Abstract
Vertical low-permeability barriers are widely used to improve the stability and seepage resistance of flood embankments. The present study evaluates three barrier technologies—vibrating beam slurry walls (VBSWs), deep soil mixing (DSM), and low-pressure grout injection (LPG)—through a series of consolidated drained triaxial tests and permeability coefficient tests on soil samples collected from the sites where different barrier installation technologies were used. All three barrier installation methods produced substantial improvements in both mechanical and hydraulic performance: the effective angle of internal friction (φ′) increased by 3–6° in samples with a plasticity index near 3.5%, and coefficients of permeability dropped from 10−8–10−7 m/s in untreated soils to below 10−9 m/s in treated specimens. The key finding of the study is that the barrier performance varies by the technology and the soil type. According to the result, DSM is the most effective technology used in clay-rich soils (φ′ increased up to 4°); LPG achieved the lowest permeability (7 × 10−11 m/s) in granular soils; and VBSWs balanced strength and impermeability, most effective in silty sands. Flow-pump tests further demonstrated that treated soils required much longer to stabilize under a constant flow rate and could sustain higher hydraulic gradients before reaching equilibrium. These findings show the importance of matching barrier technology to soil plasticity and liquidity characteristics and highlight saturation as essential for reliable laboratory evaluation. The results provide a scientific basis for selecting and designing vertical barriers in flood-preventing infrastructure, offering performance benchmarks for improving hydraulic and geotechnical structures.
1. Introduction
The increasing frequency and intensity of extreme weather events and ageing infrastructure have triggered the urgency for the modernisation of flood protection systems, particularly dykes and earth dams. Ensuring these critical infrastructure systems’ structural integrity and hydraulic performance is essential for mitigating flood risk and protecting both lives and property. Flood prevention infrastructure restoration efforts typically involve improving the impermeability of the embankment body and its foundation through ground-stabilisation techniques, which must be carefully designed based on detailed filtration analyses and stability assessments. These analyses rely on geotechnical parameters derived from comprehensive field investigations and laboratory testing. When the embankment foundation exhibits low permeability, it is often sufficient to insulate the downstream slope using materials such as bentonite mats, geomembranes or geocomposites, which would provide both geotechnical and hydraulic safety [1,2]. In cases where both the embankment and its foundation require sealing, constructing a continuous barrier from the crest of the subsoil is considered one of the most effective approaches. The selection of barrier construction methods depends on several factors, including the structure of the embankment, distance to existing infrastructure, and the contractor’s technical capabilities. Recent studies have emphasised the importance of selecting appropriate sealing technologies tailored to specific site conditions. Skutnik et al. [3,4] highlighted the effectiveness of various trenchless methods, such as deep soil mixing (DSM) and low-pressure injection, in creating low-permeability barriers for hydrotechnical structures using in situ tests. These methods have been extensively used to address seepage issues and improve the stability of flood embankments. Furthermore, the integration of geosynthetic materials, like geosynthetic clay liners (GCLs), has shown promise in enhancing the impermeability of embankments. Studies have demonstrated that the use of GCLs, in combination with other sealing techniques, can significantly reduce seepage and improve the overall performance of flood protection systems, ensuring an increase in the factor of safety [5]. Despite the growing use of vertical barrier technologies in flood embankment restoration, there is no common and standardised framework for evaluating their quality and performance. The evolving nature of construction materials and techniques demands the implementation of strict monitoring protocols to assess the permeability and geotechnical safety of the installed barriers over time. These methods vary in terms of material composition, installation techniques, and structural configuration, but all aim to create continuous, low-permeability cut-offs within or beneath the hydraulic structure.
The present paper involves a comparative evaluation of selected barrier technologies, with particular emphasis on their structural effectiveness, ease of implementation, and long-term performance using laboratory tests. The objective is to provide guidance for choosing appropriate solutions in flood embankment restoration projects based on current engineering practices and technical constraints. Low-permeability barriers, as part of flood prevention measures, are designed to restrict groundwater flow, thereby reducing the risk of soil saturation and subsequent flood-related failures of earth structures. Their primary advantage lies in minimizing seepage, which is critical in maintaining the stability and integrity of dykes and dams during extreme hydrological events. Effectively designed barriers can significantly increase the hydraulic gradient resistance, reducing the likelihood of detrimental pore water pressures accumulating in the structure or its foundation. The hydraulic conductivity of low-permeability barriers is a critical factor influencing their effectiveness in flood prevention. Studies have shown that barriers composed of clay, bentonite, and cement-bentonite mixtures exhibit significantly lower permeability than conventional soil profiles. For example, soil-bentonite barriers can achieve hydraulic conductivities of 10−7 to 10−9 m/s, which effectively limits seepage flow [6,7,8,9]. Moreover, integrating geosynthetic layers within barrier designs can further enhance hydraulic performance by providing additional mechanical support and controlling seepage more effectively. Several advanced installation methods are employed to create low-permeability barriers, each offering unique advantages based on site conditions and project requirements. One of the most common nowadays is deep soil mixing (DSM), which involves the mixing of in situ soil with cementitious materials to create a vertical wall. This process can be tailored to create barriers of varying permeability depending on the binder used and the mixing method applied. With DSM, the resultant composite material displaces weak soil layers, significantly improving the strength and hydraulic performance of the barrier. Studies demonstrate that DSM can create barriers with effective sealing capabilities against floodwaters, particularly when implemented in clay-rich soil profiles [10,11,12,13]. Another well-established method is low-pressure grout injection, which is also considered to be a viable method for constructing low-permeability barriers. This technique involves injecting a slow-moving slurry of cement or polymer into the ground to fill voids and displace water, significantly reducing permeability in targeted areas. This method is particularly advantageous in saturated conditions where excavation is challenging. Numerical simulations suggest that effectively executed grout injections can significantly reduce the hydraulic conductivity of the treated volumes, enhancing flood resilience in vulnerable areas [14,15,16]. Commonly used technology, such as vibrated beam slurry walls (VBSWs), is installed using a combination of vibration and hydraulic pressure to create a barrier that can withstand compressive loads and lateral stress from floodwaters. This method utilizes a vibrating beam to penetrate through soil layers, creating a trench that is backfilled with a low-permeability slurry. The advantage of this approach lies in its ability to form continuous barriers that minimize seepage along weak geological interfaces. Research indicates that vibrated beam slurry walls exhibit improved resistance to lateral soil movements caused by flooding, enhancing the overall stability of earthen structures [17].
Utilizing these advanced installation techniques results in distinct performance advantages. Barriers constructed with low-permeability properties demonstrate reduced permeability rates, significantly lowering the risk of liquefaction during flood events. Furthermore, the enhanced structural integrity of earthworks following the installation of these barriers contributes to the increased safety and operational longevity of dykes and dams in flood-prone areas. Studies have emphasized that the longevity and robustness of flood embankments are essential in minimizing the risk of catastrophic failures during extreme weather events [18,19,20]. The safety of dykes and flood embankments during floods is characterized by their ability to withstand hydraulic loading and resist internal erosion. Some of these failures could be avoided by the implementation of vertical drains to accelerate the consolidation of the embankment [21]. Recent research highlights the importance of monitoring the performance and durability of these structures in the context of climate change. For instance, ref. [20] discussed how the presence of dams plays a significant role in reducing global flood exposure, thereby underlining the necessity of maintaining their integrity [19]. Moreover, studies reveal that effective flood mapping and in situ measures can significantly reduce potential damage caused by sudden flooding events [22]. It is clear that sustaining the operational lifespan of flood protection structures is vital for ongoing public safety and resource management. Implementing low-permeability barriers in earth dykes and dams plays a pivotal role in flood mitigation strategies. The choice of installation method—whether deep soil mixing, low-pressure grout injection, or vibrated beam slurry walls—should be informed by specific site conditions, soil types, and desired performance characteristics. The integration of contemporary sealing technologies, such as GCLs, alongside innovative construction techniques, ensures the resilience of flood embankments [23]. Ongoing research and development in barrier technologies and installation methods will be vital in addressing the challenges posed by flooding and ensuring the resilience of civil infrastructure. The comparative analysis of permeability, hydraulic parameters, and mechanical properties between earth dykes and dams constructed from untreated soil and those treated with hydraulic barriers reveals significant differences that can influence flood resilience. Natural soils typically display variable permeability characteristics, leading to inconsistent water retention and seepage rates under high hydraulic loads. In contrast, barriers made from engineered materials such as soil-bentonite mixtures, cement-bentonite composites, or biopolymer additives are specifically designed to exhibit substantially lower hydraulic conductivity, often on the order of 10−7 to 10−9 m/s [24,25]. Such engineered barriers effectively restrict water flow, thereby preventing the saturation of the soil matrix and reducing the risk of failure during flood events. The mechanical properties of treated soil, especially those using cement or other hydraulic binders, often surpass the characteristics of their natural counterparts. For instance, cement-treated soils demonstrate enhanced drained shear strength and durability, essential for maintaining structural integrity under fluctuating saturation conditions [26,27]. Studies have shown that introducing additives improves mechanical strength and stabilizes the soil’s microstructure, improving its long-term performance in flood-prone environments [28]. Moreover, the detailed examination of soil barriers highlights the potential of modified elastoplastic constitutive models to more accurately represent the behaviour of treated soils compared to naturally deposited soils, promoting their application in flood control mechanisms [26]. Furthermore, the systematic application of advanced construction techniques, such as the use of bio-engineering methods, provides innovative solutions for enhancing water retention capacity, thereby improving flood prevention systems [29]. Ultimately, geotechnical works and technologies employed in constructing dykes and dams through hydraulic barriers yield substantial advantages over untreated soils, as they ensure greater control over hydraulic behaviour and enhance mechanical stability, crucial for effective flood risk management. Bearing all this in mind, the present study aims at introducing an integrated and complex approach that combines geotechnical and hydraulic laboratory tests to evaluate the efficiency and performance of impermeable barrier technologies. By comparing three different methods, the research provides a broader understanding of their application limits with respect to soil type and consistency.
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Tested Soil Samples
The tested material consists of soil samples collected from dykes where impermeable vertical barriers were implemented using three technologies: VBSWs, DSM, and low-pressure grout injection (LPG). The main reason for choosing the proposed technologies to be investigated is the fact they are the most commonly used for flood protection infrastructure restoration and improvement [3,10]. The soil samples collected using thin wall Shelby tubes were transported to the laboratory to determine the principal physical parameters, perform triaxial tests, and obtain hydraulic parameters. The physical property tests included grain size distribution analysis and soil classification. The soil material used in the study consisted of clayey, silty and fine sands as well as fine grained soils, i.e., saclSi and sasiCl. All were collected in situ condition as undisturbed samples. Further parameters such as natural moisture content and consistency limit: plastic limit (wP) and liquid limit (wL), allowing for the determination of the plasticity index (PI) and liquidity index (LI), are given in Table 1. Strength parameter tests were performed using a triaxial compression rig while applying the consolidation drained method (CD). The triaxial rig was also used to measure permeability coefficients using the flow-pump technique. Triaxial compression tests were conducted on samples with a diameter of 50 mm and a height of 100 mm. To determine changes in strength parameters and filtration characteristics, the tests were also conducted on soil samples consisting of untreated material, where no impermeable barrier construction technology was implemented. This was to give a broad picture of the hydro-mechanical behaviour of soil depending on the vertical barrier methodology used and to compare with soil samples where no soil treatment was applied. Detailed characterization of the soil samples’ physical parameters is presented in Table 1.

Table 1.
Physical parameters of soil samples collected from the sites of different barrier construction methods used.
2.2. Methodology of Laboratory Testing
To determine the strength parameters of the soil samples, 22 series of triaxial CD tests were conducted, including 11 series on soil samples treated with insulating materials and 11 series on untreated soil samples without additives used for barrier construction, as reference tests to determine the changes in cohesion and angle of internal friction parameters. The tests were conducted in a standard triaxial apparatus equipped with an additional module—a flow pump, equipped with rods and a rigid connection between the cell and the piston rod. The saturation was performed using the equalization pressure > 250 kPa, followed by consolidation and then shearing in CD conditions at a rate determined according to PN-EN ISO 17892-9:2018-05 [30], with a shear rate lower than 0.001 mm/min [31]. All samples were fully saturated (B > 0.95) using the back-pressure saturation method. The next stage was consolidation. Samples collected from a single core were consolidated under isotropic effective stresses ranging from 100 to 400 kPa. The consolidation process was conducted under back-pressure conditions. CD tests were chosen for their suitability in measuring shear strength under steady-state drainage and filtration conditions. Such tests better simulate long-term dyke performance.
Shearing was performed according to the standard procedure, i.e., at a constant chamber pressure with increasing vertical stress. The laboratory tests also involved hydraulic parameters determination, focusing on permeability measurements using the flow pump technique. This method was originally introduced by Olsen et al. [32], and over the years, it has been improved and used in geotechnical laboratories worldwide. This method changed the approach to determining flow parameters during testing. It forces a constant water flow rate through the sample and measures the pressure difference at both ends of the sample. This approach ensures more accurate and unambiguous measurements since pressure differences are easier to measure than small volumes of water flows. The flow range is broad enough to allow the technique to determine the permeability coefficient in all cohesive soils. Water is introduced at a constant flow rate from the bottom of the sample, gradually increasing the hydraulic pressure at its lower surface. The schematic set-up of the research stage with all the components is presented in Figure 1.
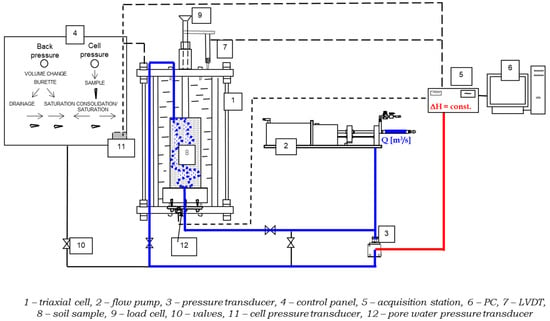
Figure 1.
Laboratory research stage set up for testing hydraulic and mechanical parameters of the soil samples.
The intensity of the pressure increase depends on the relationship between the applied (forced) flow rate and the permeability of the profile. At that stage, the flow has not yet stabilized over time. The ability to set a wide range of flow rates makes it relatively easy to adjust the flow so that even in very low-permeability soils, the pressure stabilization time remains short (up to 20 min). The stabilized pressure difference between the bottom and top of the sample does not exceed 150 kPa, which is within the measurement range of the differential pressure transducers. Another advantage of this method is its ability to integrate the pump with a sample tested in a triaxial cell or a consolidometer. This allows the sample to be saturated using the back-pressure method, eliminating uncertainties related to the lack of control over full saturation of soil, which is a crucial condition for accurate testing.
The back-pressure method and the criteria that should be met for saturating pre-consolidated cohesive and granular soil samples were described earlier. To determine the permeability parameters of the soils collected from the tested sites, 22 tests were conducted (11 tests on untreated soils and 11 tests on soils collected from vertical barriers installation sites) using a triaxial apparatus equipped with a flow pump to enforce a constant water flow rate through the sample. In tests using the flow pump, a constant water flow rate is forced through the sample, and the pressure difference between the ends of the sample is measured [33]. This method ensures highly accurate measurements since pressure is easier to measure than within small water flows. The broad flow rate range makes this technique suitable for determining the permeability coefficient in low-permeability materials. Water is introduced at a constant rate from the bottom of the sample, gradually increasing the hydraulic pressure at its lower surface. The intensity of the pressure increase depends on the relationship between the applied flow rate and the permeability of the medium. At this stage, the flow is not yet stabilized over time. The ability to set a very wide range of flow rates allows for easy adjustment, ensuring that even in extremely low-permeability materials, the pressure stabilization time remains short (up to several hundred minutes). The stabilized pressure difference between the bottom and top of the sample does not exceed the applied effective stress value. The integration of the pump with a sample in a triaxial compression apparatus allows for saturation using the back-pressure method, eliminating uncertainties related to the lack of control over full soil saturation. Several different flow rates (Q) were applied through the sample, and measurements were recorded for each of them. The recorded data included time and pore water pressure increase (Δu). Measurements continued until pore water pressure stabilization was achieved. The diagram of the complete testing procedure is presented in Figure 2. It should be emphasized that permeability measurement using the gradient stabilization method is conducted under back-pressure conditions. This means that the air dissolved during saturation will not undergo de-condensation. The samples were tested in two series: untreated soil samples without additives, and soil samples mixed with insulating materials used for barriers construction.
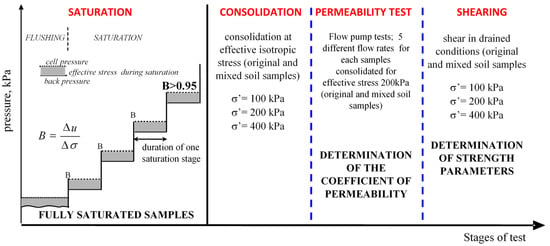
Figure 2.
Stages and characterization of triaxial and permeability testing procedure.
3. Results
3.1. Drained Shear Strength Tests
Based on the results of triaxial tests (CD), relationships between the mechanical and physical properties of the tested soils were presented. The plasticity index (PI) was adopted as the most reliable factor characterizing the variability of mechanical parameters in relation to the physical properties of the soils. Figure 3 shows the relationship between the values of the angle of internal friction obtained from tests conducted with and without additives and the plasticity index. The tests were carried out under various ranges of average effective stresses at the end of the consolidation stage, although the stress values did not exceed 400 kPa. To better understand the mechanical behaviour of tested soil samples, Figure 4 illustrates the variability of the angle of internal friction corresponding to the liquidity index (LI). The lower the value of the tested sample, the smaller the change of angle of internal friction. Similar relationships were presented in works by [34,35] for tested soil samples with and without additives used for constructing impermeable barriers.
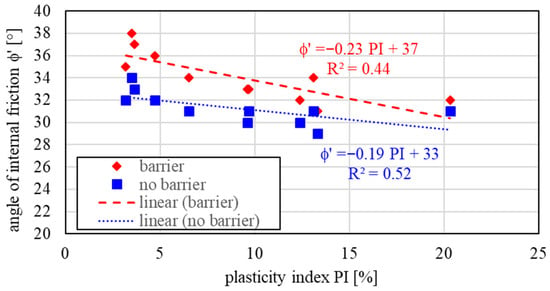
Figure 3.
Plasticity index and angle of internal friction relationship for treated and untreated soil samples.
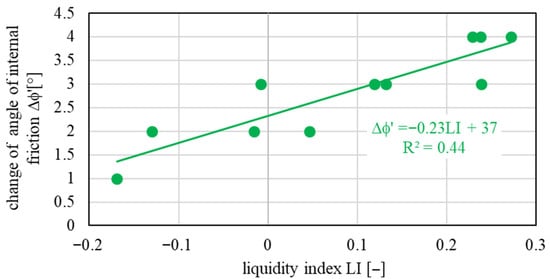
Figure 4.
Change in angle of internal friction between treated and untreated soil samples vs. liquidity index.
For all tested soils, higher values of the angle of internal friction were obtained for the treated samples (barrier). As the LI increases, the changes in φ are more significant. This means that in stiffer soil samples, the changes are smaller, while in plastic soils, they are larger. This justifies the higher effectiveness of using barriers in sandy soils rather than in more cohesive ones. Figure 5 shows the effective stress paths from sample soil tests with and without additives for soil with PI = 3.64%. Soil samples representing parameters of the constructed barriers are characterised by a higher angle of internal friction than untreated soil samples (where no reinforcement was used). Based on triaxial tests, it was found that the use of impermeable barriers results in an increase in the effective angle of internal friction (φ’) by 3–6° compared to untreated soil samples (no barrier). For example, for soils with a plasticity index PI ≈ 3.5%, the φ’ value was as follows: without the additives (no barrier): 30–32°, and with the additives (barrier): 35–38°.
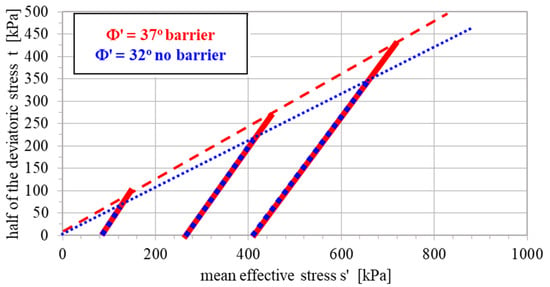
Figure 5.
Stress paths representing changes in shear strength for untreated and improved soil samples at plasticity index of PI = 3.64%.
Shear strength tests confirm that vertical barrier systems—whether constructed using vibrating beam slurry walls (VBSWs), deep soil mixing (DSM), or low-pressure grout injection (LPG)—lead to improvements in the mechanical performance of soils. Triaxial testing consistently recorded increases in the angle of internal friction (φ′) by approximately 3–6° in treated samples compared to untreated ones, with values rising from 30–32° to 35–38° for soils with a plasticity index (PI) of about 3.5%. The highest values of angle of internal friction, however, were measured for VBSWs technology. When it comes to soil type, however, the improvement is most evident in those of lower plasticity, suggesting that barrier technologies provide stronger reinforcement under such conditions giving the lowest values for LPG for same soil type used for construction of the barrier. In contrast, soils with higher plasticity shows a smaller relative increase in φ′.
3.2. Permeability Test Results
To obtain a complete characterization of the flow velocity as a function of the gradient, multiple gradient stabilization tests were performed for each sample at a given flow rate. The gradient stabilization process is largely dependent on the degree of pore water saturation. Figure 6 presents example of pressure stabilization characteristics at different initial gradients for soil samples before and after soil was treated with additives.
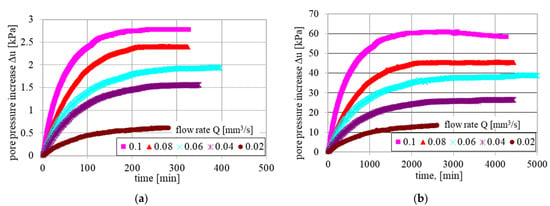
Figure 6.
Pressure stabilisation paths change in time at different flow rates for (a) untreated and (b) improved soil samples.
In the case of untreated (untreated) soil samples, stabilization occurs relatively quickly. There is a noticeable trend of increasing stabilization time as the flow rate increases. The pressures for reinforced (treated) soil samples take significantly longer to stabilise compared to untreated samples, with differences of several magnitudes. For example, at the lowest flow rate of 0.02 mm3/min, the gradient stabilization time for treated samples is approximately 3000 min, which is nearly ten times longer than for untreated soil samples (about 300 min). The gradient stabilization curves for samples with identical flow rates also differ in terms of the final stabilized gradient values. The stabilized gradients for modified soils are higher than those for untreated soil samples. To compare the permeability characteristics of the studied soils before and after reinforcements, the relationship between flow velocity and stabilized hydraulic gradient is presented in Figure 7.
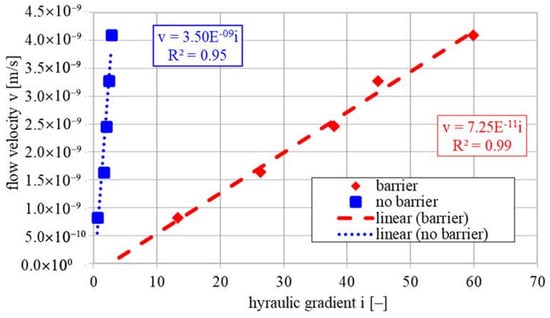
Figure 7.
Relationship between flow velocity and hydraulic gradient and their characteristics for both sets of samples.
It is important to note that the presented results are based on multi-test measurements and allow determining the function over a wide range of gradient variability. For the hydraulic parameters testing, the major focus was placed on determining the permeability coefficient analyses (Figure 8 and Figure 9) for untreated and modified (reinforced) samples and representing their changes depending on plasticity and consistency conditions.
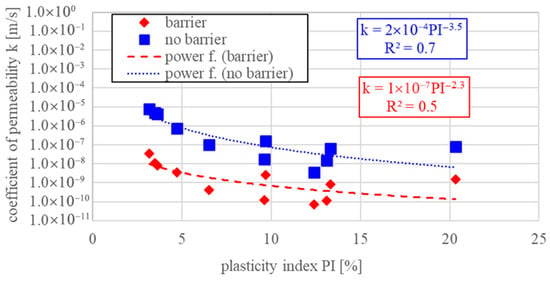
Figure 8.
Permeability coefficient results for untreated and reinforced samples depending on plasticity index.
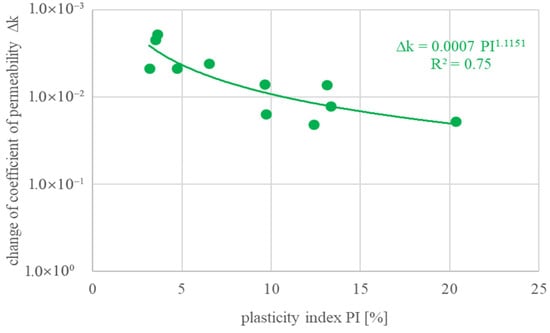
Figure 9.
Permeability coefficient changes in untreated and reinforced soil samples with changes in plasticity index.
For the samples collected from the sites where vertical barriers were installed, a significant reduction in the permeability coefficient is observed. For untreated soil samples, the permeability coefficient (k) reached values in the range of 10−8 to 10−7 m/s, whereas for treated samples, this value dropped down to 10−9 m/s, meeting the requirements for impermeable hydraulic structures. On average, the coefficient of permeability decreased by at least one order of magnitude. Additionally, the time required to stabilize the hydraulic gradient in treated samples was up to 10 times longer than in samples without treatment, clearly indicating the effectiveness of filtration potential reduction. The laboratory tests revealed significant differences in the behaviour of soils before and after the application of additives for impermeable barriers construction. Detailed results of the effective angle of friction and the coefficient of permeability for selected tested materials, depending on the barrier technology, are presented in Table 2.

Table 2.
Mechanical and hydraulic parameters of soil samples before and after treatment.
In particular, an increase in the effective angle of internal friction (φ′) was observed in reinforced soil samples, suggesting an improvement in their drained shear strength. This increase appears especially in soils with a lower plasticity index (PI), i.e., less cohesive (granular) materials, which may indicate higher effectiveness of barriers in such types of soil. With regard to filtration parameters, the use of additives resulted in a significant extension of the hydraulic gradient stabilization time, as well as an increase in stabilized gradient values at the same flow rate. The obtained flow velocity characteristics as a function of gradient for the modified soils indicate a substantial decrease. This confirms the effectiveness of the applied technologies in limiting filtration within flood embankments. The relationships shown in the graphs suggest that the lower the soil’s plasticity index, the greater the impact of the barriers on reducing the permeability coefficient. This may be important when designing barriers depending on local soil conditions. Furthermore, higher soil consistency (higher PI) appears to limit the effectiveness of the barriers in reducing permeability.
4. Discussion
The laboratory investigations reveal that the installation of vertical barriers, whether via vibrating beam slurry walls (VBSWs), deep soil mixing (DSM), or low-pressure grout injection (LPG), substantially enhances both the mechanical and hydraulic performance of the soils. Triaxial tests demonstrated a consistent increase in the angle of internal friction (φ′) by an average of 3–6° for treated samples compared to untreated soils, with values rising from approximately 30–32° to 35–38° for samples with a plasticity index (PI) around 3.5%. This improvement in shear strength is mostly noticed in soils of lower plasticity (lower PI), indicating that barrier technologies result in a greater reinforcing effect in tested ground conditions. In more plastic soils, the relative increase angle of internal friction is reduced, suggesting that the intrinsic soil fabric may limit the interaction between the barrier and the natural soil matrix. This is due to the higher permeability of granular material, favorable hydraulic gradients, and increased retention. In these soils, barriers better control and redirect groundwater flow compared to cohesive soils, where seepage can cause pressure build-up and failures. Their efficiency is further supported by hydrodynamic behavior, which ensures stability and prevents leakage over time. Hydraulic tests revealed that untreated soils exhibited permeability coefficients (k) in the range of 10−8 to 10−7 m/s, whereas treated soils uniformly achieved k < 10−9 m/s, satisfying the technical criteria for anti-filtration structures. The flow-pump technique, which enforces a constant water flow rate, reveals that treated soil samples required up to an order of magnitude longer to reach gradient stabilization—3000 min versus 300 min at a flow rate of 0.02 mm3/min—indicative of the barrier’s ability to limit pore-water dissipation. Moreover, treated soils stabilize at higher hydraulic gradients under identical flow conditions, reflecting a fundamental shift in the soil’s permeability characteristics. The relationship between flow velocity and stabilized gradient further illustrates that barriers not only slow the seepage but also alter the soil’s response to hydraulic loading, thereby mitigating the risk of internal erosion and liquefaction under flood conditions. Bearing all of the above observations in mind, it is important to highlight the alternative of using more sustainable materials for soil treatment to achieve same impermeability efficiency. This could be achieved by following circular economy practices by using recycled aggregates, particularly those derived from construction and demolition debris, since they are gaining attention due to their potential to reduce reliance on natural materials and minimize waste production.
5. Conclusions
The comparative performance of the three barrier technologies suggests that all methods can achieve the desired hydraulic and mechanical improvements, yet practical considerations such as site accessibility, soil composition, and contractor expertise should guide technology selection. The present study proposes a complex approach of combining geotechnical and hydraulic laboratory tests to compare the efficiency and performance of impermeable barriers technologies. Comparing three methods gives a wider view on the limitations of application depending on soil type and consistency. Here are the main conclusions deriving from the study:
- Barrier performance varies according to the technology and the soil type: DSM is most effective in clay-rich soils (φ′ up to 4°); LPG achieved the lowest permeability (7 × 10−11 m/s) in granular soils; VBSWs balanced strength and impermeability and were most effective in silty sands.
- Efficiency strongly depends on plasticity and liquidity indices; however, detailed geotechnical characterization is essential.
- Back-pressure saturation and gradient stabilization ensured reliable shear strength and permeability measurements for each test performed in the study.
- All three barrier types improved hydraulic performance and shear strength, achieving a permeability of <1 × 10−9 m/s, with the greatest benefits in granular soils.
- Higher soil plasticity reduces barrier efficiency; thus, it is essential to choose installation technology depending on local conditions.
- The findings support integrated geotechnical and hydraulic testing as a basis for selecting and designing impermeable barriers in flood protection and embankment restoration.
Author Contributions
Conceptualization, M.W. and M.L.; methodology, M.W. and K.N.; software, M.W. and K.N.; validation, M.W., M.L. and P.O.; formal analysis, M.W. and M.L.; investigation, M.W. and K.N.; resources, M.W.; data curation, M.W. and K.N.; writing—original draft preparation, M.W. and P.O.; writing—review and editing, M.W., M.L. and P.O.; visualization, M.W. and P.O.; supervision, M.W. and M.L.; project administration, M.W. and M.L.; funding acquisition, P.O. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This research received no external funding.
Institutional Review Board Statement
Not applicable.
Informed Consent Statement
Not applicable.
Data Availability Statement
Research data is available upon formal request to the authors.
Acknowledgments
The authors acknowledge developers of AI tools that helped format the references.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
Abbreviations
The following abbreviations are used in this manuscript:
| VBSW | Vibrating beam slurry walls |
| DSM | Deep soil mixing |
| LPG | Low-pressure grouting |
References
- Farooq, K.; ur Rehman, Z.; Shahzadi, M.; Mujtaba, H.; Khalid, U. Optimization of Sand-Bentonite Mixture for the Stable Engineered Barriers Using Desirability Optimization Methodology: A Macro-Micro-Evaluation. KSCE J. Civ. Eng. 2023, 27, 40–52. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khalid, U.; ur Rehman, Z.; Liao, C.; Farooq, K.; Mujtaba, H. Compressibility of Compacted Clays Mixed with a Wide Range of Bentonite for Engineered Barriers. Arab. J. Sci. Eng. 2019, 44, 5027–5042. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Skutnik, Z.; Bajda, M.; Lech, M. The Selection of Sealing Technologies of the Subsoil and Hydrotechnical Structures and Quality Assurance. Open Eng. 2019, 9, 420–427. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Skutnik, Z.; Bajda, M.; Lech, M.; Wdowska, M.; Kuś, R. Application of CPT Soundings and BAT Permeability Tests for Evaluation of the Durability of Slurry Cutoff Walls in Modernized Flood Embankments. Inżynieria I Bud. 2017, 3, 143–146. [Google Scholar]
- Mirecki, J.; Pitera, P. Optimization of Sealing Screen Dimensions in Levees. Acta Sci. Pol. Archit. 2013, 12, 147–156. [Google Scholar]
- Lipinski, M.J.; Koda, E.; Wdowska, M. Assessment of Key Geotechnical Characteristics of a Groundwater Protective Vertical Barrier. In Proceedings of the 14th European Conference on Soil Mechanics and Geotechnical Engineering: Geotechnical Engineering in Urban Environments, Madrid, Spain; Cuélla, V., Cuéllar, V., Dapena, E., Alonso, E., Echave, J.M., Gens, A., De Justo, J.L., Oteo, C., Rodríguez-Ortiz, J.M., Sagaseta, C., Sola, P., Soriano, A., Eds.; Millpress Science Publishers: Rotterdam, The Netherlands, 2007; pp. 767–772. [Google Scholar]
- Lipinski, M.J.; Koda, E.; Wdowska, M. Laboratory Assessment of Permeability of a Groundwater Protective Barrier. Ann. Wars. Univ. Life Sci.—SGGW. Land Reclam. 2008, 38, 69–79. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chung, Y.W.; Kim, J.; Kong, S.-H. Performance Prediction of Permeable Reactive Barriers by Three-Dimensional Groundwater Flow Simulation. Int. J. Environ. Sci. Dev. 2011, 2, 138–141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Koda, E.; Osinski, P. Bentonite Cut-off Walls: Solution for Landfill Remedial Works. Environ. Geotech. 2017, 4, 223–232. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Higgins, M.R.; Olson, T.M. Life-Cycle Case Study Comparison of Permeable Reactive Barrier versus Pump-and-Treat Remediation. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2009, 43, 9432–9438. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Slater, L.; Baker, J.; Binley, A.; Glaser, D.; Utne, I. Electrical Imaging of Permeable Reactive Barrier (PRB) Integrity. In Proceedings of the Symposium on the Application of Geophysics to Engineering and Environmental Problems, Las Vegas, NV, USA, 10–14 February 2002; p. ESC3. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abdullah, H.H.; Shahin, M.A. Geomechanical Behaviour of Clay Stabilised with Fly-Ash-Based Geopolymer for Deep Mixing. Geosciences 2022, 12, 207. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shah, A.S.N.; Zali, M.A. Potential of Tropical Expansive Clays as Natural Sealing Layer in Nuclear Waste Repository System: A Preliminary Study. IOP Conf. Ser. Mater. Sci. Eng. 2023, 1285, 012018. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, D.; Han, J. Remediation of Multiply Contaminated Ground via Permeable Reactive Barrier and Electrokinetic Using Recyclable Food Scrap Ash (FSA). Appl. Sci. 2020, 10, 1194. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, S.; Sun, W.; Wang, X.; Sun, L.; Liu, S. The Role of Geological Methods in the Prevention and Control of Urban Flood Disaster Risk: A Case Study of Zhengzhou. Appl. Sci. 2024, 14, 1839. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Villamizar, M.L.; Stoate, C.; Biggs, J.; Szczur, J.; Williams, P.; Brown, C.D. A Model for Quantifying the Effectiveness of Leaky Barriers as a Flood Mitigation Intervention in an Agricultural Landscape. River Res. Appl. 2024, 40, 365–378. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, S.; Wu, J.; Cai, P.; Chen, C.; Ye, S.; Xu, J.; Chen, L.; Luo, X.; Wei, J. Modelling of Contaminant Transport in Heterogeneous Vertical Barrier. Water Environ. J. 2024, 38, 169–177. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wasson, R.; Saikia, A.; Bansal, P.; Chuah, C.J. Flood Mitigation, Climate Change Adaptation and Technological Lock-In in Assam. Ecol. Econ. Soc.—INSEE J. 2020, 3, 83–104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Harada, N.; Satofuka, Y.; Mizuyama, T. A Proposal for Sediment Control Countermeasures in Non-Flowing Mountain Streams. Water 2024, 16, 1197. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boulange, J.; Hanasaki, N.; Yamazaki, D.; Pokhrel, Y. Role of Dams in Reducing Global Flood Exposure under Climate Change. Nat. Commun. 2021, 12, 417. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Basu, D.; Basu, P.; Prezzi, M. Analytical Solutions for Consolidation Aided by Vertical Drains. Geomech. Geoengin. Int. J. 2006, 1, 63–71. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sukerta, I.M.; Chen, T.C.; Mardizal, J.; Salih, S.M.; Zulkarnain, I.; Islam, M.Z.; Majeed, M.S.; Mahdi, A.B.; Mutlak, D.A.; Aravindhan, S. Comparison of Lateral Spillway and Morning Glory Spillway Performance in Flood Control. J. Water Land Dev. 2022, 53, 187–191. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sha, S.; Zhou, X.; Zhang, C.; Yuan, Y. Research on Urban Embankment Reinforcement—Example of Dadu River Embankment in Leshan City. ce/papers 2025, 8, 1798–1806. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cao, B.; Xu, J.; Wang, F.; Zhang, Y.; O’connor, D. Vertical Barriers for Land Contamination Containment: A Review. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2021, 18, 12643. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, K.; Zhang, Y. Evaluation of the Service Performance of Soil–Bentonite Vertical Cut-Off Walls at Heavy Metal Contaminated Sites: A Review. Appl. Sci. 2025, 15, 5215. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yamada, S.; Sakai, T.; Nakano, M.; Noda, T. Method to Introduce the Cementation Effect into Existing Elastoplastic Constitutive Models for Soils. J. Geotech. Geoenviron. Eng. 2022, 148, 04022013. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, W.; Liu, B.; Wu, J.; Xu, W.; Liu, B.; Wu, J. Construction Technology and Service Performance of Waterproof Curtain for Foundation Pit in Large-Particle Pebble Gravel Layer of Yangtze River Floodplain. Appl. Sci. 2024, 14, 5962. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, X.; Liu, Y.; Yin, W.; Wang, X.; Guo, S. Experimental Study on Strength and Microstructure of Loess Improved by CG-2 Curing Agent and Cement. Buildings 2024, 14, 877. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Petalas, A.L.; Tsiampousi, A.; Zdravkovic, L.; Potts, D.M. Numerical Investigation of the Performance of Engineered Barriers in Reducing Flood Risk. MATEC Web Conf. 2021, 337, 04003. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- PN-EN ISO 17892-9:2018-05; In Geotechnical Investigation and Testing—Laboratory Testing of Soil—Part 9: Consolidated Triaxial Compression Test on Water Saturated Soils. International Organization for Standardization (ISO): Geneva, Switzerland, 2018.
- Lipiński, M.J.; Wdowska, M.K.; Wudzka, A. Capability of Triaxial Apparatus with Respect to Evaluation of Nonlinearity of Soil Stiffness. Arch. Civ. Eng. 2020, 66, 69–80. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Olsen, H.W.; Morin, R.H.; Nichols, R.W. Flow Pump Applications in Triaxial Testing; ASTM Selected Technical Papers; ASTM International: West Conshohocken, PA, USA, 1988; Volume STP977-EB, pp. 68–81. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lipinski, M.J.; Wdowska, M.K. Evaluation of Void Ratio of Sands with Various Amount of Fines on the Basis of Shear Wave Velocity Measurement. IOP Conf. Ser. Mater. Sci. Eng. 2019, 471, 042026. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barman, D.; Dash, S.K. Stabilization of Expansive Soils Using Chemical Additives: A Review. J. Rock Mech. Geotech. Eng. 2022, 14, 1319–1342. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jamiolkowski, M.; Leroueil, S.; Lo Presti, D. Design Parameters from Theory to Practice. In Proceedings of the GEO-COAST ’91, Yokohama, Japan, 3–6 September 1991; Volume 2, pp. 877–917. [Google Scholar]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).