Abstract
In this study, we evaluated the antibacterial effect of floating electrode–dielectric barrier discharge (FE-DBD) plasma (1.1 kV, 43 kHz, N2 1.5 m/s, 1–60 min) against Staphylococcus aureus and Salmonella Typhimurium in fried fish paste. In addition, a quality evaluation (pH, VBN) of fried fish paste was conducted after the FE-DBD plasma treatment. When FE-DBD plasma was used for treatment for 1, 5, 10, 20, 30, and 60 min, S. aureus decreased by 0.16–1.13 log10 CFU/g, and S. Typhimurium decreased by 0.25–1.13 log10 CFU/g. Both decreased > log10 CFU/g at 60 min. The D-value was 58.92, and R2 was 0.97 for S. aureus using first-order kinetics, and the D-value was 43.60, and R2 was 0.97 for S. Typhimurium using the Weibull model. There was no significant difference in pH after the FE-DBD plasma treatment (p > 0.05). Additionally, volatile basic nitrogen (VBN) significantly decreased as the treatment time increased (p < 0.05), and it was the lowest 3.46 at 60 min. Therefore, this FE-DBD plasma treatment could be considered a technology for preserving the quality of processed foods.
1. Introduction
Surimi-based products are among the processed seafood items that are most frequently expected to be an accessible source of protein with the expansion of convenience foods due to the diversification of dietary patterns and, particularly, in situations where raw materials for processing livestock are limited, such as in Korea [1]. Fish paste is a processed meal made, with reasonably sophisticated technology, from seafood surimi. It may be used as raw fish meat from a variety of fish species and has convenient food qualities [2].
There are many issues with hygiene preservation, and even in the case of vacuum-packed fried fish pastes, the number of days available for distribution is as little as 12. However, fish paste produced in Korea is either not packaged or packaged in various forms and distributed at room temperature or low temperatures. Additionally, fried fish pastes sold in traditional markets are more likely to be contaminated by microorganisms than if produced in factories because they are immediately fried and left on display until sold to consumers. Fried fish paste is treated as a hygienic and storable food because it is heated at high temperatures (160–170 °C) during the manufacturing process, but most of it is distributed in a non-vacuum state, and lipid trans-fat can occur because of lipid rancidity and high-temperature treatments. Additionally, it can easily deteriorate because of residual harmful microorganisms that have not been sterilized or that enter during the packaging and distribution process [3]. Therefore, the inactivation of harmful microorganisms is essential to ensuring the hygienic stability of food. Studies have been conducted to extend the storage period of fish paste using techniques such as chlorine dioxide treatment [1], gamma-ray irradiation [4], bactosis treatment [5], and acetic acid treatment [6].
Plasma constitutes one of the four fundamental states of matter, alongside liquids, solids, and gases. It is similar to gaseous states, or a state of matter in which electrons in an atom are no longer bound to an atomic nucleus and can move freely [7]. Plasma is composed of electrons, ions, and nonionized particles. It can be produced by direct contact with water and is frequently employed in the production of gaseous reactive species [8]. Previously, plasma treatment was performed under vacuum conditions, but the discovery of atmospheric pressure plasma has reduced costs, increased processing speeds, and increased its potential for industrial applications [9]. These atmospheric pressure plasmas are applied in various fields such as agriculture and medicine, especially in agro-industrial applications, to address issues such as food security and increased crop yields. It is also recognized as an eco-friendly sterilization technology because of its proven ability to control pathogens [10]. Plasma can be classified by the degree of ionization; it can also be classified based on the thermal equilibrium state of particles. Based on this, plasma is classified into two types: thermal and nonthermal. In thermal plasma (TP), there is a thermal equilibrium between electrons and heavy particles. In contrast, nonthermal plasma maintains a lower overall temperature by keeping heavy particles at nearly room temperature, while electrons achieve significantly higher temperatures than those in TP [11,12].
Nonthermal plasma is a technology that inhibits microorganisms from contaminating food at low temperatures and is a new sterilization technology with considerable potential for food preservation because of its high efficiency and limited side effects. This technology has a variety of applications for the food industry, including the dry disinfection of food surfaces (fish and meat) and sprouting seeds [9]. Floating electrode–dielectric barrier discharge (FE-DBD) plasma is distinct from conventional DBD plasma. In this form, NTP can be discharged by air into the atmosphere [13,14]. Therefore, plasma is generated on the surface of the skin without external gas injection, and the plasma generation area is much larger than that of plasma jets [15]. The term “floating electrode” implies that a metal object is separated from the ground. These techniques are used in skin care because of their ability to prevent cavities and burn damage. Additionally, by applying FE-DBD plasma, a complete skin sterilization effect can be achieved without blood clotting and damaging surrounding tissues, and its ability to sterilize microorganisms has recently been proven [16]. Therefore, FE-DBD plasma is currently used for HuNoV GⅡ.4 treatment in salted clams [12] and the control of highly resistant Escherichia coli, methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus (MRSA), and Bacillus stratosphericus [17,18]. However, there have been no studies confirming or evaluating the effectiveness of FE-DBD plasma treatments on S. aureus and Salmonella Typhimurium in fried fish paste.
Hence, in this study, the antibacterial efficacy of FE-DBD plasma therapy against S. aureus and S. Typhimurium on fried fish paste was verified. Additionally, the physicochemical characteristics of plasma-treated fried fish paste were evaluated in this study.
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Sample Preparation and Bacteria Inoculation
The fried fish paste was purchased from an online market (Busan, Korea). Before the experiment, each sample was cut into 3.0 × 3.0 × 0.3 (L × W × H) pieces. To completely remove microorganisms, we disinfected the surface of the samples with 70% ethanol before inoculation.
S. aureus (ATCC 6538 and ATCC 12600) and S. Typhimurium ATCC 14028 were obtained from the American Type Culture Collection (ATCC) and used for inoculation. Stock cultures were preserved at −80 °C in tryptic soy broth (TSB, Difco Laboratories, Detroit, MI, USA) supplemented with 30% glycerol. Following this, each strain underwent a 24 h incubation at 37 °C in 5 mL TSB, followed by centrifugation at 5400× g for 10 min at 4 °C. This process was repeated twice to ensure optimal activation of bacteria. The resulting pellets of S. aureus were then combined by resuspending them in 9 mL of sterile NaCl saline (0.85%).
Both S. aureus and S. Typhimurium were spot-inoculated onto the surface of the fried fish paste at a concentration of 100 μm. The initial titer of S. aureus and S. Typhimurium was about 4–4.2 log10 colony forming unit (CFU/g). After inoculation, it was put in a biological safety cabinet (CHC Lab Co. Ltd., Daejeon, Korea) for 1 h so that the inoculated bacteria could be well absorbed into the sample.
2.2. FE-DBD Plasma Treatment on Fried Fish Paste
Figure 1 illustrates a schematic diagram of the FE-DBD plasma device employed in this study. A high-voltage electrode of 0.7 mm thickness was constructed using glass, with a screen-printed silver electrode with a thickness of 10 μm and a dielectric material composed of SiO2 screen-printed to a thickness of 100 μm. The electrical voltage and current of the FE-DBD were measured utilizing a high-voltage probe (P6015A, Tektronix, Beaverton, OR, USA) and a pickup probe (P6021A, Tektronix, Beaverton, OR, USA). The operational voltage was generated by an inverter producing a 47 kHz sinusoidal wave with an amplitude of 2.8 kV. Notably, the FE-DBD plasma discharge primarily occurred at 1 kV, with the maximum discharge current measured at 16 mA. Power consumption was recorded at 0.55 W, and the RMS (root mean square) voltage and current were measured at 2.0 kV and 13.5 mA, respectively. N2 gas for FE-DBD plasma generation was allowed to flow through the gas inlet at 1.5 L per min, and plasma was generated between the glass under the powered electrode with the surface of the fried fish paste serving as a virtual ground. During plasma treatment, the separation between the plasma emission electrode and the sample was consistently kept at 3 mm. FE-DBD plasma on the surface of the fried fish paste was treated for 1, 5, 10, 20, 30, and 60 min.
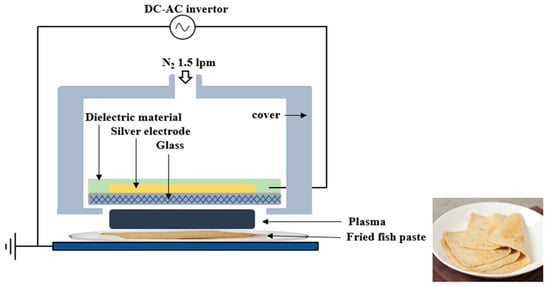
Figure 1.
Schematic representation of FE-DBD plasma system used for treating fried fish paste.
2.3. Quantification of Bacterial Analysis
This experiment was conducted based on Ministry of Food and Drug Safety (MFDS) [19] guidelines to quantitatively detect S. aureus and S. Typhimurium in samples after FE-DBD plasma treatment. Samples inoculated with S. aureus and S. Typhimurium were placed in a sterile stomacher bag (Korea, Seoul, Korea 3M) with 0.85% sterile NaCl and homogenized. Subsequently, 1 mL of homogenized solution was then diluted with 9 mL of 0.85% sterile NaCl solution. In total, 1 mL of diluted sample was added to a Petri dish and mixed with tryptic soy agar (TSA, Difco Laboratories, Detroit, MI, USA). Thereafter, S. aureus and S. Typhimurium were incubated at 37 °C for 48 h and 24 h, respectively.
2.4. Modeling of Decimal Reduction Times
The first-order kinetics model was used to calculate the D-value for the reduction of S. aureus. The D-value represents the FE-DBD treatment time required to reduce 1 log10 CFU of microorganisms. The closer the R2 value is to 1, the better the data point fits the regression line.
- The initial microbial population (CFU/g) is N0.
- The microbial population multiplied by FE-DBD plasma treatment time (CFU/g) is N.
- The FE-DBD plasma treatment time (min) is t.
- The reduction rate constant is k.
For the determination of the D-value of S. Typhimurium, the Weibull model, a two-parameter nonlinear model, was used. The calculation formula is expressed as follows:
- Nt is the number of microorganisms (log CFU/g) after the FE-DBD plasma treatment time, t.
- N0 is the initial microbial population (log CFU/g).
- t is the FE-DBD plasma treatment time (min).
- b indicates the time needed to reduce the population for one log unit.
- n (parameter) indicates the shape of the survival curve.
An n value of 1 corresponds to a linear survival curve, and n values correspond to downward and upward concavity.
To obtain the D-value from the Weibull parameters, we used the equation of Buzrul and Alpas [20]:
D represents the time required to decrease the microorganism by 90%. The Weibull model was analyzed using the GraphPad Prism software for Windows, version 5.0 (GraphPad Software, San Diego, CA, USA).
2.5. Physicochemical Quality Evaluation [pH Value, VBN]
To measure the pH, 3 g of fried fish paste treated with FE-DBD plasma and 30 mL of distilled water were mixed in a sterilized bag. The mixture was homogenized for 1 min using a stomacher (Bagmixer, Interscience, Troy, MI, USA). Subsequently, the pH value was determined using a pH meter (A211, Thermo Orion, Benchtop, MI, USA).
VBN was analyzed using the Conway microdiffusion method [21]. This was repeated in triplicate per sample, and the blank was distilled water as a sample. Samples of 2 g 20% trichloroacetic acid (TCA) and 16 mL of distilled water were put in a stomacher bag. After homogenization, 1 mL of the filtered sample solution was put in the left side of the outer chamber of the Conway unit, and 1 mL of 50% K2CO3 was added to the right side of the outer chamber of the Conway unit. Then, we put 1 mL of 0.01 N H3BO3 in the inner chamber of the Conway unit and closed the lid tightly so that there was no gap. Then, we mixed the sample with K2CO3. After being left at room temperature (25 °C) for 100 min, titration was performed using 0.01 N HCl.
2.6. Statistical Analysis
All experiments were conducted three times for each sample, and the data are represented as the mean ± standard deviation (SD). Statistical analysis was conducted to find out the significant difference between the average reduction (log CFU/g) of S. aureus and S. Typhimurium and the D-value, pH, and VBN of the two bacteria over time after the FE-DBD plasma treatment. We performed ANOVA and Duncan’s multiple range tests using SPSS version 12.7 software (SPSS Inc., Chicago, IL, USA). They were verified with a significant difference at the probability level of 5% (p < 0.05).
3. Results
3.1. Reduction and D-Value of S. aureus and S. Typhimurium in Fried Fish Paste after FE-DBD Plasma Treatment
To confirm the sterilization effect of FE-DBD plasma, the reduction in S. aureus and S. Typhimurium in fried fish paste was confirmed (Table 1). S. aureus and S. Typhimurium tended to decrease significantly as the treatment time increased (p < 0.05). When the fried fish paste was treated for 1, 5, 10, 20, 30, and 60 min, S. aureus was identified as experiencing 0.16, 0.24, 0.36, 0.43, 0.86, and 1.13 log reduction, respectively. There was no significant difference until 10 min (p > 0.05). However, a significant difference was observed at 20 min (p < 0.05), showing the highest decrease compared with the control group (4.22 log10 CFU/g) at the maximum treatment time. The results for S. aureus and S. Typhimurium after the FE-DBD plasma treatment were obtained using two models: a first-order kinetics model and the Weibull model. Based on the survival curve of S. aureus, a first-order kinetics model was applied (Figure 2). The R2 and D-values are shown in Table 2. The D-value was 58.92 min, and the R2 value was 0.97. The fit of the log-linear kinetics model for S. aureus was estimated to be R2. It was close to 1.0, so it was appropriate for the determining slope and the D-value.

Table 1.
Reduction in S. aureus and S. Typhimurium in fried fish paste using FE-DBD plasma.
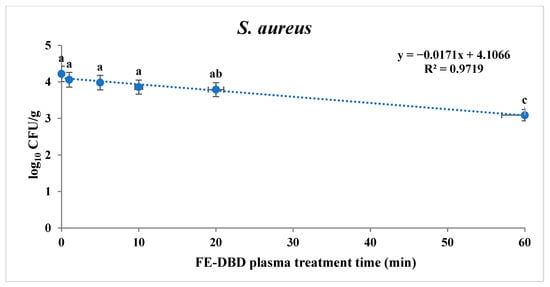
Figure 2.
The effects of FE-DBD plasma treatment on S. aureus in fried fish paste and fitted survival curves from the first-order kinetics model. The letters a, b, and c represent significant differences (p < 0.05) in the reduction of S. aureus.

Table 2.
Model parameters of S. aureus and S. Typhimurium in fried fish paste using FE-DBD plasma.
The reduction in S. Typhimurium levels caused by FE-DBD plasma was significantly decreased (p < 0.05). After being treated with FE-DBD plasma for 1, 5, 10, 20, 30, and 60 min, the reductions were 0.25, 0.35, 0.77, 0.83, 0.85, and 1.13 log10 CFU/g, respectively. It was confirmed that it gradually decreased as treatment time increased. It significantly decreased after 5 min of treatment (p < 0.05) and decreased gradually after 20, 30, and 60 min, but there was no significant difference (p > 0.05) between the groups. The reduction effect of FE-DBD plasma on S. Typhimurium was evaluated, and the results were applied to the Weibull model (Figure 3). The parameters (b, n, R2, D) of the Weibull model are shown in Table 2. The values of R2 and D were 0.97 and 43.60, respectively. Because the R2 value of S. Typhimurium was close to 1.0, this model was appropriate for the survival curve. Although the experimental reduction effects for the two bacteria were similar or the same for FE-DBD plasma after 30 and 60 min of treatment, when microbial survival modeling was applied, S. aureus and S. Typhimurium showed linear (Figure 2) and non-linear concave downward survival patterns (Figure 3), respectively.
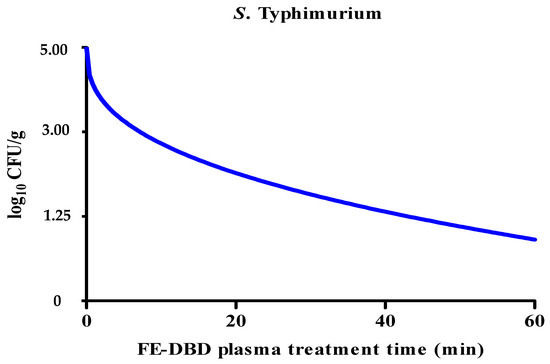
Figure 3.
The effects of FE-DBD plasma treatment on S. Typhimurium in fried fish paste and fitted survival curves for the Weibull model.
3.2. Quality (pH and VBN) of Fried Fish Paste after FE-DBD Plasma Treatment
The pH and VBN of fried fish paste were determined according to the FE-DBD plasma treatment time (Table 3). The pH of fried fish paste was 5.37 at all plasma treatment times, and there was no significant difference between the samples (p > 0.05).

Table 3.
Physicochemical quality evaluation of fried fish paste after FE-DBD plasma treatment.
For VBN, there was no significant difference when the control group (8.15) was treated for 5 min (p > 0.05). When plasma was used for 10, 20, 30, and 60 min, the VBN values were 6.98, 4.71, 3.48, and 3.46, respectively. With a 10 min treatment, the VBN value decreased significantly compared with the control group (p < 0.05).
4. Discussion
The consumption of fish-based products is not high compared with that of other foods because they are cumbersome to preprocess and cook despite their excellent nutritional and health benefits. However, fish pastes, which are easy to cook and have the fish odor removed, have shown a gradual increase in production in the 2000s [3]. These products are anticipated to be protein resources with the increased consumption of convenience foods according to changes in dietary patterns and raw materials for processing livestock that are difficult to obtain in Korea. Fish paste is a processed food that can be easily consumed. Its consumption is high because it is relatively inexpensive. There are many different types of fish pastes, but among them, fried fish paste is treated as a food that can be stored for long periods. Therefore, it has the highest preference among fish pastes. Additionally, as high-temperature heat treatments (160–170 °C), it is generally considered hygienic and safe from microorganisms. However, it can easily deteriorate because of residual harmful microorganisms that have not been completely sterilized during the manufacturing process or that enter during the storage and distribution processes. The shelf life of vacuum-packed fried fish paste is only approximately 10 days when stored at low temperatures [1].
The deterioration of food caused by microbial contamination results in food poisoning or quality degradation. Hence, the inactivation of harmful microorganisms is essential to ensuring the hygienic stability of food. Moreover, in the case of fried fish pastes, their hygienic stability must be ensured immediately, as they are street foods. Hence, aside from addressing bactosis [5], numerous studies currently propose methods to extend the storage duration of fish pastes while maintaining their hygienic qualities. A study on a chlorine dioxide treatment of fish pastes [1] reported that microorganisms decreased as the chlorine dioxide treatment concentration increased. Another study on a gamma-irradiation treatment [4] reported that the total aerobic bacteria were effectively reduced at 2.5 kGy and that the detection limit (2 log CFU/g) was significantly reduced at 7.5 kGy. In spite of these studies, sterilization and microbial reduction studies on fish paste are still insufficient, particularly on nonthermal methods for microbial inhibition.
Floating electrode–dielectric barrier discharge plasma differs from the existing DBD method in that, when alternating current (AC) or pulse-type power is applied to one electrode, a charge is accumulated in the dielectric surrounding the electrode. Afterward, when the polarity of the electrode is changed, the charge accumulated in the dielectric is released, and plasma is formed between the electrodes [15]. In addition, Aadim et al. [22] showed that the intensity of the emission spectrum lines of cold plasma varies with the flow of gas, and the emission intensity increases with increasing gas flow, which increases the number of gas molecules. In fact, Svarnas et al. [23] reported that Salmonella Typhimurium was not detected as a result of treating sewage with an FE-DBD (10 kHz, 18 kV, 3 slm) treatment of sewage for 10 min. The operating conditions of the FE-DBD treatment were set higher than in this study, and the microbial reduction effect depends on the operating conditions of the FE-DBD plasma. FE-DBD plasma is an eco-friendly technology that is applied to various fields such as skin treatment and food because it does not cause environmental problems such as the release of mercury and other wastes like radiation treatment, and it does not release harmful components to the human body [24,25]. Given these advantages, many studies have reported the microbial sterilization effect of DBD plasma on food. However, further research is needed on the antimicrobial activity of FE-DBD plasma.
Chen et al. [26] reported that, when chub mackerel was treated with atmospheric cold plasma (ACP) at an optimal voltage (60 kV), the total viable count decreased by 3.15 log CFU/g in 60 s. In addition, ACP treatment is a potential and promising alternative to seafood conservation technology. According to Abdi et al. [27], microorganisms were reduced after the exposure of L. sativa seeds to FE-DBD plasma. Moreover, no bacteria were detected after 40 min of treatment; the FE-DBD plasma treatment effectively controlled the microorganisms. Jeon et al. [12] reported that human norovirus in Jogaejeotgal (a Korean traditional fermented food) decreased as processing time increased after FE-DBD plasma treatment, and it decreased the most after 30 min to about 1–1.30 log10 CFU/g. However, in this experiment, S. aureus and S. Typhimurium were reduced by about 1.13 log10 CFU/g when treated for 30 min. Both the aforementioned studies showed a greater decrease than this study. Fish paste is made by mixing fish meat with a small amount of salt and other ingredients, such as starch, in a meaty paste. After the formation process, it is gelled via steaming, boiling, baking, or frying [28]. Therefore, the bacterial reduction may be decreased because it has a harder structure than Jogaejeotgal. Additionally, plasma treatment can affect the inhibitory effect differently depending on several factors, such as the species of microorganisms, the injected gas type, the exposure type, and the cell layer number in the sample [29].
Floating electrode–dielectric barrier discharge plasma breaks covalent bonds with cations, anions, electrons, and ultraviolet (UV) photons; it is brought into contact with chemically activated species, resulting in microbial sterilization. Among several active species, active oxygen species such as oxygen radicals can affect cells by reacting with various macromolecules [29,30]. Active species cause the formation of unsaturated fatty acids and peroxides, which damage the lipids and proteins in the cell membranes of microorganisms and sterilize them while spreading into cells. The active species (ROS and RNS) generated by plasma can create air pollutants that are harmful to humans [8,31]. However, Mann et al. [32] reported that the duration of a plasma treatment did not exceed the permissible exposure, so the risk from plasma treatment is expected to be low.
Mathematical models such as the first-order kinetics and Weibull models improve food safety by predicting the survival characteristics of pathogenic microorganisms. Reduction kinetics modeling is useful for assessing the risk of quantitative microorganisms [33]. First-order kinetics is utilized to determine inactivation data such as D-values and is based on linear microbial survival curves [34,35]. However, microbial survival curves may not always be linear; hence, the Weibull model was applied in this study to determine D-values based on nonlinear microbial survival curves [34,36]. As the R2 values of S. aureus and S. Typhimurium in fried fish paste after using FE-DBD plasma were close to one, two models were utilized to determine the most appropriate survival curve model. In the case of S. aureus, the R2 and D-values were 0.97 and 58.92, respectively, which were obtained with a linear model. However, the R2 value for S. Typhimurium was 0.97, and the D-value was 43.60, and both were more appropriate for the Weibull model, a nonlinear curve, than the linear model.
The pH and VBN of the fried fish paste were measured after the FE-DBD plasma treatment based on setting time. The pH was not significantly different (p > 0.05), and the sample quality was not significantly affected. Jeon et al. [12] also reported that the FE-DBD plasma treatment did not affect the pH of Jogaejeotgal. VBN measures the amount of nitrogen produced during the process of the decomposition of protein into amino acids and inorganic nitrogen as the fish paste deteriorates; it is mainly produced by bacterial decomposition [37,38]. Although the VBN content of the initial fish paste was within the fresh meat range (5–10 mg/%), it decreased further as the plasma treatment time of the fried fish paste increased. This is because the FE-DBD plasma treatment deactivates the activity of endogenous enzymes and spoilage bacteria that form compounds such as ammonia and trimethylamine, which are the primary substances of odor [37,39]. Therefore, nonthermal plasma treatment can increase the quality of processed foods and fish-based products.
5. Conclusions
This study examined the impact of FE-DBD treatment on S. aureus and S. Typhimurium in fried fish paste. Both decreased the most down to 1.13 log10 CFU/g in the 60 min plasma treatment. The survival curve for S. aureus was fitted with a first-order kinetics model (R2 = 0.97), and the D-value was 58.92. The Weibull model was appropriate for S. Typhimurium (R2 = 0.97), and its D-value was confirmed to be 43.60. Although no significant difference (p < 0.05) was observed in the pH of fried fish paste based on plasma treatment time (0–60 min), VBN significantly decreased (p > 0.05) from 8.15 to 3.46 mg/%. The results suggest that the FE-DBD plasma treatment is an effective technique for ensuring microbial safety and preserving food quality.
Author Contributions
Conceptualization, S.H.K. and S.Y.P.; methodology, S.H.K.; software, S.H.K.; validation, S.H.K., P.K.R. and S.Y.P.; formal analysis, S.H.K.; investigation, S.H.K.; resources, S.H.K.; data curation, S.H.K.; writing—original draft preparation, S.H.K. and P.K.R.; writing—review and editing, S.H.K., P.K.R. and E.B.J.; visualization, S.H.K. and P.K.R.; supervision, S.Y.P.; project administration, S.Y.P.; funding acquisition, S.Y.P. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This research was supported by the Basic Science Research Program through the National Research Foundation of Korea (NRF) funded by the Ministry of Education (2021R1I1A3A04037468).
Institutional Review Board Statement
Not applicable.
Informed Consent Statement
Not applicable.
Data Availability Statement
Data are contained within the article.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
References
- Shin, H.Y.; Lee, Y.J.; Park, I.Y.; Kim, J.Y.; Oh, S.J.; Song, K.B. Effect of chlorine dioxide treatment on microbial growth and qualities of fish paste during storage. J. Korean Soc. Appl. Biolo. Chem. 2007, 50, 42–47. [Google Scholar]
- Bashir, K.M.I.; Kim, J.S.; An, J.H.; Sohn, J.H.; Choi, J.S. Natural food additives and preservatives for fish-paste products: A review of the past, present, and future states of research. J. Food Qual. 2017, 2017, 31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ryu, H.S.; Choi, N.D.; Lee, S.Y. Food quality and shelf-life of Korean commercial fried Kamaboko. Korean J. Fish. Aquat. Sci. 2014, 47, 211–219. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Kim, J.H.; Jeon, J.Y.; Ryu, S.R.; Kim, Y.J.; Suh, C.S.; Lee, J.W.; Byun, M.W. Microbial quality and physiochemical changes of grilled fish paste in a group-meal service affected by gamma-irradiation. Korean J. Food Preserv. 2004, 11, 522–529. [Google Scholar]
- Kang, J.H.; Ra, C.H.; Kim, S.H.; Shon, H.W.; Chung, H.Y. Effects of bactocease treatment on microbial growth and quality of fried fish paste during storage. Food Eng. Prog. 2022, 26, 19–26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, J.S.; Cho, M.L.; Heu, M.S. Quality improvement of heart-induced surimi gel using calcium powder of cuttle, Sepia esculenta bone treated with acetic acid. Korean J. Fish. Aquat. Sci. 2003, 36, 198–203. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Butscher, D.; Van Loon, H.; Waskow, A.; von Rohr, P.R.; Schuppler, M. Plasma inactivation of microorganisms on sprout seeds in a dielectric barrier discharge. Int. J. Food Microbiol. 2016, 238, 222–232. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liao, X.; Liu, D.; Xiang, Q.; Ahn, J.; Chen, S.; Ye, X.; Ding, T. Inactivation mechanisms of non-thermal plasma on microbes: A review. Food Control 2017, 75, 83–91. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Misra, N.N.; Tiwari, B.K.; Raghavarao, K.S.M.S.; Cullen, P.J. Nonthermal plasma inactivation of food-borne pathogens. Food Eng. Rev. 2011, 3, 159–170. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Konchekov, E.M.; Gusein-zade, N.; Burmistrov, D.E.; Kolik, L.V.; Dorokhov, A.S.; Izmailov, A.Y.; Shokri, B.; Gudkov, S.V. Advancements in plasma agriculture: A review of recent studies. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2023, 24, 15093. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Graves, D.B. The emerging role of reactive oxygen and nitrogen species in redox biology and some implications for plasma applications to medicine and biology. J. Phys. D Appl. Phys. 2012, 45, 263001. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jeon, E.B.; Choi, M.S.; Kim, J.Y.; Choi, E.H.; Lim, J.S.; Choi, J.S.; Ha, K.S.; Kwon, J.Y.; Jeong, S.H.; Park, S.Y. Assessment of potential infectivity of human norovirus in the traditional Korean salted clam product “Jogaejeotgal” by floating electrode-dielectric barrier discharge plasma. Food Res. Int. 2021, 141, 110107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Adil, B.H.; Al-Shammari, A.M.; Murbat, H.H. Breast cancer treatment using cold atmospheric plasma generated by the FE-DBD scheme. Clin. Plasma Med. 2020, 19, 100103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, M.G.; Roy, P.K.; Jeon, E.B.; Kim, S.H.; Heu, M.S.; Lee, J.S.; Choi, J.S.; Kim, J.S.; Park, S.Y. Effect of Dielectric Barrier discharge plasma against Listeria monocytogenes mixed-culture biofilms on food-contact surfaces. Antibiotics 2023, 12, 609. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, J.H.; Park, C.J.; Kim, C.K. Atmospheric pressure floating electrode-dielectric barrier discharge (FE-DBDs) having flexible electrodes. Korean J. Chem. Eng. Res. 2019, 57, 432–437. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arserim, E.H.; Salvi, D.; Fridman, G.; Schaffner, D.W.; Karwe, M.V. Microbial inactivation by non-equilibrium short-pulsed atmospheric pressure dielectric barrier discharge (cold plasma): Numerical and experimental studies. Food Eng. Rev. 2021, 13, 136–147. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cooper, M.; Fridman, G.; Fridman, A.; Joshi, S.G. Biological responses of Bacillus stratosphericus to floating electrode-dielectric barrier discharge plasma treatment. J. Appl. Microbiol. 2010, 109, 2039–2048. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Joshi, S.G.; Paff, M.; Friedman, G.; Fridman, G.; Fridman, A.; Brooks, A.D. Control of methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus (MRSA) in planktonic form and biofilms: A biocidal efficacy study of non-thermal DBD plasma. Am. J. Infect. Control 2010, 38, 293–301. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ministry of Food and Drug Safety (MFDS). Standard for Food. 2022. Available online: http://various.foodsafetykorea.go.kr/fsd/#/ext/Document/FC (accessed on 30 June 2022).
- Buzrul, S.; Alpas, H. Modeling inactivation kinetics of food borne pathogens at a constant temperature. LWT Food Sci. Technol. 2007, 40, 632–637. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cho, H.S.; Kim, K.H. An evaluation of the physicochemical properties of salted and fermented shrimp for HACPP. J. East Asian Soc. Diet. Life 2009, 19, 395–400. [Google Scholar]
- Aadim, K.A.; Mazhir, S.N.; Abdalameer, N.K.; Ali, A.H. 2020. Influence of gas flow rate on plasma parameters produced by a plasma jet and its spectroscopic diagnosis using the OES technique. IOP Conf. Ser. Mater. Sci. Eng. 2020, 987, 012020. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Svarnas, P.; Giannakopoulos, E.; Kalavrouziotis, I.; Krontiras, C.; Georga, S.; Pasolari, R.S.; Papadopoulos, P.K.; Apostolou, I.; Chrysochoou, D. Sanitary effect of FE-DBD cold plasma in ambient air on sewage biosolids. Sci. Total Environ. 2020, 705, 135940. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ryu, Y.H.; Uhm, H.S.; Park, G.S.; Choe, E.H. Sterilization of Neurospora crassa by noncontacted low temperature atmospheric pressure surface discharged plasma with dielectric barrier structure. J. Korean Vac. Soc. 2013, 22, 55–65. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Özdemir, E.; Başaran, P.; Kartal, S.; Akan, T. Cold plasma application to fresh green leafy vegetables: Impact on microbiology and product quality. Compr. Rev. Food Sci. Food Saf. 2023, 22, 4484–4515. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, J.; Wang, S.Z.; Chen, J.Y.; Chen, D.Z.; Deng, S.G.; Xu, B. Effect of cold plasma on maintaining the quality of chub mackerel (Scomber japonicus): Biochemical and sensory attributes. J. Sci. Food Agric. 2018, 99, 39–46. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abdi, S.; Moslehishad, M.; Dejam, L. Effect of atmospheric pressure floating-electrode dielectric-barrier discharge (FE-DBD) plasma on microbiological and chemical properties of Nigella sativa L. J. Bas. Res. Med. Sci. 2020, 7, 61–69. [Google Scholar]
- Park, Y.K.; Kim, H.J.; Kim, M.H. Quality characteristics of fried fish paste added with ethanol extract of onion. J. Korean Soc. Food Sci. Nutr. 2004, 33, 1049–1055. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, H.P.; Kim, B.; Choe, J.H.; Jung, S.; Moon, S.Y.; Choe, W.H.; Jo, C.R. Evaluation of atmospheric pressure plasma to improve the safety of sliced cheese and ham inoculated by 3-strain cocktail Listeria monocytogenes. Food Microbiol. 2009, 26, 432–436. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fujii, J.; Homma, T.; Osaki, T. Superoxide radicals in the execution of cell death. Antioxidants 2022, 11, 501. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lu, H.; Patil, S.; Keener, K.M.; Cullen, P.J.; Bourke, P. Bacterial inactivation by high-voltage atmospheric cold plasma: Influence of process parameters and effects on cell leakage and DNA. J. Appl. Microbiol. 2014, 116, 784–794. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mann, M.S.; Tiede, R.; Gavenis, K.; Daeschlein, G.; Bussiahn, R.; Weltmann, K.D.; Emmert, S.; Woedtke, T.V.; Ahmed, R. Introduction to DIN-specification 91315 based on the characterization of the plasma jet kINPen® MED. Clin. Plasma Med. 2016, 4, 35–45. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Choi, M.S.; Jeon, E.B.; Kim, J.Y.; Choi, E.H.; Lim, J.S.; Choi, J.S.; Park, S.Y. Impact of non-thermal dielectric barrier discharge plasma on Staphylococcus aureus and Bacillus cereus and quality of dried blackmouth angler (Lophiomus setigerus). J. Food Eng. 2020, 278, 109952. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Park, S.Y.; Kang, S.J.; Ha, S.D. Inactivation of murine norovirus-1 in the edible seaweeds Capsosiphon fulvescens and Hizikia fusiforme using gamma radiation. Food Microbiol. 2016, 56, 80–86. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Calsolari, A. Microbial death. In Physiological Models in Microbiology; CRC Press: Boca Raton, FL, USA, 2018; pp. 1–44. [Google Scholar]
- Buzrul, S. The Weibull model for microbial inactivation. Food Eng. Rev. 2022, 14, 45–61. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bahmani, Z.A.; Rezai, M.; Hosseini, S.V.; Regenstein, J.M.; Boehme, K.; Alishahi, A.; Yadollahi, F. Chilled storage of golden gray mullet (Liza aurata). LWT Food Sci. Technol. 2011, 44, 1894–1900. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qian, Y.F.; Cheng, Y.; Ye, J.X.; Zhao, Y.; Xie, J.; Yang, S.P. Targeting shrimp spoiler Shewanella putrefaciens: Application of ε-polylysine and oregano essential oil in Pacific white shrimp preservation. Food Control 2021, 123, 107702. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liao, X.; Su, Y.; Liu, D.; Chen, S.; Hu, Y.; Ye, X.; Wang, J.; Ding, T. Application of atmospheric cold plasma-activated water (PAW) ice for preservation of shrimps (Metapenaeus ensis). Food Control 2018, 94, 307–314. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).