Abstract
There have been limited studies on slow-moving landslides in South Korea despite their frequent occurrence. Moreover, a national slow-moving landslide hazard information system (SMLHIS) is needed. Herein, we conducted an overlap analysis of 15 slow-moving landslide areas with clear occurrence timings with national landslide hazard maps (LHMs) using the geographic information system data. Additionally, internal and external factors causing slow-moving landslides were analyzed. The results of the overlap analysis showed that slow-moving landslide areas occurred in low-hazard and excluded non-hazard areas on the LHM. The study of internal factors revealed that slow-moving landslides occurred mainly in the Gyeongsang supergroup, which has sedimentary rock type and sandy loam. The analysis of external factors, e.g., rainfall, showed that slow-moving landslides occurred during intensive rainfall, with continuous and 15-day antecedent rainfall exceeding 100 and 200 mm, respectively. The longer the continuous rainfall duration before a slow-moving landslide; the greater the rainfall on the day of the landslide; the greater the maximum hourly rainfall; the greater the 3-, 5-, and 7-day antecedent rainfalls; and the greater the rainfall intensity during the landslide, the greater the size of the slow-moving landslide. This study provides information for developing a national SMLHIS, presenting novel perspectives for slow-moving landslide research.
1. Introduction
Disasters are a frequent phenomenon worldwide, and climate change is accelerating the hazard of disasters [1]. The world has a total forest area of 4.06 billion ha, which accounts for 31% of the total land area [2]. One of the most frequent sediment disasters affecting forest soils is landslides. According to a World Bank report, approximately 300 million people worldwide live in landslide-prone areas, and nearly 600 people die because of landslides every year [3]. Furthermore, the economic losses caused by landslides are estimated to be USD 20 billion per year globally [4]. Recently, South Korea experienced increased landslide occurrence due to frequent heavy rains. In particular, the total area damaged by localized heavy rains and typhoons Maysak and Haisen in 2020 was 1343 ha, and the restoration cost was USD 350 million. Moreover, there were nine fatalities [5].
Recently, South Korea has generally classified forest soil sediment disasters into landslides, debris flows, and slow-moving landslides. According to a United States Geological Survey (USGS) report, “landslide” is a general term used to describe the downslope movement of soil, rock, and organic material under the influence of gravity and the resulting landscape deformation. Landslides are classified into various types, such as falls (rockfall, topple), slides (rotational landslide, translational landslide), spreads (lateral spreads), and flows (debris flows, lahars (volcanic debris flows), debris avalanche, earthflow, slow earthflow (creep), flows in permafrost). Among them, South Korean slow-moving landslides can be described as slow earthflows (creep). Creep is an informal name for slow earthflow, a phenomenon in which soil or rock forming a slope moves downward slowly and steadily to the point at which it is not noticeable. In other words, the movement is caused by internal shear stress sufficient to cause deformation of the terrain but insufficient to cause sudden breakage. Creep is also widely distributed worldwide and is the most common type of landslide. It often occurs before faster and more destructive types of landslides [6]. Meanwhile, South Korean slow-moving landslides can be explained as “earth flow” according to Varnes’ landslide type classification [7].
It was only in 1996 that slow-moving landslides were recognized as a natural disaster with a different underlying mechanism than that of landslides. In South Korea, a landslide that occurred in 1995 was first reported as a slow-moving landslide rather than a general landslide [8], and this sparked interest in slow-moving landslides in the academic community. However, until now, South Korea has yet to develop SMLHIS through a selection of slow-moving-landslide-vulnerable areas at the national level (e.g., a slow-moving landslide hazard map). Consequently, slow-moving landslides are still being managed by the public authorities as general landslides. In addition, damage to communities and infrastructure is not classified as forest soil sediment disasters.
However, slow-moving landslides differ from typical landslides in their mechanism of occurrence [9,10]. Slow-moving landslides typically occur during heavy rainfall in areas with clayey soils and abundant groundwater. The clayey soils in these slow-moving landslide areas are saturated by rainwater, and as the clay is pushed in the direction of gravity under the weight of rainwater, the soil moves downward with the water, forming tension cracks and steps along the slope plane [8,11]. In contrast, a landslide is a phenomenon wherein rainwater fills the bedrock and the soil on the bedrock slides downward. Thus, a landslide is a phenomenon wherein water acts as a lubricant at the interface of soil and bedrock, causing the mountain to collapse instantaneously [11]. In addition, the occurrence mechanism of landslides can be better understood through centrifuge modeling research based on typical landslide triggering factors such as centrifugal acceleration, rainfall, earthquakes [12,13], or machine-learning-based reservoir slope stability research [14].
The number of slow-moving landslide areas is gradually increasing in South Korea. Most of these occurred in the past and were not classified as slow-moving landslide phenomena but were determined as general landslides [8,15]. Recently, it has been found that slow-moving landslides differ in signs, phenomena, frequency, and scale from general landslides [6,8,11], and the areas identified as such landslide areas are increasing.
In South Korea, forest soil sediment disasters are mostly caused by the loss of balance and collapse of natural slopes due to rapid urban expansion and land development in mountainous or hill areas that have been stable. The causes of the disaster are mainly divided into internal and external factors. Internal factors are potential factors such as stratigraphy, topography, geology, soil quality, and clinical conditions of mountain slopes, which cause progressive destruction, weathering, and erosion to reduce the shear strength of slope components. External factors are changes in topography, increased land surface load, vibration and shock, and fluctuations in groundwater levels, which combine with internal factors to cause forest soil sediment disasters. The most influential factor is known to be rainfall. In particular, it is known that the 7-day antecedent rainfall and continuous rainfall days significantly impact the landslide characteristics [16].
However, slow-moving landslides can occasionally accelerate rapidly, travel long distances, or even collapse catastrophically [17]. Slow-moving landslides occur widely and can cause relatively more damage than caused by landslides or debris flows. Increases in soil temperature and groundwater levels [18,19] and various types of anthropogenic forest development [20] have been cited as the main causes. In addition, triggering factors for slow-moving landslides including geological properties [17,21,22], clay content in the soil [22], rainfall [23,24,25], topography [21,26], slopes in the mountains [27,28], and reservoir water level [29] have been researched.
Until recently, South Korea did not clearly distinguish between slow-moving and general landslides and treated both as general landslides. However, applying existing vulnerability assessment criteria for landslides to slow-moving landslide vulnerability determination may be problematic regarding accuracy and reliability. Furthermore, incorrect judgments could result in loss of life or property damage.
In this study, we conducted an overlap analysis with the national landslide hazard map for 15 slow-moving-landslide-prone areas in South Korea with a clear timing of landslide occurrence. We analyzed the difference in the hazards of occurrences of landslides and slow-moving landslides. In addition, we aimed to present compelling evidence to highlight the urgency of national slow-moving landslide vulnerability assessment and the need to establish an SMLHIS (slow-moving landslide hazard map). Moreover, the geology, topography, and the scale of occurrence of slow-moving landslide areas were analyzed to examine the internal factors of slow-moving landslides. Finally, we analyzed the impact of rainfall, a major influential external factor among the triggering factors for sediment disasters affecting forest soils, and the correlation between rainfall factors and the scale of slow-moving landslides (range, length, and depth). This study aimed to provide information on slow-moving-landslide-triggering factors for developing vulnerability assessment criteria for such landslides. The findings of this study contribute to understanding the geology and geomorphology of slow-moving landslide sites, specifically toward improving our understanding of the impact of rainfall on the magnitude of such landslides and developing effective strategies to mitigate their impact on communities and infrastructure.
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Overlap Analysis of Landslide Hazard Map and Slow-Moving Landslide Area
Herein, the hazard grades of slow-moving landslide areas on the landslide hazard map were analyzed using a geographic information system (GIS). For this purpose, we selected 15 slow-moving landslide areas in South Korea with clear dates of landslide occurrence (Figure 1) and set the boundaries of these landslide areas using a global positioning system (GPS). Next, we overlapped the slow-moving landslide area boundaries with the landslide hazard map of South Korea (1:25,000; provided by Korea Forest Service). The landslide hazard map used in this study was a thematic map created by weighting the probability of landslide occurrence calculated via logistic regression analysis using information on landslides that have occurred in all forests in South Korea in the past. The landslides were classified into five grades based on the influence of the following nine factors: forest type, diameter class, slope degree, slope aspect, slope length, slope curvature, parent rock, soil depth, and topographical wetness index.
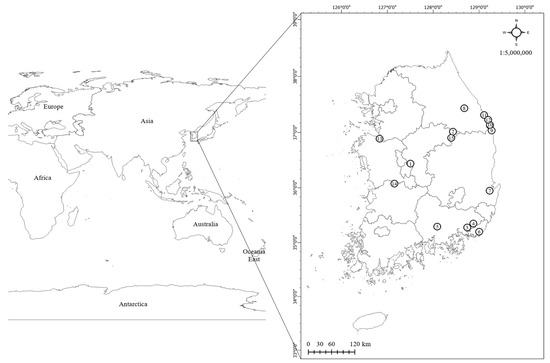
Figure 1.
Geographic locations of slow-moving landslide sites. Note: (1) = Site No. 1: 12 Mt., Sindae-ri, Munui, Cheongju, Chungbuk, (2) = Site No. 2: 46-7 Mt., Sang-ri, Yeongchun, Danyang, Chungbuk, (3) = Site No. 3: 1082-1, Naesam-ri, Juchon, Gimhae, Gyeongnam, (4) = Site No. 4: 131-29 Mt., Mae-ri, Sangdong, Gimhae, Gyeongnam, (5) = Site No. 5: 1415, Deogo-ri, Jiphyeon, Jinju, Gyeongnam, (6) = Site No. 6: 54-49 Mt., Daeyeon-dong, Busan, (7) = Site No. 7: 29 Mt., Honggye-ri, Daesong, Pohang, Gyeongbuk, (8) = Site No. 8: 1 Mt., Gujeol-ri, Yeoryang, Jeongseon, Gangwon, (9) = Site No. 9: 95-5 Mt., Nogok-ri, Wondeok, Samcheok, Gangwon, (10) = Site No. 10: 204-9 Mt., Nogok-ri, Wondeok, Samcheok, Gangwon, (11) = Site No. 11: 74 Mt., Sangmaengbang, Geundeok, Samcheok, Gangwon, (12) = Site No. 12: 51, Chogok-ri, Geundeok, Samcheok, Gangwon, (13) = Site No. 13: 143-10, Bugok-ri, Songak, Dangjin, Chungnam, (14) = Site No. 14: 108, Hwanghwajeong-ri, Yeonmu, Nonsan, Chungnam, and (15) = Site No. 15: 8-2 Mt., Geumho-ri, Jicheon, Chilgok, Gyeongbuk, South Korea.
The landslide hazard map was clipped using overlapped boundaries of slow-moving landslide areas, and the area for each grade was determined. The South Korean Forest Service categorizes landslide hazard maps from 1 to 5. The highest risk level corresponds to grade 1 and the lowest to grade 5. The spatial resolution of the landslide hazard map was 10 m × 10 m, and the number of cells in each grade was used to calculate the area. The finalized graded areas were used to compare the difference between the degree (grade) of landslide hazard and the occurrence of slow-moving landslides. The difference in graded areas was also statistically verified. The statistical analysis was performed using a normality test (Shapiro–Wilk test) for these graded areas followed by the Kruskal–Wallis test, a non-parametric test [30]. Non-parametric tests were conducted because parametric tests (analysis of variance: ANOVA) using non-normally distributed data are statistically unreliable. For the post hoc test, ranked data were generated using area data based on grade, and a post hoc test for differences between groups (Duncan’s multiple range test) was conducted. For the post hoc test of group differences in non-normally distributed data, rank data were generated [31]. In addition, GIS analysis—including overlap analysis—was performed using ArcMap 10.8.2 (ESRI, Redlands, CA, USA). Statistical analysis was performed using SPSS ver. 21 (IBM, Armonk, NY, USA) with the confidence level set at p < 0.05.
2.2. Analysis of Stratigraphy, Topography, and the Scale of Occurrence
Herein, fieldwork was conducted in 15 slow-moving landslide areas in South Korea where tension cracks and steps occurred during slow-moving landslides and were reported to the Forest Service. For the analysis of stratigraphy and topography, a digital geological map (1:50,000; provided by Korea Institute of Geoscience and Mineral Resources) was used to analyze the supergroups, constituent rocks, rock weathering degree, presence of intrusive rock, number of joints, presence of stony slope, rock weathering degree, soil depth, and soil texture of the slow-moving landslide areas. We also analyzed the altitude and the degree and direction of the slopes of these slow-moving landslide areas using digital topographic maps (1:25,000; provided by the National Geographic Information Institute) and GPS coordinates and calculated the scale (range, length, and depth) of the scale of such landslides.
2.3. Analysis of Rainfall Effects
Among the external factors that cause slow-moving landslides, we analyzed rainfall-related factors such as rainfall amount, continuous rainfall days, continuous rainfall, maximum hourly rainfall, rainfall intensity, and antecedent rainfall (3, 5, 7, and 15 days) [16,25,32]. We also analyzed the correlation (Pearson correlation coefficient) between these rainfall factors and the scale of slow-moving landslides. The data on these rainfall factors were obtained from the data of weather stations in the areas where slow-moving landslides occurred [33].
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. Overlap Analysis
The slow-moving landslide area was overlapped on the landslide hazard map to analyze the difference in the risk of occurrence of slow-moving landslides and general landslides. The percentage area occupied by slow-moving landslide regions on the landslide hazard map was highest in the excluded non-hazard area at 28.8%, followed by Grade 3 at 25.8% and Grade 4 at 17.5%. Regarding the characteristics of each slow-moving landslide area, Sites No. 2, 10, and 13 had area ratios of 92.4, 79.5, and 68.3% of the excluded area, respectively, which were significantly different from the data on the hazards of the occurrences of slow-moving landslides and general landslides. In addition, Site No. 8 had an area ratio of 66.1% for Grade 5, and Site No. 15 had an area ratio of 53.5% for Grade 3. Thus, 83.3% of the area (including excluded areas) was in Grade 3 or lower, which is a moderate hazard (Table 1). Landslides in South Korea and slow-moving landslides are different forest soil sediment disasters with geology, soil, topography, cause, and slope differences [11]. Because the landslide hazard map was created using landslide triggering factors, the slow-moving landslide areas in the landslide hazard map were judged to include low hazard grades and especially grade-excluded areas.

Table 1.
Results of overlap analysis of landslide hazard map and slow-moving landslide areas.
We analyzed the statistical significance of the results of the overlap analysis, i.e., the difference in area by grade. Specifically, we conducted normality testing of the area data based on grade using the Shapiro–Wilk test. The combined analysis of skewness, kurtosis, and significance probability revealed that the grade-based area data were not normally distributed (Table 2). Thus, we conducted a non-parametric test to analyze the difference in graded area.

Table 2.
Normality test results for the slow-moving landslide areas based on grade.
The non-parametric test (Kruskal–Wallis test) on the area data revealed that the difference in area based on grade was significant (p < 0.001). ANOVA conducted on the difference between grades using the ranking data of the slow-moving landslide areas based on grade revealed a significant difference between various grades (p < 0.001). In particular, the post hoc analysis showed that Grades 1 and 5 were characterized by low rankings, whereas Grades 2, 3, and 4 and excluded areas (non-hazardous areas) were characterized by high rankings (Table 3). Thus, slow-moving landslides occurred mainly in relatively low landslide hazard areas on the landslide hazard map, particularly in excluded areas (non-hazardous areas).

Table 3.
Results of non-parametric tests and analysis of variance (ANOVA) for differences in slow-moving landslide areas based on grade.
Until recently, slow-moving landslides were treated as a type of landslide in South Korea. Unlike landslides, which are a type of surface failure type of mountain erosion, slow-moving landslides can cause large-scale damage because the soil layer moves slowly over a long period [8,34]. Predicting and responding to the risk of slow-moving landslides is not possible with a landslide hazard map. Therefore, slow-moving landslides must be treated as a distinctly different phenomenon from landslides. Moreover, there is an urgent need to establish a national SMLHIS (slow-moving landslide hazard map) like the one for landslides. Landslides are downslope movements of rock, soil, or both that occur on curved (rotational slide) or planar (translational slide) rupture surfaces. The material often moves as a coherent or semicoherent mass with slight internal deformation. On the other hand, slow-moving landslides can occur on gentle-to-moderate slopes, generally in fine-grained soils, such as clay or silt, but also in very weathered, clay-bearing bedrock. The mass in a slow-moving landslide moves as a plastic or viscous flow with internal solid deformation [6].
3.2. Analysis of Stratigraphy, Topography, and the Scale of Occurrence
We examined the stratigraphy and constituent rocks of the 15 sites in the slow-moving landslide areas. The Cretaceous and Precambrian periods were the most common geologic ages, with five (33.3%) and four sites (26.7%), respectively. The Gyeongsang supergroup was the most common at four sites (26.7%) among the supergroups. The Pyeongan group, Sobaeksan gneiss complex, and Okcheon group were each found at two sites (13.3%). These slow-moving landslides were most common in the Gyeongsang supergroup, corresponding to sedimentary rocks. The main constituent rocks of these slow-moving landslide areas were igneous rocks at three (20.0%), metamorphic rocks at six (40.0%), and sedimentary rocks at six sites (40.0%). The grain of these rocks corresponded with the degree and direction of the slope, believed to have facilitated the slow-moving landslide phenomena [9,11] (Table 4).

Table 4.
Stratigraphy, topography, and the scale of slow-moving landslide areas.
In these slow-moving landslide area stations, 2 (13.3%) had intrusive rock, and 13 (86.7%) did not have intrusive rock. In terms of the number of joints, slow-moving landslides occurred at eight sites (53.3%) with two joints, seven sites (46.7%) with three or more joints, and all sites with two or more joints. Joint spacing was dense (6–20 mm) in 12 sites (80.0%). It has been analyzed that denser joint spacing is relatively more prone to slow-moving landslides [9,25]. In the areas in which slow-moving landslides occurred, stony slopes existed in 5 sites (33.3%) and did not exist in 10 sites (66.7%). There were 13 sites (86.7%) with weathered rocks, indicating that weathered rocks mainly caused slow-moving landslides.
In most areas in which slow-moving landslides occurred, the soil depth was 30–60 cm (8 places, 53.3%). Slow-moving landslides were found to occur frequently in the general soil depths of forest land in South Korea [35]. The soil texture of the slow-moving landslide area was sandy loam at seven sites (46.7%) (Table 4). The average soil in South Korea is 41.7% sand, 41.5% silt, and 16.8% clay. The dominant soil textures are sandy loam (44.5%) and clay loam (34.1%), which account for 78.6% of the total soil [36]. The predominance of sandy loam and clay loam in South Korea’s soil texture makes slow-moving landslides possible in any region in the country. These results suggest that it is necessary to identify rocks or soils vulnerable to slow-moving landslides and prepare appropriate countermeasures to minimize the human and material damage caused by slow-moving landslides.
The average altitude of the slow-moving landslide areas was 128.9 m (27.5–587.5 m), corresponding to hill areas, which is consistent with the finding that slow-moving landslides mainly occurred in hill areas [11,15]. However, one slow-moving landslide area occurred at an altitude of 587.5 m, which was a unique case in which the slow-moving landslide phenomenon affected the summit of the mountain due to the cutting of the lower part under the quarrying project. The average slope of slow-moving landslides in South Korea is 24°, ranging from 16.7° to 35°. Approximately 51% of Korean mountainous regions have steep slopes of 20° or more [35]. The slope direction of the slow-moving landslide area was northwest in 12 sites (80.0%) and northeast in 3 sites (20.0%) (Table 4). The direction of the slow-moving landslides corresponded with the slope direction in all 15 sites. The slow-moving landslide was analyzed as occurring in the direction of the flow of materials comprising the slope of the mountainous area based on the slope degree.
The analysis of the scale of slow-moving landslides revealed that their average range was 191.9 m (84.2–446.9 m), the average length was 203.2 m (108.2–467.2 m), and the average depth was 2.5 m (1.2–5.8 m) (see Table 5). These scales were smaller than those reported in an analysis of 100 nationally representative slow-moving landslide areas in Japan (200–270 m wide, 300–360 m long, and 18.3–18.6 m deep) [9]. However, the scale of occurrence of slow-moving landslides in South Korea has been gradually increasing compared with that of slow-moving landslides reported in the past [8].

Table 5.
Results of the analysis of the scale of the occurrence of slow-moving landslides and rainfall factors.
3.3. Analysis of Rainfall Effects
3.3.1. Effects of Rainfalls
The area with the highest number of continuous rainfall days before the slow-moving landslide occurred was Site 6, with 21 days of continuous rainfall of 611.7 mm. The areas with more than 100 mm of continuous rainfall comprised sites 1, 3, 6, 9, 10, 11, 12, and 14, which accounted for approximately 53% of the total slow-moving landslide area. It has been shown that when the continuous rainfall is more than 100 mm, the probability of mountain disasters such as slow-moving landslides is high [37]. Furthermore, when slow-moving landslides occurred, Sites No. 1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6, 8, 13, 14, and 15 accounted for about 67% of the total slow-moving landslide area, with rainfall intensity of 30 mm/h or more. The remaining sites with rainfall intensity less than 30 mm/h were also close to the rainfall intensity of 30 mm/h, such as Site No. 7 with 29.2 mm/h and Sites No. 9, 10, 11, and 12 with 29.5 mm/h. It has been found that slow-moving landslides mainly occur when the rainfall intensity is 30 mm/h [37], and all the sites in this study showed similar results (Table 5).
The three-day antecedent rainfall was the highest at Site No. 3 with 162.5 mm, and the five-day antecedent rainfall was the highest at Site No. 8 with 166.0 mm. The 7-day and 15-day antecedent rainfalls were the highest at Site No. 8, with 173.0 and 334.2 mm, respectively. Slow-moving landslides have been reported to occur when the antecedent rainfall is more than 200 mm [37], and the areas with 15-day antecedent rainfall of more than 200 mm were Sites 6, 8, 9, 10, and 11. It has been reported that mountain disasters such as slow-moving landslides occur as a direct effect of rainfall [38]. All sites were found to have experienced slow-moving landslides due to intensive rainfall and internal factors such as strata and terrain vulnerable to slow-moving landslides.
3.3.2. Correlation Analysis of the Scale of Occurrence of Slow-Moving Landslides and Rainfall Factors
The width of the slow-moving landslide area significantly correlated (0.533) with the number of continuous rainfall days before the slow-moving landslide occurred. The length of the slow-moving landslide area also significantly correlated (0.517) with the number of continuous rainfall days (Table 6). It has been shown that among the factors affecting slow-moving landslides, the number of continuous rainfall days is crucial [16]. As the number of continuous rainfall days before the occurrence of slow-moving landslides increases, the scale of slow-moving landslides increases. The occurrence of slow-moving landslides is known to be strongly influenced by compressed groundwater in the clay layer or rock layer within the soil layer [11]. Continuous rainfall was considered a powerful source of moisture in the soil layer.

Table 6.
Results of the correlation analysis of the scale of occurrence of slow-moving landslides and rainfall factors.
The depth of the slow-moving landslide area was significantly correlated with rainfall on the date of slow-moving landslide and maximum hourly rainfall, with correlation coefficients of 0.765 and 0.659, respectively (Table 6). It was found that higher-than-normal rainfall and maximum hourly rainfall at the time of the occurrence of slow-moving landslides implies relatively more infiltration of rainwater from rainfall, which leads to a deeper-than-usual, slow-moving landslide phenomenon.
The width and length of the slow-moving landslide area showed significant definitional correlations with rainfall intensity at the time of slow-moving landslide occurrence, with correlation coefficients of 0.590 and 0.602, respectively (Table 6). It was analyzed that the larger the rainfall intensity, the larger the size of the slow-moving landslide. It was reported that slow-moving landslides occurred relatively more when the 15-day antecedent rainfall ranged from 301–400 mm [39]. However, this study did not show a significant result with the slow-moving landslide area size. Meanwhile, the depth of the slow-moving landslide area was significantly correlated with the three-day, five-day, and seven-day antecedent rainfalls, with correlation coefficients of 0.696, 0.738, and 0.821, respectively (Table 6). It has been reported that among the rainfall factors affecting slow-moving landslides, seven-day antecedent rainfall has a significant effect [16]. The more the antecedent rainfall, the deeper the water infiltrates into the ground in the direction of gravity. Furthermore, it was found that the slow-moving landslide phenomenon occurs deeper in the soil layer containing a large amount of clayey soil subjected to earth pressure and water pressure than in other layers, accelerating the chemical weathering of rocks and soil [40].
4. Conclusions
The phenomenon of slow-moving landslides is one of the most frequent landslide hazards caused by a combination of various factors. Slow-moving landslides can occasionally accelerate rapidly and collapse catastrophically [17]. As opposed to landslides, slow-moving landslides have not been actively studied until recently, and we need to conduct various studies on their triggering factors. This should lead to the development of early warning systems at the national level to minimize the damage to infrastructure and local communities caused by slow-moving landslides.
In this study, the landslide hazard map and the slow-moving landslide area were overlapped for analysis to investigate the difference in the occurrence of landslides and slow-moving landslides using GIS. Consequently, it was inferred that slow-moving landslides occur mainly in areas with low risk ratings on the landslide hazard map, particularly in excluded areas (non-hazardous areas). Until recently, the phenomenon of slow-moving landslides has been treated as a type of landslide in South Korea. However, unlike landslides, which are a type of surface failure type of mountain erosion, slow-moving landslides can cause large-scale damage to human life, property, and social infrastructure because the soil layer moves slowly for a long time. Predicting and responding to the risk of slow-moving landslides is impossible with a landslide hazard map. Hence, slow-moving landslides should be regarded as a distinctly different phenomenon from landslides. The establishment of a national SMLHIS (slow-moving landslide hazard map) is urgently needed.
Slow-moving landslides were found to occur most frequently in the Gyeongsang supergroup, which corresponds to sedimentary rocks. Slow-moving landslides also occurred in igneous, metamorphic, and sedimentary rocks, but slow-moving landslides were more likely to occur when the grain of the rock was the same as the slope degree direction. Soil textures were found most frequently in sandy loam. The results of this study are expected to help to understand the causes of slow-moving landslides related to soil factors and to prepare measures to prevent slow-moving landslides.
However, slow-moving landslides were relatively more likely to occur due to intensive rainfall, particularly when the continuous rainfall was more than 100 mm and the 15-day antecedent rainfall was more than 200 mm. Furthermore, slow-moving landslides are caused by the influence of intensive rainfall in addition to internal factors such as strata or topography that are vulnerable to slow-moving landslides. The width and length of the slow-moving landslide area were significantly and positively correlated with continuous rainfall days before the slow-moving landslide occurred. The depth of the slow-moving landslide area was significantly and positively correlated with rainfall on the date of slow-moving landslide; maximum hourly rainfall; and three-, five-, and 7seven-day antecedent rainfall. The width and length of the slow-moving landslide area were significantly and positively correlated with rainfall intensity during the slow-moving landslide. These results suggest that slow-moving landslides are triggered by both the amount and intensity of rainfall. In particular, the longer the number of continuous rainfall days before the slow-moving landslide occurred; the greater the rainfall on the date of slow-moving landslide; the maximum hourly rainfall; the three, five, and seven-day antecedent rainfall; and the greater the rainfall intensity at the time of slow-moving landslide occurrence, the greater the magnitude of slow-moving landslide.
Slow-moving landslides, which are not easy to detect, can cause forest disasters such as large-scale forest collapse and sediment runoff. Therefore, to prevent slow-moving landslides, it will be necessary to protect forests in preparation for intensive rainfall and to identify slow-moving landslide-vulnerable areas through the establishment of an SMLHIS to undertake appropriate preventive measures.
The Forest Service of South Korea aims to develop a slow-moving landslide hazard map in the future. Therefore, we needed to develop slow-moving-landslide-triggering factors by evaluating such factors—including stratigraphy, topography, and rainfall in the mountains—in this study in addition to other diverse factors. Furthermore, we should comprehensively analyze the correlation between various factors and the scale of occurrence, identify the weight of each factor, develop a more reliable slow-moving landslide hazard map, and build a national slow-moving landslide risk information system.
This study analyzed slow-moving landslide areas’ stratigraphy, topography, and scale. In particular, the correlation between various rainfall factors and the scale of slow-moving landslides was scientifically analyzed. This will help to understand the causes of slow-moving landslides and apply the results to developing technologies to prevent their occurrence. In particular, the factors correlated with the scale of slow-moving landslides analyzed in this study can be used to construct a slow-moving landslide hazard prediction model to identify areas with a high hazard of slow-moving landslides. This will lead to the establishment of a national SMLHIS and the development of a slow-moving landslide hazard map, which will allow for more accurate prediction of the hazard of slow-moving landslides and the development of effective damage prevention measures against slow-moving landslides.
This study analyzed the correlation between the scale of slow-moving landslides and rainfall factors based on 15 cases of slow-moving landslides with precise occurrence dates. However, if any future slow-moving landslides with accurate occurrence dates are confirmed, the results of this study can be reinterpreted by re-analyzing the data with a more significant number of study sites. Additionally, this study analyzed the correlation between the scale of slow-moving landslides and rainfall data before and after the occurrences. However, it is believed that a comprehensive analysis is needed that considers not only the geological and topographical factors of the slow-moving landslide area, but also various climatic factors that can affect the occurrence of slow-moving landslides, such as temperature and snowfall. Nevertheless, this study is still meaningful because it provides essential information on the occurrence characteristics and triggering factors of slow-moving landslides. If additional research is conducted to overcome the research limitations in the future, more effective and flexible methods for the rapid prediction and prevention of slow-moving landslide occurrences are expected to be developed.
Author Contributions
Conceptualization, J.-H.P., S.-H.L. and H.K.; methodology, J.-H.P. and H.K.; software, J.-H.P. and H.K.; validation, J.-H.P., S.-H.L. and H.K.; formal analysis, H.K.; investigation, J.-H.P. and S.-H.L.; resources, J.-H.P. and H.K.; data curation, J.-H.P. and H.K.; writing—original draft preparation, S.-H.L. and H.K.; writing—review and editing, H.K.; visualization, J.-H.P. and H.K.; supervision, J.-H.P. and H.K.; project administration, J.-H.P.; funding acquisition, J.-H.P. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This study was conducted with the support of the R&D Program for Forest Science Technology (Project No. 2021347B10-2123-CD01) funded by the Korea Forest Service (Korea Forestry Promotion Institute, Seoul, South Korea).
Institutional Review Board Statement
Not applicable.
Informed Consent Statement
Not applicable.
Data Availability Statement
The data presented in this study are available on request from the corresponding author.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
References
- Senanayake, A.; Fernando, N.; Wasana, M.; Amaratunga, D.; Haigh, R.; Malalgoda, C.; Jayakody, C. Landslide induced displacement and relocation option: A case study of owner driven settings in Sri Lanka. Sustainability 2022, 14, 1906. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Food and Agriculture Organization of the United Nations. Global Forest Resources Assessment 2020: Key Findings; FAO: Rome, Italy, 2000; p. 1. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Das, G.; Lepcha, K. Application of logistic regression (LR) and frequency ratio (FR) models for landslide susceptibility mapping in Relli Khola River Basin of Darjeeling Himalaya, India. SN Appl. Sci. 2019, 1, 1453. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Klose, M.; Maurischat, P.; Damm, B. Landslide impacts in Germany: A historical and socioeconomic perspective. Landslides 2016, 13, 183–199. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Korea Forest Service. Landslide Information System: Landslide Occurrence Trends 2023. Available online: https://sansatai.forest.go.kr (accessed on 13 September 2023). (In Korean).
- Highland, L.M.; Bobrowsky, P. The Landslide Handbook: A Guide to Understanding Landslides (Circular 1325); U.S. Geological Survey (USGS): Reston, VA, USA, 2008; pp. 4–26.
- Hungr, O.; Leroueil, S.; Picarelli, L. The Varnes classification of landslide types, update. Landslides 2014, 11, 167–194. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Woo, B.; Park, J.; Choi, H.; Jeon, G.; Kim, K. A study on the characteristics of the landslide in Hyuseok-Dong (I): Topographical characteristics and surface displacement. J. Korean Soc. For. Sci. 1996, 85, 565–570, (In Korean with English Abstract). [Google Scholar]
- Takaya, S. Facts of Land Creep; Kajima Publisher: Tokyo, Japan, 2017; p. 255. (In Japanese) [Google Scholar]
- Tian, S.; Hu, G.; Chen, N.; Rahman, M.; Ni, H.; Somos-Valenzuela, M. Effects of tectonic setting and hydraulic properties on silent large-scale landslides: A case study of the Zhaobishan landslide, China. Int. J. Disaster Risk Sci. 2023, 14, 600–617. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- National Institute of Forest Science. 15 Things Needed to be Known about Land Creeps in a Nutshell; National Institute of Forest Science: Seoul, Republic of Korea, 2021; p. 4. (In Korean) [Google Scholar]
- Miao, F.; Wu, Y.; Török, Á.; Li, L.; Xue, Y. Centrifugal model test on a riverine landslide in the Three Gorges Reservoir induced by rainfall and water level fluctuation. Geosci. Front. 2022, 13, 101378. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fang, K.; Tang, H.; Li, C.; Su, X.; An, P.; Sun, S. Centrifuge modelling of landslides and landslide hazard mitigation: A review. Geosci. Front. 2023, 14, 101493. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, W.; Wu, C.; Tang, L.; Gu, X.; Wang, L. Efficient time-variant reliability analysis of Bazimen landslide in the Three Gorges Reservoir Area using XGBoost and LightGBM algorithms. Gondwana Res. 2022, 123, 41–53. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Choi, K. Land creep and geology in Korea. In Forest Environment; Won, H., Ahn, B.Y., Kim, J.H., Shim, W.B., Jeong, Y.S., Eds.; Korean Society of Forest Environment Research Publication No. 21; Korea Society of Forest Environment Research: Suwon, Republic of Korea, 2018; pp. 108–117. (In Korean) [Google Scholar]
- Lee, S.; Sun, G. A study on landslide characteristics by using shear strength between rock and soil. Inst. Ind. Technol. J. Univ. Seoul 2003, 11, 1–7, (In Korean with English Abstract). [Google Scholar]
- Lacroix, P.; Handwerger, A.L.; Bièvre, G. Life and death of slow-moving landslides. Nat. Rev. Earth Environ. 2020, 1, 404–419. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, H.; Kim, M.; Lee, M.; Park, Y.; Kwak, J. Correlation of deep landslide occurrence and variation of groundwater level. J. Korea Soc. For. Eng. Technol. 2017, 15, 1–12, (In Korean with English Abstract). [Google Scholar]
- Lee, M.; Park, J.; Park, Y. Analysis of characteristics using geotechnical investigation on the slow-moving landslide in the Pohang-si area. J. Korean Soc. For. Sci. 2019, 108, 233–240, (In Korean with English Abstract). [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Choi, J.; Choi, B.; Kim, N.; Lee, C.; Seo, J.; Jeon, B. Estimation of potential risk and numerical simulations of landslide disaster based on UAV photogrammetry. KSCE J. Civil Environ. Eng. Res. 2021, 41, 675–686, (In Korean with English Abstract). [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, S.; Kim, J.; Kim, K.; Kwon, I. Delineation of the slip weak zone of land creeping with integrated geophysical methods and slope stability analysis. J. Eng. Geol. 2020, 30, 289–302, (In Korean with English Abstract). [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, J.; Kim, J.; Lee, S.; Cho, K.; Kim, J. Interpretation of electrical resistivity tomogram with contents of clay minerals for the land creeping area. J. Eng. Geol. 2021, 31, 187–197, (In Korean with English Abstract). [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hilley, G.E.; Burgmann, R.; Ferretti, A.; Novali, F.; Rocca, F. Dynamics of slow-moving landslides from permanent scatterer analysis. Science 2004, 304, 1952–1955. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Handwerger, A.L.; Roering, J.J.; Schmidt, D.A. Controls on the seasonal deformation of slow-moving landslides. Earth Planet. Sci. Lett. 2013, 377–378, 239–247. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jeon, B.; Lee, S. A study on the effect of collector well on the land creep slope. J. Eng. Geol. 2019, 29, 123–136, (In Korean with English Abstract). [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, N.; Choi, B.; Choi, J.; Jeon, B. Time series analysis of soil creep on cut slopes using unmanned aerial photogrammetry. J. Eng. Geol. 2020, 31, 447–456, (In Korean with English Abstract). [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Choi, J.; Eom, K.; Jeon, K.; Yoon, Y. Monitoring ground movements for deep seated landslide risk areas during an earthquake episode. Regul. Conf. Korean Soc. Civil Eng. 2019, 960–961, (In Korean with English Abstract). [Google Scholar]
- Park, J.; Seo, J.; Lee, C. Analysis of GIS for characteristics on the slow-moving landslide: With a special reference on slope and grade of landslide. J. Korean Soc. For. Sci. 2019, 108, 311–321, (In Korean with English Abstract). [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, S.; Li, D.Q.; Du, W. Recent advances in the investigation of slow-moving landslide in the Three Gorges Reservoir area, China. River 2022, 1, 91–103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, J.; Kim, B.; Jeong, H.; Shin, S. Environmental Statistics and Data Analysis; Hannarae Publishing, Co.: Seoul, Republic of Korea, 2018; pp. 158–173. (In Korean) [Google Scholar]
- Woo, S. PASW: Statistics 18.0; Human and Welfare: Seoul, Republic of Korea, 2010; p. 383. (In Korean) [Google Scholar]
- Yoo, N.; Park, B. A case study of landslides due to heavy rainfall. J. Ind. Technol. 2001, 21, 303–315, (In Korean with English Abstract). [Google Scholar]
- Korea Meteorological Administration. KMA Open MET Data Portal: ASOS (Automated Synoptic Observing System) Data, 2020. Available online: https://data.kma.go.kr/data/grnd/selectAsosRltmList.do?pgmNo=36 (accessed on 13 September 2023). (In Korean).
- Jau, J.; Park, S.; Son, D.; Joo, S. The effects of geological and topographical features on landslide and land-creep. J. Korean Soc. For. Sci. 2000, 89, 323–334, (In Korean with English Abstract). [Google Scholar]
- National Geography Information Institute. The National Atlas of Korea II 2020: Characteristics of Forest Soil. Available online: http://nationalatlas.ngii.go.kr/pages/page_2305.php (accessed on 13 September 2023).
- National Geography Information Institute. The National Atlas of Korea II 2020: Soil Properties. Available online: http://nationalatlas.ngii.go.kr/pages/page_2303.php (accessed on 13 September 2023).
- Kim, Y.; Jung, S. A study on the rainfall-triggered landslides in Taijon-Chungnam area. KSCE J. Civil Environ. Eng. Res. 2000, 20, 341–355, (In Korean with English Abstract). [Google Scholar]
- Olivier, M.; Bell, F.G.; Jermy, C.A. The effect of rainfall on slope failure with examples from the Greater Durban area. In Proceedings of the 7th International Congress International Association of Engineering Geology, Lisboa, Portugal, 5–9 September 1994; pp. 1629–1636. [Google Scholar]
- Park, J.; Lee, C.; Kang, M.; Kim, K. Analysis of characteristics of forest environmental factors on land creeping occurrence. J. Agric. Life Sci. 2015, 55, 133–144, (In Korean with English Abstract). [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jeong, J.; Koo, K.; Lee, C.; Kim, C. Physico-chemical properties of Korean forest soils by regions. J. Korean Soc. For. Sci. 2002, 91, 694–700, (In Korean with English Abstract). [Google Scholar]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).