Abstract
Estrone (E1) is a female hormone present in large quantities in animal farming, which has, in recent decades, resulted in increasing water and soil pollution. Research into its behaviour in the environment has been more focused on water pollution than on soil or soil groups. Three agricultural soils from the Czech Republic—cambisol, fluvisol, and chernozem—were analyzed in a pot experiment to determine their influence on estrone transformation, with laccase, and Mn-oxidoreductases enzymes being measured for this purpose. From the initial concentration of 50 μg·kg−1 soil E1 solution, 1.36 μg·kg−1 were measured on average in the soils after 28 days. There was a clear transition in estrone concentration between 24 h and day 3, reflected in all three soils by increased enzymatic activity. Aside from this, the three soils behaved differently. Results showed that fluvisol was the most different to both cambisol and chernozem. It had the highest enzymatic activity, but also the highest estrone levels in soil at 28 days (5.09 μg·kg−1) vs. cambisol (1.36 μg·kg−1) and chernozem (0.94 μg·kg−1). The removal mechanisms were considered a combination of estrone soil sorption and enzymatic activity, with each soil exhibiting an individual combination of the two. In fluvisol, sorption was considered predominant, thoughenzymatic activity was also relevant; cambisol presented an alternation of sorption and biodegradation, with neither deemed the main mechanism; and chernozem exhibited predominantly high enzymatic activity at the end of the experiment, which resulted in the lowest estrone in soil at the end of the experiment. Overall, all three soils presented good estrone degradation potential through their various soil properties.
Keywords:
estrone biotransformation; enzymatic activity; laccase; Mn-enzymes; fluvisol; chernozem; cambisol 1. Introduction
Estrone (E1) is a natural and synthetic female hormone encountered extensively in industrial farming [1,2], produced by animals daily or added to their diet as concentrated animal feeding operations (CAFOs) [3], and as a result, it is now one of the emergent pollutants of concern found in water [4,5] and soil [6,7]. It is released into the water system through human consumption and animal farming [8] and as such, enters the sewage treatment process. By law, sewage waters undergo treatment in the wastewater plant, but the removal of pollutants depends on the efficiency of the treatment plant [9,10]; therefore, at the end of the process, the resulting products can still be contaminated. These products, like contaminated irrigation water [11] and fertilizers (sludge and biosolids) [12,13] are distributed into the environment for agricultural use, or simply as effluent leaving the treatment plant. Estrone can also be released directly from animal husbandry into the environment [3,14] without undergoing any removal treatment. Among the organic wastes, manure is likely the heaviest estrogen loaded, ranging from an average of 400 μg/animal day up to 1000 μg/animal per day excretion rate during the reproductive stage [15]. Furthermore, the high amount of organic matter and carbon contained by manure leads to high estrogens sorption that can be 20 to 150 times more than in soils with poor organic carbon [16]. Lastly, estrone contamination can result from other estrogens transformation (mainly from 17-β-estradiol) [17,18]; therefore, it accumulates more in the environment than other estrogens before its own transformation occurs.
E1 was first mentioned as a pollutant of concern by the European Union in 2008 (Article 8b of Directive 2008/105/EC) related to environmental quality standards in the field of water policy, when a union-wide watch list of substances was established to be monitored in water sources. In this list, there were three estrogen hormones included: 17-α-ethinylestradiol (EE2), 17-β-estradiol (E2), and Estrone (E1), together with their maximum acceptable limits, which for E1 was set up at 3.6 ng/L. Water was the chosen medium as it is found in the aquatic environment, where the effects of estrogens on the environment have been first investigated [19], especially in fish communities, which exhibited sexual dysmorphism [20]. However, estrogen presence and behaviour in soil received much less attention; although, lately, the body of knowledge in this field has increased. More has been achieved in understanding how the different estrogen hormones behave, and relationships between their properties and various environmental factors.
For estrone, there have been studies on its transformation in aerobic [17] and anae- robic conditions [21], on prevalent microorganisms that degrade it [22,23,24], on metabolic transformation paths [25,26], and on soil characteristics that affect its mobility and transformation [27,28], but less on how soil groups influence estrone transformation.
The main focus of this research is to compare estrone transformation in different agricultural soils from the Czech Republic, and by extension, from Central and Eastern Europe where these three soils are used extensively in agriculture. At the same time, it was considered necessary to gather more information about estrone in fluvisol, a soil on which there is no current data in the scientific literature related to estrone contamination and removal.
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Soil
Information on estrone soils was present in the literature, but more from a biogeographical perspective [29], and even in these studies, the focus was more on soils with a much larger extension, such as chernozems and cambisols, and much less or nothing on less common soil groups. When the internet search was carried out for the current work on fluvisol, there was no information present (on Web of Science, search criteria ‘estrogens AND fluvisol’ and ‘estrone AND fluvisol’). To address this knowledge gap, three soil groups from the Czech Republic used in agriculture were chosen for comparison: cambisol, chernozem, and fluvisol. Factors considered when choosing them were (1) how widespread they are in the Czech agriculture (cambisol is the most widespread soil type in the Czech Republic, chernozem is considered the best soil for such use, and fluvisol is the predominant soil in the riverine areas used in agriculture), and (2) their general soil properties, mainly (i) organic matter content (generally high in chernozem, low in cambisol and varying in fluvisols, depending on the quantity and quality of the alluvial sediments), (ii) texture and porosity (expected to be small for fluvisol as it can contain very fine sediments, and higher in chernozem and cambisol) and (iii) hydraulic properties (good drainage in chernozems and cambisols, and less in fluvisols) (https://www.fao.org/soils-portal/data-hub/soil-classification/world-reference-base/en/, accessed on 22 October 2024). These factors influence estrone mobility and transformation, but also the structure of microbial communities in the soils and hence the estrone degradation ability.
The soils were taken from the Czech University of Life Sciences Prague experimental fields from Suchdol, Humpolec, and Patek sites, air-dried, manually ground in a mortar and passed through a 2 mm plastic sieve before use. Soils characteristics are included in Table 1. pH was determined after extraction with 0.01 M CaCl2 solution (1:2.5, w/v). Total C and N contents were determined by the CHNS Vario MACRO cube (Elementar Analysensysteme GmbH, Langenselbold, Germany) from air-dried samples, while the content of available nutrients (K, P, Ca, Mg, Mn, S, Zn, Fe, Cu, Cr) was estimated by the Mehlich III method [30] with a subsequent determination by inductively coupled plasma optical emission spectrometry (ICP-OES, Agilent 720, Agilent Technologies Inc., Santa Clara, CA, USA). The instrument was equipped with a two-channel peristaltic pump, a Struman–Masters spray chamber, and a V-groove pneumatic nebulizer made of inert material (experimental conditions: power of 1.2 kW, plasma flow of 15.0 L min–1, auxillary flow of 0.75 L min–1, nebulizer flow of 0.9 L min–1). Calibration curves were prepared as aqueous solutions of the stock solution acidified by 1.5% HNO3 with the concentration range varying between 1 and 100 mg·L−1 for K, Ca, Mg, 0.5–50 mg·L−1 for S and P, and 0.01–1 mg·L−1 for Mn, Zn, Fe, Cu, and Cr. The limits of detection (LOD) were estimated at 0.1 mg·L−1 for P, 0.05 mg·L−1 for S, 0.005 mg·L−1 for Ca, Mg, Fe, Cu, 0.002 mg·L−1 for Zn, and 0.001 mg·L−1 for Mn. The limits of quantification (LOQ) were estimated at 0.33 mg·L−1 for P, 0.16 mg·L−1 for S, 0.017 mg·L−1 for Ca, Mg, Fe, Cu, 0.007 mg·L−1 for Zn, and 0.003 mg·L−1 for Mn.
2.2. Experimental Design
2.2.1. Estrone Treatment
Estrone (E1) was purchased from TCI EUROPE N.V. Zwijndrecht Belgium (≥99% purity), and the internal standard 13C from Chromservis s.r.o. Prague, Czech Republic (99% purity). A single concentration of 50 μg·kg−1 was used according to Mashtare et al. [31]. A total of 5 mg of E1 was dissolved in 10 mL dimethyl sulfoxide (DMSO) and subsequently diluted in demi water until it reached 0.5 μg/mL concentration. 10 mL E1 solution was added with a 10 mL pipette in each treatment pot and mixed to homogenize the soil.
2.2.2. Pot Experiment
A total of 100 g of dry soil was added to 0.5 l pots, where the experiment was established in triplicates for each sampling time (i.e., 21 pots per each soil). Soil microcosms were brought to 60% water holding capacity and maintained as such throughout the experiment by regularly weighing the pots (every 2–3 days, depending on the temperature variations) and adding the missing water as needed. A total of 50 μg·kg−1 estrone solution was added to the treatments at the beginning of the experiment, which was carried out in a greenhouse in Central European summer conditions (temperatures ranging between 25 °C and 30 °C). Microcosms were collected in triplicates at 7 designated times over 28 days and approximately 20 g per sample were taken and stored at −80 °C for later analysis.
2.3. Analytical Procedures
2.3.1. Enzymatic Activity
For the analysis, enzymatic activity was measured for laccase (lacc) and some Mn-enzymes (peroxidase and oxidase). These enzymes belong to the oxidoreductase group and were chosen based on the estrone molecular structure—a steroid with 4 aromatic rings, and a hydroxyl (-OH) and a ketone (=O) functional groups—that can be transformed by oxidative enzymes: laccase [32], and peroxidases [33]. They work together by oxidizing and breaking up the phenol structure of the hormone.
Activity for laccase and manganese enzymes was determined in 96-well microplates. Extraction solutions were prepared from 0.2 g soils with 20 mL phosphate buffer (50 mM, pH 7) and homogenized in Ultra-Turrax (IKA Labortechnik, Staufen im Breisgau, Germany) for 30 s at 8000 rpm). Enzymatic activity was measured in four replicates for each sample. A total of 50 μL of sample were mixed with 200 μL specific reagent buffer (citrate buffer pH 5 for laccase, and succinate-lactate buffer 100 mM pH 4.5 for Mn-enzymes, respectively), and substrate (2,2′-Azino-bis(3-ethylbenzothiazoline-6-sulfonic acid) diammonium salt for laccase, and p-Dimethylaminobenzaldehyde for Mn-enzymes) then pipetted into the corresponding microplate wells [34]. The spectrophotometry was measured using a Tecan Infinite® M200 (Tecan Austria GmbH, Salzburg, Austria).
2.3.2. LC/MS Analysis
Treatments were weighed (0.5 g of freeze-dried soil) and spiked with 50 ng E1-13C3 12 h prior to extraction, mixed with 5 mL HPLC (High Performance Liquid Chromatography) methanol, sonicated for 15 min, and centrifuged at 4500 rpm, 20 °C for 10 min, and then the supernatant was collected. The procedure was repeated twice, and 1.5 mL of final supernatant (total volume of 10 mL) were filtered through 0.22 mm PTFE filters in HPLC vials, ready for analysis.
E1 was quantified using a stable-isotope dilution method with E1-13C3 as the internal standard by LC-ESI-MS/MS (Liquid Chromatography-Electrospray Ionization-Mass Spectrometry) on a C18 (Carbon 18) column with mobile phase water with NH4F (ammonium fluoride) and MeCN (methyl cyanide) in an Agilent 1290 Infinity II machine (Agilent Technologies Inc., Santa Clara, CA, USA).
The gradient was linear, starting at 5% MeCN and rising to 100% MeCN at the 13th minute with a flow of 0.560 mL·min−1. MRMs (Multiple Reaction Monitoring) for E1 were 269.1 to 159/145/143.2, MRMs for E1-13C3 were 272.1 to 148/146 and RT (retention time) of E1 was 8.65. A matrix-matched calibration curve was prepared from composite extracts of control treatments. To assess method recovery, control soil samples were spiked with 50 ng of E1, and recovery was calculated as the response ratio between the calibration standard and the extract. Across all three tested soils, recovery ranged from 98 ± 4%. The limit of detection (LOD) was estimated at 0.3 ng/g, and the limit of quantification (LOQ) at 0.9 ng/g, both based on the matrix-matched calibration.
2.4. Statistics
All data were run in RStudio 4.4.2 statistical software. For estrone concentrations, the triplicate values for each soil replicate were used, and for enzymes, all the enzymatic replicates (four per each enzyme) for each soil replicate. Comparison between soils was determined with the Brown–Forsythe test and, depending on its p-value, the appropriate ANOVA was performed to calculate results. Changes in estrone concentrations in each soil individually were calculated with the Friedman test.
3. Results
Statistical analysis covered individual soil properties as well as comparison between soils. Table 1 shows general soil properties, including nutrients. Table 2 records estrone concentrations and enzymatic activity statistics, which are then visualized in Figure 1—enzymatic activity and Figure 2—estrone in soils.

Table 2.
Soils statistical analysis for changes in enzymatic activity and estrone concentrations.
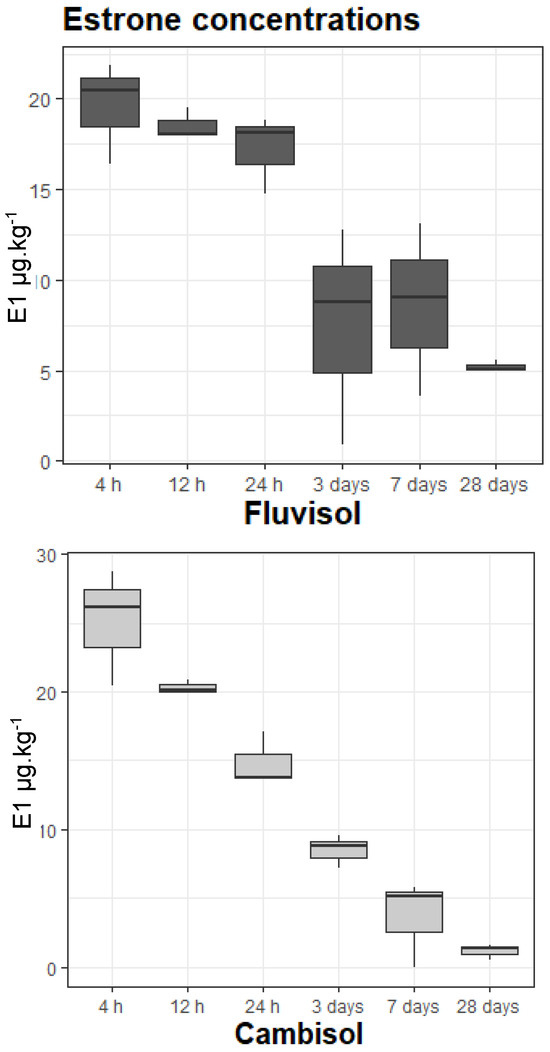
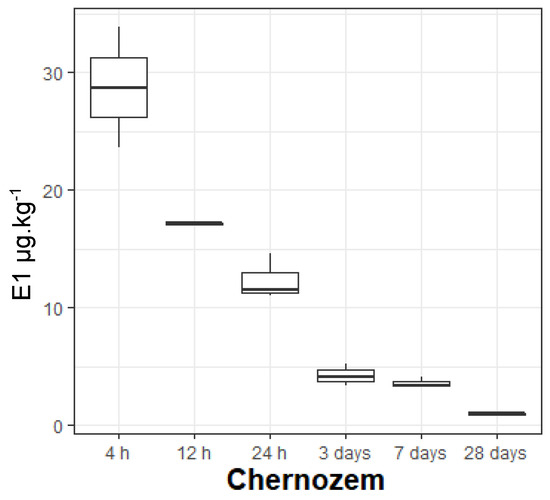
Figure 1.
Estrone concentrations.
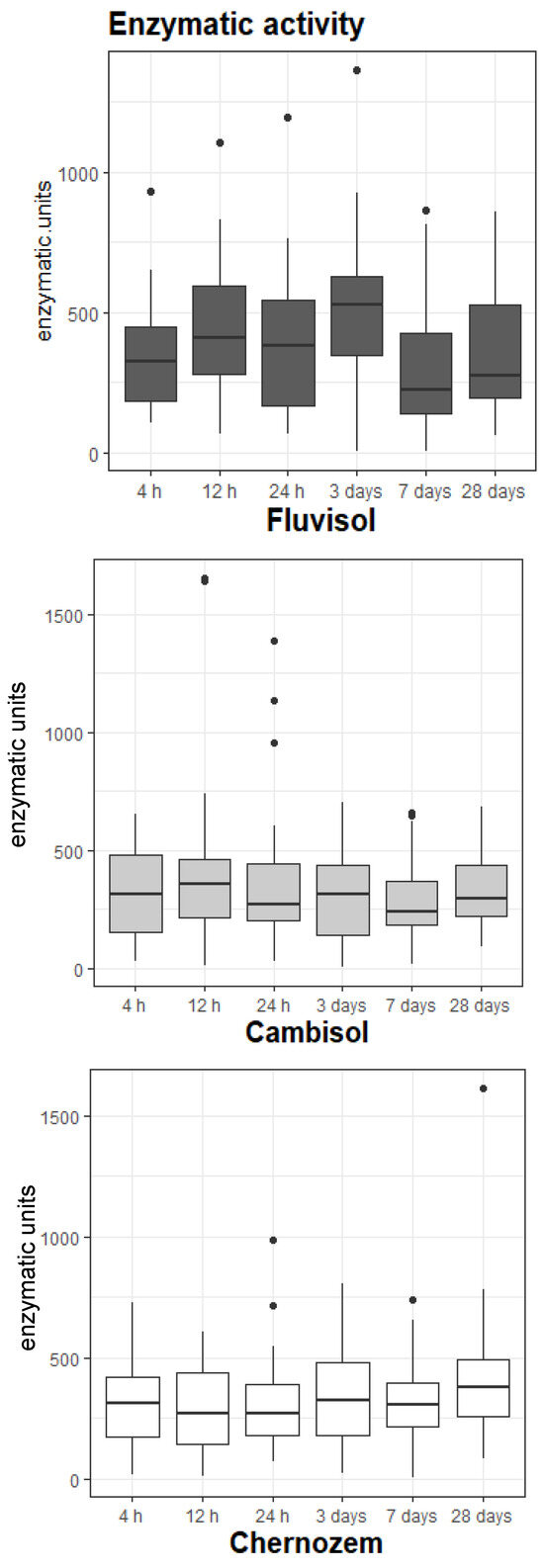
Figure 2.
Enzymatic activity.

Table 1.
Soil properties.
Table 1.
Soil properties.
| Soils | Cambisol | Fluvisol | Chernozem |
|---|---|---|---|
| Latitude | 49°33′15″ N | 50°09′50″ N | 50°07′40″ N |
| Longitude | 15°21′02″ E | 15°09′24″ E | 14°22′33″ E |
| Site | Humpolec | Patek | Suchdol |
| texture | sandy loam | silty clay | loamy |
| pH | 6.5 | 7.5 | 7.0 |
| WHC 1 | 14.77 | 13.71 | 14.78 |
| C (mg·kg−1) | 20,512 | 76,509 | 28,304 |
| N (mg·kg−1) | 2055 | 2882 | 2333 |
| C/N ratio | 10 | 26 | 12 |
| C/H ratio | 2 | 12 | 4 |
| K (mg·kg−1) 2 | 140 | 390 | 340 |
| P (mg·kg−1) 2 | 60 | 30 | 40 |
| Ca (mg·kg−1) 2 | 1540 | 26,290 | 6480 |
| Mg (mg·kg−1) 2 | 160 | 370 | 220 |
| Mn (mg·kg−1) 2 | 80 | 30 | 160 |
| S (mg·kg−1) 2 | 60 | 150 | 80 |
| Zn (mg·kg−1) 2 | 2.88 | 4.02 | 5.66 |
| Fe (mg·kg−1) 2 | 26 | 28 | 6 |
| Cu (mg·kg−1) 2 | 2.68 | 0.91 | 3.81 |
| Cr (mg·kg−1) 2 | 0.24 | 0.09 | 0.09 |
1 soil water holding capacity calculated for 60% in mL/100 g dw soil; 2 available element contents released by Mehlich III extraction procedure [30].
3.1. Soil Characteristics
Table 1 encompasses general soils properties. Fluvisol had the highest pH and best C:N ratio, as well as good presence of nutrients. It also had the lowest water holding capacity (WHC) and a more clay-like texture. Chernozem and cambisol were close in values; they still possessed a good amount of nutrients, but had lower pH and C:N ratios. Their textures were loamier and more had a better WHC.
3.2. Estrone Concentrations
Estrone presence was determined by LC/MS. Data exceeding the detection limits (LOD) were observed only for estrone treatments, while the estrone content in controls was <LOD in all cases.
Estrone concentration changes in each soil were individually determined with the Friedman test, covering data from the entire experiment, while for soil comparisons, the Brown–Forsythe test was employed for 0 and 28 days, followed by one-way ANOVA and Tukey post hoc pairs comparisons.
The soils showed a significant difference in estrone concentrations between the start and the end of the experiment, with chernozem presenting the highest variation (from 28.71 μg·kg−1 to 0.94 μg·kg−1), and fluvisol presenting the lowest (from 20.48 μg·kg−1 at 4 h to 5.09 μg·kg−1 at 28 days). At the same time, fluvisol had the highest median, 13.93 μg·kg−1, and the clearest transition in the phases of estrone at 24 h; chernozem had the lowest median (8.10 μg·k−1) and presented several transition phases (4 h to 12 h, 24 h to 3 days, and the last one between 7 and 28 days), while cambisol showed no significant differences between consecutive sampling times.
Soil comparison regarding the entire experiment gave p-value = 0.94. (Table 2—Estrone). However, analysis of the first (0 day) and last day (28 day) separately presented a more detailed insight into the differences in estrone transformation in each soil. For day 0, although the overall p-value was 0.10, there were already differences between soils, although not yet significant ones. Pairwise comparisons confirmed that the most different soil was fluvisol and the highest degree of variation was with chernozem (p-value 0.08). By day 28, the differences became significant: fluvisol presented a marked contrast with both chernozem (p = 0.00001) and cambisol (p-value 0.00002). On the other hand, cambisol and chernozem were more similar at 28 days than at 0 days (p-value 0.76 vs. 0.56).
3.3. Enzymatic Activity
The Brown–Forsythe test (equality of variance) showed that there was a significant difference between the soils with p-value = 0.005 (Table 2—Enzymatic activity). Further pairwise comparison established that fluvisol was significantly different from both cambisol and chernozem, with the highest difference being between fluvisol and chernozem (p = 0.023), while cambisol and chernozem exhibited very similar behaviours (p = 1.000).
The graph (Figure 2) is based on all the individual enzymatic replicates for each soil replicate (i.e., one soil replicate has four enzymatic replicates for each enzyme measured (laccase and Mn-enzymes) separately), hence the presence of a higher number of outliers. The measurement unit is U (μmol.min−1), which represents the enzymatic unit from the SI that measures the amount of enzyme that catalyzes the conversion of one micro mole of substrate per minute under the specified conditions of the assay method.
Overall, fluvisol had the highest median activity (371 U), followed by chernozem (308 U) and cambisol (296 U). On the other hand, cambisol presented the biggest variation in its values, registering the highest individual enzymatic measurement throughout the experiment (1652 U) (Table 2—Enzymatic activity values at each sampling time show differences in and between soils).
The highest median in the experiment was associated with fluvisol at day 3 (527 U), and it also had the highest values in four out of six sampling points. The boxes and whis-kers show that the distribution of the values was more spread out in this soil. Furthermore, the graph shows that it presented much clearer differences between the sampling times, with the most important one being between 24 h and 3 days. For this soil, the least intense activity was after one week into the experiment.
Cambisol and chernozem showed less variation between sampling times, and the values were more concentrated (smaller boxes). For cambisol, Table 2 shows that higher enzymatic activity was registered in the first 24 h and afterwards, alternated between sampling times. Chernozem, on the other hand, started with a slow and constant decrease in activity between 4 h and 24 h, and exhibited its highest values at 28 days.
Irrespective of these differences, all three soils had the most important change in enzymatic activity at 24 h–3 days, where all three saw an important increase in activity.
4. Discussion
Research shows that estrone mobility in soil experiences a linear decrease in the first 24 h [35,36] followed by a nonlinear phase [37]. This behaviour is attributed mainly to sorption/desorption processes, considering the main mechanisms that affect estrone mobility in soil [29,38].
The change between the phases is generally between 24 h and 3 days and was confirmed by Song et al. [38] among others, who discovered that an apparent sorption equilibrium is reached after 3 days. If estrone is not completely removed soon after that through further mechanisms, sorption becomes almost irreversible, and the contaminant accumulates in soil [39].
Though all three soils were different, looking at Figure 1 (Estrone) and Figure 2 (Enzymes) and at the values at each sampling time (Table 2), it is obvious that this transition pattern was present in each soil. It was the clearest in fluvisol, followed by chernozem, and lastly, although cambisol did not have a visible change in estrone values at 24 h, the enzymatic activity for this period suggested changes were happening here as well. No soil removed the estrone permanently by the end of the experiment; there were still traces of estrone in all the studied soils.
Estrone behaviour in soil is influenced by many factors, with the most common being molecular structure [40,41,42], environmental parameters [36], soil properties [43], and soil hydrophobicity [27]. Texture [28,36,44] and hydrophobicity are considered to be the most relevant here, based on previous studies. They were taken together with the soils’ characteristics measured and summarized in Table 1—soil properties used to analyze and compare estrone changes in the three soils.
Its molecular structure indicates that estrone is a hydrophobic compound, and as soils tend to be generally more hydrophobic, estrone’s sorption is high. This could explain why, at only 4 h into the experiment, already half of the initial concentration was gone (median 23.63 μg·kg−1 was left from initial 50 μg·kg−1).
Soil hydrophobic character is directly influenced among others by the amount of carbon [29,45,46] and its type (aromatic C is more hydrophobic than aliphatic one) [27]. This property seems to be one of the most relevant soil properties in regard to the behaviour of pollutants in soils, and Song et al. [38] described the first 24 h of a compound transformation as the fast sorption phase, which occurs through the hydrophobic mechanism. This mechanism involves the attachment of the pollutant’s molecules on the soil surface (generally hydrophobic), starting with the bigger pores until they fill up (normally in 24 h for estrone). This marks the point at which estrone transformation changes, from a fast to a slow sorption phase [47], when it is the turn of the micropores to fill up. These mechanisms show the importance of soil texture in addition to the amount of carbon.
Soils properties from Table 1 show that fluvisol had the highest amount of carbon (C:N was 26) and a silty-clay texture. A first-order kinetics model calculated that estrone half-life was at 2.9 h from the start of the experiment, before the first sampling time (4 h). Silt has a higher soil surface area where estrone can bound strongly [48], but also smaller macropores than sand or loam. These factors could explain why fluvisol had the lowest measured estrone amount from the three soils at 4 h (it was sorbed the most), and why the changes in concentrations were less pronounced (smaller pores need more time to fill up). At the same time, the presence of estrone on the soil surface encouraged enzymatic activity, which was the highest between all the three soils in this fast phase (4 h–24 h) and increased even more during the transition phase (24 h–3 days), where it reached the highest average in the entire experiment (527 U). This increase was likely due to more estrone becoming available to microorganisms (it could not be sorbed as quickly into the clay pores anymore), and possibly due to the presence of more adapted microorganisms. According to the findings of Schmitt et al. [49], communities can adapt to specific pollutants, which could have been the case for fluvisol, where estrone was easily accessible in the first 24 h (and up to day 3) and the soil properties (carbon and nutrients) would have encouraged a fast development of these microorganisms. By day 3, estrone concentration had halved from that at 24 h (from 18 µg·kg−1 to 9 µg·kg−1), while enzymatic activity reached its peak (527 U). Concentration remained constant until day 7 and halved again by the end of the experiment (day 28 had 5 ug·kg−1 estrone), but enzymatic activity remained relatively similar until day 7.
At this stage, estrone sorption would have occurred in the clay micropores (very slowly), which would explain the slow changes in concentration, as well as the decrease in microbial activity—due to much more limited access to estrone. But, as enzymatic activity was still recorded, it could be concluded that sorption and desorption phases alternated, and this provided enough carbon source (i.e., estrone) to microorganisms to function.
The conclusion for fluvisol would be that the first half-time in estrone transformation happened very fast in the first 24 h of the experiment, and the estrone transformation was due to strong soil surface adsorption coupled with very good microbial activity. The transition period saw the second half-life of the estrone concentration, but the main mechanism was microbial degradation; after this, estrone concentration changed slowly, reaching its last recorded half-life at 28 days, but now the changes were mainly through adsorption and accumulation. It was the only soil where clear correlation (Spearman rank correlation) could be established between enzymatic activity and estrone concentrations (ρ = −0.8), and it was the soil most different to both cambisol and chernozem.
Cambisol did not have the visible estrone transition between the fast and slow sorption, instead presenting a constant decrease in concentration between consecutive sampling times; its estrone kinetics showed a half-life that was around 4 h, which was later than the one in fluvisol, and it did not present any other half-lives, but it finished with an average of only 1 ug·kg−1 estrone, which was five times lower than fluvisol.
There was no relevant correlation between estrone and enzymes (ρ = 0.25), and the only clear findings that could be supported by evidence (the averaged enzymatic values) were that its highest enzymatic activity was at the beginning of the experiment (the first 12 h), and that this soil had an alternation of ups and downs in enzymes’ activity, without strong differences between sampling times.
This behaviour was attributed to its texture—sandy loam (predominance of bigger pores than in fluvisol)—which probably encouraged good estrone sorption throughout the entire experiment at a constant pace. This ensured almost constant access to estrone by microorganisms; therefore, when estrone was more abundant, enzymatic activity increased (the ‘ups’), and when sorption was more predominant and estrone was bound to the soil particles, microbial communities and their activity decreased (the ‘downs’). The sorption rate was lower than in fluvisol, at least in the beginning (20 ug·kg−1 fluvisol vs. 26 ug·kg−1 cambisol), and this was considered a consequence of the different textures, as clay (fluvisol) is more hydrophobic than sand and loam (cambisol). Also, there was less estrone left at 28 days (1 ug·kg−1), with a slight increase in enzymatic activity. This suggested that estrone remained available to microorganisms for the entire period more than it did in fluvisol, so the question was why the enzymatic activity was lower than that in fluvisol? A possible reason could be the nutrients availability in the two soils, Table 1 showing that cambisol had lower nutrient concentrations than fluvisol; therefore, the microbial communities were probably not able to grow much. Although not clearly visible in the data, the 24 h–3 days transition was supposed to have occured; nevertheless, as the macropores (sand) would have eventually filled up and sorption would have moved to smaller pores (loam), an increase in enzymatic activity was recorded for this period (from 272 U to 314 U by day 3). Cambisol was, in general, different from fluvisol, but very similar to chernozem.
Chernozem did not show any reliable pattern of biodegradation (rho = 0.14). It presented the general estrone transition after 24 h, but Figure 1 shows this soil had three main times when estrone concentrations decreased more: at 4 h, at 24 h, and at 28 days. The first decreasing period also included the half-time in estrone degradation, calculated at approx. 8 h, which was the longest of the soils. This soil started with the highest concentration at 4 h (29 ug·kg−1), indicating sorption was less than in the other soils, and finished with the lowest concentration at 28 days (0.9 ug·kg−1). This was also the only soil where enzymatic activity decreased at the beginning of the experiment, from 308 U at 4 h to 266 U at 24 h. It could be that estrone might have had a negative effect on the microbial communities initially, and only later (after 24 h) did they adapt to this pollutant, as this soil had its highest enzymatic activity from day 3 onwards. The hypothesis of microorganism adaptation is supported by the fact that this soil had just one predominant texture (loam); hence, the microorganisms’ access to estrone could be considered constant, and not influenced by different textures. Adaptation is supported also by the nutrient characteristics of this soil (the second-best after fluvisol), which would have encouraged a good development of microbial communities. The soil presented a very clear 24 h–3 days transition, this period also demonstrating a clear separation between the enzymatic behaviour stages in the soil. In the first 24 h, as both estrone and enzymes decreased, estrone mobility was attributed to adsorption, mainly, and some microbial activity. The 24 h–3 days transition experienced a relevant increase in activity that was maintained until the end of the experiment and in fact, chernozem’s highest average was registered at day 28 (379 U). Analyzed together with the corresponding estrone concentrations, it can be concluded that chernozem needed approximately 3 days to develop estrone-tolerant microbial communities. Before that, estrone was mainly adsorbed on the loam; after that, estrone transformation was mainly performed by microorganisms in a very successful way (lowest E1 values and highest enzymatic activity). Chernozem was the most similar to cambisol, but most different to fluvisol.
5. Conclusions
The soils presented distinct patterns in dealing with the estrone presence, and these differences were illustrated by variations in enzymatic activities considered to have been mainly influenced by soil physical properties.
All soils degraded the estrone, though none completely degraded it in 28 days. The comparison of the three soils considered that the most relevant factors influencing estrone transformation were (i) soil hydrophobicity, (ii) texture, and (iii) adaptiveness of microbial communities to estrone pollution. The combination of these factors provided an adsorption–microorganisms activity situation specific to each soil, which resulted in the three distinct outcomes. Fluvisol was the most different soil in both enzymatic activity and estrone transformation. This soil had a clear correlation between estrone concentration changes in time and the values of enzymatic activity; therefore, it can be considered that the main degradation process here was through microbial activity. This was a consistent process. Cambisol and chernozem were more similar overall, with no significant differences. Also, neither estrone, nor the enzymatic activity showed significant differencesP. There was no obvious correlation between enzymatic activity and estrone levels in these soils, but the fact that at the end of the experiment, they had the lowest levels of estrone indicates that microbial transformation was important here as well, as it demonstrates that the mechanisms were more varied than in fluvisol. It is considered that the microbial communities in these two soils went through successive intense highs and lows, but when the communities became strong again, their estrone degradation would have been intense (as mentioned, these soils had the lowest remaining estrone levels at 28 days).
Author Contributions
Funding acquisition and supervision were provided by J.S. Conceptualization and methodology were performed by A.C.D. and J.S. Investigation and data curation were carried out by A.C.D. and S.C. The first draft of the manuscript was written by A.C.D. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
The investigation was supported by European Regional Development Fund—Project No. CZ.02.1.01/0.0/0.0/16_019/0000845.
Institutional Review Board Statement
Not applicable.
Informed Consent Statement
Not applicable.
Data Availability Statement
The data that support the findings of this study are available from the corresponding author upon reasonable request.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
References
- Abdellah, Y.A.Y.; Zang, H.; Li, C. Steroidal estrogens during composting of animal manure: Persistence, degradation, and fate, a Review. Water Air Soil. Pollut. 2020, 231, 547. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bartelt-Hunt, S.; Snow, D.D.; Damon-Powell, T.; Miesbach, D. Occurrence of steroid hormones and antibiotics in shallow groundwater impacted by livestock waste control facilities. J. Cont. Hydrol. 2011, 123, 94–103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gall, H.E.; Sassman, S.A.; Jenkinson, B.; Lee, L.S.; Jafvert, C.T. Comparison of export dynamics of nutrients and animal-borne estrogens from a tile-drained Midwestern agroecosystem. Water Res. 2015, 72, 162–173. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Barel-Cohen, K.; Shore, L.S.; Shemesh, M.; Wenzel, A.; Mueller, J.; Kronfeld-Schor, N. Monitoring of natural and synthetic hormones in a polluted river. J. Environ. Manag. 2006, 78, 16–23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sutaswiriya, N.; Homklin, S.; Kreetachat, T.; Vaithanomsat, P.; Kreetachat, N. Monitoring estrogen and androgen residues from livestock farms in Phayao Lake, Thailand. Environ. Monit. Assess. 2021, 193, 812. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dutta, S.; Inamdar, S.; Tso, J.; Aga, D.S.; Sims, J.T. Free and conjugated estrogen exports in surface-runoff from poultry litter–amended soil. J. Environ. Qual. 2010, 39, 1688–1698. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ying, G.G.; Kookana, R.S.; Kumar, A.; Mortimer, M. Occurrence and implications of estrogens and xenoestrogens in sewage effluents and receiving waters from South East Queensland. Sci. Total Environ. 2009, 407, 5147–5155. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ciślak, M.; Kruszelnicka, I.; Zembrzuska, J.; Ginter-Kramarczyk, D. Estrogen pollution of the European aquatic environment: A critical review. Water Res. 2023, 229, 119413. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ting, Y.F.; Praveena, S.M. Sources, mechanisms, and fate of steroid estrogens in wastewater treatment plants: A mini review. Environ. Monit. Assess. 2017, 189, 178. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grdulska, A.; Kowalik, R. Estrogen removal from wastewater. Struct. Environ. 2020, 12, 133–141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mina, O.; Gall, H.E.; Elliott, H.A.; Watson, J.E.; Mashtare, M.L.; Langkilde, T.; Harper, J.P.; Boyer, E.W. Estrogen occurrence and persistence in vernal pools impacted by wastewater irrigation practices. Agric. Ecosyst. Environ. 2018, 257, 103–112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Combalbert, S.; Hernandez-Raquet, G. Occurrence, fate, and biodegradation of estrogens in sewage and manure. Appl. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 2010, 86, 1671–1692. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stumpe, B.; Marschner, B. Long-term sewage sludge application and wastewater irrigation on the mineralization and sorption of 17β-estradiol and testosterone in soils. Sci. Total Environ. 2007, 374, 282–291. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, G.Y.; Liang, Y.Q.; Liu, Y.S.; Shi, W.J.; Liu, S.S.; Hu, L.X.; Xie, L.; Ying, G.G. Swine farm wastewater discharge causes masculinization of western mosquitofish (Gambusia affinis). Environ. Int. 2019, 123, 132–140. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lucas, S.D.; Jones, D.L. Biodegradation of estrone and 17 β-estradiol in grassland soils amended with animal wastes. Soil. Biol. Biochem. 2006, 38, 2803–2815. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Popova, I.E.; Morra, M.J. Environmental transport of endogenous dairy manure estrogens. J. Environ. Sci. Health Part B 2017, 52, 817–822. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ma, L.; Yates, S.R. Degradation and metabolite formation of estrogen conjugates in an agricultural soil. J. Pharm. Biomed. Anal. 2017, 145, 634–640. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ye, X.; Wang, H.; Kan, J.; Li, J.; Huang, T.; Xiong, G.; Hu, Z. A novel 17β-hydroxysteroid dehydrogenase in Rhodococcus sp. P14 for transforming 17β-estradiol to estrone. Chem. Biol. Interact. 2017, 276, 105–112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jobling, S.; Reynolds, T.; White, R.; Parker, M.G.; Sumpter, J.P. A variety of environmentally persistent chemicals, including some phthalate plasticizers, are weakly estrogenic. Environ. Health Perspect. 1995, 103, 582–587. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Janssen, P.A.H.; Lambert, J.G.D.; Vethaak, A.D.; Goos, H.J.T. Environmental pollution caused elevated concentrations of oestradiol and vitellogenin in the female flounder, Platichthys flesus (L.). Aquat. Toxicol. 1997, 39, 195–214. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fernández, L.; Louvado, A.; Esteves, V.I.; Gomes, N.C.M.; Almeida, A.; Cunha, Â. Biodegradation of 17β-estradiol by bacteria isolated from deep sea sediments in aerobic and anaerobic media. J. Hazard. Mat. 2017, 323, 359–366. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, C.P.; Roh, H.; Chu, K.H. 17β-Estradiol-Degrading Bacteria Isolated from Activated Sludge. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2007, 41, 486–492. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pratush, A.; Yang, Q.; Peng, T.; Huang, T.; Hu, Z. Identification of non-accumulating intermediate compounds during estrone (E1) metabolism by a newly isolated microbial strain BH2-1 from mangrove sediments of the South China Sea. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2020, 27, 5097–5107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nakai, S.; Yamamura, A.; Tanaka, S.; Shi, J.; Nishikawa, M.; Nakashimada, Y.; Hosomi, M. Pathway of 17β-estradiol degradation by Nitrosomonas europaea and reduction in 17β-estradiol-derived estrogenic activity. Environ. Chem. Lett. 2011, 9, 1–6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Z.; Nandakumar, R.; Madayiputhiya, N.; Li, X. Proteomic Analysis of 17β-Estradiol Degradation by Stenotrophomonas maltophilia. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2012, 46, 5947–5955. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Y.L.; Yu, C.P.; Lee, T.H.; Goh, K.S.; Chu, K.H.; Wang, P.H.; Ismail, W.; Shih, C.J.; Chiang, Y.R. Biochemical mechanisms and catabolic enzymes involved in bacterial estrogen degradation pathways. Cell Chem. Biol. 2017, 24, 712–724. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, X.; Guo, X.; Yang, Y.; Tao, S.; Xing, B. Sorption Mechanisms of Phenanthrene, Lindane, and Atrazine with Various Humic Acid Fractions from a Single Soil Sample. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2011, 45, 2124–2130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, Z.; Xiao, B.; Huang, W.; Peng, P. Sorption of steroid estrogens to soils and sediments. Environ. Toxicol. Chem. 2004, 23, 531–539. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Caron, E.; Farenhorst, A.; Zvomuya, F.; Gaultier, J.; Rank, N.; Goddard, T.; Sheedy, C. Sorption of four estrogens by surface soils from 41 cultivated fields in Alberta, Canada. Geoderma 2010, 155, 19–30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mehlich, A. Mehlich 3 soil test extractant: A modification of Mehlich 2 extractant. Commun. Soil. Sci. Plant Anal. 1984, 15, 1409–1416. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mashtare, M.L.; Green, D.A.; Lee, L.S. Biotransformation of 17α- and 17β-estradiol in aerobic soils. Chemosphere 2013, 90, 647–652. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bilal, M.; Iqbal, H.M.N. Persistence and impact of steroidal estrogens on the environment and their laccase-assisted removal. Sci. Total Environ. 2019, 690, 447–459. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tamagawa, Y.; Yamaki, R.; Hirai, H.; Kawai, S.; Nishida, T. Removal of estrogenic activity of natural steroidal hormone estrone by ligninolytic enzymes from white rot fungi. Chemosphere 2006, 65, 97–101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Štursová, M.; Baldrian, P. Effects of soil properties and management on the activity of soil organic matter transforming enzymes and the quantification of soil-bound and free activity. Plant Soil. 2011, 338, 99–110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Casey, F.X.M.; Šimůnek, J.; Lee, J.; Larsen, G.L.; Hakk, H. Sorption, mobility, and transformation of estrogenic hormones in natural soil. J. Environ. Qual. 2005, 34, 1372–1379. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Renaud, F.G.; Leeds-Harrison, P.B.; Brown, C.D.; van Beinum, W. Determination of time-dependent partition coefficients for several pesticides using diffusion theory. Chemosphere 2004, 57, 1525–1535. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, E.; Jung, C.; Han, J.; Her, N.; Park, C.M.; Jang, M.; Son, A.; Yoon, Y. Sorptive removal of selected emerging contaminants using biochar in aqueous solution. J. Ind. Eng.Chem. 2016, 36, 364–371. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, X.; Zhang, Z.; Wen, Y.; Zhang, W.; Xie, Y.; Cao, N.; Sun, D.; Yang, Y. The response of steroid estrogens bioavailability to various sorption mechanisms by soil organic matter extracted with sequential alkaline-extraction method from an agriculture soil. Environ. Pollut. 2022, 308, 119630. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, S.; Pardue, J.H.; Moe, W.M.; Kim, D.J. Effect of sorption and desorption-resistance on biodegradation of chlorobenzene in two wetland soils. J. Hazard. Mat. 2009, 161, 492–498. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Flogeac, K.; Guillon, E.; Aplincourt, M. Adsorption of several metal ions onto a model soil sample: Equilibrium and EPR studies. J. Coll. Interf. Sci. 2005, 286, 596–601. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, S.; Kommalapati, R.R.; Valsaraj, K.T.; Pardue, J.H.; Constant, W.D. Rate-Limited Desorption of Volatile Organic Compounds from Soils and Implications for the Remediation of a Louisiana Superfund Site. Environ. Monit. Assess. 2002, 75, 93–111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Neale, P.A.; Escher, B.I.; Schäfer, A.I. Quantification of solute–solute interactions using negligible-depletion solid-phase microextraction: Measuring the affinity of estradiol to bulk organic matter. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2008, 42, 2886–2892. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qualls, R.G. Comparison of the behavior of soluble organic and inorganic nutrients in forest soils. Forest Ecol. Manag. 2000, 138, 29–50. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Loffredo, E.; Senesi, N. Fate of anthropogenic organic pollutants in soils with emphasis on adsorption/desorption processes of endocrine disruptor compounds. Pure Appl. Chem. 2006, 78, 947–961. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Drahorad, S.L.; Jehn, F.U.; Ellerbrock, R.H.; Siemens, J.; Felix-Henningsen, P. Soil organic matter content and its aliphatic character define the hydrophobicity of biocrusts in different successional stages. Ecohydrology 2020, 13, e2232. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Durán–Álvarez, J.C.; Prado, B.; Ferroud, A.; Juayerk, N.; Jiménez-Cisneros, B. Sorption, desorption and displacement of ibuprofen, estrone, and 17β estradiol in wastewater irrigated and rainfed agricultural soils. Sci. Total Environ. 2014, 473–474, 189–198. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pan, B.; Xing, B.; Liu, W.; Tao, S.; Lin, X.; Zhang, Y.; Yuan, H.; Dai, H.; Zhang, X.; Xiao, Y. Two-compartment sorption of phenanthrene on eight soils with various organic carbon contents. J. Environ. Sci. Health Part B 2006, 41, 1333–1347. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Takigami, H.; Taniguchi, N.; Shimizu, Y. Sorption and desorption of 17β-estradiol to natural sediment. Water Sci. Technol. 2011, 64, 1473–1478. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schmitt, H.; Haapakangas, H.; van Beelen, P. Effects of antibiotics on soil microorganisms: Time and nutrients influence pollution-induced community tolerance. Soil. Biol. Biochem. 2005, 37, 1882–1892. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).