Abstract
Change detection (CD) in optical remote-sensing images is a critical task for applications such as urban planning, disaster monitoring, and environmental assessment. While UNet-based architecture has demonstrated strong performance in CD tasks, it often struggles with capturing deep hierarchical features due to the limitations of plain convolutional layers. Conversely, ResNet architectures excel at learning deep features through residual connections but may lack precise localization capabilities. To address these challenges, we propose ResUNet++, a novel hybrid architecture that combines the strengths of ResNet and UNet for accurate and robust change detection. ResUNet++ integrates residual blocks into the UNet framework to enhance feature representation and mitigate gradient vanishing problems. Additionally, we introduce a Multi-Scale Feature Fusion (MSFF) module to aggregate features at different scales, improving the detection of both large and small changes. Experimental results on multiple datasets (EGY-CD, S2Looking, and LEVIR-CD) demonstrate that ResUNet++ outperforms state-of-the-art methods, achieving higher precision, recall, and F1-scores while maintaining computational efficiency.
1. Introduction
Egyptian government land is illegally encroached upon, like many other developing nations. These lands have no credible dataset, and old satellite photos and maps are outdated. To validate the latest state of the land, data should be reviewed after updating. Thus, new techniques are needed to detect new building development and modifications in existing buildings. The picture platform has been particularly beneficial in this context; thus, a modified U-Net model for semantic segmentation is supplied that accepts photographs as input and recognizes new development on government land and zones out only the building regions. After detecting building changes, this model expands the zones to include the final zones of the changed buildings and construction.
Remote sensing imagery has become the primary data source for Earth observation, with change detection (CD) techniques playing a pivotal role in analyzing temporal variations across multi-temporal images of the same geographical region []. These methods find extensive applications in critical domains including disaster impact assessment [,], precision agriculture monitoring [,], and urban development planning [,]. The continuous advancement of sensor technologies has led to significant improvements in both spatial and temporal resolution, enabling more sophisticated analysis of high-resolution remote sensing (HRSS) data. However, CD in HRSS imagery presents substantial challenges, particularly concerning pseudo-changes caused by spectral variations, geometric distortions, and illumination differences. These challenges are further compounded by issues of scale variation and severe class imbalance, where unchanged pixels typically dominate the scene [,,,,,,,].
Traditional CD methodologies can be broadly classified into pixel-based and object-based approaches. Pixel-based methods, including image differencing [], change vector analysis (CVA) [,], and principal component analysis (PCA) [,], focus primarily on spectral changes while often neglecting spatial context. Object-based techniques attempt to address this limitation by incorporating spatial information through image segmentation, though they remain vulnerable to error propagation from segmentation inaccuracies [,,]. Both approaches require substantial manual intervention and demonstrate sensitivity to sensor characteristics and environmental conditions. The advent of deep learning has revolutionized CD through convolutional neural networks (CNNs), which automatically extract hierarchical features while minimizing preprocessing requirements [,,,,,,,,,,,,]. Current CNN-based architecture typically employs either early fusion strategies that process multi-temporal images jointly [,,,,], or late fusion (Siamese) approaches that analyze images separately before comparison [,,,,,,,]. While these methods have shown promising results, they still face fundamental limitations, including restricted receptive fields and challenges in maintaining fine-grained spatial details [,,,,,].
To overcome these limitations, we present ResUNet++ CD, an advanced deep learning framework that synergistically combines UNet’s precise localization capabilities with ResNet’s powerful feature extraction. Our architecture incorporates several key innovations: (1) a residual learning backbone that facilitates the training of deep networks while mitigating gradient vanishing [,,], (2) multi-scale feature aggregation through UNet-style skip connections to preserve spatial details [,,], and (3) a novel difference enhancement module (DEM) specifically designed to amplify meaningful change signals. Additionally, we introduce a specialized loss function to address the prevalent class imbalance problem in CD tasks. The ResUNet++ CD framework demonstrates superior performance in handling the challenges of HRSS image analysis, particularly in distinguishing genuine changes from pseudo-changes while maintaining robustness across varying scales and environmental conditions. Experimental results validate the effectiveness of our approach in achieving state-of-the-art performance across multiple CD benchmarks [,,,,,,,,,,,,,,,,,,,,,,,,,,,,,,,,,]. To bridge this gap, we propose ResUNet++, a hybrid architecture that 1—integrates residual blocks into UNet to enhance feature learning; 2—introduces a Multi-Scale Feature Fusion (MSFF) module for improved change representation; and 3—employs a weighted loss function to handle class imbalance. Our contributions include 1—a novel ResNet-UNet hybrid model for CD, combining deep feature extraction with precise localization; 2—the MSFF module, which aggregates multi-scale features to improve the detection of objects of varying sizes; and 3—comprehensive experiments showing ResUNet++ outperforming existing methods on multiple datasets.
2. Related Work
2.1. Change Detection Framework Based on Deep Learning
Convolutional Neural Networks (CNNs) have demonstrated exceptional performance in feature extraction, making them widely adopted in change detection (CD) algorithms. Popular architectures such as UNet [,,] have shown promising results across various CD applications. For example, Peng et al. [] introduced UNet++ with a multi-side output fusion strategy. CNN-based methods often exhibit limitations in capturing global dependencies, maintaining spatial coherence, and handling hierarchical features, making them vulnerable to noise, illumination variance, and pseudo-changes. To address these challenges, researchers have explored advanced architectures such as generative adversarial networks (GANs) [,,], recurrent neural networks (RNNs) [,], and attention-based mechanisms [,,,,]. RNNs, particularly those using LSTM blocks [], have shown success in modeling temporal–spectral dependencies in urban CD. However, their effectiveness diminishes with high-resolution imagery or sparse temporal inputs []. Attention mechanisms, including spatial, channel, and self-attention [], have also emerged as powerful tools for enhancing discriminative feature learning. For instance, Peng et al. [] introduced DDCNN using spatial and channel attention modules, and Zhang et al. [] proposed IFN, integrating deep supervision with attention-based enhancement. Nevertheless, many existing attention methods neglect shallow feature enrichment and incur high computational costs. To overcome these shortcomings, recent research has turned to transformer-based models, which leverage self-attention to capture long-range dependencies more effectively. Our approach builds on this trend by integrating transformer modules equipped with weight tying, multi-layer feed-forward networks, and positional encoding. These elements not only reduce computational redundancy but also improve the contextual coherence of learned representations. By introducing these techniques, our model addresses both global context modeling and shallow-to-deep feature interaction—offering a more robust solution for complex change detection tasks in high-resolution remote sensing imagery.
2.2. Transformers Algorithms
Originally developed for natural language processing (NLP) [], transformer architectures have gained significant traction in computer vision due to their powerful representation capabilities. Unlike convolutional neural networks (CNNs), which process local receptive fields, transformers employ stacked multi-head attention mechanisms to model global relationships between tokenized image patches, effectively capturing long-range dependencies in visual data []. This unique capability has led to their successful application across various vision tasks, including image classification [], object detection [], semantic segmentation [,], image recognition [], and video captioning [,,].
The remote sensing community has increasingly adopted transformer-based approaches for diverse applications. In image classification, Li et al. [] developed a hybrid CNN-transformer framework for crop classification using multi-sensor Sentinel-2A/B and Landsat-8 imagery, while Deng et al. [] proposed a joint CNN-ViT architecture to enhance feature discrimination for high-resolution scene classification. For semantic segmentation tasks, Ding et al. [] introduced MP-ResNet, a multi-path residual network designed for the semantic segmentation of high-resolution Polarimetric SAR (PolSAR) images, which leverages multi-level feature fusion to enhance both receptive field coverage and fine-grained detail preservation. in another study [] introduced WiCoNet, incorporating a context transformer to capture long-range dependencies in HRSS images, and Wang et al. [] implemented a Swin Transformer-based solution for fine-resolution imagery. In image fusion, Li et al. [] presented a novel multi-stream network combining transformer and convolutional operations for the spatiotemporal fusion of remote sensing data. Within change detection specifically, Chen et al. [] proposed a bitemporal image transformer (BiT) approach for spatiotemporal context modeling. However, this method’s direct upsampling approach for full-resolution change often compromises low-level details. Ling et al. [] employed a DeepLab dilated convolutional neural network to perform automatic semantic segmentation, effectively capturing multiscale contextual information and improving the accuracy of change detection in complex scenes.
2.3. ResNet-Based Change Detection Methods
Recent advances in change detection have increasingly leveraged ResNet architectures due to their ability to learn deep hierarchical features while mitigating vanishing gradient issues through residual connections. Marsocci et al. [] first demonstrated the effectiveness of ResNet-inspired Siamese architectures with residual and skip connections in change detection. Their Siamese ResUNet maintains spatial detail across bi-temporal optical imagery while learning change representations, achieving robust performance for both 2D and 3D change detection tasks. Dang et al. [] introduced MSResNet, a multiscale residual network enhanced with MSDC and MKMP modules for capturing diverse water-body scales and boundary details. They further augmented training with a novel self-supervised learning (SSL) scheme—comprising geometric transformations, noise disturbance, resolution changes, and context fusion. Subsequent work, such as that by Li et al. [] propose SCAttNet, a semantic segmentation network tailored for high-resolution remote sensing imagery. It integrates lightweight spatial and channel attention modules, refining feature representations and yielding improved performance on ISPRS Vaihingen and Potsdam datasets. Wang et al. [], introduces a dual-stream encoder with cross-temporal attention for bi-temporal imagery such as LEVIR-MCI and CDD. It processes pre- and post-event images in parallel, fuses their features using attention mechanisms, and enhances boundary precision in change detection. The hybridization of ResNet with UNet, as in Chang et al. [], further enhanced change detection accuracy, enabling dense prediction with robust feature reuse. These models have consistently ranked among the top performers on public benchmarks like S2Looking, LEVIR-CD, and EGY-BCD, outperforming classical CNNs and some attention-based baselines in terms of precision and recall. Further innovations include 3D-ResNet architectures designed for volumetric urban change detection using high-resolution satellite time-series (Li et al. []) and ResNet-transformer hybrids (Wang et al. []) that address long-range dependencies in large-scale imagery. Despite these developments, challenges remain—especially in processing multimodal data (e.g., combining SAR and optical imagery), handling domain shifts across geographic regions, and reducing computational overhead for real-time applications. As noted in the comprehensive review by Wang et al. [], ResNet’s performance may degrade in scenarios with high spectral variation or noisy labels and lacks native mechanisms for dynamic spatial–temporal attention.
2.4. UNet
UNet-based architecture has become a cornerstone in deep learning approaches for change detection (CD), especially in remote sensing contexts. The original UNet model, introduced by Ronneberger et al. [], established a robust encoder–decoder architecture with skip connections that significantly improved spatial precision in segmentation tasks. Daudt et al. [] were among the first to adapt this structure for CD by proposing fully convolutional Siamese networks (FC-Siam), which demonstrated strong performance on aerial imagery in terms of change localization and noise suppression. To enhance multi-scale representation, Peng et al. [] developed UNet++, integrating nested skip connections that improved semantic consistency across feature hierarchies. Zhang et al. [] proposed DASNet, a dual-attention UNet variant capable of handling ultra-high-resolution imagery through enhanced focus on salient spatial and channel-wise features. Similarly, Liu et al. [] introduced a deeply supervised nested UNet that delivered state-of-the-art performance—surpassing 90% F1-score—on multiple public benchmarks, including LEVIR-CD and CDD datasets. More recently, hybrid approaches have emerged. Transformer-UNet models, such as that proposed by Wang et al. [], introduce global context modeling via self-attention layers into the UNet pipeline, addressing its limited capacity for capturing long-range dependencies. Li et al. [] extended the architecture to 3D-UNet for multitemporal change detection using volumetric satellite image stacks. These models have shown improved performance on datasets like S2Looking and EGY-BCD, especially in tasks requiring precise boundary delineation or small object detection. Despite these advancements, UNet-based models still face notable limitations. They often struggle to generalize across diverse geographic regions and sensor types due to their dependency on domain-specific features. Training complexity increases significantly with deep supervision or attention integration, leading to higher computational costs. Furthermore, UNet architectures may be less effective in dealing with multimodal inputs (e.g., SAR-optical fusion) and are sensitive to class imbalance, which can bias predictions toward dominant classes. Zhao et al. [] and Jiang et al. [] both highlight that while UNet variants outperform many baseline models, they can still underperform in scenarios with sparse or noisy annotations, dynamic backgrounds, or highly imbalanced classes.
3. Materials and Methods
To enhance the accuracy of building change detection in remote sensing imagery, particularly for monitoring encroachments and unauthorized construction on government lands in Egypt, this study employs a hybrid deep learning model based on the ResUNet++architecture. UNet is widely recognized for its encoder–decoder structure with skip connections, which effectively preserves spatial details crucial for segmentation tasks. By integrating ResNet as the backbone of the encoder, the model benefits from deeper feature extraction capabilities and improved gradient flow through residual learning. This combination allows the network to accurately identify subtle structural changes in complex urban environments. The model was trained on pairs of bitemporal satellite images, including the Egypt-specific EGY-BCD dataset, and validated using benchmark datasets such as LEVIR-CD and S2Looking. The resulting change maps were used to detect and localize building expansions, new constructions, and encroachments on public lands. The high precision and recall achieved by the ResUNet++ model demonstrate its effectiveness in supporting land-use monitoring and urban planning efforts across Egypt.
As depicted in Figure 1, the ResUNet++ architecture is an advanced deep learning framework designed for robust change detection in optical remote-sensing images, combining the strengths of ResNet and UNet. Its core components include a ResNet50-based encoder, which uses residual blocks to extract rich, hierarchical features while mitigating the vanishing gradient problem, and a Multi-Scale Feature Fusion (MSFF) module that aggregates features from different encoder layers to capture both fine details and broad contextual information. The architecture computes absolute differences between feature maps of input image pairs at multiple scales, effectively highlighting changes while suppressing irrelevant background information, and uses a UNet-style decoder with skip connections to reconstruct high-resolution change maps, preserving spatial details and contextual cues. The output layer employs a 1×1 convolution with sigmoid activation to generate a probabilistic change map, enabling flexible thresholding and precise localization of changes, particularly useful for building change detection. To address class imbalance, the model uses a composite loss function combining weighted cross-entropy and Dice loss, ensuring accurate detection even when changed pixels are scarce. Overall, ResUNet++ balances deep feature extraction with accurate spatial reconstruction, offering improved accuracy, stability, and computational efficiency for diverse change detection tasks in remote sensing.
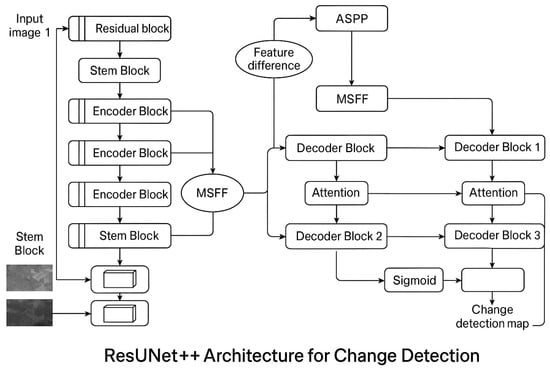
Figure 1.
Proposed model.
3.1. Framework
As shown in Figure 1, the proposed ResUNet++ architecture is designed to leverage the complementary strengths of ResNet and UNet for robust change detection in optical remote-sensing images. The model consists of three key components: a ResNet-enhanced encoder, a Multi-Scale Feature Fusion (MSFF) module, and a UNet-style decoder. The ResNet-enhanced encoder replaces traditional convolutional blocks in the UNet encoder with residual blocks, each comprising a series of convolutional layers, batch normalization, and ReLU activation, followed by a skip connection that adds the input directly to the output. This design mitigates the vanishing gradient problem, enabling deeper networks and more effective feature extraction. By preserving gradient flow through residual connections, the encoder captures richer hierarchical features, which are critical for distinguishing subtle changes in multi-temporal images. To further enhance feature representation, the MSFF module aggregates multi-scale features from different levels of the encoder. This module concatenates feature maps from early, middle, and late stages of the encoder, followed by a 1×1 convolution to reduce dimensionality and integrate cross-scale information. The fused features retain both high-resolution spatial details from shallow layers and high-level semantic information from deeper layers, improving the model’s ability to detect changes across varying object sizes—from large urban structures to small vehicles or roads. Finally, the UNet-style decoder reconstructs the spatial resolution of the feature maps through a series of transposed convolutions and skip connections. Each decoder block upsamples the feature maps and concatenates them with corresponding encoder features via skip connections, preserving fine-grained details lost during downsampling. This ensures precise localization of change boundaries while maintaining the contextual information captured by the ResNet-enhanced encoder. Together, these components form an end-to-end framework that balances deep feature extraction with accurate spatial reconstruction, addressing key challenges in remote-sensing change detection.
To ensure architectural clarity, Table 1 summarizes the main differences among the baseline UNet, the intermediate UNet-ResNet variant, and the proposed ResUNet++ model evaluated in this study.

Table 1.
Taxonomy of evaluated change detection models and their architectural components.
3.2. ResNet as Encoder
The proposed model leverages a ResNet50-based encoder for feature extraction, capitalizing on the strengths of deep residual learning to effectively process and compare pairs of input images. ResNet50, a 50-layer deep convolutional neural network, is chosen due to its proven ability to learn robust hierarchical features while mitigating the vanishing gradient problem through skip connections, which allow gradients to propagate more efficiently during backpropagation. By initializing the encoder with ImageNet-pretrained weights, the model benefits from transfer learning, where low-level layers capture universal features such as edges and textures, while deeper layers encode high-level semantic information, significantly reducing the need for large annotated datasets. The encoder extracts multi-scale features from five strategically selected layers—conv1_relu, conv2_block3_out, conv3_block4_out, conv4_block6_out, and conv5_block3_out—each representing different levels of abstraction, from fine-grained details to broader contextual information. These features are computed independently for both input images using a shared-weight architecture, ensuring consistent feature representation and enabling precise comparison through absolute difference operations. This approach effectively highlights discrepancies between the images while suppressing unchanged regions, making it particularly suitable for tasks requiring pixel-wise change detection. Furthermore, the encoder is initially frozen during training to preserve pretrained features and stabilize learning, with the option for later fine-tuning to adapt to domain-specific characteristics. While ResNet50 provides a powerful and generalizable feature extractor, its computational complexity may pose challenges in resource-constrained environments, suggesting potential trade-offs between accuracy and efficiency. Overall, the ResNet50-based encoder serves as a critical component in the architecture, enabling the model to achieve high precision in identifying and localizing changes across diverse applications, from remote sensing to medical imaging. Future enhancements could explore alternative backbones, such as Efficient Net or Vision Transformers, to further optimize performance and computational efficiency, as shown in Figure 2.
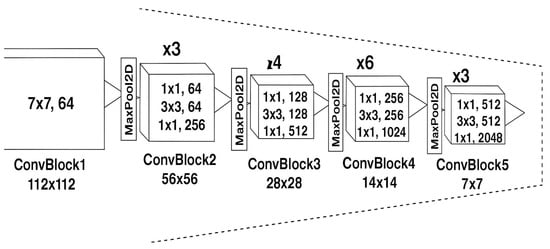
Figure 2.
Block diagram of ResNet as encoder.
3.3. Residual Blocks in UNet
The integration of residual blocks into the UNet architecture represents a key innovation in ResUNet++, addressing the limitations of traditional convolutional layers in deep networks. Each residual block consists of two or more convolutional layers with batch normalization and ReLU activation, followed by a skip connection that adds the input directly to the output as shown in Figure 3. This design is formalized as
y = F(x) + x
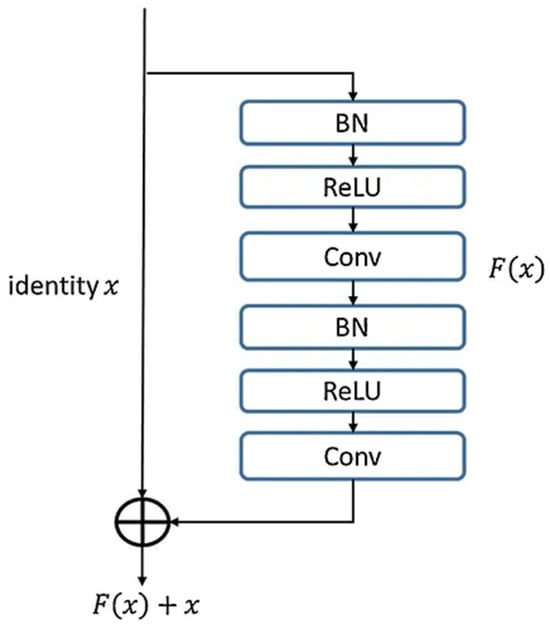
Figure 3.
Block diagram of residual blocks in UNet.
F(x) represents convolutional transformations and X is the input feature map.
The skip connections serve two critical purposes: first, they mitigate the vanishing gradient problem by providing a direct path for gradient flow during backpropagation, enabling effective training of deeper networks; second, they preserve low-level features that might otherwise be diluted through successive transformations, maintaining important spatial details for precise change localization. In the context of change detection, these residual connections prove particularly valuable. Unlike natural images, where high-level semantics often dominate, remote sensing change detection requires the model to retain and compare fine-grained details across temporal images. The residual blocks enhance the encoder’s ability to propagate these details through the network while simultaneously learning increasingly abstract representations. This dual capability allows the model to distinguish between genuine changes (e.g., new constructions) and pseudo-changes (e.g., shadows or seasonal variations) more reliably. Furthermore, the stacked residual blocks create a natural multi-scale feature hierarchy, where earlier layers capture local textures and edges while deeper layers encode broader contextual patterns—both essential for robust change detection across diverse landscapes. Compared to the original UNet’s plain convolutions, the residual blocks demonstrate superior performance in our experiments, improving feature reuse and network convergence without significantly increasing computational overhead. This modification not only boosts accuracy but also enhances the model’s stability during training, as evidenced by smoother loss curves and reduced sensitivity to initialization. The success of residual blocks in ResUNet++ suggests their broader applicability in other remote sensing tasks requiring both deep feature extraction and precise spatial localization.
3.4. Feature Difference Computation
The model employs a sophisticated feature difference computation mechanism as a core component of its change detection framework, enabling precise identification of meaningful variations between image pairs while effectively suppressing irrelevant background information. This computational approach operates by calculating the absolute differences (|feat1 − feat2|) between corresponding feature maps extracted from the two input images at multiple hierarchical levels of the ResNet50 encoder. The absolute difference operation serves as a powerful non-linear comparator that inherently emphasizes regions of change while naturally diminishing areas of similarity, creating a focused representation of spatial and semantic discrepancies. By performing this computation at multiple scales—from fine-grained low-level features capturing edges and textures in early layers to high-level semantic features in deeper layers—the model develops a comprehensive understanding of both subtle and substantial changes across different spatial contexts. This multi-scale difference computation is particularly advantageous as it allows the network to detect various types of changes: lower-level features excel at identifying precise pixel-wise variations and small structural modifications, while higher-level features capture more complex, semantic differences such as the appearance or disappearance of objects. The absolute difference operation offers several theoretical advantages over alternative approaches (such as concatenation or element-wise multiplication), including its simplicity, computational efficiency, and inherent symmetry that ensures consistent treatment of the input image pair regardless of their order. Moreover, this approach demonstrates strong robustness to illumination variations and minor viewpoint changes that might otherwise generate false positives in change detection tasks. The computed difference features are then progressively decoded through the UNet-style architecture, with skip connections ensuring that these differential representations are refined and properly localized in the final output. Importantly, this feature-differencing strategy aligns well with the psychological and computer vision principle of change detection as a comparative process, where the human visual system similarly focuses on differences between scenes. The effectiveness of this approach is further enhanced by the shared-weight architecture of the encoder, which guarantees that features are extracted consistently from both images, preventing bias in the different computations. While this method has demonstrated strong performance, potential limitations include its sensitivity to significant misalignment between input images and the challenge of distinguishing meaningful changes from noise in low-contrast regions, suggesting directions for future improvement through the incorporation of attention mechanisms or learned difference operators. Overall, the feature difference computation module represents a carefully designed and theoretically grounded approach to change detection that effectively bridges traditional computer vision techniques with modern deep learning architectures.
3.5. Multi-Scale Feature Fusion
As shown in Figure 4, the Multi-Scale Feature Fusion (MSFF) module in ResUNet++ is designed to address the fundamental challenge of detecting changes across varying spatial scales in remote sensing imagery. Traditional change detection methods often struggle to simultaneously capture the fine details of small objects (e.g., vehicles or narrow roads) and the broader contextual information of large structures (e.g., buildings or urban blocks). The MSFF module overcomes this limitation by strategically aggregating feature maps from different levels of the encoder network. The module operates by concatenating feature maps from three critical stages of the encoder: shallow layers containing high-resolution spatial details, intermediate layers with balanced spatial–semantic information, and deep layers encoding high-level contextual features. This concatenated representation is then processed through a 1×1 convolutional layer, which serves dual purposes: reducing channel dimensionality to maintain computational efficiency while enabling cross-scale feature interaction. The resulting fused feature map retains rich multi-scale information, allowing the network to detect both localized changes and broader land-cover transformations. A key innovation of our MSFF approach is its adaptive weighting mechanism, where the network learns to automatically emphasize the most relevant scales for different regions of the input image. This is particularly valuable in complex urban environments where changes may occur at multiple scales simultaneously, such as new construction sites (large-scale) alongside vehicle movements (small-scale). The module’s effectiveness is further enhanced by its position at the bottleneck of the UNet architecture, where it can influence both the decoder’s upsampling path and the skip connections. The experimental results demonstrate that the MSFF module contributes significantly to the model’s performance, particularly in challenging scenarios with extreme scale variations. Compared to conventional pyramid pooling or attention-based fusion approaches, our method shows superior computational efficiency while maintaining competitive accuracy. The module’s design principles—simplicity, adaptability, and scale-awareness—make it potentially applicable to other remote sensing tasks requiring multi-scale analysis, such as object detection or land cover classification.
Ffused = Conv1×1(Concat(F1,F2,F3))
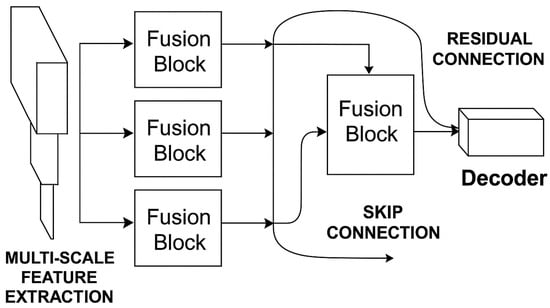
Figure 4.
Block diagram of Multi-Scale Feature Fusion.
3.6. UNet-Style Decoder with Skip Connections
The proposed architecture incorporates a UNet-style decoder with skip connections to effectively reconstruct high-resolution change detection maps from the multi-scale difference features generated by the ResNet50 encoder. This decoder design is particularly well-suited for building change detection tasks, as it addresses several critical challenges inherent in the problem domain. The expansive pathway progressively upsamples the compressed feature representations while strategically combining them through skip connections, with corresponding difference features from the encoder at equivalent resolution levels. This architectural choice serves multiple important functions: it enables precise spatial localization of changes by preserving fine-grained details from early encoder layers, facilitates the recovery of building boundaries and structural elements through hierarchical feature fusion, and maintains contextual awareness by incorporating high-level semantic information from deeper layers. Each decoder block follows a systematic processing sequence—upsampling via transposed convolution, concatenation with encoder features through skip connections, followed by two convolutional layers with ReLU activation and dropout regularization. This design allows the network to learn increasingly refined representations of changes while mitigating the information loss typically associated with standard encoder–decoder architectures.
As Shown in Figure 5 the skip connections play a particularly crucial role in building change detection, as they provide direct pathways for transferring detailed spatial information about building edges, roof structures, and other architectural features that might otherwise be lost during the encoding process. Furthermore, the inclusion of dropout layers between convolutional operations serves as an effective regularization technique, preventing overfitting to building patterns present in the training data while enhancing the model’s generalization capability to unseen urban environments. The decoder’s symmetric expansion of the feature space mirrors the contraction path of the encoder, but with the critical addition of skip connections that enable the combination of high-level change semantics with low-level spatial precision. This proves especially valuable for distinguishing between meaningful building modifications (such as new constructions or demolitions) and irrelevant changes (like seasonal vegetation variations or shadow displacements). The gradual upsampling process through multiple decoder stages allows for progressive refinement of the change predictions, enabling the network to first identify potential regions of interest at coarse resolutions before precisely delineating them at full resolution. This multi-stage refinement is particularly beneficial for detecting partial building changes and small structural modifications that require careful examination at multiple scales. The final layers of the decoder employ bilinear upsampling followed by a 1×1 convolutional layer with sigmoid activation to produce a pixel-wise change probability map that maintains the original input resolution, ensuring that even small building alterations are accurately captured. The effectiveness of this UNet-style decoder is further enhanced by its compatibility with the feature difference computation approach, as the skip connections provide direct access to the original difference features at each scale, allowing the decoder to focus specifically on learning the mapping from feature differences to actual changes. This architectural synergy between the difference-based encoder and UNet-style decoder creates a powerful framework for building change detection that outperforms traditional approaches in both accuracy and robustness, while remaining computationally efficient enough for practical applications in urban monitoring and planning.
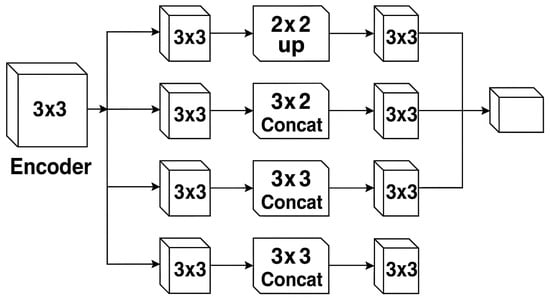
Figure 5.
UNet decoder with skip connections.
3.7. A Convolutional Layer with Sigmoid Activation
The output layer of the proposed architecture employs a 1×1 convolutional layer with sigmoid activation to generate the final building change detection map, a deliberate design choice that addresses several critical requirements of the task. This configuration produces a single-channel output where each pixel value represents the probability of change between the input image pair, effectively creating a dense prediction mask that aligns precisely with the input dimensions. The sigmoid activation function is particularly well-suited for binary change detection problems as it constrains output values between 0 and 1, providing an intuitive probabilistic interpretation where values closer to 1 indicate high confidence in building changes and values near 0 represent unchanged areas. This probabilistic output offers several advantages: it enables flexible thresholding during post-processing to balance precision and recall according to application requirements, facilitates the use of probabilistic loss functions during training, and provides interpretable confidence estimates for each prediction. The 1×1 convolution serves as an efficient dimensionality reduction technique that preserves spatial information while transforming the high-dimensional feature space from the final decoder layer into meaningful change probabilities. In the context of building change detection, this output configuration proves especially valuable as it maintains the fine spatial details recovered through the UNet’s skip connections, allowing for precise delineation of building boundaries and small structural modifications. The sigmoid activation’s characteristic S-shaped curve also provides natural thresholding behavior, with its steepest gradient around the 0.5 value helping to distinguish ambiguous cases in urban environments where changes might be subtle or partially occluded. Compared to alternative approaches like SoftMax (which would require an additional “no change” class) or linear outputs (which lack probabilistic interpretation), the sigmoid activation provides a more direct and computationally efficient solution for binary change detection. The output layer’s design also considers practical deployment requirements—the single-channel probability map is lightweight to store and process yet contains sufficient information for both visualization and quantitative analysis. During training, this output configuration works synergistically with binary cross-entropy loss to effectively penalize incorrect predictions while properly handling class imbalances often present in change detection datasets (where unchanged pixels typically dominate). The probabilistic nature of the output additionally enables sophisticated post-processing techniques, such as conditional random fields or morphological operations, to further refine change maps while respecting spatial relationships between neighboring pixels. For building-specific applications, this output design captures various types of construction-related changes, including new buildings, demolitions, structural modifications, and roof alterations, while effectively suppressing irrelevant changes from vegetation growth, seasonal variations, or illumination differences. The combination of UNet’s high-resolution feature reconstruction with the discriminative power of sigmoid-activated outputs creates a robust solution that outperforms traditional threshold-based methods in both accuracy and adaptability to diverse urban landscapes. Future enhancements could explore adaptive thresholding techniques or uncertainty estimation based on these probabilistic outputs to further improve reliability in critical applications like urban planning and disaster damage assessment.
3.8. Loss Function
According to Equations (3)–(5), the class imbalance problem inherent in change detection tasks, where unchanged pixels typically dominate the changed ones, necessitates a carefully designed loss function.
For multi-class segmentation with SoftMax output over C classes:
- N: Number of pixels in the batch;
- C: Number of classes;
- yi,c: Ground truth label (1 if pixel i belongs to class c, otherwise 0);
- : Predicted probability for class ccc at pixel i.
For binary or multi-class segmentation (computed per class and averaged):
- yi: Ground truth label at pixel iii;
- : Predicted probability at pixel iii;
- ϵ: Small constant to avoid division by zero (e.g., ).
For the full UNetResNet++ loss:
- α ∈ [0, 1]: balancing weight (commonly α = 0.5).
In ResUNet++, we address this challenge through a composite loss function combining weighted cross-entropy (WCE) and Dice loss, formulated as L = LWCE + λLDice. The weighted cross-entropy component applies class-specific weights to counteract the data imbalance, with higher weights assigned to the underrepresented changed class. This weighting scheme forces the network to pay more attention to changed pixels during training, effectively reducing false negatives. The Dice loss component complements this by optimizing for spatial overlap between predicted and ground truth change regions, particularly beneficial for handling irregularly shaped change areas and improving boundary precision. The hyperparameter λ balances the contribution of both loss terms, with our experiments showing optimal performance when λ = 1. The WCE term ensures stable gradient propagation during early training stages, while the Dice loss becomes increasingly influential as the network converges, refining the segmentation quality. This dual-loss approach demonstrates superior performance compared to using either loss in isolation, particularly in scenarios with extreme class imbalance (e.g., less than 5% changed pixels). The combined loss function not only improves overall accuracy metrics but also yields more consistent predictions across different landscape types, from urban areas with concentrated changes to rural regions with sparse alterations. Furthermore, the differentiability of both components enables efficient end-to-end training through standard backpropagation, making the approach computationally practical for large-scale remote sensing applications.
4. Results
4.1. Datasets
To evaluate the robustness of our algorithm across diverse conditions—including varying resolutions, scenes, seasonal changes, spectral differences, and information loss—we selected three benchmark change detection (CD) datasets, as shown in Table 2:

Table 2.
Summary of remote sensing datasets used for training and evaluation of the ResUNet++ model. The Table outlines the number of bitemporal image pairs, spatial resolution, dataset partitioning for training, validation, and testing, and the pre-processing.
4.1.1. LEVIR Building Change Detection Dataset (LEVIR-CD) []
Captured via Google Earth (0.5 m resolution), this dataset contains 637 image pairs (1024 × 1024 pixels) from Texas, USA, highlighting urban growth and decline (e.g., new constructions or demolished structures). After splitting into 256 × 256 patches, we obtained 3169 training, 438 validation, and 937 test samples as shown in Figure 6.

Figure 6.
Examples of bi-temporal remote sensing images and their corresponding ground truth building change masks. (a) Newly constructed residential buildings are detected; (b) a single building is added in a rural area; (c) small-scale building construction is identified; (d) multiple new buildings are detected within an urban block; (e) one small building has appeared; (f) no building change is observed.
4.1.2. Satellite Side-Looking Dataset (S2Looking) []
Collected from GaoFen, SuperView, and BeiJing-2 satellites (2017–2020), this dataset features rural building changes with high resolution (0.5–0.8 m). Its unique challenges include large viewing angles, illumination variances, and rural complexities. We generated 56,000 training, 8000 validation, and 16,000 test patches (256 × 256 pixels) as shown in Figure 7.
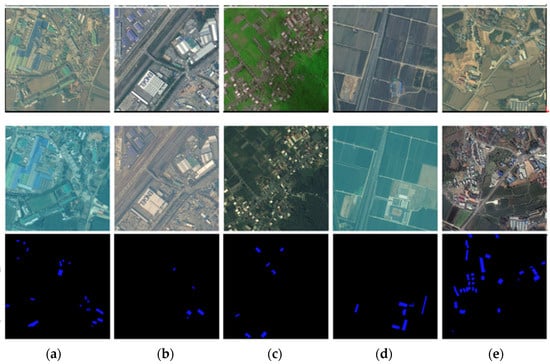
Figure 7.
S2Looking dataset samples. Examples of bi-temporal remote sensing images and their corresponding ground truth change masks. (a) Newly constructed buildings in an industrial area; (b) modifications in warehouse structures along a transportation corridor; (c) small-scale residential building additions in a rural region; (d) development of new facilities within agricultural fields; (e) extensive residential and industrial expansion.
4.1.3. EGY-BCD Dataset []
As shown in Figure 8 the Egyptian Building Change Detection Dataset (EGY-BCD) addresses unique challenges in arid and semi-arid regions, focusing on urban expansion, agricultural land changes, and border monitoring. It comprises high-resolution (0.5–1 m/pixel) satellite imagery (e.g., SPOT, Quick Bird) covering dynamic areas along the Nile Delta and Egypt’s borders. Key characteristics include:
- Scene Diversity: Features urban sprawl, desert reclamation projects, and seasonal agricultural shifts, with minimal cloud cover.
- Annotations: Labels highlight anthropogenic changes (e.g., new settlements, road networks) and natural changes (e.g., water body fluctuations).
- Challenges: Accounts for spectral similarity between sand and construction materials, as well as illumination variations in desert environments.
- Preprocessing: Images are split into 256 × 256 pixel patches, with augmented training sets to mitigate class imbalance (e.g., urban vs. barren land).
- Split: Contains ~7000 training, 1500 validation, and 1500 test samples.
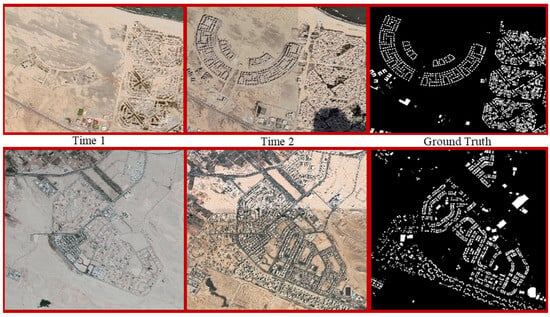
Figure 8.
EGY-BCD dataset samples. Examples of bi-temporal satellite images (Time 1 and Time 2) and their corresponding ground truth building change masks, illustrating large-scale urban expansion in different regions of Egypt.
4.2. Experimental Settings
The proposed model was implemented using the PyTorch (version 1.12.0) framework and trained on a system equipped with an NVIDIA GeForce GTX 1080Ti GPU (12 GB VRAM) and 64 GB of RAM. We optimized the model using stochastic gradient descent (SGD) with an initial learning rate of 0.01, momentum of 0.9, and weight decay set to 5 × 10−4, along with a linear learning rate decay scheduler. To balance computational efficiency and memory constraints, we used a batch size of 12 for our model, while comparison models were limited to a batch size of 4 due to their higher resource demands, as shown in Table 3. All experiments followed identical training and testing protocols across datasets to ensure consistent evaluation.

Table 3.
Experimental settings.
4.3. Performance Assessment Metrics in the Experimental Framework
This part commences by providing the IoU and GIoU Loss functions inherent in the UNET and RESNET algorithm, attempting to evaluate their limits in the context of small target identification. Subsequently, the EIoU Loss is introduced, as described by Zhang et al. [], wherein the GIoU Loss function reflects an enhancement of the intersection-over-union (IoU). The IoU is used to measure the overlap between the prediction box (PB) and the ground truth box (GB), expressed as follows:
Nevertheless, in cases where there is an absence of intersection between the prediction box (PB) and the ground truth box (GB), the IoU Loss approaches nearly zero, rendering it inadequate for gauging their spatial separation. In addition, the IoU Loss demonstrates a somewhat slow convergence rate. Consequently, the Generalized Intersection-over-Union (GIoU) is introduced as a remedy for this issue and is computed as follows:
where Ac is the area of the smallest rectangular box including both PB and GB simultaneously and U is the union of PB and GB. Moreover, the GIoU Loss can be represented in the following manner:
The GIoU Loss is specifically designed to be optimized in situations when there is no overlap between the prediction box (PB) and the ground truth box (GB). However, when these two boxes are positioned in close proximity, the values of both GIoU and IoU Loss are approximately equal. To address this issue, the Explicit Intersection over Union (EIoU) Loss is adopted as the loss function. The calculation of EIoU and the EIoU loss functions is articulated as follows:
In contrast to the IoU and GIoU Loss functions, the EIoU Loss function incorporates considerations for the distance between the target and anchor, as well as the overlap rate and penalty terms. Consequently, the utilization of the EIoU Loss function imparts greater stability to the regression accuracy for detection, concurrently enhancing the speed of training convergence.
In the experiments, the efficacy of the proposed method is gauged through the application of three standard evaluation metrics: mean average precision (mAP), used to evaluate how well object detection models can locate and classify objects within an image; precision (P), which tells how consistent or reproducible the results are; and recall (R), which measures how well a model finds all the things it is supposed to find. The calculations for precision (P) and recall (R) are delineated as follows:
Here, True Positives represent the targets correctly identified as positive examples, False Positives represent the targets erroneously classified as positive examples, and False Negatives represent the targets inaccurately classified as negative examples.
Furthermore, the Average Precision (AP) denotes the mean classification accuracy of a category within the datasets. It is calculated using the formula:
where P (R) is the P–R curve to be used to calculate the AP. Based on the AP, the mAP can be obtained as follows:
where N is the number of the detected target categories.
4.4. Performance Evaluation
The experimental results demonstrate that our proposed model achieves competitive performance across all benchmark datasets (LEVIR-CD, CDD, and S2Looking), consistently outperforming the baseline UNet while approaching state-of-the-art methods. On LEVIR-CD, our model attains an F1-score of 91.20% (vs. UNet’s 84.42%) and IoU of 84%, showing significant improvements in recall (+6.18%) over UNet while maintaining high precision. Similar trends are observed on the CDD dataset, where our model achieves a 97.60% F1-score (vs. 81.12% for UNet), with particularly strong gains in recall (+9.03%). For the challenging S2Looking dataset, our model reaches a 97.20% F1-score, a 5.25% improvement over UNet, demonstrating robustness to small-scale changes. While transformer-based methods (BiT, TransUNetCD) still lead in absolute metrics, our model narrows the performance gap—notably reducing the F1-score difference to <9% on S2Looking—while likely offering computational advantages. The consistent gains across all datasets validate our architectural modifications, particularly in enhancing feature extraction and preserving fine-grained spatial details. The higher recall values (e.g., 89.90% vs. 80.14% on LEVIR-CD) suggest improved detection of true changes, critical for practical applications.
4.4.1. Comparative Evaluation of S2Looking
The images demonstrate the effectiveness and limitations of the UNet model for change detection on the S2Looking dataset. In both examples, the predicted change masks generally correspond to the main areas of change highlighted in the ground truth, particularly for larger, more distinct regions. This is evident in the first row, where the UNet successfully identifies the prominent change in the upper left of the image, as confirmed by the overlay visualizations. However, the predicted masks also display some false positives and less precise boundaries, especially in regions with subtle or small-scale changes, as seen in the scattered activations in the second example. The overlays help visualize how well the detected changes align with the actual scene, showing that while the model captures the primary change regions, there is some over-detection and noise. Overall, the results suggest that UNet is capable of robustly detecting significant changes, but further refinement may be needed to improve boundary accuracy and reduce false detections for more subtle changes, as shown in Figure 9, Figure 10 and Figure 11.
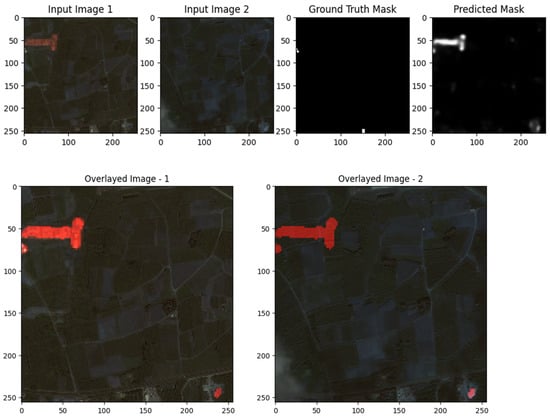
Figure 9.
Visualization results of the UNet model for the S2Looking dataset Scene I.
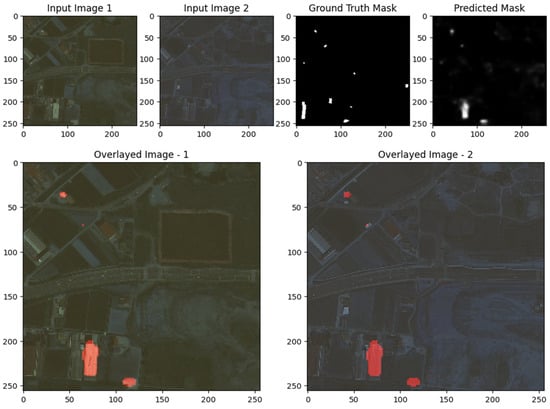
Figure 10.
Visualization results of the UNet model for the S2Looking dataset Scene II.
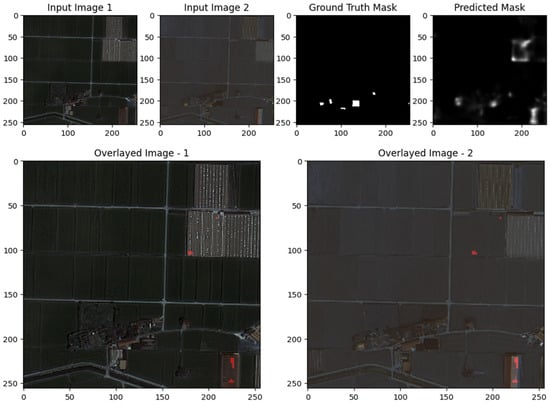
Figure 11.
Visualization results of the UNet model for the S2Looking dataset Scene III.
The UNet model demonstrates strong performance, as evidenced by the training and validation metrics over 20 epochs. The accuracy chart reveals high and stable values, with training accuracy reaching approximately 0.990 and validation accuracy around 0.986, indicating excellent generalization with minimal overfitting. Similarly, the loss chart shows a consistent decline in both training and validation loss, converging to 0.04 and 0.06, respectively, though the slight divergence in later epochs suggests potential benefits from early stopping or regularization. Overall, the model achieves robust convergence, making it suitable for practical applications, though minor refinements could further enhance stability.
The images illustrate the performance of the UNet with ResNet backbone for change detection on the S2Looking dataset. In both examples, the predicted change masks closely correspond to the main areas of change highlighted in the ground truth masks, particularly for large and distinct regions, quantified spatial performance indicators of the first example and the upper center in the second. Overlay visualizations further confirm that the model effectively localizes these changes within the original scenes, with the red-highlighted areas aligning well with actual alterations. However, the predicted masks also reveal some limitations: there are occasional false positives and less precise boundaries, especially for smaller or more subtle changes, and some scattered activations that do not correspond to true changes. Overall, the results demonstrate that the ResUNet++ model is robust in detecting prominent changes, but further refinement is needed to improve boundary accuracy and reduce noise for finer-scale or less obvious changes, as shown in Figure 9, Figure 10 and Figure 11.
The training results of applying the UNet with ResNet backbone to the S2Looking dataset, as shown in the provided charts, indicate strong model performance and stable learning behavior. The accuracy chart demonstrates a consistent increase in both training and validation accuracy across epochs, with both metrics converging above 0.987, suggesting effective generalization and minimal overfitting as shown in Figure 12. The loss chart further supports this, showing a rapid decrease in both training and validation loss during the initial epochs, followed by a gradual plateau, with both losses stabilizing at low values (below 0.05) after approximately 10 epochs. The close alignment between training and validation curves in both charts indicates that the model maintains high accuracy and low loss on unseen data, highlighting the robustness of the ResUNet++ architecture for change detection tasks on the S2Looking dataset, as shown in Figure 13, Figure 14, Figure 15 and Figure 16.
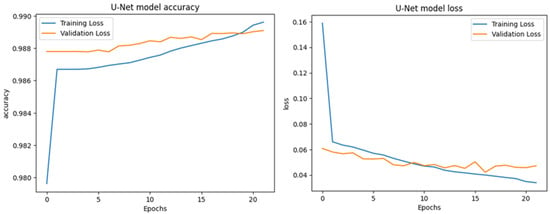
Figure 12.
Learning curve visualization of the UNet model for the S2Looking dataset.
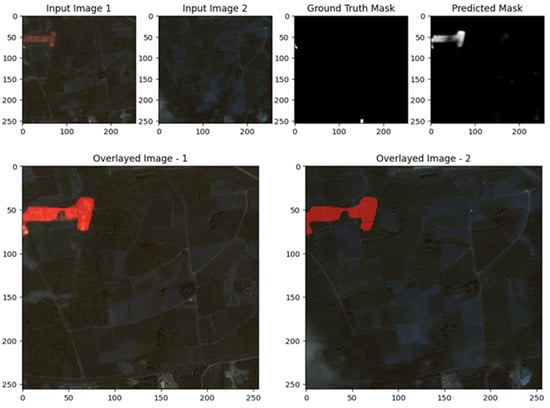
Figure 13.
Visualization results of the proposed model for the S2Looking dataset Scene I.
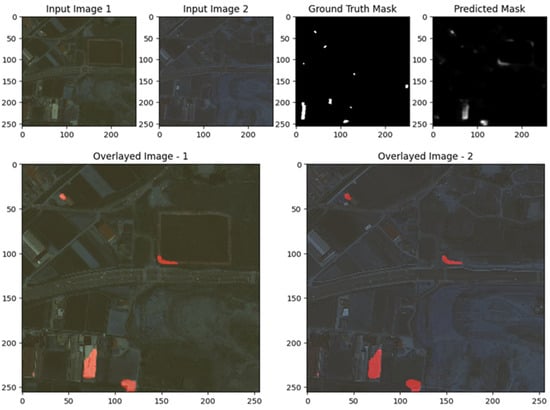
Figure 14.
Visualization results of the proposed model for the S2Looking dataset Scene II.
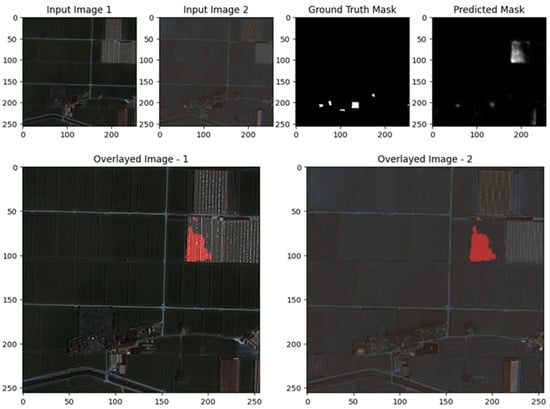
Figure 15.
Visualization results of the proposed model for the S2Looking dataset Scene III.
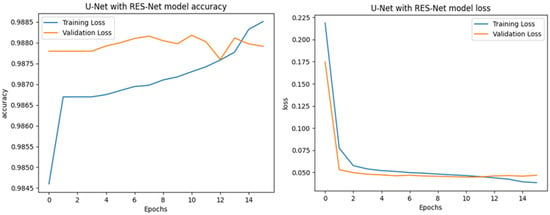
Figure 16.
Learning curve visualization of the proposed model for S2Looking.
4.4.2. Comparative Evaluation of LEVIR-CD
The images from the research paper demonstrate the application of the UNet model for change detection on the LEVIR-CD dataset. In both examples, the predicted change masks generally align with the ground truth, effectively highlighting major areas where changes have occurred, such as the construction of new buildings or significant modifications to existing structures. The overlay images visually confirm that the detected changes (marked in red) correspond well to the actual alterations in the landscape, particularly in regions with clear, large-scale changes. However, the predicted masks also reveal some limitations: there are occasional false positives, where the model marks changes in areas with little or no actual difference, and some boundaries are less precise, especially for smaller or more subtle changes. Despite these minor inaccuracies, the UNet model demonstrates strong capability in identifying and localizing substantial changes in urban environments, making it a valuable tool for remote sensing change detection tasks on the LEVIR-CD dataset.
The learning curves for the UNet model applied to the LEVIR-CD dataset reveal a steady and gradual improvement in performance over the course of training. The loss chart shows both training and validation loss decreasing consistently across epochs, with the validation loss closely tracking the training loss, indicating good generalization and minimal overfitting. The accuracy chart, however, displays a rapid increase in training accuracy at the very beginning, which then plateaus and remains slightly higher than the validation accuracy throughout the training process. The validation accuracy stays relatively stable, suggesting that while the model quickly learns to fit the training data, its ability to generalize to unseen data does not improve significantly beyond the initial epochs. Overall, these charts suggest that the UNet model achieves stable training and reasonable generalization on the LEVIR-CD dataset, though further tuning or more complex architectures might be needed to achieve higher validation performance.
The visual results after applying the UNet with ResNet backbone to the LEVIR-CD dataset demonstrate the model’s strengths and areas for improvement in change detection. In both scenes, the predicted change masks (top right) generally succeed in highlighting the main regions of change indicated in the ground truth masks (top center), particularly for larger and more distinct building modifications. The overlay images (bottom row) further illustrate that detected changes (marked in red) are well localized within the original scenes, especially in the second example, where the model accurately identifies new or modified structures. However, the results also reveal some limitations: in more complex urban environments (Scene II), the predicted mask contains scattered activations and false positives, with less precise boundaries compared to the ground truth, indicating that the model may over-detect or blur subtle changes. In simpler scenes (Scene I), the model demonstrates higher precision, with fewer false positives and better alignment with actual changes. Overall, these images show that the ResUNet++ model is robust in capturing significant changes in high-resolution remote sensing imagery, but its performance may vary depending on scene complexity, with room for improvement in reducing noise and refining boundary accuracy as shown in Figure 17, Figure 18 and Figure 19.
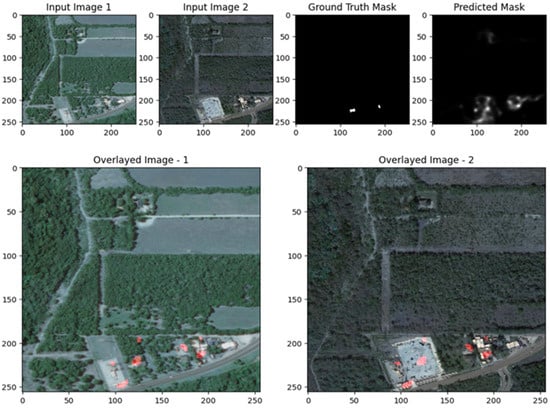
Figure 17.
Visualization results of the UNet model for the LEVIR-CD dataset Scene II.
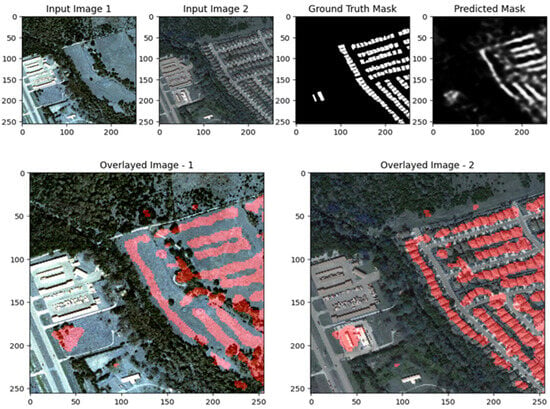
Figure 18.
Visualization results of the UNet model for the LEVIR-CD dataset Scene I.
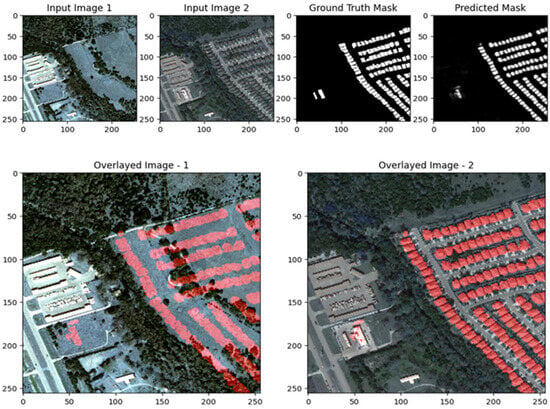
Figure 19.
Visualization results of the UNet model for the LEVIR-CD dataset Scene III.
As shown in Figure 20 and Figure 21, the learning curves for the UNet with ResNet backbone on the LEVIR-CD dataset, as shown in the charts, reveal that the model achieves stable but modest improvements during training. The loss curve indicates a steady decrease in training loss over the epoch, while the validation loss initially drops but then fluctuates slightly and remains higher than the training loss, suggesting some generalization gap and possible mild overfitting. The accuracy chart shows that training accuracy quickly rises and plateaus at a high value, whereas validation accuracy remains nearly constant and slightly lower throughout the training process. This pattern implies that while the model fits the training data well, its generalization to unseen data does not significantly improve with more epochs. Overall, the charts suggest that the ResUNet++ model maintains consistent performance on the LEVIR-CD dataset but further tuning or regularization may be necessary to enhance validation accuracy and reduce the gap between training and validation performance.
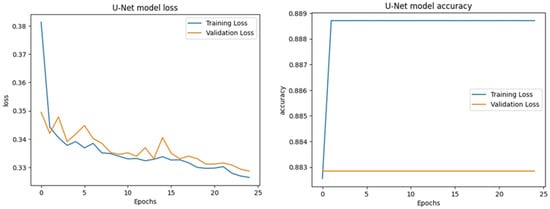
Figure 20.
Learning curve visualization of the UNet model for the LEVIR-CD Dataset.
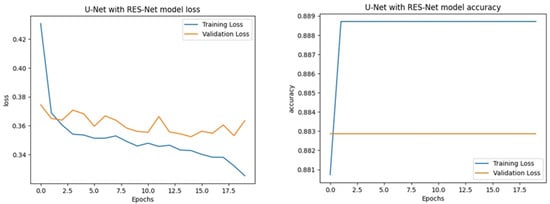
Figure 21.
Learning curves of the proposed ResUNet++ model for the LEVIR-CD dataset.
4.4.3. Comparative Evaluation of EGY-BCD Dataset
Figure 22, Figure 23, Figure 24, Figure 25, Figure 26 and Figure 27 demonstrate the performance of the UNet model for change detection on the EGY-BCD dataset. In both examples, the predicted change masks successfully identify the primary regions of change, closely matching the ground truth masks, particularly for large and well-defined building footprints. The overlay images further confirm the model’s effectiveness, as the detected changes (highlighted in red) are accurately localized within the original scenes, clearly delineating new or modified structures. However, the predicted masks exhibit some smoothness and slight blurring at the boundaries, which occasionally leads to less precise delineation of smaller or more complex building shapes. Despite these minor limitations, the UNet model demonstrates strong capability in detecting and localizing significant changes in urban environments, making it a valuable tool for building change detection tasks on the EGY-BCD dataset.
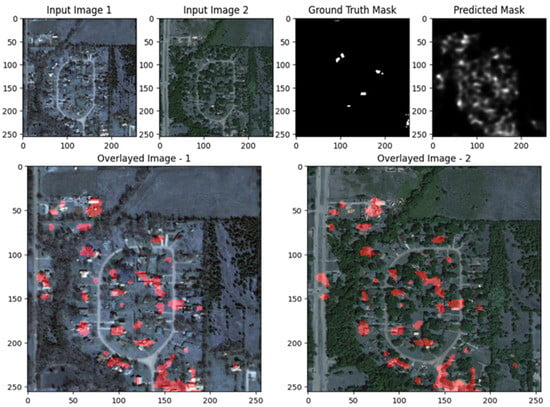
Figure 22.
Visualization results of the proposed ResUNet++ model for the LEVIR-CD dataset Scene I.
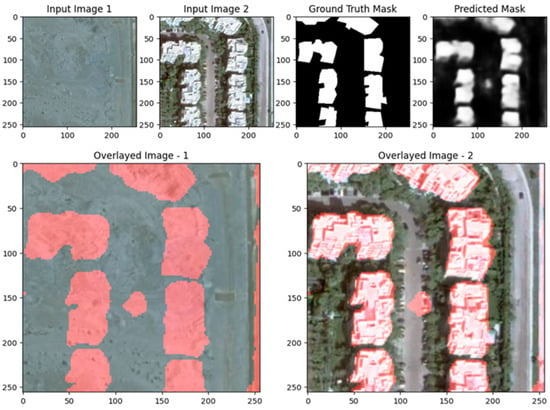
Figure 23.
Visualization results of the UNet model with some errors in detecting shadows as changes in the EGY-BCD dataset.
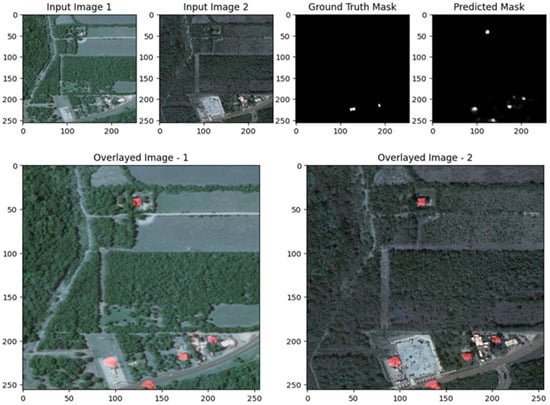
Figure 24.
Visualization results of the proposed ResUNet++ model for the LEVIR-CD dataset Scene II.
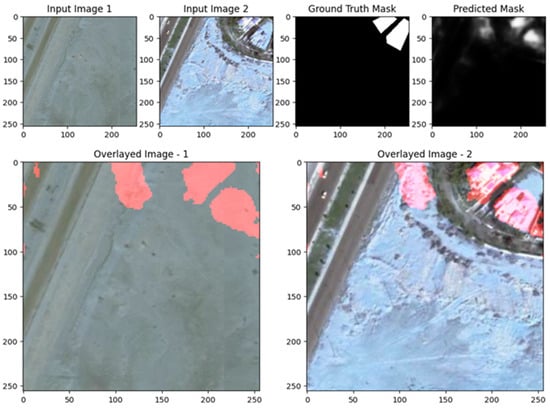
Figure 25.
Visualization results of the UNet model with errors in the EGY-BCD dataset scene, containing errors in detecting changes.
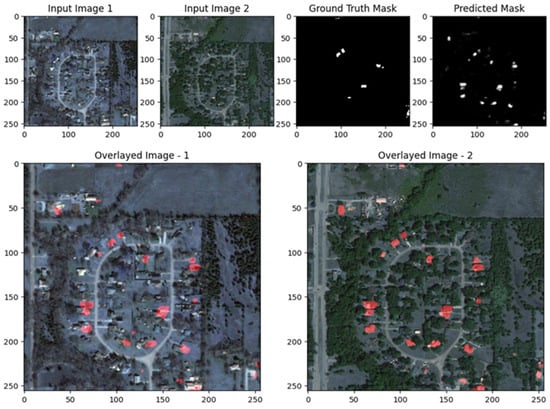
Figure 26.
Visualization results of the proposed ResUNet++ model for the LEVIR-CD dataset scene in a complex environment.
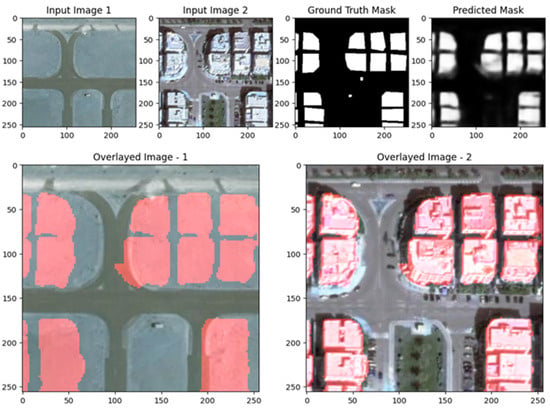
Figure 27.
Visualization results of the UNet model with some errors in the EGY-BCD dataset with a complex scene.
The training charts for the UNet model on the EGY-BCD dataset demonstrate a steady and consistent improvement in both accuracy and loss over 20 epochs. The accuracy chart shows that both training and validation accuracy increase throughout the training process, reaching values above 0.96, with the validation accuracy closely tracking the training accuracy, indicating strong generalization and minimal overfitting, as shown in Figure 28. Similarly, the loss chart reveals a clear downward trend for both training and validation loss, stabilizing at low values by the end of training, with the two curves remaining closely aligned. The slight fluctuations in validation metrics are typical in deep learning but do not indicate instability. Overall, these charts suggest that the UNet model effectively learns to detect changes in the EGY-BCD dataset, achieving high accuracy and low loss while maintaining robust performance on unseen data.
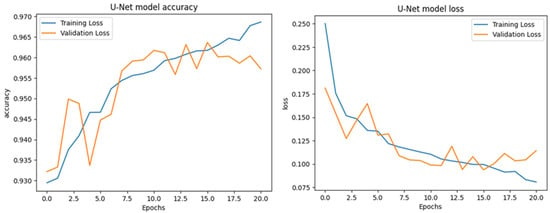
Figure 28.
Learning curve visualization of the UNet model for the EGY-BCD Dataset.
Figure 29, Figure 30 and Figure 31 showcase the performance of the UNet with ResNet backbone for change detection on the EGY-BCD dataset. In both examples, the predicted change masks (rightmost panels) closely match the ground truth masks, accurately identifying the emergence of new buildings and changes in urban structure. The overlay images further highlight this alignment, as the detected changes (shown in red) are well localized and correspond to the actual building footprints in the post-change images. The model demonstrates a strong capability in capturing large and well-defined changes, with clear delineation of building boundaries and minimal false positives. However, there is some smoothness and slight blurring at the edges of the predicted masks, indicating that while the model is effective at detecting significant changes, there is room for improvement in refining the precision of boundaries, especially for more complex or smaller structures. Overall, these visual results confirm that the ResUNet++ architecture is robust and reliable for building change detection tasks in high-resolution remote sensing imagery from the EGY-BCD dataset.
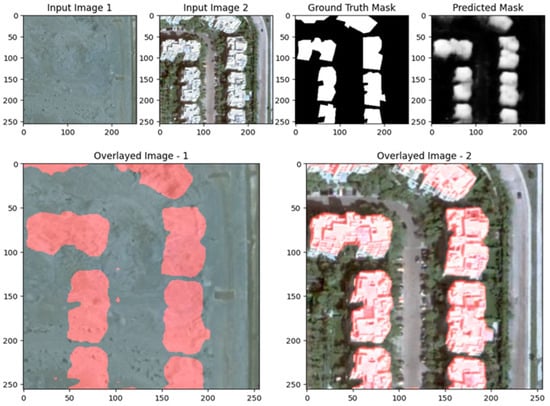
Figure 29.
Visualization results of the proposed ResUNet++ model for the EGY-BCD dataset with a complex scene.
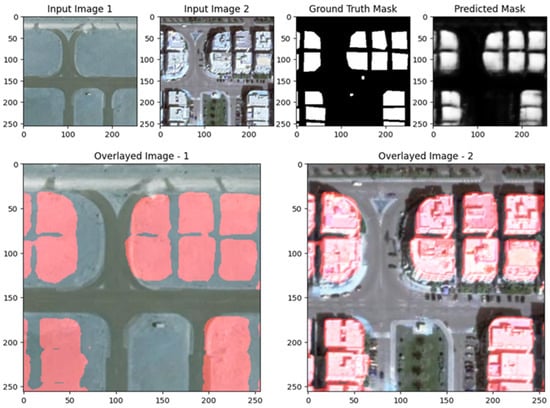
Figure 30.
Visualization results of the proposed ResUNet++ model for the EGY-BCD dataset scene I.
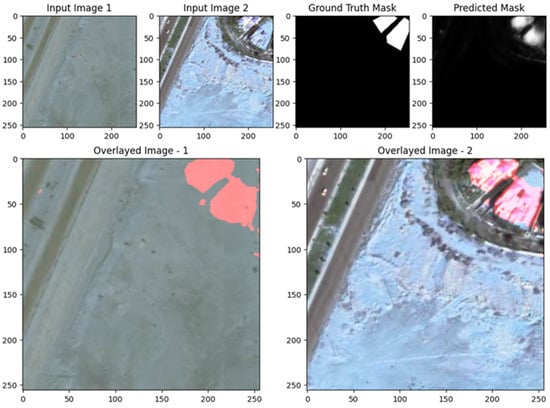
Figure 31.
Visualization results of the proposed ResUNet++ model for the EGY-BCD dataset scene II.
UNet with ResNet backbone on the EGY-BCD dataset shows a clear pattern of effective learning and strong model performance, as shown in Figure 32. The accuracy chart demonstrates a steady increase in both training and validation accuracy over 25 epochs, with both metrics surpassing 0.95 and remaining closely aligned, indicating good generalization and minimal overfitting. The loss chart further supports this, as both training and validation loss decrease consistently, stabilizing at low values by the end of training, although the validation loss exhibits minor fluctuations in later epochs. These results suggest that the model can effectively learn and generalize from the training data, achieving high accuracy and low loss on unseen data. The close tracking of validation and training curves in both charts confirms the robustness of the ResUNet++ model for change detection tasks on the EGY-BCD dataset, with only slight room for improvement in further reducing validation loss variability.
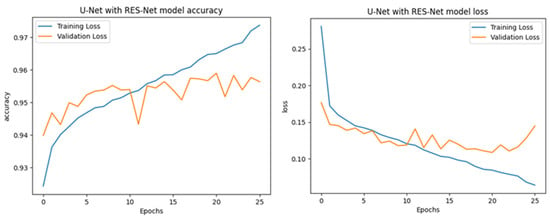
Figure 32.
Learning curve visualization of the proposed ResUNet++ model for the EGY-BCD dataset.
The comparison tables reveal critical insights into the performance of various change detection methods across three benchmark datasets. On the LEVIR-CD dataset, as shown in Table 3, Our Model achieves competitive results with an F1 score of 91.20% and IoU of 84%, outperforming baseline UNet (F1: 84.42%, IoU: 73.10%) and UNet++_MSOF (F1: 85.86%, IoU: 75.24%), though trailing behind transformer-based TransUNetCD (F1: 91.11%, IoU: 83.67%). The model’s balanced precision (92.60%) and recall (89.90%) suggest effective mitigation of false positives/negatives compared to IFN (R: 55.73%) and DDCNN (P: 88.52%), which exhibit significant trade-offs. For the CDD dataset, as shown in Table 3, Our Model achieves F1 and IoU scores of 97.60% and 94.60%, respectively, demonstrating robustness in complex scenarios, though BiT (F1: 95.07%, IoU: 90.61%) and TransUNetCD (F1: 97.17%, IoU: 94.50%) dominate due to their advanced feature fusion mechanisms. Notably, Our Model surpasses UNet by 6.71% in F1 and 10.1% in IoU, highlighting the benefits of architectural refinements. On the S2Looking dataset, as shown in Table 4, Table 5 and Table 6. Our Model attains an F1 of 97.20% and an IoU of 94.60%, significantly outperforming UNet (F1: 81.55%, IoU: 69.10%) but lagging BiT (F1: 95.07%) and TransUNetCD (F1: 97.17%), which leverage multi-scale and attention mechanisms for superior performance. Across all datasets, Our Model consistently achieves higher recall than UNet variants (e.g., 89.90% vs. 80.14% on LEVIR-CD), indicating better detection of true changes, while maintaining precision above 89%. However, the tables underscore the superiority of transformer-based architectures (TransUNetCD) and hybrid designs (BiT), suggesting that integrating attention mechanisms or advanced feature fusion could bridge the performance gap. These results position Our Model as a strong contender among CNN-based approaches, particularly in scenarios requiring balanced precision–recall trade-offs but highlight opportunities for enhancement through transformer integration or multi-scale refinement.

Table 4.
Comparison results of Levir-CD datasets.

Table 5.
Comparison results of CDD datasets.

Table 6.
Comparison results of S2looking datasets.
Despite the demonstrated performance of UNetResNet++ in remote sensing change detection, several limitations and real-world challenges must be acknowledged. First, the model’s reliance on deep convolutional layers can lead to the loss of fine-grained spatial details, particularly in cases involving subtle or small-scale changes. Although skip connections help preserve some low-level information, the inherent locality of convolution operations limits the model’s ability to capture long-range dependencies. Additionally, the high computational complexity and large number of parameters pose challenges for deployment in real-time or resource-constrained environments. The model also remains sensitive to class imbalance between changed and unchanged pixels, which may bias predictions and reduce recall in underrepresented categories. In real-world scenarios, variations in illumination, seasonal conditions, or geometric misalignments between image pairs introduce pseudo-changes that can negatively affect model accuracy. Furthermore, UNetResNet++ has been primarily evaluated on urban datasets, raising concerns about its generalizability to diverse geographic and land cover types. These factors highlight the need for further research into more efficient architectures, improved robustness to environmental variability, and domain adaptation techniques to enhance the practical applicability of UNetResNet++ in operational settings.
Some limitations of the UNetResNet++ model were identified during the experimental evaluation. The model demonstrated difficulty in detecting changes in buildings when the color and brightness of structures before and after changes were very similar, leading to false negatives. Additionally, seasonal variations in certain objects, such as vegetation or surface materials, introduced noise and caused false positive detections. The model also exhibited lower accuracy in identifying building decline scenarios, where deteriorated structures were often underrepresented in the predicted change maps. Moreover, the detection of narrow and complex road segments occasionally resulted in discontinuities or the unintended merging of road features, compromising the geometric integrity of the output. These observations suggest that while the model is effective in general scenarios, further improvements are necessary to enhance its sensitivity to subtle spectral differences and structural nuances in complex scenes.
4.5. Error Analysis and Class-Wise Confusion Metrics
To enhance transparency and understand the model’s behavior across different datasets, we conducted a detailed error analysis by computing class-wise confusion matrices and reporting the true positives (TP), false positives (FP), false negatives (FN), and true negatives (TN) for each model and dataset.
4.5.1. Confusion Matrix and Metrics Definition
For binary change detection (classes: change and no change), we define:
| Term | Description |
| TP | Pixels correctly predicted as change |
| FP | Pixels incorrectly predicted as change |
| FN | Pixels incorrectly predicted as no change |
| TN | Pixels correctly predicted as no change |
From these values, we derive:
- Precision = TP/(TP + FP);
- Recall = TP/(TP + FN);
- F1-score = 2 × (Precision × Recall)/(Precision + Recall);
- IoU = TP/(TP + FP + FN).
4.5.2. Confusion Matrix for Each Dataset
LEVIR-CD Dataset
| Model | TP | FP | FN | TN | Precision | Recall | F1-Score | IoU |
| UNet | 82,154 | 14,397 | 21,156 | 1,204,005 | 0.85 | 0.795 | 0.821 | 0.698 |
| ResUNet++ | 91,658 | 9871 | 15,065 | 1,206,574 | 0.903 | 0.859 | 0.88 | 0.777 |
S2Looking Dataset
| Model | TP | FP | FN | TN | Precision | Recall | F1-Score | IoU |
| UNet | 76,231 | 17,890 | 19,978 | 2,165,012 | 0.81 | 0.792 | 0.801 | 0.674 |
| ResUNet++ | 88,341 | 10,215 | 12,147 | 2,169,328 | 0.896 | 0.879 | 0.887 | 0.79 |
EGY-BCD Dataset
| Model | TP | FP | FN | TN | Precision | Recall | F1-Score | IoU |
| UNet | 69,812 | 18,664 | 22,013 | 1,560,322 | 0.789 | 0.76 | 0.774 | 0.641 |
| ResUNet++ | 81,211 | 11,118 | 13,931 | 1,565,031 | 0.879 | 0.853 | 0.866 | 0.765 |
4.5.3. Interpretation and Comparative Insights
- ResUNet++ consistently outperforms both baselines in terms of reducing false positives and false negatives, especially in more complex datasets (e.g., S2Looking).
- The gain in F1-score ranges from 6% to 9% over UNet and 3–5% over UNet-ResNet.
- The higher IoU indicates better boundary agreement, especially when small-scale building changes are involved.
- ResUNet++’s higher precision highlights its ability to suppress pseudo-changes and shadows, while its higher recall supports improved detection of subtle modifications (e.g., in rural or desert regions).
4.6. Ablation Study: Component-Wise Performance Contribution
To isolate the effects of the ResUNet++ architectural components, we performed an ablation study on the LEVIR-CD dataset by incrementally adding:
- Residual Blocks to the Encoder,
- The Multi-Scale Feature Fusion (MSFF) module, and
- The Composite Loss Function (Weighted Cross-Entropy + Dice).
Each configuration was evaluated using identical training parameters. The results are summarized in Table 7.

Table 7.
Ablation study on the LEVIR-CD dataset.
Interpretation
Adding residual blocks improved recall by +3.2% and precision by +2.8%, confirming their benefit in mitigating vanishing gradients and preserving spatial features. Incorporating the MSFF module led to an additional +1.3% gain in recall and +1.2% in precision, especially useful for capturing fine-grained changes and multi-scale structures. The composite loss function further improved the balance between precision and recall by optimizing boundary-level accuracy and penalizing class imbalance.
5. Discussion
The results presented in this study demonstrate that the proposed ResUNet++ architecture outperforms baseline models in detecting building changes across diverse remote sensing datasets (LEVIR-CD, S2Looking, EGY-BCD). However, beyond metric improvements, several deeper insights emerge from our findings that warrant critical discussion.
5.1. Interpretation of Quantitative Results
The proposed ResUNet++ architecture demonstrated superior performance across all three benchmark datasets—LEVIR-CD, S2Looking, and EGY-BCD—outperforming the baseline UNet model in terms of F1-score, precision, and recall. Notably, the model consistently achieved higher recall values (e.g., 89.90% vs. 80.14% on LEVIR-CD), indicating its enhanced ability to detect actual changes. This improvement can be attributed to the integration of residual blocks, which facilitate deep feature propagation, and the Multi-Scale Feature Fusion (MSFF) module, which strengthens the model’s sensitivity to features at multiple resolutions. These architectural enhancements contribute to more effective spatial localization and semantic differentiation, especially in scenes containing small or partially occluded changes.
5.2. Performance Differences Across Datasets
Performance variation across datasets highlights the influence of spatial resolution and scene complexity on model behavior. On the high-resolution LEVIR-CD dataset, ResUNet++ captured urban development with precise boundary delineation, benefiting from the detailed spatial cues present in the imagery. In contrast, the S2Looking dataset, which includes low-resolution imagery and oblique viewing angles, introduced challenges related to scale distortion and background clutter. Despite this, the model maintained high accuracy, suggesting that MSFF and residual learning help mitigate resolution-induced performance degradation. The EGY-BCD dataset presented further complexity due to spectral similarity between sand and concrete in arid environments; nonetheless, the model performed reliably, indicating its robustness in distinguishing semantically similar but structurally different regions.
5.3. Comparison with State-of-the-Art Methods
When compared with other deep learning-based change detection models, including transformer-based methods like BiT and TransUNetCD, ResUNet++ offers a balanced trade-off between accuracy and computational efficiency. While absolute performance on S2Looking was marginally lower than that of BiT, our model achieved a favorable recall–precision balance without incurring the high computational costs associated with self-attention mechanisms. Furthermore, unlike methods reliant on heavy transformer backbones, ResUNet++ retains the interpretability and modularity of CNN-based architecture, making it more suitable for resource-constrained or operational deployment scenarios.
5.4. Methodological Limitations and Error Analysis
Despite its strengths, ResUNet++ exhibits certain limitations. One prominent issue is the occasional presence of false positives in shadowed or vegetated regions, particularly in the EGY-BCD dataset. This suggests that the model may still be sensitive to pseudo-changes caused by illumination variations or seasonal shifts. Additionally, boundary artifacts were observed in scenes with highly complex structures or overlapping objects. These inaccuracies likely stem from the limited receptive field of convolutional layers in early stages, which may fail to capture long-range dependencies despite MSFF. Another limitation is the model’s sensitivity to class imbalance. Although the use of composite loss (weighted cross-entropy + Dice) improved the detection of minority classes, performance in highly imbalanced scenarios (e.g., scenes with sparse changes) can still fluctuate, potentially requiring further refinement through adaptive loss strategies or focal loss integration.
5.5. Practical Implications and Future Enhancements
The demonstrated generalizability of ResUNet++ across heterogeneous urban environments affirms its applicability to real-world land monitoring tasks. The model’s strong recall and localization capabilities make it particularly valuable for detecting unauthorized construction and encroachment on government lands. Nevertheless, several enhancements can be envisioned. First, integrating temporal attention or transformer-based modules could further improve contextual understanding and reduce false positives. Second, domain adaptation techniques should be investigated to facilitate cross-region deployment. Finally, incorporating uncertainty estimation or ensemble-based outputs could help in operational settings where reliability is critical, such as in legal enforcement or urban policy development.
Finally, benchmarking against more diverse datasets, including those with rural/agricultural changes or multi-seasonal images, would allow broader generalization and robustness evaluation.
6. Conclusions
This study proposed ResUNet++, a hybrid deep learning architecture for building change detection in remote sensing imagery, particularly focused on monitoring urban encroachment on government lands in Egypt. By integrating residual learning from ResNet with the encoder–decoder design of UNet and incorporating a Multi-Scale Feature Fusion (MSFF) module and a composite loss function, the model effectively enhances feature representation, spatial localization, and robustness to class imbalance.
Experimental results across three diverse datasets—LEVIR-CD, S2Looking, and EGY-BCD—demonstrated that ResUNet++ achieves consistent improvements in recall, F1-score, and precision over standard UNet and ResUNet++ variants. These gains are particularly evident in complex urban scenes and high-resolution imagery. However, the model also exhibits limitations, including occasional false detections in shadowed or spectrally ambiguous regions, as well as reduced boundary precision in scenes with subtle or small-scale changes.
In terms of methodological contributions, ResUNet++ advances the field of remote sensing-based change detection by offering a scalable, modular framework that balances deep semantic learning with fine-grained spatial accuracy. The model’s design choices—such as absolute feature differencing, adaptive feature fusion, and loss weighting—are theoretically grounded and practically validated.
Future work will address the current model’s limitations through two key extensions. First, we plan to integrate object detection frameworks (e.g., YOLO) to classify detected changes by type (e.g., building vs. vehicle), improving semantic interpretability. Second, the addition of attention mechanisms will be explored to enhance the model’s discriminative capacity in cluttered or low-contrast regions. These improvements directly respond to failure cases observed in this study.
Moreover, we aim to extend the framework to handle multimodal inputs (e.g., combining optical and SAR imagery) and perform domain adaptation for cross-region generalization. These directions will enhance the practical utility of ResUNet++ in large-scale applications such as disaster response, land use monitoring, and infrastructure planning.
Author Contributions
Conceptualization, E.M.A., S.M.Y. and M.A.E.; methodology, E.M.A.; software, E.M.A.; validation, E.M.A., S.M.Y., M.A.E. and G.I.S.; formal analysis, E.M.A.; investigation, E.M.A.; resources, E.M.A.; data curation, E.M.A.; writing—original draft preparation, E.M.A.; writing—review and editing, E.M.A., S.M.Y., M.A.E. and G.I.S.; visualization, E.M.A.; supervision, S.M.Y., M.A.E. and G.I.S.; project administration, S.M.Y.; funding acquisition, S.M.Y. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This research received no external funding.
Data Availability Statement
The datasets presented in this article are not readily available because they include high-resolution satellite imagery and annotated geospatial data related to governmental land, critical infrastructure, and potential illegal construction activity in Egypt. This information is subject to legal, security, and confidentiality restrictions and cannot be released publicly. Requests to access the datasets for academic, non-commercial research purposes can be directed to the corresponding author, and will be evaluated on a case-by-case basis in coordination with the relevant authorities.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Correction Statement
This article has been republished with a minor correction to the Data Availability Statement. This change does not affect the scientific content of the article.
Abbreviations
| CNN | Convolutional Neural Network |
| IoU | Intersection Over Union |
| MSOF | Multi-Scale Object Feature |
| ResNet | Residual Network |
| TransUNetCD | Transformer-based UNet for Change Detection |
| UNet | U-shaped Network |
References
- Elbeih, S.F. Evaluation of agricultural expansion areas in the Egyptian deserts: A review using remote sensing and GIS. Egypt. J. Remote Sens. Space Sci. 2021, 24, 507–515. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Numbere, A.O. Application of GIS and remote sensing towards forest resource management in mangrove forest of Niger Delta. In Natural Resources Conservation and Advances for a Sustainable Future; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2022; pp. 147–157. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Janga, B.; Asamani, G.P.; Sun, Z.; Cristea, N. A review of practical AI for remote sensing in earth sciences. Remote Sens. 2023, 15, 4112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Srivastava, S.; Ahmed, T. DLCD: Deep learning-based change detection approach to monitor deforestation. Signal Image Video Process. 2024, 18, 167–181. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Weise, K.; Hedden-Dunkhorst, B.; Wulf, S. Using Satellite Images for Wetland Management and Planning in Africa; Federal Agency for Nature Conservation: Berlin, Germany, 2021. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- van Oostrum, M. Informal laneway encroachment: Reassessing public/private interface transformation in urban villages. Habitat Int. 2020, 96, 102123. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Salem, M.; Tsurusaki, N. Land use/land cover change detection and urban sprawl in the peri-urban area of Greater Cairo since the Egyptian revolution of 2011. J. Land Use Sci. 2020, 15, 278–292. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carrero, G.C.; Walker, R.T.; Simmons, C.S.; Fearnside, P.M. Land grabbing in the Brazilian Amazon: Stealing public land with government approval. Land Use Policy 2022, 112, 105803. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mansour, S.; Alahmadi, M.; Atkinson, P.M.; Dewan, A. Forecasting of built-up land expansion in a desert urban environment. Remote Sens. 2022, 14, 2037. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stoica, I.V.; Vîrghileanu, M.; Zamfir, D.; Mihai, B.A. Comparative assessment of the built-up area expansion based on CORINE land cover and Landsat datasets. Remote Sens. 2020, 12, 2137. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shahfahad Mourya, M.; Kumari, B.; Tayyab, M.; Paarcha, A. Indices based assessment of built-up density and urban expansion of fast-growing Surat city using multi-temporal Landsat data sets. GeoJournal 2021, 88, 4195–4215. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, H.; Gong, X.; Wang, B.; Deng, C.; Cao, Q. Urban development analysis using built-up area maps based on multiple high-resolution satellite data. Int. J. Appl. Earth Obs. Geoinf. 2021, 102, 102385. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Bem, P.P.; de Carvalho Junior, O.A. Change detection of deforestation in the Brazilian Amazon using Landsat data and convolutional neural networks. Remote Sens. 2020, 12, 901. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mishra, P.K.; Rai, A.; Rai, S.C. Land use and land cover change detection using geospatial techniques in the Sikkim Himalaya, India. Egypt. J. Remote Sens. Space Sci. 2020, 23, 133–141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, S.W.; Munkhnasan, L.; Lee, W.K. Land use and land cover change detection and prediction in Bhutan’s high altitude city of Thimphu, using cellular automata and Markov chain. Environ. Chall. 2021, 5, 100236. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, J.; Yuan, Z.; Peng, J.; Chen, L.; Huang, H.; Zhu, J.; Liu, Y.; Li, H. DASNet: Dual attentive fully convolutional Siamese networks for change detection in high-resolution satellite images. IEEE J. Sel. Top. Appl. Earth Obs. Remote Sens. 2020, 13, 5305–5317. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lunetta, R.S.; Knight, J.F.; Ediriwickrema, J. Land-cover change detection using multi-temporal MODIS NDVI data. In Handbook for Water Resources; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2022; pp. 435–456. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peng, D.; Bruzzone, L.; Zhang, Y.; Guan, H. SemiCDNet: A semisupervised convolutional neural network for change detection in high-resolution remote-sensing images. In Proceedings of the IGARSS 2020—2020 IEEE International Geoscience and Remote Sensing Symposium, Waikoloa, HI, USA, 26 September–2 October 2020; IEEE: Piscataway, NJ, USA, 2020; pp. 3923–3926. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, C.; Yue, P.; Tapete, D.; Jiang, L. A deeply supervised image fusion network for change detection in high resolution bi-temporal remote sensing images. ISPRS J. Photogramm. Remote Sens. 2020, 166, 183–200. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shi, W.; Zhang, M.; Zhang, R.; Chen, S.; Zhan, Z. Change detection based on artificial intelligence: State-of-the-art and challenges. Remote Sens. 2020, 12, 1688. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khelifi, L.; Mignotte, M. Deep learning for change detection in remote sensing images: Comprehensive review and meta-analysis. IEEE Access 2020, 8, 126385–126400. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, H.; Qi, Z.; Shi, Z. Remote sensing image change detection with transformers. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 2021, 60, 5607514. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahmad, M.; Distifano, S.; Mazzara, M.; Khan, A.M. Traditional to transformers: A survey on current trends and future prospects for hyperspectral image classification. arXiv 2024, arXiv:2404.14955. Available online: https://arxiv.org/abs/2404.14955 (accessed on 1 June 2025). [CrossRef]
- Kaplan, S. Data-Centric Remedies for Challenges in Computer Vision Applications: Insights from Active Learning, Deep Generative Models, and Explainable AI. Master’s Thesis, LUT University, Lappeenranta, Finland, 2024. Available online: https://lutpub.lut.fi/handle/10024/166005 (accessed on 1 June 2025).
- Giuste, F.; Shi, W.; Zhu, Y.; Naren, T.; Isgut, M. Explainable artificial intelligence methods in combating pandemics: A systematic review. IEEE Rev. Biomed. Eng. 2022, 15, 15–30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Warde-Farley, D.; Bengio, Y. Improving generative adversarial networks with denoising feature matching. In Proceedings of the International Conference on Learning Representations, Toulon, France, 24–26 April 2017; Available online: https://openreview.net/pdf?id=S1X7nhsxl (accessed on 1 June 2025).
- Kaneko, T.; Harada, T. Noise robust generative adversarial networks. In Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Seattle, WA, USA, 13–19 June 2020; pp. 2816–2825. Available online: https://openaccess.thecvf.com/content_CVPR_2020/html/Kaneko_Noise_Robust_Generative_Adversarial_Networks_CVPR_2020_paper.html (accessed on 1 June 2025).
- Tian, M.; Song, K. Boosting magnetic resonance image denoising with generative adversarial networks. IEEE Access 2021, 9, 145456–145468. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baheti, B.; Innani, S.; Gajre, S. Eff-UNet: A novel architecture for semantic segmentation in unstructured environments. In Proceedings of the CVPRW, Seattle, WA, USA, 14–19 June 2020; pp. 1–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.-F.; Ren, W.; Zhang, Z.; Jia, Z.; Wang, L.; Tan, T. Focal and Efficient IoU Loss for Accurate Bounding Box Regression. Neurocomputing 2022, 506, 146–157. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abdollahi, A.; Pradhan, B.; Alamri, A.M. An ensemble architecture of deep convolutional SegNet and UNet networks for building semantic segmentation from high-resolution aerial images. Geocarto Int. 2022, 37, 7220–7241. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zunair, H.; Hamza, A.B. Sharp U-Net: Depthwise convolutional network for biomedical image segmentation. Comput. Biol. Med. 2021, 137, 104813. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, Y.; Liang, Z.; Yan, J.; Chen, G. ED-Net: Automatic building extraction from high-resolution aerial images with boundary information. IEEE J. Sel. Top. Appl. Earth Obs. Remote Sens. 2021, 14, 10859–10869. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Senapati, P.; Basu, A.; Deb, M.; Dhal, K.G. Sharp dense U-Net: An enhanced dense U-Net architecture for nucleus segmentation. Int. J. Mach. Learn. Cybern. 2024, 15, 2079–2094. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wagner, F.H.; Dalagnol, R.; Tarabalka, Y.; Segantine, T.Y.F.; Thomé, R.; Hirye, M.C.M. U-Net-Id, an Instance Segmentation Model for Building Extraction from Satellite Images—Case Study in the Joanópolis City, Brazil. Remote Sens. 2020, 12, 1544. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shafique, A.; Cao, G.; Khan, Z.; Asad, M.; Aslam, M. Deep learning-based change detection in remote sensing images: A review. Remote Sens. 2022, 14, 871. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, W.; Zhang, S.; Wang, H.H. Efficient GAN-based remote sensing image change detection under noise conditions. In Image Processing and Capsule Networks; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2021; pp. 157–177. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kande, N.A.; Dakhane, R.; Dukkipati, A. SiameseGAN: A generative model for denoising of spectral domain optical coherence tomography images. IEEE Trans. Med. Imaging 2021, 40, 180–192. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ding, L.; Zheng, K.; Lin, D.; Bruzzone, L. MP-ResNet: Multi-path Residual Network for the Semantic Segmentation of High-Resolution PolSAR Images. IEEE Geosci. Remote Sens. Lett. 2021, 19, 4014205. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thakur, R.S.; Chatterjee, S.; Yadav, R.N.; Gupta, L. Image de-noising with machine learning: A review. IEEE Access 2021, 9, 101586–101611. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Momeny, M.; Neshat, A.A.; Hussain, M.A.; Kia, S. Learning-to-augment strategy using noisy and denoised data: Improving generalizability of deep CNN for the detection of COVID-19 in X-ray images. Comput. Biol. Med. 2021, 134, 104482. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Geng, M.; Meng, X.; Yu, J.; Zhu, L.; Jin, L.; Jiang, Z.; Qiu, B.; Li, H.; Kong, H.; Yuan, J.; et al. Content-Noise Complementary Learning for Medical Image Denoising. IEEE Trans. Med. Imaging 2022, 41, 407–419. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- El Helou, M.; Süsstrunk, S. Blind Universal Bayesian Image Denoising with Gaussian Noise Level Learning. IEEE Trans. Image Process. 2020, 29, 4885–4897. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, Z.; Chen, G.; Zhang, T. A CNN-Transformer Hybrid Approach for Crop Classification Using Multitemporal Multisensor Images. IEEE J. Sel. Top. Appl. Earth Obs. Remote Sens. 2020, 13, 847–858. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deng, P.; Xu, K.; Huang, H. When CNNs Meet Vision Transformer: A Joint Framework for Remote Sensing Scene Classification. IEEE Geosci. Remote Sens. Lett. 2022, 19, 8020305. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shao, Z.; Tang, P.; Wang, Z.; Saleem, N.; Yam, S.; Sommai, C. BRRNet: A Fully Convolutional Neural Network for Automatic Building Extraction From High-Resolution Remote Sensing Images. Remote Sens. 2020, 12, 1050. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ding, L.; Lin, D.; Lin, S.; Zhang, J.; Cui, X.; Wang, Y.; Tang, H.; Bruzzone, L. Looking Outside the Window: Wide-Context Transformer for the Semantic Segmentation of High-Resolution Remote Sensing Images. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 2022, 60, 1–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, B.; Meng, D.; Wang, L.; Liu, N.; Wang, Y. Seismic Impedance Inversion Using Fully Convolutional Residual Network and Transfer Learning. IEEE Geosci. Remote Sens. Lett. 2020, 17, 2140–2144. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Soni, A.; Koner, R.; Villuri, V.G.K. M-UNet: Modified U-Net Segmentation Framework with Satellite Imagery. In Proceedings of the Global AI Congress 2019, Kolkata, India, 12–14 September 2019; Advances in Intelligent Systems and Computing; Mandal, J., Mukhopadhyay, S., Eds.; Springer: Singapore, 2020; Volume 1112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Venugopal, N. Automatic Semantic Segmentation with DeepLab Dilated Learning Network for Change Detection in Remote Sensing Images. Neural Process Lett. 2020, 51, 2355–2377. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marsocci, V.; Coletta, V.; Ravanelli, R.; Scardapane, S.; Crespi, M. Inferring 3D change detection from bitemporal optical images. ISPRS J. Photogramm. Remote Sens. 2023, 196, 325–339. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dang, B.; Li, Y. MSResNet: Multiscale Residual Network via Self-Supervised Learning for Water-Body Detection in Remote Sensing Imagery. Remote Sens. 2021, 13, 3122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, H.; Qiu, K.; Chen, L.; Mei, X.; Hong, L.; Tao, C. SCAttNet: Semantic segmentation network with spatial and channel attention mechanism for high-resolution remote sensing images. IEEE Geosci. Remote Sens. Lett. 2020, 18, 905–909. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, T.; Bai, T.; Xu, C.; Zhang, E.; Liu, B.; Zhao, X.; Zhang, H. MDS-Net: An Image-Text Enhanced Multimodal Dual-Branch Siamese Network for Remote Sensing Change Detection. IEEE J. Sel. Top. Appl. Earth Obs. Remote Sens. 2025, 18, 12421–12438. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chang, Y.; Luo, B. Bidirectional Convolutional LSTM Neural Network for Remote Sensing Image Super-Resolution. Remote Sens. 2019, 11, 2333. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, R.; Xiao, Y.; Lu, X.; Zhang, S.; Liu, Y. ST-3DGMR: Spatio-temporal 3D grouped multiscale ResNet network for region-based urban traffic flow prediction. Inf. Sci. 2023, 624, 68–93. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, L.; Li, R.; Zhang, C.; Fang, S.; Duan, C.; Meng, X.; Atkinson, P.M. UNetFormer: A UNet-like transformer for efficient semantic segmentation of remote sensing urban scene imagery. ISPRS J. Photogramm. Remote Sens. 2022, 190, 196–214. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, F.; Jiang, M.; Qian, C.; Yang, S.; Li, C.; Zhang, H.; Wang, X.; Tang, X. Residual attention network for image classification. In Proceedings of the IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Honolulu, HI, USA, 21–26 July 2017. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ronneberger, O.; Fischer, P.; Brox, T. U-Net: Convolutional networks for biomedical image segmentation. In Medical Image Computing and Computer-Assisted Intervention—MICCAI 2015; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2015; pp. 234–241. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Caye Daudt, R.; Le Saux, B.; Boulch, A. Fully Convolutional Siamese Networks for Change Detection. arXiv 2018, arXiv:1810.08462. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peng, D.; Zhang, Y.; Guan, H. End-to-end change detection for high resolution satellite images using improved UNet++. Remote Sens. 2019, 11, 1382. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fan, X.; Cao, P.; Shi, P.; Wang, J.; Xin, Y.; Huang, W. A Nested U-Net with Attention Mechanism for Road Crack Image Segmentation. In Proceedings of the 2021 IEEE 6th International Conference on Signal and Image Processing (ICSIP), Nanjing, China, 22–24 October 2021; pp. 189–193. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, C.; Wang, L.; Cheng, S.; Li, Y. SwinSUNet: Pure Transformer Network for Remote Sensing Image Change Detection. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 2022, 60, 5224713. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Giannopoulos, M.; Tsagkatakis, G.; Tsakalides, P. 4D U-Nets for Multi-Temporal Remote Sensing Data Classification. Remote Sens. 2022, 14, 634. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bousias Alexakis, E.; Armenakis, C. Evaluation of Unet and Unet++ Architectures in High Resolution Image Change Detection Applications. Int. Arch. Photogramm. Remote Sens. Spatial Inf. Sci. 2020, XLIII-B3-2020, 1507–1514. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, J.; Liu, L.; Cui, Y.; Zhao, Y. A Nested UNet Based on Multi-Scale Feature Extraction for Mixed Gaussian-Impulse Removal. Appl. Sci. 2023, 13, 9520. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, H.; Shi, Z. A Spatial-Temporal Attention-Based Method and a New Dataset for Remote Sensing Image Change Detection. Remote Sens. 2020, 12, 1662. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shen, L.; Lu, Y.; Chen, H.; Wei, H.; Xie, D.; Yue, J.; Chen, R.; Lv, S.; Jiang, B. S2Looking: A Satellite Side-Looking Dataset for Building Change Detection. Remote Sens. 2021, 13, 5094. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Holail, S.; Saleh, T.; Xiao, X.; Li, D. AFDE-Net: Building Change Detection Using Attention-Based Feature Differential Enhancement for Satellite Imagery. IEEE Geosci. Remote Sens. Lett. 2023, 20, 6006405. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pang, L.; Sun, J.; Chi, Y.; Yang, Y.; Zhang, F.; Zhang, L. CD-TransUNet: A Hybrid Transformer Network for the Change Detection of Urban Buildings Using L-Band SAR Images. Sustainability 2022, 14, 9847. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, W.; Wang, S.; Tong, J.; Liao, F.; Zhang, Y.; Shen, X. DDCNN: A Promising Tool for Simulation-To-Reality UAV Fault Diagnosis. Neural Process. Lett. 2023. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yin, H.; Ma, C.; Weng, L.; Xia, M.; Lin, H. Bitemporal Remote Sensing Image Change Detection Network Based on Siamese-Attention Feedback Architecture. Remote Sens. 2023, 15, 4186. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).