Three-Dimensional Modeling of Tidal Delta Reservoirs Based on Sedimentary Dynamics Simulations
Abstract
1. Introduction
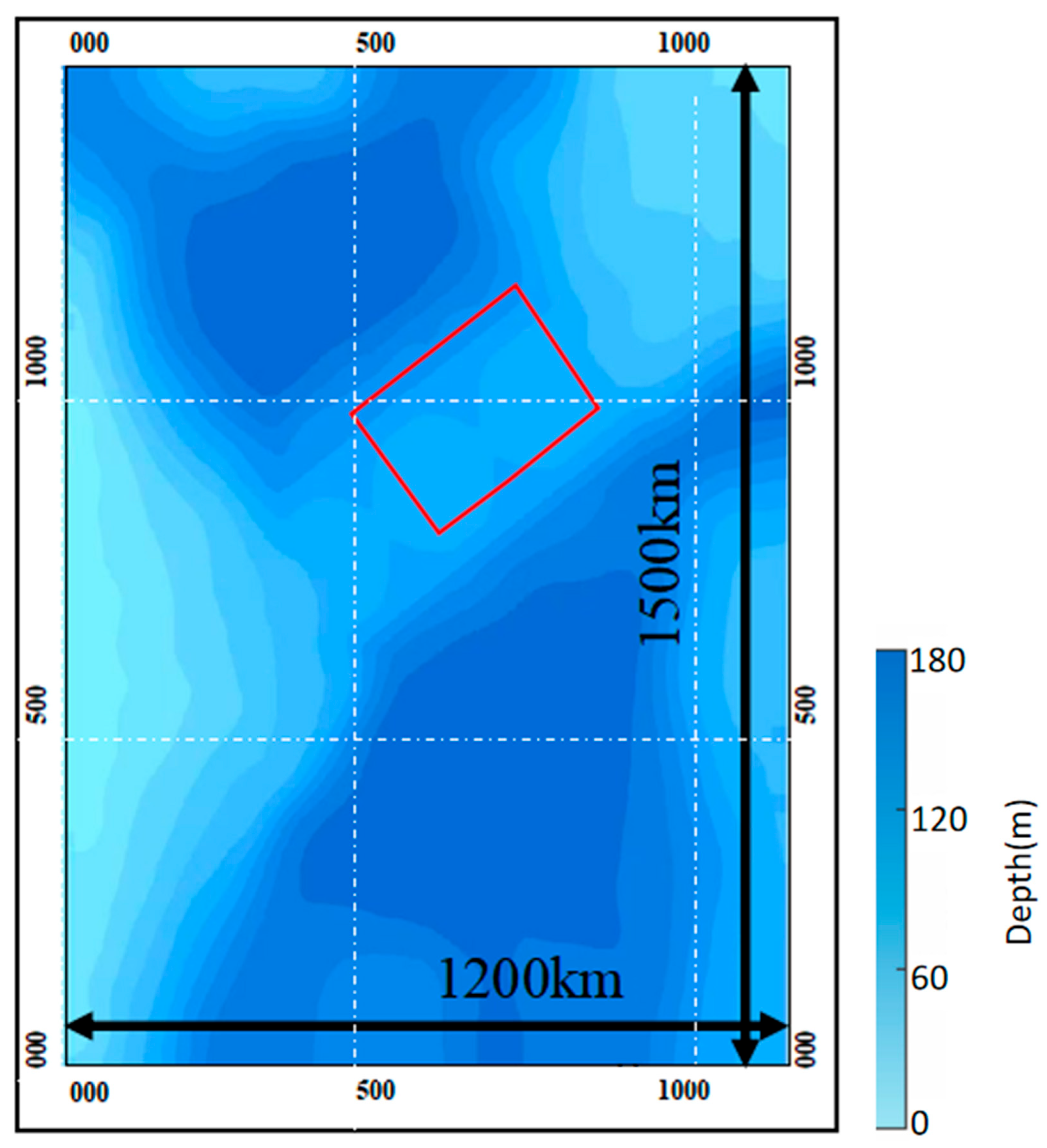
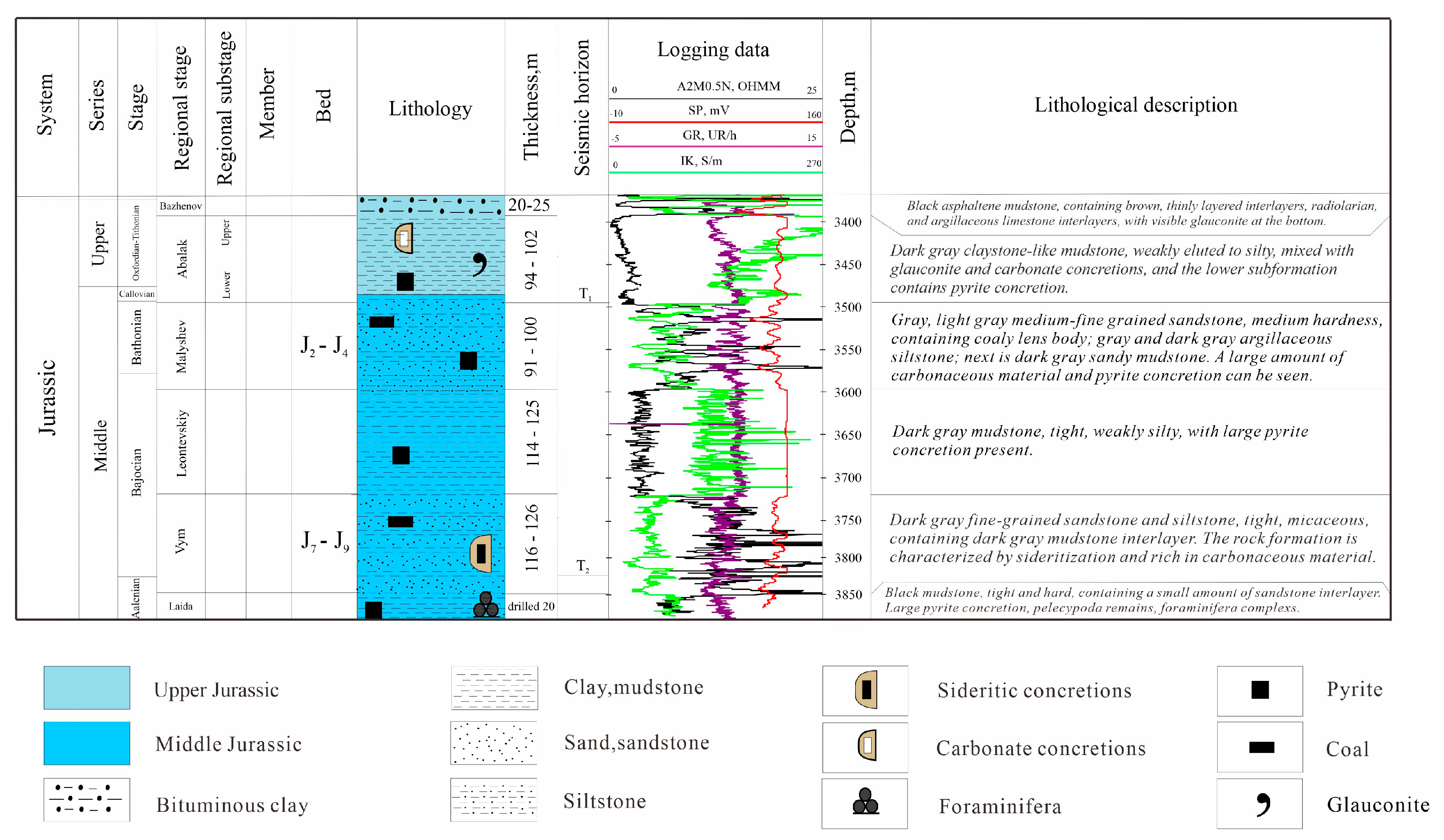
2. Regional Research Background
3. Sedimentary Dynamics Simulation
3.1. Basic Principles of Sedimentary Dynamics Simulation
3.2. Parameter Selection
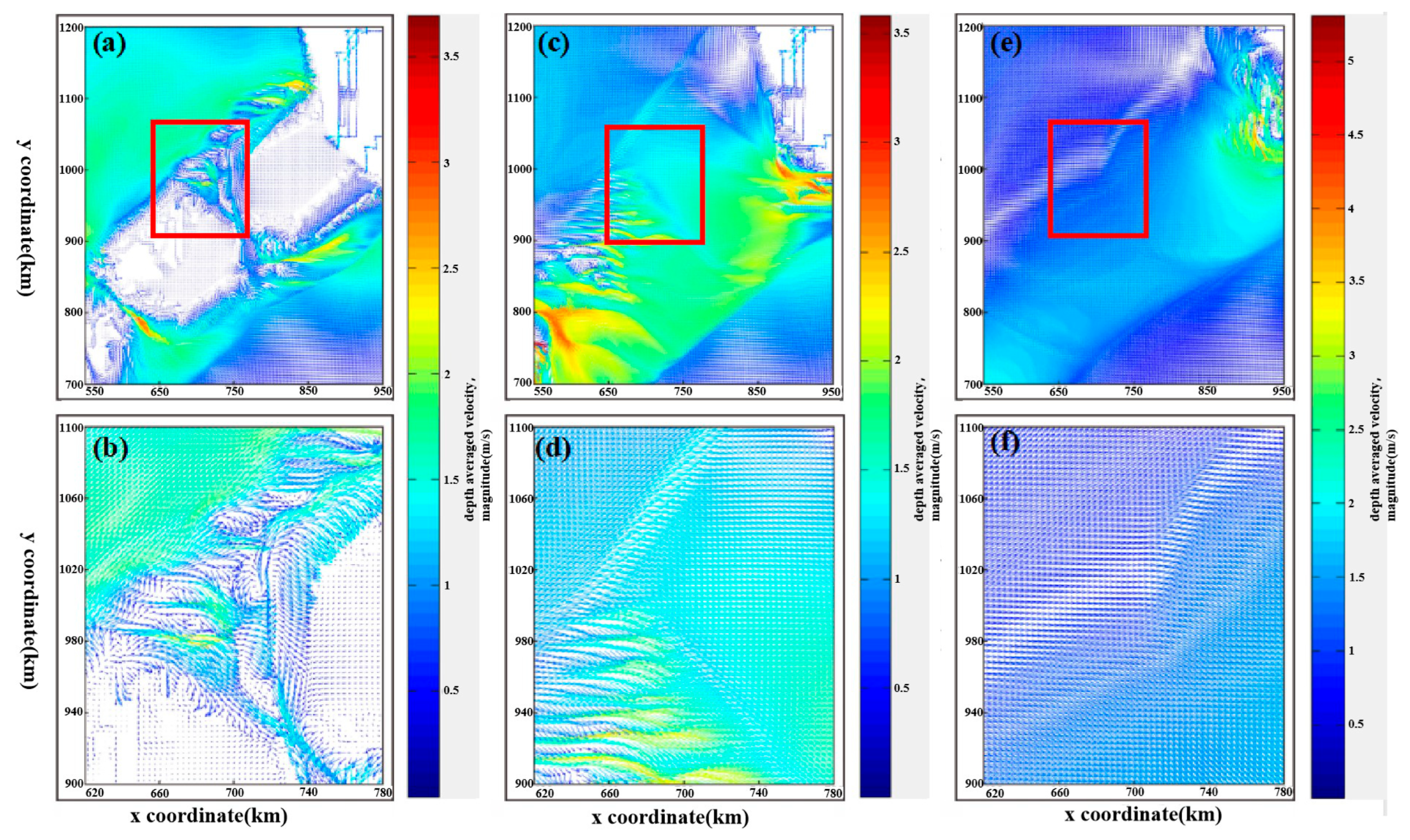
3.3. Results and Discussions
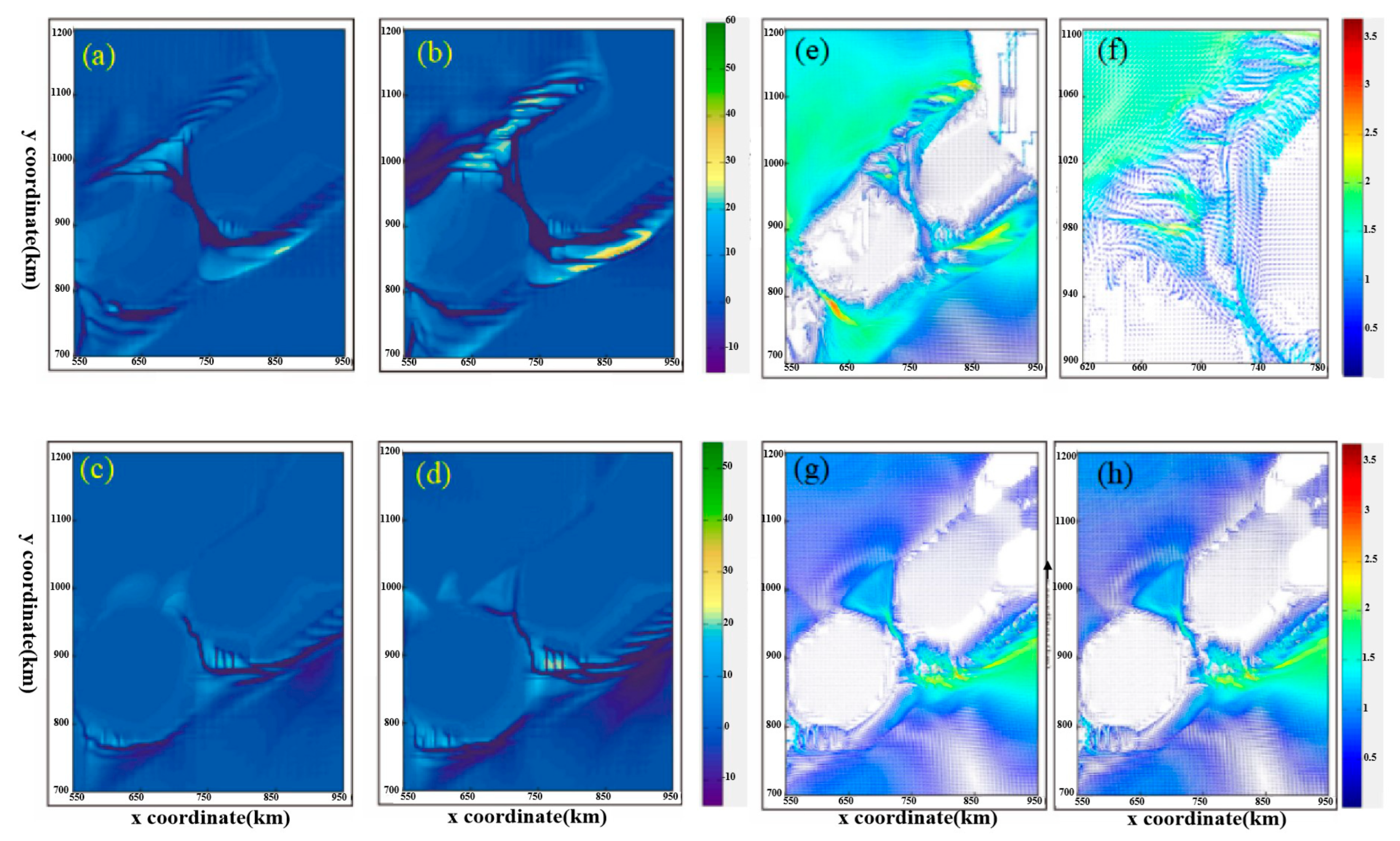
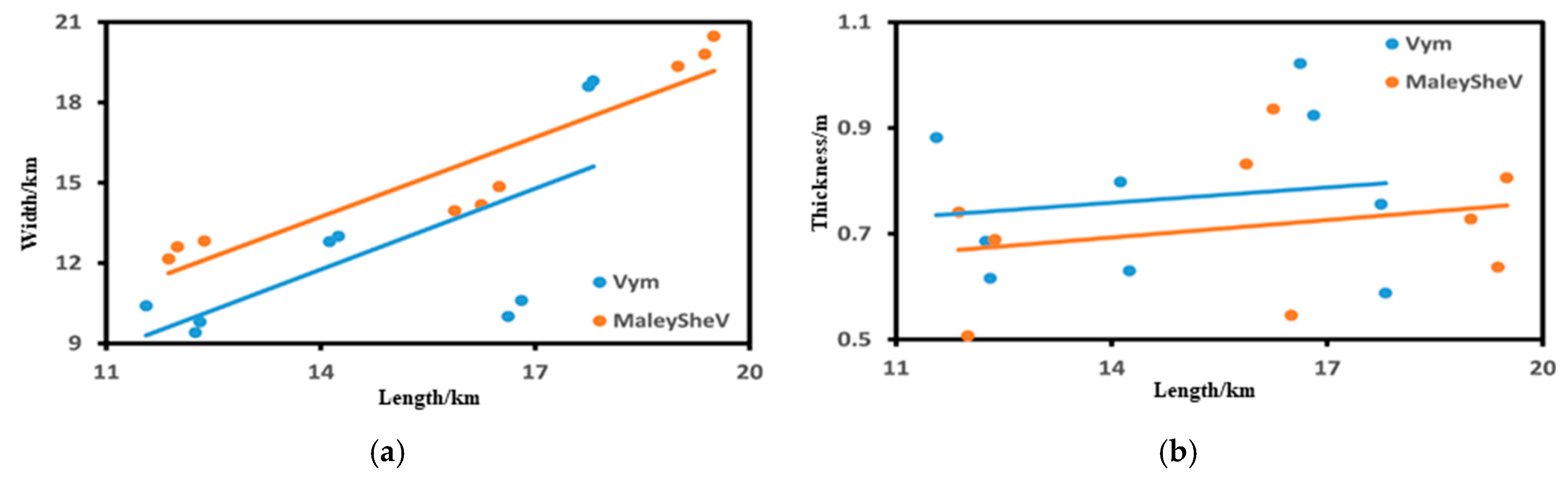
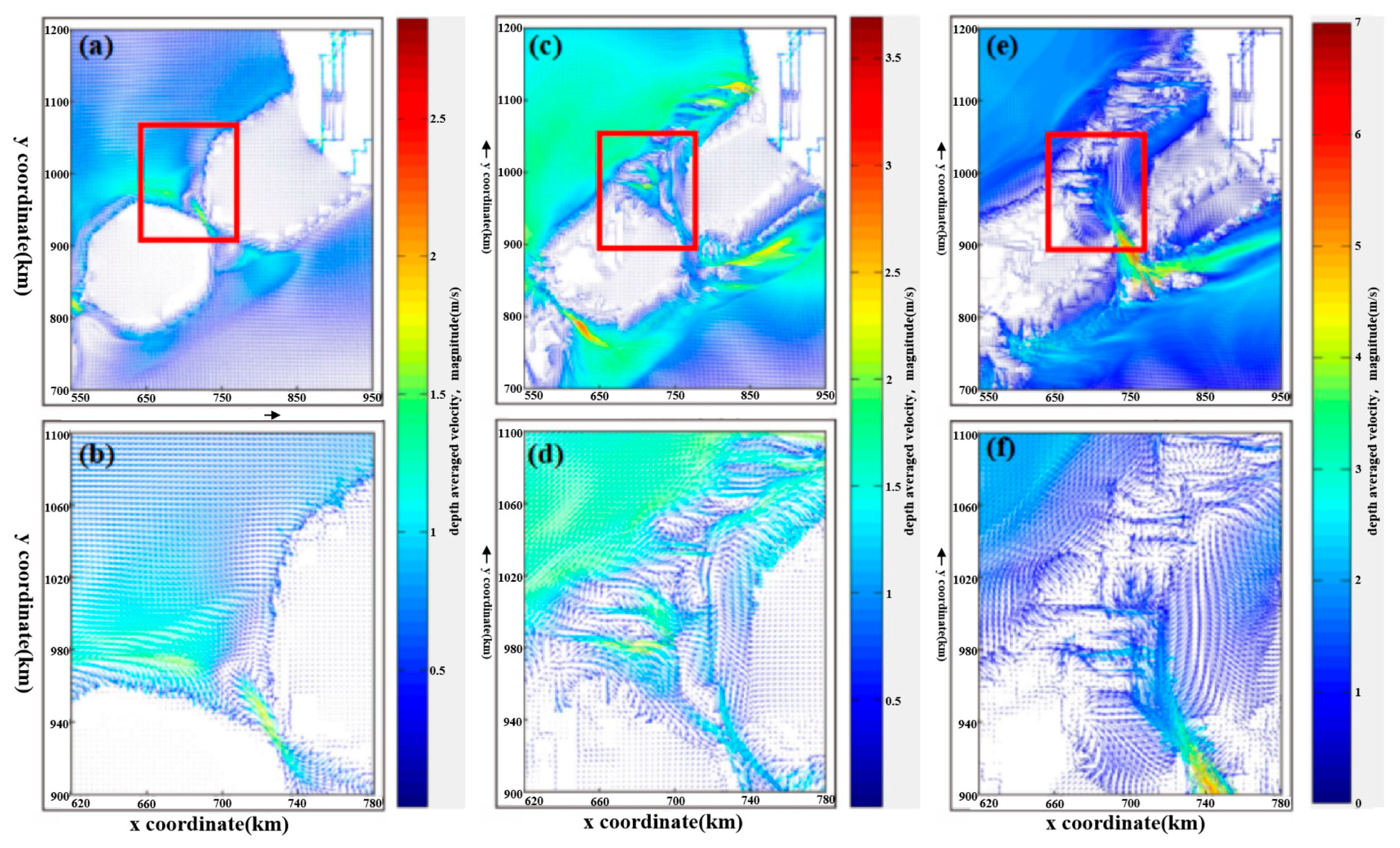
3.3.1. Analysis of Bottom Shape Factors
- Sedimentary distribution analysis
- 2.
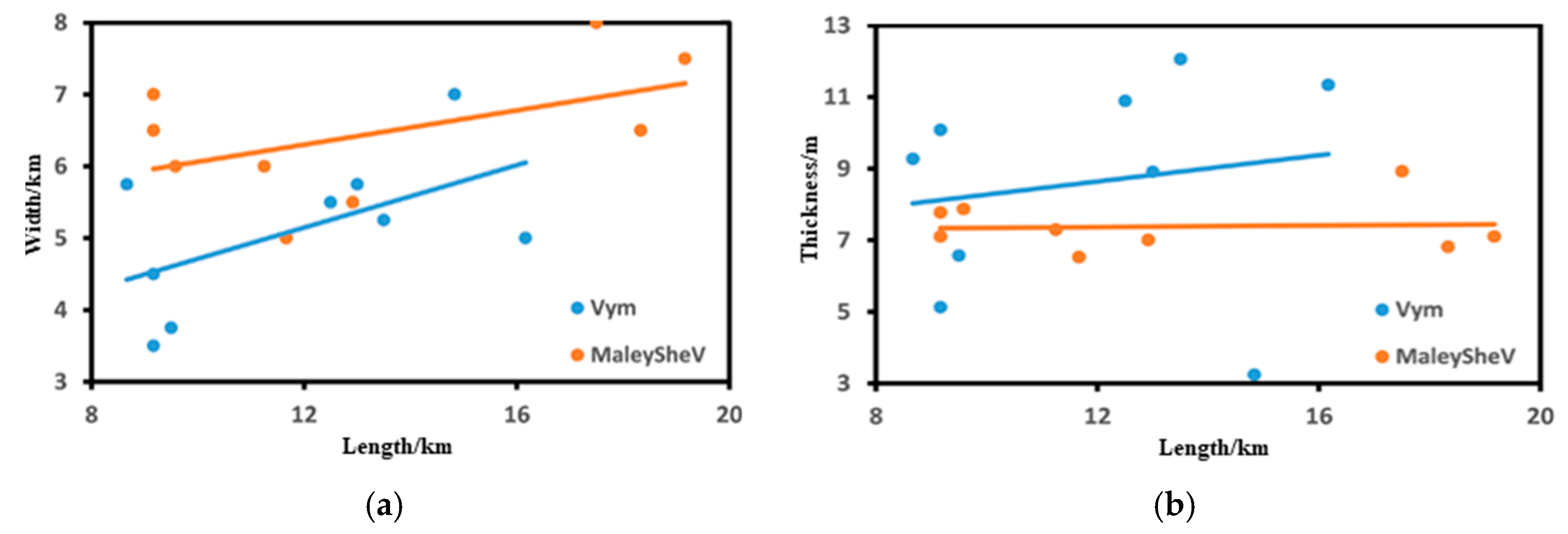
- Analysis of bar characteristics
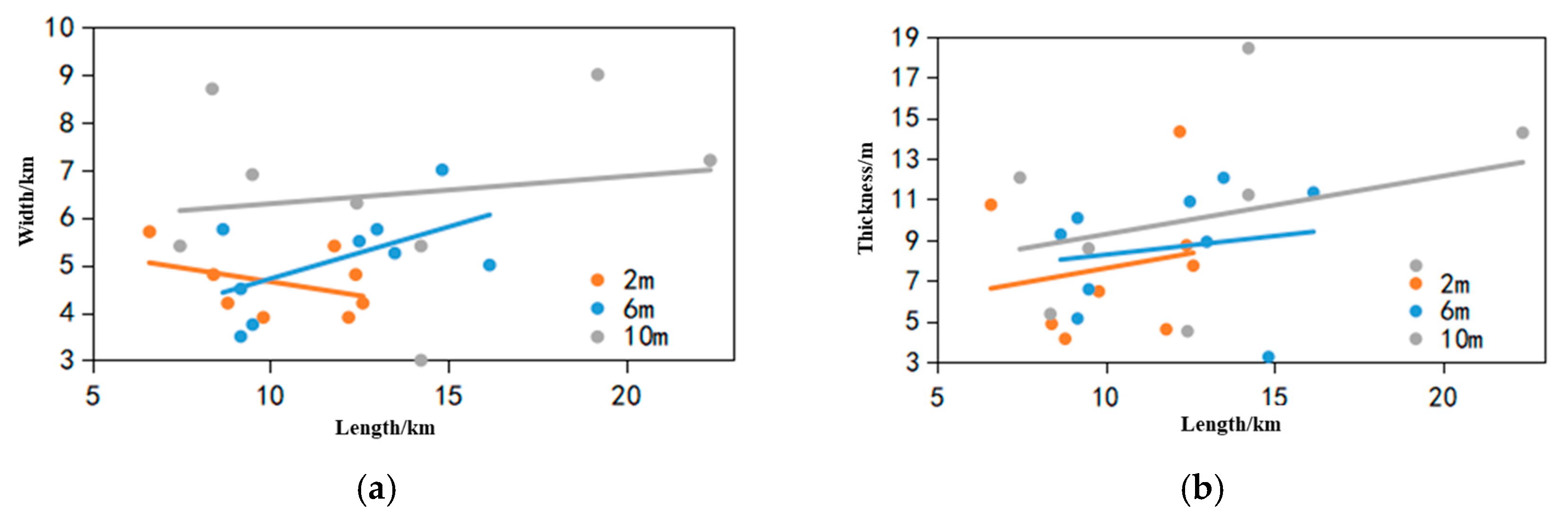
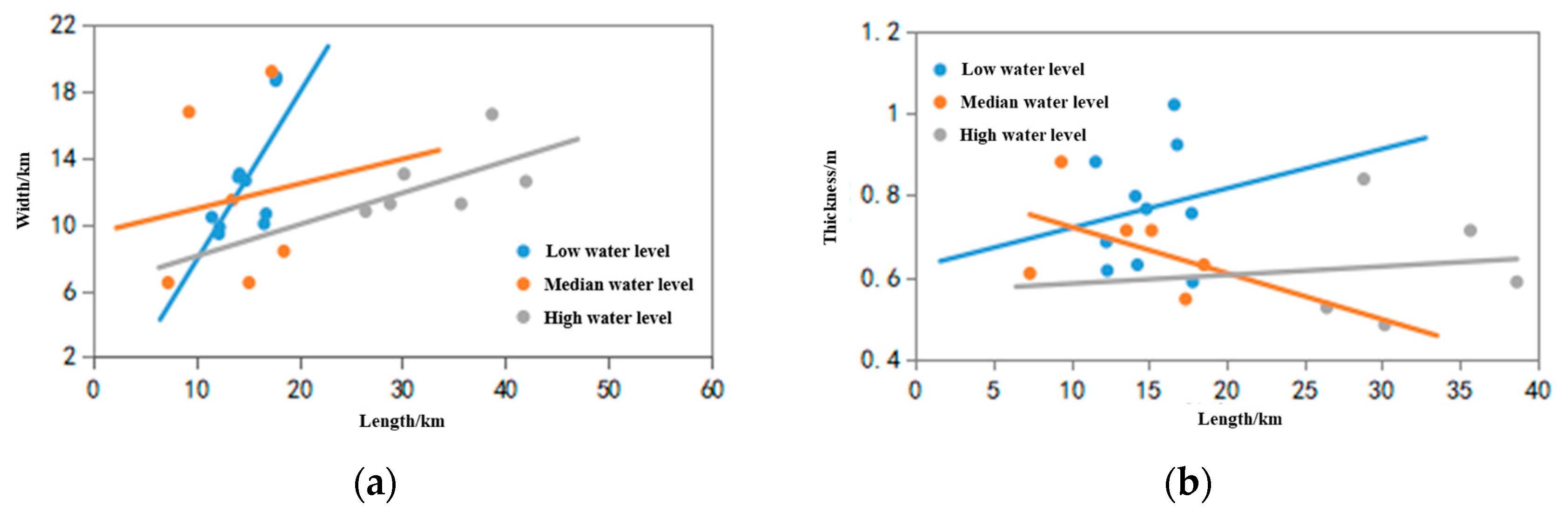
3.3.2. Tidal Range Factor Analysis
- Sedimentary distribution analysis
- 2.
- Velocity distribution analysis
- 3.
- Analysis of bar characteristics
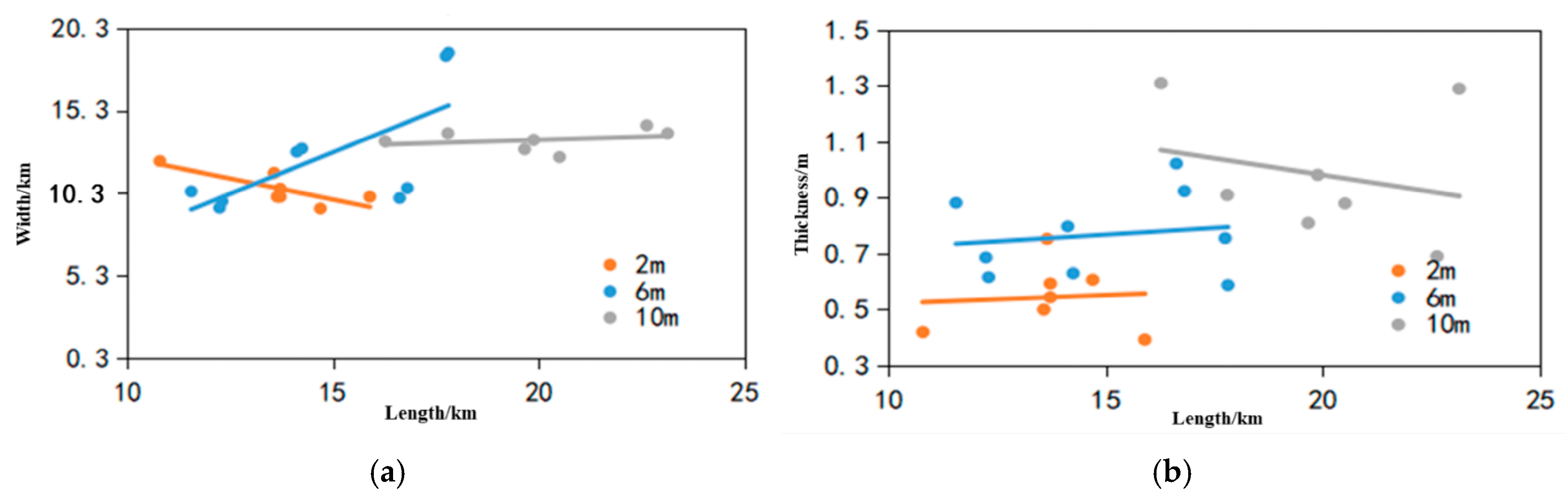
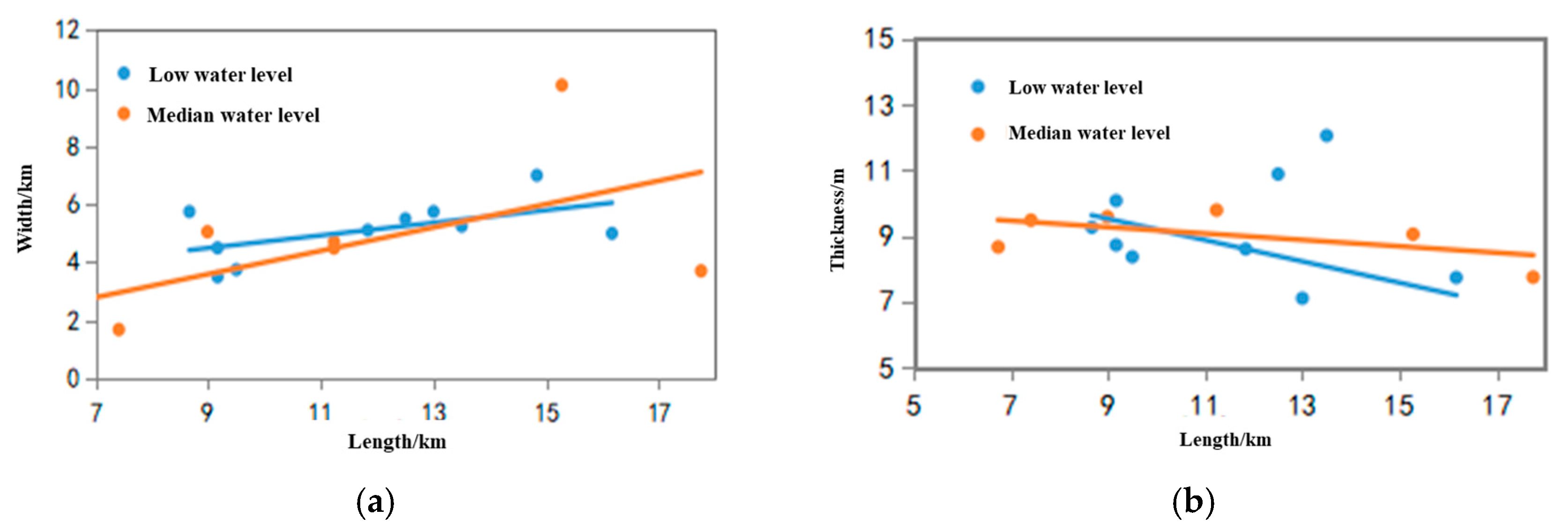
3.3.3. Water Level Factor Analysis
- Sedimentary distribution analysis
- 2.
- Velocity distribution analysis
- 3.
- Analysis of bar characteristics
3.4. Simulation Results
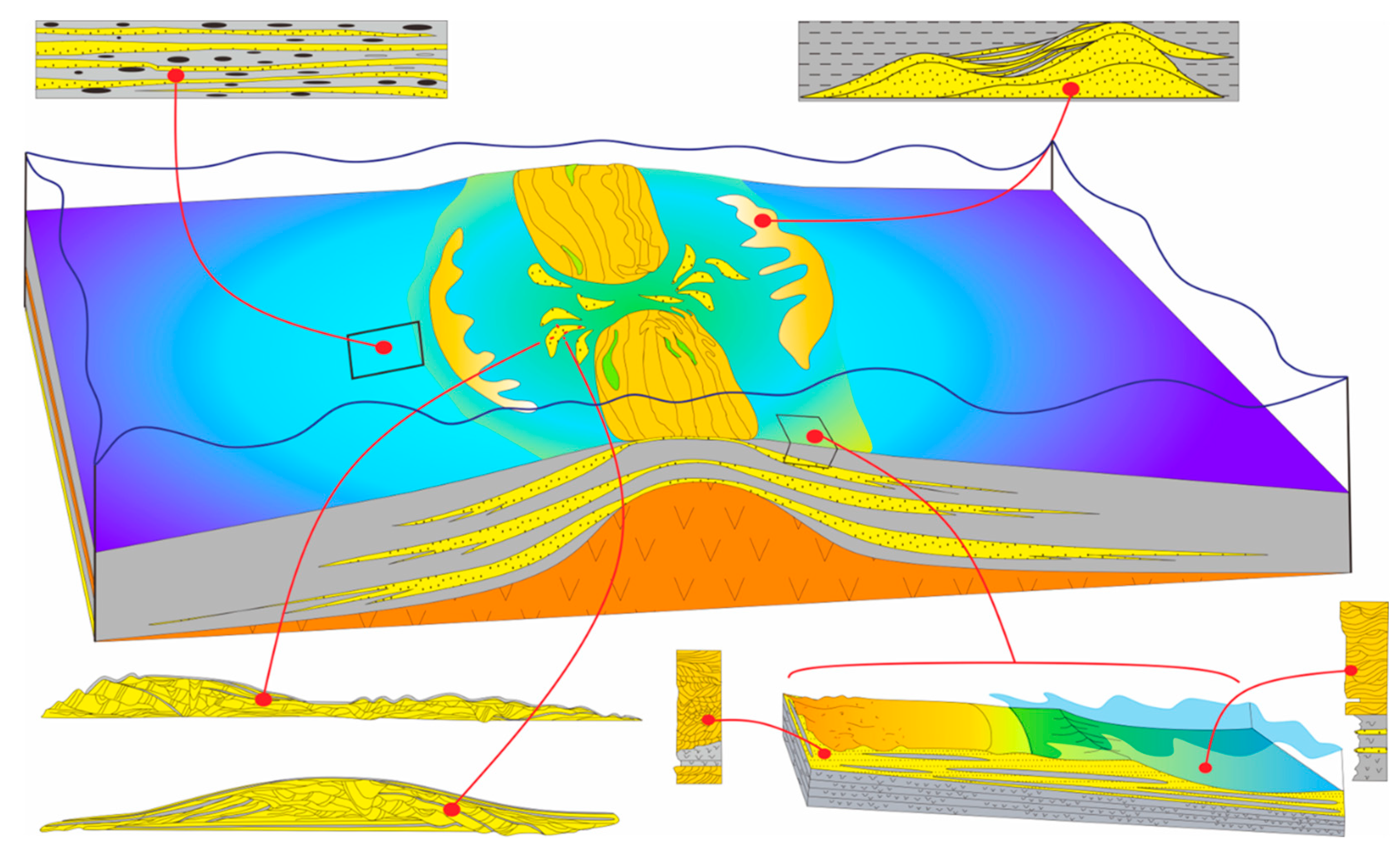
4. Geological Modeling Process
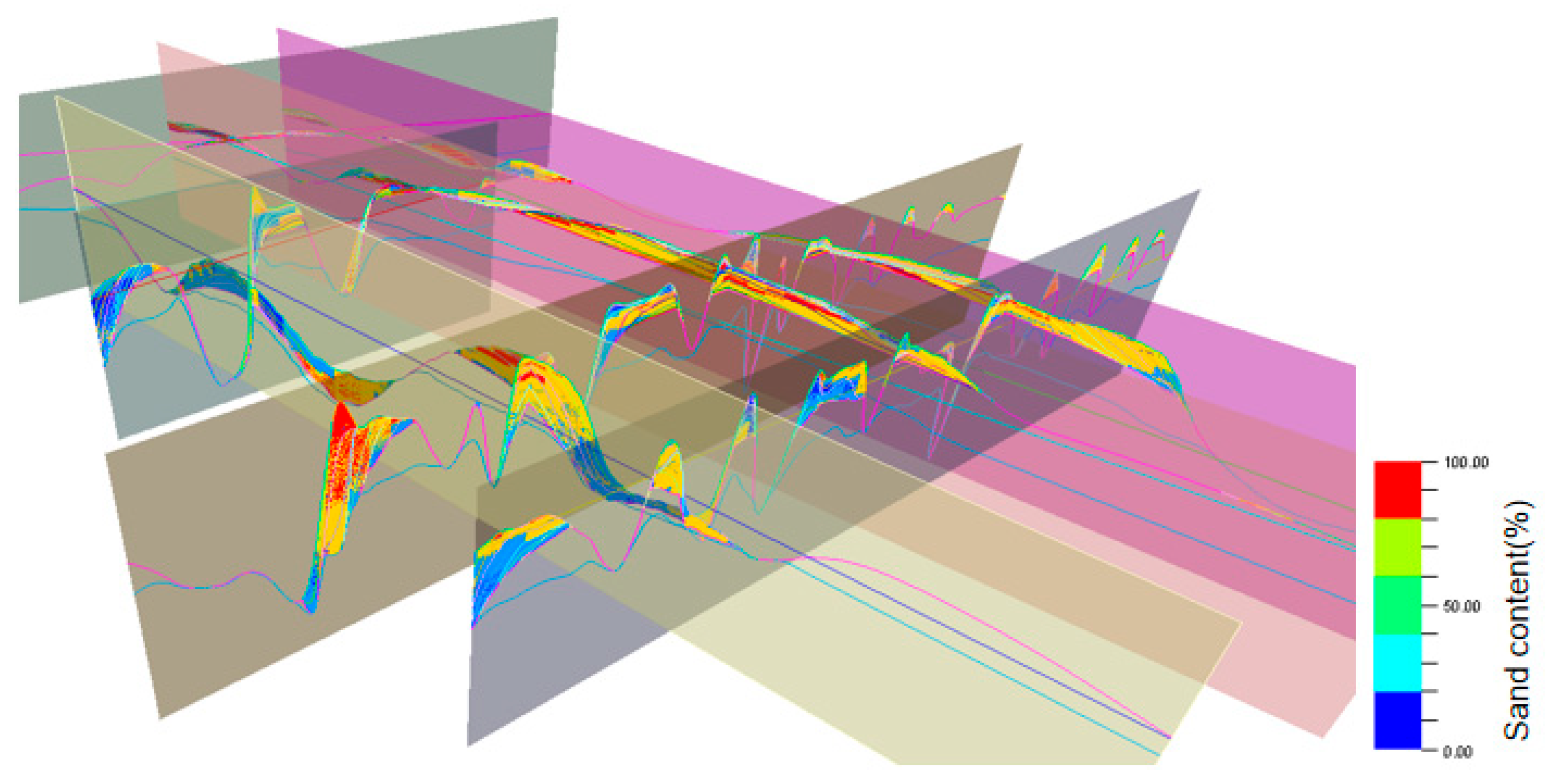
4.1. Analysis of Sedimentary Dynamics Data
4.2. Generation of 3D Training Images on the Basis of Deposition Dynamics
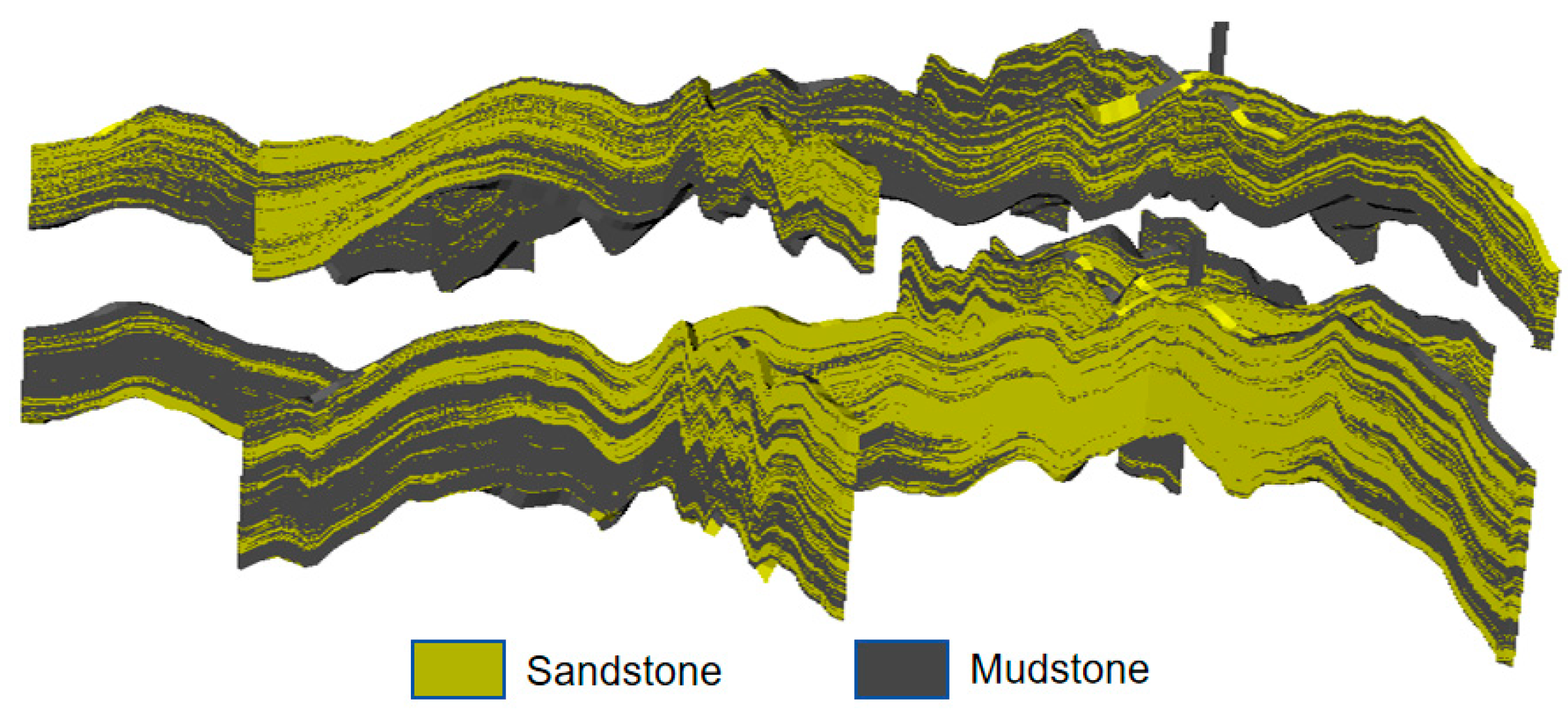
4.3. D Lithologic Model
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Wightman, D.M.; Pemberton, S.G. The lower Cretaceous (Aptian) McMurray Formation: An overview of the Fort McMurray area, northeastern Alberta. Pet. Geol. Cretac. Mannville Group West. Can. 1997, 18, 312–344. [Google Scholar]
- Dalrymple, R.W.; Choi, K. Morphologic and facies trends through the fluvial-marine transition in tide-dominated depositional systems: A schematic framework for environmental and sequence-stratigraphic interpretation. Earth Sci. Rev. 2007, 81, 135–174. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qian, W.; Yin, T.; Hou, G. A new method for clastic reservoir prediction based on numerical simulation of diagenesis: A case study of the ed1 clastic sandstones in the bozhong depression, bohai bay basin, China. Adv. Geo-Energy Res. 2019, 3, 82–93. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luo, S.; Dai, R.; Liu, Z.; Lyu, Q. Experimental Study on Sedimentary Simulation of Large Area Sand Body Formation in the He 8 Member of the Sulige Region; Petroleum Industry Press: Beijing, China, 2014; pp. 98–136. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, Y.; Sun, Y.; Xiu, Z.; Song, Y.; Wang, K.; Xie, Q. Numerical simulation of turbidity current and sediment characteristics in submarine canyons. Haiyang Xuebao 2020, 42, 75–87. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, X.; Lu, S.; Tang, M.; Sun, D.; Tang, J.; Zhang, K.; He, T.; Qi, N.; Lu, M. Numerical simulation of sedimentary dynamics to estuarine bar under the coupled fluvial-tidal Control. Earth Sci. 2021, 46, 2944–2957. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, K.; Wu, S.; Feng, W.; Zheng, D.; Yu, C.; Liu, Z. Discussion on evolution of bar in sandy braided river: Insights from sediment numerical simulation and modern bar. Acta Sedimentol. Sin. 2018, 36, 81–91. [Google Scholar]
- Schramkowski, G.P.; Schuttelaars, H.M.; Swart, H.E.D. The effect of geometry and bottom friction on local bed forms in a tidal embayment. Cont. Shelf Res. 2002, 22, 1821–1833. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Toffolon, M.; Crosato, A. Developing macroscale indicators for estuarine morphology: The case of the scheldt estuary. J. Coast. Res. 2007, 23, 195–212. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hillen, M.M.; Geleynse, N.; Storms, J.E.A.; Walstra, D.J.R.; Groenenberg, R.M. Morphodynamic modelling of wave reworking of an alluvial delta and application of results in the standard reservoir modelling workflow. Depos. Syst. Sediment. Successions Nor. Cont. Margin 2014, 46, 167–185. [Google Scholar]
- Weisscher, S.A.H.; Shimizu, Y.; Kleinhans, M.G. Upstream perturbation and floodplain formation effects on chute-cutoff-dominated meandering river pattern and dynamics. Earth Surf. Process. Landf. J. Br. Geomorphol. Res. Group 2019, 44, 2156–2169. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tang, M.; Lu, S.; Zhang, K.; Yin, X.; Ma, H.; Shi, X.; Liu, X.; Chu, C. A three dimensional high-resolution reservoir model of Napo Formation in Oriente Basin, Ecuador, integrating sediment dynamic simulation and geostatistics. Mar. Pet. Geol. 2019, 110, 240–253. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, H.; Huang, J.; Feng, W.; Liu, S.; Yin, Y. Analysis on formation factors and development characteristics of sand bar in tide-dominated estuaries—A case study based on Qiantang River. Geol. Rev. 2020, 66, 101–112. [Google Scholar]
- Yin, Y.; Wu, S. The progress of reservoir stochastic modeling. Nat. Gas Geosci. 2006, 17, 210–216. [Google Scholar]
- Wu, S.; Li, W. Multiple-point geostatistics: Theory, application and perspective. J. Palaeogeogr. 2005, 7, 137–144. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, T. Incorporating geological conceptual models and interpretations into reservoir modeling using multiple-point geostatistics. Earth Sci. Front. 2008, 15, 26–35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, W.; Lin, C.; Dong, C. Application of multiple-point geostatistics in geological modeling of D Oilfield in Peru. J. China Univ. Pet. (Nat. Sci. Ed.) 2008, 32, 24–28. [Google Scholar]
- Hua, C.; Yu, M.; Wei, H.; Liu, C. The mechanisms of energy transformation in sharp open-channel bends: Analysis based on experiments in a laboratory flume. J. Hydrol. 2019, 571, 723–739. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shemin, G.G.; Deev, E.V.; Vernikovsky, V.A.; Drachev, S.S.; Moskvin, V.I.; Vakulenko, L.G.; Pervukhina, N.V.; Sapyanik, V.V. Jurassic paleogeography and sedimentation in the northern West Siberia and South Kara Sea, Russian Arctic and Subarctic. Mar. Pet. Geol. 2019, 104, 286–312. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shemin, G.G.; Vernikovskiy, V.A.; Moskvin, V.I.; Vakulenko, L.G.; Deev, E.V.; Pervukhina, N.V. Lithologic and paleographic reconstruction of Jurassic system in West Siberian sedimentary basin. Oil Gas Geol. 2018, 6, 35–61. [Google Scholar]
- Kontorovich, A.E.; Kontorovich, V.A.; Ryzhkova, S.V.; Shurygin, B.N.; Yan, P.A. Jurassic paleogeography of the West Siberian sedimentary basin. Russ. Geol. Geophys. 2013, 54, 747–779. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Van der Vegt, H.; Storms, J.E.A.; Walstra, D.J.R.; Howes, N.C. Can bed load transport drive varying depositional behaviour in river delta environments? Sediment. Geol. 2016, 345, 19–32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yin, X.; Lu, S.; Liu, K.; Jiang, S.; Sun, B. Non-uniform subsidence and its control on the temporal-spatial evolution of the black shale of the Early Silurian Longmaxi Formation in the western Yangtze Block, South China. Mar. Pet. Geol. 2018, 98, 881–889. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, H.; Wei, Q. The Theory and Application of Delft 3D Model; China Ocean Press: Beijing, China, 2018; pp. 1–7. [Google Scholar]
- Thanh, V.Q.; Reyns, J.; Wackerman, C.; Eidam, E.F.; Roelvink, D. Modelling suspended sediment dynamics on the subaqueous delta of the Mekong River. Cont. Shelf Res. 2017, 147, 213–230. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nowacki, D.J.; Ogston, A.S.; Nittrouer, C.A.; Fricke, A.T.; Van, P.D.T. Sediment dynamics in the lower Mekong River: Transition from tidal river to estuary. J. Geophys. Res. Ocean. 2015, 120, 6363–6383. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tang, T.; Huang, J.; Yin, Y.; Feng, W. Analysis of influence factors of tide-dominated estuaries based on deposition numerical simulation. Open J. Yangtze Oil Gas 2018, 3, 139–146. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Gugliotta, M.; Saito, Y. Matching trends in channel width, sinuosity, and depth along the fluvial to marine transition zone of tide-dominated river deltas: The need for a revision of depositional and hydraulic models. Earth Sci. Rev. 2019, 191, 93–113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, K.; Wren, P.A.; Ma, Y. Tidal and storm impacts on hydrodynamics and sediment dynamics in an energetic ebb tidal delta. J. Mar. Sci. Eng. 2020, 8, 810. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tang, J.; Tang, M.; Lu, S.; Liu, X.; Zhang, K.; He, T.; Han, D. Three-dimensional modeling of estuary reservoir based on coupling sedimentary dynamics simulation and multipoint geostatistics method. Earth Sci. 2024, 49, 174–188. [Google Scholar]


| Parameter Setting | Numerical Value |
|---|---|
| Work area size, km | 1500 × 1200 |
| Grid size, km | 3 × 3 |
| Discrete time step, min | 1 |
| Bottom shape setting | Vym |
| Tidal height, m | 6 |
| Initial water level, m | 1 |
| River flow, m3/s | 3000 |
| Sediment particle size, μm | 130, 65, mud |
| Coarse: fine: mud | 1:1:1 |
| Maximum water depth, m | 176 |
| Wave height, m | 1 |
| Deposition acceleration factor | 100 |
| Scale | Model Name | Factors | Type | Parameters | Reason for Selection |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| BASIN | HST | bottom shape | \ | Malyshev | Secondary main force layer |
| BASE | \ | Vym | Main layer/Base model | ||
| HIGHWATER | water level | High water level | 45 m | The study area is all below the storm wave base level | |
| MEDIUMWATER | Medium water level | 15 m | The study area is below the wave base | ||
| BASE | Low water level | 1 m | The study area is near the wave base | ||
| HIGHTIDE | tide | High tide | 10 m | Maximum possible tide | |
| BASE | Medium tide | 6 m | Mean tide | ||
| LOWTIDE | Low tide | 2 m | Minimum tide | ||
| HIGHFLUVIAL | discharge | High discharge | 6000 m3/s | Large rivers | |
| BASE | Medium discharge | 3000 m3/s | Compared with Hudson Bay at the same latitude | ||
| LOWFLUVIAL | Low discharge | 1500 m3/s | Small rivers | ||
| HIGHWAVE | wave | High wave | 1.5 m | Large wave amplitude | |
| BASE | Medium wave | 1 m | Average wave amplitude | ||
| LOWWAVE | Low wave | 0.5 m | Small wave amplitude |
| Bottom Shape Factor | Average Length/km | Average Width/km | Average Thickness/m | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Tidal Bar | Sheet Sand-Sand Flat | Tidal Channel | Tidal Bar | Sheet Sand-Sand Flat | Tidal Channel | Tidal Bar | Sheet Sand-Sand Flat | Tidal Channel | |
| Vym | 11.83 | 14.83 | 77.47 | 5.11 | 12.60 | 3.72 | 8.61 | 0.77 | 7.43 |
| MalyShev | 13.19 | 15.86 | 57.06 | 6.44 | 15.58 | 2.44 | 7.38 | 0.71 | 3.41 |
| Tidal Range Amplitude | Average Length/km | Average Width/km | Average Thickness/m | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Tidal Bar | Sheet Sand-Sand Flat | Tidal Channel | Tidal Bar | Sheet Sand-Sand Flat | Tidal Channel | Tidal Bar | Sheet Sand-Sand Flat | Tidal Channel | |
| Low tide (2 m) | 10.33 | 13.73 | 69.64 | 4.61 | 10.56 | 2.23 | 7.70 | 0.54 | 5.55 |
| Medium tide (6 m) | 11.83 | 14.83 | 77.47 | 5.11 | 12.60 | 3.72 | 8.61 | 0.77 | 7.43 |
| High tide (10 m) | 13.48 | 19.88 | 81.40 | 6.49 | 13.52 | 4.31 | 10.27 | 0.98 | 7.17 |
| Water Level Height | Average Length/km | Average Width/km | Average Thickness/m | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Tidal Bar | Sheet Sand-Sand Flat | Tidal Channel | Tidal Bar | Sheet Sand-Sand Flat | Tidal Channel | Tidal Bar | Sheet Sand-Sand Flat | Tidal Channel | |
| Low water level (2 m) | 11.83 | 14.83 | 77.47 | 5.11 | 12.60 | 3.72 | 8.61 | 0.77 | 7.43 |
| Medium water level (6 m) | 11.23 | 13.55 | 70.55 | 4.49 | 11.43 | 3.09 | 9.06 | 0.68 | 5.76 |
| High water level (10 m) | - | 49.21 | - | - | 13.29 | - | - | 0.64 | - |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Liu, Y.; Ju, B.; Mo, W.; Chen, Y.; Zhao, L.; Tang, M. Three-Dimensional Modeling of Tidal Delta Reservoirs Based on Sedimentary Dynamics Simulations. Appl. Sci. 2025, 15, 9527. https://doi.org/10.3390/app15179527
Liu Y, Ju B, Mo W, Chen Y, Zhao L, Tang M. Three-Dimensional Modeling of Tidal Delta Reservoirs Based on Sedimentary Dynamics Simulations. Applied Sciences. 2025; 15(17):9527. https://doi.org/10.3390/app15179527
Chicago/Turabian StyleLiu, Yunyang, Binshan Ju, Wuling Mo, Yefei Chen, Lun Zhao, and Mingming Tang. 2025. "Three-Dimensional Modeling of Tidal Delta Reservoirs Based on Sedimentary Dynamics Simulations" Applied Sciences 15, no. 17: 9527. https://doi.org/10.3390/app15179527
APA StyleLiu, Y., Ju, B., Mo, W., Chen, Y., Zhao, L., & Tang, M. (2025). Three-Dimensional Modeling of Tidal Delta Reservoirs Based on Sedimentary Dynamics Simulations. Applied Sciences, 15(17), 9527. https://doi.org/10.3390/app15179527








