1. Error in Figure/Table
In the original publication [1], there was a mistake in Figure 1 and Figure 2 as published. The place of the figures was amended. The corrected figures appear below. The authors apologize for any inconvenience caused and state that the scientific conclusions are unaffected. This correction was approved by the Academic Editor. The original publication has also been updated.
2. Effect of Bacterial Isolates on Viscosity of Bouri Crude Oil
Specific quantitative lab procedures using a Rotational Viscometer (CV100) were carried out to measure the shift in rheological properties in treated (inoculated) samples. The reduction of oil viscosity to enhance the flow properties occurs due to effects of bacterial degradation of oil or excreting of components such as surfactants into the oil phase. Figure 1 at 37 °C and Figure 2 at 55 °C show a sharp decrease in viscosity at a shear rate below 3 s−1, and after 50 s−1 the viscosity remains steady.
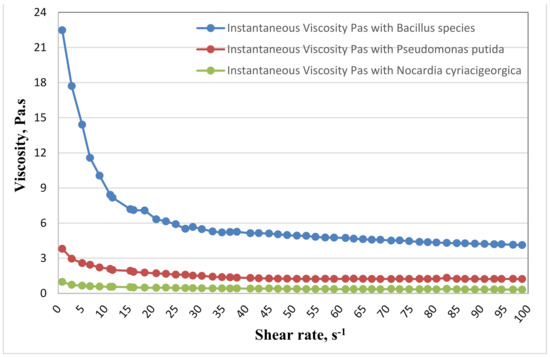
Figure 1.
Reduction in viscosity of crude oil treated with Bacillus species, Pseudomonas putida, and Nocardia cyriacigeorgica at 37 °C.
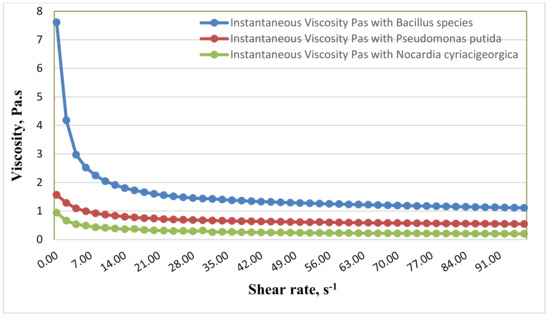
Figure 2.
Reduction in viscosity of crude oil treated with Bacillus species, Pseudomonas putida, and Nocardia cyriacigeorgica at 55 °C.
Reference
- Althalb, H.A.; Elmusrati, I.M.; Banat, I.M. A Novel Approach to Enhance Crude Oil Recovery Ratio Using Selected Bacterial Species. Appl. Sci. 2021, 11, 10492. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).