Artificial Intelligence-Based Sensorless Control of Induction Motors with Dual-Field Orientation
Abstract
1. Introduction
- Signal injection methods. These techniques are used particularly at low or zero speeds [21].
2. Dual-Field-Oriented Control of Induction Machines
3. Sensorless Control
- Sensorless vector control structure of an IM with DFOC containing an MRAS estimator in the loop;
- Sensorless vector control structure of an IM with DFOC, where the speed was estimated based on an ANN;
- Sensorless vector control structure of an IM with DFOC, where the speed was estimated based on an RNN.
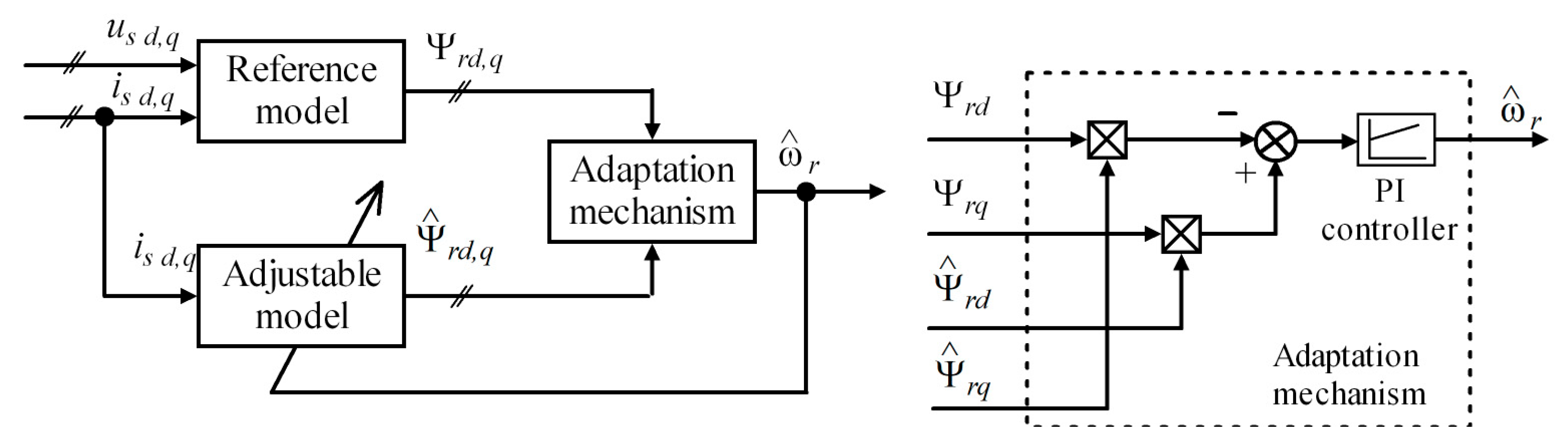
- MRAS uses an Adaptation algorithm based on (14) that uses a PI controller to generate the estimated speed (see Figure 3). The input is only the error signal (red in Figure 1). The procedure is discussed in Section 3.1.
- In both the ANN and RNN approaches, the inputs consist of the error signal (shown in red in Figure 1) and its integral (shown in blue in Figure 1). For these two AI-based methods, the PI controller used in MRAS is replaced by the respective training algorithms described in Section 3.2 and Section 3.3.
3.1. MRAS-Based Procedure
3.2. ANN-Based Procedure
3.3. RNN-Based Procedure
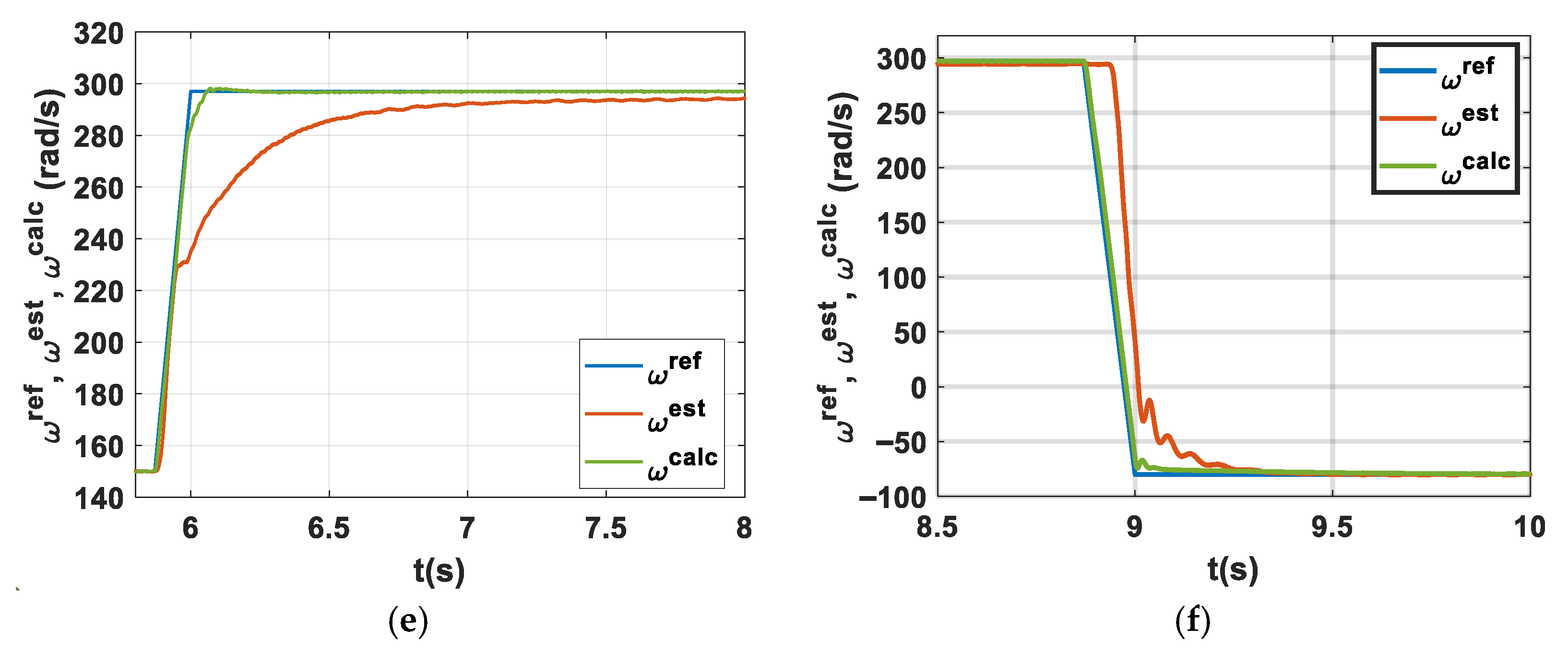
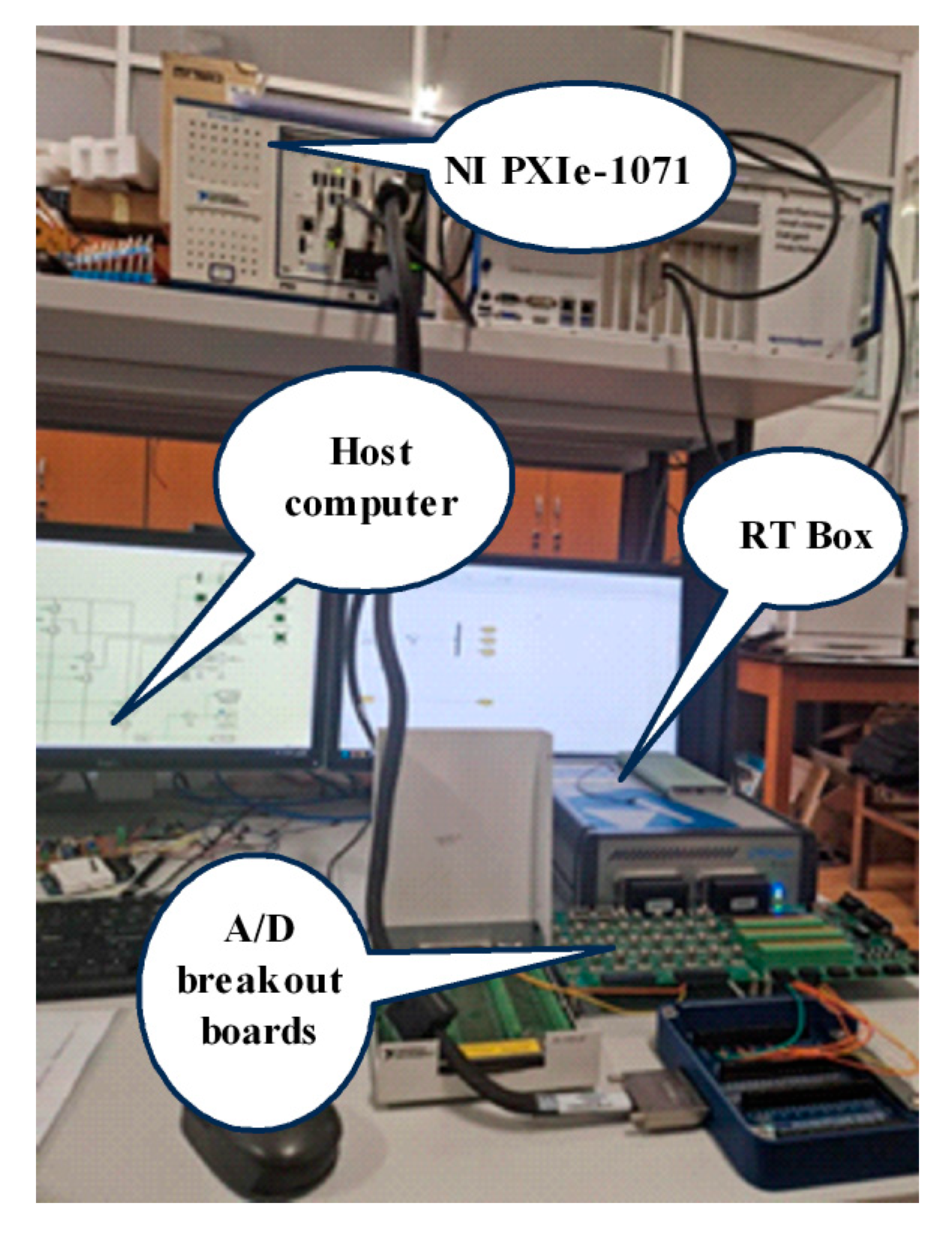
4. Real-Time Simulation
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Wang, F.; Zhang, Z.; Mei, X.; Rodríguez, J.; Kennel, R. Advanced Control Strategies of Induction Machine: Field Oriented Control, Direct Torque Control and Model Predictive Control. Energies 2018, 11, 120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mon-Nzongo, D.L.; Jin, T.; Ekemb, G.; Bitjoka, L. Decoupling Network of Field-Oriented Control in Variable-Frequency Drives. IEEE Trans. Ind. Electron. 2017, 64, 5746–5750. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reddy, B.; Poddar, G.; Muni, B.P. Parameter Estimation and Online Adaptation of Rotor Time Constant for Induction Motor Drive. IEEE Trans. Ind. Appl. 2022, 58, 1416–1428. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, F.; Zhang, J.; Wu, D.; Liu, G.; Lang, W.; Wang, P. The Effects of Parameter Variations on the Torque Control of Induction Motor. In Proceedings of the 2020 4th CAA International Conference on Vehicular Control and Intelligence (CVCI), Hangzhou, China, 18–20 December 2020; IEEE: Hangzhou, China, 2020; pp. 757–760. [Google Scholar]
- Tang, J.; Yang, Y.; Blaabjerg, F.; Chen, J.; Diao, L.; Liu, Z. Parameter Identification of Inverter-Fed Induction Motors: A Review. Energies 2018, 11, 2194. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zeb, K.; Din, W.U.; Khan, M.A.; Khan, A.; Younas, U.; Busarello, T.D.C.; Kim, H.J. Dynamic Simulations of Adaptive Design Approaches to Control the Speed of an Induction Machine Considering Parameter Uncertainties and External Perturbations. Energies 2018, 11, 2339. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ding, C.-W.; Tung, P.-C. A New Approach to Field-Oriented Control That Substantially Improves the Efficiency of an Induction Motor with Speed Control. Appl. Sci. 2025, 15, 4845. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luo, Y.-C.; Huang, W.-A. Sensorless Rotor Field Direct Orientation Controlled Induction Motor Drive with Particle Swarm Optimization Algorithm Flux Observer. J. Low Freq. Noise Vib. Act. Control 2019, 38, 692–705. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Szőke Benk, E.; Imecs, M.; Szabo, C.; Incze, I. Double field oriented sensorless control of cage induction motor. In Proceedings of the 2014 IEEE 15th International Symposium on Computational Intelligence and Informatics (CINTI), Budapest, Hungary, 19–21 November 2014; pp. 403–408. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bonet-Jara, J.; Quijano-Lopez, A.; Morinigo-Sotelo, D.; Pons-Llinares, J. Sensorless Speed Estimation for the Diagnosis of Induction Motors via MCSA. Review and Commercial Devices Analysis. Sensors 2021, 21, 5037. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Elbarbary, Z.M.S.; Al-Harbi, O.K.; Al-Gahtani, S.F.; Irshad, S.M.; Abdelaziz, A.Y.; Mossa, M.A. Review of Speed Estimation Algorithms for Three- Phase Induction Motor. MethodsX 2024, 12, 102546. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shyaa, S. Review-Sensorless Techniques for Stabilization Control of Induction Motor Drives. Kerbala J. Eng. Sci. 2024, 4, 87–102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Białoń, T.; Pasko, M.; Niestrój, R. Developing Induction Motor State Observers with Increased Robustness. Energies 2020, 13, 5487. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- You, J.; Wu, W.; Wang, Y. An Adaptive Luenberger Observer for Speed-Sensorless Estimation of Induction Machines. In Proceedings of the 2018 Annual American Control Conference (ACC), Milwaukee, WI, USA, 27–29 June 2018; pp. 307–312. [Google Scholar]
- Yildiz, R.; Barut, M.; Demir, R. Extended Kalman Filter Based Estimations for Improving Speed-Sensored Control Performance of Induction Motors. IET Electr. Power Appl. 2020, 14, 2471–2479. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miloud, I.; Cauet, S.; Etien, E.; Salameh, J.P.; Ungerer, A. Real-Time Speed Estimation for an Induction Motor: An Automated Tuning of an Extended Kalman Filter Using Voltage–Current Sensors. Sensors 2024, 24, 1744. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mansouri, S.A.; Ahmarinejad, A.; Javadi, M.S.; Heidari, R.; Catalão, J.P.S. Improved Double-Surface Sliding Mode Observer for Flux and Speed Estimation of Induction Motors. IET Electr. Power Appl. 2020, 14, 1002–1010. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khan, U.; Sami, I.; Salman, K.; Khan, B.; Mehmood, C.A.; ALI, S.M. Sliding Mode Based Speed Observer Design for Speed Control of Five Phase Induction Motor. In Proceedings of the 2019 International Conference on Robotics and Automation in Industry (ICRAI), Rawalpindi, Pakistan, 21–22 October 2019; pp. 1–6. [Google Scholar]
- Hamdi, W.; Hammoudi, M.Y.; Betka, A. Sensorless Speed Control of Induction Motor Using Model Reference Adaptive System and Deadbeat Regulator. Eng. Proc. 2023, 56, 16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Karlovský, P.; Lettl, J. Application of MRAS Algorithm to Replace the Speed Sensor in Induction Motor Drive System. Procedia Eng. 2017, 192, 421–426. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Damkhi, S.; Said, M.S.N.; Said, N.N. Speed Estimation of Induction Motor at Low and Zero Speed Using High Frequency Signal Injection for Rotor Slot Harmonics Detection. RE PQJ 2018, 16, 782–788. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Laadjal, K.; Bento, F.; Antunes, H.R.P.; Sahraoui, M.; Cardoso, A.J.M. Speed Estimation of Six-Phase Induction Motors, Using the Rotor Slot Harmonics. Sensors 2022, 22, 8157. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Diarra, M.N.; Zhao, X.; Wu, X.; Nketsiah, I.A.; Li, Y.; Zhao, H. Induction Motors Speed Estimation by Rotor Slot Harmonics Frequency Using Zoom Improved Chirp-Z Transform Algorithm. Energies 2022, 15, 7877. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Golsorkhi, M.S.; Binandeh, H.; Savaghebi, M. Online Efficiency Optimization and Speed Sensorless Control of Single-Phase Induction Motors. Appl. Sci. 2021, 11, 8863. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Diab, A.A.Z.; Elsawy, M.A.; Denis, K.A.; Alkhalaf, S.; Ali, Z.M. Artificial Neural Based Speed and Flux Estimators for Induction Machine Drives with Matlab/Simulink. Mathematics 2022, 10, 1348. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ramdani, D.R. Sensorless Speed Estimation of Induction Motor Using ANFIS. J. Inf. Syst. Eng. Manag. 2025, 10, 557–571. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lai, Y.-S. Machine Modeling and Universal Controller for Vector-Controlled Induction Motor Drives. IEEE Trans. Energy Convers. 2003, 18, 23–32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahire, H.; Karuppasamy, I. Sensor-Less Speed Estimation Using Improved Stator Current Model Reference Adaptive System for Induction Motor. In Proceedings of the 2023 IEEE 20th India Council International Conference (INDICON), Warangal, India, 14–17 December 2023; pp. 572–577. [Google Scholar]
- Fan, B.; Yang, Z.-X.; Wang, X.-B.; Song, L.; Song, S.-Z. Model Reference Adaptive Vector Control for Induction Motor without Speed Sensor. Adv. Mech. Eng. 2017, 9, 1687814016683086. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zorgani, Y.A.; Jouili, M.; Koubaa, Y.; Boussak, M. A Very-Low-Speed Sensorless Control Induction Motor Drive with Online Rotor Resistance Tuning by Using MRAS Scheme. Power Electron. Drives 2019, 4, 125–140. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Norambuena, M.; Galvez, D. Model Free Artificial Neural Network for an Induction Machine. In Proceedings of the 2023 IEEE Conference on Power Electronics and Renewable Energy (CPERE), Luxor, Egypt, 15–17 February 2023; IEEE: Luxor, Egypt, 2023; pp. 1–6. [Google Scholar]
- Elgohary, M.; Gouda, E.; Eskander, S.S. Intelligent Control of Induction Motor without Speed Sensor. IJPEDS 2021, 12, 715. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Purwahyudi, B. RNN Based Rotor Flux and Speed Estimation of Induction Motor. Int. J. Power Electron. Drive Syst. (IJPEDS) 2011, 1, 58–64. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marinov, E.Y.; Zhekov, Z.S. Neural Sensorless Control of Induction Motor. In Proceedings of the Second International Scientific Conference “Intelligent Information Technologies for Industry” (IITI’17), Varna, Bulgaria, 14–16 September 2017; Abraham, A., Kovalev, S., Tarassov, V., Snasel, V., Vasileva, M., Sukhanov, A., Eds.; Advances in Intelligent Systems and Computing. Springer International Publishing: Cham, Germany, 2018; Volume 679, pp. 411–418, ISBN 978-3-319-68320-1. [Google Scholar]
- Merabet, A.; Kanukollu, S.; Al-Durra, A.; El-Saadany, E.F. Adaptive Recurrent Neural Network for Uncertainties Estimation in Feedback Control System. J. Autom. Intell. 2023, 2, 119–129. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pintilie, L.-N.; Teodosescu, P.-D.; Hedeșiu, H.-C.; Gros, I.-C.; Suciu, V.-M.; Iuoraş, A.-M. Real-Time Hardware in the Loop Simulation Setup for Automotive Grid Interfacing System Based on PLECS RT BOX and National Instruments PXI. In Proceedings of the 2024 IEEE International Conference on Electrical Systems for Aircraft, Railway, Ship Propulsion and Road Vehicles & International Transportation Electrification Conference (ESARS-ITEC), Naples, Italy, 26–29 November 2024; pp. 1–7. [Google Scholar]
- RT Box 1 Plexim. Available online: https://www.plexim.com/products/rt_box/rt_box_1 (accessed on 30 June 2025).
- PXIe-1071 Specifications-NI. Available online: https://www.ni.com/docs (accessed on 30 June 2025).













| Parameter | Value | Parameter | Value |
|---|---|---|---|
| Rated power | 2.2 kW | Magnetizing inductance (Lm) | 0.249 H |
| Pole pairs (Zp) | 2 | Stator leakage inductance (Lσs) | 0.017 H |
| Inertia (J) | 0.02 kgm2 | Rotor leakage inductance (Lσr) | 0.011 H |
| Stator inductance (Ls) | 0.266 H | Stator resistance (Rs) | 2.918 Ω |
| Rotor inductance (Lr) | 0.260 H | Rotor resistance (Rr) | 2.7 Ω |
| Learning rate | 0.02 |
| Value of momentum | 0.075 |
| Training epochs | 300 |
| Minimum performance gradient | 1 × 10−8 |
| Performance goal | 1 × 10−10 |
| Learning rate | 0.0001 | Gradient threshold | 1 |
| Value of momentum | 0.075 | Learning regularization | 0.001 |
| Training epochs | 300 | Validation frequency | 30 |
| Ref. Speed [rad/s] | MRAS | ANN | RNN | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Settling Time [s] | Overshoot [%] | Steady-State Error [%] | Settling Time [s] | Overshoot [%] | Steady-State Error [%] | Settling Time [s] | Overshoot [%] | Steady-State Error [%] | |
| 80 | 0.13 | no | 1.25 | 0.23 | 6.80 | no | 0.12 | 1.85 | no |
| 150 | 0.08 | no | 0.30 | 0.22 | 4.00 | no | 0.12 | 1.00 | no |
| 297 | 0.15 | no | 0.60 | 1.15 | no | 0.90 | 0.60 | 1.13 | no |
| −80 | 0.45 | no | 0.60 | 0.33 | no | no | 0.30 | 6.00 | no |
| −150 | 0.05 | no | 0.30 | 0.20 | 3.60 | no | 0.11 | 1.00 | no |
| −297 | 0.14 | no | 0.16 | 1.15 | no | 1.00 | 0.60 | 1.20 | no |
| Speed Transition [rad/s] | ANN-HIL | ||
|---|---|---|---|
| Settling Time [s] | Overshoot [%] | Steady-State Error [%] | |
| 100 to −80 | 1.50 | no | no |
| 100 to 150 | 1.00 | no | no |
| Criteria | MRAS | ANN | RNN |
|---|---|---|---|
| Computational complexity | Low | Medium to high | High |
| Parameter sensibility | High | High | Very high |
| Real-time applicability | Simple to implement | Need moderate hardware resources | Need hardware acceleration |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Szoke, E.; Szabo, C.; Pintilie, L.-N. Artificial Intelligence-Based Sensorless Control of Induction Motors with Dual-Field Orientation. Appl. Sci. 2025, 15, 8919. https://doi.org/10.3390/app15168919
Szoke E, Szabo C, Pintilie L-N. Artificial Intelligence-Based Sensorless Control of Induction Motors with Dual-Field Orientation. Applied Sciences. 2025; 15(16):8919. https://doi.org/10.3390/app15168919
Chicago/Turabian StyleSzoke, Eniko, Csaba Szabo, and Lucian-Nicolae Pintilie. 2025. "Artificial Intelligence-Based Sensorless Control of Induction Motors with Dual-Field Orientation" Applied Sciences 15, no. 16: 8919. https://doi.org/10.3390/app15168919
APA StyleSzoke, E., Szabo, C., & Pintilie, L.-N. (2025). Artificial Intelligence-Based Sensorless Control of Induction Motors with Dual-Field Orientation. Applied Sciences, 15(16), 8919. https://doi.org/10.3390/app15168919








