Abstract
The effect of the extraction conditions on the DPPH radical scavenging activity and isolation of bioactive compounds from the maca (Lepidium meyenii) root was investigated. Different extraction techniques (maceration, maceration with shaking, ultrasound-assisted extraction, and reflux extraction) were compared. Moreover, the effect of the extraction time and two various solvents (water and ethanol) was studied. The antioxidant activity of extracts was determined by the spectrophotometric method with the DPPH radical, while total phenolic content (TPC) was analyzed by the Folin–Ciocalteu method. Using gas chromatography with a mass selective detector (GC-MS), some characteristics of maca bioactive compounds were identified in the extracts: benzylalkamides (macamides), sterols, nitriles, fatty acids, and their derivatives. The influence of various factors on the extraction process of health-promoting antioxidant compounds from maca root was discussed. It was found that water was a more effective solvent than ethanol for obtaining extracts characterized by high radical scavenging activity and phenolics content. Nevertheless, some ethanol-extractable valuable compounds specific for maca, e.g., macamides or fatty acids derivatives, were not present in water extracts. In developing nutritional and therapeutic formulations based on maca extracts, it is important to take into account that the bioactivity of maca extracts varies depending on the solvent used.
1. Introduction
Today, both scientists and consumers are looking for food of natural origin that would have a health-promoting effect on the human body and could be used in a daily diet. In this search, more and more often, plants are used that have been used as dietary components for centuries, but they have also been used as medicinal plants in folk medicine on many continents, including natural medicine, which developed in China, India, and in the countries of North and South America. Such plants are often characterized by specific properties, and it is difficult to find their equivalents in our daily diet. The biologically active compounds contained in these plants are mostly not used in modern medicine, which very often uses biologically active compounds obtained by chemical synthesis. Often, single biologically active substances are not as active as extracts obtained from plants with healing and nutritional effects, which contain compositions of many ingredients that can have a health-promoting effect on our body and often support each other in this action (synergistic effect). An example of such a plant is maca (Lepidium meyenii Walp.). Maca has been used for centuries by the Indians inhabiting the Peruvian Andes as a dietary ingredient (it has been considered a superfood) but also as a medicinal plant (increasing concentration, energy, alertness, mental abilities, improving mood, physical resistance, as well as improving sexual function and fertility) [1].
L. meyenii is a plant that currently grows only in some regions of Peru at an altitude of 2000 to 5000 m above sea level. It grows in a zone with low temperatures and strong winds; in addition, this plant is exposed to strong UV radiation and low oxygen levels. Despite such difficult conditions, maca perfectly adapts to them [1,2,3]. The main medicinal raw material of this plant is the root (leaves are used as animal feed), which resembles a beetroot or, less often, a pear. The root can reach approximately 20 cm in circumference (its diameter varies from 2 to 8 cm). There are several varieties of maca differing in the color of the above-ground part and roots. The root is usually similar in color to a potato, but there are also roots covered with white, yellow, white-pink, white-purple, red, purple, and even black skin [1,2]. The leading producer of L. meyenii is Peru, while the countries where maca enjoys great consumer interest and is eagerly bought are the USA, Canada, Great Britain, Germany, China, Japan, and the Netherlands. There are also attempts to cultivate this plant on a large scale on other continents, e.g., in Asia (in China in Yunnan Province) [1]. Maca roots are used fresh (raw or baked), processed into jam or a sweet, fermented drink, dried (dried roots can be stored for up to 7 years), and macerates are also prepared from them. There are commercially available pills or capsules containing powdered maca root, flour (dried and milled), gelatinized flour (dried, extruded, and milled), plain or encapsulated hydroalcoholic extracts, liqueurs, mayonnaises, chocolate, coffee, and tonic drinks [1,2,3,4].
Maca roots contain many compounds with nutritional and pharmacological significance, such as starch, dietary fiber, protein, minerals, vitamins, essential amino acids, non-starch polysaccharides, polyphenols (e.g., flavonolignans), macaenes and macamides (the specific and unique unsaturated acids and amides present only in maca), glucosinolates, and macahydantoins [1,2,3,4,5,6,7]. Thanks to these ingredients, maca has a positive effect on our health [1,2,4,5]. L. meyenii, due to its nutritional properties, can be used in human malnutrition, as well as during growth or pregnancy [2]. The ingredients contained in the maca root have the following biological effects: neuroprotective (improving memory and learning ability, preventing the development of diseases such as Parkinson’s and Alzheimer’s) [1,2,4,5], antioxidant [1,4], antifatigue (energizing effect, increasing muscle endurance, treatment of chronic fatigue syndromes, depression) [2,4,5], anticancer (stomach cancer) [1,4], liver protective [1,4], and immunomodulatory (treatment of tuberculosis) [2]. In addition, maca is used in the treatment of hormonal disorders associated with menopause and andropause [2,4,5], prevents insomnia [2] and osteoporosis [2], and also has antiarthritic properties [2]. It is recommended to use it during convalescence and as a tonic in old age [2,4]. Maca has a bacteriostatic and fungistatic effect (this action is due to mustard oils contained in their composition) [1,2,5] and can promote wound healing [2,5]. Moreover, the antiviral activity of this plant has been demonstrated (tests were performed on human influenza A and B viruses) [5]. Maca has also been observed to prevent and mitigate UV-induced skin damage and accelerate wound healing at high altitudes [3,5]. Maca can also prevent the development of diabetes—lower glucose levels and a lower degree of lipid sedimentation were observed during studies [3,7]. Scientific research also indicates that maca roots could be considered a promising candidate as an antihypertensive drug [6]. Other studies indicate the effectiveness of maca in improving fertility and sexual functions: it improves the quality of a man’s semen, increases a woman’s ability to conceive, relieves the symptoms of premenstrual tension, and stimulates the maturation of Graafian follicles [1,4,8,9,10].
Particularly interesting and worth further research are the antioxidant properties of compounds contained in the maca root, which can be obtained in the form of extracts. Information on the antioxidant activity of extracts obtained from maca may in the future be used in research on the prevention and treatment of such diseases as atherosclerosis, asthma, diabetes, cancer, rheumatoid arthritis or in the prevention of neurodegenerative diseases associated with old age, such as Parkinson’s and Alzheimer’s. In the scientific literature, there are reports related to the antioxidant activity of maca, but some aspects still should be expanded, especially various comparative studies are needed. Particular attention should be paid to the development of effective methods for obtaining maca extracts, as well as the development of effective methods for determining their composition.
The aim of this work was to determine the effect of various extraction conditions on the DPPH radical scavenging activity and the isolation of phenolics and other bioactive compounds from maca root (L. meyenii). A comparison of different extraction techniques, including maceration, maceration with shaking, ultrasound-assisted extraction, and reflux extraction using two popular solvents (ethanol and water) and different extraction times, was carried out. The antioxidant activity of extracts obtained in various conditions was determined by using a DPPH radical scavenging activity method, and total phenolic content was analyzed by the Folin–Ciocalteu method. Moreover, the composition of ethanolic and water extracts was compared by means of gas chromatography with the mass selective detector method (GC-MS).
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Plant Material—Origin and Composition
The studied plant material was a commercially available powdered root of maca (L. meyenii) that originated from Peru (producer: Purella, Warsaw, Poland). A characteristic of the product delivered by the producer states that the contents of the main constituents per 100 g are as follows: carbohydrates 55 g, fiber 22 g, protein 11 g, and fat 1.2 g. The micronutrient contents are niacin 10 mg, riboflavin 0.43 mg, magnesium 100 mg, potassium 1580 mg, calcium 260 mg, iron 4.5 mg, and copper 0.75 mg per 100 g of product. A suggested portion of daily consumption is 1 spoon (3 g), added to a cup of hot drink (120 mL).
2.2. Extraction Techniques and Procedures
Maca root was subjected to extraction by using 2 different solvents: ethanol 96% (Stanlab, Poznan, Poland) and demineralized water. The experiments were performed by the application of four different extraction techniques: maceration (M), maceration with shaking (MSH), ultrasound-assisted extraction (UAE), and reflux extraction (RE). Moreover, the influence of the extraction time was also studied for each method by performing processes at 15, 30, and 60 min.
In all experiments, 0.50 g of maca root and 20 mL of solvent (water or 96% ethanol) was used, which was in accordance with the proportions recommended by the producer. The plant material and solvent were placed in a 50-mL round bottom flask and subjected to the extraction process. In the case of maceration and maceration with shaking processes, which were conducted at room temperature (21 °C), the flasks were equipped with round glass stoppers. Reflux extraction and ultrasound-assisted extraction were performed in the 50-mL round bottom flasks equipped with the reflux condensers, using a water bath (temperature setting: 95 °C) and a Sonis 4 (Iskra PIO, Šentjerna, Slovenia) ultrasonic bath (75 W, 40 kHz frequency). During UAE processes, the temperature in the ultrasonic bath increased from room temperature to 27 °C (15 min), 35 °C (30 min), and 44 °C (60 min), respectively. After completing the extraction process, samples were left for 5 min for a plant material decantation. During this time, samples from reflux extraction and ultrasound-assisted extraction were also cooled using running water at room temperature. Next, decanted extracts were subjected to centrifugation for 15 min at 2320 RCF using an MPW-223e Centrifuge (MPW Med. Instruments, Warsaw, Poland) to obtain clear samples for the analyses.
2.3. Analysis of the Antioxidant Activity
Antioxidant properties of obtained extracts were investigated spectrophotometrically by the DPPH method [11] and with the Folin–Ciocalteu reagent [12]. The analyses were carried out using a 1600PC UV–VIS spectrophotometer (VWR International) in 1 cm cuvettes. A radical scavenging activity of extracts was determined using the DPPH method with a 2,2-diphenyl-1-picrylhydrazyl radical (DPPH). For this purpose, a 0.002 mM/mL stock solution of DPPH in methanol was freshly prepared before analysis. To prepare a DPPH working solution, 3 mL of the stock solution was diluted with methanol to 50 mL in a volumetric flask, protected from light by aluminum foil. Next, to 0.5 mL of the extract, 3 mL of the DPPH working solution was added, mixed, and left in darkness for 30 min. A reference sample containing 0.5 mL of solvent was prepared analogously. All analyses were carried out in 3 repetitions, and the absorbance was measured at 517 nm. The radical scavenging activity (RSA) of maca extracts was calculated from the absorbance of the sample after 30 min incubation (A30) and the absorbance of reference sample A0, using the following formula:
RSA [%] = 100 (A0 − A30)/A0
The results of DPPH radical scavenging activity measurements were also expressed as Trolox Equivalents Antioxidant Capacity (TEAC). For this purpose, the RSA values of various concentrations of Trolox (Acros Organics, Geel, Belgium) standard solutions were determined, and a calibration curve of RSA [%] vs. CTrolox [µM/L] was prepared. The obtained linear regression equation in the range of linearity (concentrations: 0.01–0.030 µM/L) was used for the calculation of TEAC [µM/L] for maca extracts obtained in various conditions. To determine the content of phenolic compounds extractable by ethanol and water in specific conditions, total phenolic content analysis was performed using the Folin–Ciocalteu (F–C) method. For this purpose, 0.5 mL of the extract, 0.5 mL of a Folin–Ciocalteu reagent (Chempur, Piekary Slaskie, Poland), and 1.5 mL of freshly prepared sodium carbonate solution (C = 200 mg/mL) were placed in a 25-mL volumetric flask, filled up to the mark with demineralized water, mixed and left for blue color development. After 30 min, the absorbance at 760 nm was measured for the extract samples and the reference samples (in 3 repetitions). The total phenolic content (TPC) was expressed as mg of Gallic Acid Equivalent per 1 L of the extract [mg GAE/L]. To create a calibration curve, gallic acid (Sigma-Aldrich) was used as a standard, and the analyses of standard solutions in a concentration range of 10–500 mg/L using the same procedure were performed.
2.4. GC-MS Analyses
For the GC-MS analyses, 10-fold more concentrated extracts were prepared using 0.50 g of the plant material in 2 mL of solvent. Extracts were prepared by the UAE method (60 min) followed by the described above procedure of decantation and centrifugation. The analysis of the obtained extracts was carried out using a 6890N gas chromatograph with a 5973 Network Mass Selective Detector (Agilent Technologies) equipped with an HP-5MS capillary column (5%-phenyl 95%-methylpolysiloxane, 30 m × 0.25 mm × 0.25 μm). The initial column temperature was 80 °C, and it increased at 5 °C/min to 320 °C. The applied Mass Selective Detector temperatures were, respectively, quadrupole 150 °C and ion source 230 °C. The carrier gas was helium (1.2 mL/min). The samples of extracts (3.0 μL) were dosed to a column in a split mode (10:1) using a 7683 Series Injector Autosampler. Electron impact ionization (70 eV) mass spectra were recorded in the range of 20–600 m/z. Identification of the particular compounds present in the obtained extracts was carried out by the comparison of their mass spectra with the mass spectra of standards from the NIST 04 library and with literature data. The quantitative GC-MS analysis was performed using an area normalization method. The relative contents [%] of particular compounds in extracts were determined as the percentages of their peak areas in a total peak area of all compounds on a chromatogram using the MestReNova 10.0.2 software.
2.5. Statistical Analysis
All determinations were carried out in at least three replicates. Statistical analysis was performed using StatSoft Statistica 13.0 (STATISTICA 13.0; StatSoft Inc., Palo Alto, CA, USA) and Microsoft Excel 2017. Distributions of values for individual parameters were analyzed using the Shapiro–Wilk test. Since the distribution of continuous variables deviated from normal, the Test Kruskal–Wallis was used to evaluate the differences between the studied parameters. Results were expressed as mean values and standard deviation (mean ± SD); however, the statistical significance of differences was determined based on median, upper quartile, and lower quartile. Spearman’s correlation test was used to determine the correlations between the parameters studied. Differences were considered significant at p ≤ 0.05. To control type I errors, the false discovery rate (FDR) approach was used. The calculations were performed using the p. adjust function of the stats package in R (R Foundation for Statistical Computing, Vienna, Austria, https://cran.r-project.org, accessed on 10 February 2023).
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. Antioxidant Activity of Maca Extracts
The results of the antioxidant activity of maca extracts obtained using two solvents (96% ethanol and water) in various extraction conditions are collected in Table 1.

Table 1.
DPPH radical scavenging activity and total phenolic contents of maca (L. meyenii) root extracts obtained using ethanol or water as the solvent in various extraction conditions.
Table 2 presents the descriptive statistics of the tested variables as follows: minimum, maximum, mean, standard deviation, median, lower quartile, and upper quartile. The values of antioxidant potential expressed as RSA ranged from 6.94% to 75.32%; the mean value was 47.45, and the median was 50.00%. The values of antioxidant activity expressed as TEAC ranged from 14.96 µM TE/L to 231.16 µM TE/L, with a mean value of 143.06 and a median of 151.11 µM TE/L. The lowest content of phenolic compounds was 2.09 mg GAE/L, and the highest was 138.45 mg GAE/L. In this case, the mean value was 82.73, and the median was 86.41 mg GAE/L.

Table 2.
Descriptive statistics of the tested variables.
Our studies of maca root extracts obtained using two different solvents and in various conditions enabled the determination of the influence of extraction conditions on the DPPH radical scavenging activity and total phenolic content of these extracts.
As can be seen in Table 1, DPPH scavenging activity expressed as TEAC varied for ethanolic extracts from 16.3 µM TE/L in the case of 15-min maceration (E 15 M) to about 150.2 µM TE/L for 15-min reflux extraction (E 15 RE). TEAC values for water extracts were significantly higher and ranged from 147.0 µM TE/L in the extract obtained by 15-min maceration (W 15 M) to about 229.6 µM TE/L in the case of 60-min maceration with shaking (W 60 MSH). Interestingly, for water extraction, a simple enhancement of maceration by shaking (MSH) in 30 and 60-min processes led to higher TEAC values than the application of ultrasounds (UAE) or higher temperature (RE). Detailed statistical analysis of correlations between the extraction time and DPPH radical scavenging activity showed that statistically significant positive correlations were found in the water extract for the M and MSH techniques (r = 0.948) and UAE (r = 0.859). In the case of the RE, the correlation was statistically significant but negative (r = −0.846), which indicates that the longer the extraction time, the lower the antioxidant potential of the water extract. Similar relationships were found in the alcoholic extract; in the M, MSH, and UAE methods, the relationships were positive and statistically significant (r = 0.948 for M and UAE and r = 0.895 for MSH). The exception was the RE technique, where a small negative but statistically insignificant correlation was found.
Analyzing the results of total phenolic contents, some similarities can be seen between the observed trends compared to DPPH radical scavenging activity. The extraction of phenolic compounds was also significantly more effective using water than ethanol. TPC values obtained for ethanolic extracts varied from 3.2 mg GAE/L (E 15 M) to 95.3 mg GAE/L (E 60 RE). Using ethanol as a solvent, the best technique for the isolation of phenolic compounds was reflux extraction (RE). Regardless of the technique used, the highest phenolics content was found after 60 min extraction. The application of water as the solvent resulted in a significantly higher content of phenolic compounds; even for the 15-min maceration, the result was 73.2 mg GAE/L (W 15 M), while the prolongation of maceration to 60 min gave the result of 111.2 mg GAE/L, being higher than the best result obtained in 60-min reflux extraction with ethanol. Isolation of phenolic compounds using water was effectively enhanced by shaking, application of ultrasounds, and higher temperature. The best result of 136.9 mg GAE/L was obtained in the 60-min ultrasound-assisted extraction (W 60 UAE) process, but it is worth noticing that maceration with shaking (MSH) was also very effective. In the case of the RE method, the extraction time had an adverse effect because the content of polyphenols slightly decreased. An in-depth analysis of the correlation between the extraction time and the content of phenolic compounds showed statistically significant positive correlations for water extraction by using M, UAE (r = 0.948), and MSH (r = 0.843) techniques, which indicates that the prolongation of extraction resulted in higher content of phenolic compounds. In the case of alcoholic extracts, significant positive correlations were found between the extraction time and the content of phenolic compounds (r = 0.948 for M, MSH, RE, and r = 0.952 for UAE).
Generally, in most cases, the prolongation of the extraction time, especially to 60 min, positively influenced DPPH scavenging activity and the amount of extracted phenolic compounds, but this trend was not observed in reflux extraction (RE), maybe due to possible decomposition processes of active compounds at higher temperatures. Nevertheless, statistical analysis of the differences among the results indicated that regardless of the extraction technique, the obtained values of both radical scavenging activity and total phenolic content in various extraction times were not statistically significant (FDR > 0.05).
For better illustration and proper interpretation of the obtained results, the graphical visualization of the influence of maca extraction conditions on DPPH radical scavenging activity was carried out. The comparison of the antioxidant potential expressed as the RSA (%) for extracts obtained in various conditions using 96% ethanol as a solvent is presented in Figure 1, while using water is in Figure 2. It was found that RSA values for ethanolic extracts varied from 7.4% in the case of the 15-min maceration (E 15 M) to 49.7% for the 15-min reflux extraction (E 15 RE). The application of water as the solvent was definitively more effective and resulted in RSA values of 48.7% for the 15 min maceration (W 15 M) to 74.8% for the 60-min maceration with shaking (W 60 MSH), which was the best result obtained among all studied process conditions. Both in the case of water and ethanol extraction, for the M, MSH, and UAE techniques, the highest values of the antioxidant potential were found for the longest extraction time (60 min), while for the RE technique, RSA slightly decreased with the prolongation of the extraction time. The observed differences among various extraction times were not statistically significant (FDR > 0.05).
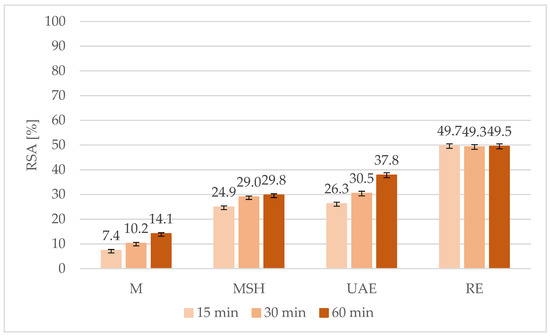
Figure 1.
Influence of extraction technique and conditions on DPPH radical scavenging activity of maca extracts obtained using 96% ethanol as the solvent (M—maceration; MSH—maceration with shaking; UAE—ultrasound-assisted extraction; RE—reflux extraction).
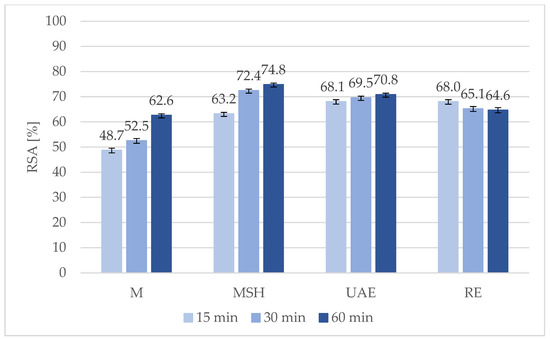
Figure 2.
Influence of extraction technique and conditions on DPPH radical scavenging activity of maca extracts obtained using water as the solvent (M—maceration; MSH—maceration with shaking; UAE—ultrasound-assisted extraction; RE—reflux extraction).
Since the majority of studied isolation processes showed the best results were obtained for 60 min of extraction, all the results obtained for this time variant using DPPH radical scavenging activity method are compared in Figure 3.

Figure 3.
Comparison of RSA values for maca extracts obtained in 60-min extraction processes using 96% ethanol and water as the solvent (M—maceration; MSH—maceration with shaking; UAE—ultrasound-assisted extraction; RE—reflux extraction); * statistically significant differences among the results obtained using two different solvents at p < 0.05.
The presented graph clearly shows that after 60 min for all extraction techniques, radical scavenging was significantly higher for water extracts than for ethanolic extracts obtained in the same conditions (p < 0.05). Performing the statistical analysis of all results for 60-min processes, it was proved that the ethanolic extract with the highest antioxidant potential was obtained by the reflux extraction (RE), while for water extraction, the best results were obtained by the maceration with shaking (MSH) technique. Importantly, in both cases, the differences in the antioxidant potential of extracts obtained in the best conditions and obtained by using the other techniques were statistically significant (p < 0.05).
Moreover, a correlation analysis between the two applied methods, DPPH and Folin–Ciocalteu, was also carried out. For water extracts, it was found that there were statistically significant positive correlations between phenolic compounds content and antioxidant potential for M, MSH, and UAE techniques (r = 0.950; r = 0.800, and r = 0.766, respectively). In the case of alcoholic extracts, the situation was analogous—the relationships between the antioxidant potential and the content of phenolic compounds were high and significant for the M, MSH, and UAE techniques (r = 0.900; r = 0.866, and r = 0.945, respectively). Such relationships were not found for reflux extraction (RE). The reason may be the possible degradation processes of some active compounds at the higher temperature during the prolonged water extraction, resulting in the observed trends in the decreasing of the total phenolic content and DPPH radical scavenging activity values, which was not observable for the extraction using ethanol. This fact needs further studies for a detailed explanation.
Studies reported in the literature so far indicate that maca contains several antioxidant compounds. The amounts of these compounds depend on the soil composition, varieties of the plant, harvest time, drying process, and extraction method. The main antioxidant compounds contained in maca include phenols, glucosinolates, alkamides, and polysaccharides. The antioxidant activity of L. meyenii may also be connected with the concentration of the extract and the microenvironment in which the active compound is located [3]. It was also described that maca contains water-soluble scavengers that may contribute to the decomposition of peroxyl radicals produced during inflammatory states. This antioxidant activity was connected with isothiocyanate content in maca. Studies on isothiocyanates have shown that these compounds have antioxidant activities and anticarcinogenic properties [4]. As there are strong indications that cardiovascular diseases are associated with the accumulation of free radicals in the body, Ibrahim et al. [6] evaluated the antioxidant potential of four extracts from maca (aqueous extract, 50% methanolic extract, dichloromethane extract, and methanolic extract) using the following methods: DPPH, ABTS, and FRAP. The results showed that the methanolic extract exhibited the most potent antioxidant activity. Sandoval et al. [13] evaluated the antioxidant activity of the aqueous extract of maca. They demonstrated that maca degraded free radicals, ameliorated peroxynitrite induced-cell death, and protected cells against hydrogen peroxide by maintaining the intracellular production of ATP. These results indicated that maca has the ability to scavenge free radicals and provides cytoprotection during oxidative stress conditions. Lee et al. [14] examined the antioxidant activities of the methanol extracts of maca leaves and roots. They identified 25 compounds in extracts (saponins, phenols, flavonoids, steroids, alkylbenzenes, and amines). Among the identified compounds, three saponins (tanshinone I, panaxytriol, and rotundifolioside), one phenol (gingerol), and one steroid (ergosterol peroxide) were found in both leaf and root extracts. Antioxidant activities (1,1-diphenyl-2-picrylhydrazyl radical scavenging activity and ferric reducing ability of plasma) of the methanol extracts of maca leaves were higher than those of the roots, and the antioxidant activities were highly correlated with total phenol content in the methanol extracts of maca leaves. Wang et al. [15] studied the antioxidant activities of six different solvent extracts (petroleum ether extract, chloroform extract, ethyl acetate extract, n-butanol extract, ethanol extract, and deionized water extract) obtained from L. meyenii. In the studies on antioxidant activities, they used the methods of scavenging activities towards 1,1-diphenyl-2-picryhydrazyl (DPPH) radical, superoxide radical, and hydroxyl radical. The extracts showed different levels of antioxidant activity. The antioxidant extract obtained using n-butanol had the highest amounts of phenolic content and antioxidant activity, as well as free radical-scavenging activity, indicating their potential application in the food industry as functional food components or food antioxidants. You et al. [16] developed the maceration-based method for extraction of phenolic compounds, flavonoids, soluble proteins, sugars, and macamide B from maca using 95% ethanol and an acidified ethanol. Optimal extraction was achieved at 40–60 °C for 5–7.5 h with the solvent-to-solid ratio of 100:10. The addition of hydrochloric acid (HCl) to ethanol significantly improved the extraction yield, and maximum extraction was achieved using 1 N solution of HCl in ethanol. The radical-scavenging activity of the ethanolic extracts showed a significant linear correlation with the total extraction yield of phenolic compounds, soluble proteins, and sugars. These results showed that polyphenolic compounds, proteins/peptides, and polysaccharides are important determinants for the antioxidant function of maca. Gan et al. [17] also tested the antioxidant capacity of maca. In these studies, chloroform was used as the solvent. The obtained results showed that alkaloids and phenols were the most important substances for the antioxidative properties of maca, but the antioxidant effect of alkaloids seemed to be higher than that of phenols.
Studies on the antioxidant capacity of polysaccharides separated from maca have also been described in the scientific literature. In studies performed by Zha et al. [18], maca was extracted with hot water (80 °C, 1 h). Next, water-soluble polysaccharides were separated from maca aqueous extract and deproteinized by the Sevag method. During the preparation process of maca polysaccharides, amylase and glucoamylase effectively removed starch in maca polysaccharides. Four L. meyenii polysaccharides were obtained by changing the concentration of ethanol in the process of polysaccharide precipitation. All of the polysaccharides were composed of rhamnose, arabinose, glucose, and galactose. Antioxidant activity tests revealed that all polysaccharides showed the capability of scavenging hydroxyl free radicals and superoxide radicals. The antioxidant capacity of polysaccharides obtained from maca has also been confirmed in the publication of Zhang et al. [19].
3.2. GC-MS Analysis of Maca Extracts
The application of the GC-MS method enabled the comparison of the composition of extracts obtained using two various solvents: 96% ethanol and water. The chromatograms of ethanolic and water extracts are shown in Figure 4, while the GC-MS results are in Table 3.
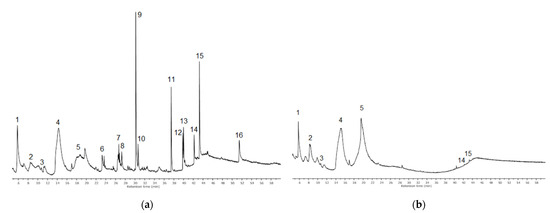
Figure 4.
GC-MS chromatograms of ethanolic (a) and water (b) extracts of maca (L. meyenii) root (peaks numbered according to Table 3).

Table 3.
Compounds identified in ethanolic (E) and water (W) extracts of maca (L. meyenii) root extracts by the GC-MS method.
GC-MS analysis allowed for the identification of 12 compounds present in maca extracts and for the comparison of their relative contents, although some compounds remained not identified (e.g., peaks no. 4, 5, 16). Mass spectra of three macamides characteristic of maca, which were present in ethanolic extracts, are shown in Figure 5.
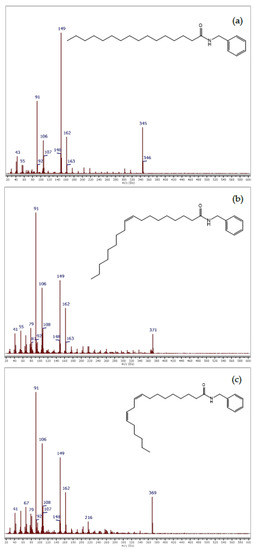
Figure 5.
Mass spectra of macamides: N-benzylhexadecanamide (a), N-benzyl-(9Z)-octadecenamide (b), and N-benzyl-(9Z,12Z)-octadecadienamide (c), identified in ethanolic extracts of maca (L. meyenii) root.
The GC-MS analyses of extracts showed that among maca components that were volatile enough and not too polar to be directly analyzed by this method, there were some nitriles, fatty acids, amides, and sterols. Analyzing the results of GC-MS analyses, it is clearly visible that using ethanol as the solvent resulted in the isolation of a wider variety of bioactive compounds than using water. Importantly, in ethanolic extracts, three compounds from the group of characteristics for maca benzylalkamides (macamides) were found: N-benzylhexadecanamide, N-benzyl-(9Z,12Z)-octadecadienamide and N-benzyl-(9Z)-octadecenamide, as well as other fatty acids amides: hexadecanamide, (9Z)-octadecenamide and octadecanamide. These compounds were not extractable by water and are not present on the chromatogram of water extract shown in Figure 4, similar to hexadecanoic acid and linoleic acid. Both macamides and fatty acids derivatives are valuable bioactive compounds that were previously identified in maca by UPLC-QTOF-MS [20] and HPLC-MS [21] methods. Comparing the obtained GC-MS data, it should be pointed out that ethanolic extract also contained significant amounts of sterols: β-sitosterol and campesterol, which are known for their bioactive properties and pharmacological effects, including high antioxidant activity [22], while in water extract their contents were only on the trace level.
Very interesting is that water extracts were characterized by significantly higher antioxidant activity, despite the absence of important bioactive compounds which were found in ethanolic extracts by the GC-MS analysis. It can be explained by the presence of water-soluble polysaccharides, being one of the main maca components characterized by high antioxidant activity, which are not soluble in ethanol [18,19]. It should be taken into consideration that water-soluble sugars can interact with the Folin–Ciocalteu reagent, which can lead to an overestimation of the TPC results obtained for the water extracts [23].
Because of the high polarity due to the presence of hydroxyl groups, direct analysis of polysaccharides by the GC-MS method is not possible, but visible on the chromatograms are non-symmetric wide peaks indicated as the unknown compounds I and II (No. 4 and 5), could probably be products of their degradation, what can be deduced from the characteristic for saccharides signals in their mass spectra (e.g., 57, 73, 43, 31 m/z) and a specific wide shape of their peaks, characteristic for highly polar compounds. Besides polysaccharides, observed antioxidant activity can also be related to other important bioactive compounds from the group of glucosinolates, which were identified in maca by HPLC and UPLC-ESI-MS methods [18,24]. Due to the high polarity, their analysis by the GC-MS method was also not possible, but identified in both ethanolic and water extracts, benzyl nitryl and benzyl isothiocyanate are probably the products of enzymolytic decomposition of maca glucosinolates. As described in the literature, naturally occurring maca enzyme myrosinase is stored in myrosin cells, and during the crushing of plant tissues, it is released, causing hydrolysis of glucosinolates, which results in the formation of isothiocyanates, thiocyanates, nitryles, and other products [25]. Another compound identified in maca extracts by the GC-MS method is 5-hydroxymethylfurfural (5-HMF), and its relative content in water extract (6.6%) was about 2.5-times higher than in ethanolic extract (2.6%). 5-HMF was found in various food samples as a product of the Maillard reaction between amino acids and reducing sugars. Apart from some controversial information related to the possible toxicity of this compound, there are studies indicating its high antioxidant and antiproliferative activity [26].
Summarizing, despite the limitations of the direct GC-MS analysis, the application of this method enabled the identification of some important bioactive compounds and the comparison of their content in water and ethanolic extracts from maca, which has not been reported in the literature so far.
4. Conclusions
From the obtained data on the radical scavenging activity and total phenolic content in maca root extracts, it can be concluded that for all studied extraction techniques, using water as the solvent was more effective than using ethanol. Presented results indicate that the simple maceration process can be effectively enhanced by different factors: shaking, ultrasounds, and using higher temperatures. In most cases, the prolongation of the extraction time, especially to 60 min, positively influenced the antioxidant activity and amount of extracted phenolic compounds; however, this trend was not observed during reflux extraction, possibly due to some degradation processes at high temperatures. The extract with the highest scavenging activity against the DPPH radical (RSA = 74.8%; TEAC = 229.6 µM TE/L) was obtained in the 60-min maceration with shaking (MSH) using water. The 60-min ultrasound-assisted extraction (UAE) using water was the most effective process for the isolation of phenolic compounds (TPC = 136.9 mg GAE/L). Nevertheless, it should be noted that the effectiveness of phenolics isolation in the 60-min maceration with shaking (MSH) was only slightly lower (TPC = 128.2 mg GAE/L). Because it is easier, more economical, and environmentally friendly in comparison to the UAE method, maceration with shaking can be recommended for the extraction of maca using water to obtain extracts characterized by high antioxidant activity and high content of phenolic compounds. In turn, using ethanol as the solvent, the best results were obtained using the reflux extraction (RE) technique, where even a 15-min process was more effective than other applied techniques, but prolonged to 60 min allowed for obtaining an extract with the highest content of phenolic compounds (TPC = 95.3 mg GAE/L) with the DPPH scavenging activity characterized by RSA = 49.5% and TEAC = 149.5 µM TE/L.
Moreover, the comprehensive analysis of data obtained from spectrophotometric and chromatographic analyses led to the conclusion that the antioxidant activity of maca extracts is the result of the presence of various bioactive compounds whose profiles differ in water and alcoholic extracts. Consequently, the specific bioactivity of extracts obtained using water and ethanol will be different, which should be taken into account during the development of some formulations on the basis of maca extracts. It is worth noticing that water extracts, although characterized by better antioxidant properties, do not contain some valuable compounds specific for maca, such as present in ethanolic extracts macamides or fatty acids derivatives, which may be responsible for some characteristic neuroprotective, neuromodulatory, anti-fatigue, or other effects.
These studies contribute to expanding the knowledge on the influence of extraction conditions on the composition and radical scavenging activity of maca extracts and can be useful in the elaboration of the appropriate conditions for the effective isolation of the bioactive compounds. The results can be applied in the development and optimization of extraction processes of maca active ingredients in order to obtain dietary supplements characterized by the best antioxidant properties and containing the highest amount of health-promoting compounds.
Given the great interest in maca and its compounds, not only as food ingredients but also as therapeutic agents, the research presented in this paper has great potential and should be further developed. One of the directions of research carried out in the future may be the search for more effective extraction methods and appropriate solvents for these methods. In terms of medical applications, maca roots have been mostly described in the literature so far, while the above-ground parts of this plant are mainly used as animal feed. A new direction could also be to investigate the therapeutic potential of the ingredients contained in maca above-ground parts, which could lead to another possible way of utilizing the waste parts of this precious plant.
Author Contributions
Conceptualization, M.D., A.W. and K.J.-M.; methodology, M.D. and K.J.-M.; software, M.D., A.W. and K.J.-M.; validation, M.D., A.W. and K.J.-M.; formal analysis, A.W.; investigation, M.D., A.W. and K.J.-M.; resources, M.D., A.W. and K.J.-M.; data curation, M.D., A.W. and K.J.-M.; writing—original draft preparation, M.D.; writing—review and editing, M.D., A.W. and K.J.-M.; visualization, M.D. and K.J.-M.; supervision, A.W.; project administration, M.D., A.W. and K.J.-M.; funding acquisition, A.W. and K.J.-M. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This research received no external funding.
Institutional Review Board Statement
Not applicable.
Informed Consent Statement
Not applicable.
Data Availability Statement
The data presented in this study are available on request from the corresponding authors.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
References
- Wang, S.; Zhu, F. Chemical composition and health effects of maca (Lepidium meyenii). Food Chem. 2019, 288, 422–443. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Żurawska, K. Ziołolecznictwo Amazońskie i Andyjskie; Tower Press: Gdańsk, Poland, 2001. [Google Scholar]
- da Silva Leitao Peres, N.; Cabrera Parra Bortoluzzi, L.; Medeiros Marques, L.L.; Formigoni, M.; Hernandez Barros Fuchs, R.; Drovald, A.A.; Reitz Cardoso, F.A. Medicinal effects of Peruvian maca (Lepidium meyenii): A review. Food Funct. 2020, 11, 83–92. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Valerio, L.G., Jr.; Gonzales, G.F. Toxicological aspects of the South American herbs cat’s claw (Uncaria tomentosa) and maca (Lepidium meyenii). A Critical Synopsis. Toxicol. Rev. 2005, 24, 11–35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kasprzak, D.; Jodlowska-Jedrych, B.; Borowska, K.; Wojtowicz, A. Lepidium meyenii (Maca)—Multidirectional health effects—Review. Curr. Issues Pharm. Med. Sci. 2018, 31, 107–112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ibrahim, R.M.; Elmasry, G.F.; Refaey, R.H.; El-Shiekh, R.A. Lepidium meyenii (maca) roots: UPLC-HRMS, molecular docking, and molecular dynamics. ACS Omega 2022, 7, 17339–17357. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gonzales, G.F. Ethnobiology and ethnopharmacology of Lepidium meyenii (maca), a plant from the Peruvian Highlands. Evid.-Based Complement. Alternat. Med. 2012, 2012, 193496. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, M.S.; Lee, H.W.; You, S.; Ha, K.-T. The use of maca (Lepidium meyenii) to improve semen quality: A systematic review. Maturitas 2016, 92, 64–69. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lee, H.W.; Lee, M.S.; Qu, F.; Lee, J.-W.; Kim, E. Maca (Lepidium meyenii Walp.) on semen quality parameters: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Front. Pharmacol. 2022, 13, 934740. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chain, F.E.; Grau, A.; Martins, J.C.; Catalan, C.A.N. Macamides from wild ‘Maca’, Lepidium meyenii Walpers (Brassicaceae). Phytochem. Lett. 2014, 8, 145–148. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kedare, S.D.; Singh, R.P. Genesis and development of DPPH method of antioxidant assay. J. Food Sci. Technol. 2011, 48, 412–422. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Prior, R.L.; Wu, X.; Schaich, K. Standardized methods for the determination of antioxidant capacity and phenolics in foods and dietary supplements. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2005, 53, 4290–4302. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sandoval, M.; Okuhama, N.N.; Angeles, F.M.; Melchor, V.V.; Condezo, L.A.; Lao, J.; Miller, M.J.S. Antioxidant activity of the cruciferous vegetable Maca (Lepidium meyenii). Food Chem. 2002, 79, 207–213. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, Y.-K.; Chang, Y.H. Physicochemical and antioxidant properties of methanol extract from Maca (Lepidium meyenii Walp.) leaves and roots. Food Sci. Technol. 2019, 39, 278–286. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, L.W.; Liang, J.; Wang, X.D.; Yuan, X.F.; Zhao, B.; Yang, Y.W. High efficient antioxidant activity of extracts from Lepidium meyenii Walp. Asian J. Chem. 2012, 24, 4795–4798. [Google Scholar]
- You, J.Y.; Joung, J.A.; Baek, S.J.; Chen, J.; Choi, J.H. Simultaneous extraction of proteins and carbohydrates, including phenolics, antioxidants, and macamide B from Peruvian maca (Lepidium meyenii Walp.). Korean J. Food Preserv. 2021, 28, 868–877. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gan, J.; Feng, Y.; He, Z.; Li, X.; Zhang, H. Correlations between antioxidant activity and alkaloids and phenols of maca (Lepidium meyenii). J. Food Qual. 2017, 2017, 3185945. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zha, S.; Zhao, Q.; Chen, J.; Wang, L.; Zhang, G.; Zhang, H.; Zhao, B. Extraction, purification and antioxidant activities of the polysaccharides from maca (Lepidium meyenii). Carbohydr. Polym. 2014, 111, 584–587. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, L.; Zhao, Q.; Wang, L.; Zhao, M.; Zhao, B. Protective effect of polysaccharide from maca (Lepidium meyenii) on Hep-G2 cells and alcoholic liver oxidative injury in mice. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2017, 99, 63–70. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xia, C.; Deng, J.; Pan, Y.; Lin, C.; Zhu, Y.; Xiang, Z.; Li, W.; Chen, J.; Zhang, Y.; Zhu, G.; et al. Comprehensive profiling of macamides and fatty acid derivatives in maca with different postharvest drying processes using UPLC-QTOF-MS. ACS Omega 2021, 6, 24484–24492. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Esparza, E.; Hadzich, A.; Kofer, W.; Mithöfer, A.; Cosio, E.G. Bioactive maca (Lepidium meyenii) alkamides are a result of traditional Andean postharvest drying practices. Phytochemistry 2015, 116, 138–148. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Salehi, B.; Quispe, C.; Sharifi-Rad, J.; Cruz-Martins, N.; Nigam, M.; Mishra, A.P.; Konovalov, D.A.; Orobinskaya, V.; Abu-Reidah, I.M.; Zam, W.; et al. Phytosterols: From preclinical evidence to potential clinical applications. Front. Pharmacol. 2021, 11, 599959. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Niu, L.; Han, D. Chemical Analysis of Antioxidant Capacity: Mechanisms and Techniques; De Gruyter: Beijing, China; Berlin, Germany; Boston, MA, USA, 2020. [Google Scholar]
- Meissner, H.O.; Xub, L.; Wan, W.; Yi, F. Glucosinolates profiles in Maca phenotypes cultivated in Peru and China (Lepidium peruvianum syn. L. meyenii). Phytochem. Lett. 2019, 31, 208–216. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yan, S.; Wei, J.; Chen, R. Evaluation of the biological activity of glucosinolates and their enzymolysis products obtained from Lepidium meyenii Walp. (Maca). Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2022, 23, 14756. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhao, L.; Chen, J.; Su, J.; Li, L.; Hu, S.; Li, B.; Zhang, X.; Xu, Z.; Chen, T. In vitro antioxidant and antiproliferative activities of 5-hydroxymethylfurfural. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2013, 61, 10604–10611. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).