Abstract
Phosphorus is a key factor controlling eutrophication processes. Out of all the parts of the lake ecosystem, the biggest pool of this element (more than 90%) is stored in the surficial layers of bottom sediment. Hence, the bottom sediment’s ability to trap and release P is very important in analyzing a lake ecosystem’s function, particularly when the lake is subjected to restoration. Studies were carried out on Lake Kortowskie (87.2 ha in area, maximum depth 17.2 m), restored in 1956 using the hypolimnetic withdrawal method. The sediment cores were taken at two research stations—experimental (max. depth 17.2 m) and control (max. depth 15.7 m). Experiments were made in laboratory conditions. The results showed that phosphorus adsorption in the bottom deposits of Lake Kortowskie was multilayered. The Freundlich, BET, and Freundlich-Langmuir adsorption models best fit the experimental data. Adsorption isotherms were concave, suggesting that P adsorption effectiveness is higher for higher P concentrations in ambient water.
1. Introduction
In recent years, more and more attention has been paid to water quality deterioration worldwide. Anthropopressure is becoming more visible due to the continuous increase in the human population. Rockström et al. [1] defined so-called planetary boundaries for nine major categories. One of the most important planetary boundaries, which has unfortunately been exceeded beyond the safe range for maintaining Holocene-like conditions, is the change in the biogeochemical cycles of two major biogenic elements, nitrogen and phosphorus, which was confirmed by numerous studies, e.g., [2,3]. Both elements are emitted to surface water from various sources, the most important of which are spatial sources (agriculture—plant and animal production) or point sources associated with the presence of human settlements and industrial facilities in catchments [2,3].
The deterioration of water quality is especially noted in water reservoirs located in urban agglomerations. Anthropogenic eutrophication causes numerous changes in the ecology of aquatic ecosystems, which impede the use of strategic water resources, such as surface waters. Water is a valuable resource, the protection of which is regulated by law (the superior act in Europe is Directive 61/EC/2000) [4]. Therefore, there is an obligation to maintain the quality of this resource. Lake restoration methods also serve this purpose [5].
The purpose of restoration treatments used in lakes is to reverse or reduce the avalanche process of eutrophication. Usually, treatments aim to change the biogeochemical circulation of both main nutrients, phosphorus and nitrogen, but above all, phosphorus [6,7,8].
Physical and chemical adsorption are one of the main mechanisms of phosphorus binding in lake bottom sediments. Recognition of P adsorption possibilities is, therefore, an important issue when considering the impact of sediments on a lake ecosystem, especially in lakes undergoing remediation treatments [9,10]
The hypolimnetic withdrawal method is the oldest lake restoration technique, which has been implemented on many lakes worldwide [11,12,13,14,15,16]. The installation on Lake Kortowskie is the oldest in the world (operating since 1956). The pipeline and small dam on the Kortówka outflow were designed by professor Przemysław Olszewski in the early 1950s. In 1976, the original wooden pipeline was replaced by a pipeline made of glass fibers and polyester resin, and this installation is still operating. Since its installation, the pipeline has been operating with different water flows (50–250 dm3 s−1) in various years [11,12,17,18,19,20]. Previous research mainly focused on the hypolimnetic withdrawal effect on water column nutrient balance in Lake Kortowskie. Only a few works, Tadajewski [21] and Wiśniewski [20], have given information concerning the chemical composition of the bottom sediment in Lake Kortowskie.
Our main study goal was to analyze the water–sediment interface chemistry and assess the sediment P adsorption characteristics of Lake Kortowskie, restored by hypolimnetic withdrawal methods for several decades. We also attempted to find whether the hypolimnetic withdrawal method created differences in the chemistry of the water–sediment interface and P adsorption characteristics.
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Study Site
The research was conducted on Lake Kortowskie, located in Olsztyn city (Olsztyn Lakeland, NE Poland). Basic morphometric characteristics are shown in Table 1.

Table 1.
Morphometric characteristics of Lake Kortowskie (data from the Department of Water Protection Engineering and Environmental Microbiology).
Lake Kortowskie is a dimictic waterbody located in the temperate climatic zone. Since 1956, the analyzed lake has been subject to restoration by the hypolimnetic withdrawal method. Cold and nutrient-rich, hypolimnetic water is removed into the Kortówka River outflow, with a maximum flow of 250 L s−1.
The total topographical catchment of Lake Kortowskie occupies 3799.7 ha, but the actual total drainage basin area is smaller [3546.2 ha] because of the development of a storm sewerage system [Lossow et al. 2005]. The main inflow, the Kortówka River, begins as the outflow from Ukiel Lake (area 412 ha, max depth. 43 m), and after running 1.6 km, the river flows into Lake Kortowskie at the NE shore. The partial catchment (Leśny Stream drainage basin) occupies 969.9 ha and aliments Lake Kortowskie at the SW shore. The other partial catchments are small, and their percentage in the total drainage basin area is between 1.0–1.7% of the total area [Table 2].

Table 2.
Partial catchment areas of Lake Kortowskie drainage basin [19].
The direct catchment of Lake Kortowskie occupies 91.9 ha. The largest area is used for agricultural purposes (35.6% arable land and orchards); 30% of the direct drainage basin is barren, forests cover 19.3%, and the remaining 15.1% of the land is urban area.
In the past, Lake Kortowskie was polluted by sewage from a pig husbandry farm located on the NE shore of the lake and domestic sewage from the Kortowo and Dajtki districts. Currently, most sewage pollution has been eliminated (point sources were cut over thirty years ago) [19]. Hence profundal deposits of the analyzed lake were formed under the influence of anthropogenic sources in the past. According to [19], assessed annual phosphorus loading (723.1 kg P/year) comes from different sources, including 28.6 kg P/year from direct anthropogenic sources (arable lands, orchards, urban areas, and recreation). Most of the P loads have been entering the lake with hydrological inflows (672.0 kg P/year) [19].
2.2. Sampling
The undisturbed deposit cores (20 cm thick) in May 2021 using Kajak bottom sampler occurred at two research stations (St. 1—located at the deepest point of the lake’s northern part and St. 2—southern lake part) restored by hypolimnetic withdrawal (Figure 1, Figure 2 and Figure 3). The water layer (10 cm thick) above every deposit core was decanted. The sediment was divided into four layers (5 cm thick) directly after sampling. Water and sediment samples were taken immediately to the laboratory for analysis, where the sediment samples for chemical analysis were centrifuged. The sediment directed to adsorption experiments was non-centrifuged, and experiments were conducted immediately after sampling. Lake water used in the experiments was taken from the same stations in 5 L plastic tanks.
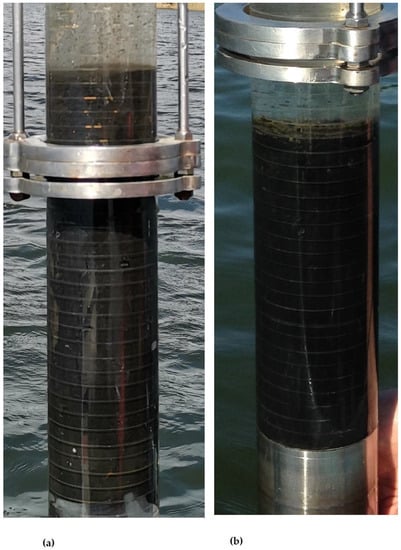
Figure 1.
Examples of sediment cores taken at St. 1 (a) and St 2. (b) (pics by R. Augustyniak-Tunowska).
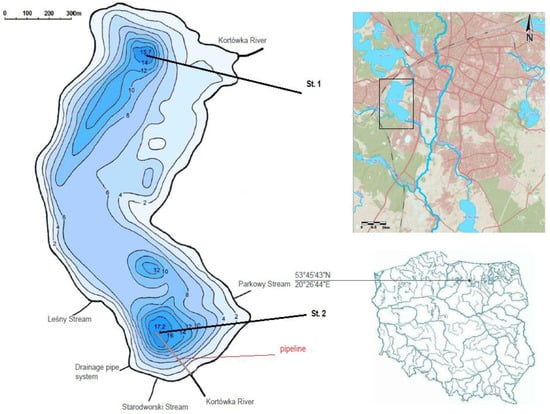
Figure 2.
Bathymetric map of Lake Kortowskie with the location of sampling stations [19] (modified).
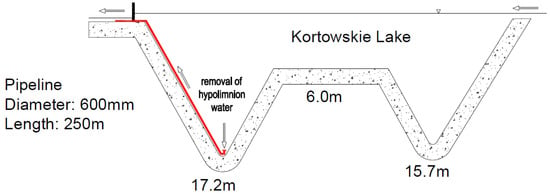
Figure 3.
Scheme of Lake Kortowskie with hypolimnetic withdrawal installation.
The taken profundal sediment cores showed no visible varves; deposits were dark and rather homogeneous at both stations (Figure 1).
The basic water parameters were analyzed in situ by a YSI multi-probe EXO2 (YSI Inc., Yellow Springs, OH, USA).
During sampling, the hypolimnetic withdrawal pipeline worked with maximum efficiency at 250 l s−1.
2.3. Water and Sediment Analysis
Water samples were analyzed [22] after being filtered through 0.45 μm pore filters. The phosphate, iron, and manganese contents were measured using Merck or Nanocolor spectrophotometers. TN was analyzed using an IL 550 TOC-TN analyzer. Measurements included pH, EC, iron, manganese, and phosphates by spectrophotometer; calcium was measured by the titration method using EDTA and eriochrome black T [22].
Water content in fresh sediment was measured gravimetrically. Results were used for calculating the dry weight (DW) of sediment samples.
The bottom sediment was dried and milled using an A10 Basic mill (IKA Works GmbH & Co. KG, Staufen, Germany). The dry weight, contents of organic matter with CO2 regeneration, and inorganic carbon were measured gravimetrically. Dried sediments were mineralized according to the methodology described by [9], and SiO2, Fe, Mn, Al, Ca, Mg, and total Kjeldahl nitrogen (TKN) contents were analyzed after mineralization using a Merck spectrophotometer. Phosphorus fractions (labile P, redox-sensitive P, aluminum-bound P and P connected to organic matter, calcium-bound P, and residual P) were analyzed according to the [23] method using an Innova 40 shaker with incubation. Soluble phosphates (SRP) and total P(TP) in extracts were measured using molybdenum blue method spectrophotometrically. The results of the water–sediment interface chemistry (significance of differences between St. 1 and St. 2) were statistically analyzed using a t-test for independent samples (Statistica 13.5), and p was set as 0.05. Obtained research results were log, log + 1, or arc sin transformed (data approximation to normal distribution).
2.4. Phosphorus Adsorption Experiments
Experiments on phosphorus adsorption and desorption were conducted in laboratory conditions (in triplicate). Portions of 2.0 g of fresh bottom deposits were put into test tubes and prepared P solutions in lake water (25 cm3) in rising concentrations (0.00; 0.15; 0.30; 0.60; 1.20; 2.40; 4.80; 9.60 mg P dm−3) were poured into tubes, adding 2 drops of CHCl3 protected samples from bacterial activity [9,24]. After 24 h equilibration (at 20 °C), samples were centrifuged, and the supernatant was filtered through 0.45 μm pore filters before analysis. SRP in the supernatant was analyzed using the molybdenum blue method (Merck spectrophotometer). The adsorbed phosphorus was calculated as the difference between the initial and final phosphorus concentration (mg) per 1 kg of sediment DW.
Desorption of P was assessed after 24 h equilibration of samples with previously adsorbed P using lake water (without P). Calculations were made according to the method described by [25,26] (Figure 4).
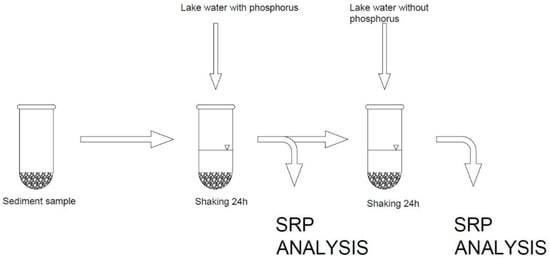
Figure 4.
Scheme of P adsorption experiment procedure.
The estimation of P adsorption parameters was conducted using Freundlich, BET, and Freundlich-Langmuir models using the non-linear estimation method (Statistica 13.5). As a measure of fitting experimental data to the tested model, the R2 coefficient was used. Langmuir and double Langmuir models were also tested, but they showed a very weak fit to experimental results, and obtained results were omitted in the presented analysis.
Used adsorption models equations:
- (a)
- Freundlich model equation [27]:
S—phosphorus amount adsorbed by bottom sediment (mg P kg−1 DW), a sum of “native” adsorbed P (S0) and P adsorbed during experiment (S’)
C—final concentration of phosphorus concentration after 24 h equilibration (mg dm−3);
Kf—Freundlich model constant (dm3 kg−1);
1/n—constant describing heterogeneity of adsorption.
The EPC0 (phosphorus equilibrium concentration) parameter was calculated using the Freundlich model. This value was corrected taking into account the amount of desorbed P (–S0) for initial P concentration 0 mg P dm−3 [28]:
The change of Gibbs free energy (kJ mol−1) was calculated with the formula [29]:
where:
Kd—division coefficient [dm3 kg−1];
R—gas constant [J mol−1 K−1];
T—temperature [K].
- (b)
- BET adsorption model, which describes multilayer adsorption [30]:
C, S—as it was in the equation [1];
SBET—maximum adsorption capacity of sediment, which corresponds to the monolayer, [mg kg−1 DW];
kBET—BET model constant [dm3 mg−1];
Cs—concentration of saturation of adsorbate monolayer [mg dm−3].
- (c)
- General Langmuir-Freundlich adsorption model [31]:
S, C—as it was in previous equations
SFL—maximum adsorption capacity [mg kg−1 DW]
kFL—Langmuir-Freundlich constant [dm3 mg−1]
α—heterogeneity factor
2.5. Statistical Analysis—RDA
Redundancy analysis (RDA) [32] was performed using the CANOCO software for Windows. The analysis aimed to find connections between P adsorption characteristics and bottom sediment chemical composition. The significance of ordination models was made using the Monte Carlo permutation test.
3. Results
3.1. Characteristic of the Water-Sediment Interface Chemistry as a Background for Sediment P Adsorption Abilities
The near-bottom and pore water of profundal Lake Kortowskie sediments were rich in nutrients. The concentrations of nitrogen and phosphorus rose together with sediment depth. During sampling, over-bottom water temperature amounted to 8.4 °C (St. 1) and 8.1 °C (St. 2). Oxygen concentration was 1.1 mg O2 dm−3 (St. 1) and 3.2 mg O2 dm−3 (St. 2). The amounts of phosphorus compounds in the overlying waters were similar at both research sites and was lower than 0.5 mg P dm−3 (Figure 5). At Station 2, the amounts of total phosphorus in the interstitial water were slightly lower, but a smaller share of mineral P form was found in all examined layers of sediments (Figure 2). The range of observed concentrations could be characterized as characteristic of eutrophic lakes [9]. A maximum concentration of total phosphorus was noted in the pore water of the deepest layer (15–20 cm) on St. 2 (9.47 ± 0.12 mg P dm−3).
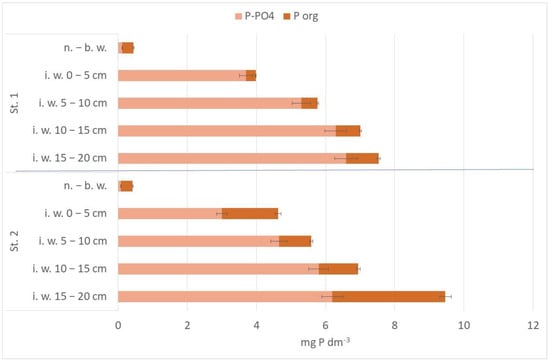
Figure 5.
Amounts of P forms (±SD) in the nearbottom and pore water of Lake Kortowskie (total bar length represents the total amount of P).
The concentration of iron and manganese (metals influencing P binding in sediment) in the analyzed water strata was not very high (Figure 6). Manganese amounts were below 5 mg Mn dm−3 at both research stations. Iron concentrations were higher than manganese (the maximum amount was noted in the deepest layer of interstitial water at St. 2—13.4 ± 0.4 mg Fe dm−3).
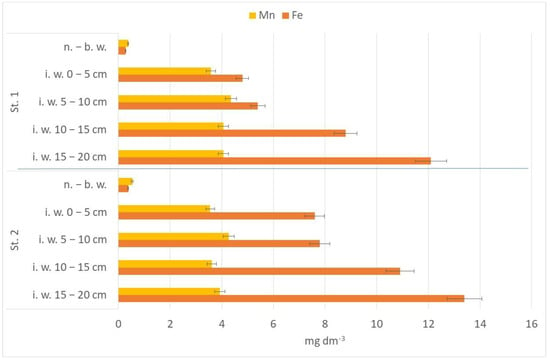
Figure 6.
Manganese and iron concentration (±SD) in the near-bottom and pore water of Lake Kortowskie.
The sediment composition of Lake Kortowskie was similar at both research stations. It can be classified as mixed-type silica-carbonate-organic; none of the major component amounts did not exceed 50% DW. Other components occurred in small amounts. Among metals responsible for phosphorus binding, Al and Mn occurred in very low concentrations (0.7–0.9%Al2O3 in DW and 0.05–0.10% MnO in DW), Fe level was higher (in the range 2.15–3.95%Fe2O3 in DW), while analyzed sediments were abundant in Ca compounds (28.8–32.5%CaCO3 in DW) (Figure 7). We did not observe significant differences between particular sediment components at research stations, except silica and phosphorus content (t-value 2.87, n = 8, p < 0.02 for log%SiO2 and (t-value −3.60, n = 8, p < 0.01 for log% P2O5).
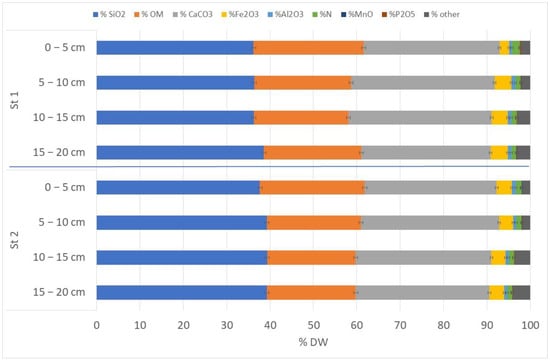
Figure 7.
Amount of components in bottom deposits (±SD) of Lake Kortowskie (in %DW).
The analyzed sediment of Lake Kortowskie was not abundant in phosphorus. The TP amounts ranged between 1.771 mg P g−1 DW (St. 2, sediment layer 10–15 cm) and 2.593 mg P g−1 DW. Performed analysis of sediment phosphorus fractions in Lake Kortowskie revealed that the main P fractions in analyzed lake sediment were hardly bioavailable fractions: res-P (residual phosphorus, permanently bound to sediment) and HCl-P (P bound to Ca), which had the highest share of TP (up to 72%TP for res-P at. St. 1 and up to 57%TP for HCl-P at St. 2). Moderately bioavailable fraction NaOH-nrP (P bound to OM) occupied up to 26%TP at St. 1. The rest of fractions occurred in low amounts. One exception was the deepest sediment layer from St. 1. This sediment was abundant in NaOH-rP (P bound to aluminum and iron oxides and hydroxides) and BD-P (redox-sensitive P) fractions (Figure 8). The significant differences in HCl-P, res-P, and TP were observed between research stations (t-value s 4.23, −4.02 and −3.63, n = 8, p < 0.01 for log (HCl-P +1), log (res-P + 1) and log (TP + 1), respectively).
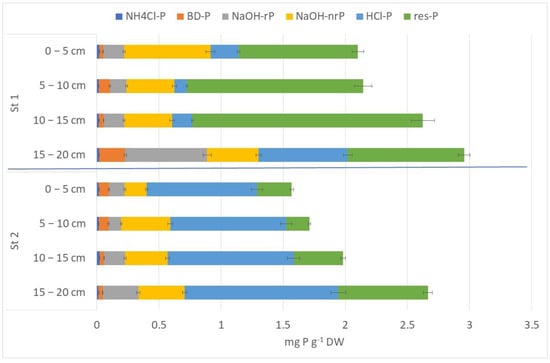
Figure 8.
The amounts of P fractions (±SD) in the bottom sediment of Lake Kortowskie (total length of bars represents TP).
3.2. Results of Phosphorus Adsorption Experiments
The conducted experiments on the sorption capacity of bottom sediments in relation to phosphorus showed that the tested sediments adsorbed phosphorus quite well, but the course of adsorption was unusual. First, the obtained adsorption characteristics indicate that it is not monolayered but multi-layered. The double Langmuir and Langmuir models did not show a significant fit to experimental data. In contrast, the BET, general Freundlich-Langmuir, and Freundlich models were suitable for describing the phosphorus adsorption processes. Those models can predict a convex adsorption isotherm, but only at much higher adsorbate concentrations—at lower concentrations, the isotherm was concave. This was indicated by 1/n coefficients higher than 1 both in the Freundlich model (1/n ranges between1.263–1.802 for sediment taken at St. 1 and between 1.164–1.615 for St. 2.) as well as for the general Freundlich-Langmuir model (1/n ranges between 1.21–2.547 at St. 1 and between 1.28–2.852 at St. 2) (Table 3 and Table 4). An exemplary course of adsorption isotherms is presented in Figure 9 (in this case, analysis was performed for S = S’ + S0). The points represent mean values of adsorbed P for different final P concentration Ce.

Table 3.
P adsorption characteristics of bottom sediment of Lake Kortowskie at St. 1 (control).

Table 4.
P adsorption characteristics of bottom sediment of Lake Kortowskie at St. 2 (experimental).
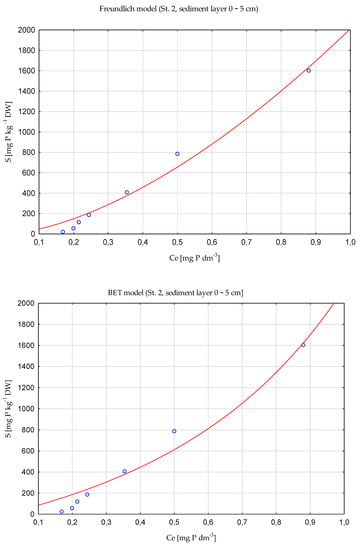
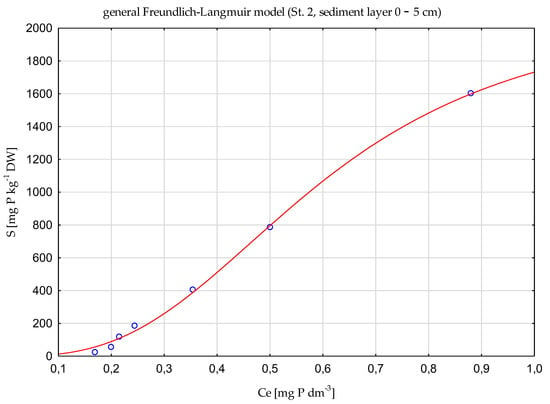
Figure 9.
Examples of modeled P adsorption isotherms fitting to experimental P adsorption data.
Phosphorus adsorption isotherms (for surficial deposits layers) were fit to the general Freundlich-Langmuir model, the deeper sediment layers to the BET model or Freundlich model, as it was indicated by determination coefficient (R2) values (Table 3 and Table 4). However, the differences in R2 values between tested models were rather small (in the range between 0.9607 to 0.9987) for all analyzed sediment layers. The assessed maximum adsorption capacities (SBET and SFL) were different, depending on the model, and varied between two orders of magnitude. It is worth noting that the much higher values of this parameter were assessed for wear-fitting the models to experimental data (lower R2 values). The maximum capacity of a single monolayer in the BET model was the highest for the surficial sediment (0–5 cm) at both research stations (15,649.34 mg P kg −1 DW at St. 1, and 13,121.06 mg P kg −1 DW at St. 2). The values of this parameter declined with sediment depth (to 354.64 mg P kg −1 DW at St. 1 for sediment layer 10–15 cm, and to 498.84 mg P kg−1 DW, for deposit layer 15–20 cm at St. 2) (Table 3 and Table 4). On the contrary, kBET values rose with sediment depth, amounting to a maximum for deeper sediment layers (7.20 dm3 mg−1 for layer 10–15 cm at St. 1 and 2.266 dm3 mg−1 for layer 15–20 cm at St. 2) (Table 3 and Table 4). It shows stronger phosphorus binding in single monolayers of the more deeply located deposits at both research stations.
The range of native adsorbed P (S0) for analyzed deposits was between 20.08 and 0.22 mg P kg−1 DW (St. 1) and between 21.23 and 2.97 mg P kg−1 DW (St. 2), with maxima for the surficial deposits (0–5 cm) at both stations. These parameter values declined with sediment depth. A similar situation was observed for P equilibrium concentrations EPC0. Higher values of this parameter were noted for upper sediment layers (Table 3 and Table 4), but the assessed EPC0 was very low for analyzed sediments.
Calculated Gibbs free energy was rather low, between −15.19 kJ mol−1 (St. 2, deposit layer 5–10 cm) and −20.38 kJ mol−1 (St. 1, layer 15–20 cm). This order of magnitude confirms the physical type of observed P adsorption. Despite this, the noted P retention by Lake Kortowskie sediment was very high and varied between 98–99% (Table 3 and Table 4).
All assessed adsorption characteristics were subjected to statistical analysis (t-test) to find the differences between research stations, but the obtained results revealed that significant differences in P retention only between St. 1 and St. 2 were found (t-value 2.88, n = 8, p < 0.02).
The performed RDA analysis showed that the main factors connected to physical P adsorption characteristics by the bottom sediment of Lake Kortowskie were organic matter (and also TN, because sedimentary nitrogen is deposited mainly in organic form), iron, and manganese, while aluminum, silicates, calcium carbonates, and TP showed no significant connections. OM was correlated with BET model characteristics (positive correlation with single monolayer capacity (SBET), adsorbate saturation concentration for single monolayer (Cs), native sorbed P (S0), and negatively correlated with iron content (positively correlated with kBET). A less weak correlation was found with free Gibbs energy, kfl, and 1/nfl (constants in the general Freundlich-Langmuir equation). EPC0 (P equilibrium concentration) and 1/n (Freundlich equation constant) parameters were positively correlated with manganese content in the sediment. Two main axes explained 99.8% of the variability (Figure 10).
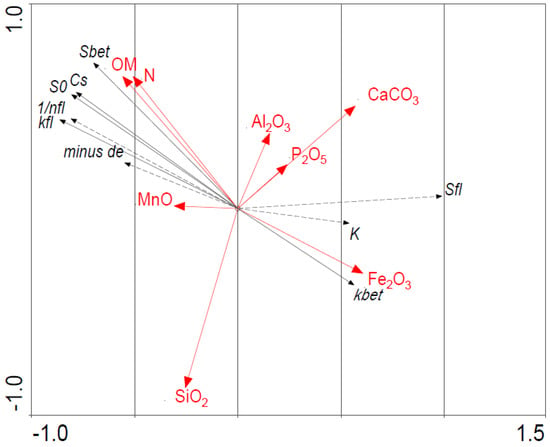
Figure 10.
Results of RDA analysis of dependence between P adsorption characteristics (response variables) and chemical composition of bottom sediment (explanatory variables).
4. Discussion
The presented research was carried out to determine whether the applied method of Lake Kortowskie restoration affects the chemistry of the water–sediment interface and the sediment P sorption abilities.
Hypolimnetic withdrawal is a method to ensure the removal of excess nutrients and other reduced compounds (e.g., hydrogen sulfide) outside the lake ecosystem, which are released from the lake deposits under anoxia. In Özkundakci et al. [33], it was shown that an internal loading is responsible for more than 50% of the SRP amount and N-NH3 in the hypolimnion. In lakes with long pollution history by sewage, the internal loading may significantly exceed external nutrient loading [34]. Therefore, in theory, using the hypolimnetic withdrawal method should improve the nutrient balance of the lake and reduce the effects of the internal loading phenomenon [13,14,15,35]. The results of many years of research into the water of Lake Kortowskie revealed a positive effect of the applied method on the nutrient balance [11,12,17,18,19]. However, using this method also has some limitations. First, the hydrological balance is important, allowing the discharge of hypolimnion water. In the case of dry periods with reduced rainfall, as has been the case in recent years [36], draining water with the full capacity of the pipeline could significantly reduce the water level in the reservoir. In addition, the removal of bottom water with maximum efficiency increases the temperature of the hypolimnion but, at the same time, improves oxygen conditions in the bottom zone. This may affect the sedimentation of matter in the lake, as well as the rate of organic matter decomposition in sediment. During the research, there were favorable hydrological conditions allowing the use of the maximum flow in the pipeline (250 l s−1).
The performed experiments showed that the bottom sediment of Lake Kortowskie was characterized by quite good phosphorus adsorption capacity. Still, the recorded contents of total phosphorus in bottom deposits were not high—the TP amounts were between 1.771 mg P g−1 DW (St. 2, deposit layer 10–15 cm) and 2.593 mg P g−1 DW, sediment layer 0–5 cm. The quantitative structure of the phosphorus fraction showed the predominance of fractions that are difficult (HCl-P) and non-bioavailable (res-P). Amounts of labile fractions (NH4Cl-P and BD-P) were low at both research stations. P retention by analyzed sediment was especially high (up to 99% earlier adsorbed P) (Table 3 and Table 4), which means that the bottom sediment of Lake Kortowskie is very effective at P trapping in oxic conditions, in which the experiments were carried out. This parameter showed statistically significant differences between the control and the experimental station. Higher P retention was noted for sediment taken at St. 1 (control site)—more than 99% of previously adsorbed P, while, at experimental station P, retention was lower (up to 98.99%). It could result from sediment forming in different conditions, affected by the used restoration method. Despite a higher temperature in the hypolimnetic zone induced by the hypolimnetic withdrawal pipeline operating, there were no significant differences in theoretical maximum adsorption capacities between the research stations. P adsorption processes are more effective in higher temperatures [10,24,37,38]. However, tested adsorption characteristics did not show significant differences between sediments taken at the research stations, except for P retention.
Performed RDA analysis showed that the OM, Fe, and Mn contents in deposits are important factors in physical P adsorption processes, influencing P adsorption characteristics. The role of OM, as well as Fe and Mn, in P adsorption by bottom sediment, was well recognized in numerous research, as they formed mobile P pools in sediment, e.g., [26,38,39].
A rather unexpected fact of the conducted research was that modeled P adsorption isotherms showed concave isotherm shape, especially in low P concentration. The obvious conclusion implied by modeled isotherm shape was that observed P adsorption was multilayered, not monolayered. According to Giles et al. [39], concave isotherm belongs to the S-class, and it occurs when cooperative adsorption occurs. It means that between the adsorbate molecules, the bond strength is of a similar order of magnitude, or stronger, than the bond strength between adsorbate and adsorbent molecules. Additionally, Al Ghouti and Da’ana [40] mention that concave isotherms occur with strong adsorbate–adsorbate bonding forces. Therefore the P adsorption by the sediment in Lake Kortowskie seems more effective in higher P concentrations in water. According to Hinz [31], S-class isotherm can be pictured by the Freundlich model with a 1/n coefficient value exceeding 1, as it was obtained in the present research.
The ion exchange isotherms were discussed in the paper by Limousin et al. [41]. According to their findings, the adsorption capacity depends on the ion exchange capacity. If exchanged ions have the same valency, the exchange occurs in the adsorption media, and the adsorption curve will be C-type. However, in the case of different valences of exchange ions, the higher valence ions are more adsorbed. Probably that mechanism could influence the concave shape of P adsorption isotherm curves because P adsorption on bottom sediment in lakes occurs in a complex matrix.
A similar concave shape of the P adsorption isotherm (with 1/n higher than 1) was obtained by Augustyniak and Serafin [26] from the sediment of Lake Klasztorne Małe. This lake was restored earlier using Phoslock (benthonite clay modified by lanthanum). This treatment also changed the calcium carbonate content in sediment compared to other lakes in the Kartuzy lakes complex. Because the sediment of Lake Kortowskie is relatively abundant in calcium carbonates, the presence of carbonates is a possible factor influencing P adsorption isotherm shape, though this hypothesis needs further research.
The concentrations of phosphorus compounds observed in the water–sediment interface were high, and they confirmed the eutrophic state of Lake Kortowskie. Similar concentrations were observed in the interstitial water of eutrophic lakes [9,26,37]. There were some differences in the concentrations of total phosphorus between the control site (St. 1) and the experimental site (St. 2), especially in mineral form amount—this was slightly lower in the experimental station than in the control site (Figure 2 and Figure 3) but was not statistically significant.
While no significant differences in analyzed water strata were found between the control and experimental sites, the differences between the research sites were marked in the chemical composition of deposits—total phosphorus content (TP), silicate amount (SiO2), fractions of calcium-bound phosphorus (HCl-P), and residual phosphorus (res-P) amounts. The silicate content was significantly higher in deposits of the experimental part, while the amount of TP was significantly lower. This may indicate changes caused by the applied restoration method. An increase in the bottom water temperature accelerates the mineralization processes, which may lead to an increase in the amount of silicate in relation to the amount of organic matter. Typically, a higher silicate content is found in shallow water sediment, which is deposited at higher water temperatures. At the same time, organic matter in warmer waters undergoes rapid mineralization. Hence the amount of OM is much less in shallow-water sediments than in profundal sediments [3,37,42]. Previous research by Wiśniewski [20] showed some changes in the sediment chemical composition since 1955 [21]—lower amounts of iron and TP and an increase in CaCO3 amounts at an experimental station.
The mineralization of organic phosphorus compounds releases phosphates into the aqueous phase, some of which can be captured by the pipeline and discharged outside the ecosystem. Some can be captured by calcium compounds and precipitated into sediments as HCl-P fractions. The binding of phosphorus by calcium compounds present in sediments is easier at higher temperatures and higher pH [43]. The bottom sediments of Lake Kortowskie were quite rich in calcium carbonate. The content of this compound in examined sediments exceeded 30% DW, which could have favored phosphorus binding by deposits of the studied lake in the form of an HCl-P fraction. Tu et al. [44] also observed an increase in the concentration of HCl-P fractions in deposits of Lake Burgäshi, Switzerland, restored by the hypolimnetic withdrawal method. They found that after installing the system for hypolimnetic withdrawal in 1977, the TP amounts in sediment decreased sharply (from 12 mg P g−1 DW to a several mg P g−1 DW). This proves the effectiveness of the hypolimnetic withdrawal method in the P removal from surficial sediment. Therefore it is possible that noted differences between sediment HCl-P and res-P fractions and TP amounts at research stations in Lake Kortowskie result from the applied restoration method.
5. Conclusions
The research on phosphorus adsorption by bottom deposits of Lake Kortowskie revealed that analyzed sediment had good P adsorption abilities; P retention was especially effective, despite fairly low TP amounts in the analyzed sediment. Phosphorus was stored in sediment mainly in mineral, hardly bioavailable forms (HCl-P and res-P). Tested P adsorption models have suggested that P adsorption was probably multi-layered. It was confirmed by a very weak fit to Langmuir and double Langmuir models (describing monolayered adsorption) and a good fit to BET, Freundlich, and general Freundlich-Langmuir models. The adsorption isotherms were concave, suggesting higher P adsorption abilities at higher P concentrations in water above sediment. The adsorption process was physical and cooperative. Applying the hypolimnetic withdrawal method on Lake Kortowskie had caused certain changes in the bottom sediment chemical composition. TP amounts were significantly lower at the experimental station, and HCl-P and res-P fractions amounts differed significantly between the control and the experimental site. This could mean that the hypolimnetic withdrawal method changes the conditions of P deposition in sediment. This method, operating at Lake Kortowskie for several decades, helps maintain the water quality of this water body in the range of a moderate eutrophic state.
Author Contributions
Conceptualization, R.A.-T., R.K., M.Ł. and J.G.; methodology, R.A.-T. and R.K.; software, J.T.; validation, R.T., J.G. and M.Ł.; investigation, R.A-T. and R.K.; writing—original draft preparation, R.A.-T. and R.K.; writing—review and editing, R.A.-T. and R.K.; supervision, J.G. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
Project financially supported by the Minister of Education and Science in the range of the program entitled “Regional Initiative of Excellence” for 2019–2023, project No. 010/RID/2018/19, with a funding amount of PLN 12,000,000.
Institutional Review Board Statement
Not applicable.
Informed Consent Statement
Not applicable.
Data Availability Statement
Data are available at the Department of Water Protection Engineering and Environmental Microbiology, University of Warmia and Mazury, Olsztyn, Poland.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declared no conflict of interest.
References
- Rockström, J.; Steffen, W.; Noone, K.; Persson, Å.; Chapin, F.S.I.; Lambin, E.; Lenton, T.M.; Scheffer, M.; Folke, C.; Schellnhuber, H.J.; et al. Planetary boundaries: Exploring the safe operating space for humanity. Ecol. Soc. 2009, 14, 32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schindler, D.W. The dilemma of controlling cultural eutrophication of lakes. Proc. R. Soc. B 2012, 279, 4322–4333. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Orihel, D.W.; Baulch, H.M.; Casson, N.J.; North, R.L.; Parsons, C.T.; Seckar, D.C.M.; Venkiteswaran, J.J. Internal phosphorus loading in Canadian fresh waters: A critical review and data analysis. Can. J. Fish. Aquat. Sci. 2017, 74, 2005–2029. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Water Framework Directive 2000/60/WE, Polish Version. Available online: www.mos.gov.pl (accessed on 27 November 2022).
- Schallenberg, M.; de Winton, M.D.; Verburg, P.; Kelly, D.J.; Hamill, K.D.; Hamilton, D.P. Ecosystem Services of Lakes. In Ecosystem Services in New Zealand–Conditions and Trends; Dymond, J.R., Ed.; Manaaki Whenua Press: Lincoln, New Zealand, 2013; pp. 203–225. [Google Scholar]
- Lossow, K. Ochrona i rekultywacja jezior. Teoria a praktyka (Protection and restoration of lakes. Theory and practice). Idee Ekol. 1998, 13, 55–70. (In Polish) [Google Scholar]
- Klapper, H. Technologies for lake restoration. J. Limnol. 2003, 62 (Suppl. 1), 73–90. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cooke, G.D.; Welch, E.B.; Peterson, S.A.; Nichols, S.A. Restoration and Management of Lakes and Reservoirs; CRC Press, Taylor&Francis Group, LLC: Boca Raton, FL, USA, 2005. [Google Scholar]
- Augustyniak, R.; Grochowska, J.; Łopata, M.; Parszuto, K.; Tandyrak, R.; Tunowski, J. Sorption properties of the bottom sediment of a lake restored by phosphorus inactivation method 15 years after the termination of lake restoration procedures. Water 2019, 11, 2175. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kang, L.; Mucci, M.; Lürling, M. Influence on temperature and pH on phosphate removal efficiency of different sorbents used for lake restoration. Sci. Total Environ. 2021, 812, 151489. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mientki, C.; Teodorowicz, M. 1996. Assessment of the Effects of Hypolimnion Water Removal from the Kortowskie Lake. In Chemistry for the Protection of the Environment 2; Plenum Press: New York, NY, USA, 1996; pp. 361–374. [Google Scholar]
- Mientki, C.; Wiśniewski, G. Characteristics of limnological seasons in restored Lake Kortowskie in years 1952–2002. Limnol. Rev. 2003, 3, 159–164. [Google Scholar]
- Nürnberg, G.K. Lake responses to long-term hypolimnetic withdrawal treatments. Lake Reserv. Manag. 2007, 23, 388–409. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Silvonen, S.; Niemistö, J.; Myyryläinen, J.O.; Kinnunen, O.K.; Huotari, S.; Nurminen, L.; Horppila, J.; Jilbert, T. Extracting phosphorus and other elements from lake water: Chemical processes in a hypolimnetic withdrawal and treatment system. Wat. Res. 2022, 218, 118507. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Silvonen, S.; Niemist¨o, J.; Csibr’an, A.; Jilbert, T.; Torma, P.; Kr’amer, T.; Nurminen, L.; Horppila, J. A biogeochemical approach to evaluate the optimization and effectiveness of hypolimnetic withdrawal. Sci. Total Environ. 2021, 755, 143202. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Renman, A.; Renman, G. Removal of phosphorus from hypolimnetic lake water by reactive filter material in a recirculating system-laboratory trial. Water 2022, 14, 819. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Teodorowicz, M. Czynniki Wpływające na Bilans Biogenów i Stan Troficzny Jeziora Kortowskiego (Factors Influencing on Nutrient Balance and Trophic State of Kortowskie Lake). Ph.D. Thesis, Akademia Rolniczo, Techniczna, Olsztyn, 1995. (In Polish). [Google Scholar]
- Dunalska, J. Wpływ Ograniczonego Usuwania Wód Hypolimnionu na Wybrane Parametry Fizyko-Chemiczne i Bilans Biogenów w Wodzie Jeziora Kortowskiego (The Influence of Limited Hypolimnetic Withrawal on the Selected Physico-Chemical Properties and Nutrient Balance of the Kortowskie Lake Water). Ph.D. Thesis, Akademia Rolniczo, Techniczna, Olsztyn, 1999. (In Polish). [Google Scholar]
- Lossow, K.; Gawrońska, H.; Mientki, C.; Łopata, M.; Wiśniewski, G. Jeziora Olsztyna, Stan Troficzny, Zagrożenia (Lakes of Olsztyn. Trophic State, Threats); Edycja, S.C.: Olsztyn, Poland, 2005. [Google Scholar]
- Wiśniewski, G. Skład Chemiczny Osadów Dennych Jeziora Kortowskiego po 50 Latach Rekultywacji (Bottom Sediment Chemical Composition of Kortowskie Lake after 50 Years of Restoration. In Ochrona i Rekultywacja Jezior (Protection and Restoration of Lakes); Wisniewski, R., Ed.; Polskie Zrzeszenie Techników Sanitarnych Oddział Toruń: Toruń, Poland, 2007; pp. 191–200. (In Polish) [Google Scholar]
- Tadajewski, A. Chemizm osadów dennych Jeziora Kortowskiego w 1955 roku (Chemistry of bottom sediments of Kortowskie Lake). Zesz. Nauk. WSR Olszt. 1965, 19, 59–79. (In Polish) [Google Scholar]
- Hermanowicz, W.; Dożańska, W.; Dojlido, J.; Koziorowski, B.; Zerbe, J. Physical and Chemical Analysis of Water and Sewage (Fizyczno–Chemiczne Badanie Wody i Ścieków); Arkady: Warszawa, Poland, 1999. (In Polish) [Google Scholar]
- van Hullebush, E.; Auvray, F.; Deluchat, V.; Chazal, P.; Baudu, M. Phosphorus fractionation and short-term mobility in the surface sediment of a polymictic shallow lake treated with low dose of alum (Courtille Lake, France). Water Air Soil Pollut. 2003, 146, 75–91. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, L.; Fu, L.; Jin Ch Gielen, G.; Lin, X.; Wang, H.; Zhang, Y. Effect of temperature on phosphorus sorption to sediments from shallow eutrophic lakes. Ecol. Eng. 2011, 37, 1515–1522. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pant, H.K.; Reddy, K.R. Phosphorus sorption characteristics of estuarine sediments under different redox conditions. J.Environ. Qual. 2001, 30, 1474–1480. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Augustyniak, R.; Serafin, A. Use of different adsorption models for characterizing P adsorption by the bottom sediment of four degraded urban lakes (Kashubian Lakeland, northern Poland). Desalination Water Treat. 2021, 218, 63–79. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jóźwiak, T.; Filipkowska, U.; Szymczyk, P.; Kuczajowska-Zadrożna, M.; Mielcarek, A. The use of cross-linked chitosan beads for nutrients (nitrate and orthophosphate) removal from a mixture of P-PO4, N-NO2 and N-NO3. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2017, 104, 1280–1293. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Łukawska –Matuszewska, K.; Voght, R.D.; Xie, R. Phosphorus pools and internal loading in a eutrophic lake with gradients in sediment geochemistry created by land use in the watershed. Hydrobiologia 2013, 713, 183–197. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kosobucki, P.; Buszewski, B. (Eds.) Fizykochemiczne Metody Analizy w Chemii środowiska. Cz.2., (Physical and Chemical Analytical Methods in the Environmental Chemistry. Part. 2); Wyd. Nauk; UMK: Toruń, Poland, 2016. (In Polish) [Google Scholar]
- Saadi, R.; Saadi, Z.; Fazaeli, R.; Fard, N.E. Monolayer and multilayer adsorption isotherm models for sorption from aqueous media. Korean J. Chem. Eng. 2015, 32, 787–799. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hinz, C. Description of sorption data with isotherm equations. Geoderma 2001, 99, 225–243. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lepš, J.; Šmilauer, P. Multivariate Analysis of Ecological Data Using CANOCO; Cambridge University Press: Cambridge, UK, 2003. [Google Scholar]
- Özkundakci, D.; Hamilton, D.P.; Gibbs, M.M. Hypolimnetic phosphorus and nitrogen dynamics in a small, eutrophic lake with a seasonally anoxic hypolimnion. Hydrobiologia 2010, 661, 5–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Søndergaard, M. Nutrient Dynamics in Lakes–With Emphasis on Phosphorus, Sediment and Lake Restoration. Ph.D. Thesis, National Environmental Research Institute, University of Aarhus, Aarhus, Denmark, 2007; 276p. [Google Scholar]
- Nürnberg, G.K. Hypolimnetic withdrawal as a lake restoration technique: Determination of feasibility and continued benefits. Hydrobiologia 2019, 847, 4487–4501. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tomczyk, A.M.; Bednorz, E. (Eds.) Atlas Klimatu Polski 1991-2020 (Atlas of Climate of Poland 1991–2020); Bogucki Wydawnictwo Naukowe: Poznań, Poland, 2022; 126p. [Google Scholar]
- Augustyniak, R. Wpływ Czynników Fizyczno-Chemicznych i Mikrobiologicznych na Zasilanie Wewnętrzne Fosforem wód Wybranych Jezior Miejskich (The Influence of Physical, Chemical and Microbiological Factors on the Phosphorus Internal Loading to the Water of Selected Urban Lakes); Polish Academy of Sciences, Environmental Engineering Committee Publishing House: Lublin, Poland, 2018. (In Polish) [Google Scholar]
- Golterman, H.L. The calcium and iron-bound phosphate phase diagram. Hydrobiologia 1988, 159, 149–151. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Giles, C.H.; Smith, D.; Huitson, A. A general treatment and classification of the solute adsorption isotherm. I. Theoretical. J. Colloid Interface Sci. 1974, 47, 755–765. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Al–Ghouti, M.A.; Da’ana, D.A. Gudelines for the use and interpretation of isotherm models: A review. J. Hazard. Mater. 2020, 393, 122383. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Limousin, G.; Gaudet, J.-P.; Charlet, L.; Szenknect, S.; Barthes, V.; Krimissa, M. Sorption isotherms: A review on physical bases, modeling and measurement. Appl. Geochem. 2007, 22, 249–275. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cyr, H.; Mc Cabe, S.K.; Nürnberg, G.K. Phosphorus sorption experiments and the potential for internal phosphorus loading in littoral areas of a stratified lake. Wat. Res. 2009, 43, 1654–1666. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bańkowska-Sobczak, A.; Blazejczyk, A.; Eiche, E.; Fisher, U.; Popek, Z. Phosphorus inactivation in lake sediments using calcite materials and controlled resuspension—Mechanisms and efficiency. Minerals 2020, 10, 223. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tu, L.; Zander, P.; Szidat, S.; Lloren, R.; Grosjean, M. The influences of historic lake trophy and mixing regime changes on long-term phosphorus fraction retention in sediments of deep eutrophic lakes: A case study from Lake Burgäschi, Switzerland. Biogeosciences 2020, 17, 2715–2729. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).