Abstract
In order to realize the stable clamping of large cabin parts, this paper studied the clamping force optimization of the clamping mechanism for large-mass and large-size cabin parts. Firstly, three kinds of contact models are introduced. Then, a clamping matrix is constructed for a particular clamping configuration. The nonlinear friction cone constraint at the contact point is transformed into a linear affine constraint in a smooth Riemannian manifold using the special structure of the positive definite symmetric matrix. Finally, a large cabin part used in the aerospace field is used as an example for calculating and simulating the clamping force optimization. Different optimization algorithms are used to calculate the initial value which is put into the gradient flow optimization method of the clamping force for optimization calculation. Meanwhile, the normal clamping force value of a 2 t object is measured using relevant experimental equipment. The simulation results and experimental results show that the gradient flow optimization method of the clamping force can quickly complete the clamping force optimization of large-mass and large-size cabin parts. The actual measured value of the normal clamping force is close to the simulated convergence value. The distribution of the normal force of the clamping mechanisms and the convergence value of the clamping force for each clamping mechanism can provide some references for determining the output clamping force of the clamping mechanism and confirming a reasonable distribution of the clamping mechanism. It also confirms the feasibility and effectiveness of this method applied to the clamping force optimization for a large axial part.
1. Introduction
The large cabin part belongs to the category of the large axial part, which is the basic part and the critical component of common equipment, special equipment or large heavy equipment. It occupies an irreplaceable position and has been widely used in some key industries such as transportation, construction machinery, marine ships, aerospace, national defense and scientific research. In the exploration and utilization of space, civil aerospace, as a strategic emerging power, has been playing an increasingly important role in the field of aeronautics and astronautics. At the same time, the maturity of aerospace technology also requires the automation and intelligence of civil aerospace to reach a higher level. For civil aerospace enterprises, how to quickly realize pose adjustment and docking of a large cabin part or pose detection and adjustment of a solid rocket motor has become a key problem. If the above functional requirements and other processing requirements of large cabin parts are realized smoothly, the accurate and stable clamping of the part should be achieved. A large cabin part has the characteristics of large size, heavy load, complex clamping, difficult pose adjustment and so on. At present, civil aerospace enterprises still use the traditional fixed clamping device. The contact area between the clamping device and the large cabin part is usually designed with fixed curvature and rigid contact. Due to the manufacturing process of large cabin parts, their shape and diameter have some dimensional errors. The actual operation of the clamping device requires frequent manual adjustment by changing the thickness of the filling layer between the clamping device and the parts to contain the dimensional errors. It not only involves complicated disassembly but also seriously affects the civil aerospace enterprises’ production efficiency. Furthermore, the clamping contact surface of the clamping mechanism with the existing constant curvature cannot effectively guarantee the stable clamping of large cabin parts. The instability of large cabin parts will cause serious safety problems. It can be concluded that the traditional fixed clamping device is time-consuming and has high cost and low clamping efficiency. In addition, the conventional fixed clamping device can cause stability problems and damage to large cabin parts. The ring pneumatic fixture can solve the above problems well and is shown in Figure 1.
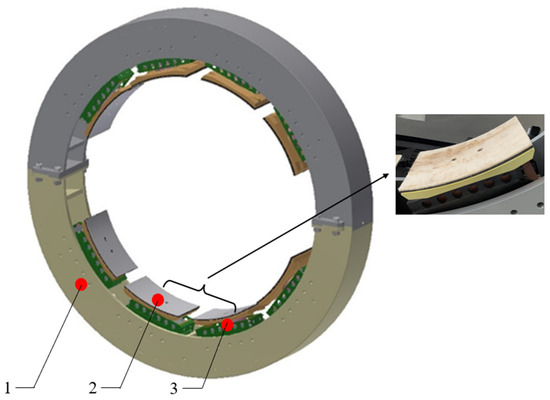
Figure 1.
3D model of the ring pneumatic fixture: 1. Body of the ring pneumatic fixture, 2. Felt at the end of the clamping mechanism, 3. Clamping mechanism.
The ring pneumatic fixture is a kind of annular centripetal fixture that can be connected with a bracket to the ground firmly and be used to achieve grinding, painting or other processing steps of the workpiece. It can also be connected to a vehicle platform to realize the workpiece’s transportation, docking and other assembly requirements, as shown in Figure 2. The ring pneumatic fixture contains several clamping mechanisms. The clamping mechanism contains self-adaptive joints consisting of a linear spring, torsional spring or other underactuated elements that can make the ring pneumatic fixture able to realize shape- and self-adaptive clamping. Each clamping mechanism contacts the surface of the workpiece and exerts a certain clamping force on the workpiece, finally realizing the shape-adaptive and stable clamping of the workpiece.

Figure 2.
The actual application scenario of the ring pneumatic fixture.
The design inspiration for the ring pneumatic fixture comes from the underactuated mechanism. It can adapt to the different shapes of the clamped objects and achieve envelope clamping of the objects, which has strong clamping flexibility. The main purpose of the ring pneumatic fixture is to realize the assembly of large cabin parts. As a multi-functional fixture system device, the ring pneumatic fixture is gradually replacing the traditional single-function fixture. The feature of shape-adaptive clamping is first proposed in the study of the underactuated mechanism. In the underactuated mechanism, the number of actuated elements is less than its DOFs and contains underactuated elements such as linear springs and torsional springs. The underactuated mechanism can be applied to the structural design of robotic hands. Underactuated robotic hands can adapt to the different shapes of objects and finally achieve the envelope clamping of the objects. If the underactuated mechanism in the robotic hands is reasonably designed, the robotic hands will have the feature of shape-adaptive envelope clamping, which can realize powerful envelope clamping of various objects of different shapes and sizes. Many scholars have studied the related features of underactuated mechanisms. Yao et al. [1] proposed that the main grasp configuration of an underactuated finger mechanism could perform self-adaptive enveloping according to the object’s shape, and they designed a linkage underactuated robotic finger mechanism in [2]. The mechanism can perform a compliant grasp for different objects’ shapes and easily achieve a powerful envelope grasp. It is also very suitable for low-cost easy-operation grasper or robotic hand applications. Chu et al. [3] proposed an underactuated hand with a spring as the design parameter. The spring’s softness and rigidity directly affect the underactuated hand’s adaptability to grasp objects with irregular shapes. Ceccarelli et al. [4] introduced linear springs and torsion springs into the finger mechanism, giving the robotic hands the shape-adaptive ability to the grasped object. Ceccarelli et al. proposed different configuration schemes of the joint and spring in the finger mechanism that provided a theoretical reference for the design of the underactuated mechanism and flexible mechanism. Deng et al. [5] pointed out that the number of DOFs was more than that of the actuated elements in the underactuated clamping fixture. Its main clamping configuration is multi-finger envelope clamping and the clamping process of the underactuated clamping fixture is easy to control and operate. Ciocarlie et al. [6,7] designed an underactuated finger based on static grasp balance criteria and optimized its connecting rod sizes and spring parameters. Odhner et al. [8,9,10] developed a low-cost underactuated robotic hand with a simple structure and moderate dexterity, which could adapt to complex grasped objects.
The ring pneumatic fixture clamping a workpiece is similar to the robotic hands grasping an object. In the clamping process, especially in the clamping process of a large cabin part, the improper adjustment of the clamping force will cause serious consequences. If the clamping force is too large, it will not only lead to the deformation and damage of the workpiece surface but also cause damage to and energy waste of the clamping mechanism, which finally affects the processing accuracy. If the clamping force is too small, it will lead to the deviation of the clamping mechanism and scraping of the workpiece, which will cause a serious accident. Therefore, in order to realize the stable clamping to the workpiece of each clamping mechanism, it is necessary to study the clamping force of the clamping mechanism. The essential requirement is to achieve the clamping force exerted by the clamping mechanism onto the workpiece balanced to the external force of the workpiece, and the friction force of each clamping mechanism needs to meet the constraints of the friction cone under a given clamping configuration. The minimum clamping force that satisfies these above conditions is the optimization problem of the clamping force. It can be seen from these conditions that the clamping force optimization problem of the clamping mechanism is similar to the grasping force optimization problem of the robotic hand. They both need to deal with the nonlinear constraints brought by the friction force and select an appropriate optimization method. It can provide a certain reference for the optimization of the clamping force. Liu et al. [11] analyzed the constraints of different contact models grasped by the robotic hand and proposed a new target function of the contact force, which contributed to the contact force programming of the robotic hand. Cai et al. [12] obtained an initial value of the grasping force using the Lagrange multiplier algorithm and introduced a concept of stability index of the friction cone to optimize the grasping force. Fok and Xia et al. [13,14] proposed two kinds of recursive neural networks for the grasping configuration of the robotic hands to optimize the grasping force. Two kinds of neural networks can balance the external force exerted on the object according to the norm of the friction cone constraint of the grasping force. Chen et al. [15] proposed a grasping force optimization method based on a generalized penalty function and introduced different penalty factors according to different grasping configurations to construct an augmented optimization target function. Mu et al. [16] proposed a projection contraction method to solve the grasping force optimization problem globally converging to the optimal grasping force. Helmke et al. [17] proposed an improved Newton algorithm of quadratic convergence to calculate the grasping force, concentrating on the linear constraints and studying the Newton algorithm’s step size.
In dealing with the nonlinear constraint of the friction cone, Li et al. [18] converted this constraint into a linear matrix inequality by further analyzing the constraint of the friction cone. Salisbury et al. [19] and Cheng et al. [20] approximated the friction cone to a multi-body cone and then regarded the nonlinear friction constraint as a linear constraint. This method simplifies the nonlinear optimization problem of the grasping force to a linear programming problem. However, this method still has large errors and extensive calculations. Buss et al. [21,22,23] note that the nonlinear constraint of the friction cone can be equivalent to the positive definite quality of a symmetric matrix with a specific structure and the force optimization problem can be transformed into a convex optimization problem on a smooth Riemannian manifold determined by the matrix. The linear gradient flow method can be used to solve this kind of optimization problem and the solution of this convex optimization is the value of the optimal grasping force. This method avoids the problems caused by linearized friction cones, but it requires an optimized value of the grasping force which satisfies each constraint as the initial value for the iteration of the gradient flow method. Based on this theory, many scholars have carried out further research. Wang et al. [24] used the Lagrange multiplier algorithm to obtain an initial grasping force value satisfying each constraint by adjusting the weight coefficient of the normal contact force, but the convergence rate of this method was slow. Jiang et al. [25] proposed a linear constrained gradient flow algorithm based on force vectors. This method replaces the symmetric positive definite matrix of a specific structure with the grasping force vectors, which can significantly improve the real-time performance of the gradient flow algorithm. Wang et al. [26,27] proposed a gradient flow optimization algorithm based on a safety initial value. This method eliminates the unreliable initial value in the optimization process by setting different safety margins. However, this method is suitable for grasping force optimization when the clamping mechanism’s output force and the object’s size and mass are small. Chen and Wang et al. [28,29] proposed a non-negative linear combination algorithm of the initial values. This method takes a group of unit forces as the basic vectors. Then, the grasping and external forces are decomposed into linear combinations of the unit forces to obtain the initial force value which satisfies each constraint. This method is fast and reduces the number of optimization iterations.
In this paper, the nonlinear constraint of the friction cone is transformed into a linear affine constraint by using the specific structure of a positive definite symmetric matrix. The gradient flow optimization method is applied for the first time to optimize the clamping force of a large cabin part and the clamping force of a specific clamping configuration for the large cabin part is optimized. The initial values that satisfy each constraint are calculated using different optimization algorithms and brought into the gradient flow algorithm for comparison. Finally, an experimental prototype of the ring pneumatic fixture and the corresponding experimental equipment are used to measure the normal clamping force of a 2 t cabin part. The results of the illustrative example and simulation curves show that the initial value of the clamping force obtained using different optimization algorithms affects the final convergence value of the gradient flow algorithm. The gradient flow optimization method can quickly optimize the clamping force of large-mass and large-size cabin parts. The convergence value of the clamping force obtained using the gradient flow algorithm by applying different initial values can provide some references for determining the output force and confirming a reasonable distribution of the clamping mechanism. The experimental results show that the actual value of the normal clamping force is close to the convergence value calculated using the gradient flow optimization method, which can further verify the rationality of the designed clamping system and the clamping configuration. It is also confirmed that the gradient flow optimization method is feasible and adaptive when the clamping mechanism clamps a large-size and large-mass axial part interfered with by an external force. The research process of this paper is shown in Figure 3.
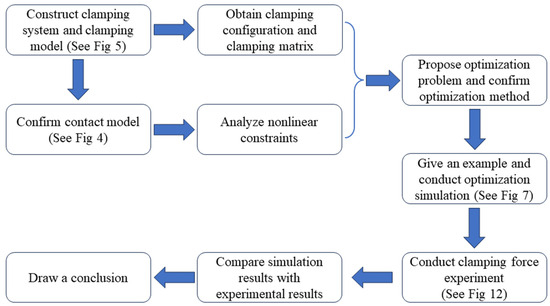
Figure 3.
Research process.
2. The Clamping Contact Model and the Basic Equation
2.1. The Contact Model
Similar to grasping, the simplified contact models can also be divided into three models according to the friction force at the contact point between the surface of the clamping mechanism and the object. It can be defined as frictionless contact, contact with friction point and soft contact [30], which are shown in Figure 4.
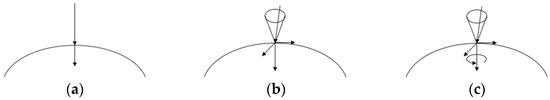
Figure 4.
Contact model: (a) Frictionless contact; (b) point contact with friction; (c) soft contact.
The frictionless contact model does not consider the friction force at the contact point, which only exists as a unidirectional positive force between the surface of the clamping mechanism and the clamped object. However, this contact model is too ideal. The friction force cannot be ignored in actual applications, so this model is not applicable.
In the point contact model with friction, the force exerted by the clamping mechanism on the object is within the range of the friction cone. The contact force consists of a unidirectional positive force and two tangential components. The components of the friction force in two tangential directions can be regarded as the functions of the normal components. According to [31], the conditions which satisfy the constraints of the friction force in this model can be summarized as follows:
It is not difficult to find that Equation (1) is the expression of the friction cone, defined as the clamping force’s friction cone constraint, where fi = [fiz, fiy, fix]T is the clamping force vector of the i-th clamping mechanism in the contact coordinate system, μ is the friction coefficient, fix and fiy represent the component force of the i-th clamping mechanism in two tangential directions in the contact coordinate system, and fiz is the normal positive force of the i-th clamping mechanism in the contact coordinate system (i = 1…n). In order to ensure the friction force at the contact point always exists, each normal positive force should meet fiz ≥ 0, which is the unidirectional force constraint of the point contact model with friction.
If a rubber layer or other soft material is attached to the surface of the clamping mechanism when the object is clamped, then the soft contact model is constructed. This contact model is a surface contact model. The torque that the contact surface generates is added based on the point contact model with friction. This torque is affected by the friction of the contact surface. But, this surface contact model is regarded as the point contact model in actual application. Although the soft contact model is more accurate, it is difficult to model in practical application and it requires a large amount of calculation, so this contact model is not applicable. In this paper, the point contact model with friction is used to analyze the clamping system composed of the clamping mechanism and the clamped object.
2.2. Clamping Matrix
After determining the contact model, it is also necessary to determine the effect of the clamping force exerted by the clamping mechanism on the object and the mapping relationship between the two coordinates. Figure 5a shows the schematic diagram of the clamping mechanism clamping a large-sized axial object. The object coordinate system B-X0Y0Z0 is located at the object’s geometric center. In order to later simplify the calculation process of the force optimization, the contact model between the surface of the clamping mechanism and the object is chosen as the point contact model with friction, which is shown in Figure 5b. The contact point is Bi (i = 1, …, N). The contact coordinate system Bi-XiYiZi is located on the contact surface between each clamping mechanism and the object. It is assumed that the position vector of the i-th contact point in the object coordinate system is described as . The corresponding unit direction vector of each coordinate axis in each contact coordinate system is denoted as zi, xi, yi. Then, the force exerted by the i-th clamping mechanism on the object which is transformed from the contact coordinate system to the object coordinate system is shown as follows:
in which:
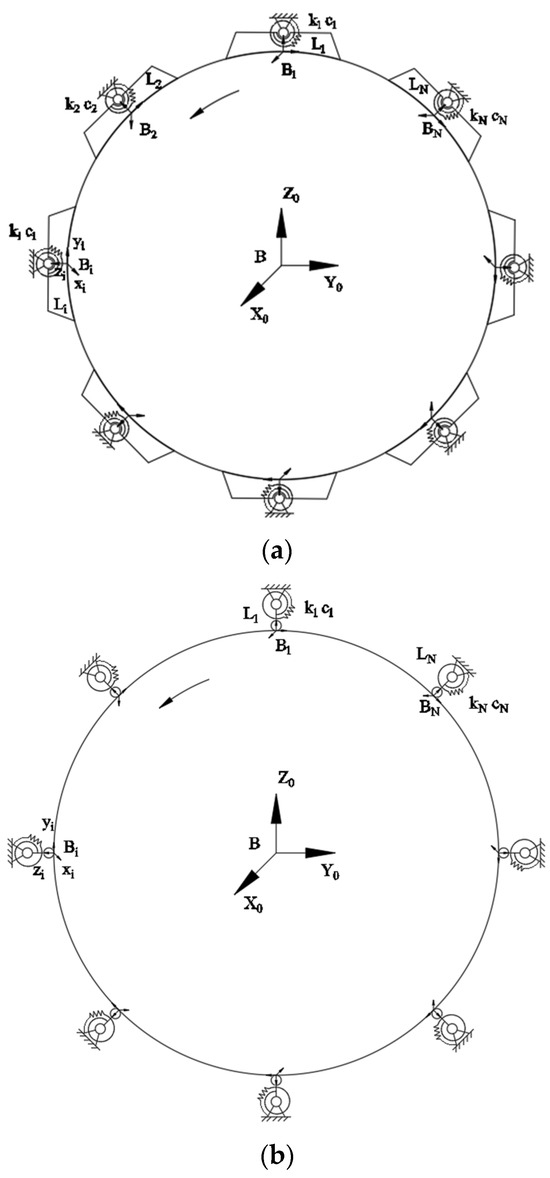
Figure 5.
The schematic of the clamping mechanism clamping an object: (a) The distribution of the clamping mechanism; (b) simplified point contact model of the clamping mechanism and object’s surface.
Let . Then, G is called the clamping matrix. After the clamping mechanisms have clamped the object, the object might deviate from its equilibrium state because of different external disturbances, such as impact, roll and vibration during transportation. At the same time, the external disturbance also causes the clamping force to change to balance the external disturbance. Finally, the clamped object will return to its original equilibrium state or change to a new equilibrium state to prevent its instability, which will cause serious consequences. In order to study the resistance ability to external disturbance of the clamping system composed of the clamping mechanism and object, assuming that the external force screw received by the object is , then the equilibrium equation between the clamping force generated by all clamping mechanisms and external force can be expressed as follows:
According to Equations (1) and (4), the optimization of the clamping force can be expressed as:
3. Calculation and Optimization Method of the Clamping Force
3.1. The Friction Cone Constraint
In the clamping process, in order to avoid excessive output clamping force causing damage to the clamping mechanism and object, it is required that the clamping force should be as small as possible which should satisfy each constraint and realize stable clamping. Among each constraint, the constraint of the friction cone is nonlinear. Buss et al. point out in their research that the constraint of the friction cone can be described as a symmetric matrix of a specific structure, so Equation (1) can be expressed as:
Let the block diagonal matrix . Then, the matrix P can be called the description matrix. Because matrix Pi is a symmetric positive definite matrix, its specific structure can be expressed using a linear homogeneous equation:
in which:
vec() is defined as the vectorization operator of the matrix. From the description matrix P and Equation (7), it can be known that:
Equation (9) shows that the nonlinear constraint of the friction cone is transformed into a linear constraint by the specific structure of the matrix, where the matrix is related to Equation (8). Equation (9) represents the constraint of the friction cone that includes all the clamping mechanisms. Similarly, according to Equation (9), Equation (4) can also be rewritten into the linear constraint form, which can be expressed as:
in which:
In Equation (10), is related to the clamping matrix G and it is also affected by the clamping configuration and the number of contact points. By combining Equations (9) and (10), it can be expressed as:
3.2. Gradient Flow Optimization Method for the Clamping Force
The linear constraints in Equation (12) are called affine constraints. Because matrix P is a symmetric positive definite matrix, Equation (5) can be transformed into a convex optimization problem which describes matrix P with affine constraints in a smooth Riemannian manifold. According to Equations (6) and (12), the convex optimization problem can be expressed as below:
The gradient flow method can solve the convex optimization problem with affine constraints. The target function of the convex optimization can be expressed as:
in which Wp and Wi are weight coefficients. The former is used to control the magnitude of the normal clamping force, and the latter is used to control the distance between the clamping force vector and the edge of the friction cone. I is the identity matrix and tr() is defined as the trace operation of the matrix. A linear constrained gradient flow using the Riemann metric can be expressed as:
in which is the Moore–Penrose generalized inverse matrix of matrix A. In order to start the iterative calculation, it is also necessary to discretize the linear constrained gradient flow, which can be expressed as:
in which is the iteration step size. Adopting the heuristic iteration step size can reduce the number of iterations. Here, the heuristic iteration step size is chosen as follows:
Then, as long as the initial optimization clamping force satisfying each constraint is determined and the convergence error is selected for iterative calculation, the final convergence value obtained after the iteration is the optimal clamping force value of each clamping mechanism. The calculation process of the gradient flow optimization method is shown in Figure 6.
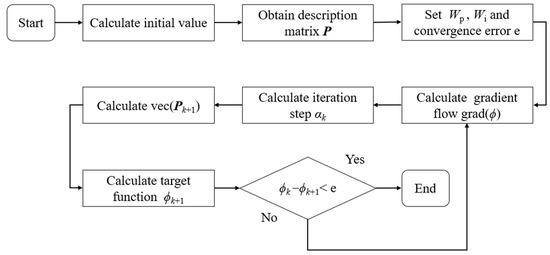
Figure 6.
Calculation process of the gradient flow optimization method.
4. The Illustrative Example and Simulation
The following is an illustrative example of the clamping mechanism clamping a large cabin part. The gradient flow optimization method is used to optimize the clamping force. All of the following calculations and simulation processes in this section are completed using MATLAB 2018b. As shown in Figure 7a, a large-size and large-mass cylindrical cabin part commonly used in the aerospace field is taken as the clamped object. Eight modular clamping mechanisms are used to clamp the object. In order to meet the operational requirements of the aerospace enterprises and the rolling function of the ring pneumatic fixture, according to the internal technical documents of the aerospace enterprise, two clamping mechanisms with an interval of 180° on the ring pneumatic fixture are regarded as the same group. The number of the same group of clamping mechanisms is adjacent in order. The number is counterclockwise from the upper side to the lower side of the clamping mechanism. The different numbering order of the clamping mechanism will affect the clamping matrix, description matrix and the numerical order of each clamping force. It will not affect the calculation process and the final optimization results. Suppose the ring pneumatic fixture is in a static state. The radius of the clamped object is r = 0.7 m. The mass of the clamped object is 15 T; B-X0Y0Z0 is the object coordinate system located at the object’s center. Bi is the contact coordinate system (i = 1, …, 8). Each contact point is regarded as the point contact model with friction, which is shown in Figure 7b. The contact point between each clamping mechanism and the object is the origin point of each contact coordinate system. The friction coefficient at each contact point has the same value. In order to prevent the rigid contact between the clamping mechanism and the clamped object from further damaging the object’s surface, the surface of the clamping mechanism in the ring pneumatic fixture is covered with a layer of 5 mm felt. Felt materials usually have a high friction coefficient. For comprehensive consideration, the friction coefficient here is set as μ = 0.4.
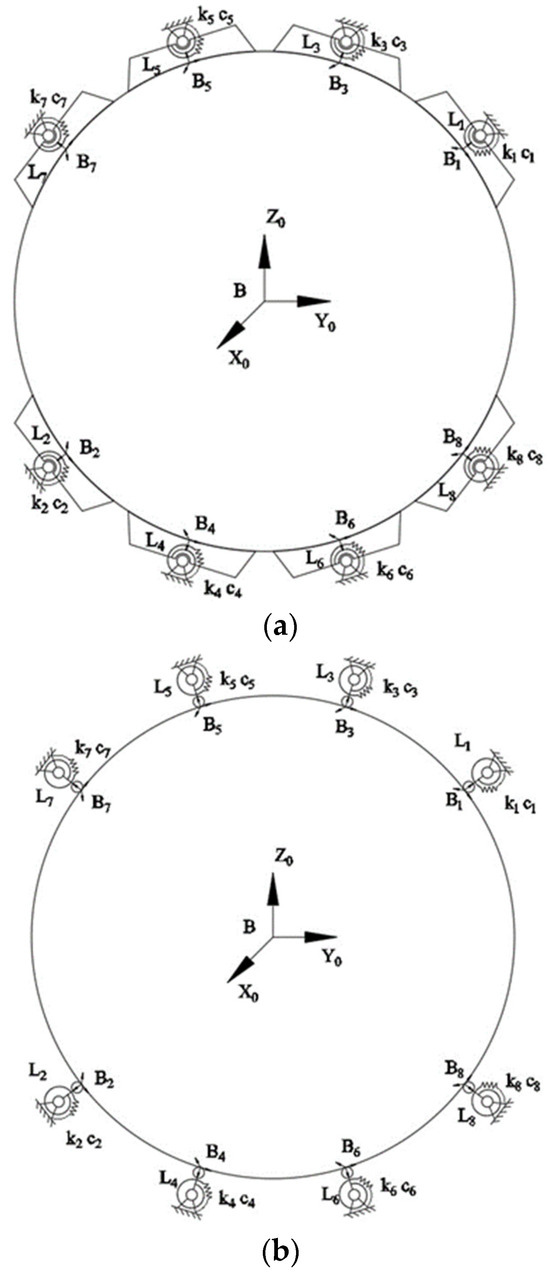
Figure 7.
The example model of 8 modular clamping mechanisms clamping the object: (a) The distribution of 8 clamping mechanisms; (b) simplified point contact model of the clamping mechanism and object’s surface.
According to the relationship between the coordinate system of the contact point and the object coordinate system, the clamping matrix of the example can be obtained using Equation (3):
Considering the gravity of the clamped object, suppose that a random external force Wext = [10, 50, −147, 2, −8, 5]T is exerted onto the object after the clamping mechanism has clamped the object. In order to obtain the initial optimization value required by the gradient flow optimization method, according to Equation (5), the objective function, number of variables, boundary conditions and constraints of the clamping force optimization are determined. The penalty function algorithm, Lagrange multiplier algorithm, sequential quadratic programming algorithm and genetic algorithm are respectively used to calculate the initial optimized value of the clamping force satisfying both Equations (1) and (4) by using the fmincon function and genetic algorithm toolbox in MATLAB 2018b. The principle of the penalty function algorithm is to define a penalty function outside the feasible domain and gradually approach the extreme point from the outside of the feasible domain. This method is suitable for optimization problems with equality constraints or inequality constraints. The principle of the Lagrange multiplier algorithm is to introduce the Lagrange multiplier and slack variable according to the KKT condition to combine the equality constraint, inequality constraint and objective function during optimization. The principle of the sequential quadratic programming algorithm is to simplify the nonlinear programming problem to a quadratic programming problem at the approximate solution of the objective function and find its optimal solution via quadratic programming. The principle of the genetic algorithm is to start from any initial population, generate a group of individuals more suitable for the environment via random selection, crossover and mutation operations and, finally, converge on a group of individuals most suitable for the environment to obtain the optimal solution to the problem. The application, calculation process and parameter settings of the above algorithms can be queried by analyzing and combining with the MATLAB 2018b help document [32]. In order to be expressed clearly, the calculated initial value vectors of each clamping mechanism are combined into a vector Fj = [f1, f2, …, f8]T, j = 1, 2, 3, 4; below, the Foptj is combined in the same way. The numbering sequence of each clamping mechanism is the same as that in Figure 7. According to the penalty function algorithm, Lagrange multiplier algorithm, sequential quadratic programming algorithm and genetic algorithm, the initial value of the clamping force optimization is calculated successively. The initial value of the clamping force optimization Fj obtained by calculation is shown in Table 1.

Table 1.
Different initial values of the clamping force optimization (N).
According to Table 1, although differences exist in the initial optimized values of the clamping force calculated using the four algorithms, it can be known via verification that all four groups of the initial optimized values of the clamping force satisfy Equations (1) and (4), which means that the initial optimized values of the clamping force satisfy the unidirectional force constraint, friction cone constraint and the external force constraint. Then, the four groups of initial values are respectively applied to the gradient flow optimization method of the clamping force. The gradient flow optimization method of the clamping force is compiled using MATLAB 2018b. The relevant parameters required by the gradient flow optimization method are constantly adjusted. Wp and Wi are finally set as 2 and 0.1, respectively, and the convergence error is set as 0.001. The target function of the gradient flow optimization method and the changes in the normal contact force at the contact point between the surface of the clamping mechanism and the object are obtained, which are shown in Figure 8, Figure 9, Figure 10 and Figure 11.
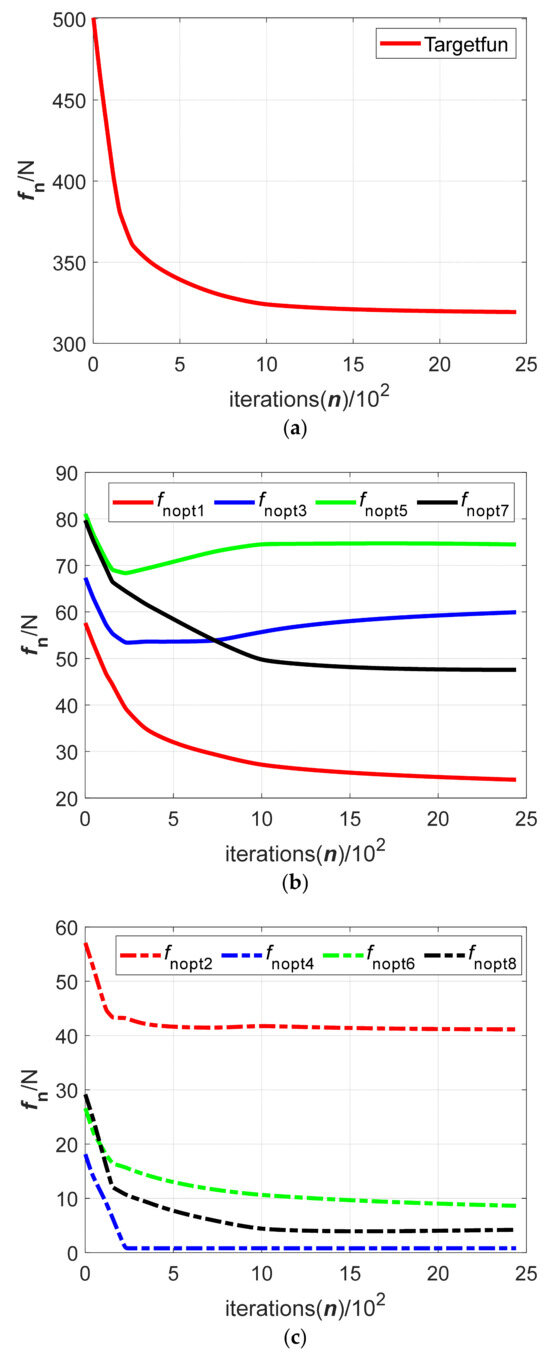
Figure 8.
The iterative process of the gradient flow method in which the initial value is calculated using the penalty function algorithm: (a) Value of the target function; (b) normal contact force of the upper clamping mechanism; (c) normal contact force of the lower clamping mechanism.
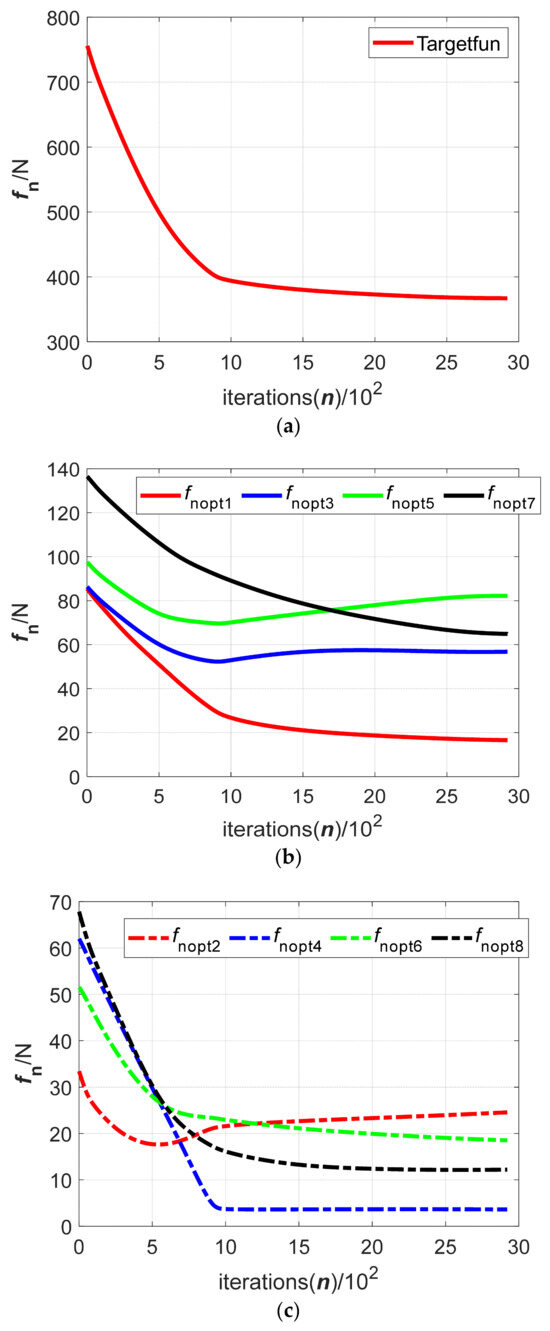
Figure 9.
The iterative process of the gradient flow method in which the initial value is calculated using the Lagrange multiplier algorithm: (a) Value of the target function; (b) normal contact force of the upper clamping mechanism; (c) normal contact force of the lower clamping mechanism.
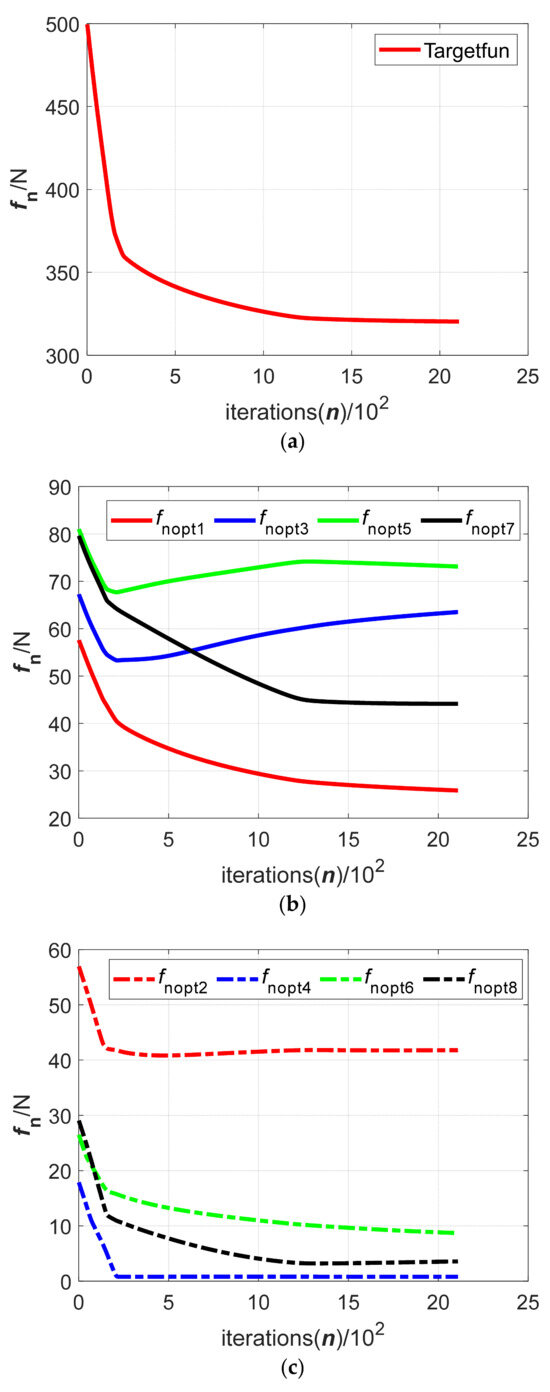
Figure 10.
The iterative process of the gradient flow method in which the initial value is calculated using the sequential quadratic programming algorithm: (a) Value of the target function; (b) normal contact force of the upper clamping mechanism; (c) normal contact force of the lower clamping mechanism.
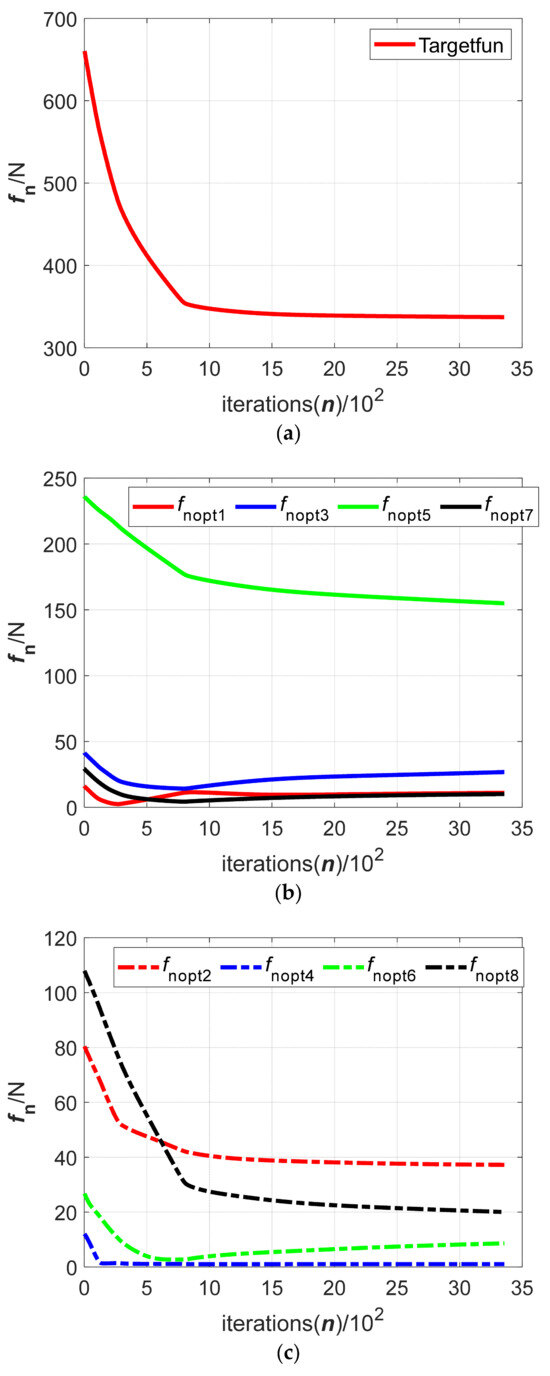
Figure 11.
The iterative process of the gradient flow method in which the initial value is calculated using the genetic algorithm: (a) Value of the target function; (b) normal contact force of the upper clamping mechanism; (c) normal contact force of the lower clamping mechanism.
The clamped object is usually a large cabin part after assembly, so its size and mass are large. The force optimization calculation of this kind of part will take a longer time and larger iterative steps compared to simple parts. By comparing the convergence curves of the target function in Figure 8a, Figure 9a, Figure 10a and Figure 11a, it can be known that the iterative steps for the gradient flow optimization method of the clamping force are roughly the same. They all reach the convergence values after about 1500 iterations. From the aspect of function convergence value, the convergence values of the gradient flow method in which initial values are obtained using the penalty function algorithm and the sequential quadratic programming algorithm are roughly the same at about 320. At the same time, the convergence values of the gradient flow method in which initial values are obtained using the Lagrange multiplier algorithm and the genetic algorithm are roughly the same at about 350. From the aspect of calculation time, the initial value obtained using the genetic algorithm takes the slowest time (about 11.2 s) for the gradient flow optimization method of the clamping force. The initial value obtained using the sequential quadratic programming algorithm takes the fastest time (about 6.9 s) for the gradient flow optimization method of the clamping force. The calculation times of the initial values obtained using the other two algorithms for the gradient flow optimization method are between those of the sequential quadratic programming algorithm and the genetic algorithm, in which the initial value obtained using the penalty function algorithm is about 7.6 s for the gradient flow optimization method and the initial value obtained using the Lagrange multiplier algorithm is about 9.4 s for the gradient flow optimization method. Therefore, the gradient flow optimization method in which the initial values are calculated using four optimization algorithms can complete the clamping force optimization of the large-mass and large-size part quickly. According to other curves in Figure 8, Figure 9, Figure 10 and Figure 11, the convergence conditions of the normal force at the contact point between the surface of the clamping mechanism and the object are compared. Then, four groups of the initial optimized values calculated using different optimizations are substituted into the gradient flow optimization method and the convergence values of the clamping force Foptj are shown in Table 2.

Table 2.
Different convergence values of the gradient flow optimization method (N).
The above data of the optimal clamping forces in Table 2 are substituted into Equations (1) and (4) for verification. It can be concluded that the optimal clamping forces satisfy the unidirectional force constraint, friction cone constraint and external force constraint. It indicates that the normal component of each clamping force and the distance between each clamping force vector and the edge of the friction cone can be controlled within a certain range by adjusting the weight coefficients Wp and Wi to a certain value. It also confirms the feasibility and effectiveness of the gradient flow optimization method applied to the clamping force optimization process of a large cabin part. However, the gradient flow optimization method of the clamping force may cause the problem that the objective function’s value and the clamping force’s value will get stuck in the local optimal value during the optimization process like in other gradient optimization methods. This problem may also be produced in the initial value calculation process of the clamping force optimization. By only analyzing the above four groups of the clamping force optimization simulations, it cannot be determined whether the iteration is getting stuck in a local optimal value. It is necessary to carry out a clamping force experiment and comprehensively analyze the experimental results and relevant simulation results.
In addition, from the convergence curves of the normal force at the contact point of each clamping mechanism and the clamped object, it can be seen that the initial optimized values calculated using different optimization algorithms for the gradient flow optimization method of the clamping force will have an influence on the distribution of the final convergence values of the normal clamping force for each clamping mechanism. When determining the output clamping force of each clamping mechanism, the output clamping force can be comprehensively considered and set according to the convergence values and distribution of the normal clamping force. The clamping mechanism where the convergence value of the normal clamping force is too large or too small can be adjusted to avoid the dangerous clamping region and unreasonable distribution of the clamping mechanism. A new clamping configuration can be obtained according to the distribution of the clamping mechanisms. Then, the gradient flow optimization method of the clamping force is applied to analyze and calculate the new clamping force convergence curves until a reasonable distribution of the normal clamping force is obtained to realize the stable clamping of a large cabin part.
5. Experiment
In order to further verify the feasibility of the clamping force’s gradient flow optimization method and the above simulation’s reliability, an experimental prototype of the ring pneumatic fixture is used to clamp an object. The normal clamping force of each clamping mechanism is measured by the force sensor measuring system and is compared with the corresponding simulation results. The prototypes of the ring pneumatic fixture and the force sensor measuring system are shown in Figure 12. The ring pneumatic fixture is set in a static state during the experimental process. The required sensor measuring system consists of four thin-film pressure sensors and a four-channel data acquisition card produced by Vaax Technology, which can simultaneously measure up to four channel pressure changes.
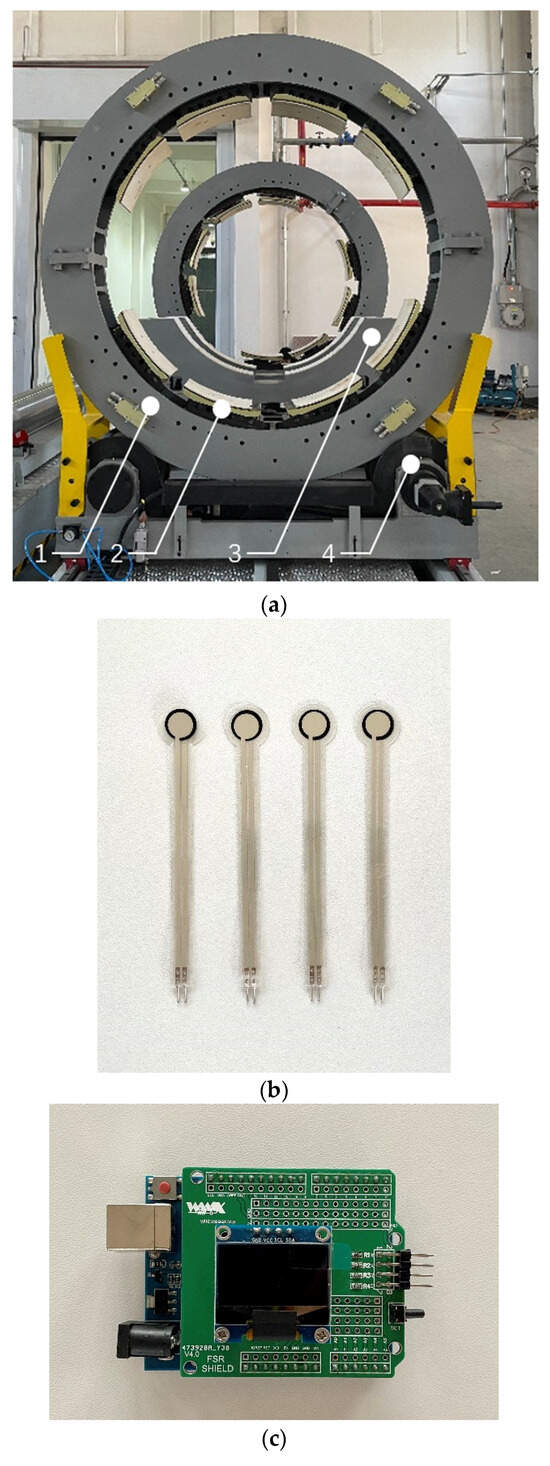
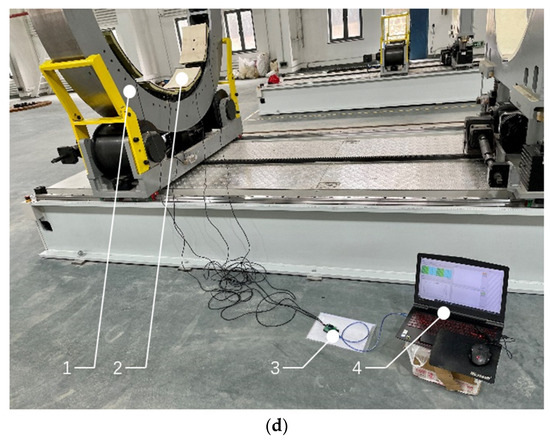
Figure 12.
Experimental equipment: (a) Experimental prototype and its supporting device of the ring pneumatic fixture: 1. Experimental prototype, 2. Clamping mechanism 3. Auxiliary support bracket, 4. Roll support bracket. (b) Experimental force sensor. (c) Four-channel data acquisition card. (d) Force measuring system with the upper computer: 1. Experimental prototype, 2. Force sensor attached to the surface of the clamping mechanism, 3. Data acquisition card, 4. Upper computer.
Since four force sensors are used in this experiment and the ring pneumatic fixture has eight clamping mechanisms, the normal clamping force of the lower clamping mechanism is first measured, and then the normal clamping force of the upper clamping mechanism is measured. The contact model between the clamping mechanism and the object is the surface contact model and the measuring area of the force sensor is small. In this experiment, the center of the contact surface between the clamping mechanism and the object is taken as the measuring position of the force sensor and the value of the normal clamping force measured at this point is taken as the normal clamping force under the equivalent point contact model of the clamping mechanism. The measuring position of the force sensor on the contact surface between the clamping mechanism and the object is shown in Figure 13.
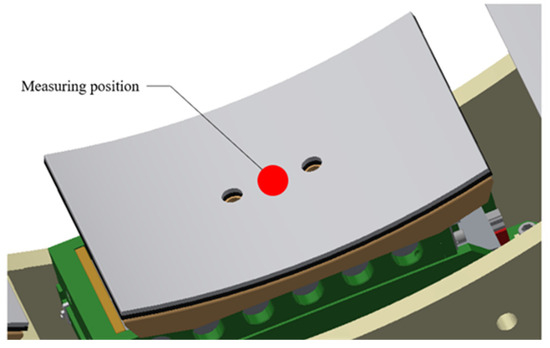
Figure 13.
Measuring position of the force sensor.
The mass of the clamped object is 2 t. The radius of the clamped object is r = 0.7 m. The sequence number of each clamping mechanism is shown in Figure 7 above. Each clamping mechanism simultaneously clamps the object. The changes in the normal clamping force of each clamping mechanism measured via the clamping force experiments are shown in Figure 14.
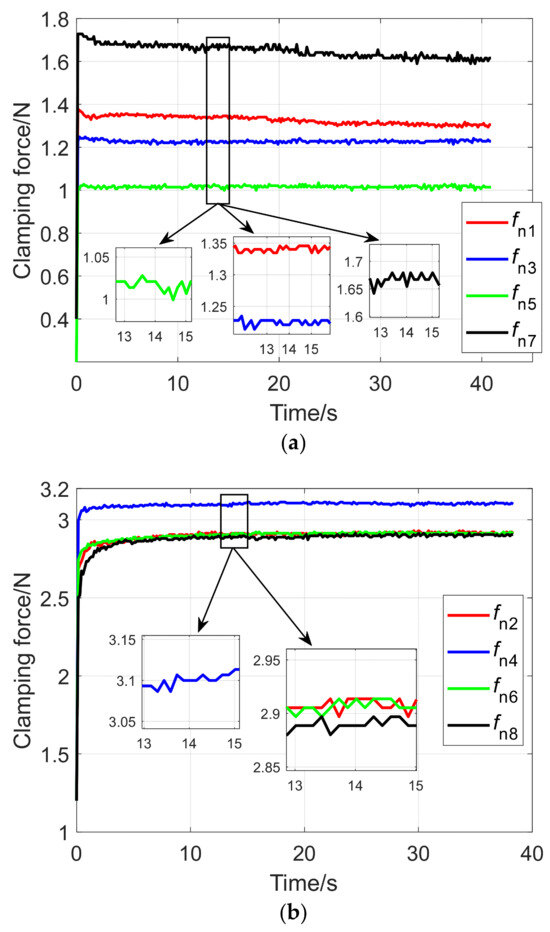
Figure 14.
Change in the normal clamping force obtained by the experiment: (a) The normal clamping force change of the upper clamping mechanism; (b) the normal clamping force change of the lower clamping mechanism.
In order to compare with the corresponding simulation results of the clamping force, it is necessary to process the clamping force data of each clamping mechanism obtained from the experiment. Here, the average value of the normal clamping force obtained via the experiment is taken as the stable clamping force under the equivalent point contact model of each clamping mechanism. Then, the normal clamping force is combined into a vector Fn = [fn1, fn2, …, fn8]T. This vector can be regarded as the normal clamping force value of each clamping mechanism after a stable clamping, which can be expressed as follows:
After the experiment and data processing, the corresponding clamping force optimization simulation is performed. The penalty function method is used for the initial value calculation of the 2 t object. The initial optimized value of the normal clamping force Fne calculated by the simulation is obtained as follows:
According to the settings of the clamping force simulation in Section 4, Wp, Wi and the convergence error are taken as 2, 0.1 and 0.001, respectively. The friction coefficient μ of each contact point is taken as 0.4. Then, the convergence value of the normal clamping force of each clamping mechanism Fnopt is obtained by using the gradient flow optimization method, which is shown as follows:
The optimization process of the target function and the normal clamping force during the simulation is shown in Figure 15. The comparison between the experimental results and the simulation results is shown in Table 3. It can be seen from Figure 15 that the iteration steps to finish the clamping force optimization is about 180 and the simulation process of the optimization takes about 1.23 s. It shows that the gradient flow optimization method can quickly optimize the clamping force of a 2 t clamped object. By comparing the average value of the experiment with the convergence value of the simulation in Table 3, it can be concluded that the value of the normal clamping force of each clamping mechanism measured via the experiment is close to that of the simulation results and the corresponding simulation of the clamping force optimization does not get stuck in its local optimal value, which can confirm the feasibility of the gradient flow optimization method of the clamping force and the reliability of the above simulation results. However, the experimental results and simulation results also show that the value of the normal clamping force of the partial clamping mechanism measured in the experiment is lower than the corresponding convergence value in the simulation and the normal clamping force of each clamping mechanism is not uniform. This may be caused by the position and posture of the clamped object, the uneven distribution of the object’s mass and because the shape of the clamped object is not a strict standard circle.
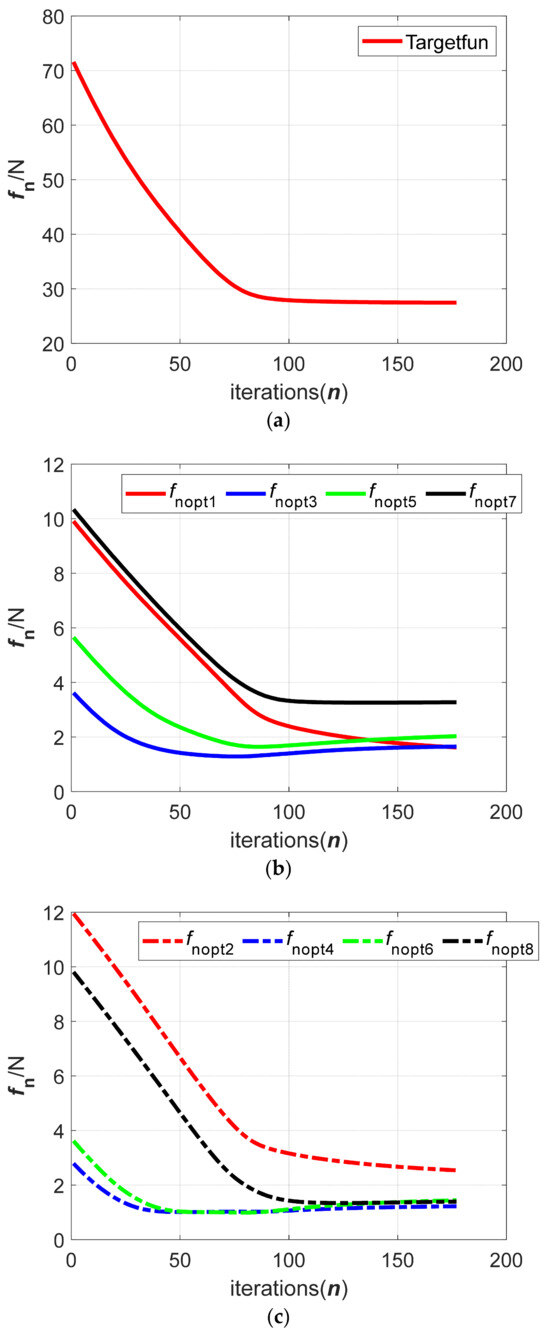
Figure 15.
The iterative process of the gradient flow method when clamping a 2 t object: (a) Value of the target function; (b) normal contact force of the upper clamping mechanism; (c) normal contact force of the lower clamping mechanism.

Table 3.
Experimental average value and the simulated convergence value of the normal clamping force (N).
According to Table 3, besides the factors of the clamped object, the clamping system and the clamping configuration also need to be considered. Because the convergence value obtained by the simulation is theoretically the minimum value of the clamping force which can be allowed in the clamping system, if the clamping force is lower than this value, the clamping object will be unstable and cause related accidents. However, some of the normal clamping force values obtained in the experiment are lower than the simulation value. From the perspective of the experimental prototype of the ring pneumatic fixture, this phenomenon may be caused by the insufficient input actuated force, the unreasonable distribution of the clamping mechanism and the poor contact between the clamping mechanism and the clamped object. In future research, the clamping configuration, the distribution of the clamping mechanism and the contact form between the clamping mechanism and the object can be further optimized and analyzed.
6. Conclusions
In this paper, the ring pneumatic fixture is first used to clamp the large cabin parts used in the aerospace enterprises to replace the traditional clamping fixture. The gradient flow optimization method of the clamping force is proposed for the first time. Then, the clamping force of each clamping mechanism in the ring pneumatic fixture is optimized and simulated, which expands the research on the clamping method and clamping force optimization of the large cabin parts used in aerospace enterprises. According to Figure 8, Figure 9, Figure 10 and Figure 11 and Table 2, the iteration steps of the gradient flow optimization method using initial force values which are calculated using the penalty function algorithm, Lagrange multiplier algorithm, sequential quadratic programming algorithm and genetic algorithm are about 1500. The calculation times of the initial values obtained using the four algorithms for the gradient flow optimization method are 7.6 s, 9.4 s, 6.9 s and 11.2 s, respectively. The gradient flow optimization method can be used to quickly optimize the clamping force of a large-mass and large-size cabin part. By comparing Figure 8b, Figure 9b, Figure 10b and Figure 11b and Figure 8c, Figure 9c, Figure 10c and Figure 11c, it can be seen that different initial optimized values will affect the distribution of the normal clamping force and convergence value of each clamping mechanism calculated using the gradient flow optimization method under the same clamping configuration. The distribution of the normal clamping force and the convergence value of the clamping force of each clamping mechanism can provide a certain reference for determining the final output clamping force and reasonable distribution of the clamping mechanism. It also confirms the feasibility and effectiveness of the gradient flow optimization method applied to the clamping force optimization process of large axial parts such as cabin parts.
The normal clamping force of each clamping mechanism is measured by using relevant experimental equipment and a prototype of the ring pneumatic fixture, which is compared with the corresponding simulation results of the clamping force. According to Table 3 and Figure 14 and Figure 15, it can be concluded that the value of the normal clamping force measured using the experimental equipment is close to the convergence value of the normal clamping force obtained using the gradient flow optimization method. This result shows that the corresponding simulation process of the gradient flow optimization method does not get stuck in its local minimum. It can further verify the reliability of the gradient flow optimization method of the clamping force. However, by further comparing the experimental results with the simulation results, it can be concluded that the normal clamping force value obtained via the experiment is lower than the corresponding convergence value obtained by the simulation. Besides the factors of the object, it also may be caused by the clamping system and the clamping configuration. The clamping configuration, the distribution of the clamping mechanism and the contact form between the clamping mechanism and the object can be further researched in future work. In addition, this paper only considers the distribution and optimization of the clamping force when the ring pneumatic fixture is in the static state. According to the rolling requirement of the ring pneumatic fixture, the dynamic force distribution of each clamping mechanism in the rolling process, the optimization method of the dynamic clamping force and the force control method under two conditions of the ring pneumatic fixture will be the key content of future research.
At the same time, the uncertainties of this method always exist, such as the convergence error, iteration step size of the initial optimization algorithm, the weight coefficients Wp and Wi, the distribution of the clamping mechanism, the configuration of the clamping mechanism and the pose of the clamped object. These uncertainties will affect the final optimization results. As a gradient optimization method, the gradient flow optimization method of the clamping force may also cause a critical problem of getting stuck in the local optimal value during the optimization process like other gradient optimization methods. This problem may also be produced when calculating the initial optimization value of the clamping force. But this problem is not discussed comprehensively in this paper. Moreover, because the clamped object is a large-mass and large-size axial part, the error of the initial optimized value and the optimal clamping force will be large. How to avoid the problem of the local optimal value which may be produced in the process of the clamping force optimization and how to more reasonably equate the surface contact model to the point contact model between the clamping mechanisms and the object when designing experiments are the factors that are the key points and difficulties during the optimization method of the clamping force that require further research.
Author Contributions
Conceptualization, S.Y. and M.C.; methodology, Y.L.; software, Y.L.; validation, Y.L.; resources, S.Y.; data curation, Y.L.; writing—original draft preparation, Y.L.; writing—review and editing, M.C., G.C. and Y.L.; supervision, M.C. and G.C.; project administration, M.C. and G.C. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This research was funded by the Foundation for Innovative Research Groups of the Natural Science Foundation of Hebei Province (Grant No. E2020203174) and Key Project of National Natural Science Foundation of China, Project (Grant No. U20A20332). And The APC was funded by University of Rome Tor Vergata.
Data Availability Statement
Data are contained within the article.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
References
- Yao, S.; Ceccarelli, M.; Carbone, G.; Lu, Z. Analysis and Design of a Modular Underactuated Mechanism for Robotic Fingers. Proc. Inst. Mech. Eng. Part C J. Mech. Eng. Sci. 2012, 266, 242–256. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yao, S.; Ceccarelli, M.; Zhan, Q. Design Considerations for an Underactuated Robotic Finger Mechanism. Chin. J. Mech. Eng. 2009, 22, 475–488. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chu, Z.; Hu, J.; Lu, S. Evaluation of Spring Stiffness for Stable Grasp in Underactuated Fingers. In Mechanism and Machine Science; Springer: Singapore, 2017. [Google Scholar]
- Ceccarelli, M.; Tavolieri, C.; Lu, Z. Design Considerations for Underactuated Grasp with a one D.O.F. Anthropomorphic Finger Mechanism. In Proceedings of the 2006 IEEE/RSJ International Conference on Intelligent Robots and Systems, Beijing, China, 9–15 October 2006; pp. 1611–1616. [Google Scholar]
- Deng, H.; Melkote, S.N. Determination of minimum clamping forces for dynamically stable fixturing. Int. J. Mach. Tools Manuf. 2006, 46, 847–857. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ciocarlie, M.; Allen, P. A constrained optimization framework for compliant underactuated grasping. Mech. Sci. 2011, 2, 17–26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kragten, G.A.; Helm, F.C.T.V.D.; Herder, J.L. A planar geometric design approach for a large grasp range in underactuated hands. Mech. Mach. Theory 2011, 46, 1121–1136. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, R.R.; Spiers, A.; Dollar, A.M. M2 Gripper: Extending the Dexterity of a Simple, Underactuated Gripper Advances in Reconfigurable Mechanisms and Robots II; Springer International Publishing: Cham, Switzerland, 2016. [Google Scholar]
- Odhner, L.U.; Jentoft, L.P.; Claffee, M.R.; Corson, N.; Tenzer, Y.; Ma, R.R.; Buehler, M.; Kohout, R.; Howe, R.D.; Dollar, A.M. A compliant, underactuated hand for robust manipulation. Int. J. Robot. Res. 2014, 33, 736–752. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Odhner, L.U.; Dollar, A.M. Stable, Open-Loop Precision Manipulation with Underactuated Hands; Sage Publications, Inc.: Thousand Oaks, CA, USA, 2015. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, Y.; Wang, H.; Zhou, W. Contact force solving and programming in multi-fingered grasp. Mechinery Des. Manuf. 2011, 4, 107–109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cai, B.; Gao, H.; Song, X.; Wang, F. Structure Design of Three-Fingered Dexterous Hand and Contact Force Planning. Mechinery Des. Manuf. 2020, 01, 127–131. [Google Scholar]
- Fok, L.-M.; Wang, J. Two recurrent neural networks for grasping force optimization of multi-fingered robotic hands. In Proceedings of the 2002 International Joint Conference on Neural Networks, IJCNN’02 (Cat. No. 02CH37290), Honolulu, HI, USA, 12–17 May 2002; Volume 1, pp. 35–40. [Google Scholar]
- Xia, Y.; Wang, J.; Fok, L.M. Grasping-force optimization for multi-fingered robotic hands using a recurrent neural network. IEEE Trans. Robot. Autom. 2004, 20, 549–554. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhong, C.; Wu, Q.; Hong, C.; Zhang, X. Multi-fingered grasping force optimization based on generalized penalty-function concepts. Robot. Auton. Syst. 2021, 135, 103672. [Google Scholar]
- Mu, X.; Zhang, Y. Grasping Force Optimization for Multi-fingered Robotic Hands Using Projection and Contraction Methods. J. Optim. Theory Appl. 2019, 183, 592–608. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Helmke, U.; Hüper, K.; Moore, J.B. Quadratically convergent algorithms for optimal dexterous hand grasping. IEEE Trans. Robot. Autom. 2002, 18, 138–146. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, L.; Trinkle, J.C.; Li, Z. Grasp analysis as linear matrix inequality problems. IEEE Trans. Robot. Autom. 2007, 16, 663–673. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Salisbury, J.K.; Roth, B. Analysis of multi-fingered hands. Int. J. Robot. Res. 1986, 4, 3–17. [Google Scholar]
- Cheng, F.T.; Orin, D.E. Effcient algorithm for optimal force distribution-the compact-dual LP method. IEEE Trans. Robot. Automat. 1990, 6, 178–187. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Buss, M.; Hashimoto, H.; Moore, J.B. Dexterous hand grasping force optimization. IEEE Trans. Robot. Automat. 1996, 12, 406–418. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Buss, M.; Kleinmann, K.P. Multi-fingered grasping experiments using real-time grasping force optimization. In Proceedings of the IEEE International Conference Robotics and Automation, Minneapolis, MN, USA, 22–28 April 1996; pp. 1807–1812. [Google Scholar]
- Buss, M.; Schlegl, T. Multi-fingered regrasping using on-line grasping force optimization. In Proceedings of the International Conference Robotics and Automation, Albuquerque, NM, USA, 20–25 April 1997; pp. 998–1003. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, B.; Li, J.; Liu, H. Optimal grasping force computation for multi-fingered robot hand. J. Jilin Univ. Eng. Technol. Ed. 2008, 1, 178–182. [Google Scholar]
- Jiang, L.; Liu, H. Real time force optimization algorithm of multi-fingered grasp. J. Mech. Eng. 2007, 12, 144–149. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xuelin, W.; Yongfei, X.; Yongguo, Z.; Xinjian, F. Grasping Force Optimization Algorithm of Soft Multi-fingered Hand Based on Safety Margin Detection. Robot 2017, 39, 844–852. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, X.; Xu, Y.; Zhang, D. Parameter Comparison of Grasping Force Optimization of Hard and Soft Multi-fingered Hands based on Safety Margin Detector. In Proceedings of the 2021 China Automation Congress (CAC), Beijing, China, 22–24 October 2021; pp. 6290–6295. [Google Scholar]
- Chen, D.; Jiang, L.; Wang, X. Computation of multi-fingered grasping force with linear combination. J. Harbin Inst. Technol. 2013, 45, 55–59. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, X.; Liu, Y.; Gao, J. Non negative linear combination grasp force optimization. In Proceedings of the 2016 IEEE International Conference on Mechatronics and Automation, Harbin, China, 7–10 August 2016; pp. 2134–2138. [Google Scholar]
- Yu, D. Grasp Position Optimization and Force Control of Multi-Finger Humanoid Hand; Beijing Institute of Technology: Beijing, China, 2018. [Google Scholar]
- Ma, X. Research on the Mechanism Model and Grasping Planning of General Tool Manipulator; Harbin Engineering University: Harbin, China, 2021. [Google Scholar]
- MathWorks Inc. MATLAB 2018 Help. Available online: https//www.mathworks.com/help/optim/ug/choosing-the-algorithm.html (accessed on 28 October 2023).
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).