res. Comput. Sci. Technol. 2018, 6, 26–30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shiva, K.; Etikani, P.; Venkata, V.; Rama, S.; Kaur, J.; Kanchetti, D.; Munirathnam, R. INTELLIGENT SYSTEMS AND APPLICATIONS IN ENGINEERING Natural Language Processing for Customer Service Chatbots: Enhancing Customer Experience. Int. J. Intell. Syst. Appl. Eng. 2024, 12, 155–164. [Google Scholar]
- Ortiz-Garces, I.; Govea, J.; Andrade, R.O.; Villegas-Ch, W. Optimizing Chatbot Effectiveness through Advanced Syntactic Analysis: A Comprehensive Study in Natural Language Processing. Appl. Sci. 2024, 14, 1737. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yigci, D.; Eryilmaz, M.; Yetisen, A.K.; Tasoglu, S.; Ozcan, A. Large Language Model-Based Chatbots in Higher Education. Adv. Intell. Syst. 2024, 7, 2400429. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Smutny, P.; Bojko, M. Comparative Analysis of Chatbots Using Large Language Models for Web Development Tasks. Appl. Sci. 2024, 14, 10048. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, X.; Wilson, S.D.; Petzold, L. Quokka: An Open-Source Large Language Model ChatBot for Material Science. arXiv 2024, arXiv:2401.01089. [Google Scholar]
- Wu, C.-S. Learning to Memorize in Neural Task-Oriented Dialogue Systems. arXiv 2019, arXiv:1905.07687. [Google Scholar]
- Wu, Q.; Yu, Z. Stateful Memory-Augmented Transformers for Efficient Dialogue Modeling. In Proceedings of the 18th Conference of the European Chapter of the Association for Computational Linguistics, St. Julians, Malta, 17–22 March 2024; pp. 853–867. [Google Scholar]
- He, J.; Zhu, L.; Wang, R.; Wang, X.; Haffari, R.; Zhang, J.; Sheffield, U. MADial-Bench: Towards Real-World Evaluation of Memory-Augmented Dialogue Generation. In Proceedings of the 2025 Conference of the Nations of the Americas Chapter of the Association for Computational Linguistics: Human Language Technologies, Albuquerque, Mexico, 29 April–4 May 2025; pp. 9902–9921. [Google Scholar]
- Camacho-Collados, J.; Pilehvar, M.T. On the Role of Text Preprocessing in Neural Network Architectures: An Evaluation Study on Text Categorization and Sentiment Analysis. In Proceedings of the 2018 EMNLP Workshop BlackboxNLP: Analyzing and Interpreting Neural Networks for NLP, Brussels, Belgium, 1 November 2018; pp. 40–46. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qiu, X.; Sun, T.; Xu, Y.; Shao, Y.; Dai, N.; Huang, X. Pre-Trained Models for Natural Language Processing: A Survey. Sci. China Technol. Sci. 2020, 63, 1872–1897. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, H.; Li, J.; Wu, H.; Hovy, E.; Sun, Y. Pre-Trained Language Models and Their Applications. Engineering 2023, 25, 51–65. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luo, Y.; Yang, Z.; Meng, F.; Li, Y.; Zhou, J.; Zhang, Y. An Empirical Study of Catastrophic Forgetting in Large Language Models During Continual Fine-Tuning. arXiv 2023, arXiv:2308.08747. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, J.; Rew, J. Large Language Models-Based Feature Extraction for Short-Term Load Forecasting. J. Korea Soc. Ind. Inf. Syst. 2024, 29, 51–65. [Google Scholar]
- Reimers, N.; Gurevych, I. Sentence-BERT: Sentence Embeddings Using Siamese BERT-Networks. In Proceedings of the 2019 Conference on Empirical Methods in Natural Language Processing and the 9th International Joint Conference on Natural Language Processing (EMNLP-IJCNLP) 2019, Hong Kong, China, 3–7 November 2019; pp. 3982–3992. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kenton, M.C.; Kristina, L.; Devlin, J. BERT: Pre-Training of Deep Bidirectional Transformers for Language Understanding. arXiv 2018, arXiv:1810.04805. [Google Scholar]
- Lee, S.; Jang, H.; Baik, Y.; Park, S.; Shin, H. A Small-Scale Korean-Specific BERT Language Model. J. KIISE 2020, 47, 682–692. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ham, J.; Choe, Y.J.; Park, K.; Choi, I.; Soh, H. KorNLI and KorSTS: New Benchmark Datasets for Korean Natural Language Understanding. In Findings of the Association for Computational Linguistics Findings of ACL: EMNLP 2020; Association for Computational Linguistics: Kerrville, TX, USA, 2020; pp. 422–430. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lahitani, A.R.; Permanasari, A.E.; Setiawan, N.A. Cosine Similarity to Determine Similarity Measure: Study Case in Online Essay Assessment. In Proceedings of the 2016 4th International Conference on Cyber and IT Service Management, CITSM 2016, Bandung, Indonesia, 26–27 April 2016; pp. 1–6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sasazawa, Y.; Yokote, K.; Imaichi, O.; Sogawa, Y.; Group, D. Text Retrieval with Multi-Stage Re-Ranking Models. arXiv 2019, arXiv:2311.07994. [Google Scholar]
- Kuzlu, M.; Catak, F.O.; Sarp, S.; Cali, U.; Gueler, O. A Streamlit-Based Artificial Intelligence Trust Platform for Next-Generation Wireless Networks. In Proceedings of the 2022 IEEE Future Networks World Forum, FNWF 2022, Montreal, QC, Canada, 10–14 October 2022; pp. 94–97. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, T.; Kishore, V.; Wu, F.; Weinberger, K.Q.; Artzi, Y. Bertscore: Evaluating Text Generation With Bert. In Proceedings of the 8th International Conference on Learning Representations, ICLR 2020, Addis Ababa, Ethiopia, 26–30 April 2020; pp. 1–43. [Google Scholar]
- Papineni, K.; Roukos, S.; Ward, T.; Zhu, W.J. BLEU: A Method for Automatic Evaluation of Machine Translation. In Proceedings of the Annual Meeting of the Association for Computational Linguistics 2002, Philadelphia, PA, USA, 6–12 July 2002; pp. 311–318. [Google Scholar]
- Lin, C.Y. Rouge: A Package for Automatic Evaluation of Summaries. In Proceedings of the workshop on text summarization branches out (WAS 2004), Barcelona, Spain, 25–26 July 2004; pp. 25–26. [Google Scholar]
- Yang, K. Transformer-Based Korean Pretrained Language Models: A Survey on Three Years of Progress. arXiv 2021, arXiv:2112.03014. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zheng, L.; Chiang, W.L.; Sheng, Y.; Zhuang, S.; Wu, Z.; Zhuang, Y.; Lin, Z.; Li, Z.; Li, D.; Xing, E.P.; et al. Judging LLM-as-a-Judge with MT-Bench and Chatbot Arena. Adv. Neural Inf. Process Syst. 2023, 36, 1–29. [Google Scholar]
- Joshi, A.; Kale, S.; Chandel, S.; Pal, D. Likert Scale: Explored and Explained. Br. J. Appl. Sci. Technol. 2015, 7, 396–403. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, M.; Fralick, D.; Zheng, J.Z.; Wang, B.; Tu, X.M.; Feng, C. The Differences and Similarities between Two-Sample t-Test and Paired t-Test. Shanghai Arch. Psychiatry 2017, 29, 184–188. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feng, F.; Yang, Y.; Cer, D.; Arivazhagan, N.; Wang, W. Language-Agnostic BERT Sentence Embedding. In Proceedings of the Annual Meeting of the Association for Computational Linguistics 2022, Dublin, Ireland, 22–27 May 2022; pp. 878–891. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wieting, J.; Neubig, G.; Berg-Kirkpatrick, T. A Bilingual Generative Transformer for Semantic Sentence Embedding. In Proceedings of the 2020 Conference on Empirical Methods in Natural Language Processing (EMNLP), Online, 16–20 November 2020; pp. 1581–1594. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qin, L.; Chen, Q.; Zhou, Y.; Chen, Z.; Li, Y.; Liao, L.; Li, M.; Che, W.; Yu, P.S. A Survey of Multilingual Large Language Models. Patterns 2025, 6, 101118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, Y.; Xiong, Y.; Wang, M.; Wang, H. Modular RAG: Transforming RAG Systems into LEGO-like Reconfigurable Frameworks. arXiv 2024, arXiv:2407.21059. [Google Scholar]
- Rawat, M.K.; Jha, S.K.; Sree Lakshmi, A.; Venkata Ramana, J.; Gonge, S.S.; De, A. Privacy Protection in Learning Management Systems’ Mobile Technology-Based Learning Analytics. Int. J. Interact. Mob. Technol. 2025, 19, 197–208. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zeng, S.; Zhang, J.; He, P.; Xing, Y.; Liu, Y.; Xu, H.; Ren, J.; Wang, S.; Yin, D.; Chang, Y.; et al. The Good and The Bad: Exploring Privacy Issues in Retrieval-Augmented Generation (RAG). In Proceedings of the Annual Meeting of the Association for Computational Linguistics 2024, Bangkok, Thailand, 11–16 August 2024; pp. 4505–4524. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Majeed, A.; Lee, S. Anonymization Techniques for Privacy Preserving Data Publishing: A Comprehensive Survey. IEEE Access 2021, 9, 8512–8545. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chatsuwan, P.; Phromma, T.; Surasvadi, N.; Thajchayapong, S. Personal Data Protection Compliance Assessment: A Privacy Policy Scoring Approach and Empirical Evidence from Thailand’s SMEs. Heliyon 2023, 9, e20648. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chakravarthy, S.S.; Raman, A.C. Educational Data Mining on Learning Management Systems Using Experience API. In Proceedings of the 2014 4th International Conference on Communication Systems and Network Technologies, CSNT 2014, Bhopal, India, 7–9 April 2014; pp. 424–427. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jung, S.; Huh, J.H. An Efficient LMS Platform and Its Test Bed. Electronics 2019, 8, 154. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Al-Emran, M.; Al Chalabi, H. Developing an IT Help Desk Troubleshooter Expert System for Diagnosing and Solving IT Problems. In Proceedings of the 2nd BCS International IT Conference 2014, Abu Dhabi, United Arab Emirates, 9–10 March 2014; pp. 1–5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Y.; Wu, A.; DePodesta, T.; Yeh, C.; Li, K.; Marin, N.C.; Patel, O.; Riecke, J.; Raval, S.; Seow, O.; et al. Designing a Dashboard for Transparency and Control of Conversational AI. arXiv 2024, arXiv:2406.07882. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aulakh, K.; Roul, R.K.; Kaushal, M. E-Learning Enhancement through Educational Data Mining with Covid-19 Outbreak Period in Backdrop: A Review. Int. J. Educ. Dev. 2023, 101, 102814. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Park, D.M.; Jeong, S.S.; Seo, Y.S. Systematic Review on Chatbot Techniques and Applications. J. Inf. Process. Syst. 2022, 18, 26–47. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).