Abstract
The continental shale oil resource in China exhibits significant potential and serves as a crucial strategic alternative to the country’s conventional oil and gas reserves. The efficacy of shale oil exploration and production is heavily contingent upon the heterogeneity of the pore structure within the reservoir. However, there remains a scarcity of research pertaining to the pore structure of continental shale and the factors that influence it. The objective of this study is to provide a quantitative characterization of the heterogeneity exhibited by the continental shale of the Funing Formation in the Gaoyou Sag. In this study, the research focus is directed toward the continental shale of the Funing Formation located in the Gaoyou Sag of the Subei Basin. This paper examines the correlation between the fractal dimension of nuclear magnetic resonance (NMR) and various factors including the total organic carbon (TOC), mineral composition, geochemical parameters, and physical properties, utilizing the principles of fractal dimension theory. The findings indicate that the primary pore types observed in the Funing Formation continental shale are inorganic matrix pores, which encompass dissolution pores, clay mineral intergranular pores, and a limited number of pyrite intergranular pores. By employing a relaxation time cutoff, the NMR fractal dimension can be categorized into two distinct dimensions: the bound-fluid-pore fractal dimension (0.5795~1.3813) and the movable-fluid-pore fractal dimension (2.9592~2.9793). The correlation between mineral composition and the fractal dimension indicates a negative relationship between the fractal dimensions of bound-fluid pores and movable-fluid pores and the content of quartz. The correlation between clay minerals and the fractal dimension indicates a significant negative relationship between the fractal dimensions of bound-fluid pores and movable-fluid pores with illite. There exists a negative correlation between the pore fractal dimension of bound fluid and the content of organic matter, whereas a positive correlation is observed between the pore fractal dimension of mobile fluid and the content of organic matter. The range of maturity of organic matter within the Funing Formation exhibits a relatively limited span, as indicated by the vitrinite reflectance (Ro) values falling between 0.8% and 0.9%. This narrow range of maturity does not exert a substantial influence on the two fractal dimensions. The NMR fractal dimension exhibits a negative correlation with permeability in relation to reservoir physical properties, while the bound-fluid-pore fractal dimension demonstrates a negative correlation with the total porosity. The findings suggest that the NMR fractal dimension can serve as a valuable indicator for evaluating the physical characteristics of reservoirs. The present study successfully examined the pore structure of continental shale through the utilization of nuclear magnetic resonance technology. This innovative technique provides a novel avenue for the assessment of continental shale reservoirs and the investigation of pore heterogeneity on a global scale.
1. Introduction
By the end of 2022, China possessed proven geological reserves of terrestrial shale oil amounting to 1.306 billion tons, with controlled reserves totaling 128 million tons and predicted reserves estimated at 2.974 billion tons [1]. In 2022, the production of continental shale oil reached approximately 3.18 million tons of crude oil, making it a vital contributor to the stable crude oil production in China [2,3,4]. At present, shale oil exploration in the Chinese Mainland has successfully developed high-yield wells in the Paleogene Funing Formation shale system of the Qintong Sag and the Gaoyou Sag in the Subei Basin, with proven reserves of 1.1 billion tons [5,6], underscoring the significant resource potential of shale oil in China [7]. Nevertheless, when juxtaposed with the marine shale formations discovered in the United States, it becomes evident that China’s geological structure exhibits a considerable level of intricacy. The presence of multiple stages of tectonic transformations and frequent climate changes have resulted in complex mineral compositions and significant heterogeneity within continental shale [2,8,9]. Moreover, shale oil demonstrates notable attributes, including the elevated viscosity of crude oil, relatively low level of maturity, constrained productivity of individual wells, brief periods of stable production, uneven distribution of wells with high and low production rates, diminished overall recovery rates, and suboptimal economic returns [3,10]. The aforementioned challenges have played a significant role in the formidable obstacles encountered during the extensive exploration and economic development of continental shale oil in China [3,11,12].
The pore structure and developmental characteristics of shale play a crucial role in determining the distribution and accessibility of shale oil, thereby influencing the overall effectiveness of shale-oil extraction. Hence, the assessment of shale reservoirs heavily relies on the analysis of pore characteristics in shale formations. Several methodologies are utilized for this objective; nevertheless, each approach is accompanied by specific constraints stemming from its fundamental principles [13]. Techniques such as the core-casting of thin sections and scanning electron microscopy (SEM) allow for the visual examination of shale pores. However, these methods have limitations in terms of sample size and fail to offer a comprehensive depiction of the pore structure characteristics of the sample. The comprehensive understanding of shale pore structure is affected by different adsorbates, posing a challenge to employing single adsorbate techniques like gas adsorption and mercury intrusion to fully capture the relevant information. In order to achieve a comprehensive characterization, it is typically imperative to augment these methodologies with experimental investigations encompassing carbon dioxide and nitrogen adsorption, along with mercury intrusion [14,15]. Significantly, the gas adsorption method necessitates sample crushing, which can result in damage to the sample’s pore structure, potentially compromising data accuracy [16]. Nano-CT technology and small-angle scattering technology offer non-destructive and quantitative means to characterize shale pore structure [17], Nevertheless, the implementation of these methods may be financially unfeasible. Conversely, the nuclear magnetic resonance (NMR) technique remains largely unaffected by the composition of the shale skeleton. The aforementioned technology possesses notable characteristics, including high velocity, a non-invasive nature, the ability to conduct measurements across multiple parameters and dimensions, and a comparatively affordable price. Consequently, nuclear magnetic resonance (NMR) has become an indispensable instrument for investigating the pore characteristics of shale reservoirs [18,19,20].
The utilization of fractal theory as a mathematical framework for assessing the intricate nature of pore structure in porous materials has garnered extensive utilization within the domain of evaluating unconventional oil and gas reservoirs. The fractal dimension is a quantitative parameter utilized to describe the roughness of solid surfaces, enabling the characterization of heterogeneity in shale reservoirs. In their study, Liang et al. [21] employed the box-dimension method and NMR fractal theory to examine the pore characteristics of the Shahezi Formation shale reservoir in the Songliao Basin. The researchers’ findings led to the determination that the fractal dimension can be considered a reliable indicator for the assessment of physical properties in shale.
Similarly, in the research conducted by Li et al. [22], a comparison of fractal dimensions was made using nuclear magnetic resonance (NMR), nitrogen adsorption, and mercury porosimetry across various experimental methods. The findings of their research demonstrated that the fractal dimension derived from NMR yielded a higher degree of precision in depicting the attributes of the pore structure in shale.
This article focuses on the continental facies shale found within the Funing Formation; specifically, within the Gaoyou Sag of the Subei Basin. The primary objective of this study is to comprehensively analyze the pore characteristics of these continental facies shale reservoirs. To achieve this, a multifaceted approach is employed, encompassing various techniques such as field-emission scanning electron microscopy (FE-SEM), total organic carbon (TOC) quantification, X-ray diffraction analysis, and nuclear magnetic resonance (NMR) investigations. Moreover, the utilization of image processing analysis serves to augment our comprehension of these pore characteristics. The incorporation of NMR fractal theory allows for the elucidation of the complexity of the pore structure within shale reservoirs of continental facies. This theory is examined in relation to various parameters, such as the composition of shale minerals, characteristics of physical properties, and geochemical attributes. The primary objective is to establish a comprehensive theoretical framework for the discipline of shale oil science and its effective advancement. The primary objective of this research is to enhance our understanding regarding the pore structure in shale reservoirs of continental facies, with a specific focus on identifying the key factors that influence these characteristics.
2. Geological Setting and Samples
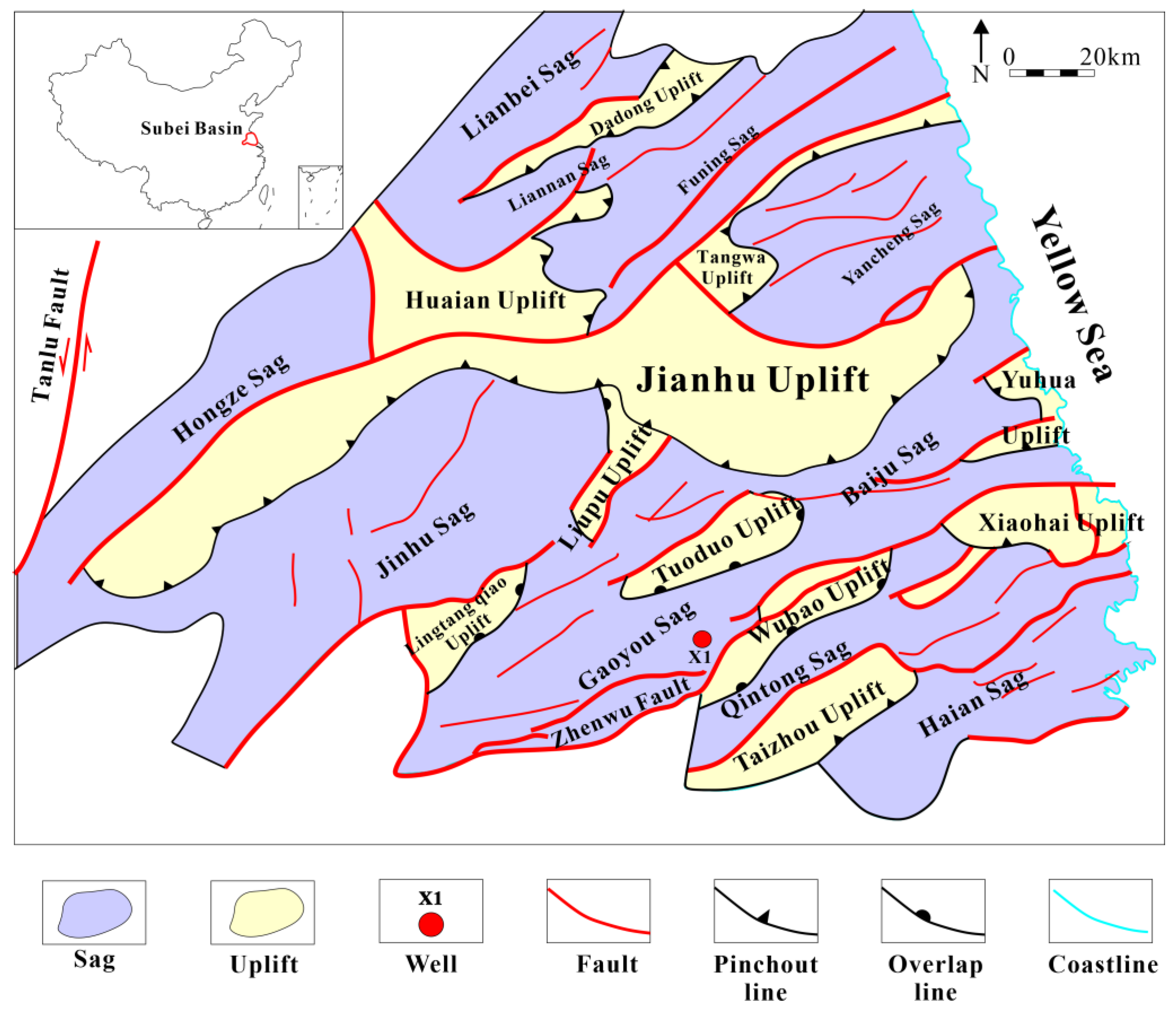
The Subei Basin is a sedimentary basin with origins dating back to the continental Mesozoic and Cenozoic periods. It formed upon the foundation of the Cretaceous-period bedrock. Encompassing a vast expanse of approximately 3.5 × 104 km2, the Subei Basin is located in the eastern region of China [7]. The basin is delimited by the Sulu uplift in the northern direction, the Sunan uplift in the southern direction, the Tanlu fault zone in the western direction, and the South Yellow Sea Basin in the eastern direction.
The Gaoyou Sag, located in the Subei Basin, underwent a comprehensive process of rift-basin evolution spanning from the Late Cretaceous to the Cenozoic. This evolution can be characterized as a sequence of stages; namely, early depression, fault depression, fault depression, and late depression. During the sedimentary period of the second member of the Tai-zhou Formation, which corresponds to the first member of the Funing Formation, the basin exhibited characteristics indicative of an early stage of rift basin evolution. The development of solely boundary faults and the presence of weak activity suggest that the basin was in a state of depression. During the sedimentary period encompassing the second and fourth members of the Funing Formation, there was a notable escalation in the degree of basin rifting and an intensification of tectonic activity. Currently, the basin has transitioned into the phase of fault-depression evolution. During the depositional phase of the Dainan Formation, the basin underwent a period characterized by fault depression. The formation of the thick Dainan Formation depression’s basic structural pattern was influenced by the common control of the first and second faults of the depression. During the sedimentary phase of the Sanduo Formation, the basin underwent a transition period characterized by a rift depression, leading to the subsequent subsidence of the basin and the formation of a multi-level fault system. The denudation was a result of the uplift of the entire basin during the late Sanduo Formation. The Neogene and Quaternary basins have transitioned into the late depression stage of evolution. The cessation of tectonic activity resulted in the deposition of the Yancheng Formation and Dongtai Formation strata throughout the basin, exhibiting a uniform distribution.
The Gaoyou Sag, with an area of 3500 km2, is one of the most important oil-bearing depressions in the southern part of the Dongtai depression of Subei Basin. It is bounded by the northward dipping Zhenwu Fault in the south, the Lingtangqiao low bulge and Zhe Tuo low bulge in the north, the southern-fault step zone, the central deep-depression zone and the northern slope zone in turn, from south to north, and the overall NE-SW trend, which has the characteristics of a steep fault in the south and a gentle fault in the south and an overlap in the north [5,7]. (Figure 1).
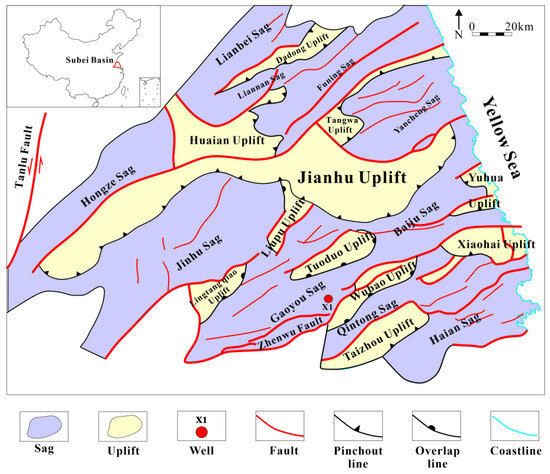
Figure 1.
Map of the study area in the Gaoyou Sag [5,7].
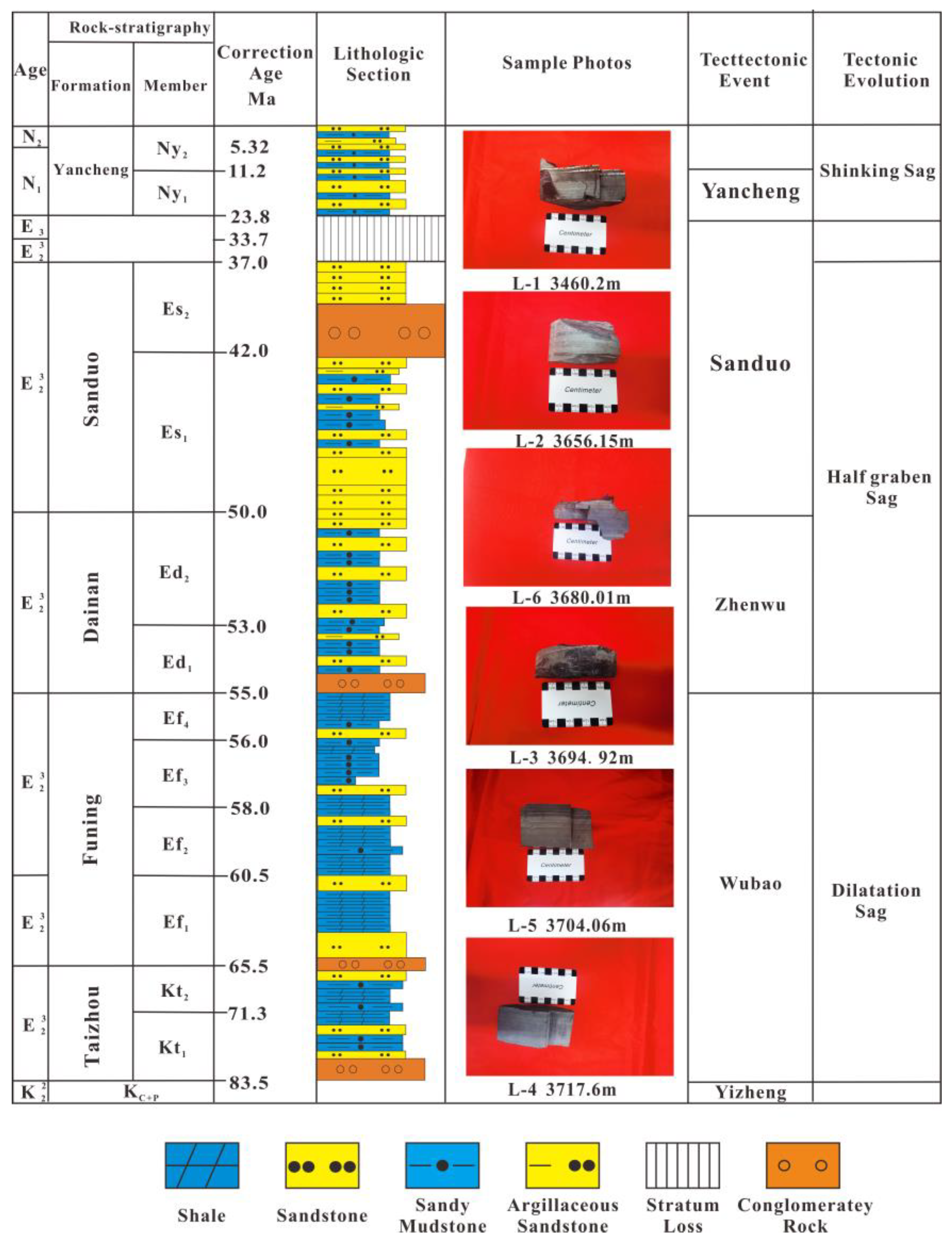
The Gaoyou Sag demonstrates a sequential geological progression from the lowermost stratum to the uppermost stratum, encompassing five significant formations: the Taizhou Formation from the Cretaceous period, the Funing Formation from the Paleogene era, the Dainan Formation, the Sanduo Formation, and the Yancheng Formation from the Neogene epoch, as depicted in Figure 2. The stratigraphic characteristics are concisely outlined as follows. The Taizhou Formation exhibits a thickness ranging from approximately 100 to 300 m. The spatial distribution of lithology exhibits significant variability. Within the Taizhou Formation, the lower section displays a consistent occurrence of interbedded (dark) brown sandstone and mudstone throughout the entire region. Additionally, the sedimentary rhythm within this formation is characterized by a lack of distinct patterns. The eastern region of the Gaoyou Sag exhibits a significant abundance of dark mudstones, serving as a prominent source rock within the Subei Basin. The Dainan Formation in the Gaoyou Sag exhibits a thickness ranging from 300 to 1500 m. This formation is distinguished by the presence of light-gray (powder) fine sandstone, variegated glutenite, and deep gray-brown mudstone, which are interbedded with varying thicknesses.
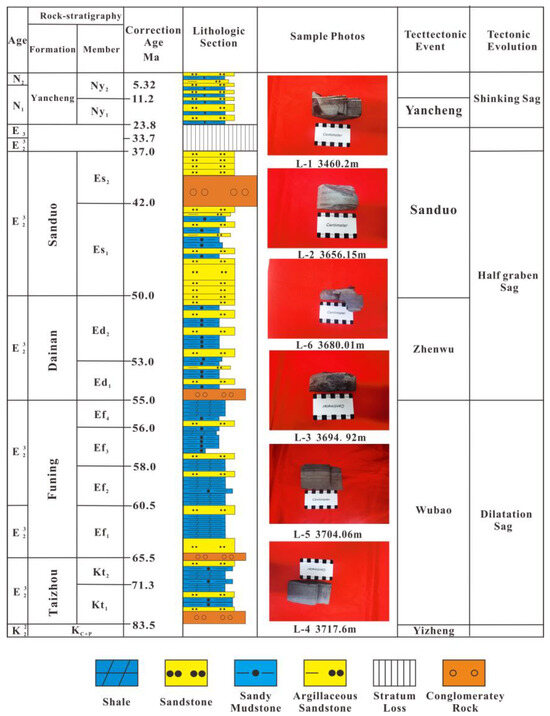
Figure 2.
Comprehensive stratigraphic column of the Gaoyou Sag.
The Funing Formation is distinguished by its alternating layers of siltstone and fine sandstone, which suggest its formation in a sedimentary environment associated with a deep or semi-deep lake. This geological formation is renowned for its abundant deposits of gray shale deposits. Typically, the Funing Formation boasts a thickness exceeding 300 m and offers highly favorable organic geochemical conditions, making it an outstanding source rock.
The thickness of the Sanduo Formation in the Gaoyou Sag is about 200–1500 m, and gray siltstone (fine) sandstone and brown-gray green-gray mudstone with different thicknesses have developed.
In the Gaoyou Sag, the Neogene Yancheng Formation exhibits a thickness ranging from approximately 800 to 1500 m. The lower section is distinguished by the formation of a substantial assemblage of gray-white conglomerates with high resistance, while the upper section consists of gray sandstones containing gravel and brown-gray mudstones of varying thicknesses.
Notably, the Funing Formation stands out as the primary shale-rich horizon within the Gaoyou Sag.
It is worth noting that multiple wells within the Funing Formation have encountered shale oil reservoirs, yielding substantial industrial oil production [5,6]. This highlights the significant capacity of shale oil reserves in the area. In this specific investigation, a total of six shale samples were chosen from the Funing Formation located within the Gaoyou Sag. These samples were exclusively obtained from Well T1 at varying depths ranging from 3460 to 3720 m.
3. Methods
3.1. TOC, Mineralogical Analysis, and SEM
Organic carbon content analysis is a common method to determine the abundance of organic matter in shale. The test implementation standard in this paper is the “determination of total organic carbon in sedimentary rocks” (GB/T19145-2022) [23]. The shale sample was weighed to determine its mass, which was found to be 5 g. Subsequently, the sample was ground into a fine powder with a particle size of 200 mesh using an agate mortar. The powdered sample was placed into a beaker and immersed in hydrochloric acid in order to eliminate carbonate minerals and other minerals that are soluble in acid from the sample. Subsequently, the substance was subjected to multiple washes utilizing deionized water until the resulting solution attained a state of neutrality. The remaining samples were subjected to a drying process in a controlled environment at a consistent temperature of 60 °C. Subsequently, the EURO 3000 elemental analyzer was utilized to determine the organic carbon content of the aforementioned samples.
The reflectance of vitrinite was measured by an MPV-SP microphotometer at room temperature of 23 °C and relative humidity below 70%. The reflected light and UV fluorescence mode were used to identify the macerals, and we referred to Xiao for the classification of the materials [24]. Before the start of the vitrinite reflectance (Ro) measurement experiment, two standard samples were used to correct the instrument, and the RO values were 0.59% and 1.72%, respectively. The vitrinite observation and reflectivity measurement of the sample were carried out with a 50X oil immersion objective lens. The measurement of RO value generally needs to be carried out on the larger and more homogeneous vitrinite. Since there are few vitrinite fragments in continental shale, in order to measure reliable RO data, it was necessary to measure the reflectance of multiple vitrinite fragments at least 20 times to obtain the average vitrinite reflection value of the sample.
To elucidate the mineral composition characteristics of shale within the study area, X-ray diffraction (XRD) analysis data were subjected to statistical analysis in this research. The testing protocol adhered to the standards outlined in “X-ray Diffraction Analysis Method for Clay Minerals and Common Non-Clay Minerals in Sedimentary Rocks” (SY/T5163-2018) [25].
XRD analysis is a highly valuable technique utilized for the identification and quantification of minerals present in shale samples. Through the utilization of a statistical analysis of XRD data, scholars are able to acquire valuable knowledge regarding the mineralogical composition of shale formations. This knowledge plays a crucial role in comprehending the properties and potential applications of these formations. The implementation of a standardized approach in this study area guarantees the dependability and uniformity of the mineral composition data acquired from the shale samples.
The XRD experimental apparatus employed in this study is a high-resolution diffractometer known as the SmartLab X-ray diffractometer [26]. This instrument is produced by Riken Science and Technology Corporation, a reputable manufacturer based in Japan. Weigh 2 g of shale sample and grind it into a powder with a particle size of less than 200 mesh in an agate mortar, then proceed to the next step. In order to ascertain the mineral composition of the shale, it is recommended to fabricate a measurement test specimen utilizing the back-pressure technique. Weigh a 20 g sample of shale, place it into distilled water, and stir to suspend. Extract the suspension and obtain clay mineral samples using a centrifuge; then, carefully slice them into a natural form. The distillation of ethylene glycol should be conducted using unaltered samples, and the resultant distilled samples should be subjected to elevated temperatures using a muffle furnace. The clay mineral composition of the shale can be determined through the analysis of three types of spectra: the natural slice spectrum, the ethylene glycol slice spectrum, and the high-temperature heating slice spectrum. The whole rock mineral composition was determined at a scanning speed of 1°2θ/min in the range of 4°~70°2θ, and the clay mineral composition was determined at a scanning speed of 1.5°2θ/min in the range of 3°~65°2θ.
In order to reduce the surface roughness of shale samples, massive shale samples were selected and polished by the Leica EM TIC 3X ion-thinning instrument to reduce the surface roughness of the shale samples. The polishing area was about 5 mm × 5 mm. The polished samples were placed in the sample chamber of the field emission scanning electron microscope (ZEISS, Germany, Gemini Merlin 540, resolution greater than 1.2 nm). After vacuum treatment, the shale samples were directly observed by secondary electron and backscatter imaging mode to obtain FE-SEM images. The FE-SEM images have high contrast and good identification of the mineral composition and micro-nanopores. Image-J software (1.51j8) was used to extract pore information from the FE-SEM photos. By adjusting the gray value of FE-SEM digital photos, the information of inorganic minerals and organic matter is filtered, and only pore information is retained. The Nano-Measurer particle-size statistical software (1.25) was used to analyze the number and pore sizes of different types of pores in the same field of view of the FE-SEM photos, and the development characteristics of different types of pores were clarified.
3.2. NMR Experiment
NMR experiments were conducted at the National Key Laboratory of Oil and Gas Resources and Engineering of China University of Petroleum (Beijing, China), utilizing the nuclear magnetic resonance analyzer manufactured by Suzhou Newmark analytical instruments Co., Ltd., (Suzhou, China) with the model number of MicroMR12-150H-I. A resonance frequency of 12.798 MHz, magnet temperature of 35 ± 0.02 °C, probe coil diameter of 25 mm, and magnetic field strength of 0.28 t were also utilized. Before conducting the experiment, all samples underwent a drying procedure in a drying oven set at a temperature of 105 °C for a duration of 6 h in order to eliminate any traces of moisture present in the samples. The dried specimen was subjected to water saturation for a duration of 24 h using a vacuum-pressure saturation apparatus, while maintaining a pressure of 30 MPa. Nuclear magnetic resonance (NMR) was used to measure the saturated and centrifuged samples in order to acquire the T2 spectrum and pore parameter data, such as porosity, permeability, and the relaxation-time cutoff. The samples were centrifuged at 10,000 rpm for 8 h using a hc-3018r high-speed freezing centrifuge, and subsequently, their T2 spectrum distribution was measured again in the NMR instrument. The echo time was 0.07 ms; the number of echoes was six thousand. The number of scans was thirty-two.
3.3. Fractal Dimension
The mathematician Mandelbrot conducted research on objective phenomena by utilizing the concept of fractal dimension. He proposed the theory of fractal geometry to quantify the degree of irregularity and self-similarity observed in intricate porous materials. Prior research has established that reservoir rocks possess fractal characteristics within their intricate pore systems [27,28]. The fractal dimension of the pore structure ranges from 2 to 3 in a three-dimensional Euclidean space. A higher fractal dimension value, approaching 2, is indicative of enhanced pore homogeneity, a more refined pore-throat surface, and improved reservoir performance of the rock. On the contrary, an augmentation in fractal dimension yields heightened heterogeneity, a coarse pore-throat surface, and degradation of rock physical properties [29,30]. Based on this characteristic, Zhang et al. conducted a comprehensive study on the pore characteristics of various rock samples [31]. They derived an approximate fractal geometry formula for nuclear magnetic resonance T2 spectra and calculated the fractal dimension of rock pore structures using a piecewise regression method. The calculation formula is as follows:
After taking logarithms from both sides, we can obtain:
where SV is the percentage of the micro-nanopores’ cumulative pore volume corresponding to pores with a relaxation time less than T2 in total pore volume; T2max is the maximum relaxation time; and D is the fractal dimension.
Equation (2) illustrates a linear relationship if the pores present in the samples demonstrate a self-similar pore structure and exhibit fractal characteristics. The fractal dimension of the rock pore structure can be determined by solving for the coefficient in the regression equation.
4. Result
4.1. TOC and Mineral Composition
Table 1 displays the organic geochemical characteristics and mineral composition of all the samples. The TOC content of six shale samples from the Funing Formation ranges from 0.55% to 1.81%, with an average of 1.11%. The range of the RO is from 0.81% to 0.91%, with an average value of 0.88%. It has been found that clay minerals do not dominate the composition of some shale reservoirs but contain a large quantity of quartz, dolomite, calcite, feldspar minerals, and their mixtures. Based on XRD analysis, the primary mineral constituents in the Funing Formation shale samples consist of quartz (with an average content of 25.53% and a range from 20.20% to 34.70%) and dolomite (with an average content of 24.23% and a range from 2.80% to 51.8%). Additionally, clay minerals (with an average content of 20.77% and a range from 14.60% to 32.70%) and feldspar (with an average content of 13.80% and a range from 2.50% to 30.40%) are also present.

Table 1.
TOC content and mineral composition of all samples.
4.2. Pore Type and Morphology
Studies have revealed that the shale reservoir within the Funing Formation in the Gaoyou Depression is characterized by a substantial presence of micro- and nano-scale pores. Loucks divided pores into organic pores and inorganic pores [32]. Within the realm of inorganic matter pores, there exist various types, including intragranular pores, which encompass intercrystalline pores and dissolution pores, as well as intergranular pores.
4.2.1. Organic Matter Pores
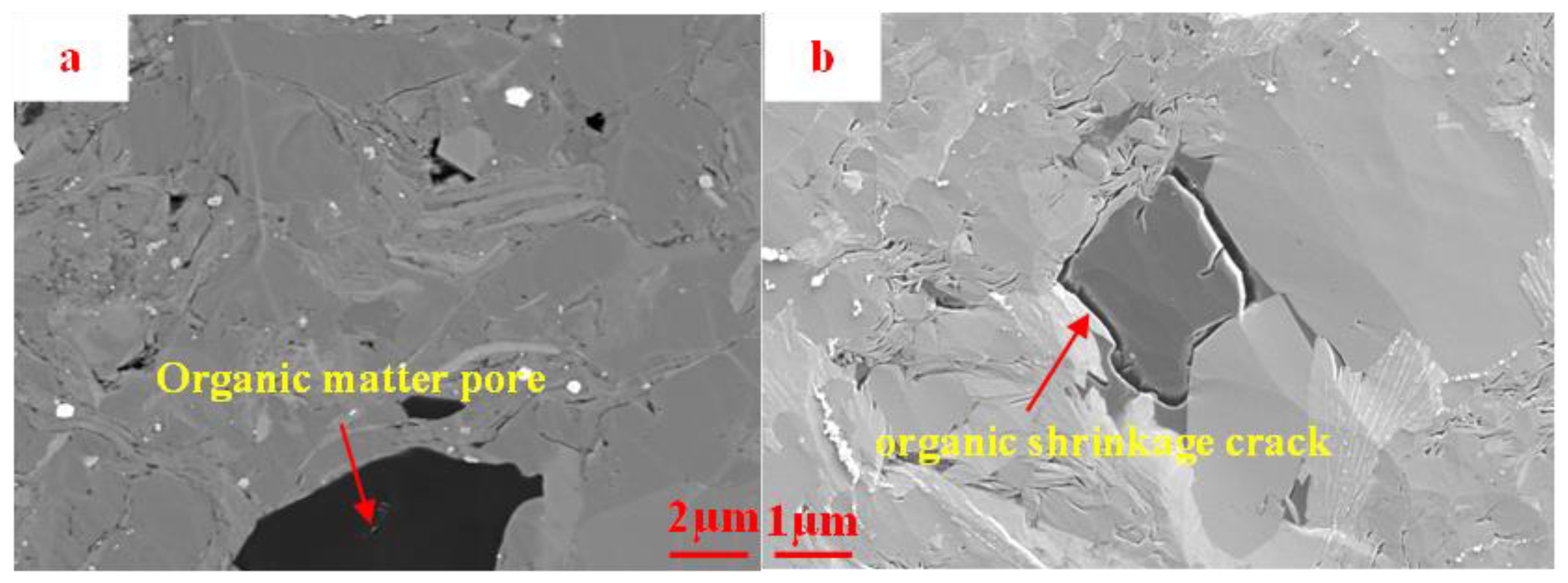
The organic matter pores in the Funing Formation shale of the Gaoyou Sag are predominantly identified by their occurrence as widespread or stratified organic matter dispersed among inorganic minerals. Irregularly shaped polygonal, circular, or oval pores are formed within the organic matter, commonly displaying average dimensions spanning from tens to hundreds of nanometers, with a smaller subset falling within the micrometer range. (Figure 3). The continental shale discovered in the study area has undergone comparatively lesser degrees of thermal maturation when compared to marine shale. As a result, it exhibits a deficiency in the well-developed honeycomb-like dense organic-matter pores that are commonly observed in marine shale formations. Nevertheless, it is worth noting that within this particular continental shale, the organic matter has the ability to establish connections with the pores present in the inorganic mineral matrix by means of contraction fractures found within the organic matter. This phenomenon plays a significant role in facilitating the availability of reservoir space and percolation channels for shale oil within the geological formation.
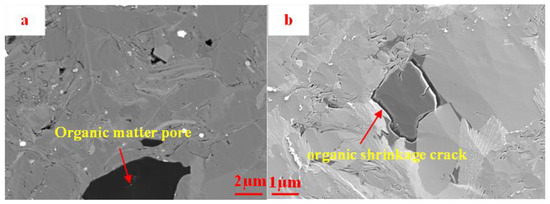
Figure 3.
BSE image of organic-matter pores in the Funing Formation shale in the Gaoyou Sag. (a) Organic matter pores, L-1. (b) Organic matter shrinkage joint, L-5.
4.2.2. Intergranular Pores
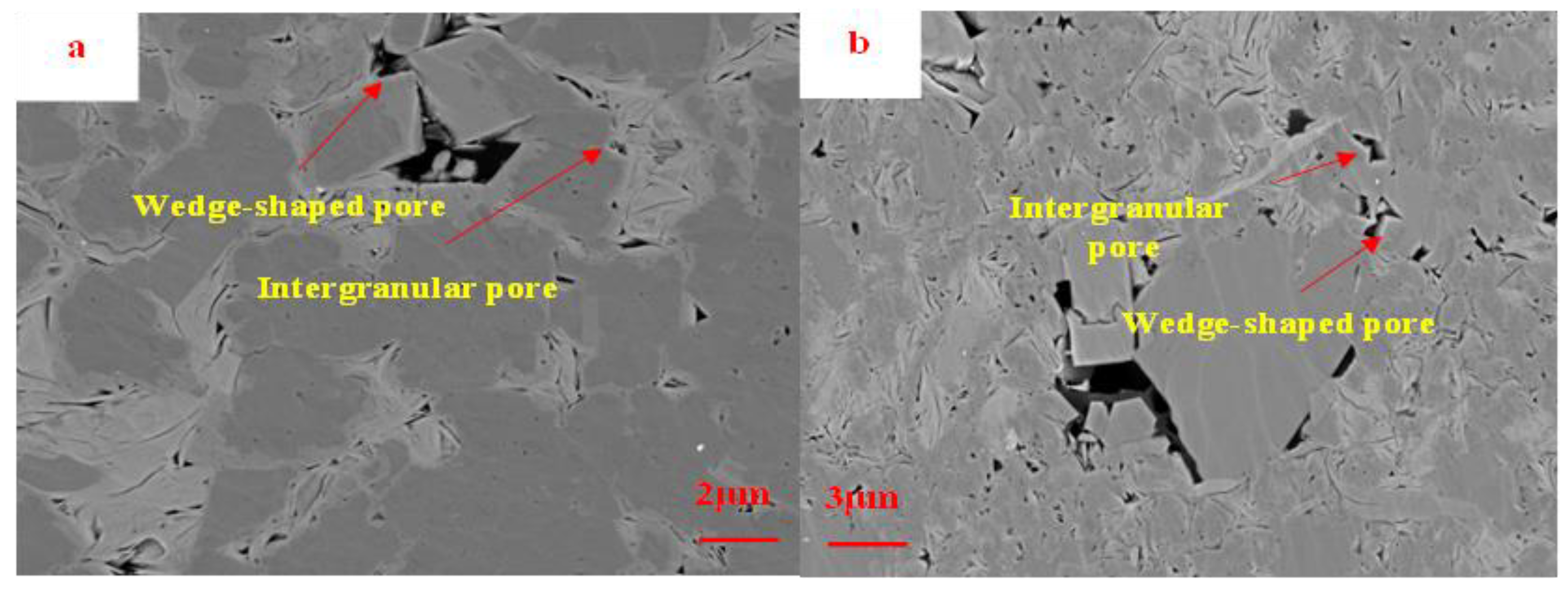
The Funing Formation shale in the Gaoyou Sag displays irregular patterns in the distribution of intergranular pores, with significant variations in their pore morphology. The predominant features of these intergranular pores can be classified as either slit-shaped or wedge-shaped (Figure 4). The pores in question exhibit an average size ranging in the hundreds of nanometers, with a smaller proportion extending into the micrometer range and often containing asphalt fillings. In comparison with marine shale, the continental shale found in the study area exhibits a comparatively recent sedimentary age and has not undergone significant compaction and transformation. Consequently, the formation of intergranular pores is notably prominent. The increased pore size and improved connectivity of the shale formation facilitate the presence of a sufficient reservoir and efficient pathways for fluid seepage. This, in turn, promotes the enrichment of shale oil.
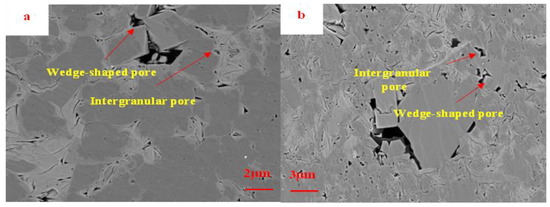
Figure 4.
SEM image of intergranular pores of Funing Formation shale in the Gaoyou Sag. (a): Intergranular pore, L-2. (b) Intergranular pore, L-5.
4.2.3. Intragranular Pores
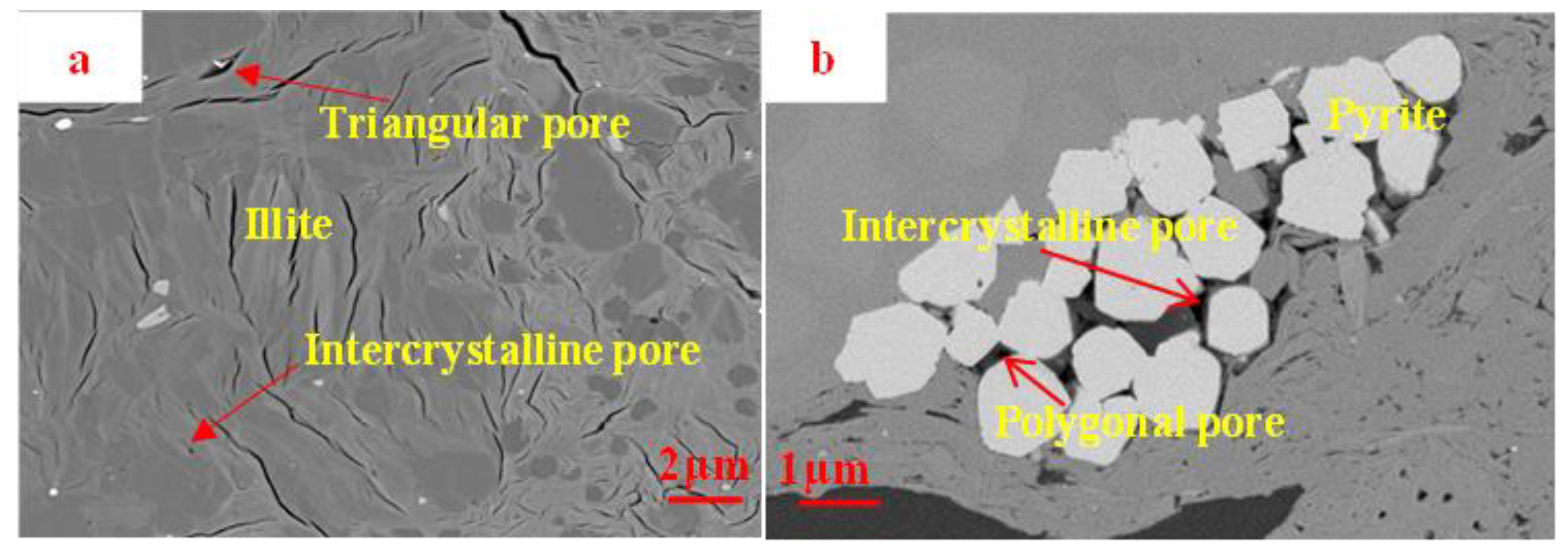
Two distinct types of intragranular pores have been observed in the Funing Formation shale of the Gaoyou Sag. One category consists of intergranular pores that form between clay minerals and pyrite crystals arising from loose aggregation during their growth mechanism. The intercrystalline pores found within clay minerals demonstrate a wide variety of shapes, encompassing triangles, quadrilaterals, and ellipses. The observed pores demonstrate a broad range of sizes, varying from a few nanometers to several hundred nanometers, with a smaller portion extending into the micron scale. On average, these pores measure in the tens of nanometers. (Figure 5a). Observations conducted using a field-emission scanning electron microscope have revealed the presence of both individual pyrite monomers and aggregates within the shale of the Funing Formation in the Gaoyou Sag (Figure 5b). In the pyrite monomer, the presence of minuscule punctiform depressions can be observed, whereas in the pyrite aggregate, intergranular voids are predominantly present. The intergranular pores display an irregular polygonal morphology, characterized by dimensions spanning from tens to hundreds of nanometers, with an average size in the tens of nanometers.

Figure 5.
SEM image of intergranular pores of the Funing Formation shale in the Gaoyou Sag. (a) Intercrystalline pores of clay minerals, L-1. (b) Intergranular pores of pyrite, L-4.
The majority of the intergranular pores present in the pyrite are filled with organic matter and various inorganic minerals. A portion of the intergranular pores, which are located between loosely accumulated pyrite aggregates, are unoccupied. The shale reservoir in the study area exhibits a low pyrite content, with an average of only 2.72%. Consequently, the influence of pyrite on the intergranular pores within the shale reservoir’s overall pore structure is relatively modest.
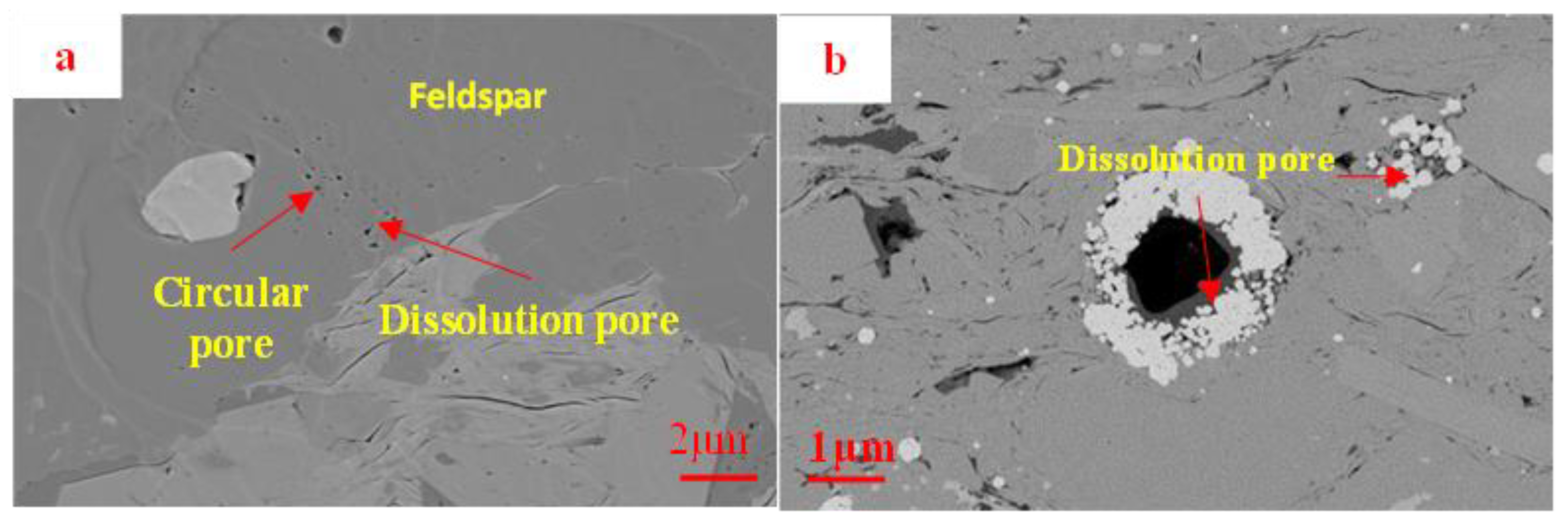
The second category of pores comprises dissolution pores, which are created by the dissolution of unstable minerals such as calcite, quartz, and feldspar as a result of the influence of organic acids released during the thermal transformation of organic matter [33]. These dissolution pores are predominantly isolated and densely distributed in circular or oval shapes (Figure 6). These materials demonstrate a relatively limited distribution of pore sizes, typically measuring in the tens of nanometers, on average. Additionally, they exhibit suboptimal connectivity between pores.
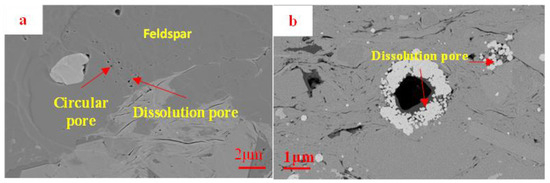
Figure 6.
SEM image of dissolution pores in the Funing Formation shale in the Gaoyou Sag. (a) Corrosion pore, L-3. (b): Corrosion pore, L-6.
The current state of the Funing Formation shale located in the Gaoyou Sag is characterized by thermal catalytic oil and gas generation. The substance exhibits a notable concentration of organic acids and a significant abundance of soluble minerals. The mineral composition of the sample consists of carbonate minerals, which make up a varying percentage between 12% and 62.4%, with an average of 37.9%. Additionally, silicate minerals are present, accounting for proportions ranging from 23% to 55.1%, with an average of 39.3%. As a result, a significant quantity of dissolution pores have formed within the shale reservoir in the examined region.
4.3. NMR Experiment and Its Fractal Characteristics
4.3.1. NMR Experimental Results and Physical Properties
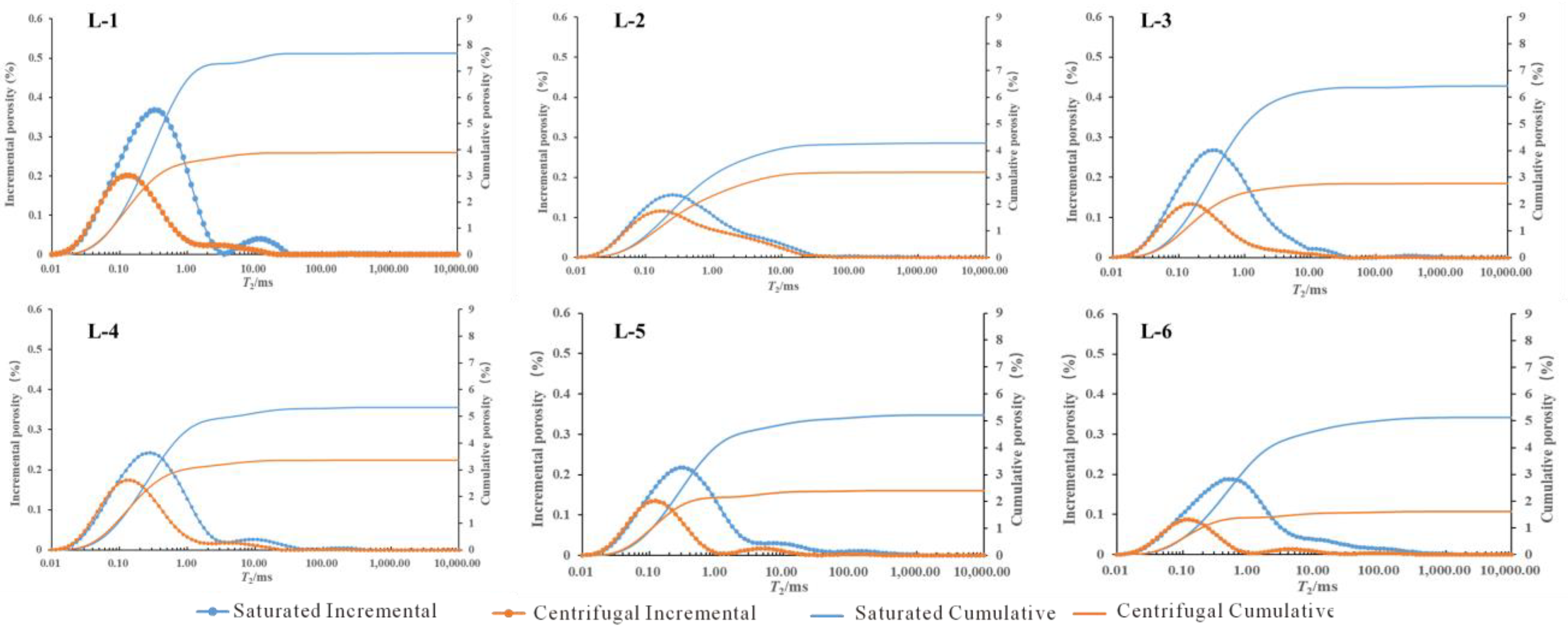
The T2 spectrum distribution of the saturated water sample and the centrifuged shale exhibits a similar pattern, characterized by a double-peak shape in which the left peak is higher than the right peak. (Figure 7). The T2 spectral distribution of sample L-1 in the water-saturated state, along with the centrifuged samples L-5 and L-6, exhibited distinct double peaks that were discontinuous in nature. In contrast, the T2 spectra of the remaining samples displayed a consistent pattern of dual peaks. Significantly, the peak area observed in sample L-1 is considerably greater in magnitude when compared to that of sample L-2. Based on the T2 spectral distribution illustrated in Figure 7, it can be categorized into two distinct types. Samples L-1, L-3, L-5, and L-6 are classified as Type I based on their unique double-peak characteristics. The significant disparity observed in relaxation times between the centrifuged samples and the saturated-water state suggests a substantial abundance of mobile fluids within the pores, leading to a high saturation of mobile fluids and favorable conditions for percolation.
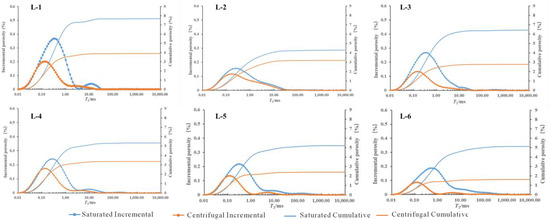
Figure 7.
T2 Spectra of NMR experiments on the Funing Formation shale in the Gaoyou Depression.
The second category comprises samples L-2 and L-4, both of which demonstrate bimodal characteristics. Nevertheless, the difference in relaxation-time distributions between the centrifuged samples and those in the saturated-water state is relatively insignificant. This observation suggests the presence of a significant volume of fluids that is confined within the pores, a low saturation of fluid that is capable of movement, and unfavorable conditions for fluid seepage.
The T2 cut-off value is an effective boundary for identifying movable-fluid pores and bound-fluid pores. The procedure involves identifying the maximum porosity signal value following centrifugation and representing it as a line parallel to the horizontal axis. Subsequently, a vertical line is drawn from the intersection of this line and the porosity value corresponding to saturated water. The corresponding relaxation time is the T2 cut-off value [21,34,35]. The distinction between cumulative saturated porosity and cumulative porosity post-centrifugation lies in the presence of movable fluid, with the porosity of the centrifugal sample representing the irreducible fluid saturation. The total porosity, movable fluid porosity, bound fluid porosity, permeability and other physical parameters were calculated from the T2 spectrum of the NMR experiment (Table 2). The calculation results show that the total porosity of Funing Formation shale in the Gaoyou Sag of Subei basin is 4.28~7.68%, with an average of 5.67%; the porosity of movable fluid is 1.10~3.78%, with an average of 2.80%, while the bound-fluid porosity is 1.60~3.90%, with an average of 2.87%.

Table 2.
Physical parameters of shale calculated based on the NMR experiment.
In this paper, Coates model is used to calculate the permeability of shale samples, and the formula is as follows:
where KC is the permeability calculated by the Coates model; φ is the porosity; C is the coefficient; SFFI is the movable fluid saturation; and SBVI is the irreducible fluid saturation.
According to Formula (3), the permeability of the Funing Formation continental shale in the Gaoyou Sag of Subei basin is 0.00083 md~0.06981 md, with an average of 0.03747 md.
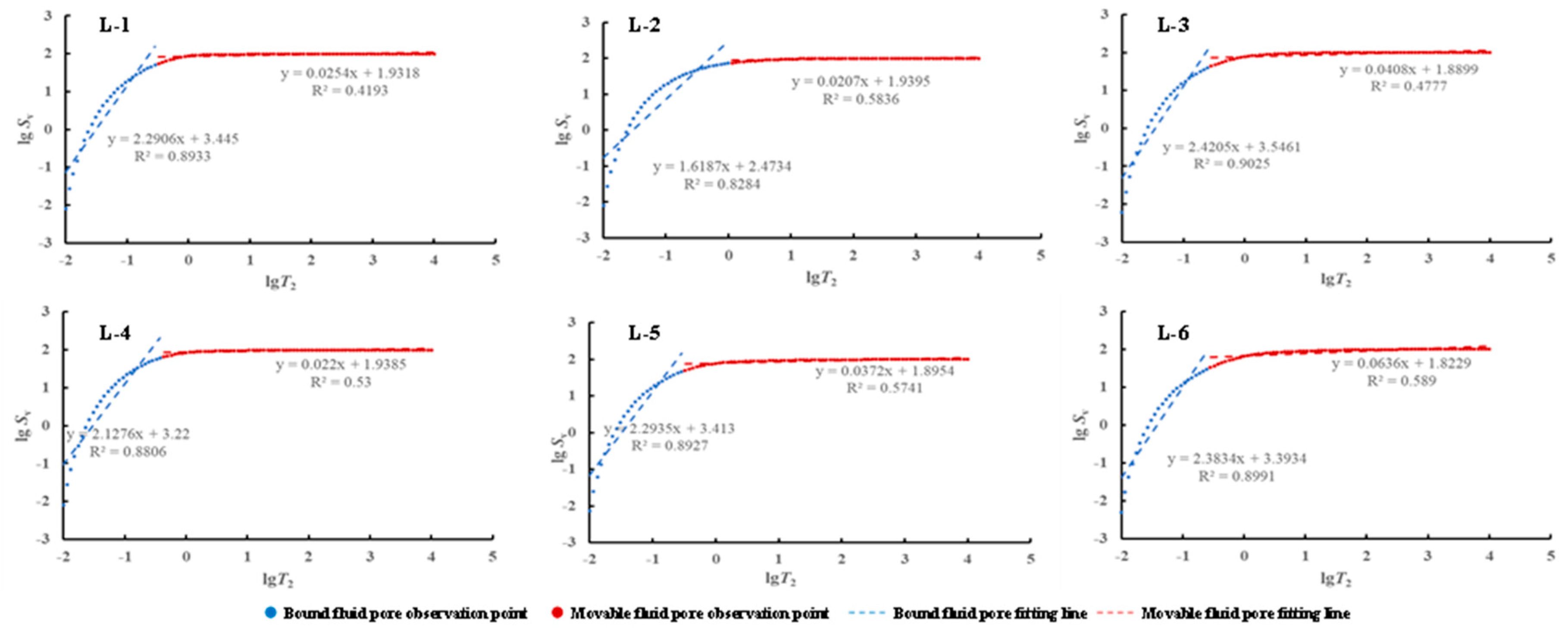
4.3.2. NMR Fractal Dimension
The NMR fractal dimension of shale samples derived from the Funing Formation in the Gaoyou Sag is depicted in Figure 8. The curve demonstrates a clearly discernible two-stage pattern. The fractal curve can be partitioned into two distinct segments, delineated by the T2C cut-off value. The segment featuring relaxation times less than T2C represents bound-fluid pores, while the segment with relaxation times exceeding T2C represents movable-fluid pores. By linear fitting of the two parts, the bound-fluid-pore fractal dimension (DMin) and the movable-fluid-pore fractal dimension (DMax) (Table 3) are obtained. The observed high values of the fitting degrees suggest that NMR fractal analysis can be employed as a viable method for characterizing the pore structure. It can be seen from Table 3 that DMin is between 0.5795~1.3813 (the average value is 0.8110); DMax ranged from 2.9592 to 2.9793 (mean 2.9651).
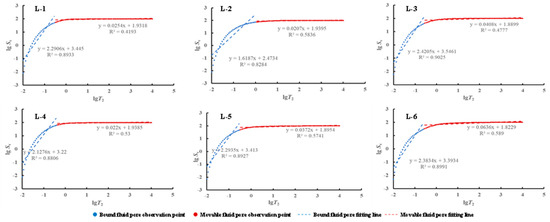
Figure 8.
NMR fractal dimension curves of the Funing Formation shale in the Gaoyou Sag.

Table 3.
Calculation results of NMR fractal dimension.
5. Discussion
5.1. Relationship between the NMR Fractal Dimension and Organic Geochemical Characteristics
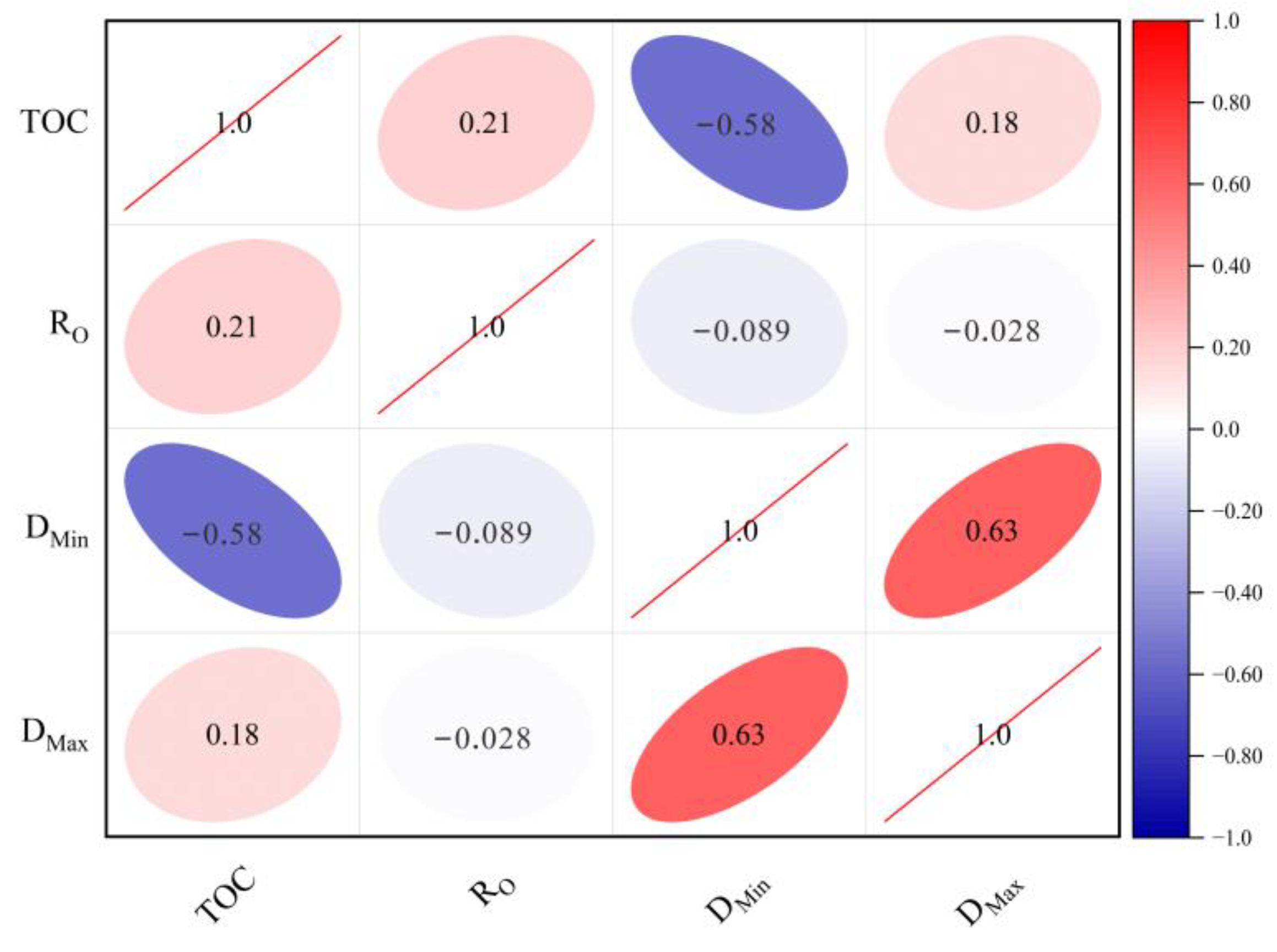
Figure 9 illustrates the relationship between the NMR fractal dimension and the organic geochemical properties of shale samples extracted from the Funing Formation in the Gaoyou sag. The results show that the two NMR fractal dimensions have different correlations with the TOC and Ro. TOC has a negative correlation with the fractal dimension DMin of bound-fluid pores and a positive correlation with the fractal dimension DMax of movable-fluid pores. During the hydrocarbon generation process from organic matter, kerogen undergoes a transformation, resulting in the production of liquid hydrocarbons and a certain quantity of gas. This transformation leads to the formation of pores within the organic matter, as well as contraction fractures that are oriented in a linear manner. These features contribute to the expansion of reservoir space and enhance connectivity to a certain degree. Therefore, TOC was positively correlated with the fractal dimension of movable-fluid pores. In Li et al.’s investigation of pore heterogeneity in the Funing Formation shale, it was observed that an increase in TOC content leads to a reduction in the number of pores and a simplification of the pore-structure complexity [7]. Consequently, there exists a negative correlation between TOC and the fractal dimension DMin of bound-fluid pores.
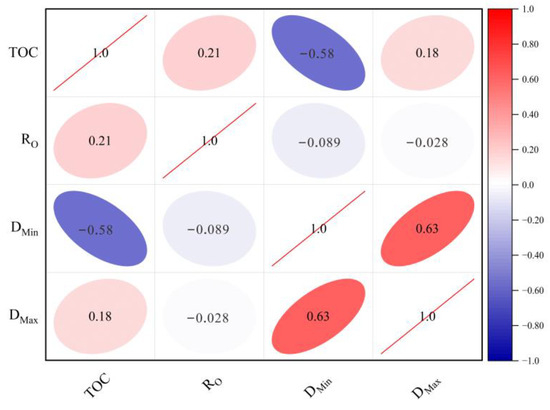
Figure 9.
Relationship between shale NMR fractal dimension and geochemical parameters.
The overall burial depth of the Funing Formation in Gaoyou Depression remains relatively constant, with RO values typically ranging from 0.8% to 0.9%. This consistency in burial depth and RO values does not exert a significant influence on the two NMR fractal dimensions.
5.2. Relationship between the NMR Fractal Dimension and Mineral Composition
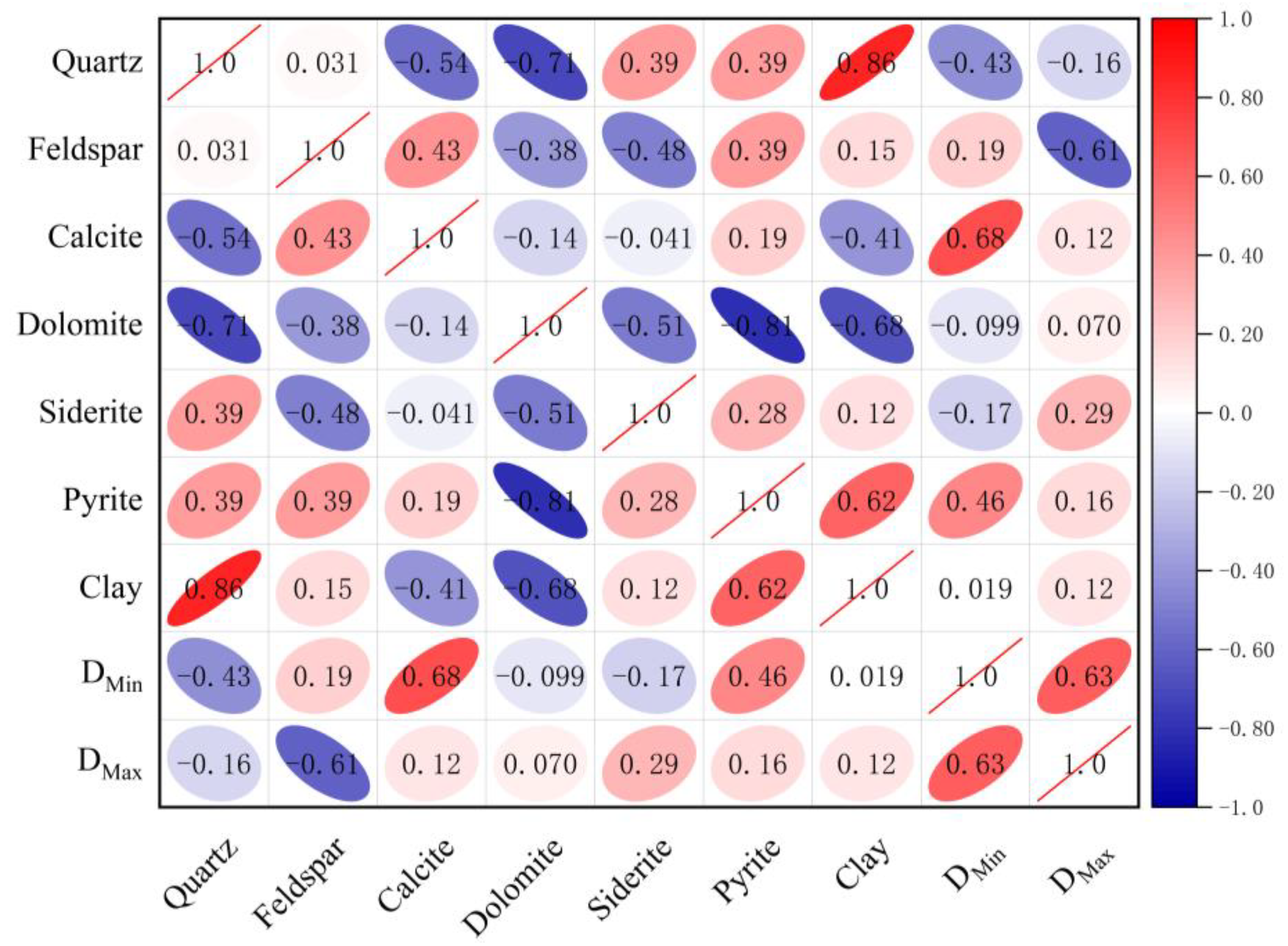
The mineral composition of shale is a significant factor in determining the pore structure and connectivity. The investigation into the relationship between NMR fractal dimensions and the mineral composition of Funing Formation shale in the Gaoyou Depression revealed notable impacts of different mineral constituents. (Figure 10). The analysis reveals that DMin and DMax exhibit negative correlations with the quartz content and that DMax displays a particularly significant negative correlation with the feldspar content. The observed phenomenon can be explained by the relatively even surfaces of quartz and feldspar minerals, which lead to a reduction in the variability of pore structures. As a result, there is a decrease in the fractal dimensions. Moreover, quartz, having fewer pores and offering limited pore complexity, leads to a reduction in the fractal dimension DMin.
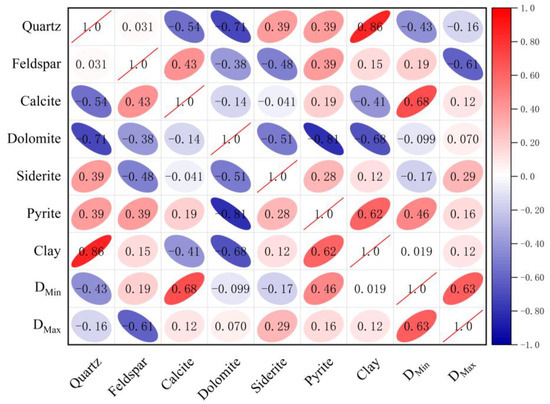
Figure 10.
Relationship between the shale NMR fractal dimension and mineral composition.
The correlation between the two NMR fractal dimensions of Funing Formation shale in the Gaoyou sag and the total amount of clay minerals may not be immediately evident [20,21,36,37]. Nevertheless, prior research indicates a positive association between clay minerals and the presence of larger pores, which can have a substantial influence on surface roughness. This relationship was observed in a study conducted by Tianhua et al. that investigated the pore characteristics of shale in the Sichuan Basin. Consequently, it is plausible that the fractal dimension of movable-fluid pores would exhibit a positive correlation with clay minerals [36].
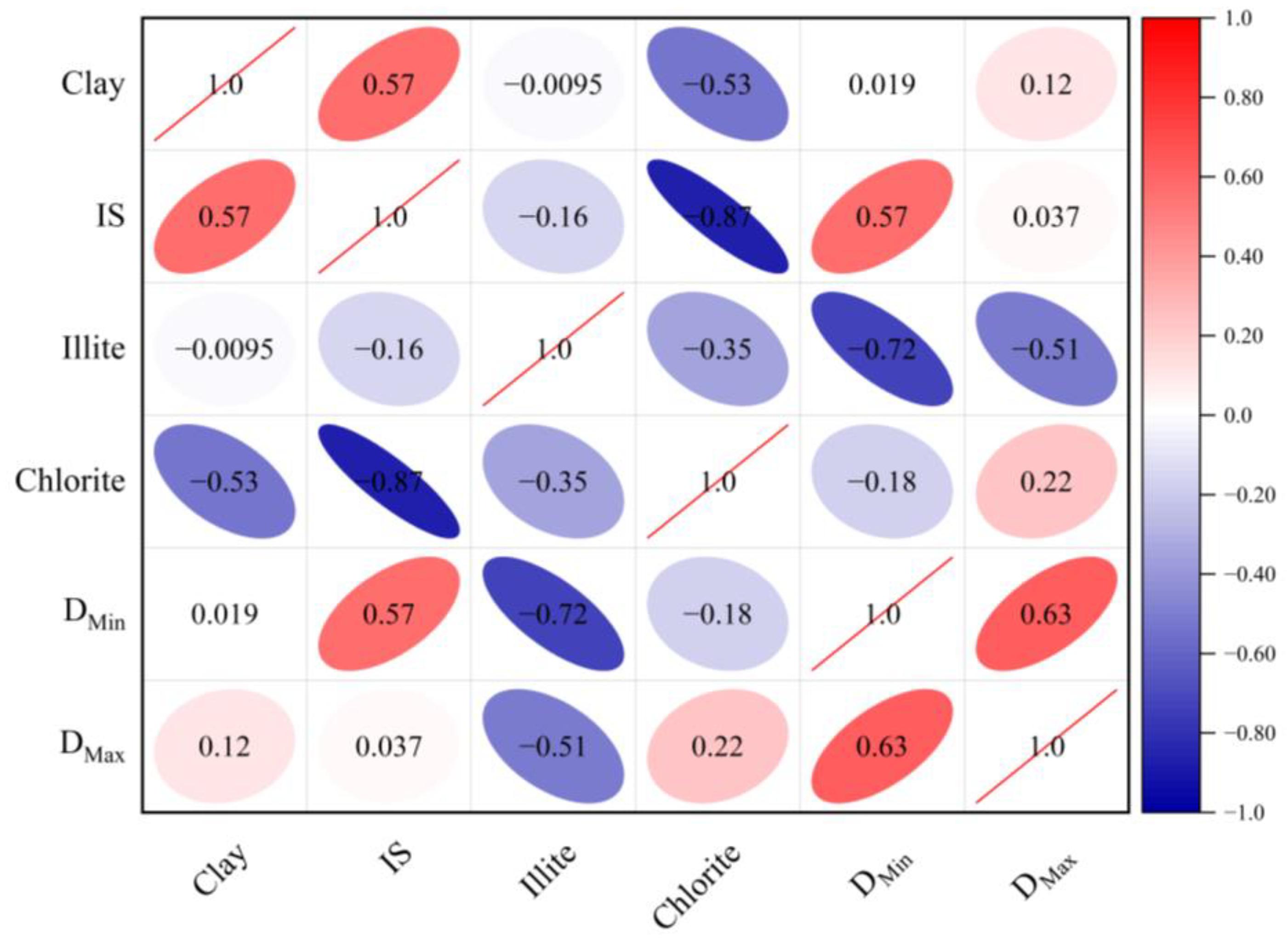
Furthermore, Liang Zhikai conducted a study on the pore structure of continental shale within the Changling fault depression. The findings of this study revealed a positive association between the fractal dimension of bound-fluid pores and clay minerals [21]. However, the observed relationship between the NMR fractal dimension of Funing Formation shale and the overall quantity of clay minerals does not correspond with prior studies, indicating the limited presence of a robust correlation. In order to enhance comprehension of this distinction, the present study delves further into the impact of diverse clay minerals on the two fractal dimensions. It was found that NMR fractal dimensions showed different correlations with different clay minerals (Figure 11). DMin and DMax exhibited robust correlations with illite, while DMin demonstrated a strong positive association with the illite mixed layer. Previous research into the adsorption capacities of various clay minerals indicated that their order of adsorption capacity is as follows: montmorillonite, smectite, smectite mixed layer, kaolinite, chlorite, and illite [38]. The increase in illite content was found to reduce the number of bound-fluid pores, resulting in a negative correlation with DMin. Furthermore, the presence of illite in shale samples can lead to pore blockage as a result of its interaction with water. Moreover, a high concentration of illite in these samples also has an impact on the fractal dimension of large-pore movable-fluid pores.
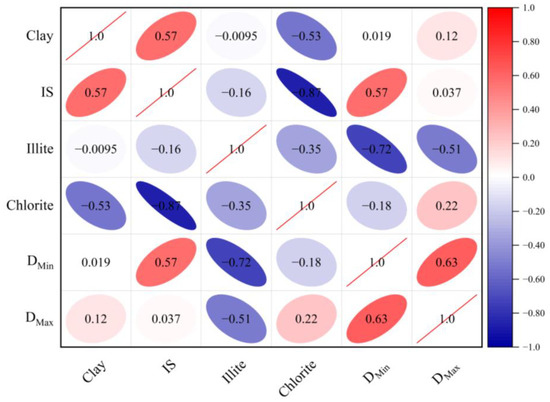
Figure 11.
Relationship between the shale NMR fractal dimension and clay mineral content.
It is worth mentioning that illite–smectite is the predominant clay mineral in the shale samples obtained from the Funing Formation in the Gaoyou Depression. The mixed layer in question exhibits a greater specific surface area in comparison with chlorite, resulting in heightened mineral surface roughness and improved adsorption capacity [39]. These factors contribute to an increase in the fractal dimension of bound-fluid pores.
The diverse sedimentary environments give rise to distinct impacts of different clay minerals on the processes of adsorption and on seepage pores, which align with previous research outcomes. A significant inflection point can be observed on the trend line in close proximity to the clay mineral content of 50% within the shale of the sea–land transitional facies situated in Northwest Guizhou. This demonstrates a pattern of “positive, then negative” trend. This indicates that when the clay mineral content is excessively high, it obstructs certain pores, resulting in their instability and unlikelihood of preservation, thereby exhibiting a detrimental impact [37]. The examination of Permian shale in the southern North China Basin demonstrates that clay minerals have a substantial impact on the creation of multiple pores as a result of tectonic stress, mineral phase alteration, dehydration, and other associated factors, thus facilitating the advancement of pore formation [40]. Therefore, it can be observed that there is considerable variation in the mechanical properties and chemical stability of different clay minerals. This variation is influenced by various factors, including the sedimentary environment, pore type, and the type and content of clay minerals. These factors collectively contribute to the impact on the fractal dimension.
5.3. Relationship between the NMR Fractal Dimension and Physical Parameters
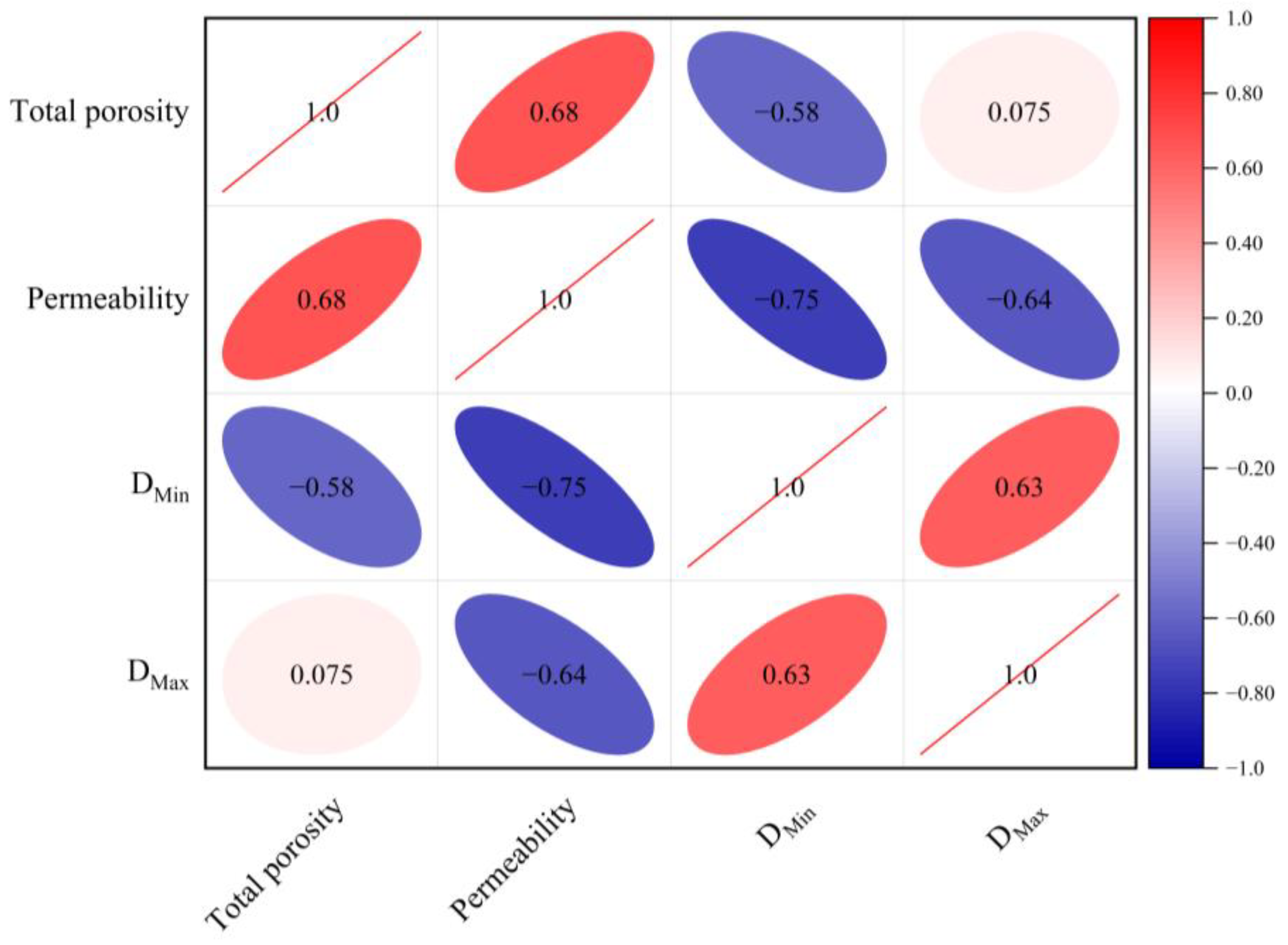
The utilization of the NMR fractal dimension can be regarded as a viable approach for evaluating the physical characteristics of shale [18,41], as depicted in Figure 12, which illustrates the relationships among total porosity, permeability, and fractal dimensions derived from NMR experiments. The findings reveal a noteworthy negative correlation between DMin and DMax with permeability. Additionally, DMin exhibits a negative correlation with total porosity. Both fixed and mobile pores contribute to the overall porosity of the specimen. The augmentation of bound-fluid pore dimensions can effectively increase porosity by expanding the available pore volume. However, this increase in pore size can reduce the heterogeneity of the pore structure, resulting in a decrease in the fractal dimension DMin.
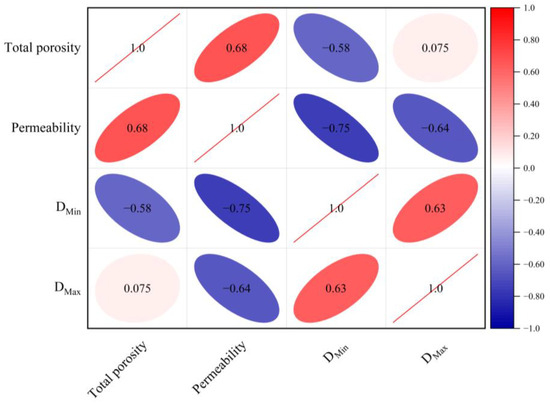
Figure 12.
Relationship between the shale NMR fractal dimension and reservoir physical properties.
The permeability of shale is dependent on the properties of its pore throats. The enlargement of pore throats with larger diameters has the potential to enhance the permeability of shale formations. However, it is important to note that this enlargement can also have an impact on the sorting of the pore throat system, leading to increased heterogeneity within shale reservoirs. Furthermore, the permeability of shale reservoirs is influenced by the curvature of pore throats. The permeability of shale is generally reduced by the existence of pore throats with significant curvature and the presence of small, rounded micropores. However, this also leads to an increase in the specific surface area. While the coarser and irregular pore-throat regions can increase DMin and DMax, they also increase the length and resistance of fluid-flow pathways, ultimately reducing shale permeability.
6. Conclusions
This study employs XRD, FE-SEM, NMR, and fractal dimension theory to assess the heterogeneity of pore structures in three-dimensional space. Additionally, an investigation is conducted on the correlation between the fractal dimension obtained from NMR analysis and various factors such as the TOC content, mineral composition, geochemical parameters, and physical parameters. In general, the relationship between the fractal dimension obtained from NMR measurements and the physical properties of reservoirs can be utilized as a means of assessing the quality of shale reservoirs. Furthermore, the presence of shale pores is intricately linked to the sedimentary environment, mineral composition, and diagenesis. The diverse nature of shale is frequently ascribed to disparities in the sedimentary milieu and diagenetic mechanisms. Hence, the determination of fractal dimensions in individual well profiles and planes facilitates the investigation of the impact of a sedimentary environment and burial history on porosity heterogeneity and reservoir quality. At the same time, attention should also be paid to avoiding environmental pollution during shale-oil exploration and development.
- (1)
- The Funing Formation shale is presently considered to be in a mature stage, as evidenced by the majority of samples displaying a total organic carbon (TOC) content surpassing 1%. This suggests the presence of favorable organic geochemical conditions. The shale samples from the Funing Formation exhibit a dominant mineral composition, with quartz comprising an average of 25.53% and dolomite comprising an average of 24.23%. Clay minerals follow closely, with an average composition of 20.77%, while feldspar constitutes an average of 13.80%. Nevertheless, it is worth noting that there is no single mineral that demonstrates a distinct dominance, as each average content remains below 40%.
- (2)
- The primary pore classifications observed in the Funing Formation shale within the Gaoyou Sag consist of inorganic matrix pores. These pores encompass dissolution pores, intergranular pores formed by clay minerals, and a limited quantity of intergranular pores associated with pyrite. The range of the pore-size distribution is extensive, spanning from a few nanometers to hundreds of nanometers, with a minority extending into the micron range. On average, the pore size measures in the tens of nanometers.
- (3)
- The Funing formation’s NMR fractal dimension displays a notable two-segment configuration, wherein the fractal dimension DMin, which characterizes the pore structure of bound fluid, spans 0.5795 to 1.3813 (with a mean value of 0.8110). Furthermore, the fractal dimension DMax, which serves as an indicator of the pore structure of fluid that can be displaced, exhibits a range of values from 2.9592 to 2.9793, with an average value of 2.9651.
- (4)
- The organic geochemical characteristics and mineral composition of shale exert varying degrees of influence on the NMR fractal dimensions characterizing the two pore structures. Specifically, TOC, quartz, calcite, illite–smectite, illite, and chlorite impact DMin, with all except calcite and illite–smectite showing negative correlations. Organic matter content and mineral composition play a significant role in controlling the fractal dimension.
- (5)
- The evaluation of reservoir performance relies heavily on the assessment of porosity and permeability, which are considered to be vital parameters. There exists a noteworthy correlation between the physical parameters and the fractal dimensions of both bound-fluid pores and movable-fluid pores. This implies that the utilization of NMR fractal dimensions can be advantageous in assessing physical properties, thereby enhancing the characterization of reservoirs.
Author Contributions
Data curation, Y.Z.; methodology, Y.Z.; project administration, Z.J.; resources, Z.J.; writing—original draft, Z.W.; writing—review and editing, H.G., Y.Y., B.W. and X.W. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This study is supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (No. 42272137, No. 41872135 and No. 42072151).
Institutional Review Board Statement
Not applicable.
Informed Consent Statement
Not applicable.
Data Availability Statement
The data presented in this study are available on request from the corresponding author. The data are not publicly available due to some basic research involving confidentiality.
Acknowledgments
We are grateful to editors and reviewers for their constructive comments and suggestions.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
References
- Zou, C.; Ma, F.; Pan, S.; Zhang, X.; Wu, S.; Fu, G.; Wang, H.; Yang, Z. Formation and distribution potential of global shale oil and the developments of continental shale oil theory and technology in China. Earth Sci. Front. 2023, 30, 128–142. [Google Scholar]
- Zhao, W.; Zhu, R.; Liu, W. Advances in theory and technology of non-marine shale oil exploration in China. Pet. Sci. Bull. 2023, 8, 373–390. [Google Scholar]
- Jin, Z.J.; Zhu, R.K.; Liang, X.P.; Shen, Y.Q. Several issues worthy of attention in current lacustrine shale oil exploration and development. Pet. Explor. Dev. 2021, 48, 1471–1484. [Google Scholar]
- Ma, Y.; Cai, X.; Zhao, P.; Hu, Z.; Liu, H.; Gao, B.; Wang, W.; Li, Z.; Zhang, Z. Geological characteristics and exploration practices of continental shale oil in China. Acta Geol. Sin. 2022, 96, 155–171. [Google Scholar]
- Duan, H.; Liu, S.; Fu, Q. Characteristics and sedimentary environment of organic-rich shale in the second member of Paleogene Funing Formation, Subei Basin. Pet. Geol. Exp. 2020, 42, 612–617. [Google Scholar]
- Yun, L.; He, X.; Hua, C.; Zan, L. Accumulation characteristics and resource potential of Paleogene continental shale oil in Qintong sag of Subei Basin. Acta Pet. Sin. 2023, 44, 176–187. [Google Scholar]
- Li, P.; Gong, H.J.; Jiang, Z.X.; Zhang, F.; Liang, Z.K.; Wang, Z.P.; Wu, Y.H.; Shao, X.D. Characteristics and Influencing Factors of Multi-Scale Pore Structure Heterogeneity of Lacustrine Shale in the Gaoyou Sag, Eastern China. Minerals 2023, 13, 359. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, R.; Wu, S.; Su, L.; Cui, J.; Mao, Z.; Zhang, X. Problems and future works of porous texture characterization of tight reservoirs in China. Acta Pet. Sin. 2016, 37, 1323–1336. [Google Scholar]
- Jiang, Z.; Tang, X.; Li, Z.; Huang, H.; Yang, P.; Yang, X.; Li, W.; Hao, J. The whole-aperture pore structure characteristics and its effect on gas content of the Longmaxi Formation shale in the southeastern Sichuan basin. Earth Sci. Front. 2016, 23, 126–134. [Google Scholar]
- Lu, S.; Li, J.; Zhang, P.; Xue, H.; Wang, G.; Zhang, J.; Liu, H.; Li, Z. Classification of microscopic pore-throats and the grading evaluation on shale oil reservoirs. Pet. Explor. Dev. 2018, 45, 436–444. [Google Scholar]
- Zhao, W.Z.; Hu, S.Y.; Hou, L.H. Connotation and strategic role of in-situ conversion processing of shale oil underground in the onshore China. Pet. Explor. Dev. 2018, 45, 563–572. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, Q.H.; Zhang, Y.X.; Meng, X.H.; Li, Z.; Xie, Z.H.; Li, M.W. Characterization of micro-nano pore networks in shale oil reservoirs of Paleogene Shahejie Formation in Dongying Sag of Bohai Bay Basin, East China. Pet. Explor. Dev. 2017, 44, 720–730. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alemdag, S.; Gurocak, Z.; Cevik, A.; Cabalar, A.F.; Gokceoglu, C. Modeling deformation modulus of a stratified sedimentary rock mass using neural network, fuzzy inference and genetic programming. Eng. Geol. 2016, 203, 70–82. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, R.; He, S.; Yi, J.Z.; Hu, Q.H. Nano-scale pore structure and fractal dimension of organic-rich Wufeng-Longmaxi shale from Jiaoshiba area, Sichuan Basin: Investigations using FE-SEM, gas adsorption and helium pycnometry. Mar. Pet. Geol. 2016, 70, 27–45. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Clarkson, C.R.; Solano, N.; Bustin, R.M.; Bustin, A.M.M.; Chalmers, G.R.L.; He, L.; Melnichenko, Y.B.; Radlinski, A.P.; Blach, T.P. Pore structure characterization of North American shale gas reservoirs using USANS/SANS, gas adsorption, and mercury intrusion. Fuel 2013, 103, 606–616. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Z.; Jiang, Y.; Fu, Y.; Lei, Z.; Xu, C.; Yuan, J.; Wen, R.; Wang, Z.; Gu, Y.; Yin, X. Characterization of Pore Structure and Heterogeneity of Shale Reservoir from Wufeng Formation-Sublayers Lon g-11 in Western Chongqing Based on Nuclear Magnetic Resonance. Earth Sci. 2022, 47, 490–504. [Google Scholar]
- Ma, Y.; Zhong, N.; Huang, X.; Guo, Z.; Yao, L. The application of focused ion beam scanning electron microscope (FIB-SEM) to the nanometer-sized pores in shales. J. Chin. Electron. Microsc. Soc. 2014, 33, 251–256. [Google Scholar]
- Yao, Y.; Liu, D. Petrophysical properties and fluids transportation in gas shale: A NMR relaxation spectrum analysis method. J. China Coal Soc. 2018, 43, 181–189. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, L.; Xu, Y.; Sun, M.; Jiang, S.; Zhang, Y.; Wu, C.; Zhang, J.; Liang, X.; Wang, G. The Structure and Evolution of Closed Pores in Shale Determined by Small Angle Neutron Scattering. Acta Sedimentol. Sin. 2021, 39, 310–323. [Google Scholar]
- Yan, J.-P.; He, X.; Geng, B.; Hu, Q.-H.; Feng, C.-Z.; Kou, X.-P.; Li, X.-W. Nuclear magnetic resonance T2 spectrum: Multifractal characteristics and pore structure evaluation. Appl. Geophys. 2017, 14, 205–215. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liang, Z.; Li, Z.; Li, L.; Jiang, Z.; Liu, D.; Gao, F.; Liu, X.; Xiao, L.; Yang, Y. Relationship between multifractal characteristics of pore size and lithofacies of shale of Shahezi Formation in Changling fault depression, Songliao Basin. Lithol. Reserv. 2020, 32, 22–35. [Google Scholar]
- Li, Z.; Wang, W.; Wang, X.; Bai, Y.; Qin, D.; Zhao, Y. Study on Fractal Characteristics of Micro-Nano Pore Structure of Shale. J. Eng. Geol. 2018, 26, 494–503. [Google Scholar]
- GB/T 19145-2022; Determination for Total Organic Carbon in Sedimentary Rock. China National Standards: Shenzhen, China, 2022.
- Xiao, X. Organic Petrology and Its Application in Oil and Gas Evaluation. Adv. Earth Sci. 1992, 7, 39–44. [Google Scholar]
- SY/T 5163-2018; X-ray Diffraction Analysis Method for Clay Minerals and Common Non Clay Minerals in Sedimentary Rocks. China National Energy Administration: Beijing, China, 2018; p. 39.
- Nefeslioglu, H.A. Evaluation of geo-mechanical properties of very weak and weak rock materials by using non-destructive techniques: Ultrasonic pulse velocity measurements and reflectance spectroscopy. Eng. Geol. 2013, 160, 8–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lai, J.; Wang, G.W. Fractal analysis of tight gas sandstones using high-pressure mercury intrusion techniques. J. Nat. Gas Sci. Eng. 2015, 24, 185–196. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Giri, A.; Tarafdar, S.; Gouze, P.; Dutta, T. Fractal pore structure of sedimentary rocks: Simulation in 2-d using a relaxed bidisperse ballistic deposition model. J. Appl. Geophys. 2012, 87, 40–45. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qu, S.; Zhang, J. Fractal and fractal dimension and their application in geophysics. J. Xi’an Shiyou Univ. 1991, 6, 8–13. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, S.; Tang, S.; Huo, T.; Tan, F.; Liu, D.; Wang, J. Pore structure and fractal characteristics of the Upper Carboniferous shale, eastern Qaidam Basin. Nat. Gas Geosci. 2020, 31, 1069–1081. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, C.; Chen, Z.; Zhang, Z.; Wang, B.; Zan, L. Fractal characteristics of reservoir rock pore structure based on NMR T2 distribution. J. Oil Gas Technol. 2007, 4, 6. [Google Scholar]
- Loucks, R.G.; Reed, R.M.; Ruppel, S.C.; Hammes, U. Spectrum of pore types and networks in mudrocks and a descriptive classification for matrix-related mudrock pores. AAPG Bull. 2012, 96, 1071–1098. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, J.; Lai, X.; Yu, B.; Chen, X.; Duo, C. The Current Situation and Developing Tendency of the Study on Diagenesis. Pet. Geol. Exp. 2006, 28, 65–72,77. [Google Scholar]
- Qu, K.X.; Guo, S.B. Investigation of the Pore Structure of Tight Sandstone Based on Multifractal Analysis from NMR Measurement: A Case from the Lower Permian Taiyuan Formation in the Southern North China Basin. Energies 2020, 13, 4067. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, F.Y.; Yang, K.; Cai, J.C. Fractal Characterization of Tight Oil Reservoir Pore Structure Using Nuclear Magnetic Resonance and Mercury Intrusion Porosimetry. Fractals 2018, 26, 1840017. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tian, H.; Zhang, S.; Liu, S.; Zhang, H. Determination of organic-rich shale pore features by mercury injection and gas adsorption methods. Acta Pet. Sin. 2012, 33, 419–427. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, P.; Huang, Y.; Zhang, J.; Liu, H.; Yang, J. Fractal characteristics of the Longtan formation transitional shale in northwest Guizhou. J. China Coal Soc. 2018, 43, 1580–1588. [Google Scholar]
- Ji, L.; Zhang, T.; Milliken, K.L.; Qu, J.; Zhang, X. Experimental investigation of main controls to methane adsorption in clay-rich rocks. Appl. Geochem. 2012, 27, 2533–2545. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mohamed, A.M.O. The role of clay minerals in marly soils on its stability. Eng. Geol. 2000, 57, 193–203. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, J.; Wu, W.; Wang, J.; Huang, X. Microscopic pore characteristics and influence factors analysis of shales in permian, yanlong area, southern north china basin. J. Geomech. 2017, 23, 829–837. [Google Scholar]
- Zhou, L.; Kang, Z.H. Fractal characterization of pores in shales using NMR: A case study from the Lower Cambrian Niutitang Formation in the Middle Yangtze Platform, Southwest China. J. Nat. Gas Sci. Eng. 2016, 35, 860–872. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).