Abstract
The dental anomaly fused teeth is defined as the union of two or more teeth. Its aetiology is unclear; to date no studies have investigated its genetic background. Therefore, this study, on the basis of a hypothesised genetic component, investigated the genetic background of patients with fused teeth using whole exome sequencing. Fifteen individuals from six families, including members with and without fused teeth, provided saliva samples that were analysed using whole exome sequencing. Patients with other congenital diseases were excluded from this study. Rare variants were extracted from the sequencing data and filtered by family grouping to identify candidate variants. As a result, ERCC6, OBSCN, SLC27A3, and KIF25 were identified as candidate variants. Our sequencing analysis identified four candidate gene variants associated with fused teeth, which now require further investigation. A genetic basis for the anomaly appears likely. This may assist in understanding the aetiology of fused teeth, which in turn supports better oral care and treatment, as well as future regenerative medicine and gene therapy.
1. Introduction
Structurally, the tooth consists of a crown above and in the upper part of the gums, and root(s) in the alveolar bone; it is composed of enamel, dentin, and cementum [1]. Dentin has a dental pulp within it, which contains nerves and blood vessels. Anomalous tooth shapes can occur [1,2], such as fused teeth, defined as the union of two or more teeth involving their enamel, dentin, and cementum [3]. Fused teeth usually appear as large crowns which contain a groove between the two originating teeth and cause malocclusion [1,2,3]. Caries, periodontal issues, and aesthetic problems can, therefore, result and may require dental treatment [4].
The most frequent fused area involves the mandibular incisor, followed by the maxillary incisor, and, rarely, the molar area [1,5,6]. The incidence of fused teeth has been reported to be 0.5–2.5% in primary dentition and 0.1% in permanent dentition [7,8,9]. Similarly, a meta-analysis has shown that the frequency of bilateral fused teeth is 0.02% for both primary and permanent dentition [10]. No sex difference has been observed [11]. A higher incidence has been observed in Asians and Native Americans [2].
The aetiology of fused teeth remains unclear. Currently, it is considered that direct contact between the teeth caused by physical force or pressure during tooth development causes fusion [1,2,3]. Genetically, the development of fused teeth has been suggested to be autosomal dominant with reduced penetrance [2]. A report of multiple fused teeth cases in a five-member family reported two members with fused teeth in the primary dentition [12]. In addition, hypodontia of the permanent teeth and fused teeth in the primary dentition of a mother as well as fused teeth in the primary dentition of her 5-year-old daughter have been reported [13].
In relation to the possible genetic origin of tooth developmental disorders, dental agenesis (absence of teeth) has been reported to be related to several gene variants. Fournier et al. [14] performed a meta-analysis of 101 articles covering 522 patients to determine the genotype–phenotype correlations between dental agenesis and the genes msh homeobox 1 (MSX1), paired box 9 (PAX9), axin 2 (AXIN2), paired like homeodomain 2 (PITX2), wnt family member 10A (WNT10A), nemo (NMO), ectodysplasin A (EDA), ectodysplasin A receptor (EDAR), EDAR associated death domain (EDARADD), and gremlin 2, DAN family BMP antagonist (GREM2). Takahashi et al. [15] analysed whole exome sequence (WES) data from four Japanese families and found that supernumerary teeth were associated with variants such as SCO-spondin (SSPO). Kimura et al. [16] discovered an association between shovel-shaped incisors and EDAR in 100 Japanese subjects from Tokyo and 100 subjects from the Sakashima Islands using the polymerase chain reaction (PCR) direct sequencing method. Gowans et al. [17] investigated taurodontism, microdontia, and dens invaginatus using WES for first-family, second-family, and linkage analyses and reported that these were related to kinesin family member 4A (KIF4A). However, no research has been conducted on gene variants causing fused teeth. Investigating the genetic causes of tooth developmental disorders and dental agenesis could be potentially useful in understanding the mechanism of fused teeth formation.
Given that similar conditions are gene-related, we hypothesised that fused teeth develop at least partially due to genetic factors. Further, we hypothesised that fused teeth follow mendelian inheritance based on reports regarding the familial expression of fused teeth. Many genetic diseases are found in the exome region. Hence, searching for single nucleotide variants (SNVs) and small insertion/deletion (indel) in the exome region is an effective method for investigating the genetic basis of a disease [18]. SNVs cause amino acid substitution, and amino acid substitution can cause pathogenic mutations. Indels can cause loss of function of the produced protein due to insertion or deletion of the specific nucleotide sequence. WES is a useful method for reading the exome region and examining SNVs and indels. The purpose of this study, therefore, is to investigate the genetic basis of fused teeth using WES.
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Samples
Saliva specimens were collected from patients with fused teeth and their family members. Patients with fused teeth were selected from those seeking orthodontic treatment at Kanagawa Dental University Hospital and Pusan National University Dental Hospital. Patient clinical examinations generated intraoral photographs, panoramic radiographs, and dental study models in all cases. Family members were diagnosed with fused teeth using either intraoral photographs or intraoral examinations by the dentist. Patients with congenital diseases showing abnormalities in number of teeth and tooth morphology, such as ectodermal dysplasia, cleft lip and palate, and Down’s syndrome, were excluded. Fifteen patients from six families, including members with and without fused teeth, were included in the study. The fused teeth were located at the union of the mandibular central incisor and mandibular lateral incisor, or the union of the mandibular lateral incisor and mandibular canine. All patients and family members providing samples gave their informed consent. DNA was collected from 5 mL of saliva using an Oragene-DNA Kit (DNA Genotek Inc., Kanata, Canada) and stored at -20 °C after collection. This study was approved by the ethical committees of Kanagawa Dental University (approval number: 746; [2-13-2020]), Kanazawa University (approval number: 597-1; [11-17-2020]), and Pusan National University (approval number: PNUDH-2020-012; [4-28-2020]) and was performed in accordance with the ethical principles defined in the Declaration of Helsinki.
2.2. Whole Exome Sequencing
DNA samples (3 μg) were analysed in accordance with the manufacturer’s instructions using the SureSelect XT Target Enrichment System Kit for Illumina Multiplexed Sequencing (Agilent Technologies, Santa Clara, CA, USA) to capture the exome. The resulting libraries were subjected to high-throughput sequencing with 150 bp paired-end reads on an Illumina HiSeq 4000 sequencer (Illumina, San Diego, CA, USA).
2.3. Data Analysis
The WES data were analysed using the workflow recommended by GATK (version 3.6; https://gatk.broadinstitute.org/hc/; accessed on 1 June 2016) for best practice in variant calling. Clinically significant variants were detected using the Human Gene Mutation Database (HGMD) (QIAGEN, Hilden, Germany) and ClinVar entries based on the ANNOVAR annotation tool (https://annovar.openbioinformatics.org/; accessed on 15 April 2018). To identify rare pathogenic amino acid substitutions, we used HGMD and ClinVar to obtain information on the relationship between gene variants and human health with reference to frequency in 3552 Japanese individuals from the Japanese Multi Omics Reference Panel (jMorp; https://jmorp.megabank.tohoku.ac.jp/201911/; accessed on 11 January 2019) and 71,702 unrelated individuals from the Genome Aggregation Database (gnomAD; https://gnomad.broadinstitute.org; accessed on 16 October 2019).
The functional effects of the variants were evaluated using combined annotation-dependent depletion (CADD) and polymorphism phenotyping v2 (PolyPhen2; http://genetics.bwh.harvard.edu/pph2/; accessed on 26 February 2019) to score the deleteriousness of noncoding variants, thus indicating clinical validity. Clinically significant variants were visually confirmed using IGV (https://software.broadinstitute.org/software/igv/; accessed on February 2012).
3. Results
3.1. Clinical Findings
The 15 individuals from six families participating in this study ranged in age from 12 to 53 years; 12 females and 3 males. Among them, seven had fused teeth.
Figure 1 shows the six family trees. Figure 2 shows intraoral photographs and panoramic radiographs of the patients with fused teeth. Table 1 summarises patient sex, the positions of the fused teeth, and the inclusion type (monoliteral or bilateral).
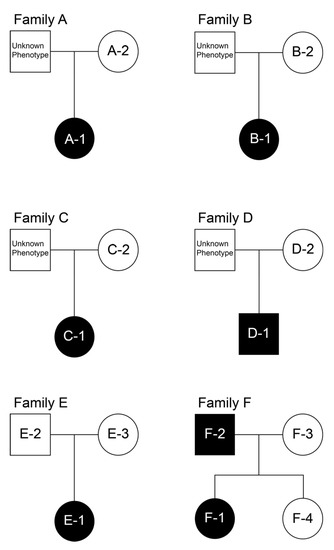
Figure 1.
The family trees of families A–F. Square: male, circle: female, black background: fused teeth present, white background: fused teeth absent.
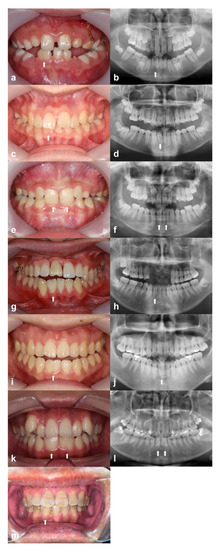
Figure 2.
Intraoral and panoramic radiographs, respectively, of: (a,b) patient A-1 (Family A); (c,d) patient B-1 (Family B); (e,f) patient C-1 (Family C); (g,h) patient D-1 (Family D); (i,j) patient E-1 (Family E); (k,l) patient F-1 (Family F); (m) intraoral photograph of patient F-2 (Family F). White arrows indicate fused teeth.

Table 1.
Clinical characteristics of the 15 patients from families A–F.
3.2. Genetic Analysis
WES was performed on 15 individuals: two each from Families A–D, three from Family E, and four from Family F. The average coverage depth of the analysed data was 152.9×, with 96.01% of target bases covered by at least 15 reads; the quality score (Q30) was 91.16%–94.08%. This finding supports a high level of confidence in the variant calling. We used the general method of extracting variants from WES [19]. Based on the genome database, we set the minor allele frequency (MAF) of each variant at 1% and extracted rare variants that were considered to be related to the disease. As a noncoding region filtering, variants not in exonic or splicing regions were excluded. Next, variants present in the subjects with and without fused teeth were extracted and excluded, respectively. The CADD score evaluates the deleteriousness of SNVs. A CADD score of ≥20 implies that the top 1% of SNVs are deleterious variants [20]. Variants with a CADD scaled score of ≥20 were then extracted.
We extracted the following: solute carrier family 27 member 3 (SLC27A3) variants (c.1385G>A (n = 1)) from Family A; SLC27A3 variants (c.1036C>T (n = 1)) from Family B; kinesin family member 25 (KIF25) variants (c.208G>A (n=1)) from Family C; and ERCC excision repair 6, chromatin remodeling factor (ERCC6) variants (c.2204G>T (n = 2)) and obscurin, cytoskeletal calmodulin, and titin-interacting RhoGEF (OBSCN) variants (c.5867C>G (n = 2)) from Family F (Table 2). No candidate variants were identified in Family D.

Table 2.
Candidate gene variants found in variant-positive patients.
The WES results for all 15 individuals from the six families showed that the genes with variants were ERCC6, OBSCN, SLC27A3, KIF25.
Table 3 summarises the scores of candidate gene variants and pathogenicity prediction tool results. ERCC6 (c.2204G>T), and SLC27A3 (c.1385G>A and c.1036C>T) showed high frequency in East Asians. CADD and PolyPhen2 were used to predict and evaluate the pathogenicity of the variants. Scaled CADD scores were particularly high in ERCC6 (c.2204G>T) and SLC27A3 (c.1036C>T and c.1385G>A), with scores above 25. Moreover, Polyphen2 scores also showed 1. ERCC6 (c.2204G>T) showed the highest value, with a scaled CADD score of 35 and a PolyPhen2 score of 1, indicating that it is more confidently predicted to be damaging.

Table 3.
Identified variants and their pathogenicity scores.
4. Discussion
This study aimed to investigate the genetic background of fused teeth, which are frequently observed in Asian populations. We used WES analysis to evaluate 15 Japanese and Korean individuals from six families. We succeeded in extracting candidate variants that may be involved in the incidence of fused teeth using exome analysis; this is the first report of such variants, as far as we are aware. These variants occur in the ERCC6, OBSCN, SLC27A3, and KIF25 genes.
In this study, when rare variants in individuals without fused teeth were excluded, no genotype–phenotype-matched variants were found in all families. This may indicate that the variants identified are only partially responsible for cases of fused teeth. The causative variants of tooth agenesis show incomplete penetrance [21,22]. Kanchanasevee et al. [23] reported that WNT10A shows incomplete penetrance in the incidence of tooth agenesis in the Thai population.
From our results alone, it is not possible to clarify whether the penetrance of the variants potentially causing the fused teeth is complete or incomplete. Additional studies on penetrance, such as WES analysis of larger families, are necessary.
ERCC6 is associated with transcription-coupled nucleotide excision repair and RNA polymerase I promoter escape. It is also one of the genes responsible for the incidence of Cockayne syndrome B (OMIM # 133540 COCKAYNE SYNDROME B; CSB), an autosomal recessive disorder classified into types I, II, and III. ERCC6 mutations are found in 65% of Cockayne syndrome (CS) cases [24,25]. More than 10% of people with CS type I have missing or hypoplastic teeth, delayed eruption of primary teeth, occlusal disharmony, or severe dental caries [26]. A CS case report noted that intraoral findings included dental caries and anomalies in tooth size and shape [27]. Another case report presented intraoral findings of hypoplastic teeth [28]. ERCC6 is associated with tooth absence and dysplasia, and it may be possible to propose a similar and possibly related mechanism for the development of fused teeth.
OBSCN is a gene encoding the obscurin protein, which is associated with myofibrillogenesis and cytoskeletal arrangement [29]. Obscurin is mainly expressed in cardiac and skeletal muscle. Obscurin is associated with tumorigenesis and was reported to be observed more frequently in normal breast epithelium when compared to advanced-stage breast cancer biopsy samples [30,31]. Relationships between OBSCN mutations and melanoma, glioblastoma, colorectal, lung, breast, and pancreatic cancer have been reported [32,33,34]. OBSCN mutations are associated with numerous cancer types, including melanomas and pharyngeal and tongue origin basal cell carcinomas [35]. Nichols et al. [36] analysed human oral squamous cell carcinoma cells of pharyngeal and tongue origin, and identified seven OBSCN mutations. OBSCN is a complex gene, and its function is unclear. There are no reported associations between OBSCN and tooth development or morphology. Further studies are needed to explore the association between OBSCN and dentition.
SLC27A3 variants were found in two of the seven patients with fused teeth, one from patient A-1 (c.1385G>A) and one from patient B-1 (c.1036C>T). SLC27A3 encodes fatty acid transport proteins (FATPs). Dysfunction of SLC27A3 may be associated with the aetiology of autism spectrum disorders. SLC27A3 was found in human neural stem cells, suggesting a relationship with the development of the central nervous system [37]. There are few reports on the function of the SLC27A3 gene. Hence, more research to investigate the function of the SLC27A3 gene is needed.
KIF25 encodes a member of the kinesin-like protein family, which performs microtubule-dependent and ATP-dependent intracellular organelle transport and moves chromosomes during cell division [38]. Protein transport plays an essential role in cell formation and function. KIF25 activity has been observed in various cancer types [39] and is associated with chromatid segregation and cancer cell proliferation [40,41]. KIF25 was reported to be possibly associated with the incidence of Kawasaki disease [42]. The oral features of Kawasaki disease include redness, swelling, vertical cracking, bleeding of the lips, redness of the tongue, and hypertrophy of tongue papillae [43]. Gowans et al. [17] reported on the relationship between KIF4A and taurodontism, microdontia, and dens invaginatus. KIF4A encodes kinesin-related proteins and is similar in mechanism to KIF25. In this study, KIF25 was identified as a potential candidate for the aetiology of fused teeth, one of the morphological abnormalities of teeth. The two results indicate that kinesin family members may be related to tooth morphology. Further research is needed on the kinesin family members and tooth morphology.
Three variants of ERCC6 (c.2204G>T) and SLC27A3 (c.1036C>T and c.1385G>A) were more frequent in East Asians. Fused teeth were reported to be more frequent in Asian populations [2], which may be related to the higher observed frequency of candidate variants.
Although we did not find FGF8 variants in our study, Chen et al. [44] examined FGF8 using the mouse model and found a unique type of fused supernumerary incisors of the dens invaginatus phenotype. FGF8 is expressed in dental epithelium and is associated with tooth development [45]; it may represent a similar mechanism in terms of tooth development. The relevance to human teeth should, however, be further investigated.
This study was limited by its sample size; the number of candidate variants was vast, requiring further studies to narrow this discrepancy. In the next stage, WES analysis of larger families and verification of the phenotype–genotype correlations of candidate variants using knockout mice are required. In addition, because the incidence of fused teeth varies by race, studies in diverse ethnic groups may also provide compelling information.
In this study, we successfully identified variants associated with the incidence of fused teeth. Family F, in which fused teeth were observed among multiple people in a family, suggested that fused teeth followed mendelian inheritance. This is significant, in that it is the first report concerning the genetic basis for fused teeth, providing clues to their previously unknown aetiology and mechanism. Furthermore, it is expected that these results will support the early molecular diagnosis of anticipated fused teeth and malocclusion, enabling their improved treatment and preventive management of associated caries and periodontal problems in the future. Understanding the genetic mechanisms involved in the development of teeth, including fused teeth, may become valuable in future regenerative medicine and gene therapy.
5. Conclusions
In this study, we investigated the aetiology of fused teeth from a genetic background and successfully extracted candidate variants ERCC6, OBSCN, SLC27A3, and KIF25. This study provides novel insights on the aetiology of fused teeth, which remains unclear. The association between the candidate variants and fused teeth should be investigated in further studies. Research on the aetiology of fused teeth may also provide new insights into the relationship between tooth development and morphology.
Author Contributions
Conceptualization, T.Y.; methodology, T.Y.; formal analysis, H.P., K.H. and A.T.; investigation, H.P., Y.-I.K. and Y.H; writing—original draft preparation, H.P., K.H., Y.H. and T.Y. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This research was funded by the Japan Society for Promotion of Science, KAKENHI program grant number 21K10173.
Institutional Review Board Statement
The study was conducted in accordance with the Declaration of Helsinki, and approved by the Ethics Committee of Kanagawa Dental University (protocol code 746; [2-13-2020]), Kanazawa University (protocol code 597-1; [11-17-2020]) and Pusan National University (protocol code PNUDH-2020-012; [4-28-2020]).
Informed Consent Statement
Informed consent was obtained from all subjects involved in the study.
Data Availability Statement
Data that support the results of this study are available from the corresponding author upon reasonable request.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
References
- Woelfel, J.B. Dental Anatomy: Its Relevance to Dentistry, 4th ed.; Lippincott Williams & Wilkins: Philadelphia, PA, USA, 1990. [Google Scholar]
- White, S.C.; Pharoah, M.J. Oral Radiology: Principles and Interpretation, 5th ed.; Mosby/Elsevier: St. Louis, MO, USA, 1994. [Google Scholar]
- Açıkel, H.; İbiş, S.; Şen Tunç, E. Primary Fused Teeth and Findings in Permanent Dentition. Med. Princ. Pract. 2018, 27, 129–132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Baratto-Filho, F.; Leonardi, D.P.; Crozeta, B.M.; Baratto, S.P.; Campos, E.A.; Tomazinho, F.S.; Deliberador, T.M. The challenges of treating a fused tooth. Braz. Dent. J. 2012, 23, 256–262. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed][Green Version]
- Le Gall, M.; Philip, C.; Aboudharam, G. Orthodontic treatment of bilateral geminated maxillary permanent incisors. Am. J. Orthod. Dentofac. Orthop. 2011, 139, 698–703. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- DaleKhurana, K.K.; Khurana, P. Esthetic and endodontic management of fused maxillary lateral incisor and supernumerary teeth with all ceramic restoration after trauma. Saudi Endod. J. 2014, 4, 23–27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Karumaran, C.S.; Kumar, A.R.; Neelakantappa, K.K.; Sundaran, R.M.; Venkatesan, R.; Naik, S.B. Cone beam computed tomography aided endodontic and aesthetic management of fused mandibular incisors with communicating canals. Indian J. Dent. Res. 2020, 31, 160–163. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pindborg, J.J. Pathology of the Dental Hard Tissues; W. B. Saunders Co.: Philadelphia, PA, USA, 1970. [Google Scholar]
- Sunny, J.; Kedilaya, V.; Pai, R.; Rai, D.S.; Rao, M. Fusion of teeth—A rare developmental anomaly. Brunei Int. Med. J. 2013, 9, 52–55. [Google Scholar]
- Duncan, W.K.; Helpin, M.L. Bilateral fusion and gemination: A literature analysis and case report. Oral. Surg. Oral. Med. Oral. Pathol. 1987, 64, 82–87. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cetinbas, T.; Halil, S.; Akcam, M.O.; Sari, S.; Cetiner, S. Hemisection of a fused tooth. Med. Oral. Pathol. Oral. Radiol. Endod. 2007, 104, e120–e124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hagman, F.T. Fused primary teeth: A documented familial report of case. ASDC J. Dent. Child 1985, 52, 459–460. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Guimarães Cabral, L.A.; Firoozmand, L.M.; Dias Almeida, J. Double teeth in primary dentition: Report of two clinical cases. Med. Oral. Patol. Oral. Cir. Bucal. 2008, 13, E77–E80. [Google Scholar]
- Fournier, B.P.; Bruneau, M.H.; Toupenay, S.; Kerner, S.; Berdal, A.; Cormier-Daire, V.; Hadj-Rabia, S.; Coudert, A.E.; de La Dure-Molla, M. Patterns of Dental Agenesis Highlight the Nature of the Causative Mutated Genes. J. Dent. Res. 2018, 97, 1306–1316. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Takahashi, M.; Hosomichi, K.; Yamaguchi, T.; Yano, K.; Funatsu, T.; Adel, M.; Haga, S.; Maki, K.; Tajima, A. Whole-exome sequencing analysis of supernumerary teeth occurrence in Japanese individuals. Hum. Genome. Var. 2017, 4, 16046. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kimura, R.; Yamaguchi, T.; Takeda, M.; Kondo, O.; Toma, T.; Haneji, K.; Hanihara, T.; Matsukusa, H.; Kawamura, S.; Maki, K.; et al. A common variation in EDAR is a genetic determinant of shovel-shaped incisors. Am. J. Hum. Genet. 2009, 85, 528–535. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gowans, L.; Cameron-Christie, S.; Slayton, R.L.; Busch, T.; Romero-Bustillos, M.; Eliason, S.; Sweat, M.; Sobreira, N.; Yu, W.; Kantaputra, P.N.; et al. Missense Pathogenic variants in KIF4A Affect Dental Morphogenesis Resulting in X-linked Taurodontism, Microdontia and Dens-Invaginatus. Front. Genet. 2019, 10, 800. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bamshad, M.J.; Ng, S.B.; Bigham, A.W.; Tabor, H.K.; Emond, M.J.; Nickerson, D.A.; Shendure, J. Exome sequencing as a tool for Mendelian disease gene discovery. Nat. Rev. Genet. 2011, 12, 745–755. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mahajan, M.C.; McLellan, A.S. Whole-Exome Sequencing (WES) for Illumina Short Read Sequencers Using Solution-Based Capture. Methods Mol. Biol. 2020, 2076, 85–108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kircher, M.; Witten, D.M.; Jain, P.; O’Roak, B.J.; Cooper, G.M.; Shendure, J. A general framework for estimating the relative pathogenicity of human genetic variants. Nat. Genet. 2014, 46, 310–315. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mues, G.; Bonds, J.; Xiang, L.; Vieira, A.R.; Seymen, F.; Klein, O.; D’Souza, R.N. The WNT10A gene in ectodermal dysplasias and selective tooth agenesis. Am. J. Med. Genet. A 2014, 164A, 2455–2460. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guazzarotti, L.; Tadini, G.; Mancini, G.E.; Sani, I.; Pisanelli, S.; Galderisi, F.; D’Auria, E.; Secondi, R.; Bottero, A.; Zuccotti, G.V. WNT10A gene is the second molecular candidate in a cohort of young Italian subjects with ectodermal derivative impairment (EDI). Clin. Genet. 2018, 93, 693–698. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kanchanasevee, C.; Sriwattanapong, K.; Theerapanon, T.; Thaweesapphithak, S.; Chetruengchai, W.; Porntaveetus, T.; Shotelersuk, V. Phenotypic and Genotypic Features of Thai Patients With Nonsyndromic Tooth Agenesis and WNT10A Variants. Front. Physiol. 2020, 11, 573214. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Troelstra, C.; van Gool, A.; de Wit, J.; Vermeulen, W.; Bootsma, D.; Hoeijmakers, J.H. ERCC6, a member of a subfamily of putative helicases, is involved in Cockayne’s syndrome and preferential repair of active genes. Cell. 1992, 71, 939–953. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Troelstra, C.; Hesen, W.; Bootsma, D.; Hoeijmakers, J.H. Structure and expression of the excision repair gene ERCC6, involved in the human disorder Cockayne’s syndrome group B. Nucleic Acids Res. 1993, 21, 419–426. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bloch-Zupan, A.; Rousseaux, M.; Laugel, V.; Schmittbuhl, M.; Mathis, R.; Desforges, E.; Koob, M.; Zaloszyc, A.; Dollfus, H.; Laugel, V. A possible cranio-oro-facial phenotype in Cockayne syndrome. Orphanet J. Rare. Dis. 2013, 8, 9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, Q.; Liu, M.; Liu, Y.; Tang, H.; Wang, T.; Li, H.; Xiang, J. Two heterozygous mutations in the ERCC6 gene associated with Cockayne syndrome in a Chinese patient. J. Int. Med. Res. 2020, 48, 300060519877997. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xin, B.; Wang, H. Identification of Two Novel ERCC6 Mutations in Old Order Amish with Cockayne Syndrome. Mol. Syndromol. 2013, 3, 288–290. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Young, P.; Ehler, E.; Gautel, M. Obscurin, a giant sarcomeric Rho guanine nucleotide exchange factor protein involved in sarcomere assembly. J. Cell Biol. 2001, 154, 123–136. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shriver, M.; Stroka, K.M.; Vitolo, M.I.; Martin, S.; Huso, D.L.; Konstantopoulos, K.; Kontrogianni-Konstantopoulos, A. Loss of giant obscurins from breast epithelium promotes epithelial-to-mesenchymal transition, tumorigenicity and metastasis. Oncogene 2015, 34, 4248–4259. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Perry, N.A.; Shriver, M.; Mameza, M.G.; Grabias, B.; Balzer, E.; Kontrogianni-Konstantopoulos, A. Loss of giant obscurins promotes breast epithelial cell survival through apoptotic resistance. FASEB J. 2012, 26, 2764–2775. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Sjöblom, T.; Jones, S.; Wood, L.D.; Parsons, D.W.; Lin, J.; Barber, T.D.; Mandelker, D.; Leary, R.J.; Ptak, J.; Silliman, N.; et al. The consensus coding sequences of human breast and colorectal cancers. Science 2006, 314, 268–274. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Balakrishnan, A.; Bleeker, F.E.; Lamba, S.; Rodolfo, M.; Daniotti, M.; Scarpa, A.; van Tilborg, A.A.; Leenstra, S.; Zanon, C.; Bardelli, A. Novel somatic and germline mutations in cancer candidate genes in glioblastoma, melanoma, and pancreatic carcinoma. Cancer Res. 2007, 67, 3545–3550. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Price, N.D.; Trent, J.; El-Naggar, A.K.; Cogdell, D.; Taylor, E.; Hunt, K.K.; Pollock, R.E.; Hood, L.; Shmulevich, I.; Zhang, W. Highly accurate two-gene classifier for differentiating gastrointestinal stromal tumors and leiomyosarcomas. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2007, 104, 3414–3419. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Guardia, T.; Eason, M.; Kontrogianni-Konstantopoulos, A. Obscurin: A multitasking giant in the fight against cancer. Biochim. Biophys. Acta Rev. Cancer 2021, 1876, 188567. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nichols, A.C.; Yoo, J.; Palma, D.A.; Fung, K.; Franklin, J.H.; Koropatnick, J.; Mymryk, J.S.; Batada, N.N.; Barrett, J.W. Frequent mutations in TP53 and CDKN2A found by next-generation sequencing of head and neck cancer cell lines. Arch. Otolaryngol. Head Neck Surg. 2012, 138, 732–739. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed][Green Version]
- Maekawa, M.; Iwayama, Y.; Ohnishi, T.; Toyoshima, M.; Shimamoto, C.; Hisano, Y.; Toyota, T.; Balan, S.; Matsuzaki, H.; Iwata, Y.; et al. Investigation of the fatty acid transporter-encoding genes SLC27A3 and SLC27A4 in autism. Sci. Rep. 2015, 5, 16239. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miki, H.; Setou, M.; Kaneshiro, K.; Hirokawa, N. All kinesin superfamily protein, KIF, genes in mouse and human. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2001, 98, 7004–7011. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, S.; Zhang, Q.; Sun, Q.; Tang, J.; Chen, J.; Ji, N.; Zheng, Y.; Fang, F.; Lei, W.; Li, P.; et al. Genome Evolution Analysis of Recurrent Testicular Malignant Mesothelioma by Whole-Genome Sequencing. Cell Physiol. Biochem. 2018, 45, 163–174. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mosley, J.D.; Van Driest, S.L.; Larkin, E.K.; Weeke, P.E.; Witte, J.S.; Wells, Q.S.; Karnes, J.H.; Guo, Y.; Bastarache, L.; Olson, L.M.; et al. Mechanistic phenotypes: An aggregative phenotyping strategy to identify disease mechanisms using GWAS data. PLoS ONE 2013, 8, e81503. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Okamoto, S.; Matsushima, M.; Nakamura, Y. Identification, genomic organization, and alternative splicing of KNSL3, a novel human gene encoding a kinesin-like protein. Cytogenet. Cell Genet. 1998, 83, 25–29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Buda, P.; Chyb, M.; Smorczewska-Kiljan, A.; Wieteska-Klimczak, A.; Paczesna, A.; Kowalczyk-Domagała, M.; Okarska-Napierała, M.; Sobalska-Kwapis, M.; Grochowalski, Ł.; Słomka, M.; et al. Association Between rs12037447, rs146732504, rs151078858, rs55723436, and rs6094136 Polymorphisms and Kawasaki Disease in the Population of Polish Children. Front. Pediatr. 2021, 9, 624798. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Scardina, G.A.; Fucà, G.; Carini, F.; Valenza, V.; Spicola, M.; Procaccianti, P.; Messina, P.; Maresi, E. Oral necrotizing microvasculitis in a patient affected by Kawasaki disease. Med. Oral. Patol. Oral. Cir. Bucal. 2007, 12, E560–E564. [Google Scholar]
- Chen, Y.; Wang, Z.; Lin, C.; Chen, Y.; Hu, X.; Zhang, Y. Activated Epithelial FGF8 Signaling Induces Fused Supernumerary Incisors. J. Dent. Res. 2022, 101, 458–464. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Balic, A.; Thesleff, I. Tissue Interactions Regulating Tooth Development and Renewal. Curr. Top. Dev. Biol. 2015, 115, 157–186. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).