Bacterial Hosts and Genetic Characteristics of Antibiotic Resistance Genes in Wastewater Treatment Plants of Xinjiang (China) Revealed by Metagenomics
Abstract
:1. Introduction
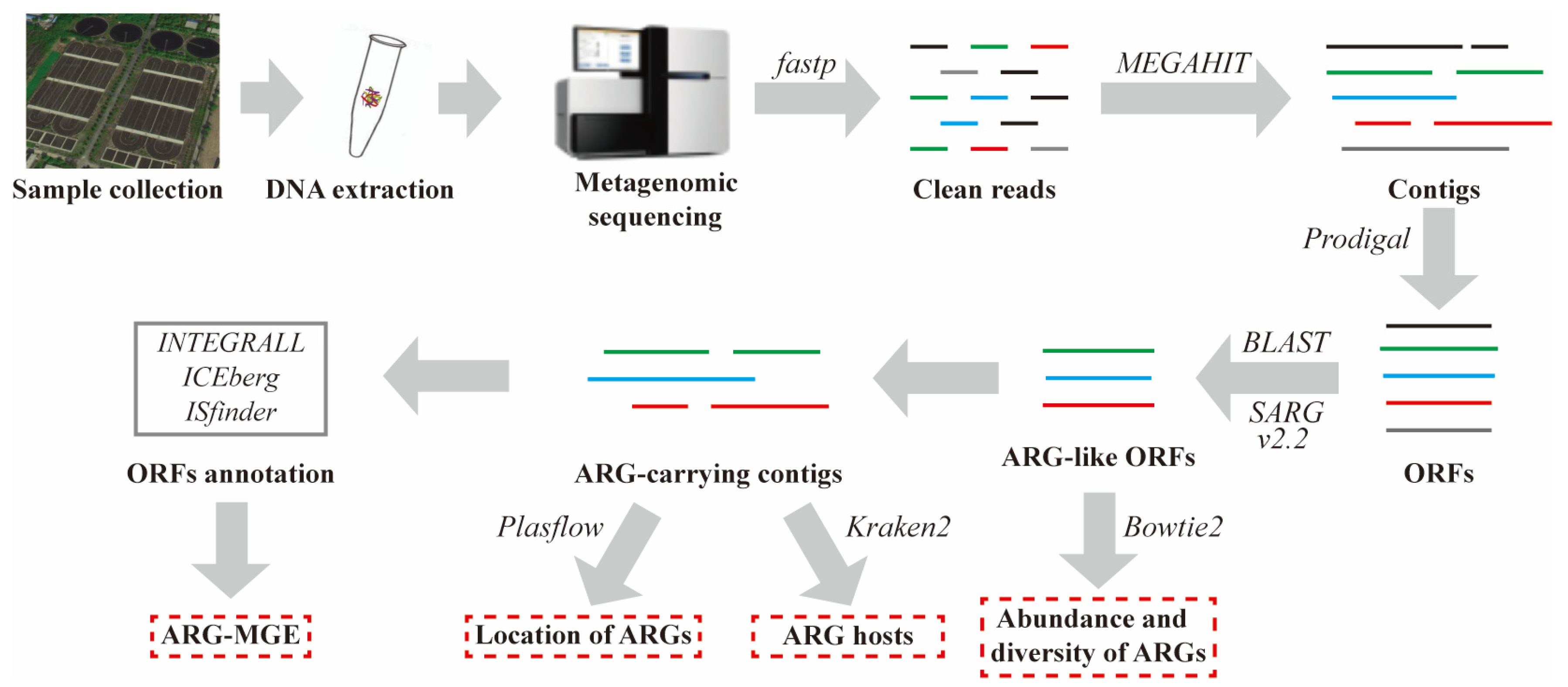
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Sample Collection, DNA Extraction, and Library Construction
2.2. Metagenomic Sequencing, Assembly, and Gene Prediction
2.3. Identification of ARG-Like ORFs and ARG-Carrying Contigs
2.4. Host Tracking, Genetic Location, and Coexistence Structure of MGEs and ARGs
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. The Abundance and Diversity of ARGs
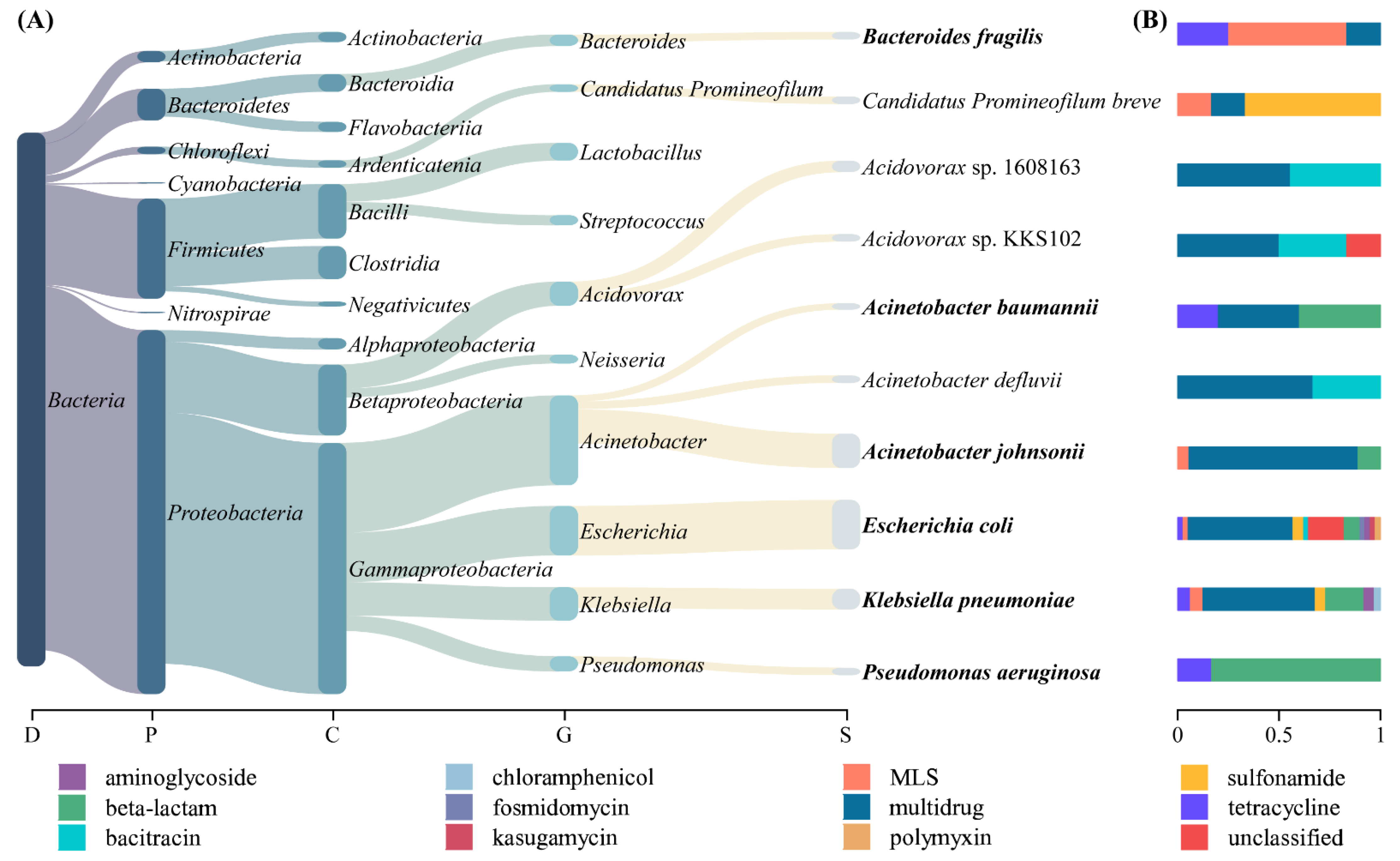
3.2. Host Tracking of ARGs
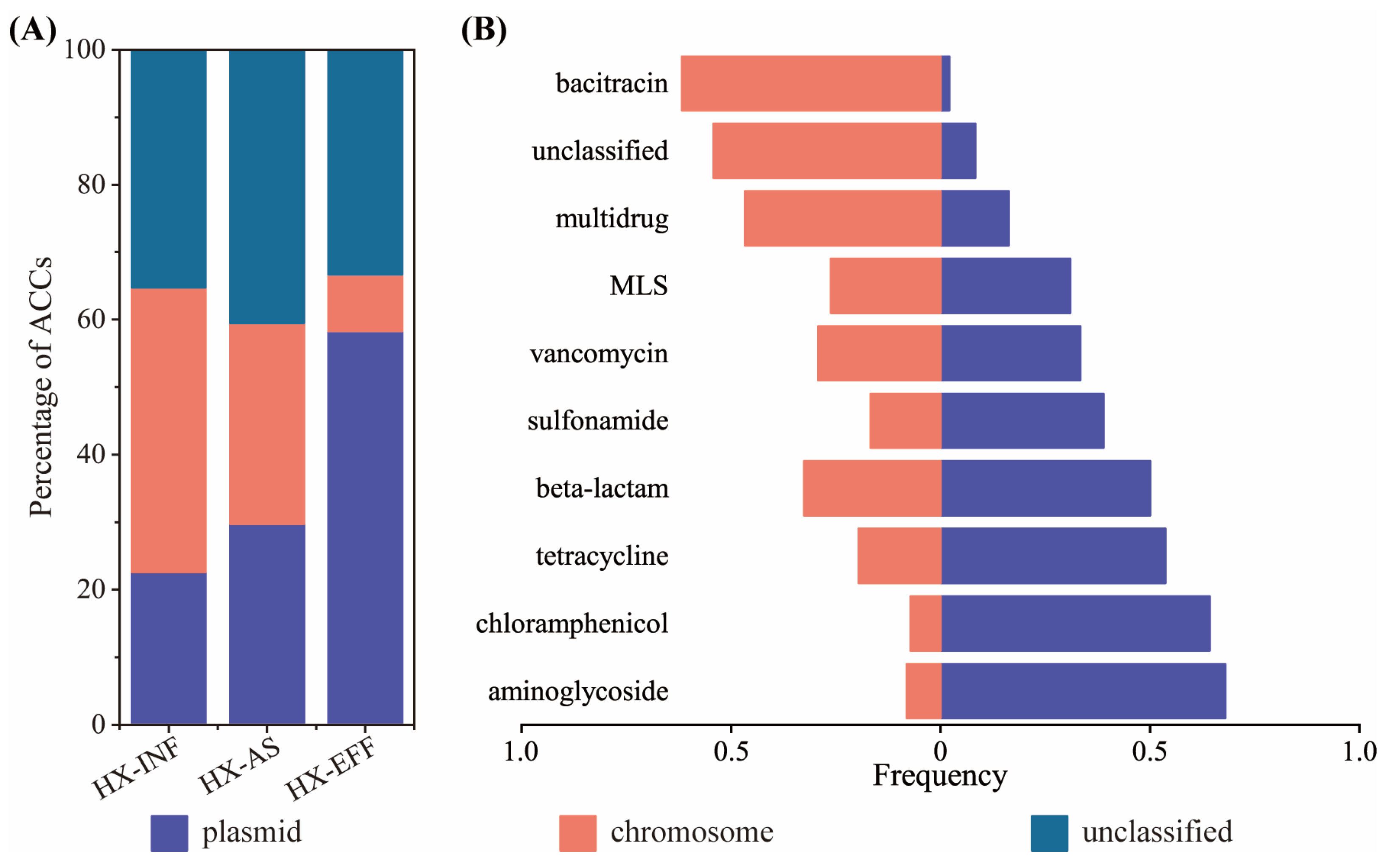
3.3. Genetic Location of ARGs
3.4. The Coexistence Structure of PARGs with MGEs
4. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| ACC | ARG-carrying contig |
| A. baumannii | Acinetobacter baumannii |
| A. johnsonii | Acinetobacter johnsonii |
| ARB | Antibiotic-resistant bacteria |
| ARG | Antibiotic resistance gene |
| ARP | Antibiotic-resistant pathogen |
| AS | Activated sludge |
| B. fragilis | Bacteroides fragilis |
| EFF | Effluent |
| E. coli | Escherichia coli |
| HGT | Horizontal gene transfer |
| ICE | Integrative and conjugative element |
| INF | Influent |
| IS | Insertion sequence |
| K. pneumoniae | Klebsiella pneumoniae |
| MGE | Mobile genetic element |
| MLS | Macrolide–lincosamide–streptogramin |
| ORF | Open reading frame |
| PARG | Persistent antibiotic resistance gene |
| P. aeruginosa | Pseudomonas aeruginosa |
| WWTP | Wastewater treatment plant |
References
- WHO. Antimicrobial Resistance: Global Report on Surveillance; World Health Organization: Geneva, Switzerland, 2014. [Google Scholar]
- Karkman, A.; Do, T.T.; Walsh, F.; Virta, M.P.J. Antibiotic-Resistance Genes in Waste Water. Trends Microbiol. 2018, 26, 220–228. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Osinska, A.; Korzeniewska, E.; Harnisz, M.; Felis, E.; Bajkacz, S.; Jachimowicz, P.; Niestepski, S.; Konopka, I. Small-scale wastewater treatment plants as a source of the dissemination of antibiotic resistance genes in the aquatic environment. J. Hazard. Mater. 2020, 381, 121221. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, Y.; Li, B.; Zou, S.; Fang, H.H.; Zhang, T. Fate of antibiotic resistance genes in sewage treatment plant revealed by metagenomic approach. Water Res. 2014, 62, 97–106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- He, L.Y.; He, L.K.; Liu, Y.S.; Zhang, M.; Zhao, J.L.; Zhang, Q.Q.; Ying, G.G. Microbial diversity and antibiotic resistome in swine farm environments. Sci. Total Environ. 2019, 685, 197–207. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zeng, J.; Pan, Y.; Yang, J.; Hou, M.; Zeng, Z.; Xiong, W. Metagenomic insights into the distribution of antibiotic resistome between the gut-associated environments and the pristine environments. Environ. Int. 2019, 126, 346–354. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Partridge, S.R.; Kwong, S.M.; Neville, F.; Jensen, S.O. Mobile Genetic Elements Associated with Antimicrobial Resistance. Clin. Microbiol. Rev. 2018, 31, e00088-17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Yu, Z.; He, P.; Shao, L.; Zhang, H.; Lu, F. Co-occurrence of mobile genetic elements and antibiotic resistance genes in municipal solid waste landfill leachates: A preliminary insight into the role of landfill age. Water Res. 2016, 106, 583–592. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Martinez, J.L.; Coque, T.M.; Baquero, F. What is a resistance gene? Ranking risk in resistomes. Nat. Rev. Microbiol. 2015, 13, 116–123. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhao, R.; Feng, J.; Yin, X.; Liu, J.; Fu, W.; Berendonk, T.U.; Zhang, T.; Li, X.; Li, B. Antibiotic resistome in landfill leachate from different cities of China deciphered by metagenomic analysis. Water Res. 2018, 134, 126–139. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jia, S.; Bian, K.; Shi, P.; Ye, L.; Liu, C.H. Metagenomic profiling of antibiotic resistance genes and their associations with bacterial community during multiple disinfection regimes in a full-scale drinking water treatment plant. Water Res. 2020, 176, 115721. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ju, F.; Beck, K.; Yin, X.; Maccagnan, A.; McArdell, C.S.; Singer, H.P.; Johnson, D.R.; Zhang, T.; Burgmann, H. Wastewater treatment plant resistomes are shaped by bacterial composition, genetic exchange, and upregulated expression in the effluent microbiomes. ISME J. 2019, 13, 346–360. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Ju, F.; Li, B.; Ma, L.; Wang, Y.; Huang, D.; Zhang, T. Antibiotic resistance genes and human bacterial pathogens: Co-occurrence, removal, and enrichment in municipal sewage sludge digesters. Water Res. 2016, 91, 1–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Luo, L.; Yao, J.; Liu, W.; Yang, L.; Li, H.; Liang, M.; Ma, H.; Liu, Z.; Chen, Y. Comparison of bacterial communities and antibiotic resistance genes in oxidation ditches and membrane bioreactors. Sci. Rep. 2021, 11, 8955. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pärnänen, K.; Karkman, A.; Tamminen, M.; Lyra, C.; Hultman, J.; Paulin, L.; Virta, M. Evaluating the mobility potential of antibiotic resistance genes in environmental resistomes without metagenomics. Sci. Rep. 2016, 6, 35790. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Guo, J.; Li, J.; Chen, H.; Bond, P.L.; Yuan, Z. Metagenomic analysis reveals wastewater treatment plants as hotspots of antibiotic resistance genes and mobile genetic elements. Water Res. 2017, 123, 468–478. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fresia, P.; Antelo, V.; Salazar, C.; Gimenez, M.; D’Alessandro, B.; Afshinnekoo, E.; Mason, C.; Gonnet, G.H.; Iraola, G. Urban metagenomics uncover antibiotic resistance reservoirs in coastal beach and sewage waters. Microbiome 2019, 7, 35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhao, R.; Yu, K.; Zhang, J.; Zhang, G.; Huang, J.; Ma, L.; Deng, C.; Li, X.; Li, B. Deciphering the mobility and bacterial hosts of antibiotic resistance genes under antibiotic selection pressure by metagenomic assembly and binning approaches. Water Res. 2020, 186, 116318. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, H.; Zhang, Z.; Song, J.; Cai, L.; Yu, Y.; Fang, H. Foam shares antibiotic resistomes and bacterial pathogens with activated sludge in wastewater treatment plants. J. Hazard. Mater. 2021, 408, 124855. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, S.F.; Zhou, Y.Q.; Chen, Y.R.; Gu, J. fastp: An ultra-fast all-in-one FASTQ preprocessor. Bioinformatics 2018, 34, 884–890. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, D.H.; Liu, C.M.; Luo, R.B.; Sadakane, K.; Lam, T.W. MEGAHIT: An ultra-fast single-node solution for large and complex metagenomics assembly via succinct de Bruijn graph. Bioinformatics 2015, 31, 1674–1676. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Hyatt, D.; Chen, G.L.; LoCascio, P.F.; Land, M.L.; Larimer, F.W.; Hauser, L.J. Prodigal: Prokaryotic gene recognition and translation initiation site identification. BMC Bioinform. 2010, 11, 11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Langmead, B.; Salzberg, S.L. Fast gapped-read alignment with Bowtie 2. Nat. Methods 2012, 9, 357–359. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Yin, X.; Jiang, X.T.; Chai, B.; Li, L.; Yang, Y.; Cole, J.R.; Tiedje, J.M.; Zhang, T. ARGs-OAP v2.0 with an expanded SARG database and Hidden Markov Models for enhancement characterization and quantification of antibiotic resistance genes in environmental metagenomes. Bioinformatics 2018, 34, 2263–2270. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Wood, D.E.; Lu, J.; Langmead, B. Improved metagenomic analysis with Kraken 2. Genome Biol. 2019, 20, 13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Yin, X.; Deng, Y.; Ma, L.; Wang, Y.; Chan, L.Y.L.; Zhang, T. Exploration of the antibiotic resistome in a wastewater treatment plant by a nine-year longitudinal metagenomic study. Environ. Int. 2019, 133, 105270. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Majeed, H.J.; Riquelme, M.V.; Davis, B.C.; Gupta, S.; Angeles, L.; Aga, D.S.; Garner, E.; Pruden, A.; Vikesland, P.J. Evaluation of Metagenomic-Enabled Antibiotic Resistance Surveillance at a Conventional Wastewater Treatment Plant. Front. Microbiol. 2021, 12, 1048. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Breitwieser, F.P.; Salzberg, S.L. Pavian: Interactive analysis of metagenomics data for microbiome studies and pathogen identification. Bioinformatics 2020, 36, 1303–1304. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, B.; Ju, F.; Cai, L.; Zhang, T. Profile and Fate of Bacterial Pathogens in Sewage Treatment Plants Revealed by High-Throughput Metagenomic Approach. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2015, 49, 10492–10502. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Krawczyk, P.S.; Lipinski, L.; Dziembowski, A. PlasFlow: Predicting plasmid sequences in metagenomic data using genome signatures. Nucleic Acids Res. 2018, 46, e35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Siguier, P.; Perochon, J.; Lestrade, L.; Mahillon, J.; Chandler, M. ISfinder: The reference centre for bacterial insertion sequences. Nucleic Acids Res. 2006, 34, D32–D36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Moura, A.; Soares, M.; Pereira, C.; Leitao, N.; Henriques, I.; Correia, A. INTEGRALL: A database and search engine for integrons, integrases and gene cassettes. Bioinformatics 2009, 25, 1096–1098. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Liu, M.; Li, X.B.; Xie, Y.Z.; Bi, D.X.; Sun, J.Y.; Li, J.; Tai, C.; Deng, Z.X.; Ou, H.Y. ICEberg 2.0: An updated database of bacterial integrative and conjugative elements. Nucleic Acids Res. 2019, 47, D660–D665. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xu, Y.; Guo, C.; Luo, Y.; Lv, J.; Zhang, Y.; Lin, H.; Wang, L.; Xu, J. Occurrence and distribution of antibiotics, antibiotic resistance genes in the urban rivers in Beijing, China. Environ. Pollut. 2016, 213, 833–840. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bouki, C.; Venieri, D.; Diamadopoulos, E. Detection and fate of antibiotic resistant bacteria in wastewater treatment plants: A review. Ecotoxicol. Environ. Saf. 2013, 91, 1–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, B.; Yang, Y.; Ma, L.; Ju, F.; Guo, F.; Tiedje, J.M.; Zhang, T. Metagenomic and network analysis reveal wide distribution and co-occurrence of environmental antibiotic resistance genes. ISME J. 2015, 9, 2490–2502. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Tong, J.; Tang, A.P.; Wang, H.Y.; Liu, X.X.; Huang, Z.H.; Wang, Z.Y.; Zhang, J.Y.; Wei, Y.S.; Su, Y.Y.; Zhang, Y.F. Microbial community evolution and fate of antibiotic resistance genes along six different full-scale municipal wastewater treatment processes. Bioresour. Technol. 2019, 272, 489–500. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wright, G.D. The antibiotic resistome: The nexus of chemical and genetic diversity. Nat. Rev. Microbiol. 2007, 5, 175–186. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lupo, A.; Coyne, S.; Berendonk, T.U. Origin and evolution of antibiotic resistance: The common mechanisms of emergence and spread in water bodies. Front. Microbiol. 2012, 3, 18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Pruden, A.; Arabi, M.; Storteboom, H.N. Correlation Between Upstream Human Activities and Riverine Antibiotic Resistance Genes. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2012, 46, 11541–11549. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Raza, S.; Jo, H.; Kim, J.; Shin, H.; Hur, H.G.; Unno, T. Metagenomic exploration of antibiotic resistome in treated wastewater effluents and their receiving water. Sci. Total Environ. 2021, 765, 142755. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Woolhouse, M.E.; Ward, M.J. Sources of antimicrobial resistance. Science 2013, 341, 1460–1461. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, Y.; Li, Z.; Song, W.; Du, L.; Ye, C.; Zhao, B.; Liu, W.; Deng, D.; Pan, Y.; Lin, H.; et al. Metagenomic insights into the abundance and composition of resistance genes in aquatic environments: Influence of stratification and geography. Environ. Int. 2019, 127, 371–380. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, C.; Lu, J.; Liu, J.; Zhang, G.; Tong, Y.; Ma, N. Exploring the correlations between antibiotics and antibiotic resistance genes in the wastewater treatment plants of hospitals in Xinjiang, China. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2016, 23, 15111–15121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhou, T.; Lu, J.; Tong, Y.; Li, S.; Wang, X. Distribution of antibiotic resistance genes in Bosten Lake, Xinjiang, China. Water Sci. Technol. 2014, 70, 925–931. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, Y.; Lu, S.; Liu, X.; Chen, J.; Han, M.; Wang, Z.; Guo, W. Profiles of antibiotic resistance genes in an inland salt-lake Ebinur Lake, Xinjiang, China: The relationship with antibiotics, environmental factors, and microbial communities. Ecotoxicol. Environ. Saf. 2021, 221, 112427. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Berendonk, T.U.; Manaia, C.M.; Merlin, C.; Fatta-Kassinos, D.; Cytryn, E.; Walsh, F.; Bürgmann, H.; Sørum, H.; Norström, M.; Pons, M.-N.; et al. Tackling antibiotic resistance: The environmental framework. Nat. Rev. Microbiol. 2015, 13, 310–317. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Che, Y.; Xia, Y.; Liu, L.; Li, A.D.; Yang, Y.; Zhang, T. Mobile antibiotic resistome in wastewater treatment plants revealed by Nanopore metagenomic sequencing. Microbiome 2019, 7, 44. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Santajit, S.; Indrawattana, N. Mechanisms of Antimicrobial Resistance in ESKAPE Pathogens. Biomed. Res. Int. 2016, 2016, 2475067. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Wushouer, H.; Zhang, Z.X.; Wang, J.H.; Ji, P.; Zhu, Q.F.; Aishan, R.; Shi, L.W. Trends and relationship between antimicrobial resistance and antibiotic use in Xinjiang Uyghur Autonomous Region, China: Based on a 3 year surveillance data, 2014–2016. J. Infect. Public Health 2018, 11, 339–346. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pakyz, A.L.; Oinonen, M.; Polk, R.E. Relationship of Carbapenem Restriction in 22 University Teaching Hospitals to Carbapenem Use and Carbapenem-Resistant Pseudomonas aeruginosa. Antimicrob. Agents Chemother. 2009, 53, 1983. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Ma, L.; Xia, Y.; Li, B.; Yang, Y.; Li, L.G.; Tiedje, J.M.; Zhang, T. Metagenomic Assembly Reveals Hosts of Antibiotic Resistance Genes and the Shared Resistome in Pig, Chicken, and Human Feces. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2016, 50, 420–427. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sugawara, E.; Nikaido, H. Properties of AdeABC and AdeIJK Efflux Systems of Acinetobacter baumannii Compared with Those of the AcrAB-TolC System of Escherichia coli. Antimicrob. Agents Chemother. 2014, 58, 7250–7257. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Wexler, H.M. Bacteroides: The Good, the Bad, and the Nitty-Gritty. Clin. Microbiol. Rev. 2007, 20, 593–621. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Page, G.L.; Gunnarsson, L.; Snape, J.; Tyler, C.R. Integrating human and environmental health in antibiotic risk assessment: A critical analysis of protection goals, species sensitivity and antimicrobial resistance. Environ. Int. 2017, 109, 155. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jia, S.; Zhang, X.X.; Miao, Y.; Zhao, Y.; Ye, L.; Li, B.; Zhang, T. Fate of antibiotic resistance genes and their associations with bacterial community in livestock breeding wastewater and its receiving river water. Water Res. 2017, 124, 259–268. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liang, J.; Mao, G.; Yin, X.; Ma, L.; Liu, L.; Bai, Y.; Zhang, T.; Qu, J. Identification and quantification of bacterial genomes carrying antibiotic resistance genes and virulence factor genes for aquatic microbiological risk assessment. Water Res. 2020, 168, 115160. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Becerra-Castro, C.; Macedo, G.; Silva, A.; Manaia, C.M.; Nunes, O.C. Proteobacteria become predominant during regrowth after water disinfection. Sci. Total Environ. 2016, 573, 313–323. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahmed, Y.; Lu, J.; Yuan, Z.; Bond, P.; Guo, J. Efficient inactivation of antibiotic resistant bacteria and antibiotic resistance genes by photo-Fenton process under visible LED light and neutral pH. Water Res. 2020, 179, 115878. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, Z.; Klumper, U.; Liu, Y.; Yang, Y.; Wei, Q.; Lin, J.G.; Gu, J.D.; Li, M. Metagenomic and metatranscriptomic analyses reveal activity and hosts of antibiotic resistance genes in activated sludge. Environ. Int. 2019, 129, 208–220. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Adamczuk, M.; Dziewit, L. Genome-based insights into the resistome and mobilome of multidrug-resistant Aeromonas sp. ARM81 isolated from wastewater. Arch. Microbiol. 2017, 199, 177–183. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Bueno, M.F.; Francisco, G.R.; De, O.G.D.; Doi, Y. Complete Sequences of Multidrug Resistance Plasmids Bearing rmtD1 and rmtD2 16S rRNA Methyltransferase Genes. Antimicrob. Agents Chemother. 2016, 60, 1928. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Tacao, M.; Moura, A.; Correia, A.; Henriques, I. Co-resistance to different classes of antibiotics among ESBL-producers from aquatic systems. Water Res. 2014, 48, 100–107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hall, J.P.J.; Williams, D.; Paterson, S.; Harrison, E.; Brockhurst, M.A. Positive selection inhibits gene mobilisation and transfer in soil bacterial communities. Nat. Ecol. Evol. 2017, 1, 1348–1353. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, X.; Ellabaan, M.M.H.; Charusanti, P.; Munck, C.; Blin, K.; Tong, Y.; Weber, T.; Sommer, M.O.A.; Lee, S.Y. Dissemination of antibiotic resistance genes from antibiotic producers to pathogens. Nat. Commun. 2017, 8, 15784. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Sentchilo, V.; Mayer, A.P.; Guy, L.; Miyazaki, R.; Tringe, S.G.; Barry, K.; Malfatti, S.; Goessmann, A.; Robinson-Rechavi, M.; Van der Meer, J.R. Community-wide plasmid gene mobilization and selection. ISME J. 2013, 7, 1173–1186. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Hall, R.M.; Collis, C.M. Mobile gene cassettes and integrons: Capture and spread of genes by site-specific recombination. Mol. Microbiol. 1995, 15, 593–600. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marathe, N.P.; Pal, C.; Gaikwad, S.S.; Jonsson, V.; Kristiansson, E.; Larsson, D. Untreated urban waste contaminates Indian river sediments with resistance genes to last resort antibiotics. Water Res. 2017, 124, 388. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Boltner, D.; Macmahon, C.; Pembroke, J.T.; Strike, P.; Osborn, A.M. R391: A Conjugative Integrating Mosaic Comprised of Phage, Plasmid, and Transposon Elements. J. Bacteriol. 2002, 184, 5158. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Roche, D.; Flechard, M.; Lallier, N.; Reperant, M.; Bree, A.; Pascal, G.; Schouler, C.; Germon, P. ICEEc2, a new integrative and conjugative element belonging to the pKLC102/PAGI-2 family, identified in Escherichia coli strain BEN374. J. Bacteriol. 2010, 192, 5026. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Botelho, J.; Mourao, J.; Roberts, A.P.; Peixe, L. Comprehensive genome data analysis establishes a triple whammy of carbapenemases, ICEs and multiple clinically relevant bacteria. Microb. Genom. 2020, 6, mgen000424. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]


| Samples | Temperature (°C) | pH | DO (mg/L) | MLSS (mg/L) | SVI | Sampling Point | Collection Date |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| HX-INF | 19.3 | 7.7 | - | - | - | Distribution well | 29 September 2020 |
| HX-AS | 18.2 | 7.2 | 1.4 | 4356 | 108 | Aerobic zone | |
| HX-EFF | 19.1 | 6.7 | - | - | - | Outlet | |
| CJ-INF | 17.9 | 6.5 | - | - | - | Distribution well | |
| CJ-AS | 17.5 | 6.8 | 2.3 | 4401 | 160 | Aerobic zone | |
| CJ-EFF | 18.2 | 6.2 | - | - | - | Outlet |
| ARP | ACCs | Carrying ARG Subtypes |
|---|---|---|
| Escherichia coli | 39 | aminoglycoside: aph(3″)-I, aph(6)-I, aac(3)-II; bacitracin: bacA; beta-lactam: TEM-1; fosmidomycin: rosA, rosB; kasugamycin: ksgA; MLS: macA; multidrug: acrA, acrB, bcr, emrA, emrB, emrD, emrE, emrK, mdfA, mdtA, mdtB, mdtC, mdtD, mdtE, mdtF, mdtG, mdtH, mdtK, mdtL, mdtM, mdtN, mdtO, mdtP, TolC; polymyxin: arnA; sulfonamide: sul2; tetracycline: tet34; unclassified: CpxR, gadX, H-NS, sdiA |
| Acinetobacter johnsonii | 27 | beta-lactam: OXA-211, OXA-309; MLS: macB; multidrug: abeS, adeJ, adeK, emrB, mdfA, mdtK, mexB, mexT, oprM, TolC |
| Klebsiella pneumoniae * | 16 | aminoglycoside: aadA; beta-lactam: CTX-M, penA, VEB-3; chloramphenicol: catB; MLS: mphA; multidrug: acrA, acrB, mdtB, mdtG, mdtK, mdtL, mdtN, qacEdelta1; sulfonamide: sul1; tetracycline: tet34 |
| Pseudomonas aeruginosa * | 6 | beta-lactam: class A beta-lactamase, OXA-10, OXA-101; tetracycline: tetA |
| Bacteroides fragilis | 6 | MLS: ermF; multidrug: abeS; tetracycline: tetQ |
| Acinetobacter baumannii * | 5 | beta-lactam: CARB-8, OXA-58; multidrug: adeB; tetracycline: tet39 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Liu, Z.; Yao, J.; Ma, H.; Rukeya, A.; Liang, Z.; Du, W.; Chen, Y. Bacterial Hosts and Genetic Characteristics of Antibiotic Resistance Genes in Wastewater Treatment Plants of Xinjiang (China) Revealed by Metagenomics. Appl. Sci. 2022, 12, 3100. https://doi.org/10.3390/app12063100
Liu Z, Yao J, Ma H, Rukeya A, Liang Z, Du W, Chen Y. Bacterial Hosts and Genetic Characteristics of Antibiotic Resistance Genes in Wastewater Treatment Plants of Xinjiang (China) Revealed by Metagenomics. Applied Sciences. 2022; 12(6):3100. https://doi.org/10.3390/app12063100
Chicago/Turabian StyleLiu, Ziteng, Junqin Yao, Huiying Ma, Abudukelimu Rukeya, Zenghui Liang, Wenyan Du, and Yinguang Chen. 2022. "Bacterial Hosts and Genetic Characteristics of Antibiotic Resistance Genes in Wastewater Treatment Plants of Xinjiang (China) Revealed by Metagenomics" Applied Sciences 12, no. 6: 3100. https://doi.org/10.3390/app12063100
APA StyleLiu, Z., Yao, J., Ma, H., Rukeya, A., Liang, Z., Du, W., & Chen, Y. (2022). Bacterial Hosts and Genetic Characteristics of Antibiotic Resistance Genes in Wastewater Treatment Plants of Xinjiang (China) Revealed by Metagenomics. Applied Sciences, 12(6), 3100. https://doi.org/10.3390/app12063100






